Stability Analysis of Plant-Root-Reinforced Shallow Slopes along Mountainous Road Corridors Based on Numerical Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
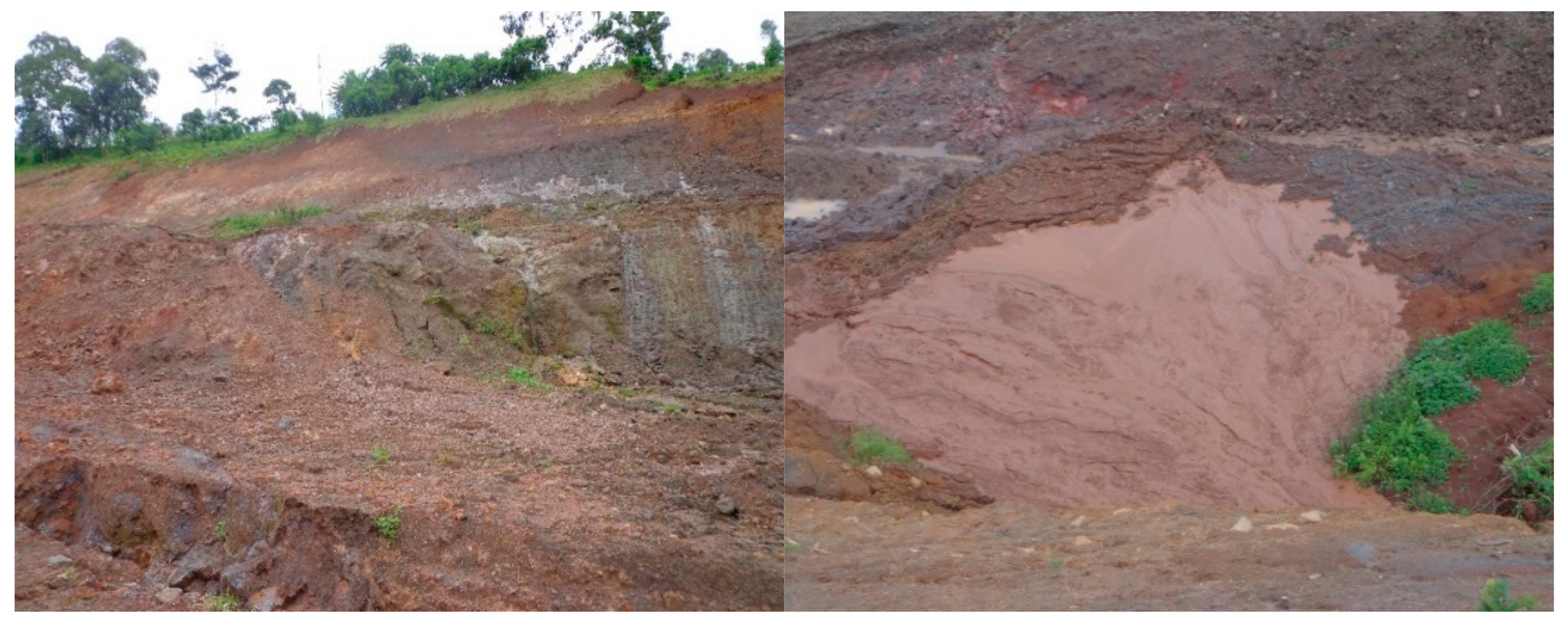
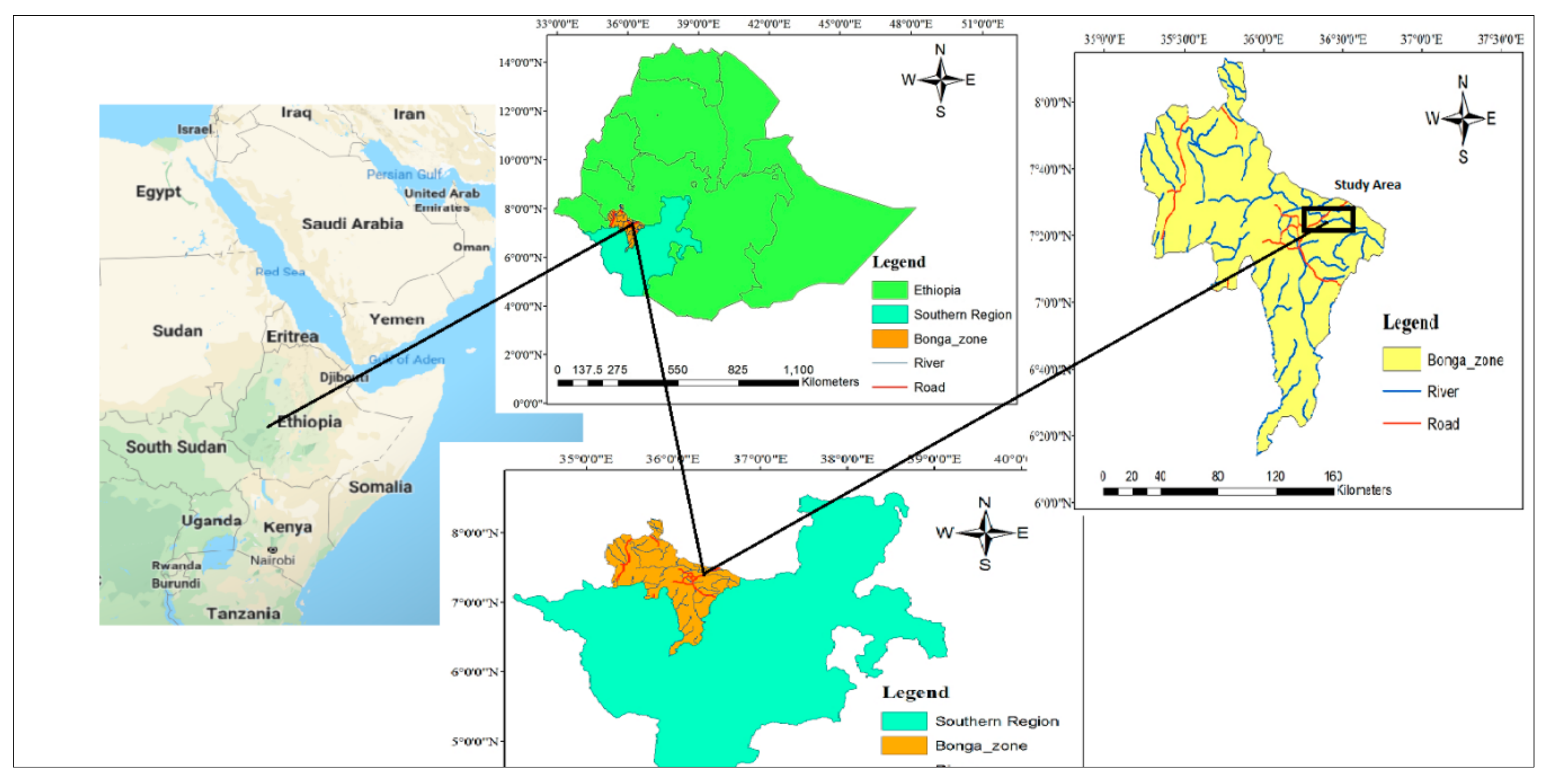
2.1. Topography of the Study Area
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Sampling and Root Excavation Techniques
2.4. Selection of Plant Species
2.5. Determination of Root Tensile Strength
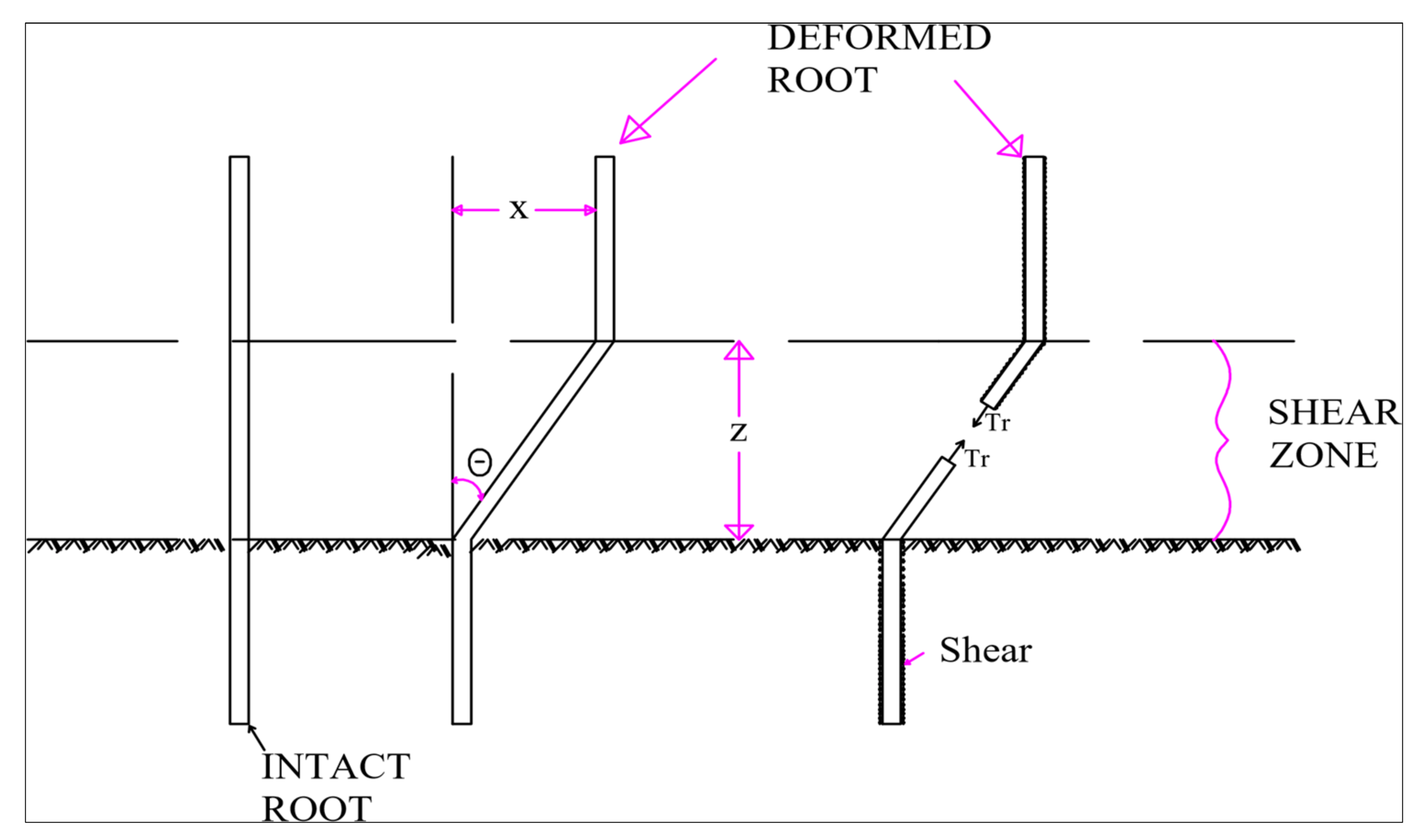
2.6. Mechanism of Soil-Root Reinforcement
2.7. Determination of Unit Weight of Soil
2.8. Triaxial Compression Test for the Determination of Soil Parameter
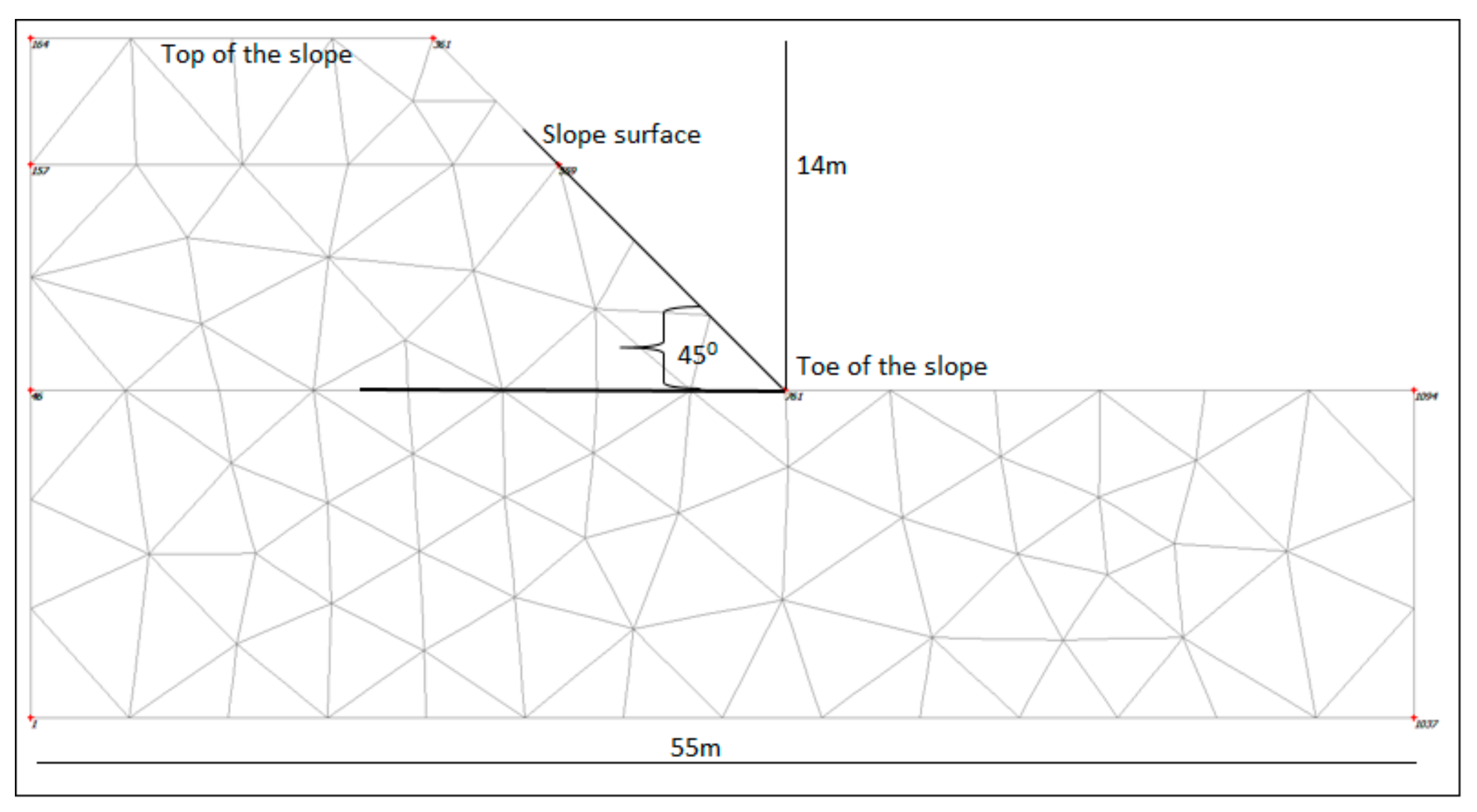
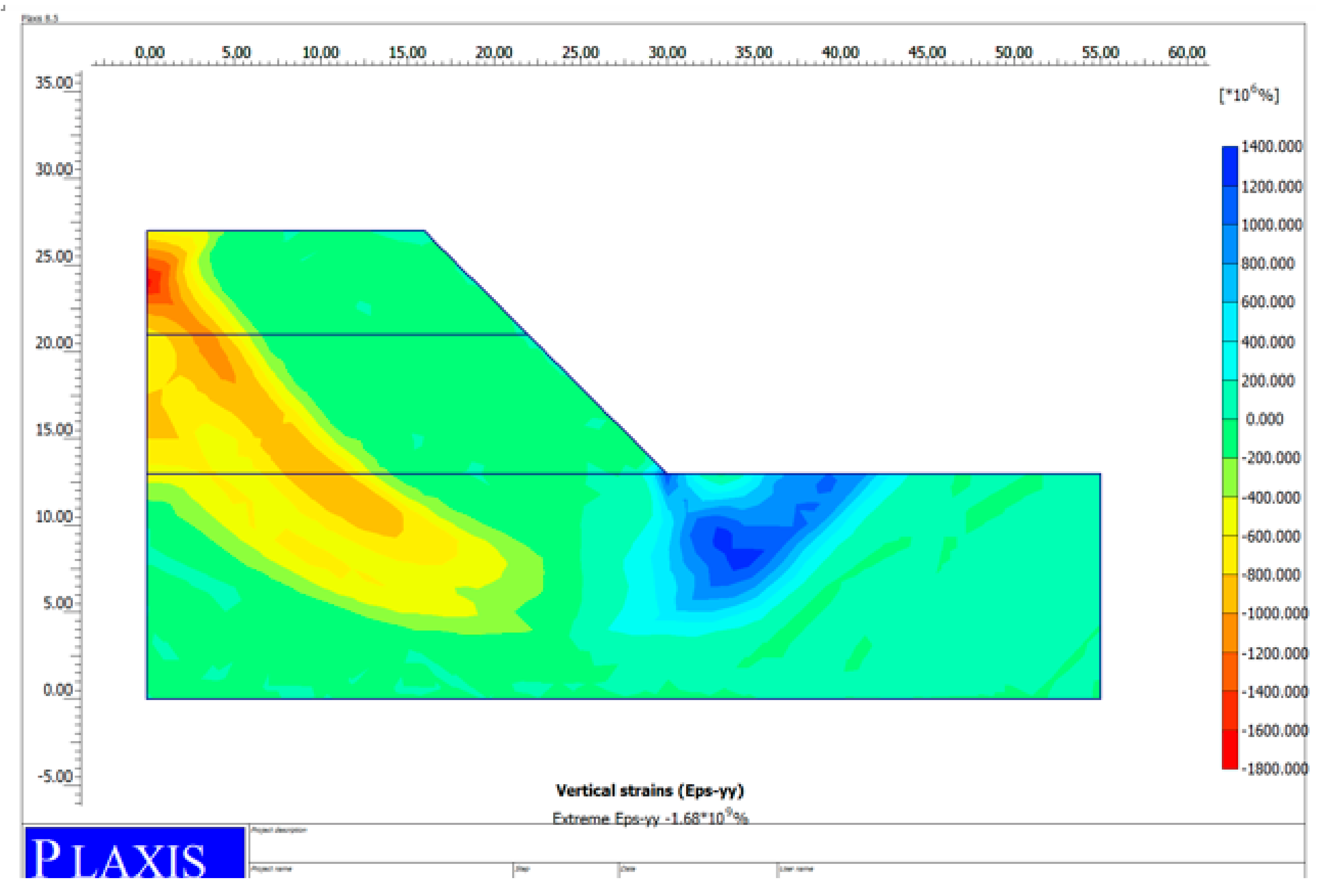
2.9. Finite Element Slope Stability Analysis Method
3. Results and Discussion
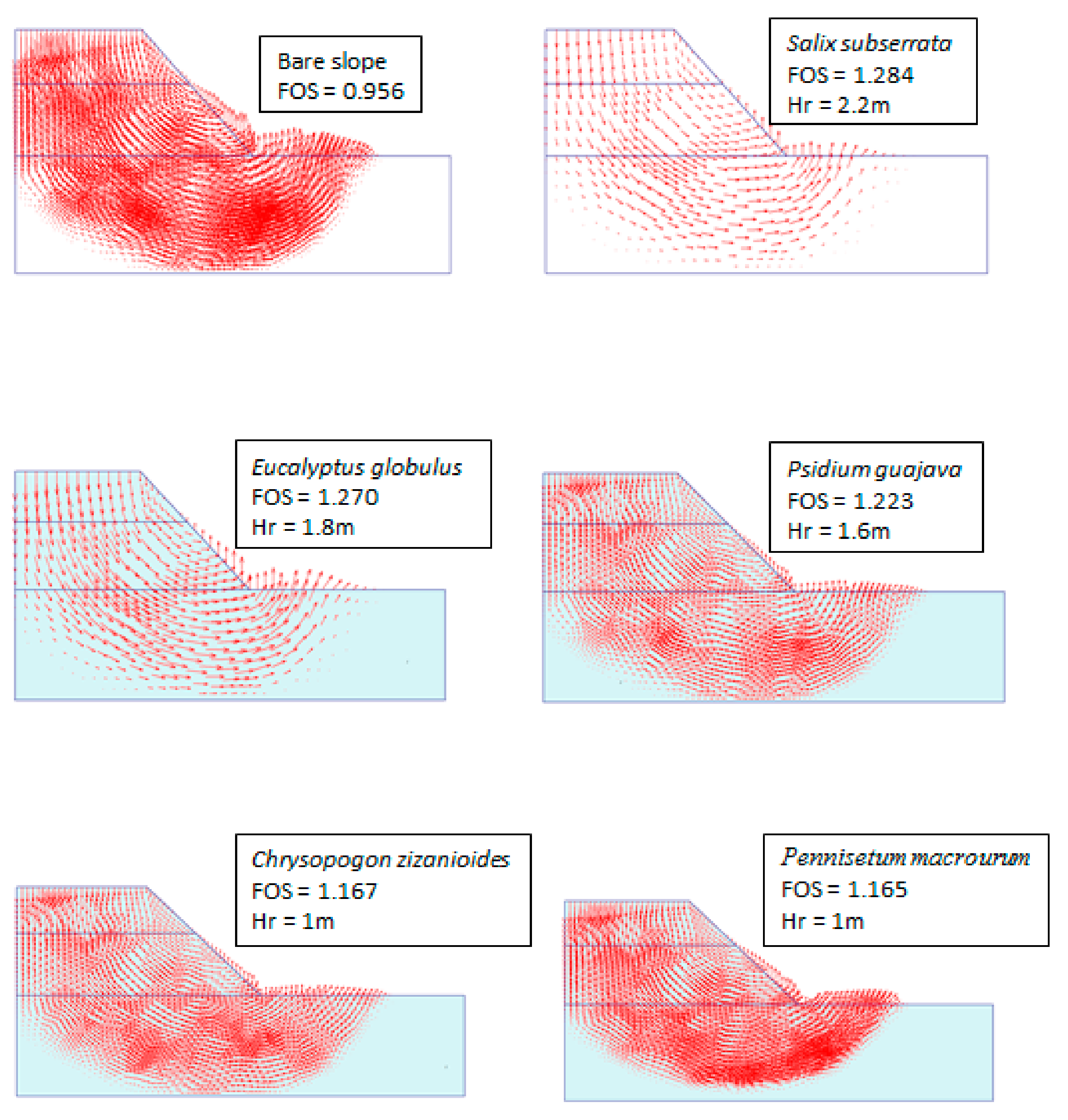
3.1. The Effect of Spatial Distribution of Vegetation on Slope Stability
3.2. Effect of Soil Moisture Variation on Slope Stability
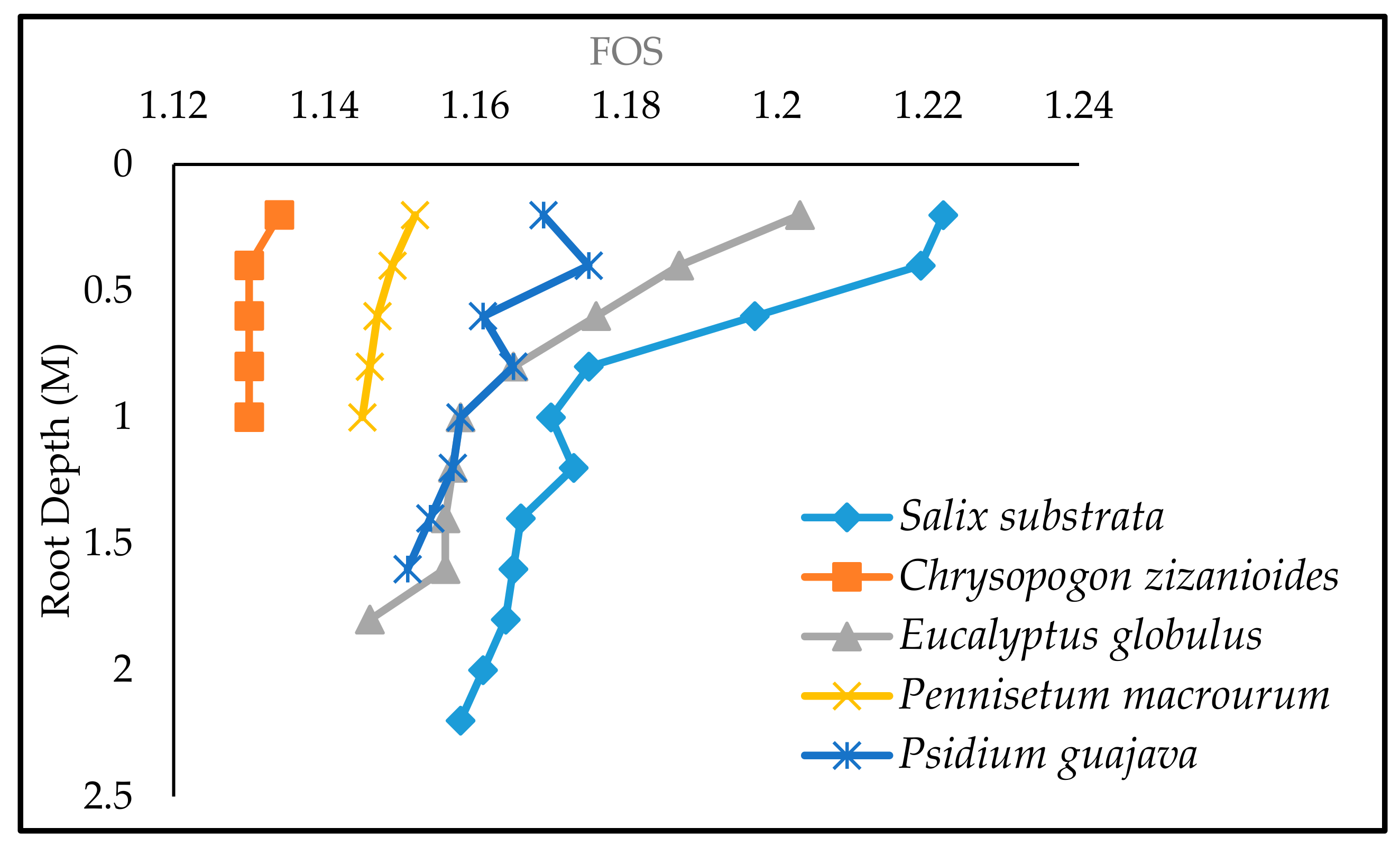
3.3. Influence of Root Penetration Depth on Factor of Safety
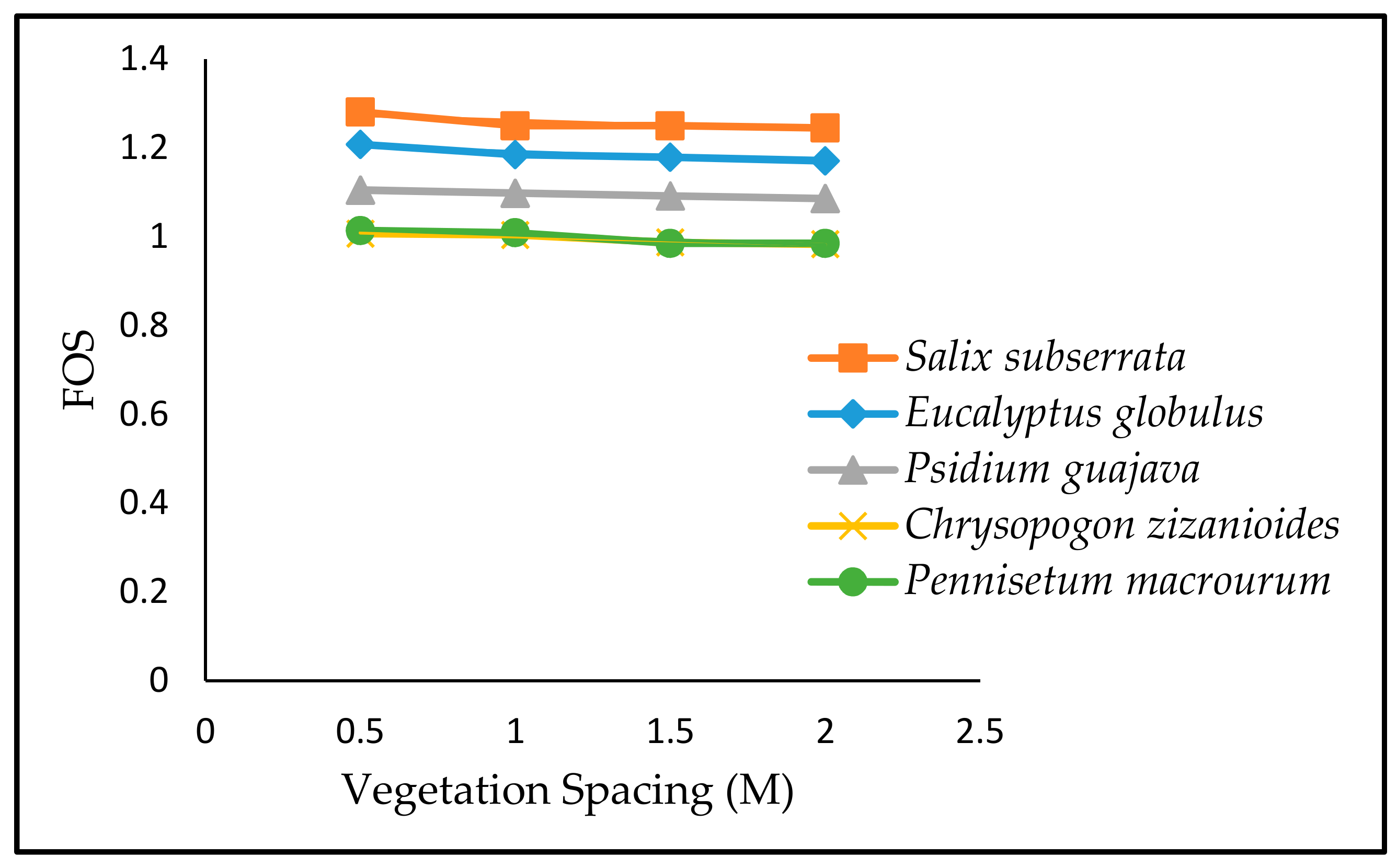
3.4. Effect of Vegetation Spacing to Safety Factor of Slope
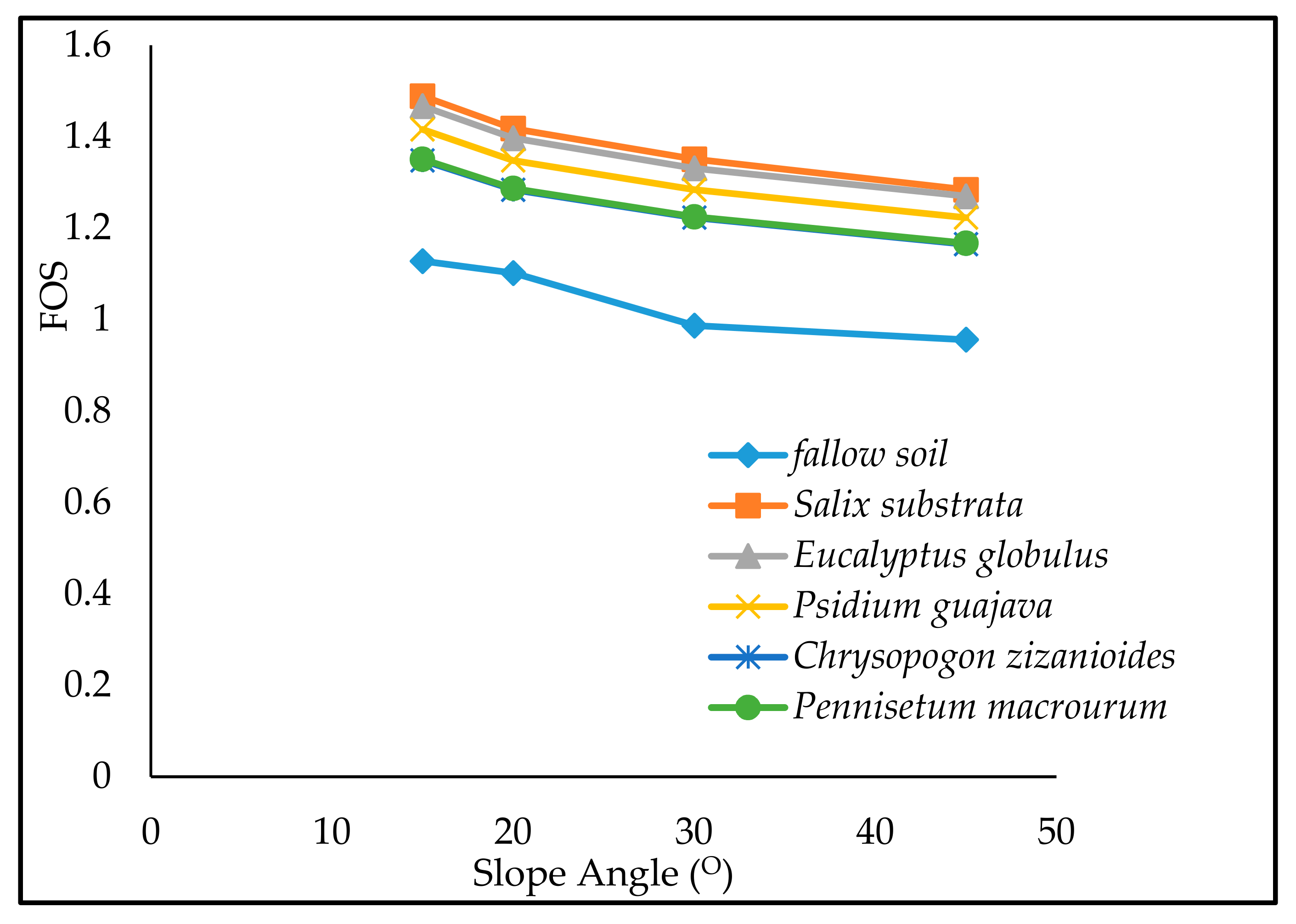
3.5. The Effect of a Change in Slope Angle on Slope Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdi, E. Effect of Oriental beech root reinforcement on slope stability (Hyrcanian forest, Iran). J. For. Sci. 2014, 60, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, R.; Maleki, S.; Abdi, E.; Mousavi, R.; Nikooy, M. Assessing the effect of Alnus roots on hillslope stability in order to use in soil bioengineering. J. For. Sci. 2013, 59, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A. Eco-and Ground Bio-engineering: The Use of Vegetation to Improve Slope Stability: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Eco-engineering 13–17 September 2004; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, J.C.; Marden, M.; Watson, A.J.; Rowan, D. Tree roots and slope stability: A comparison between pinus radiata and känuka. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 1997, 27, 216–233. [Google Scholar]
- Genet, M.; Stokes, A.; Fourcaud, T.; Norris, J.E. The influence of plant diversity on slope stability in a moist evergreen deciduous forest. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldearegay, K.; Schubert, W.; Klima, K.; Mogessie, A. Review of the occurrences and influencing factors of landslide in the highlands of Ethiopia: With implication of infrastructure development. Momona Ethiop. J. Sci. 2013, 5, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengiyumva, J.B.; Lou, G.; Nahayo, L.; Huang, X.; Peng, C. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using Spatial Multi-Criteria Evaluation Model in Rwanda. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temgoua, A.G.T.; Kokutse, N.K.; Kavazović, Z. Influence of forest stands and root morphologies on hillslope stability. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q. Effect of root moisture content and diameter on root tensile properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibah, L.; Nazi, A.; Ghassem, H.B. Investigation of Root Distribution and Tensile Strength of Acacia mangium Willd (Fabaceae) in the Rainforest. Greener J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 4, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Nghiem, Q.M.; Iwasa, N. Reinforcement of tree roots in slope stability: A case study from the Ozawa slope in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. In Eco-and Ground Bio-Engineering: The Use of Vegetation to Improve Slope Stability; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Su, C.F. Effect of soil moisture content on the deformation behaviour of root-reinforced soils subjected to shear. Plant Soil 2009, 324, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, M.F.; Ali, N.; Kassim, A. The Effect of Tree Induce Suction On Slope Stabilization Analysis. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Geo Environ. J. 2013, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Igwe, O.; Abiye, B.; Effiong, M.; Raphael, I.; Ifeanyi, A. Landslide Investigation of Ikwette, Obudu Local Government Area of Cross River State, Nigeria. IOSR J. Appl. Geol. Geophys. 2015, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, H.F.; Tsai, Y.J. Effect of Variations in Long-Duration Rainfall Intensity on Unsaturated Slope Stability. Water 2018, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizio, L.; Marco, P. Landslide Disasters Triggered by Extreme Rainfall Events: The Case of Montescaglioso (Basilicata, Southern Italy). Geosciences 2018, 8, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilis, M.; Georgios, S.; Costas, P. Landslide Hazard and Risk Assessment for a Natural Gas Pipeline Project: The Case of the Trans Adriatic Pipeline, Albania Section. Geosciences 2019, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubens, B. Woody Vegetation for Gully Rehabilitation in Northern Ethiopia Species Suitability, Root Structure, and Seedling Establishment, Growth and Managt; Katholieke Universiteit Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Boldrin, D.; Leung, A.K.; Bengough, A.G. Desirable leaf traits for hydrological reinforcement of soil. E3S Web Conf. 2016, 9, 12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.; Giadrossich, F.; Cohen, D. Modeling root reinforcement using a root-failure Weibull survival function. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4367–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Mickovski, S.B. Hydrological effect of vegetation against rainfall-induced landslides. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Meisina, C.; Vercesi, A.; Bischetti, G.B.; Chiaradia, E.; Bassanelli, C.; Vergani, C.; Valentino, R.; Bittelli, M.; Chersich, S. Grapevine root system strength in an area susceptible to shallow landslides for slope stability assessment. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1136, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Meisina, C.; Vercesi, A.; Bischetti, G.B.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Vergani, C.; Chersich, S.; Valentino, R.; Bittelli, M.; Comolli, R.; et al. Quantifying the contribution of grapevine roots to soil mechanical reinforcement in an area susceptible to shallow landslides. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannoppen, W.; De Baets, S.; Keeble, J.; Dong, Y.; Poesen, J. How do root and soil characteristics affect the erosion-reducing potential of plant species? Ecol. Eng. 2017, 109, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetta, C.; Luca, S.; Lorenzo, B.; Francine, T.; chamaleu, P.; Luca, P.; Alberto, B. Composite Anchors for Slope Stabilization: Monitoring of their In-Situ Behavior with Optical Fibre. Geosciences 2019, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, K.; John, I.; Masoud, N. Coupled Effect of Wet-Dry Cycles and Rainfall on Highway Slope Made of Yazoo Clay. Geosciences 2019, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Zhu, M.; Loizeaux, D.; Manning, S. Numerical study of an anchor reinforced vegetation system. In Geotechnical Frontiers 2017; Hyatt Regency Orlando: Orlando, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 406–415. [Google Scholar]
- Chok, Y.; Kaggwa, W. Modelling the effects of vegetation on stability of slopes. In Australia-New Zealand Conference on Geomechanics; Centre for Continuing Education, Uni Auckland: Auckland, New Zealand, 2004; pp. 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Nyambane, O.S.; Mwea, S.K. Root tensile strength of 3 typical plant species and their contribution to soil shear strength; a case study: Sasumua Backslope, Nyandarua District, Kenya. J. Civ. Eng. Res. Pract. 2011, 8, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, L.; Fourcaud, T.; Stokes, A. A numerical investigation into the influence of soil type and root architecture on tree anchorage. Plant Soil 2005, 278, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burylo, M.; Hudek, C.; Rey, F. Soil reinforcement by the roots of six dominant species on eroded mountainous marly slopes (Southern Alps, France). Catena 2011, 84, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Islam, A. Numerical Analysis of the Effects of Soil Nail on Slope Stability. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 141, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chok, Y.H.; Jaksa, M.B.; Kaggwa, W.S.; Griffiths, D.V. Assessing the influence of root reinforcement on slope stability by finite elements. Int. J. Geo Eng. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W.W.; Hau, B.C.H. Effects of Plant Transpiration on Suction Distribution in a Vegetated Soil Slope. In Unsaturated Soils: Research and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- De Baets, S.; Poesen, J.; Reubens, B.; Wemans, K.; De Baerdemaeker, J.; Muys, B. Root tensile strength and root distribution of typical Mediterranean plant species and their contribution to soil shear strength. Plant Soil 2008, 305, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.G.; Liu, W.T.; Lin, S.H. Estimating the effect of shear strength increment due to root on the stability of Makino bamboo forest slopeland. J. Geoeng. 2011, 6, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.G.; Huang, B.S.; Lin, S.H. 3-D numerical investigations into the shear strength of the soil-root system of Makino bamboo and its effect on slope stability. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 992–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Liu, J.L. Slope Stability Analysis with Finite Element Method. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 538, pp. 819–822. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, F.; Elia, G.; Elia, R. Analysis of the stability of slopes reinforced by roots. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 138, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ige, O.O.; Oyeleke, T.A.; Baiyegunhi, C.; Oloniniyi, T.L.; Sigabi, L. Liquefaction, landslide and slope stability analyses of soils: A case study of soils from part of Kwara, Kogi and Anambra states of Nigeria. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2016, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Castillo, L.; Kubota, T.; Hasnawir; Cantu-Silva, I. Influence of root reinforcement of forest species on the slope stability of sierra madre oriental, Mexico. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2017, 62, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Lateh, H.; Bakar, M.A.; Khan, Y.A. Influence of tensile force of agave and tea plants roots on experimental prototype slopes. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2011, 6, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar]
- Sutejo, Y.; Gofar, N. Effect of area development on the stability of cut slopes. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Zhu, J. Influence of the spatial layout of plant roots on slope stability. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Goswami, D. Prediction of critical safety factor of slopes using multiple regression and neural network. J. Geo Eng. Sci. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Army Corps. Engineering and Design, Slope Stability, Engineer Manual; EM 1110-2-1902; US. Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 49. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandary, N.P.; Yatabe, R.; Dahal, R.K.; Hasegawa, S.; Inagaki, H. Areal distribution of large-scale landslides along highway corridors in central Nepal. Georisk 2013, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Lau, C.K. A study on factor of safety evaluation in slope stability analysis. HKIE Trans. Hong Kong Inst. Eng. 2001, 8, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muceku, Y.; Korini, O. Landslide and slope stability evaluation in the historical town of Kruja, Albania. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.C.; Bhandary, N.P.; Yatabe, R.; Bhat, D.R. Evaluation of factor of safety for vegetated and barren soil slopes with limit equilibrium computations. Geomech. Geoeng. 2013, 8, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.M.; Xiao, T.; Li, X.Y. Enhancement of slope stability by vegetation considering uncertainties in root distribution. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 85, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushira, K.M.; Gebregiorgis, Y.B.; Verma, R.K.; Sheng, Z. Cut soil slope stability analysis along National Highway at Wozeka–Gidole Road, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talema, A.; Poesen, J.; Muys, B.; Reubens, B.; Dibaba, H.; Diels, J. Multi-criteria-based Plant Species Selection for Gully and Riverbank Stabilization in a Sub-humid Tropical Area. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Ziemer, R.R. Effect of Tree Roots on Shallow-Seated Landslides; Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-130; Pacific Southwest Research Station, Forest Service, US Department of Agriculture: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1991; Volume 130, pp. 11–20.
- M’Bou, A.T.; Jourdan, C.; Deleporte, P.; Nouvellon, Y.; Saint-André, L.; Bouillet, J.; Mialoundama, F.; Mabiala, A.; Epron, D. Root elongation in tropical Eucalyptus plantations: Effect of soil water content. Ann. For. Sci. 2008, 65, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baets, S.; Poesen, J.; Knapen, A.; Barberá, G.G.; Navarro, J.A. Root characteristics of representative Mediterranean plant species and their erosion-reducing potential during concentrated runoff. Plant Soil 2007, 294, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, T.S.; Cheang, W.; Hai, O.P.; Tan, D. Finite Element Analysis of A Soil Nailed Slope-Some Recent Experience. In Proceedings of the 3rd Asian Regional Conference on Geosynthetics: Now and Future of Geosynthetics in Civil Engineering, Seoul, Korea, 21–23 June 2004; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J. Non-deterministic analysis of slope stability based on numerical simulation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Fawaz, A. Slope Stability Analysis Using Numerical Modelling. Am. J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 2, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.R.; Norris, J.E.; Wint, J. Site investigation for the effects of vegetation on ground stability. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2006, 24, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, D.; Pei, X.; Shi, B. Effect of discrete fibre reinforcement on soil tensile strength. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 6, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.H.; Osman, N. Shear strength of a soil containing vegetation roots. Soils Found. 2008, 48, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, N.; Abdullah, M.N.; Abdullah, C.H. Pull-out and tensile strength properties of two selected tropical trees. Sains Malays. 2011, 40, 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Saifuddin, M.; Osman, N. Evaluation of hydro-mechanical properties and root architecture of plants for soil reinforcement. Curr. Sci. 2014, 107, 845–852. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, A.; Atger, C.; Bengough, A.G.; Fourcaud, T. Desirable plant root traits for protecting natural and engineered slopes against landslides. Plant Soil 2009, 324, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likitlersuang, S.; Takahashi, A.; Eab, K.H. Modeling of root-reinforced soil slope under rainfall condition. Eng. J. 2017, 21, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Goswami, D. State of the art: Three Dimensional (3D) Slope-Stability Analysis. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 10, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Su, C.F. Role of roots in the shear strength of root-reinforced soils with high moisture content. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 33, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Lai, Y.F. Influence of the spatial layout of vegetation on the stability of slopes. Plant Soil 2014, 377, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



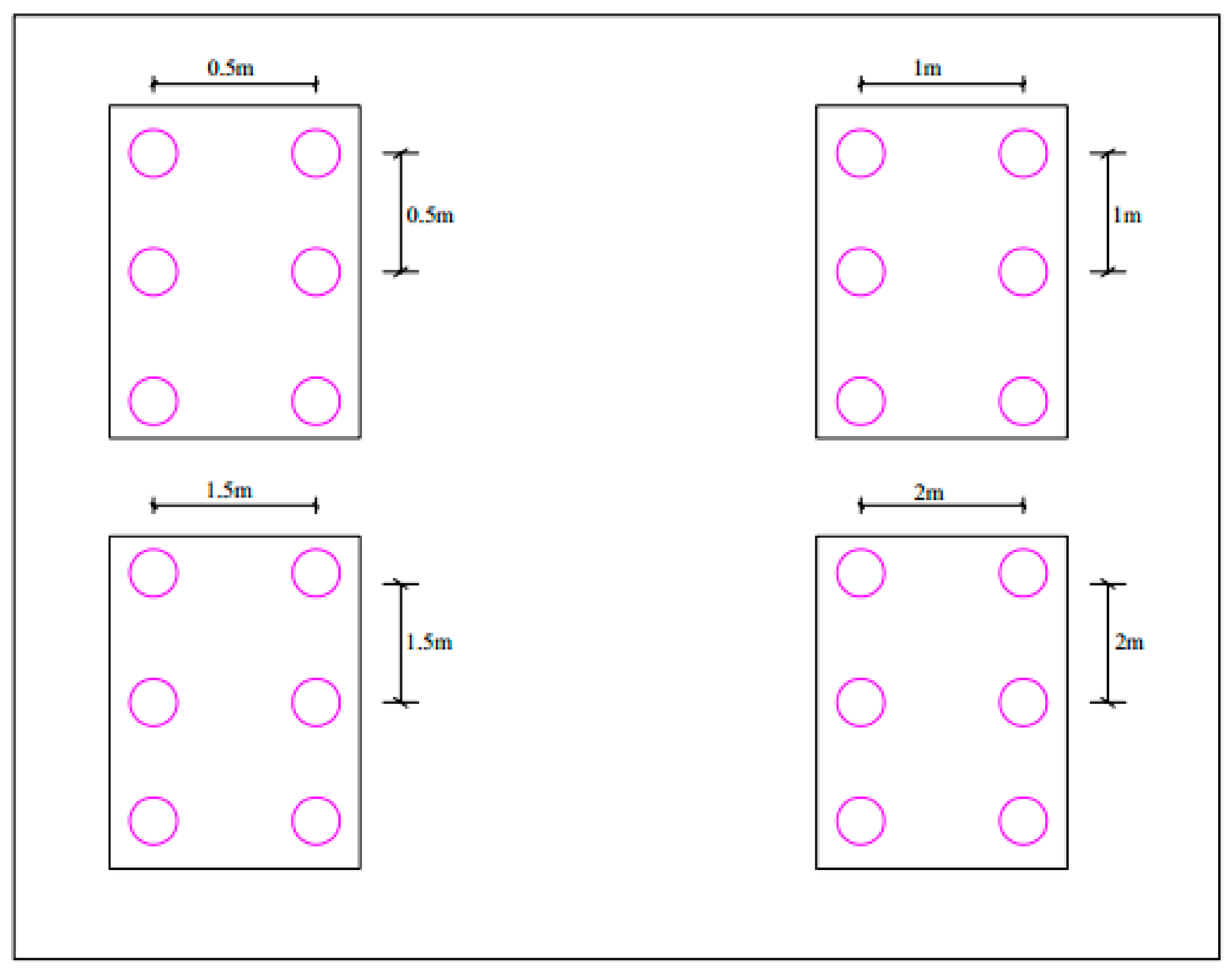
| Soil Parameters at (16%) Moisture Content | |||||
| Saturated Unit Weight of Soil (kN/m3) | Un Saturated Unit Weight of Soil (kN/m3) | Poisson’s Ratio | Elastic Modules of Soil (kN/m3) | Soil fiction Angle (°) | Cohesion of Soil (kN/m2) |
| 18 | 16 | 0.2 | 3125 | 4 | 47 |
| Root Parameters | |||||
| Plant Species | Diameter Range (mm) | Apparent Root Cohesion (kPa) | Root Tensile Strength (MPa) | Effective Root Zone (m) | |
| Salix subserrata | 0.25–6.5 | 9.9 | 41.85 | 2.2 | |
| Eucalyptus globules | 0.26–5.8 | 7.44 | 32.18 | 1.8 | |
| Psidium guajava | 0.74 | 4.27 | 38.47 | 1.6 | |
| Chrysopogon zizanioides | 4.20.36–1.94 | 0.91 | 33.08 | 1 | |
| Pennisetum macrourum | 0.25–2.1 | 0.84 | 23.13 | 1 | |
| Plant Species | Vegetation Scenarios | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Slope | Increment in (%) | Slope Surface | Increment in (%) | Top Slope | Increment in (%) | Toe of Slope | Increment in (%) | |
| bare soil | 0.956 | - | 0.956 | - | 0.956 | - | 0.956 | - |
| Salix subserrata | 1.284 | 34.3 | 1.263 | 32.1 | 1.066 | 11.5 | 1.113 | 16.4 |
| Eucalyptus globules | 1.270 | 32.8 | 1.245 | 30.2 | 1.057 | 10.6 | 1.103 | 15.4 |
| Psidium guajava | 1.223 | 27.9 | 1.198 | 25.3 | 1.023 | 7.0 | 1.065 | 11.4 |
| Pennisetum macrourum | 1.165 | 21.9 | 1.143 | 19.6 | 0.979 | 2.4 | 1.014 | 6.1 |
| Chrysopogon zizanioides | 1.167 | 22.1 | 1.140 | 19.3 | 0.984 | 2.9 | 1.015 | 6.2 |
| Plant Species | When Soil Moisture Content (16%) | When Soil Moisture Content (23%) | Percent Decrement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fallow soil | 0.956 | 0.884 | 8.14 |
| Salix subserrata | 1.284 | 1.192 | 7.71 |
| Eucalyptus globules | 1.270 | 1.141 | 11.3 |
| Psidium guajava | 1.223 | 1.086 | 12.6 |
| Pennisetum macrourum | 1.165 | 1.025 | 13.7 |
| Chrysopogon zizanioides | 1.167 | 1.035 | 12.8 |
| Salix subserrata | Eucalyptus globules | Psidium guajava | Chrysopogon zizanioides | Pennisetum macrourum | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | Cr (Kpa) | FOS | Cr (Kpa) | FOS | Cr (Kpa) | FOS | Cr (Kpa) | FOS | Cr (Kpa) | FOS |
| 0.2 | 2.44 | 1.222 | 2.06 | 1.203 | 0.91 | 1.169 | 0.3 | 1.134 | 0.32 | 1.152 |
| 0.4 | 2.2 | 1.219 | 1.49 | 1.187 | 1.08 | 1.175 | 0.18 | 1.13 | 0.21 | 1.149 |
| 0.6 | 1.53 | 1.187 | 1.09 | 1.176 | 0.59 | 1.161 | 0.18 | 1.13 | 0.14 | 1.147 |
| 0.8 | 0.77 | 1.165 | 0.73 | 1.165 | 0.67 | 1.165 | 0.15 | 1.13 | 0.1 | 1.146 |
| 1 | 0.61 | 1.15 | 0.48 | 1.158 | 0.36 | 1.158 | 0.1 | 1.13 | 0.06 | 1.145 |
| 1.2 | 0.68 | 1.143 | 0.43 | 1.157 | 0.33 | 1.157 | ||||
| 1.4 | 0.44 | 1.136 | 0.42 | 1.156 | 0.19 | 1.154 | ||||
| 1.6 | 0.41 | 1.125 | 0.39 | 1.156 | 0.13 | 1.151 | ||||
| 1.8 | 0.37 | 1.114 | 0.35 | 1.146 | ||||||
| 2 | 0.28 | 1.11 | ||||||||
| 2.2 | 0.17 | 1.108 | ||||||||
| Plant Species | Vegetation Spacing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 m | Increment in (%) | 1 m | Increment in (%) | 1.5 m | Increment in (%) | 2 m | Increment in (%) | |
| bare soil | 0.956 | - | 0.961 | - | 0.961 | - | 0.961 | - |
| Salix subserrata | 1.284 | 34.3 | 1.250 | 30.07 | 1.250 | 30.07 | 1.245 | 29.5 |
| Eucalyptus globules | 1.270 | 32.8 | 1.185 | 23.3 | 1.179 | 22.7 | 1.171 | 21.8 |
| Psidium guajava | 1.223 | 27.9 | 1.098 | 14.3 | 1.092 | 13.6 | 1.086 | 13 |
| Pennisetummacrourum | 1.165 | 21.9 | 1.004 | 4.5 | 0.987 | 2.7 | 0.983 | 2.3 |
| Chrysopogon zizanioides | 1.167 | 22.1 | 1.009 | 4.9 | 0.985 | 2.5 | 0.985 | 2.5 |
| Plant Species | The Factor of Safety, FOS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope Angle 45° | Slope Angle 30° | Slope Angle 20° | Slope Angle 15° | % Increase | |
| Fallow soil | 0.956 | 0.987 | 1.102 | 1.128 | 17.99 |
| Salix subserrata | 1.284 | 1.351 | 1.418 | 1.489 | 15.96 |
| Eucalyptus globules | 1.270 | 1.331 | 1.397 | 1.467 | 15.50 |
| Psidium guajava | 1.223 | 1.284 | 1.348 | 1.416 | 15.78 |
| Pennisetummacrourum | 1.165 | 1.223 | 1.284 | 1.348 | 15.70 |
| Chrysopogon zizanioides | 1.167 | 1.225 | 1.287 | 1.351 | 15.70 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsige, D.; Senadheera, S.; Talema, A. Stability Analysis of Plant-Root-Reinforced Shallow Slopes along Mountainous Road Corridors Based on Numerical Modeling. Geosciences 2020, 10, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10010019
Tsige D, Senadheera S, Talema A. Stability Analysis of Plant-Root-Reinforced Shallow Slopes along Mountainous Road Corridors Based on Numerical Modeling. Geosciences. 2020; 10(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsige, Damtew, Sanjaya Senadheera, and Ayalew Talema. 2020. "Stability Analysis of Plant-Root-Reinforced Shallow Slopes along Mountainous Road Corridors Based on Numerical Modeling" Geosciences 10, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10010019
APA StyleTsige, D., Senadheera, S., & Talema, A. (2020). Stability Analysis of Plant-Root-Reinforced Shallow Slopes along Mountainous Road Corridors Based on Numerical Modeling. Geosciences, 10(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10010019





