Abstract
In this study, 117,718 ionospheric perturbations, with a space size (t) of 20–300 s but no amplitude (A) limit, were automatically globally searched via software utilizing ion density data measured by the DEMETER satellite for over 6 years. The influence of geomagnetic storms on the ionosphere was first examined. The results demonstrated that storms can globally enhance positive ionospheric irregularities but rarely induce plasma variations of more than 100%. The probability of PERs with a space size falling in 200–300 s (1400–2100 km if a satellite velocity of 7 km/s is considered) occurring in a geomagnetically perturbed period shows more significance than that in a quiet period. Second, statistical work was performed on ion PERs to check their dependence on local time, and it was shown that 24.8% of the perturbations appeared during the daytime (10:30 LT) and 75.2% appeared during the nighttime (22:30 LT). Ionospheric fluctuations with an absolute amplitude of A < 10% tend to be background variations, and the percentages of positive perturbations with a small A < 20% occur at an amount of 64% during the daytime and 26.8% during the nighttime, but this number is reversed for mid–large-amplitude PERs. Large positive PERs with A > 100% mostly occurred at night and negative ones with A < −100% occurred entirely at night. There was a demarcation point in the space size of t = 120 s, and the occurrence probabilities of day PERs were always higher than that of nighttime ones before this point, while this trend was contrary after this point. Finally, distributions of PERs according to different ranges of amplitude and space scale were characterized by typical seasonal variations either in the daytime or nighttime. EIA only exists in the dayside equinox and winter, occupying two low-latitude crests with a lower Np in both hemispheres. Large WSAs appear within all periods, except for dayside summer, and are full of PERs with an enhanced amplitude, especially on winter nights. The WN-like structure is obvious during all seasons, showing large-scale space. On the other hand, several magnetically anomalous zones of planetary-scale non-dipole fields, such as the SAMA, Northern Africa anomaly, and so on, were also successfully detected by extreme negative ion perturbations during this time.
1. Introduction
As a conductive component of layers of the atmosphere, investigations of various properties of the ionosphere have always been a controversial issue due to different sources from above and below that contribute to ionospheric variations. Solar activity mainly includes sunspots, solar winds, solar flares, etc. These activities can release a large number of energy particles, causing a direct or indirect impact on the formation and characteristics of the Earth’s ionosphere, while during geomagnetic storms, vast amounts of energy and momentum in the form of increased particle precipitation and Joule heating from solar wind and the magnetosphere have been deposited into the Earth’s upper atmosphere and ionosphere, causing global disturbances of the ionosphere. On the other hand, the ionosphere is subject to tremendous responses to natural and artificial events, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, communication engineering, etc. Ionospheric irregularities caused by inhomogeneous ionization density in the topside ionosphere have been described as early as the 1930s [1,2,3]. Following several decades of research, ionospheric structures, and even their inner various features, have gradually gained more and more clear configurations from ground-based remote ionospheric responding and satellite in situ instruments [4,5,6,7]. Some, such as the equatorial ionization anomaly (EIA) and mid-latitude ionospheric trough (MIT), have been well reconstructed by different parameters, although parts of the potential mechanisms of these various ionospheric irregularities are yet to be fully understood [8,9,10,11,12].
Plasma density is the primary parameter that is commonly utilized to reconstruct the ionosphere configuration and test the reliability of the data measured from different instruments. Electron density (Ne) is a key parameter to characterize the status of ionospheric plasma, and O+ is the main component among the ions, although this depends on certain factors such as local time and altitude [7,13,14,15]. Electron density measured employing in situ DEMETER (Detection of Electro-Magnetic Emissions Transmitted from Earthquake Regions) and Swarm satellites or from FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC radio occultation measurements were employed to investigate the properties of ionospheric irregularities, with variations such as EIA, MIT, middle latitudinal band structures, Wedell Sea Anomaly, etc. [11,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Other parameters such as O+, H+, and He+ densities and total electron densities are also used to research the ionospheric characteristics of background, seasonal, and day-to-day variations, as well as the large-scale depletion of oxygen ions [22,23,24].
However, it must be mentioned that variations in ionospheric parameters are not only due, in large part, to sources from above, such as solar and geomagnetic activity variations, but also natural hazards and meteorological sources from below [25]. As the Earth’s observation from space has developed, seismo-ionospheric influences have been highlighted as a possible candidate for earthquake forecasting and potential seismogenic electromagnetic energy transmitted along the lithosphere, atmosphere, ionosphere, and even magnetosphere [26,27,28,29,30,31]. As a weak factor of strong ionospheric background variations, weak information potentially associated with seismic activities is always submerged in other enhanced irregularities. Aside from a case study in a relatively small region and within a specified short time, statistical investigations on seismo-ionospheric influence have always been a way to distinguish anomalous features of earthquake precursors [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. With an alternative statistical method, Parrot [31] correlated DEMETER ion perturbations (PERs), automatically searched via software, with strong earthquake events occurring during the DEMETER period, and the results have shown that the number and intensity of the ionospheric PERs are a little larger prior to earthquakes than prior to random events. A similar method has also been utilized by Li et al. [42,43] to correlate ionospheric PERs measured by the DEMETER satellite with strong seismic activities occurring within a corresponding period. They found that the obtained results are inadequate, because not all ionospheric PERs are caused by EQs, and the number of false alarms is large, even with the detection range reaching up to 1500 km. Furthermore, Li et al. [15] conveyed that CSES (China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite) ion PERs, with a space size of 200–300 s, are located collectively in the equatorial area, with no specified correlation to the main seismic zones of the world. Contrastingly, Li et al. [44] found that there are different properties for ion PERs and electron ones obtained from a CSES satellite for more than three years and ionospheric PERs with large amplitudes and space sizes tend to collocate with large-scale ionospheric structures such as EIA and MIT.
Therefore, all evidence indicates that it will be of great significance to explore ionospheric PERs caused by various interferences. A comprehensive investigation of the properties of ionospheric PERs with different amplitudes and space sizes can help us fully understand their producing mechanisms and correctly distinguish earthquake precursors. Hence, in this paper, DEMETER data and the data processing method are introduced in Section 2. In Section 3, different seasonal and local time characteristics of ion PERs are comparatively exhibited. Finally, the discussion and conclusions are presented in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
2. Data and Data Processing Method
2.1. Dataset
DEMETER was launched in June 2004, measuring electromagnetic waves and plasma parameters around the globe, except in the auroral zones [45]. It is a low-orbit satellite with an altitude of 710 km, decreased to 660 km in December 2005. The orbit of DEMETER is nearly sun-synchronous, and the upgoing and downgoing half-orbits correspond to nighttime (22:30 LT) and daytime (10:30 LT), respectively. Its payload IAP (plasma analyzer instrument) outputs the plasma density of ion density with data resolutions of 4 s in the survey mode and 2 s in the burst mode for all data. This satellite’s science mission stopped measuring at the end of December 2010. More details can be found in the study by Parrot et al. [45].
This investigation is based on the ion (O+) density (Ni) data from IAP onboard the DEMETER in situ measurements of over 6 years (from November 2004 to August 2010). All data were transmitted into the resolution of 4 s for ion density issued by the original recordings. At the same time, the SAVGOL method was employed to smooth the data, eliminating pulse-like peaks before searching for PERs. The SAVGOL function returns the coefficients of the Savitzky–Golay smoothing filter [46].
2.2. Automatic Search for Ionospheric PERs
The plasma data processing method employed here is similar to the one used by Li et al. [45]. Ionospheric PERs in the ion dataset were automatically searched by software (code) globally rather than around the main seismic zones, as in our previous work [42,43]. Here, two key parameters are specified: the PER spatial scale (t, in situ measurement time) was kept within the 20–300 s range (140–2100 km if a satellite velocity of 7 km/s is considered), and there were still no limits for the value of various amplitudes (A) in the PER database. The minimum size was also set to 20 s in order to avoid spurious impulsions caused by one or two points [42]. Each ionospheric disturbance is described by several parameters, such as peak appearing time, orbit number, location (latitude and longitude), amplitude, spatial scale, etc. Eight three-hourly averaged Kp index values each day were available from Li and Parrot [42], and the Kp value was also examined when each ionospheric PER detected occurred.
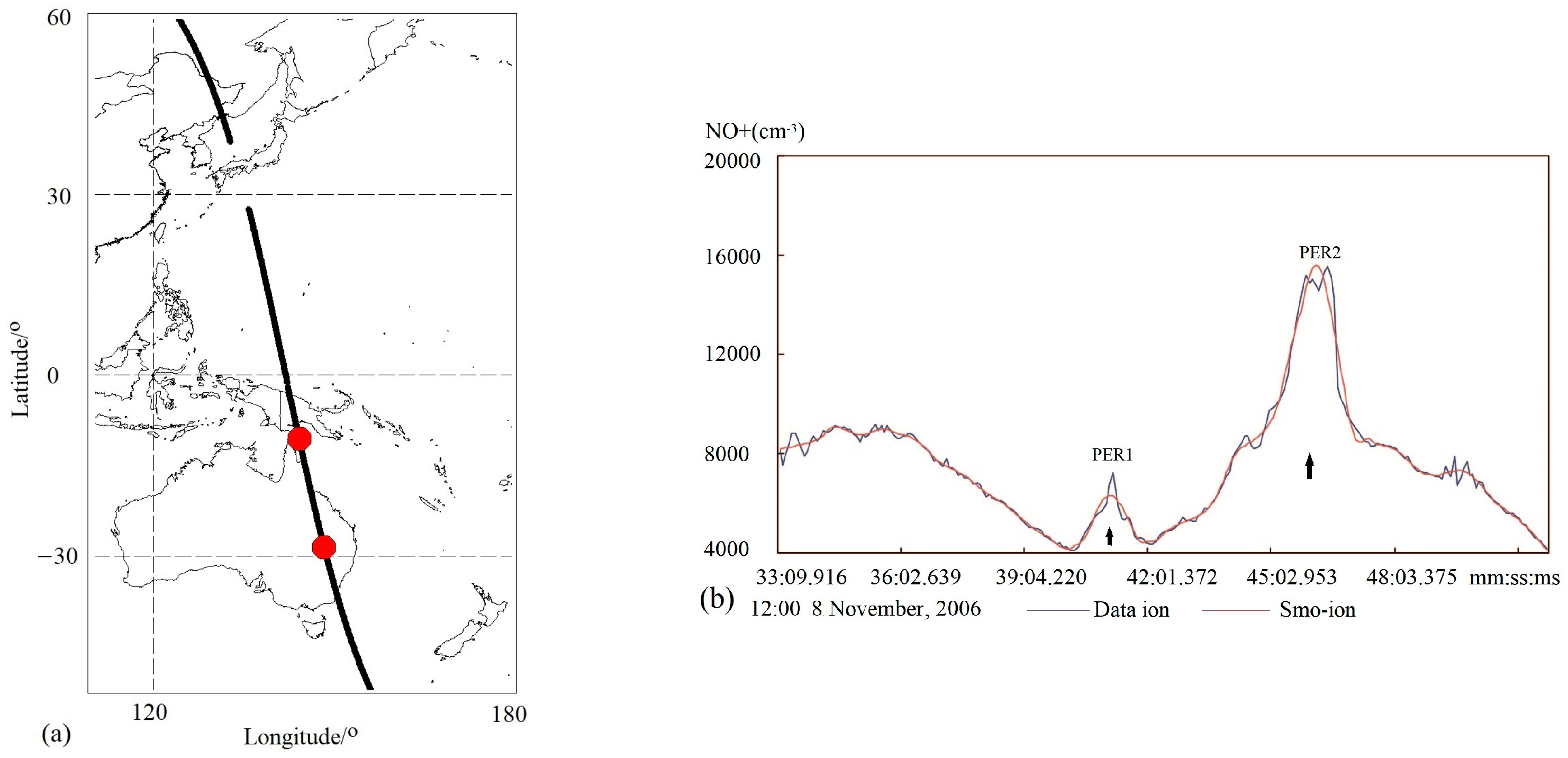
Figure 1a represents the upgoing orbit of 12545 (black line) measured by DEMETER on 8 November 2006. The O+ density recorded along this orbit during nighttime is denoted by a blue line (data-ion) in Figure 1b, and its smoothed data using the SAVGOL function is lined in red (Smo-ion).
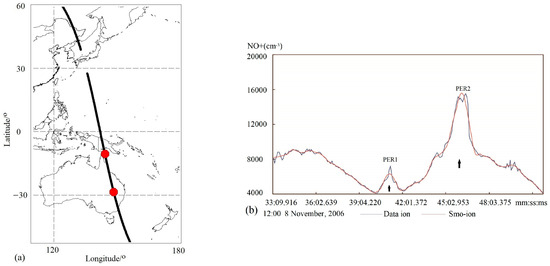
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the flight path (upgoing orbit 12545) conducted by DEMETER on 8 November 2006. Two red dots represent the peak values of (b) two ionospheric PERs (indicated by two black arrows) detected by the software (the code) in smoothed ion data of the DEMETER orbit 12545 at night.
Two ionospheric perturbations were automatically detected within this Smo-ion line by the software, with a defined space size of 20–300 s and without amplitude limits. The corresponding parameters of these two PERs are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters of two PERs detected by the software along the DEMETER orbit of 12545 at nighttime.
In total, 117,718 ion PERs were attained from the ion density dataset measured by the DEMETER satellite during this considered period.
3. Properties of Ionospheric PERs
3.1. Effect of a Geomagnetic Storm on the Ionosphere
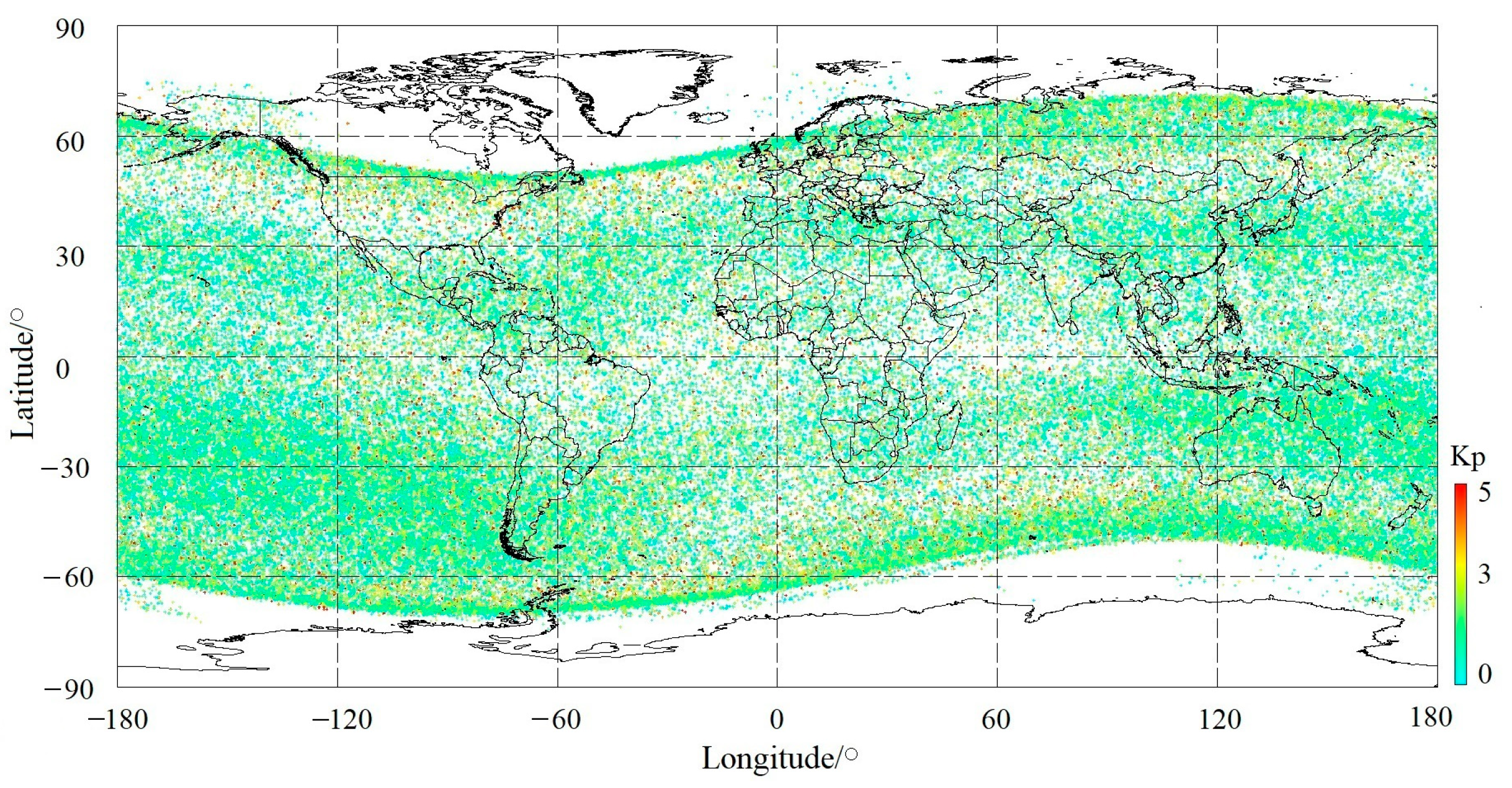
In this study, the Kp index was first used to examine the geomagnetic effect on plasma densities. Figure 2 shows the distributions of all 117,718 ion PERs with an increasing value of corresponding Kp indexes as one PER occurs. In Figure 2, it is clear that the distributions of plasma variations in light of the Kp index present no special areas where PERs with large Kp values appear collectively, although solar activity tends to have a slightly heavier effect on equatorial and high-latitude ionospheric areas. The response of the ionosphere to solar and geomagnetic activity variations depends on the season, latitude, and storm time occurrence [15,32,44,47,48].
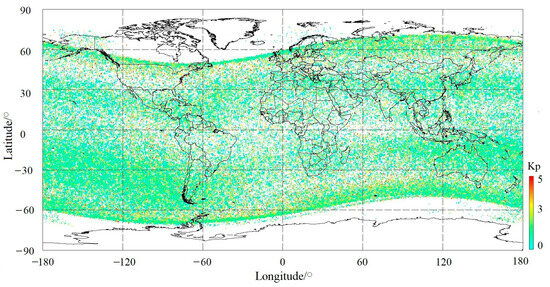
Figure 2.
Distribution of 117,718 ion PERs with respect to different ranges of the Kp index during the DEMETER satellite period considered in this paper.
Usually, Kp ≥ 3 implies that there is an effect on space weather from geomagnetic storms. To further examine the exact influence of the geomagnetic storm on the amplitude and space size of ionospheric PERs and attain obviously comparable results, PERs with Kp > 4 within the perturbed period and Kp ≤ 2 within the quiet period were selected from all 117,718 ion PERs to form two new groups of PERs: 87,057 with Kp ≤ 2 and 4263 with Kp > 4. Second, for each group of PERs, the number for certain PERs (n, the same in the following parts) and their occurrence probability (p, the same in the following parts) were calculated as a function of different ranges of amplitude (A): ≥100, 90–100, 80–90, 70–80, 60–70, 50–60, 40–50, 30–40, 20–30, 10–0, 0–−100, and <−100; and space size (t): 20–40, 40–60, 60–80, 80–100, 100–120, 120–140, 140–160, 160–180, 180–200, and 200–300. The results are listed in Table 2 and Table 3 as the number of each sub-group of PERs and its corresponding percentage.

Table 2.
Number and its corresponding percentage of sub-group PERs with different ranges of amplitude (A) for two-group ion PERs (Kp > 4 and Kp ≤ 2).

Table 3.
Number and its corresponding percentage of sub-group PERs with different ranges of space size (t) for two-group ion PERs (Kp > 4 and Kp ≤ 2).
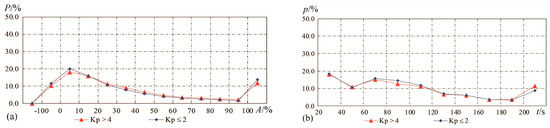
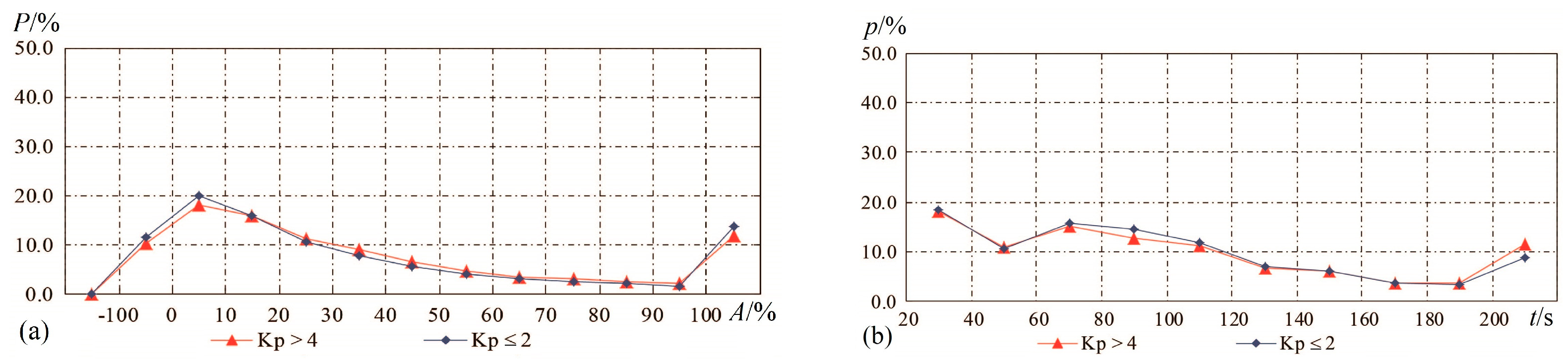
Figure 3.
Polyline of percentages for different groups of perturbations: PERs for Kp > 4 in red, ones for Kp ≤ 2 in blue line, as a function of (a) an amplitude (A) and (b) a space size (t).
Table 2 and Figure 3a show the percentage values corresponding to different scales of amplitude during a geomagnetically perturbed period (Kp > 4) and a quiet period (Kp ≤ 2); for positive PERs, the occurrence probabilities for plasma variations with a magnitude covering the range A = 0–10% is 18.3% and 20.1%, for 10% < A < 100% it is 59.3% and 54.3%, and for A > 100% is 12% and 13.8%, respectively. From this point, it is easy to infer that geomagnetic storms can accelerate ionospheric variations but rarely induce plasma irregularities of more than 100%. On the other hand, it is possible, but unlikely, for magnetic storms to give rise to negative ionospheric variations even beyond 100% (see Table 2 and Figure 3a), which is coincident with the results attained by Prölss [49], who presented that the increase in geomagnetic activity gave rise to negative ionospheric variations at the nightside during the summer season. Xiong et al. [50] also reported that positive and negative ionospheric responses were observed during the recovery phase of a geomagnetic storm on the dayside.
In Table 3 and Figure 3b, there is no obvious discrepancy between the space sizes of PERs appearing during the disturbed period and quiet time when t < 200 s. Contrastingly, there is a relatively obvious gap between the percentages during Kp > 4 and Kp ≤ 2 when t = 200–300 s, which indicates that geomagnetic storms tend to induce larger ionospheric disturbances. Alternatively, the space size defined here does not cover the range of geomagnetically perturbed ionospheric variations well. Large-scale ionospheric density enhancements are frequently observed during geomagnetic storms [50].
3.2. Local Time Discrepancy of Ionospheric PERs
The DEMETER measurement heavily depends on two local times: 22:30 LT for nighttime and 10:30 LT for the morning. For all 117,718 ion PERs, 29,226 occurred during daytime and 88,492 for nighttime, accounting for 24.8% and 75.2%, respectively. To check the dependence of the occurrence of plasma PERs on local time, PERs were separated into two groups according to their occurrence time of daytime and nighttime. Then, for each group of PERs (dayside or nightside), the percentage for different ranges of amplitude, A, and space size, t, were calculated and are presented in Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 4.
Number and its corresponding percentage of sub-group PERs with different ranges of amplitude (A) for two-group ion PERs (daytime and nighttime).

Table 5.
Number and its corresponding percentage of sub-group PERs with different ranges of space size (t) for two-group ion PERs (daytime and nighttime).
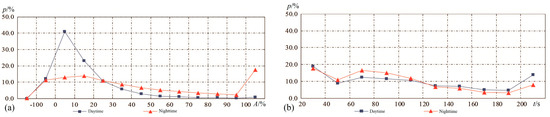
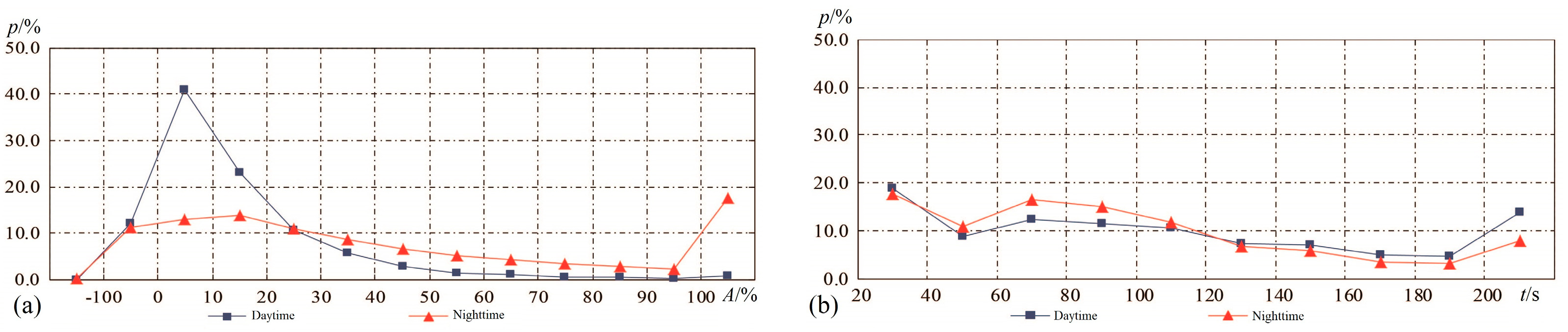
Figure 4.
Polyline of percentages for different groups of perturbations: PERs during nighttime in red and daytime in blue as a function of (a) amplitude range (A) and (b) space size (t).
From Table 4 and Figure 4a, the percentages for all amplitude segments varied widely, and this property was more obvious during the daytime. The significant feature is that plasma PERs with small amplitudes <20% made up a prominent proportion of 64% on the dayside. Contrastingly, this parameter only accounts for 26.8% on the nightside. The number of each group of PERs with an amplitude between 0 and −10% was also checked: 3406 and 5603 for day and night ion PERs, accounting for 11.7% and 6.3% of all 29,226 day ion PERs and 88,492 night ones, respectively. That means that most ionospheric variations with a positive and negative magnitude of less than 10% tend to be background irregularities. This conclusion seems more correct during nighttime than daytime, when sunlight can speed the ionization of plasma, giving rise to more positive ionospheric irregularities. The occurrence probabilities of mid–large-amplitude perturbations, for instance, >20%, account for 24% and 61.9% for daytime and nighttime, respectively. Comparatively, the ionosphere can enhance amplitudes to more than 100% easily during nighttime but rarely decrease to 100%. From the space size, the probability for various sections keeps a relative balance, but there is a demarcation point, t = 120 s. The occurrence probabilities of day PERs were always higher than that of nighttime before this point, while this result was reversed after this point (See Table 5 and Figure 4b). A primary conclusion was almost attained on the basis of these statistical results: relatively, the ionosphere varies more frequently and more violently during nighttime but with a relatively small space size.
3.3. Seasonal Variation in Ionospheric PERs
The ionosphere is also characterized by local time [19,23], as well as seasonal variations [23,51]. According to the Lloyd criteria [52], the months of winter for the Northern Hemisphere (summer for the Southern Hemisphere) include November, December, January, and February; equinox covers March, April, September, and October; and summer (winter for the Southern Hemisphere) contains the months of May, June, July, and August.
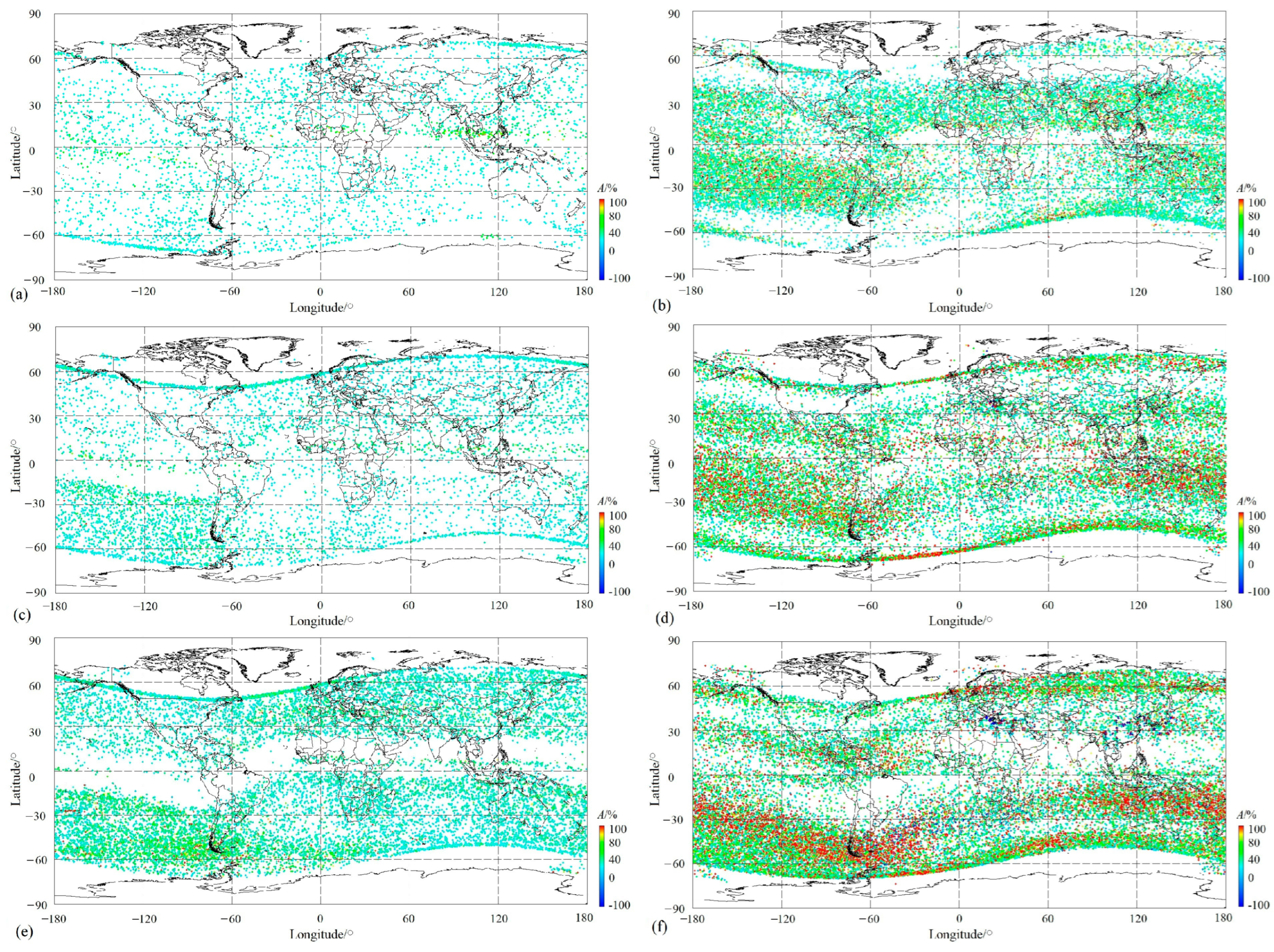
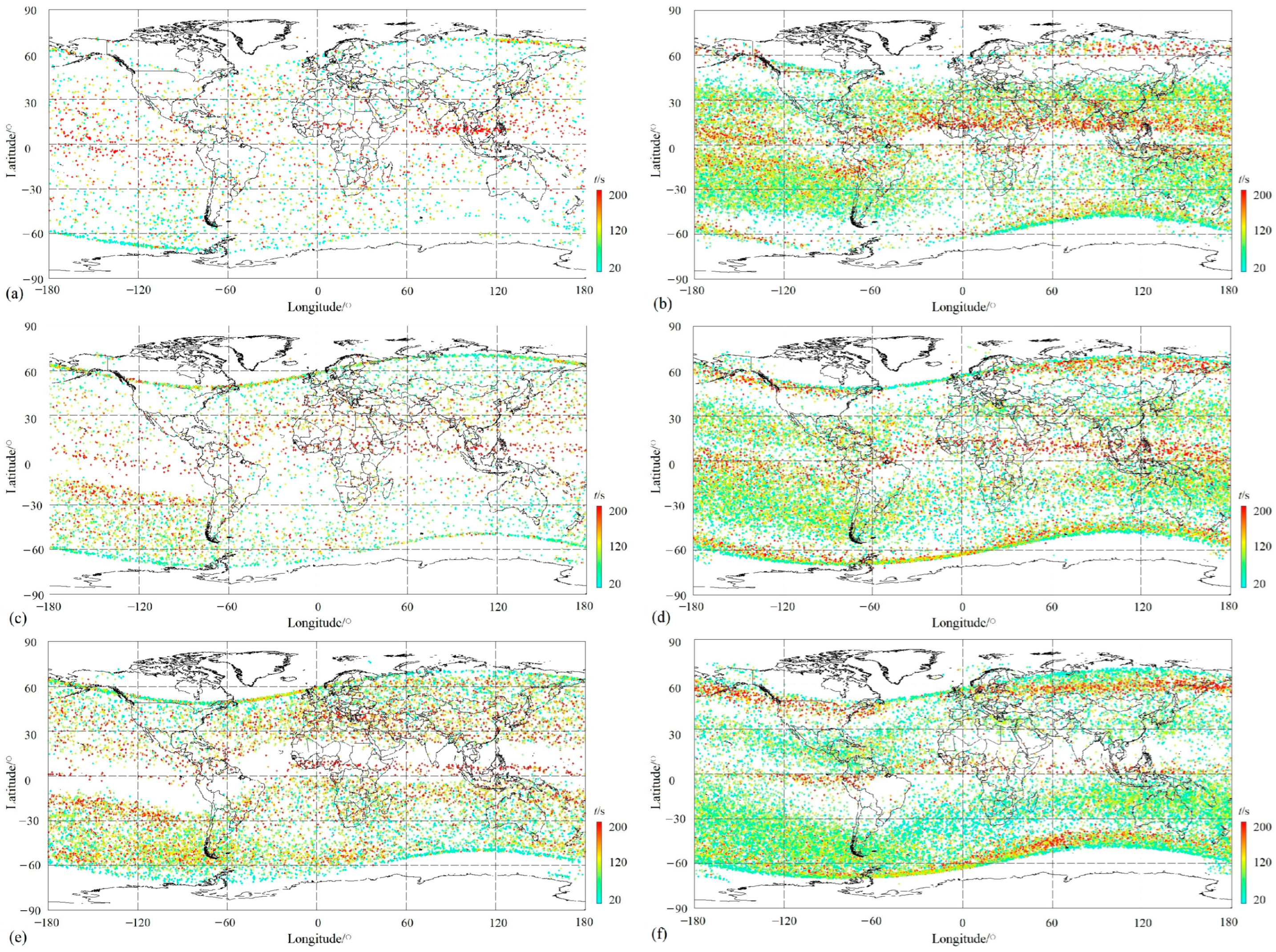
On the basis of dividing ion PERs into different groups according to their occurrence at local time (dayside and nightside), plasma PERs issued by ion density in this section were further divided into different groups by seasons. However, before that, we eliminated PERs with Kp ≥ 3 (18,169 PERs) in order to eliminate the global influence from solar activities and only keep PERs with Kp < 3 (99,549 PERs) to a statistical in this part. For all 99,549 PERs with Kp < 3, 25,780 PERs occurred on the dayside and 73,769 on the nightside. Furthermore, each group of these PERs was separated into three sub-groups according to different seasons: 3862 for summer, 6680 for equinox, and 15,238 for winter on the dayside; and 22,852, 22,389, and 28,528 on the nightside. Their distributions corresponding to various amplitudes, A, as well as space size, t, are exhibited in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. In Figure 5, the left panels represent the distributions of ion PERs appearing on the dayside in summer, equinox, and winter from the top to the bottom, and the right panels correspond to ones on the nightside. Figure 6 shows the same arrangement as Figure 5.
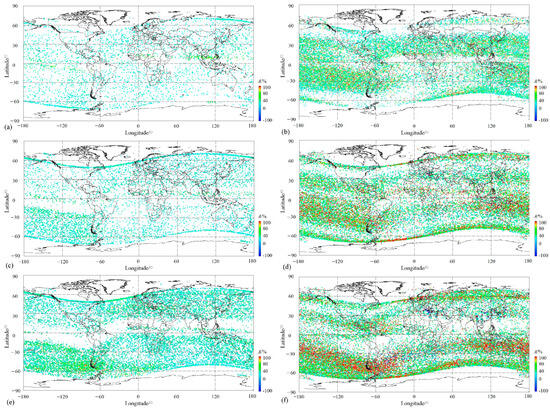
Figure 5.
Distribution of various amplitude ion PERs with respect to different seasons and local times. (a) Daytime in summer; (b) nighttime in summer; (c) daytime in equinox; (d) nighttime in equinox; (e) daytime in winter; and (f) nighttime in winter.
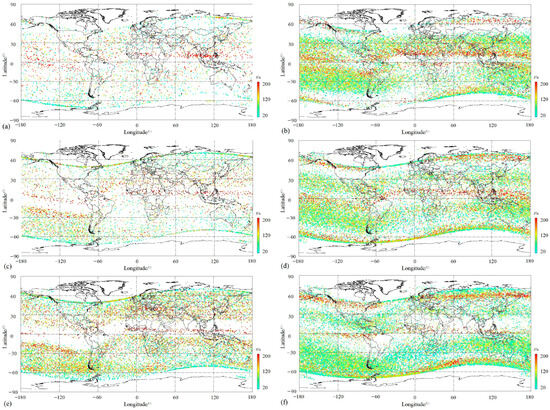
Figure 6.
Distribution of various-space size ion PERs with respect to different seasons and local times. (a) Daytime in summer; (b) nighttime in summer; (c) daytime in equinox; (d) nighttime in equinox; (e) daytime in winter; and (f) nighttime in winter.
The equatorial ionization anomaly (EIA) is one of the ionospheric phenomena during daytime occurring in a low-latitude F-region and characterized by an electron density trough above the magnetic equator and double crests of enhanced plasma density at approximately 15° north and south of the magnetic equator [4,53]. The longitudinal arranged wavenumber-4 (WN4) in the summer and autumn and wavenumber-3 (WN3) in the winter of plasma density also developed in the morning within the equator [54]. On the dayside, the EIA structure was exhibited well in equinox and winter, as shown in Figure 5c,e, but not in the summer, as shown in Figure 5a. This structure displays a typical feature of low-plasma PER density (Np) on both sides of the magnetic equator at a low latitude and a sudden enhancement of Np at about 15° on both sides of magnetic latitudes. At the same time, this daytime anomaly is also clearly presented with the simultaneous enhancement both in Np and space size, even beyond 200 s (Figure 6c,e). Except for this, the WN4 structure arranged longitudinally was outlined from the distributions of O+ PERs with a relatively obvious Np during equinox daytime either according to the amplitude (Figure 5c) or strengthened large space size (Figure 6c), and in winter, this structure gives way to the WN3 (See Figure 5e and Figure 6e). Additionally, a WN-like structure along the east longitude ~60° E–120° E on the magnetic equator was discovered on the dayside in summer, with an obviously enhanced amplitude (Figure 5a) and space size (Figure 6a), which seems the most outstanding phenomenon occurring on the dayside in summer. On the other hand, on the dayside in winter, the symmetric structure of both sides of the North and South Hemispheres is also significant for the distributions of O+ PERs as a function of amplitude, as well as space size (see Figure 5e and Figure 6e).
On the topside of the ionosphere, there is a large Wedell Sea Anomaly (WSA) zone (30° W–180° W and 30° S–75° S) [16], a summer ionospheric anomaly, which is characterized by a greater nighttime ionospheric density than that in daytime in the region near the Weddell Sea (20° W–150° W and 40° S–70° S) [55]. However, during this time, this WSA structure appeared at all times, except daytime in summer (left panels in Figure 5 and Figure 6). On the dayside amplitude shown in Figure 5, the WSA was found both in the equinox and winter, occupying a zone (60° W–180° W and 15° S–60° S) with an enhanced Np, as well as moderate magnitude (Figure 5c,e) and large space size (Figure 5e and Figure 6c), but this was not the case for daytime in summer (Figure 5a and Figure 6a). Comparatively, the WSA shows its pattern more clearly during nighttime than daytime, covering a zone (30° W–180° W, 100° E–180° E, and 20° S–50° S) (See Figure 5 and Figure 6 comparing right panels with the left ones). Contrastingly, during the daytime, with the exception of a high Np in the WSA area during nighttime, PERs with large amplitudes, for example, A > 100%, displayed their significance (as can be seen in the right panels in Figure 5), especially in winter during the night (Figure 5f), but not so much ones with a large space size, for example, t > 200 s (as seen from the right panels in Figure 6).
The mid-latitude ionospheric trough during nighttime was characterized by a lower Np than around the area centered at 50° latitude in both hemispheres from the right panels in Figure 5 and Figure 6. A thin WN-like structure constructed by lager-space size PERs clearly runs longitudinally above the magnetic equator on the nightside in summer (Figure 6b) and in equinox (Figure 6b). However, this pattern is slightly confusing in winter (Figure 6f) regarding space size, and the amplitude completely disappears in winter (Figure 5f), possibly due to the winter oxygen ion (O+)-depleted (WOD) region at a latitude about 20°–60° at different longitudes during nighttime [23].
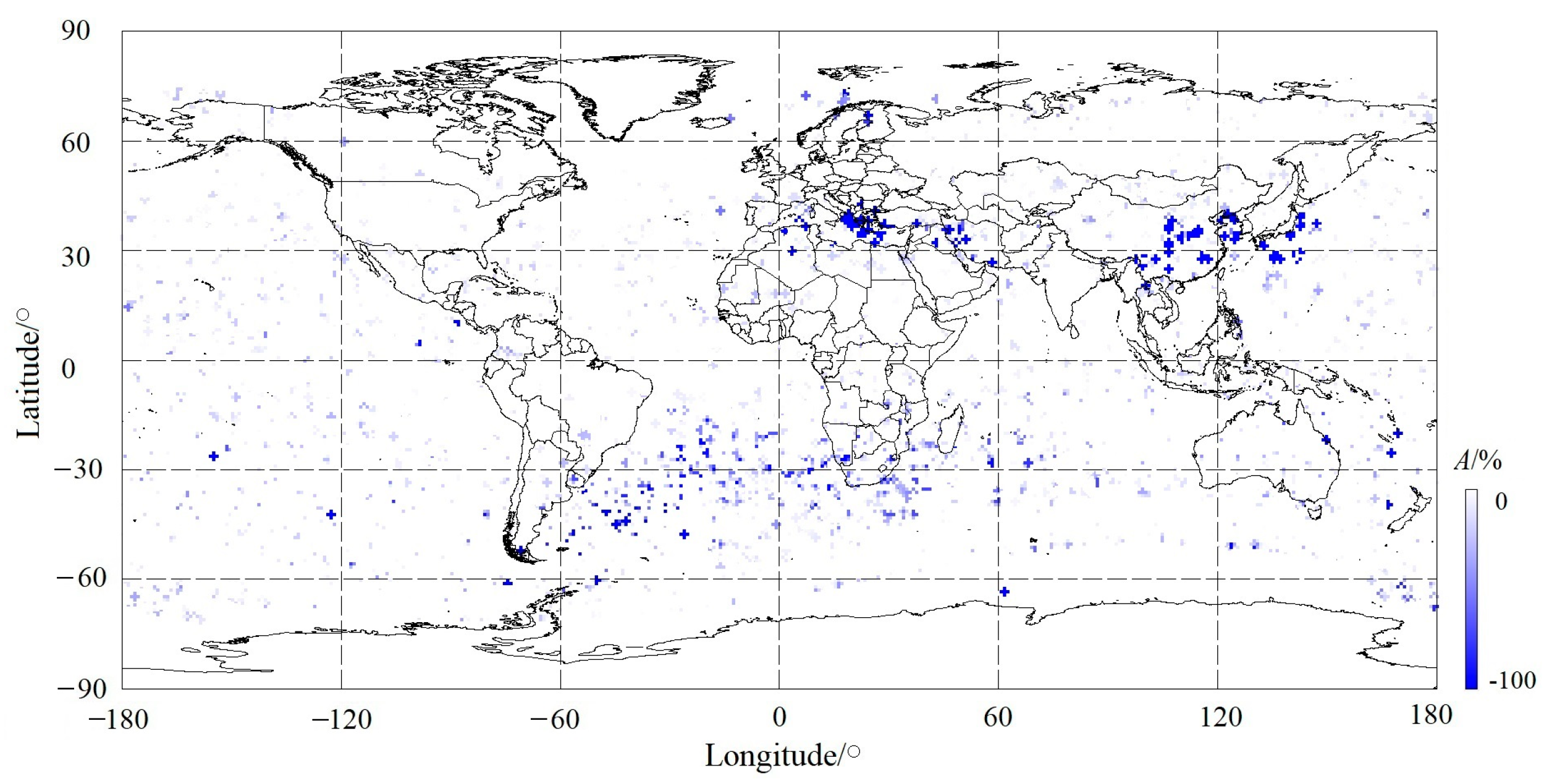
The nighttime South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly (SAMA) developed mainly in equinox, especially in winter, with a high Np but without an outstanding amplitude (Figure 5d,f) or space size (Figure 6d,f) due to its negative varying properties [16,20,23,56]. At the same time, we found the phenomenon of large negative-amplitude PERs collecting locally during the night equinox and winter seasons (Figure 5d,f). For a desirable statement, we distributed all negative PERs as a function of magnitude in the map in Figure 7. In Figure 7, it can be seen that PERs with a magnitude of less than −100% gather mainly in Northern Africa, Southeast China to the Japanese Ocean, and the South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly area, as well as a few anomalies such as the Eurasian continent and Australia. Among these, the negative ionospheric anomaly seems to be stronger in Northern Africa and Eastern Asia than in other areas.
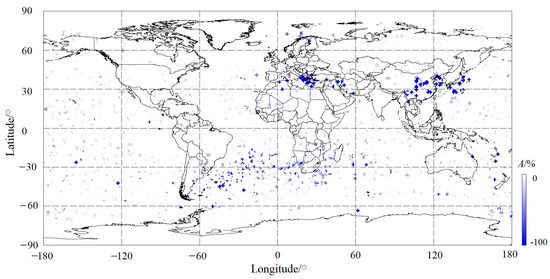
Figure 7.
Distribution of night PERs with respect to various negative-amplitude ranges.
We examined all night PERs and found that there are 196 with an amplitude less than −100% in total, and they occurred mostly in equinox and winter, with a few occurring in summer. The occurrence probability in winter was 82.7%. The key point is that these PERs are of similar space size at ~100 s, 700 km, if a velocity of the DEMETER satellite of 7 km/s is considered, possibly illustrating the outcome of the satellite flying over the same region at different times. Xu et al. [57] reported that there are mainly five planetary-scale geomagnetic anomalies worldwide: Australia, Africa, the Southern Atlantic Ocean, the Eurasian continent, and Northern America. However, in these areas, a strong negative ionospheric anomaly was not detected in Northern America but in Eastern Asia, including Southeast China and Japan during this time.
4. Discussion
Ionospheric irregularity has always been a main topic of investigations of ionospheric dynamics systems, and various data from ground-based sensors and in situ measurement onboard satellites have been utilized to establish ionospheric models and main large-scale ionospheric structures [2,3,4,5,6,7,9,10,11,12,13,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24], as well as their inner structure and property [58]. Unlike previous works using continuous data, during this time, automatically searched ion PERs were investigated for properties such as varied amplitude, space scale, location, and occurrence time. During this period, the influence of geomagnetic storms on the ionospheric ion density was first examined by analyzing two-group PERs occurring at a perturbed period when Kp > 4 and quiet time Kp ≤ 2, respectively. The results indicate that strong storms can enhance overall ionospheric irregularities more in amplitudes and less in space sizes. The impact of geomagnetic storms tends to be global, although this effect in equatorial and subauroral regions exhibits its significance more than in other areas. Geomagnetic storms generally give rise to global disturbances in the ionosphere, but ionospheric irregularities perform quite differently from one to another, and a strong spatial and local time dependency from either model or observational results mainly due to complex coupling mechanisms of the Earth’s magnetosphere–ionosphere–thermosphere system [48,50]. In a geomagnetic storm, the solar wind and magnetosphere output a large amount of energy and momentum into the Earth’s upper layers of atmosphere and ionosphere via enhanced particle precipitation and Joule heating. The enhanced electric fields at high latitudes can penetrate the equatorial region almost instantaneously, causing equatorial ionospheric disturbances [59,60]. Accompanying this process, the expansion of the neutral atmosphere via enhanced Joule heating at the auroral region can further drive traveling atmospheric/ionospheric disturbances [61,62]. Therefore, the influence of geomagnetic storms on ionospheric perturbance on the basis of this automatic detection method needs further research.
The dependence of PERs on local time has also been checked, and the appearance probability was 24.8% during daytime and 75.2% during nighttime, respectively. The statistical results, with respect to various amplitudes and space scales of PERs occurring at different local times, also revealed that the ratio of PERs with small amplitudes (A < 20%) accounts for 64% on the dayside and 26.8% on the nightside, respectively. On the other hand, large-amplitude PERs (A > 100%) occurred entirely at night. Nevertheless, the condition associated with space sizes has presented a contrary conclusion: PERs with space size t > 120 s occurred more frequently on the dayside than the nightside. This conclusion was also drawn from the left panels shown in Figure 6 of the dayside: PERs with a large space size appear collectively in the EIA area, which is the typical ionospheric feature during the daytime. Daytime EIA is driven by the equatorial plasma fountain effect. In the equatorial region, magnetic field lines are primarily horizontal, pointing northward, and the daytime eastward electric field drives the plasma upward via E × B drift. Under the combined force of gravity and pressure gradient, the up-lifted plasma diffuses poleward and sediments downward along the geomagnetic field lines into both hemispheres, forming two density crests alongside the magnetic equator [63,64]. The interhemispheric asymmetry EIA phenomena were constructed via daytime equinox and winter O+ PERs, having two clear crests with a higher density of large-space size PERs but a lower density between them. Moreover, the WN running along the magnetic equator longitude was also established during all periods considered in this timeframe. Therefore, the equatorial plasma fountain effect can simultaneously lead to large-scale ionospheric fluctuations.
The Wedell Sea Anomaly (WSA) displays its clear boundary within the area of 60° W–180° W longitude and 15° S–60° S latitude on the dayside in equinox and winter seasons from distributions of PERs, both on amplitude and on space size. Comparatively, this phenomenon occurs during nighttime and all seasons and is characterized typically by a high density of PERs with large positive amplitudes, especially in winter during nighttime (see the right panels in Figure 5), but without obviously increased space sizes (see Figure 6). Another feature of this structure is an expanded occupation area, covering a longitude of almost 30°–180° in the West Hemisphere, 100°–180° in the East Hemisphere, and a latitude of 15° S–60° S during the night in the winter. Chen et al. [65] have presented that the WSA can extend from South America and Antarctica to the Central Pacific. The major physical mechanisms of its formation involve equatorward neutral wind, an electric field, photoionization, and downward diffusion from the plasmasphere [55,65]. In this research, an enhanced PER density also appeared at a middle latitude of 20° N–40° N and along the entire longitude in the Northern Hemisphere in summer (See Figure 5a and Figure 6a). Horvath and Lovell [56] reported a WSA-like feature with an electron density enhancement occurring near Northeast Asia in the Northern Hemisphere. During a mid-latitude night, a plasma density enhancement exists in both hemispheres [66,67], which is known as the Mid-Latitude Summer Nighttime Anomaly (MSNA) [55]. On the other hand, the mid-latitude ionospheric trough (MIT) can also be understood based on the night seasons shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6; this phenomenon presents a narrow latitudinal extension of several degrees (±50°–55°) with a lower Np than the surroundings in both hemispheres. Its formation mechanism is the plasma “stagnation” mechanism with the interaction of high-latitude plasma convection and mid-latitude corotation flow, as well as other forces, such as a subauroral ion drift, subauroral electron temperature enhancement, and frictional heating [68,69,70].
Ion PERs with large negative amplitudes, for example, A < −100%, were successfully detected predominantly in winter during the night in most mentioned magnetic anomalies of the world, like the Africa anomaly and SAMA (Figure 7). Xu and Bai [57] concluded that these planetary-scale non-dipole fields could heavily control the secular variation in geomagnetic fields, and the combined effect from the Africa anomaly and SAMA have tremendously modified the shape and position of the magnetic equator. Unexpectedly, we also found a large negative ion density anomaly from Southeast China to the Japanese Ocean (Figure 7), but its formation mechanism remains unknown.
5. Conclusions
In this research, ion density measured by the DEMETER satellite for nearly 6 years was first collected. Then, software was utilized to automatically search ion perturbations globally, and 117,718 ion PERs were attained in total. All PERs were distributed on the map with various Kp indexes to examine the effects of solar activity. The effect of the geomagnetic storm was exhibited globally, although there were regions surrounding the equator of 0° and mid-latitude of 50° in both hemispheres where this effect showed more prominently. The occurrence probabilities of PERs appearing during the disturbed period (Kp > 4) and quiet period (Kp ≤ 2) were checked as functions of various amplitudes and space sizes, and the results present that geomagnetic storms can completely enhance ionospheric-positive variations but rarely beyond 100% and can sometimes also induce negative ones. On the other hand, the statistical results show no clear discrepancy between the space sizes of two-group PERs occurring during the disturbed time and quiet time, although the geomagnetic storm tends to induce ionospheric irregularities with relatively larger space sizes to some degree.
Statistical work was also performed on ion PERs occurring at different local times on the dayside (10:30 LT) and nightside (22:30 LT) for the DEMETER satellite. It was testified that ionospheric variations depend heavily on the local time: 24.8% during the day and 75.2% during the night, respectively. The statistical results of the PERs occurring during daytime or nighttime according to different scales of amplitude and space size indicated that I ionospheric fluctuations with an absolute A < 10% tend to be background variations; II PERs on the dayside with a small positive amplitude (< 20%) show a significance of 64%, while this number is only 26.8% for the nightside, but there is a contrary conclusion for ones with a mid–large-amplitude of A > 20%; III large positive PERs (A > 100%) predominantly occurred on the nightside but rarely the dayside, and large negative ones (A < −100%) only occurred on the nightside; IV there is a critical point for space size t = 120 s and occurrence probabilities of day PERs are always higher than that of night ones before this point, while this result is reverse after this point, which indicates that, comparatively, the ionosphere varies more frequently and more violently during the nighttime, causing relatively small-scale perturbations.
The distributions of seasonal PERs on the dayside and at nightside have displayed that there are more complex regional collections during the nighttime. These zonal collections generally show different aspects of main ionospheric structures during various seasons and local times. The EIA only exists on the dayside in equinox and winter, occupying two low-latitude crests with a lower Np in both hemispheres. The huge WSA appears during all periods except for on the dayside in summer, and is full of PERs with an enhanced amplitude, especially in winter during night. The WN-like structure can be clearly found in all seasons, showing absolutely large-scale spaces. Furthermore, several magnetically anomalous zones of planetary-scale non-dipole fields were also successfully detected by extremely negative ion PERs in this study. Therefore, the inner properties and formation physical mechanisms of these phenomena determined via automatically searched ion PERs will be the main focus of future investigations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, review, and editing, M.L.; validation and visualization, H.Y.; investigation and funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Special Expenses for Basic Scientific Research under grant no. CEAIEF2022030206 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under grant no. 41774084.
Data Availability Statement
Ion density data utilized here are available by directly contacting the first author, Mei Li, via the email mei_seis@163.com.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales. It is based on observations with the plasma analyzer IAP embarked on DEMETER.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Eckersley, T.L. Studies in radio transmission. Inst. Electr. Eng.-Proc. Wirel. Sect. Inst. 1932, 71, 405–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckersley, T.L. Irregular ionic clouds in the E layer of the ionosphere. Nature 1937, 140, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, H.G.; Wells, H.W. Scattering of radio waves by the F-region of the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1938, 43, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, E.V. Two anomalies in the ionosphere. Nature 1946, 157, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarons, J. Global morphology of ionospheric scintillations. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S. VHF ionospheric Scintillationsat L = 2.8 and formation of stable auroral red arcs by magnetospheric heat conduction. J. Geophys. Res. 1974, 79, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.K. Principles of the ionosphere at middle and low latitude. In The Solar-Terrestrial Environment. An Introduction to Geospace-the Science of the Terrestrial Upper Atmosphere, Ionosphere, and Magnetosphere; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houminer, Z.; Aarons, J. Production and dynamics of high-latitude irregularities during magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 9939–9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krankowski, A.; Shagimuratov, I.I.; Ephishov, I.I.; Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Yakimova, G. The occurrence of the mid-latitude ionospheric trough in GPS-TEC measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Stolle, C.; Lühr, H.; Park, J.; Fejer, B.G.; Kervalishvili, G.N. Scale analysis of the equatorial plasma irregularities derived from Swarm constellation. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaslak, B.; Przepiorka, D.; Rothkaehl, H. Seasonal Variations of Mid-Latitude Ionospheric Trough Structure Observed with DEMETER and COSMIC. Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 2734–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Park, J.; Lühr, H.; Stolle, C.; Ma, S. Comparing plasma bubble occurrence rates at CHAMP and GRACE altitudes during high and low solar activity. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomidze, L.; Knudsen, D.J.; Burchill, J.; Kouznetsov, A.; Buchert, S.C. Calibration and validation of Swarm plasma densities and electron temperatures using ground-based radars and satellite radio occultation measurements. Radio Sci. 2018, 53, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, R.W.; Nagy, A.F. Introduction. In Ionospheres: Physics, Plasma Physics, and Chemistry; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, X.; Parrot, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yan, R.; Liu, D.; Lu, H.; Guo, F.; et al. Primary joint statistical seismic influence on ionospheric parameters recorded by the CSES and DEMETER satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Cao, J.; Lu, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, D. Statistical backgrounds of topside ionospheric electron density and temperature and their variations during geomagnetic activity. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Lei, J.; Yue, X.; Luan, X.; Dou, X. Middle-latitudinal band structure observed in the nighttime ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, e2018JA026059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wan, W.; Liu, L.; Zhao, B.; Wei, Y.; Yue, X.; Heelis, R. Longitudinal variations of electron temperature and total ion density in the sunset equatorial topside ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Z. Nighttime enhancements in the midlatitude ionosphere and their relation to the plasmasphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 7686–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Berthelier, J.; Lebreton, J.-P. Semiannual and solar activity variations of daytime plasma observed by demeter in the ionosphere-plasmasphere transition region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 120, e2015JA021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Paxton, L.; Kil, H. Nightside midlatitude ionospheric arcs: TIMED/GUVI observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, X. The spatial distribution of hydrogen ions at topside ionosphere in local daytime. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2017, 28, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Berthelier, J. Large-scale depletion of nighttime oxygen ions at the low and middle latitudes in the winter hemisphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2022JA030688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Li, Q.; Zhong, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Yoshikawa, A.; Hu, L.; Xie, H.; Huang, C.; Yu, X.; et al. The ionosphere at middle and low latitudes under geomagnetic quiet time of December 2019. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, M. Statistical analysis of the ion density measured by the satellite DEMETER in relation with the seismic activity. Earthq. Sci. 2011, 24, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, G.; Boudjada, M.Y. Investigation of TEC and VLF space measurements associated to L’Aquila (Italy) earthquakes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X. Indications of Ground-based Electromagnetic Observations to A Possible Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Electromagnetic Coupling before the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan MS 8.0 Earthquake. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M. VLF/LF Radio Sounding of Ionospheric Perturbations Associated with Earthquakes. Sensors 2007, 7, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Boyarchuk, K.A.; Hegai, V.V.; Kim, V.P.; Lomonosov, A.M. Quasielectrostatic model of atmosphere-thermosphere-ionosphere coupling. Adv. Space Res. 2000, 26, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A. (Eds.) Seismo-Electromagnetics: Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Parrot, M.; Li, M. Statistical analysis of the ionospheric density recorded by the DEMETER satellite during seismic activity. In Pre-Earthquake Processes: A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to Earthquake Prediction Studies; Ouzounov, D., Pulinets, S., Hattori, K., Taylor, P., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series 234; AGU and John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Legen, A.D.; Gaivoronskaya, T.V.; Depuev, V.K. Main phenomenological features of ionospheric precursors of strong earthquakes. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2003, 65, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolsky, I.R.; Zubkov, S.I.; Myachkin, V.I. Estimation of the size of earthquake preparation zones. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1979, 117, 1025–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.I.; Chuo, Y.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Pulinets, S.A. Statistical study of ionospheric precursors of strong Earthquakes at Taiwan area. In Proceedings of the XXVIth General Assembly of The International Union of Radio Science, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–21 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Píša, D.; Němec, F.; Parrot, M.; Santolík, O. Attenuation of electromagnetic waves at the frequency ~1.7 kHz in the upper ionosphere observed by the DEMETER satellite in the vicinity of earthquakes. Ann. Geophys. 2012, 55, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Píša, D.; Němec, F.; Santolík, O.; Parrot, M.; Rycroft, M. Additional attenuation of natural VLF electromagnetic waves observed by the DEMETER spacecraft resulting from preseismic activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 5286–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němec, F.; Santolík, O.; Parrot, M.; Berthelier, J.J. Spacecraft observations of electromagnetic perturbations connected with Seismic Activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němec, F.; Santolík, O.; Parrot, M. Decrease of intensity of ELF/VLF Waves observed in the upper ionosphere close to earthquakes: A statistical study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, A04303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y. Using a spatial analysis method to study the Seismo-Ionospheric Disturbances of Electron Density Observed by China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 811658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunova, L.P.; Khegai, V.V. Analysis of seismo-ionospheric disturbances at the chain of Japanese stations for vertical sounding of the ionosphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 2008, 48, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, A.; Perrone, L.; Santis, A.D.; Sabbagh, D. Ionosonde data analysis in relation with the 2016 central italian earthquakes. Geosciences 2020, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Parrot, M. “Real time analysis” of the ion density measured by the satellite DEMETER in relation with the seismic activity. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Parrot, M. Statistical analysis of an ionospheric parameter as a base for earthquake prediction. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X. Temporal-spatial characteristics of seismo-ionospheric influence observed by the CSES satellite. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, M.; Berthelier, J.J.; Lebreton, J.P.; Sauvaud, J.A.; Santolík, O.; Blecki, J. Examples of unusual ionospheric observations made by the DEMETER satellite over seismic regions. Phys. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, B.; Raita, T.; Liu, J.; Zhima, Z.; Shen, X. Ionospheric Pc1 waves during a storm recovery phase observed by the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite. Ann. Geophys. 2020, 38, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhong, J.; Xiong, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Kuai, J.; Weng, L.; Cui, J. Persistent occurrence of strip-like plasma density bulges at conjugate lower-mid latitudes during the September 8–9, 2017 geomagnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA029020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prölss, G.W. Ionospheric F-Region Storms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.; Lühr, H.; Yamazaki, Y. An opposite response of the low-latitude ionosphere at Asian and American sectors during storm recovery phases: Drivers from below or above. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 6266–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhima, Z.; Xiong, C.; Shen, X.; Huang, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, C. Comparison of electron density and temperature from the CSES satellite with other space-borne and ground-based observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, H. On earth-currents, and their connexion with the diurnal changes of the horizontal magnetic needle. Trans. R. Ir. Acad. 1861, 24, 115–141. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.H. F2 ionization and geomagnetic latitudes. Nature 1947, 160, 642–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Liu, L.; Wan, W.; Lei, J.; Zhao, B. Longitudinal modulation of the O/N2 column density retrieved from TIMED/GUVI measurement. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenkova, I.; Cherniak, I.; Shagimuratov, I. Observations of the Weddell Sea Anomaly in the ground-based and space-borne TEC measurements. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2017, 161, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Lovell, B.C. Investigating the relationships among the South Atlantic magnetic Anomaly, southern nighttime midlatitude trough, and nighttime Weddell Sea Anomaly during southern summer. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A02306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Bai, C. Role of the African magnetic anomaly in controlling the magnetic configuration and its secular variation. Chin. J. Geophys 2009, 52, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiong, C.; Wan, X.; Lai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Ou, M. Instability mechanisms for the F-region plasma irregularities inside the midlatitude ionospheric trough: Swarm observations. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2021SW002785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Luhr, H.; Kitamura, T.; Saka, O.; Schlegel, K. Direct penetration of the polar electric field to the equator during a DP 2 event as detected by the auroral and equatorial magnetometer chains and the EISCAT radar. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 17161–17173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A. Coherence of geomagnetic DP 2 fluctuations with interplanetary magnetic variations. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocke, K.; Schlegel, K. A review of atmospheric gravity waves and traveling ionospheric disturbances: 1982–1995. Ann. De Geophys. 1996, 14, 917–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, A.D.; Matsushita, S. Thermospheric response to a magnetic substorm. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.A. The equatorial F-region of the ionosphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1960, 18, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Rang, X.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Jiang, G.Y.; Hu, K.; Luo, W.H. Latitudinal four-peak structure of the nighttime F region ionosphere: Possible contribution of the neutral wind. Rev. Geophys. Planet. Phys. 2024, 55, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Huba, J.D.; Saito, A.; Lin, C.H.; Liu, J.Y. Theoretical study of the ionospheric Weddell sea anomaly using SAMI2. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, A04305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Wang, W.; Burns, A.; Solomon, S.C.; Lei, J. Midlatitude nighttime enhancement in F region electron density from global COSMIC measurements under solar minimum winter condition. J. Geophys. Res. Sp. Phys. 2008, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Liu, C.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Burns, A.G.; Wang, W. Midlatitude summer nighttime anomaly of the ionospheric electron density observed by FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A03308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’ Ionosphere, Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.C.; Heelis, R.A.; Hanson, W.B. The ionospheric signatures of rapid subauroral ion drifts. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 5785–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Kadokura, A.; Hiraki, Y.; Haggstrom, I. Seasonal variation and solar activity dependence of the quiet-time ionospheric trough. J. Geophys. Res. Sp. Phys. 2014, 119, 6774–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).