Migration of Natural Hydrogen from Deep-Seated Sources in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The São Francisco Basin
3. H2 Seepages in the Bambuí Group in the Southern Part of the São Francisco Basin
4. A Possible Deep Origin for H2
4.1. Production of H2 by Water Radiolysis
4.2. Production of H2 by Serpentinization or Hydration
4.3. Presence of Ultramafic Rocks
4.4. Temperature Ranges at Depth
4.5. Possible H2 Bubbling at Depth
5. Draining Fault System in the São Francisco Basin
6. Possible Temporary Shallow Zones of H2 Accumulation
7. Putting It All Together: A Potential H2 System within the São Francisco Basin
8. Discussing the H2 Production from Radiolysis and Hydration Reactions in the São Francisco Basin
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Truche, L.; McCollom, T.M.; Martinez, I. Hydrogen and Abiotic Hydrocarbons: Molecules that Change the World. Elem. Int. Mag. Miner. Geochem. Pet. 2020, 16, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.J.P. It’s time for explorationists to take hydrogen more seriously. First Break 2002, 20, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, N.J.P.; Shepherd, T.J.; Styles, M.T.; Williams, G.M. Hydrogen exploration: A review of global hydrogen accumulations and implications for prospective areas in NW Europe. In Petrology Geology: North-West Europe and Global Perspectives—Proceedings of the 6th Petroleum Geology Conference; Doré, A.G., Vining, B.A., Eds.; Petroleum Geology Conference Series; Geological Society: London, UK, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Truche, L.; Bazarkina, E.F. Natural hydrogen the fuel of the 21st century. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; Volume 98, p. 03006. [Google Scholar]
- Gaucher, E.C. New Perspectives in the Industrial Exploration for Native Hydrogen. Elem. Int. Mag. Miner. Geochem. Pet. 2020, 16, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgonnik, V. The occurrence and geoscience of natural hydrogen: A comprehensive review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.; Stanger, G. Hydrogen generation from mantle source rocks in Oman. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1983, 66, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, R.M., Jr.; Goebel, E.D.; Zeller, E.J.; Angino, E.E. Serpentinization and the origin of hydrogen gas in Kansas. AAPG Bull. 1987, 71, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Abrajano, T.A.; Sturchio, N.C.; Kennedy, B.M.; Lyon, G.L.; Muehlenbachs, K.; Bohlke, J.K. Geochemistry of reduced gas related to serpentinization of the Zambales ophiolite, Philippines. Appl. Geochem. 1990, 5, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlou, J.L.; Fouquet, Y.; Donval, J.P.; Auzende, J.M.; Jean-Baptiste, P.; Stievenard, M. Mineral and gas chemistry of hydrothermal fluids on an ultrafast spreading ridge: East Pacific Rise, 17° to 19°S (Naudur cruise, 1993) phase separation processes controlled by volcanic and tectonic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewald, J.S.; Cruse, A.; Saccocia, P. Aqueous volatiles in hydrothermal fluids from the Main Endeavour Field, northern Juan de Fuca Ridge: Temporal variability following earthquake activity. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 216, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larin, N.; Zgonnik, V.; Rodina, S.; Deville, E.; Prinzhofer, A.; Larin, V.N. Natural molecular hydrogen seepage associated with surficial, rounded depressions on the European craton in Russia. Nat. Resour. Res. 2015, 24, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgonnik, V.; Beaumont, V.; Deville, E.; Larin, N.; Pillot, D.; Farrell, K.M. Evidence for natural molecular hydrogen seepage associated with Carolina bays (surficial, ovoid depressions on the Atlantic Coastal Plain, Province of the USA). Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzhofer, A.; Cissé, C.S.T.; Diallo, A.B. Discovery of a large accumulation of natural hydrogen in Bourakebougou (Mali). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 19315–19326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzhofer, A.; Moretti, I.; Francolin, J.; Pacheco, C.; d’Agostino, A.; Werly, J.; Rupin, F. Natural hydrogen continuous emission from sedimentary basins: The example of a Brazilian H2-emitting structure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 5676–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathles, L.; Prinzhofer, A. What Pulsating H2 Emissions Suggest about the H2 Resource in the São Francisco Basin of Brazil. Geosciences 2020, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flude, S.; Warr, O.; Magalhães, N.; Bordmann, V.; Fleury, J.M.; Reis, H.L.S.; Trindade, R.I.; Hillegonds, D.; Sherwood Lollar, B.; Ballentine, C.J. Deep crustal source for hydrogen and helium gases in the São Francisco Basin, Minas Gerais, Brazil. AGUFM 2019, 2019, EP51D-2111. [Google Scholar]
- Heilbron, M.; Cordani, U.G.; Alkmim, F.F. The São Francisco craton and its margins. In São Francisco Craton 2017, Eastern Brazil; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Anhaeusser, C.R. Archaean greenstone belts and associated granitic rocks—A review. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 100, 684–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, W.; Oliveira, E.P.; Marques, L.S. Nature and evolution of the Archean crust of the São Francisco Craton. In São Francisco Craton 2017, Eastern Brazil; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Delpomdor, F.R.; Ilambwetsi, A.M.; Caxito, F.A.; Pedrosa-Soares, A.C. New interpretation of the basal Bambuí Group, Sete Lagoas High (Minas Gerais, SE Brazil) by sedimentological studies and regional implications for the aftermath of the Marinoan glaciation: Correlations across Brazil and Central Africa. Geol. Belg. 2020, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, J.B.; Pires, A.C.; Silva, A.M.; Crósta, Á.P. The role of airborne geophysics for detecting hydrocarbon microseepages and related structural features: The case of Remanso do Fogo, Brazil. Geophysics 2012, 77, B35–B41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Solon, F.F.; Fontes, S.L.; Meju, M.A. Magnetotelluric imaging integrated with seismic, gravity, magnetic and well-log data for basement and carbonate reservoir mapping in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil. Pet. Geosci. 2015, 21, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiro-Silva, P.C.; Zalán, P.V. Contribuição da sísmica de reflexão na determinação do limite oeste do Cráton do São Francisco. In Proceeding of the III Simpósio Sobre o Cráton do São Francisco, Salvador, Brazil, 14–18 August 2005; pp. 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, H.L.; Alkmim, F.F. Anatomy of a basin-controlled foreland fold-thrust belt curve: The Três Marias salient, São Francisco basin, Brazil. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guélard, J.; Beaumont, V.; Rouchon, V.; Guyot, F.; Pillot, D.; Jézéquel, D.; Ader, M.; Newell, K.D.; Deville, E. Natural H2 in Kansas: Deep or shallow origin? Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 1841–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Hall, J.; Lippmann-Pipke, J.; Ward, J.A.; Sherwood Lollar, B.; DeFlaun, M.; Rothmel, R.; Moser, D.; Gihring, T.M.; Mislowack, B.; et al. Radiolytic H2 in continental crust: Nuclear power for deep subsurface microbial communities. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2005, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, E.D.; Coveney, R.M.J.; Angino, E.E.; Zeller, E.J.; Dreschhoff, G.A.M. Geology, composition, isotopes of naturally occurring H2/N2 rich gas from wells near Junction City, Kansas. Oil Gas J. 1984, 82, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Lollar, B.S.; Onstott, T.C.; Lacrampe-Couloume, G.; Ballentine, C.J. The contribution of the Precambrian continental lithosphere to global H 2 production. Nature 2014, 516, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, J.; Blamey, N. Global hydrogen reservoirs in basement and basins. Geochem. Trans. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.L.S.; Barbosa, M.S.C.; Alkmim, F.F.D.; Soares, A.C.P. Magnetometric and gamma spectrometric expression of southwestern São Francisco Basin, Serra Selada quadrangle (1:100.000), Minas Gerais state. Rev. Bras. Geofísica 2012, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sighinolfi, G.P.; Figueredo, M.C.H.; Fyfe, W.S.; Kronberg, B.I.; Oliveira, M.T. Geochemistry and petrology of the Jequie granulitic complex (Brazil): An Archean basement complex. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 78, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatti-Filho, J.P.; Tappe, S.; Oliveira, E.P.; Heaman, L.M. Age and origin of the Neoproterozoic Brauna kimberlites: Melt generation within the metasomatized base of the São Francisco craton, Brazil. Chem. Geol. 2013, 353, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Slater, G.F.; Lollar, B.S.; Lacrampe-Couloume, G.; Onstott, T.C. The yield and isotopic composition of radiolytic H2, a potential energy source for the deep subsurface biosphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlindwein, V.; Schmid, F. Mid-ocean-ridge seismicity reveals extreme types of ocean lithosphere. Nature 2016, 535, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horning, G.; Sohn, R.A.; Canales, J.P.; Dunn, R.A. Local seismicity of the rainbow massif on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foustoukos, D.I.; Savov, I.P.; Janecky, D.R. Chemical and isotopic constraints on water/rock interactions at the Lost City hydrothermal field, 30 N Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5457–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proskurowski, G.; Lilley, M.D.; Seewald, J.S.; Früh-Green, G.L.; Olson, E.J.; Lupton, J.E.; Sylva, S.P.; Kelley, D.S. Abiogenic hydrocarbon production at Lost City hydrothermal field. Science 2008, 319, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, J.C.C.; Martins-Neto, M.A.; Marinho, M.S. Estilos estruturais e evolução tectônica da porção mineira da bacia proterozóica do São Francisco. Rev. Bras. Geociências 2008, 38 (Suppl. S2), 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkmim, F.F.; Martins-Neto, M.A. Proterozoic first-order sedimentary sequences of the São Francisco craton, eastern Brazil. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 33, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.L.; Suss, J.F.; Fonseca, R.C.; Alkmim, F.F. Ediacaran forebulge grabens of the southern São Francisco basin, SE Brazil: Craton interior dynamics during West Gondwana assembly. Precambrian Res. 2017, 302, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.L.; Alkmim, F.F.; Fonseca, R.C.; Nascimento, T.C.; Suss, J.F.; Prevatti, L.D. The São Francisco Basin. In São Francisco Craton, Eastern Brazil; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 117–143. [Google Scholar]
- Chemale, F., Jr.; Dussin, I.A.; Alkmim, F.F.; Martins, M.S.; Queiroga, G.; Armstrong, R.; Santos, M.N. Unravelling a Proterozoic basin history through detrital zircon geochronology: The case of the Espinhaço Supergroup, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.G.; Andrade, J.B.F. Interpretação Geofísica dos Principais Domínios Tectônicos Brasileiros. In Metalogênese da Províncias Tectônicas Brasileiras, 1st ed.; Silva, M.G., Rocha Neto, M.B., Jost, H., Kuyumjian, R.M., Eds.; CPRM—Serviço Geológico do Brasil: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.S.; Fuck, R.A. Archean nucleii and the distribution of kimberlite and related rocks in the São Francisco craton, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Geociências 2016, 35 (Suppl. S4), 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Correa, R.T. Mapa da Anomalia Magnética do Brasil (Terceira Edição); Escala 1:5.000.000; SGB-CPRM—Serviço Geológico do Brasil: Brasília, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, L.G.R.; Ussami, N.; Sá, N.C.D. Aquisição e interpretação de anomalias gravimétricas do Quadrilátero Ferrífero, SE do Cráton São Francisco. Rev. Bras. Geofísica 2007, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrino, C.H.; Hamza, V.M. Estimates of heat flow and heat production and a thermal model of the São Francisco craton. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2008, 97, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, F.; Bach, W.; McCollom, T.M. Compositional controls on hydrogen generation during serpentinization of ultramafic rocks. Lithos 2013, 178, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, L.E.; Ellison, E.T.; McCollom, T.M.; Trainor, T.P.; Templeton, A.S. Hydrogen generation from low-temperature water–rock reactions. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.M.; Mayhew, L.E.; Ellison, E.T.; Kelemen, P.; Kubo, M.; Templeton, A.S. Low temperature hydrogen production during experimental hydration of partially-serpentinized dunite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 209, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrino, C.H.; Hamza, V.M. Improved assessment of Deep Crustal Thermal Field based on Joint Inversion of Heat Flow, Elevation and Geoid Anomaly data. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2012, 13, EGU2011-10079. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, B.M.; Kharaka, Y.K.; Evans, W.C.; Ellwood, A.; DePaolo, D.J.; Thordsen, J.; Ambats, G.; Mariner, R.H. Mantle fluids in the San Andreas fault system, California. Science 1997, 278, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzé, F.V.; Tsopela, A.; Guglielmi, Y.; Henry, P.; Gout, C. Fluid migration in faulted shale rocks: Channeling below active faulting threshold. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truche, L. Transformations Minéralogiques et Géochimiques Induites par la Présence D’hydrogène dans un site de Stockage de Déchets Radioactifs. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Toulouse, Université Toulouse III-Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- De Carvalho, O.A.; Guimarães, R.F.; Montgomery, D.R.; Gillespie, A.R.; Trancoso Gomes, R.A.; de Souza Martins, É.; Silva, N.C. Karst depression detection using ASTER, ALOS/PRISM and SRTM-derived digital elevation models in the Bambuí Group, Brazil. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 330–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, D.M.; Sanchez, E.A.; Santucci, R.M. Morphological and petrographic analysis of newly identified stromatolitic occurrences in the Lagoa do Jacaré Formation, Bambuí Group, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Paleontol. 2018, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, P.; Halihan, T.; Hirata, R. The karst permeability scale effect of Sete Lagoas, MG, Brazil. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarkina, E.F.; Chou, I.M.; Goncharov, A.F.; Akinfiev, N.N. The Behavior of H2 in Aqueous Fluids under High Temperature and Pressure. Elem. Int. Mag. Mineral. Geochem. Petrol. 2020, 16, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlou, J.L.; Donval, J.P.; Konn, C.; OndréAs, H.; Fouquet, Y.; Jean-Baptiste, P.; Fourré, E. High production and fluxes of H2 and CH4 and evidence of abiotic hydrocarbon synthesis by serpentinization in ultramafic-hosted hydrothermal systems on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. GMS 2010, 188, 265–296. [Google Scholar]
- Keir, R.S. A note on the fluxes of abiogenic methane and hydrogen from mid-ocean ridges. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannat, M.; Fontaine, F.; Escartin, J. Serpentinization and associated hydrogen and methane fluxes at slow spreading ridges. In Diversity of Hydrothermal Systems on Slow Spreading Ocean Ridges; Rona, P.A., Devey, C.W., Dyment, J., Murton, B.J., Eds.; AGU Geophysical Monograph Series; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 188. [Google Scholar]
- Myagkiy, A.; Brunet, F.; Popov, C.; Krüger, R.; Guimarães, H.; Sousa, R.S.; Charlet, L.; Moretti, I. H2 dynamics in the soil of a H2-emitting zone (São Francisco Basin, Brazil): Microbial uptake quantification and reactive transport modelling. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 112, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

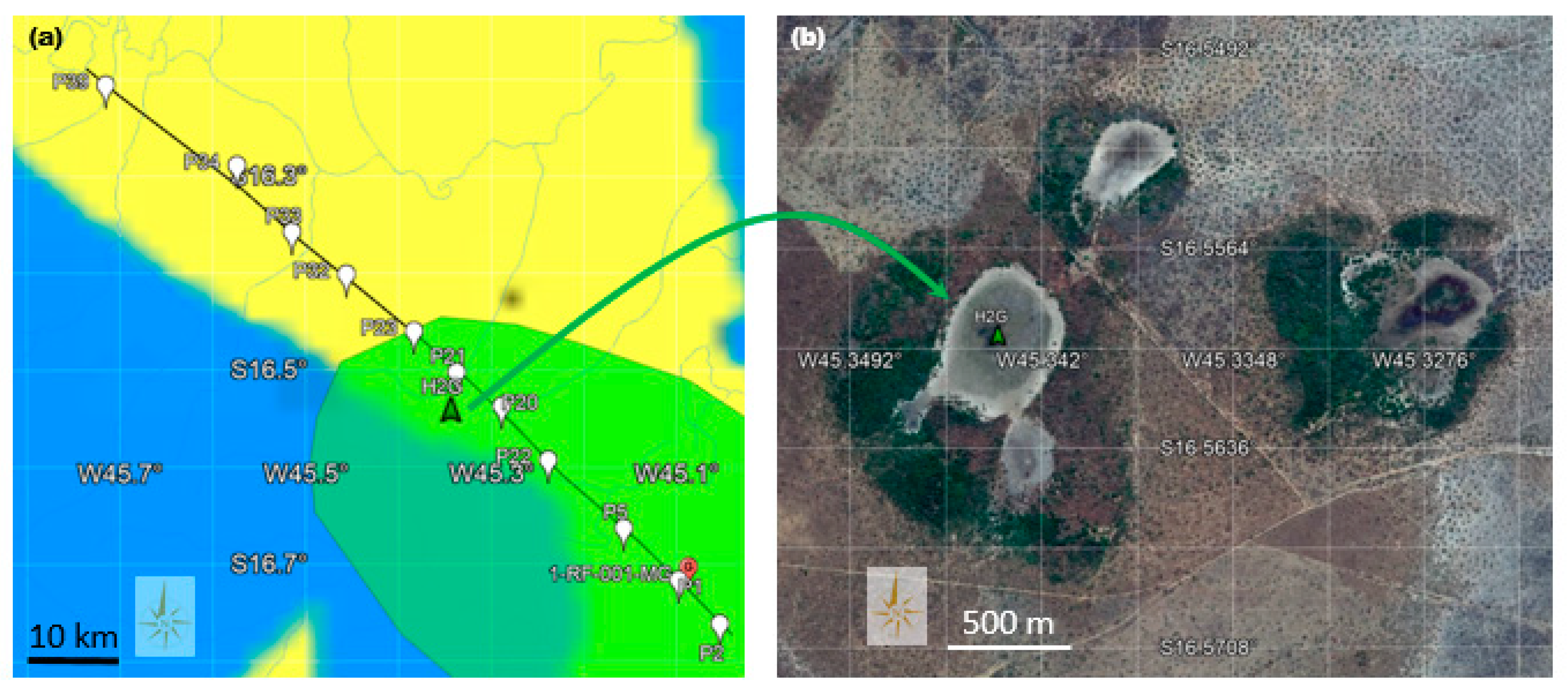

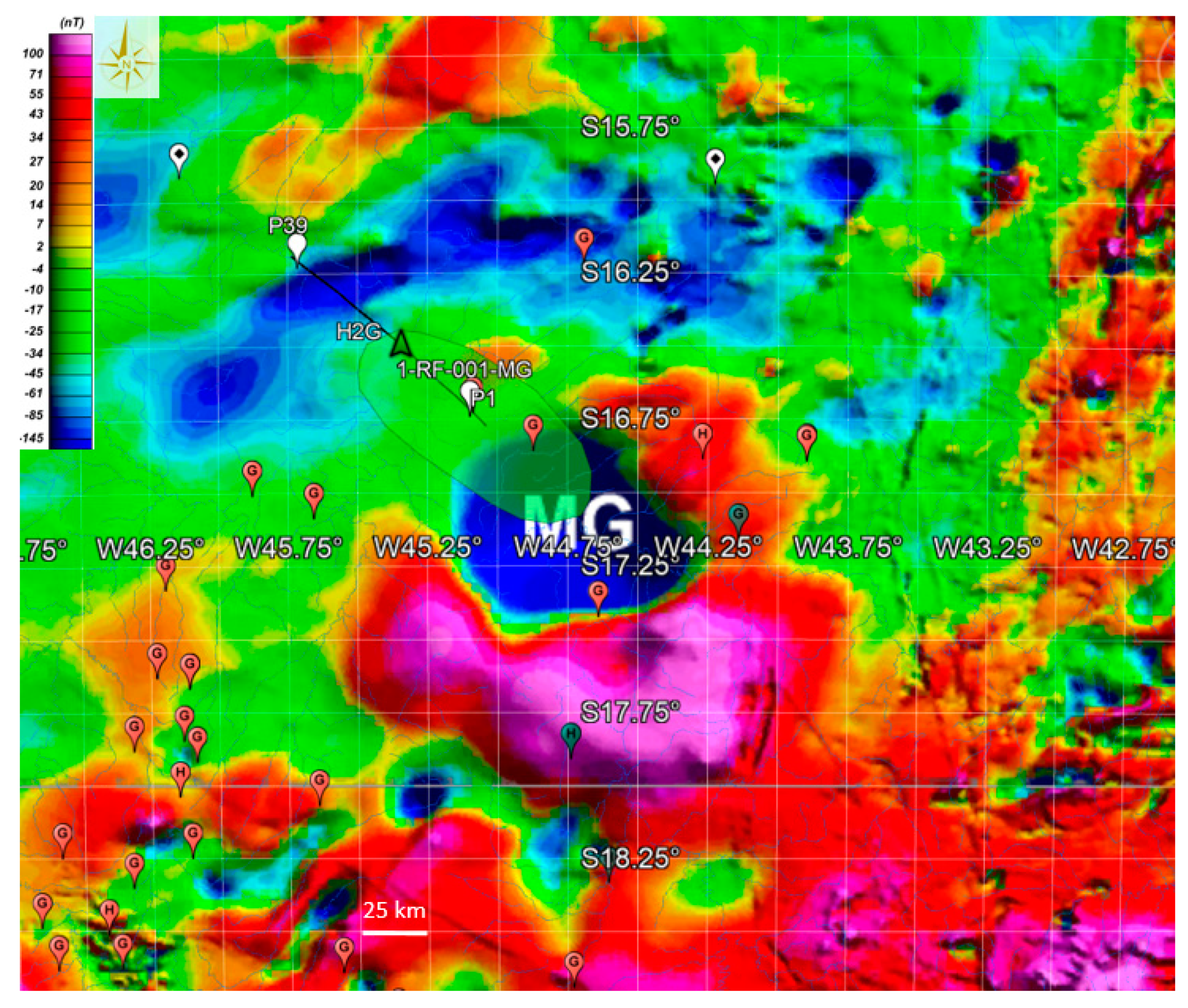
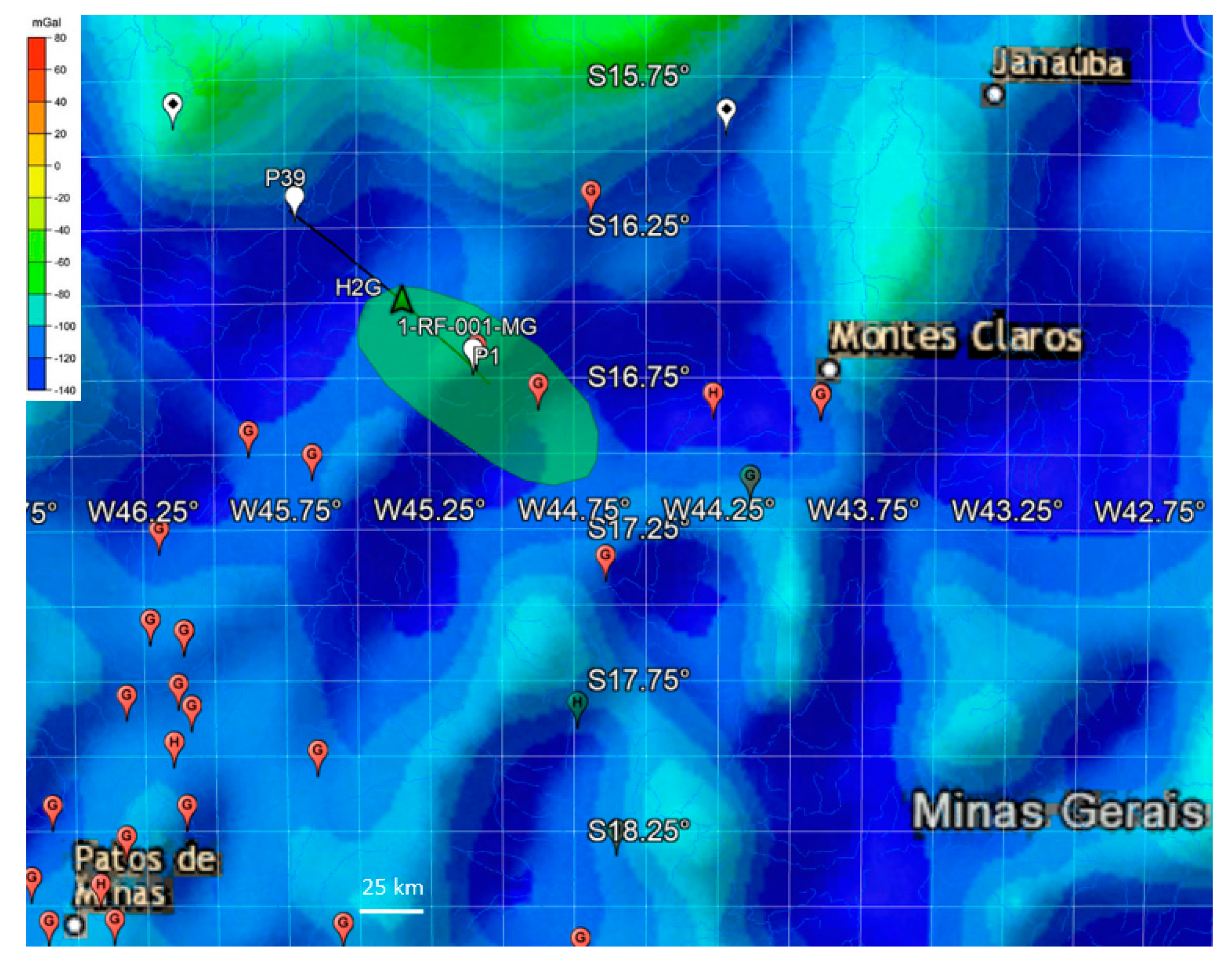

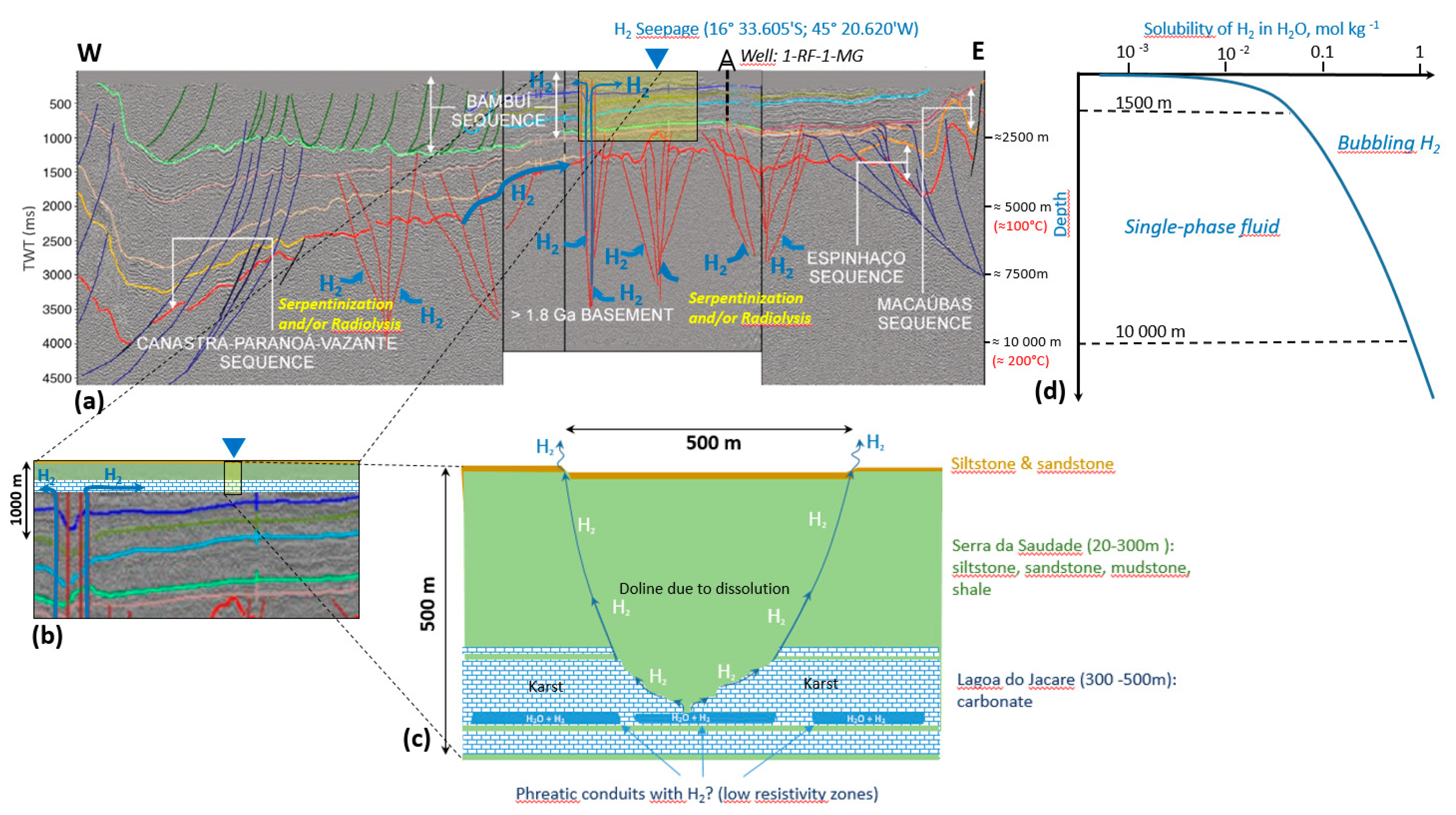
| Depth | Composition | Lithology |
|---|---|---|
| surface to ~30 m | • Siltstones and sandstone. | Serra de Saudade Formation |
| ~30 m to ~320 m | • Mainly composed of sandstone, siltstone, mudstone and shale. | |
| ~320 m to ~480 m | • Limestone. | Lagoa do Jacaré Formation |
| ~480 m to ~680 m | • Intercalations of limestone and shale. | |
| ~680 m to ~980 m | • Mainly composed of siltstone. | Serra de Santa Helena Formation |
| ~980 m to ~1200 m | • Mainly consisting of limestone and dolomite. | |
| ~1200 m to ~1240 m | • Mainly consisting of limestone and dolomite. | Sete Lagoas Formation |
| ~1240 m to ~1640 m | • Composed of intercalations of shales and limestone, conglomerates and diamictite. | Jequitaí Formation |
| below ~1640 m | • Composed of shale, limestone and conglomerate. |
| Radioelement | Archean Granulitic Rocks of the Jequie Complex 1 | Brauna Kimberlite Present in the Archean Basement 2 | Bambuí Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uranium (U) | up to 5 ppm | up to 4.81 ppm | up to 2.5 ppm |
| Thorium (Th) | up to 100 ppm | up to 35.8 ppm | up to 16 ppm |
| Potassium (K) | up to 4.5% | NA | up to 3% |
| System | ×109 mol·yr−1 | tons·yr−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| São Francisco basin (radiolysis and hydration combined) | 0.101–0.643 | 204–1284 | This study |
| H2G seepage zone São Francisco basin | 0.105–3.68 | 213–5400 | From Cathles and Prinzhofer, 2020 [16] |
| Rainbow hydrothermal field | ~0.1 | 200 | Charlou et al., 2010 [60] |
| Ultramafic vents along the Mid-Oceanic ridges | ~10–100 | 20,000–200,000 | Keir, 2010 [61]; Cannat et al., 2010 [62] |
| Global Precambrian continental lithosphere: (radiolysis and hydration combined) | 36–227 | 72,000–454,000 | Sherwood Lollar et al., 2014 [29] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donzé, F.-V.; Truche, L.; Shekari Namin, P.; Lefeuvre, N.; Bazarkina, E.F. Migration of Natural Hydrogen from Deep-Seated Sources in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil. Geosciences 2020, 10, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090346
Donzé F-V, Truche L, Shekari Namin P, Lefeuvre N, Bazarkina EF. Migration of Natural Hydrogen from Deep-Seated Sources in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil. Geosciences. 2020; 10(9):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090346
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonzé, Frédéric-Victor, Laurent Truche, Parisa Shekari Namin, Nicolas Lefeuvre, and Elena F. Bazarkina. 2020. "Migration of Natural Hydrogen from Deep-Seated Sources in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil" Geosciences 10, no. 9: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090346
APA StyleDonzé, F.-V., Truche, L., Shekari Namin, P., Lefeuvre, N., & Bazarkina, E. F. (2020). Migration of Natural Hydrogen from Deep-Seated Sources in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil. Geosciences, 10(9), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10090346





