The Effect of the Use of a Settling Chamber in the Cultivation of Penaeus vannamei and Salicornia neei in Aquaponics with Bioflocs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
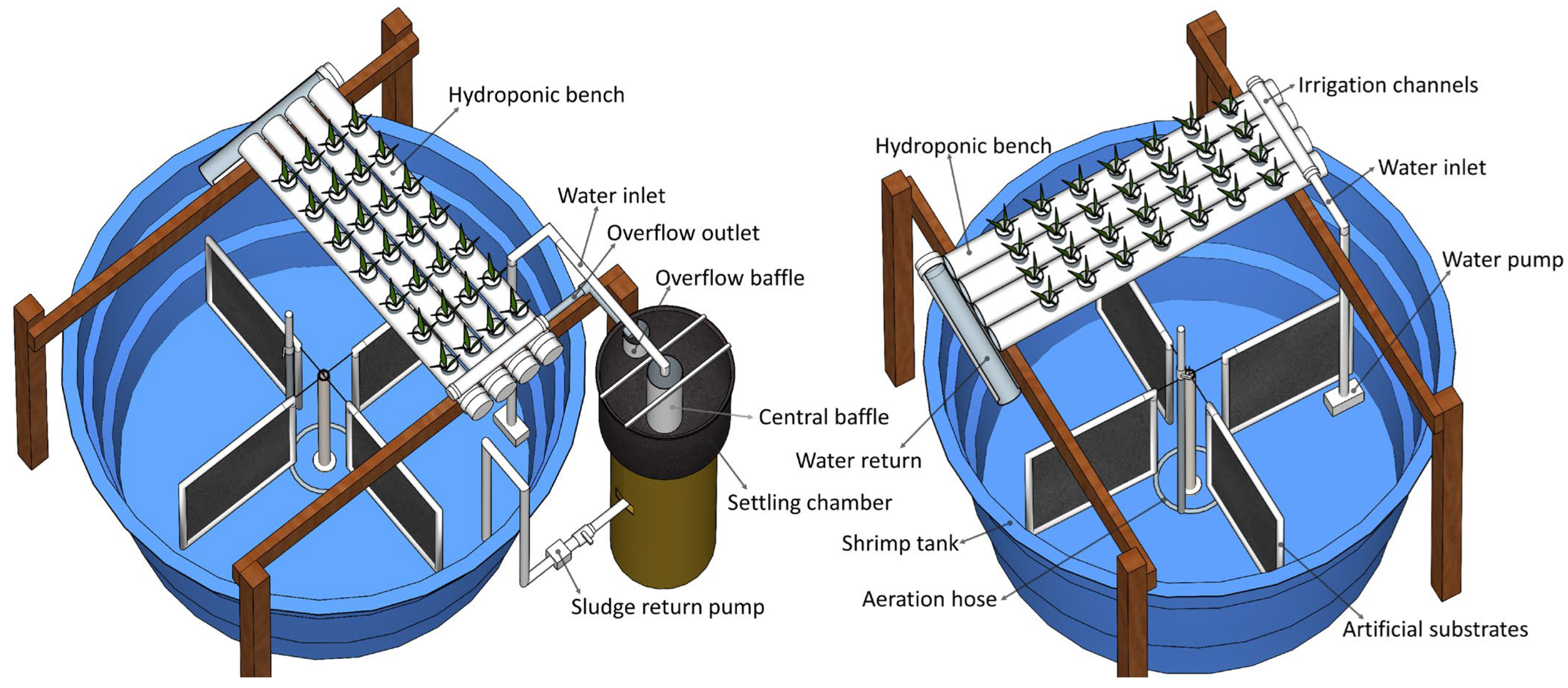
2.2. Experimental Design and System Management
2.3. Production Indexes of Shrimp and Plants
2.4. Water Quality Variables
2.5. Sludge Quantification
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Production of Shrimp and Plants
3.2. Water Quality
3.3. Solids Concentration and Sludge Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.; Lee, J.W.; Chandran, K.; Kim, S.; Brotto, A.C.; Khanal, S.K. Effect of Plant Species on Nitrogen Recovery in Aquaponics. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 188, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakocy, J.E. Aquaponics—Integrating Fish and Plant Culture. In Aquaculture Production Systems; Tidwell, J.H., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: West Sussex, UK, 2012; pp. 344–386. ISBN 9781118250105. [Google Scholar]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.; Mankasingh, U.; Ragnarsdottir, K.; Jijakli, H.; Thorarinsdottir, R. Challenges of Sustainable and Commercial Aquaponics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4199–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Joyce, A.; Kotzen, B.; Dos-Santos, M. Aquaponics and Global Food Challenges. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–17. ISBN 978-3-030-15943-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lekang, O.I. Natural Systems, Integrated Aquaculture, Aquaponics, Biofloc. In Aquaculture Engineering; Lekang, O.I., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 275–284. ISBN 9781119489047. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, Y.; Sagi, M. Halophyte Crop Cultivation: The Case for Salicornia and Sarcocornia. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzen, B.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Moheimani, N.; Burnell, G. Aquaponics: Alternative Types and Approaches. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 301–330. [Google Scholar]
- Barreira, L.; Resek, E.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Rocha, M.I.; Pereira, H.; Bandarra, N.; da Silva, M.M.; Varela, J.; Custódio, L. Halophytes: Gourmet Food with Nutritional Health Benefits? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, M.; Villasante, S.; Cremades, J.; Calado, R.; Lillebø, A.I. Unravelling the Potential of Halophytes for Marine Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA)—A Perspective on Performance, Opportunities and Challenges. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2017, 9, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, R.L.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Borges, G.d.S.C.; Azevedo, M.S.; Maltez, H.F.; Heller, M.; Micke, G.A.; Tavares, L.B.B.; Fett, R. Nutrient Composition and, Identification/Quantification of Major Phenolic Compounds in Sarcocornia Ambigua (Amaranthaceae) Using HPLC–ESI-MS/MS. Food Res. Int. 2014, 55, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard, W.A.; Leonard, B.V. A Comparison of Three Different Hydroponic Sub-Systems (Gravel Bed, Floating and Nutrient Film Technique) in an Aquaponic Test System. Aquac. Int. 2006, 14, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology—A Practical Guide Book, 3rd ed.; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781888807219. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, S.M.; De Lima, J.P.; David, L.H.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Goddek, S.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Keesman, K.J.; Portella, M.C. FLOCponics: The Integration of Biofloc Technology with Plant Production. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 647–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Miranda-Baeza, A. Biofloc Technology (BFT): A Tool for Water Quality Management in Aquaculture. In Water Quality; InTech: Penang, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wasielesky, W.; Atwood, H.; Stokes, A.; Browdy, C.L. Effect of Natural Production in a Zero Exchange Suspended Microbial Floc Based Super-Intensive Culture System for White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.M.; Molinari, D.; Mello, G.L.; Fitzsimmons, K.M.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Effluent from a Biofloc Technology (BFT) Tilapia Culture on the Aquaponics Production of Different Lettuce Varieties. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncato, K.B.; Costa, C.S.B. Micronutrient Supplementation Needs for Halophytes in Saline Aquaponics with BFT System Water. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Carneiro, R.F.S.; Vieira, F.d.N.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Costa, A.C.d.O.; Magallón-Barajas, F.J.; Seiffert, W.Q. Aquaponic Production of Sarcocornia Ambigua and Pacific White Shrimp in Biofloc System at Different Salinities. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncato, K.B.; Costa, C.S.B. Growth and Mineral Composition of Two Lineages of the Sea Asparagus Sarcocornia Ambigua Irrigated with Shrimp Farm Saline Effluent. Exp. Agric. 2018, 54, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, M.A.; Legarda, E.C.; de Lorenzo, M.A.; Pinheiro, I.; Martins, M.A.; Seiffert, W.Q.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Integrated Multitrophic Aquaculture Applied to Shrimp Rearing in a Biofloc System. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Arantes, R.; do Espírito Santo, C.M.; Vieira, F.d.N.; Lapa, K.R.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Barcelos-Oliveira, J.L.; Seiffert, W.Q. Production of the Halophyte Sarcocornia Ambigua and Pacific White Shrimp in an Aquaponic System with Biofloc Technology. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 100, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.J.; Lewis, B.L.; Browdy, C.L.; Leffler, J.W. Suspended Solids Removal to Improve Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Production and an Evaluation of a Plant-Based Feed in Minimal-Exchange, Superintensive Culture Systems. Aquaculture 2010, 299, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona, C.A.P.; Poersch, L.H.; Krummenauer, D.; Foes, G.K.; Wasielesky, W.J. The Effect of Solids Removal on Water Quality, Growth and Survival of Litopenaeus vannamei in a Biofloc Technology Culture System. Int. J. Recirc. Aquac. 2011, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, M.B.; Ebeling, J.M. Recirculating Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; Cayuga Aqua Ventures: Freeville, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780971264625. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Biofloc Production Systems for Aquaculture; SRAC Publication No. 4503; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schveitzer, R.; Arantes, R.; Costódio, P.F.S.; do Espírito Santo, C.M.; Arana, L.V.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Andreatta, E.R. Effect of Different Biofloc Levels on Microbial Activity, Water Quality and Performance of Litopenaeus vannamei in a Tank System Operated with No Water Exchange. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 56, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.J.; Dillon, K.S.; Lotz, J.M. Water Quality Dynamics and Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Production in Intensive, Mesohaline Culture Systems with Two Levels of Biofloc Management. Aquac. Eng. 2011, 45, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schveitzer, R.; Baccarat, R.F.C.; Gaona, C.A.P.; Wasielesky, W.; Arantes, R. Concentration of Suspended Solids in Superintensive Culture of the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei with Biofloc Technology (BFT): A Review. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Cordova, L.R.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Pinho, S.M.; Garibay-Valdez, E.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Advancing toward a More Integrated Aquaculture with Polyculture > Aquaponics > Biofloc Technology > FLOCponics. Aquac. Int. 2023, 31, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, P. Nutrition and Feeding of Litopenaeus vannamei in Intensive Culture Systems. In Farming Marine Shrimp in Recirculating Freshwater Systems; Van Wyk, P., Davis-hodgkins, M., Laramore, R., Main, K.L., Mountain, J., Scarpa, J., Eds.; Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J.J. Engineering Analysis of the Stoichiometry of Photoautotrophic, Autotrophic, and Heterotrophic Removal of Ammonia–Nitrogen in Aquaculture Systems. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.; Parsons, T.R. Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis, 1st ed.; Fish Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- APHA Method 2540 (Solids). In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Martins, M.A.; Poli, M.A.; Legarda, E.C.; Pinheiro, I.; Carneiro, R.F.S.; Pereira, S.A.; Martins, M.A.M.L.; Gonçalves, P.; Schleder, D.D.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Heterotrophic and Mature Biofloc Systems in the Integrated Culture of Pacific White Shrimp and Nile Tilapia. Aquaculture 2020, 514, 734517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, R.; Schveitzer, R.; Magnotti, C.; Lapa, K.R.; Vinatea, L. A Comparison between Water Exchange and Settling Tank as a Method for Suspended Solids Management in Intensive Biofloc Technology Systems: Effects on Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Performance, Water Quality and Water Use. Aquac. Res. 2016, 48, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.; Körner, O.; Jijakli, M.H. Nutrient Cycling in Aquaponics Systems. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 231–246. ISBN 978-3-030-15943-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkiew, S.; Hu, Z.; Chandran, K.; Lee, J.W.; Khanal, S.K. Nitrogen Transformations in Aquaponic Systems: A Review. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 76, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Guimbaud, C.; Fang, Y. Effects of PH on Nitrogen Transformations in Media-Based Aquaponics. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.R.; Araneda, J.; Osses, A.; Orellana, J.; Gallardo, J.A. Efficiency of Salicornia Neei to Treat Aquaculture Effluent from a Hypersaline and Artificial Wetland. Agriculture 2020, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintã, R.; Santos, R.; Thomas, D.N.N.; Vay, L.L.; Le Vay, L.; Quinta, R.; Santos, R.; Thomas, D.N.N.; Le Vay, L. Growth and Nitrogen Uptake by Salicornia Europaea and Aster Tripolium in Nutrient Conditions Typical of Aquaculture Wastewater. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhu, R.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, T. The Optimal Ammonium-Nitrate Ratio for Various Crops: A Meta-Analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 307, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, P.S.; Valenzuela, M.A.J.; Rodriguez-Fuentes, G.; Campos, B.R.; Wasielesky, W.; Gaxiola, G. Chronic Effect of Nitrite on the Rearing of the White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in Two Salinities. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2016, 49, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, P.S.; Campos, B.R.; Serra, F.P.; Klosterhoff, M.; Romano, L.A.; Wasielesky, W. Effects of Nitrate Toxicity in the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, Reared with Biofloc Technology (BFT). Aquac. Int. 2015, 23, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C. Acute Toxicity of Ammonia on Litopenaeus vannamei Boone Juveniles at Different Salinity Levels. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 259, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samocha, T.M.; Prangnell, D.I. System Treatment and Preparation. In Sustainable Biofloc Systems for Marine Shrimp; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 119–131. ISBN 9780128180402. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, K.R.; Wasielesky, W.; Abreu, P.C. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Dynamics in the Biofloc Production of the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2013, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.; Martins, M.A.; Castilho-Barros, L.; do Espírito Santo, C.M.; do Nascimento Vieira, F.; Seiffert, W.Q. Reducing the Feed Input per Unit of Plant Area as a Means to Improve the Efficiency of Sea Asparagus and Pacific White Shrimp Biofloc Technology-Based Aquaponics. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 6536–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Treatment | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With Settling | Without Settling | ||
| Performance of P. vannamei | |||
| Survival (%) | 88.7 ± 6.7 | 86.8 ± 5.1 | 0.6745 |
| Mean initial weight (g) | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4683 |
| Mean final weight (g) | 10.2 ± 0.3 | 10.1 ± 0.3 | 0.6431 |
| Weekly weight gain (g week−1) | 1.17 ± 0.04 | 1.15 ± 0.04 | 0.6283 |
| Final biomass (kg tank−1) | 2.71 ± 0.14 | 2.62 ± 0.07 | 0.3936 |
| Productivity (kg m−3) | 3.04 ± 0.16 | 3.27 ± 0.09 | 0.1125 |
| Total feed input (kg) | 3.60 ± 0.05 | 3.63 ± 0.05 | 0.4713 |
| Feed conversion ratio (FCR) | 1.54 ± 0.11 | 1.61 ± 0.07 | 0.3757 |
| Performance of S. neei | |||
| Mean final weight (g) | 14.5 ± 5.9 | 12.8 ± 4.8 | 0.3597 |
| Final biomass (g tank−1) | 383.3 ± 58.4 | 338.2 ± 33.0 | 0.4510 |
| Survival (%) | 93.8 ± 1.8 | 94.0 ± 2.1 | 0.6964 |
| Productivity (kg m−2) | 1.26 ± 0.24 | 1.13 ± 0.11 | 0.4510 |
| Shrimp plus Salicornia | |||
| Total final biomass (kg) | 3.09 ± 0.11 | 2.95 ± 0.04 | 0.1703 |
| Total yield (kg m−3) | 3.47 ± 0.13 | 3.65 ± 0.06 | 0.1096 |
| Parameter | Treatment | RM ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Settling | Without Settling | T | D | T × D | |
| Salinity (psu) | 33.2 ± 1.6 | 32.5 ± 2.3 | ns | <0.0001 | 0.0030 |
| (30.0–35.8) | (28.7–35.7) | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | 28.7 ± 0.9 | 28.9 ± 0.8 | ns | 0.0010 | ns |
| (27.3–32.0) | (27.4–32.0) | ||||
| Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | ns | 0.0020 | ns |
| (5.0–7.6) | (5.1–7.3) | ||||
| pH | 8.11 ± 0.07 | 8.00 ± 0.12 | 0.0013 | 0.0006 | <0.0001 |
| (7.99–8.30) | (7.72–8.23) | ||||
| Alkalinity (mg CaCO3 L−1) | 164.8 ± 18.8 | 138.1 ± 16.6 | 0.0043 | 0.0091 | <0.0001 |
| (132–212) | (112–168) | ||||
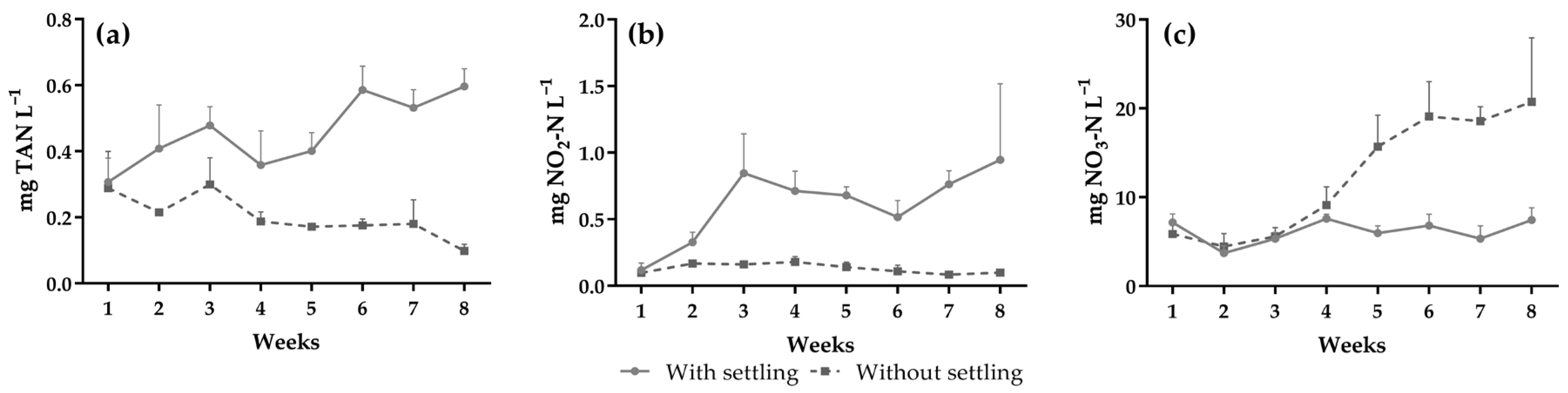
| Total ammonia nitrogen (mg L−1) | 0.49 ± 0.15 | 0.22 ± 0.16 | 0.0028 | ns | 0.0034 |
| (0.20–0.84) | (0.07–1.09) | ||||
| Nitrite (mg NO2-N L−1) | 0.68 ± 0.49 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 0.0047 | 0.0368 | <0.0001 |
| (0.01–2.25) | (0.01–0.30) | ||||
| Nitrate (mg NO3-N L−1) | 6.09 ± 1.49 | 12.28 ± 6.76 | 0.0025 | 0.0016 | <0.0001 |
| (2.92–8.94) | (2.76–28.92) | ||||
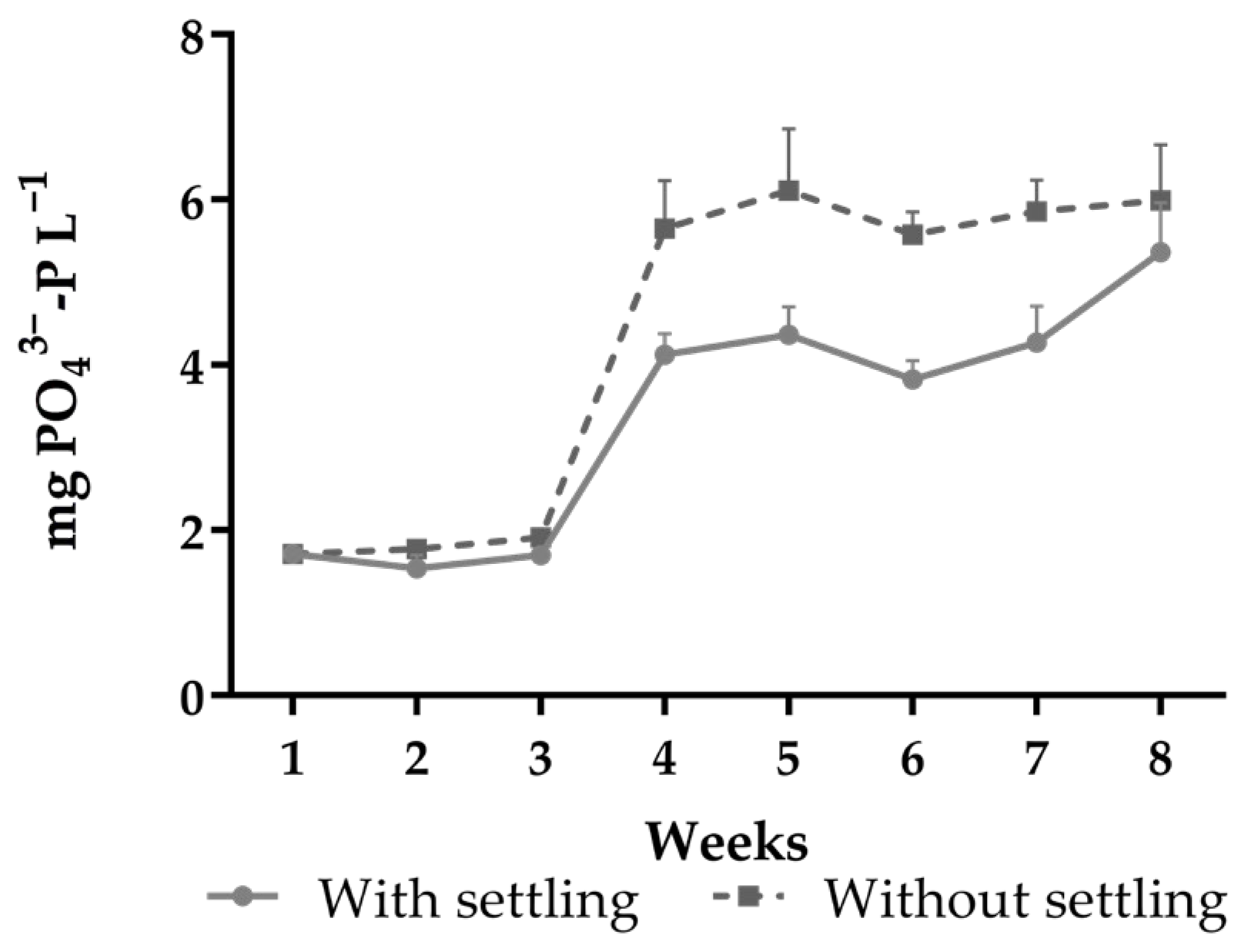
| Orthophosphate (mg PO43−-P L−1) | 3.48 ± 1.46 | 4.35 ± 1.95 | 0.0055 | 0.0016 | 0.0101 |
| (1.33–6.26) | (1.68–6.72) | ||||
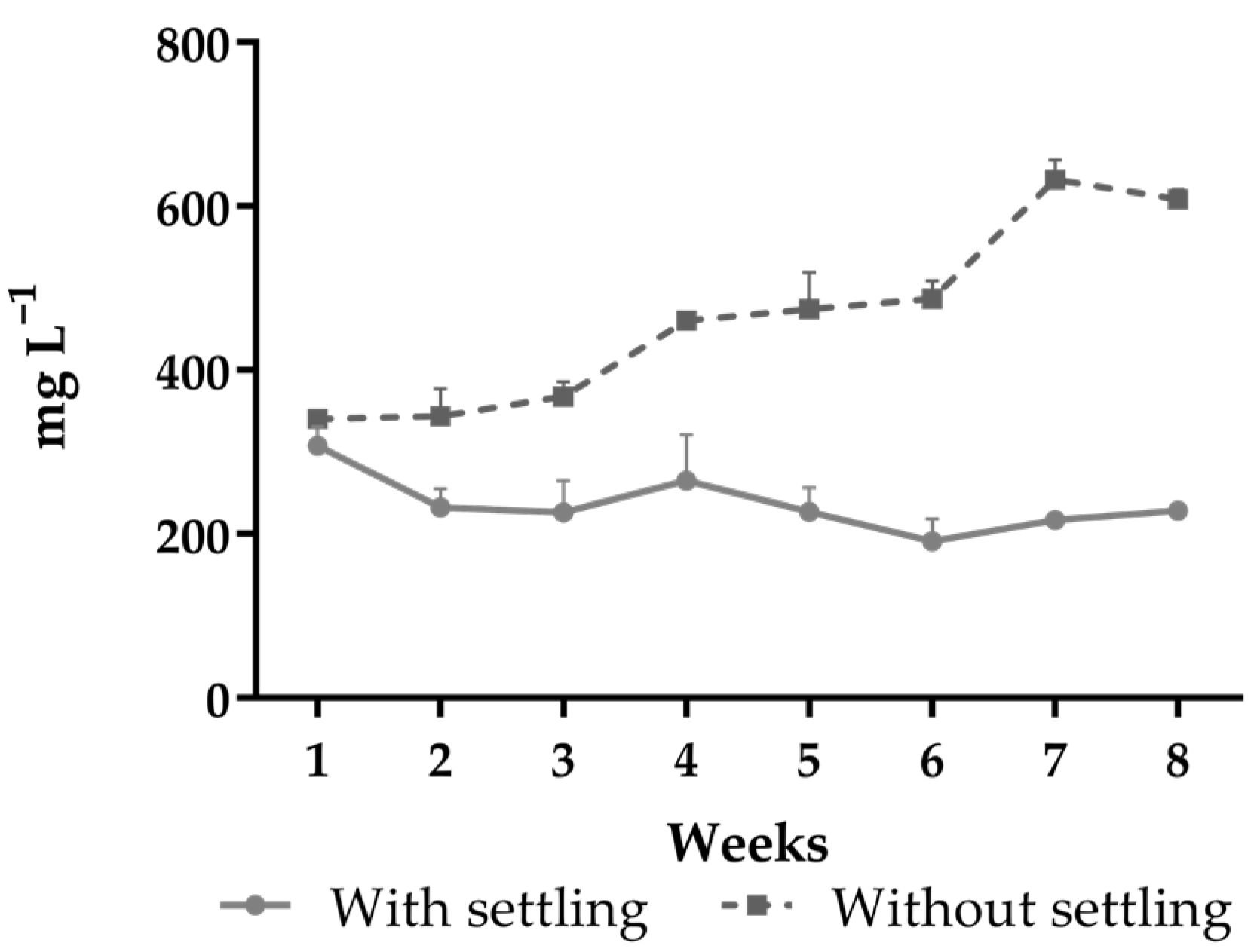
| TSS (mg L−1) | 230.0 ± 39.8 | 464.2 ± 118.2 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| (140–350) | (287–717) | ||||
| VSS (%) | 27.7 ± 5.9 | 40.1 ± 4.7 | 0.0025 | ns | 0.0071 |
| (4.5–47.5) | (29.3–48.0) | ||||
| Settleable solids (mL L−1) | 0.09 ± 0.17 | 9.17 ± 8.02 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| (0.0–1.0) | (0.3–27.0) | ||||
| Parameter | Treatment | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With Settling | Without Settling | ||
| TSS (mg L−1) | 231.3 ± 10.9 | 608.5 ± 94 | <0.0001 |
| VSS (%) | 31.3 ± 2.0 | 46.1 ± 2.0 | 0.0012 |
| FSS (%) | 72.3 ± 5.9 | 59.9 ± 4.7 | 0.0012 |
| Settleable solids (mL L−1) | 0.08 ± 0.08 | 19.17 ± 6.15 | 0.0095 |
| Total sludge produced (g tank−1) | 122.3 ± 17.3 | 905.5 ± 101.8 | 0.0046 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinheiro, I.; Banderó Höffling, F.; Boéchat Vieira, F.; Quadros Seiffert, W. The Effect of the Use of a Settling Chamber in the Cultivation of Penaeus vannamei and Salicornia neei in Aquaponics with Bioflocs. Animals 2025, 15, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091294
Pinheiro I, Banderó Höffling F, Boéchat Vieira F, Quadros Seiffert W. The Effect of the Use of a Settling Chamber in the Cultivation of Penaeus vannamei and Salicornia neei in Aquaponics with Bioflocs. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091294
Chicago/Turabian StylePinheiro, Isabela, Flávia Banderó Höffling, Felipe Boéchat Vieira, and Walter Quadros Seiffert. 2025. "The Effect of the Use of a Settling Chamber in the Cultivation of Penaeus vannamei and Salicornia neei in Aquaponics with Bioflocs" Animals 15, no. 9: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091294
APA StylePinheiro, I., Banderó Höffling, F., Boéchat Vieira, F., & Quadros Seiffert, W. (2025). The Effect of the Use of a Settling Chamber in the Cultivation of Penaeus vannamei and Salicornia neei in Aquaponics with Bioflocs. Animals, 15(9), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091294







