The Sacred Waterscape of the Temple of Bastet at Ancient Bubastis, Nile Delta (Egypt)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
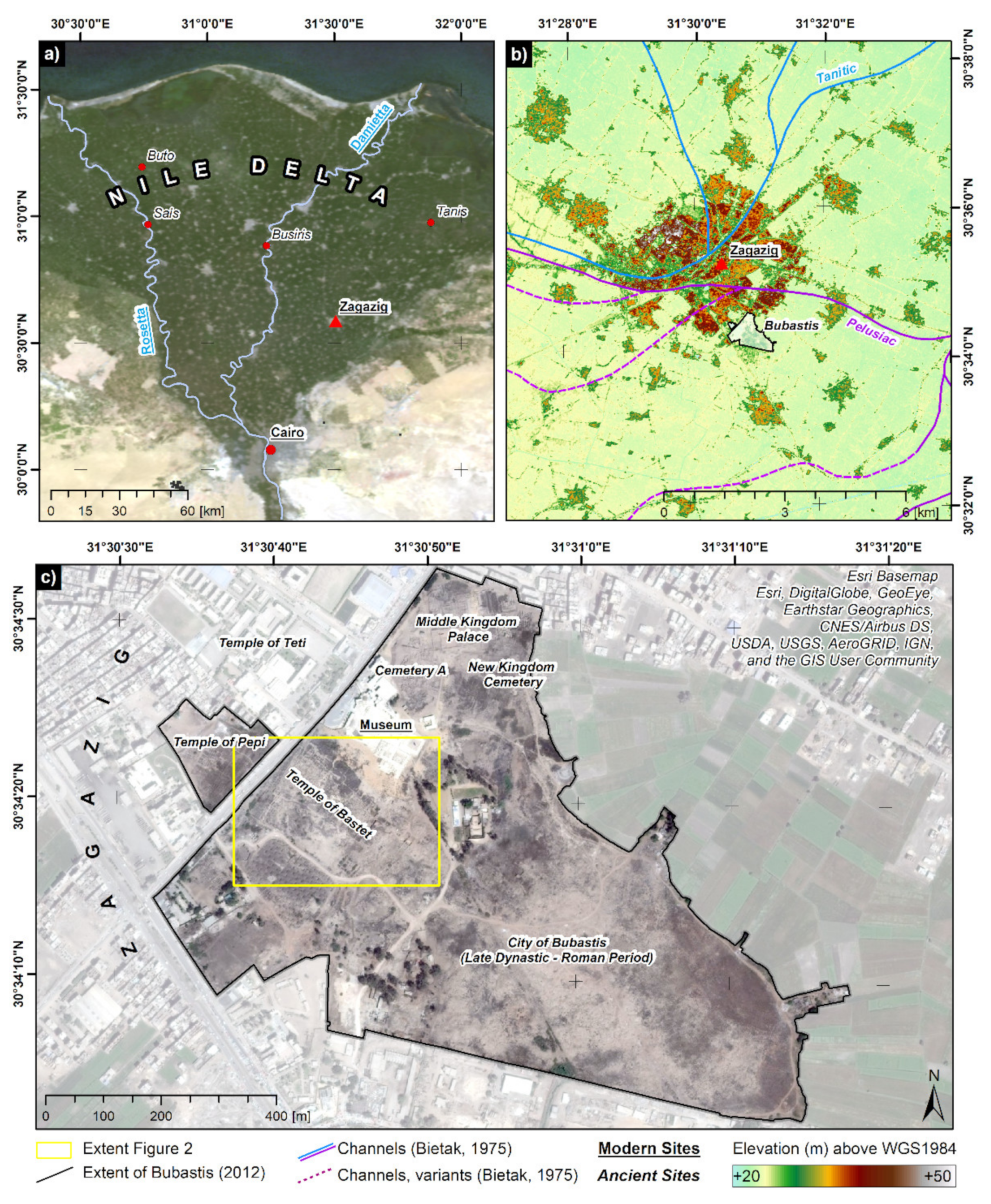
2. Study Area
2.1. Holocene Nile Delta Evolution and Settlement Activities
2.2. The Ancient City of Bubastis (Tell Basta)
3. Materials and Methods
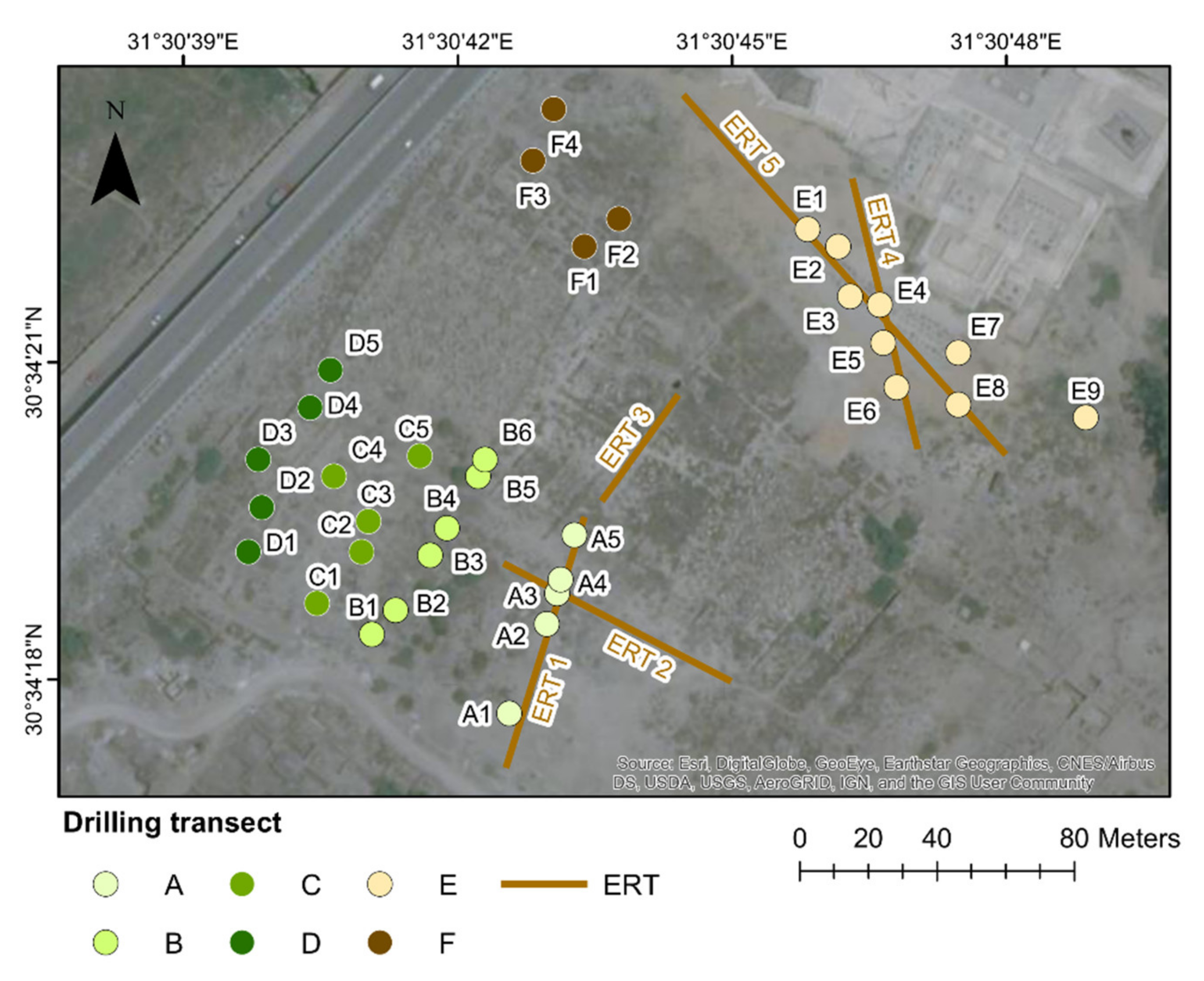
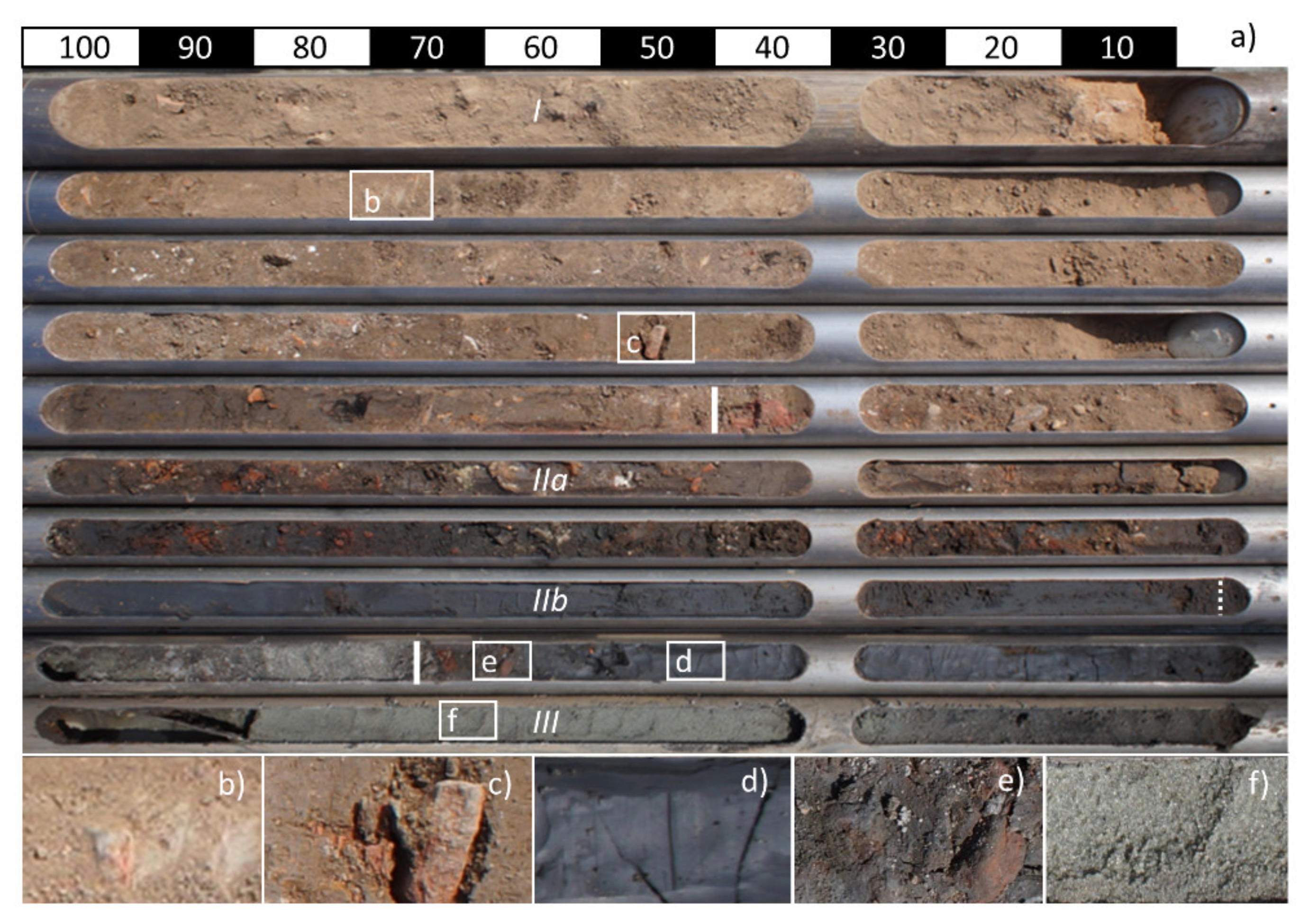
3.1. Drillings and Sediment Analyses
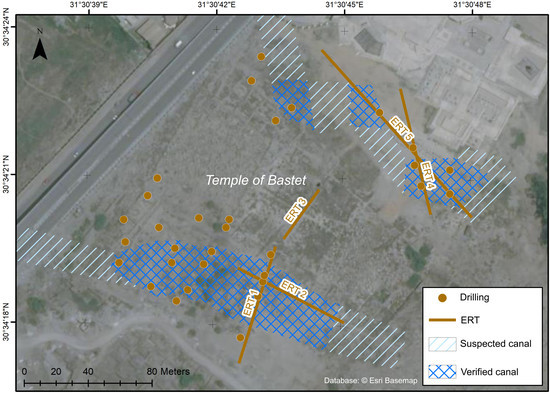
3.2. Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
4. Results
4.1. Distribution of Sedimentary Units
4.1.1. South of the Temple of Bastet (Drilling Transects A–D)
4.1.2. North of the Temple of Bastet (Drilling Transects E–F)
4.2. Electrical Resistivity Ranges and Distributions
4.2.1. South of the Temple of Bastet (Profiles ERT 1–2)
4.2.2. Center of the Temple of Bastet (Profile ERT 3)
4.2.3. North of the Temple of Bastet (Profiles ERT 4–5)
5. Discussion
5.1. Sedimentary Units and ERT Surveying
5.2. Canal Reconstruction
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bussmann, R. Die Provinztempel Ägyptens Von der 0. Bis Zur 11. Dynastie. In Probleme der Ägyptologie; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 978-90-04-17933-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Athinodorou, E.; El-Raouf, A.A.; Ullmann, T.; Trappe, J.; Meister, J.; Baumhauer, R. The sacred canals of the Temple of Bastet at Bubastis (Egypt): New findings from geomorphological investigations and Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2019, 26, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange-Athinodorou, E. Implications of geoarchaeological investigations for the contextualization of sacred landscapes in the Nile Delta. EG Quat. Sci. J. 2021, 70, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessler-Löhr, B. Die Heiligen Seen Ägyptischer Tempel: Ein Beitrag Zur Deutung Sakraler Baukunst im Alten Ägypten. In Hildesheimer Ägyptologische Beiträge; Gerstenberg: Hildesheim, Germany, 1983; Volume 21, ISBN 978-3-8067-8080-2. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, B.A. On the Heels of the Wandering Goddess: The Myth and the Festival at the Temples of the Wadi el-Hallel and Dendera. In 8. Ägyptologische Tempeltagung: Interconnections between Temples; Dolińska, M., Beinlich, H., Eds.; Harrassowitz Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tillier, A. Notes sur l’icherou. Égypte Nilotique Mediterr. 2010, 3, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Trampier, J. Reconstructing the Desert and Sown Landscape of Abydos. J. Am. Res. Cent. Egypt. 2005, 42, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Atya, M.A.; Al Khateeb, S.O.; Ahmed, S.B.; Musa, M.F.; Gaballa, M.; Abbas, A.M.; Shaaban, F.F.; Hafez, M.A. GPR investigation to allocate the archaeological remains in Mut temple, Luxor, Upper Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2012, 1, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, P. The survey of Saïs (Sa el-Hagar) 1997–2002. In Egypt Exploration Society, Excavation Memoir; Egypt Exploration Society: London, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-85698-175-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, P. Gateway to the underworld: The cult areas at Sais. Stud. Anc. Egypt. Sudan 2019, 24, 341–364. [Google Scholar]
- Leclère, F. Les Villes de Basse Égypte au Ier Millénaire av. J.-C.: Analyse Archéologique et Historique de la Topographie Urbaine; Bibliothèque d’étude; Institut Français D’archéologie Orientale: Cairo, Egypt, 2008; Vol. 2, ISBN 978-2-7247-0489-1. [Google Scholar]
- Montet, P. Le lac sacré de Tanis. In Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres (Extrait des Mémoires de l’Académie, Tome XLIV); Imprimerie Nationale: Paris, France, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann, T.; Lange-Athinodorou, E.; Göbel, A.; Büdel, C.; Baumhauer, R. Preliminary results on the paleo-landscape of Tell Basta/Bubastis (eastern Nile delta): An integrated approach combining GIS-Based spatial analysis, geophysical and archaeological investigations. Quat. Int. 2019, 511, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, G.M.; Rizzo, E.; Revil, A.; Vella, C. High Resolution Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) in a Transition Zone Environment: Application for Detailed Internal Architecture and Infilling Processes Study of a Rhône River Paleo-channel. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2005, 26, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, J.; Strutt, K.D. Geophysical survey and sub-surface investigations at Quesna and Kom el-Ahmar (Minuf), governorate of Minufiyeh: An integrated strategy for mapping and understanding sub-surface remains of mortuary, sacred and domestic contexts. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Achievements and Problems of Modern Egyptology”, Moscow, Russia, 29 September–2 October 2009; Belova, G.A., Ivanov, S.V., Eds.; Russian Academy of Sicences, Center for Egyptological Studies: Moscow, Russia, 2012; pp. 328–345. [Google Scholar]
- Torrese, P.; Rainone, M.L.; Colantonio, F.; Signanini, P. Identification and investigation of shallow paleochannels in the chamelecon valley (Honduras): 1D vs. 2D electrical resistivity surveys. In Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems 2013; Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society: Denver, CO, USA, 2013; pp. 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kenawy, A.; Metwaly, M.; Gemail, K.; El-Raouf, A.A. Contribution of geoelectrical resistivity sounding for paleoenvironment assessment at Saft El-Henna and Tell El-Dab’a archaeological sites, eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Explor. Geophys. 2013, 44, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, M.; Traczyk, A. LiDAR and 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography as a Supplement of Geomorphological Investigations in Urban Areas: A Case Study from the City of Wrocław (SW Poland). Pure Appl. Geophys. 2014, 171, 835–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Gamili, M.M.; Shaaban, F.F.; El-Morsi, O.A. Electrical resistivity mapping of the buried stream channel of the Canopic branch in the western Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1994, 19, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gamili, M.M.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Hassaneen, A.R.G.; Abdalla, M.A.; Ismael, A.M. Defunct Nile Branches Inferred from a Geoelectric Resistivity Survey on Samannud area, Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2001, 28, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toonen, W.H.J.; Graham, A.; Pennington, B.T.; Hunter, M.A.; Strutt, K.D.; Barker, D.S.; Masson-Berghoff, A.; Emery, V.L. Holocene fluvial history of the Nile’s west bank at ancient Thebes, Luxor, Egypt, and its relation with cultural dynamics and basin-wide hydroclimatic variability. Geoarchaeology 2018, 33, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altmeyer, M.; Seeliger, M.; Ginau, A.; Schiestl, R.; Wunderlich, J. Reconstruction of former channel systems in the northwestern Nile Delta (Egypt) based on corings and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT). EG Quat. Sci. J. 2021, 70, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.; Ghazala, H. Sandhills, sandbanks, waterways, canals and sacred lakes at Sais in the Nile Delta. EG Quat. Sci. J. 2021, 70, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shata, A.A.; El Fayoumy, I.F. Remarks on the regional geological structure of the Nile Delta. In Proceedings of the Bucharest Symposium on Hydrogeology of Deltas, Bucharest, Romania, 6–14 May 1969; Gentbrugge Belgium: Paris, France, 1970; pp. 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Butzer, K.W. Early Hydraulic Civilization in Egypt: A Study in Cultural Ecology; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1976; ISBN 978-0-226-08635-4. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geological Evolution of the River Nile; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; ISBN 978-1-4612-5843-8. [Google Scholar]
- Andres, W.; Wunderlich, J. Late Pleistocene and Holocene Evolution of the Eastern Nile Delta and Comparisons with the Western Delta. In Von der Nordsee bis Zum Indischen Ozean. Ergebnisse der 8. Jahrestagung des AK Geographie der Meere und Küsten; Brückner, H., Ratdke, U., Eds.; Erdkundliches Wissen: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, D.J.; Warne, A.G. Nile Delta in Its Destruction Phase. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 795–825. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, D.J.; Warne, A.G. Nile Delta: Recent Geological Evolution and Human Impact. Science 1993, 260, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfriend, G.A.; Stanley, D.J. Rapid strand-plain accretion in the northeastern Nile Delta in the 9th century A.D. and the demise of the port of Pelusium. Geology 1999, 27, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, B.T.; Sturt, F.; Wilson, P.; Rowland, J.; Brown, A.G. The fluvial evolution of the Holocene Nila. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 170, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butzer, K.W. Geoarchaeological implications of recent research in the Nile Delta. In Egypt and the Levant: Interrelations from the 4th through the Early 3rd Millennium BCE; van den Brink, E.C.M., Levy, T.E., Eds.; Leicester University Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, J.; Lange-Athinodorou, E.; Ullmann, T. Preface: Special issue “Geoarchaeology of the Nile Delta". EG Quat. Sci. J. 2021, 70, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, E.C.M. A geo-archaeological survey in the north-eastern Nile Delta. Mitt. Dtsch. Archäol. Inst. Abt. Kairo 1986, 43, 7–31. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The River Nile: Geology, Hydrology and Utilization; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA; Seoul, Korea; Tokyo, Japan, 1993; ISBN 978-0-08-041886-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bietak, M. Tell El-Dab’a II, Der Fundort im Rahmen Einer Archäologisch-Geographischen Untersuchung Über das Ägyptische Ostdelta. In Untersuchungen der Zweigstelle Kairo des Österreichischen Archäologischen Instituts; Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenaschaften: Wien, Austria, 1975; ISBN 978-0-00-343931-1. [Google Scholar]
- El Mahmoudi, A.; Gabr, A. Geophysical surveys to investigate the relation between the Quaternary Nile channels and the Messinian Nile canyon at East Nile Delta, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2009, 2, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, T.; Nill, L.; Schiestl, R.; Trappe, J.; Lange-Athinodorou, E.; Baumhauer, R.; Meister, J. Mapping buried paleogeographical features of the Nile Delta (Egypt) using the Landsat archive. EG Quat. Sci. J. 2020, 69, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, E. Die Ka-Anlage Pepis I. in Bubastis im Kontext königlicher Ka-Anlagen des alten Reiches. Z. Ägypt. Sprache Altert. 2006, 133, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, M.I.; Lange, E. Die Nekropolen des Alten Reichs in Bubastis. In Ägypten Begreifen. Erika Endesfelder in Memoriam; Feder, F., Sperveslage, G., Steinborn, F., Eds.; IBAES 19: Berlin, Germany; London, UK, 2017; pp. 31–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Athinodorou, E.; Es-Senussi, A. A royal ka-temple and the rise of Old Kingdom Bubastis. Egypt. Archaeol. 2021, 53, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bietak, M.; Lange, E. Tell Basta: The palace of the Middle Kingdom. Egypt. Archaeol. 2014, 44, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, E. The So-called Governors’ Cemetery at Bubastis and Provincial Elite. Tombs in the Nile Delta: State and Perspectives of Research. In The World of Middle Kingdom Egypt (2000–1550 BC); Grajetzki, M., Ed.; GHP Egyptology: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, E.; Ullmann, T.; Baumhauer, R. Remote Sensing in the Nile Delta: Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Bubastis/Tell Basta. Ägypt. Levante/Egypt Levant 2016, 26, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, E. Legitimation und Herrschaft in der Libyerzeit. Eine neue Inschrift Osorkons I. aus Bubastis (Tell Basta). Z. Ägypt. Sprache Kult 2008, 135, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, E. The Sed-festival of Osorkon II. at Bubastis: New investigations. In The Libyan Period in Egypt. Historical and Cultural Studies into the 21st–24th Dynasties: Proceedings of a Conference at Leiden University, 25–27 October 2007; Broekman, G.P.F., Demare, R.J., Kaper, O., Eds.; Nederlands Instituut voor het Nabije Osten: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Athinodorou, E. Der "Tempel des Hermes" und die Pfeile der Bastet: Zur Rekonstruktion der Kulturlandschaft von Bubastis. In Festschrift Hans-Werner Fischer-Elfert; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 549–585. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Athinodorou, E. Sedfestritual und Königtum: Die Reliefdekoration am Torbau Osorkons II. im Tempel der Bastet von Bubastis. In Ägyptologische Abhandlungen; Harrassowitz: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-447-11192-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen, K.A. The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (1100-650 BC); Aris & Philipps: Warminster, UK, 1986; ISBN 978-0-85668-298-8. [Google Scholar]
- Naville, E. Bubastis (1887–1889). In Memoir of the Egypt Exploration Fund; Kegan Paul, Trench, Truebner: London, UK, 1891. [Google Scholar]
- Meeks, D. Mythes et légendes du Delta d’après le papyrus Brooklyn 47.218.84. In Mémoires Publiés par les Membres de l’Institut Français d’Archéologie Orientale; Institut Français d’Archéologie Orientale: Cairo, Egypt, 2006; ISBN 978-2-7247-0427-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, N.G. Herodoti Historiae; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-0-19-956071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann, T.; Büdel, C.; Brauneck, J.; Lange, E.; Baumhauer, R. Landoberflächenanalyse zur Identifikation antiker Wasserwege im Umfeld der Tempelanlagen von Bubastis im südöstlichen Nildelta. DGPF Tag. 2015, 24, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Ad-hoc-Arbeitsgruppe Boden. Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung. KA5 [Manual of Soil Mapping], 5th ed.; Eckelmann, W., Ed.; Schweizerbart Science Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-3-510-95920-4. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps–Update 2015; World Soil Resources Reports; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015; ISBN 978-92-5-108369-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T.; Zhou, B. A numerical comparison of 2D resistivity imaging with 10 electrode arrays. Geophys. Prospect. 2004, 52, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Tsourlos, P.; Tsokas, G.N.; Sarris, A. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional resistivity imaging in archaeological site investigation. Archaeol. Prospect. 2006, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Barker, R.D. Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method1. Geophys. Prospect. 1996, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginau, A.; Schiestl, R.; Wunderlich, J. Integrative geoarchaeological research on settlement patterns in the dynamic landscape of the northwestern Nile delta. Quat. Int. 2019, 511, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.G. Alluvial Geoarchaeology: Floodplain Archaeology and Environmental Change. In Cambridge Manuals in Archaeology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-521-56097-9. [Google Scholar]
- Toonen, W.H.J.; Kleinhans, M.G.; Cohen, K.M. Sedimentary architecture of abandoned channel fills. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, J. Investigations on the development of the Western Nile Delta in Holocene times. In The Archaeology of the Nile Delta, Egypt: Problems and Priorities: Proceedings of the Seminar Held in Cairo, 19–22 October 1986; van den Brink, E.C.M., Ed.; Netherlands Foundation for Archaeological Research in Egypt: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, L.P.; Sheriff, R.E. Applied Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; ISBN 978-0-521-32693-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-471-48535-3. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, K.; Saha, D.K.; Chakraborty, P. Geophysical study for saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain. J. Appl. Geophys. 2001, 46, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, F.F.; Shaaban, F.A. Use of two-dimensional electric resistivity and ground penetrating radar for archaeological prospecting at the ancient capital of Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2001, 33, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
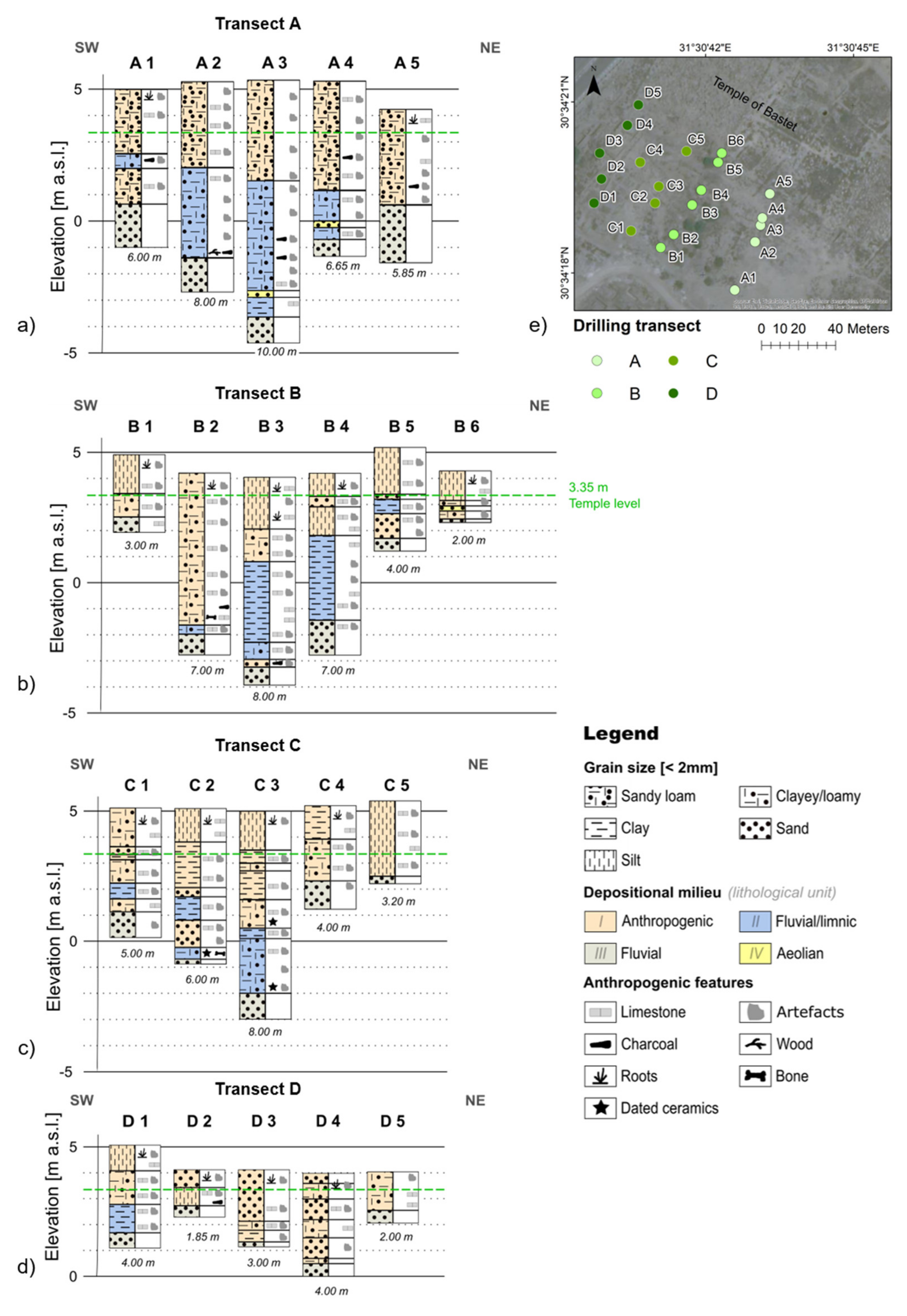
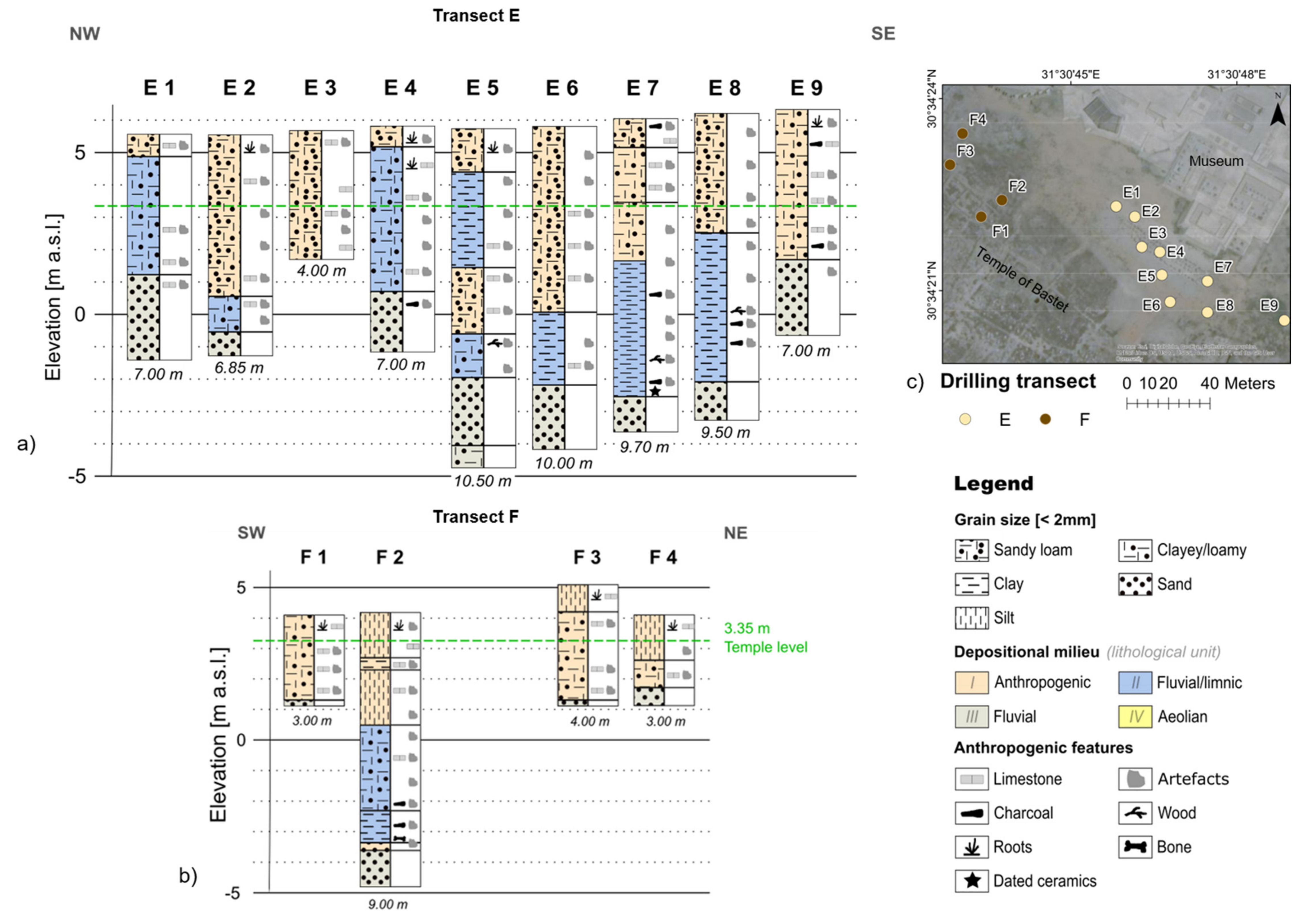
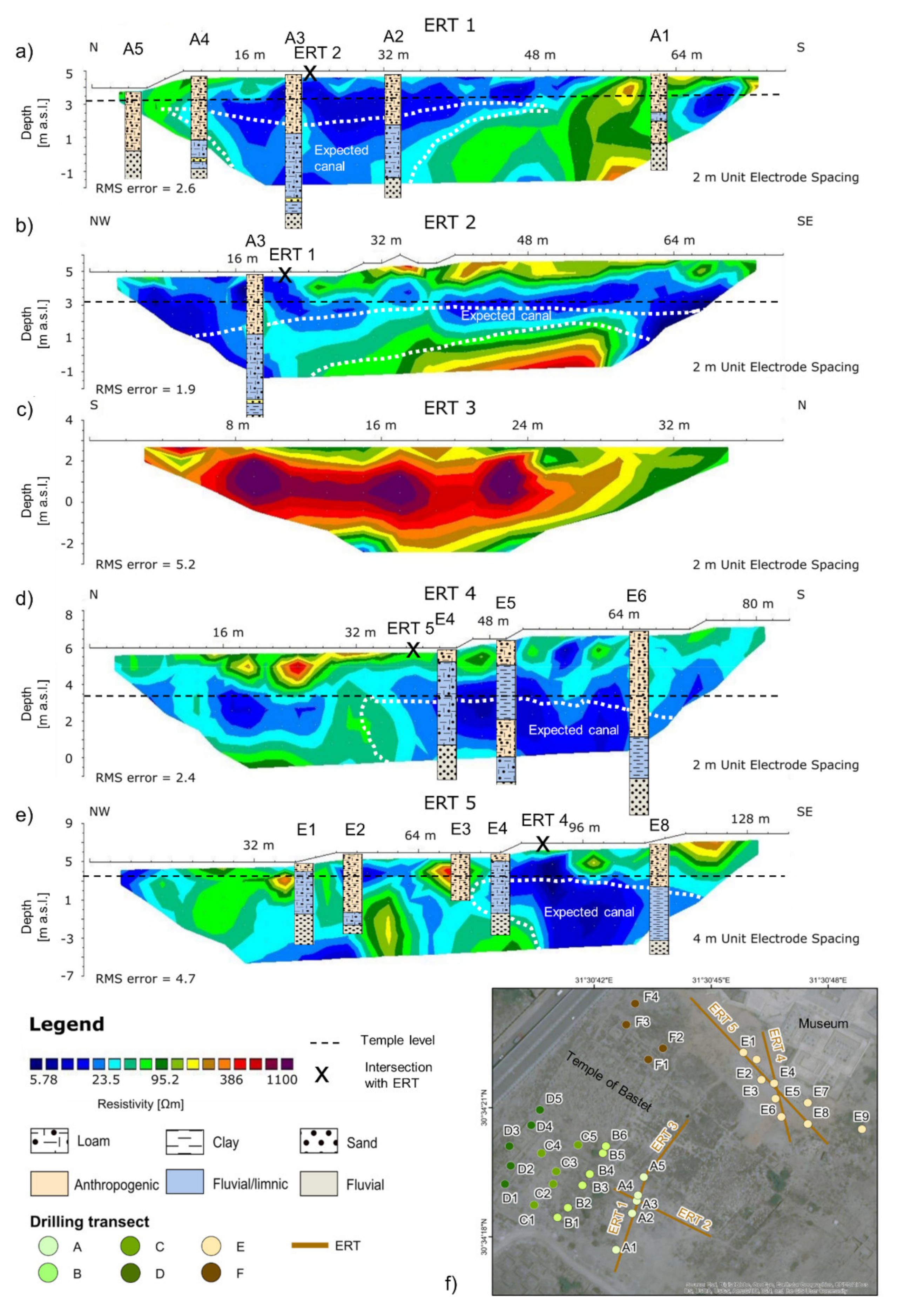

| Profile | Length [m] | Electrode Spacing [m] | Drilling Locations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERT 1 | 76 | 2 | A1–A5 |
| ERT 2 | 76 | 2 | A3 |
| ERT 3 | 38 | 2 | n.a. |
| ERT 4 | 84 | 2 | E4–E6 |
| ERT 5 | 136 | 4 | E1–E4, E8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meister, J.; Garbe, P.; Trappe, J.; Ullmann, T.; Es-Senussi, A.; Baumhauer, R.; Lange-Athinodorou, E.; El-Raouf, A.A. The Sacred Waterscape of the Temple of Bastet at Ancient Bubastis, Nile Delta (Egypt). Geosciences 2021, 11, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11090385
Meister J, Garbe P, Trappe J, Ullmann T, Es-Senussi A, Baumhauer R, Lange-Athinodorou E, El-Raouf AA. The Sacred Waterscape of the Temple of Bastet at Ancient Bubastis, Nile Delta (Egypt). Geosciences. 2021; 11(9):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11090385
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeister, Julia, Philipp Garbe, Julian Trappe, Tobias Ullmann, Ashraf Es-Senussi, Roland Baumhauer, Eva Lange-Athinodorou, and Amr Abd El-Raouf. 2021. "The Sacred Waterscape of the Temple of Bastet at Ancient Bubastis, Nile Delta (Egypt)" Geosciences 11, no. 9: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11090385
APA StyleMeister, J., Garbe, P., Trappe, J., Ullmann, T., Es-Senussi, A., Baumhauer, R., Lange-Athinodorou, E., & El-Raouf, A. A. (2021). The Sacred Waterscape of the Temple of Bastet at Ancient Bubastis, Nile Delta (Egypt). Geosciences, 11(9), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11090385