Unraveling Fish Community Diversity and Structure in the Yellow Sea: Evidence from Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Bottom Trawling
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
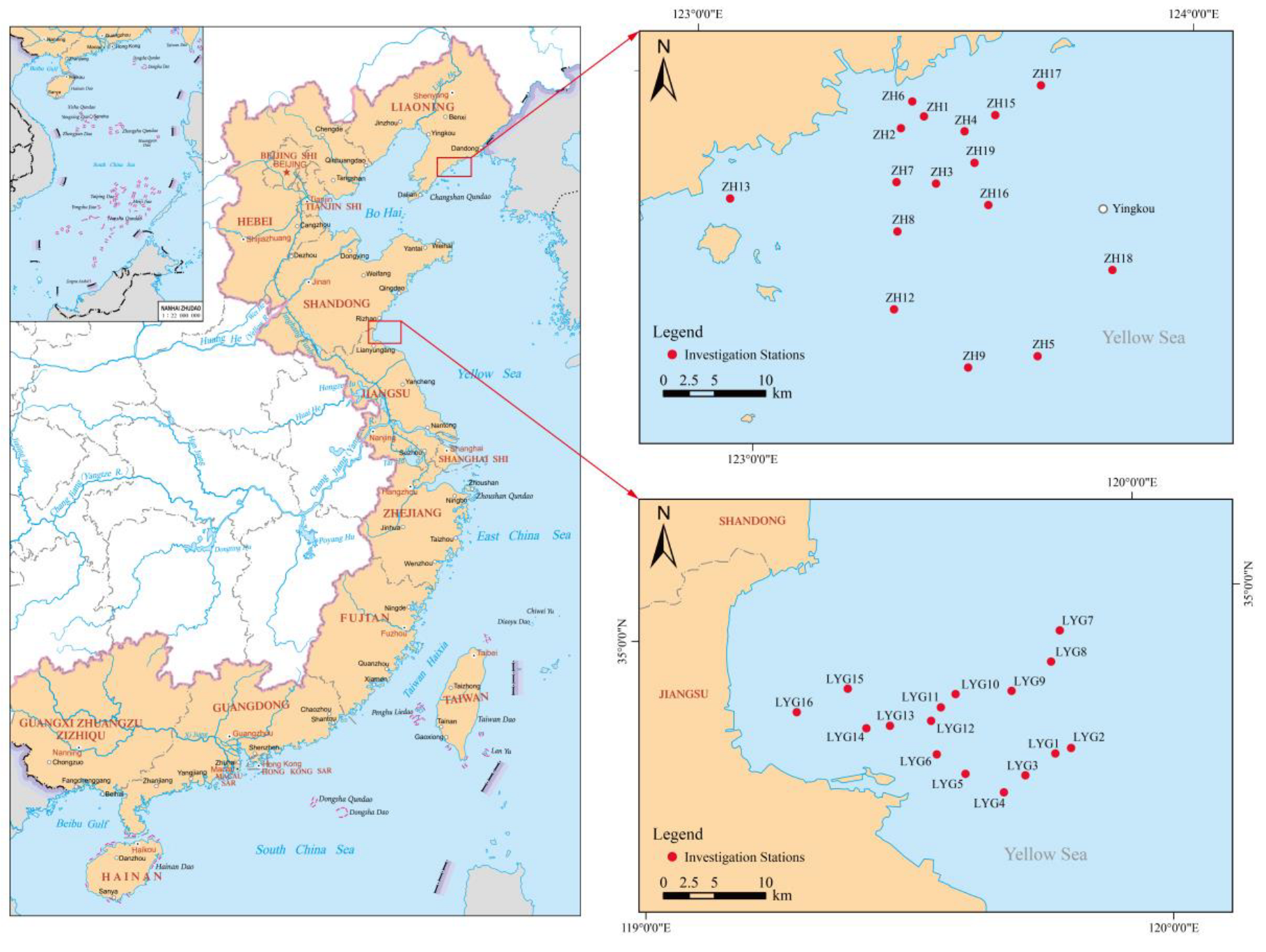
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
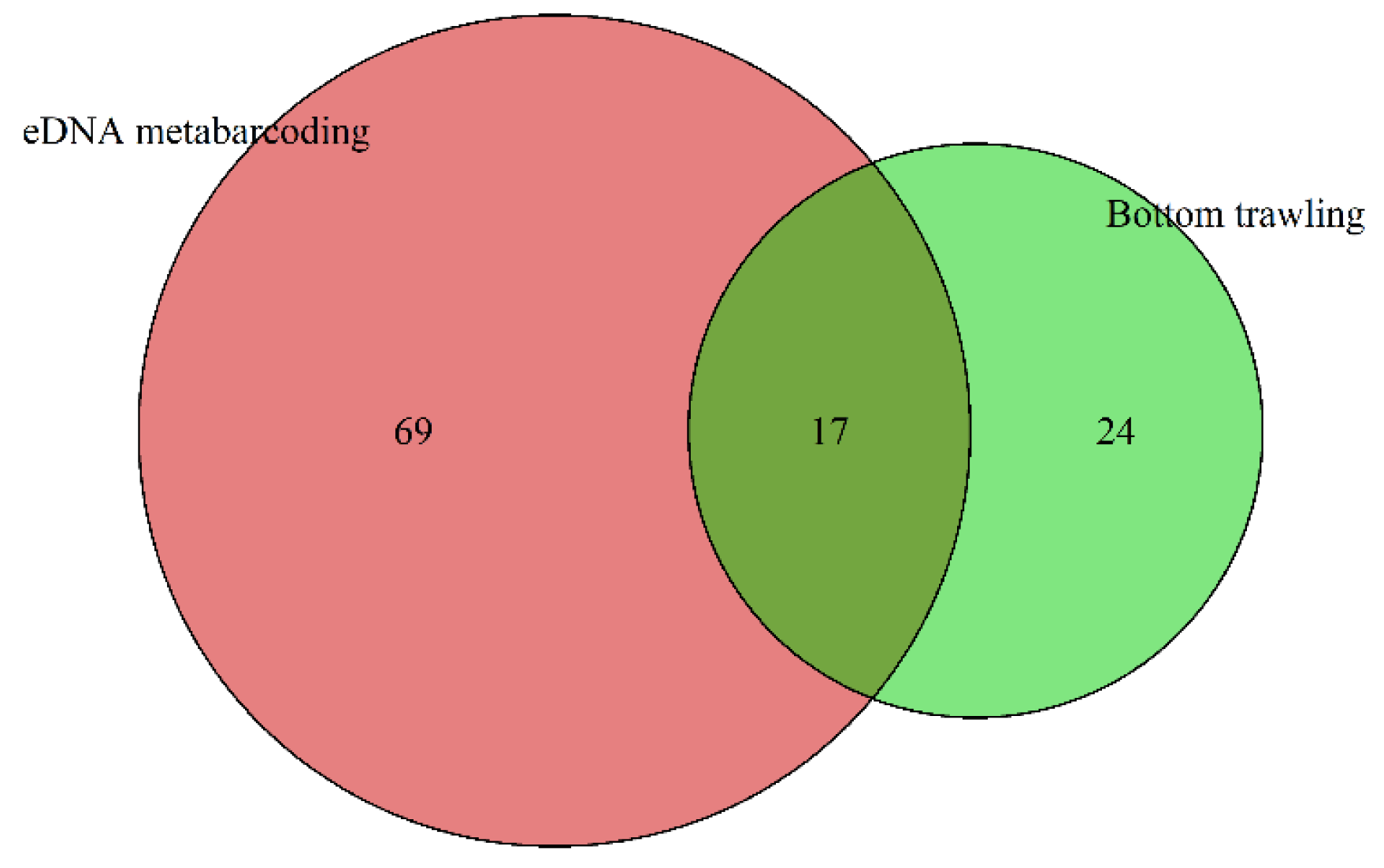
3.1. Composition and Relative Abundance of Fish Communities in the Yellow Sea
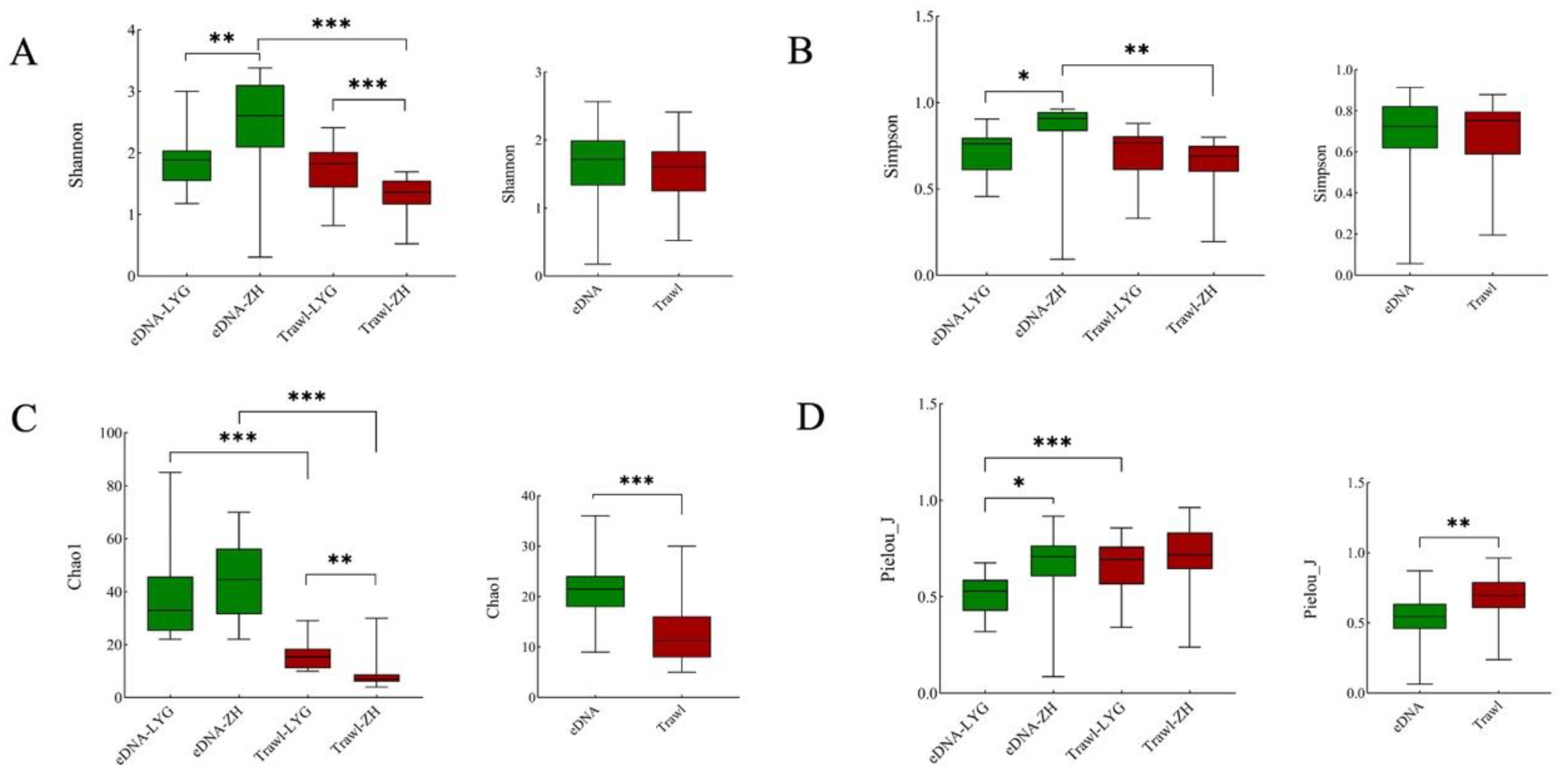
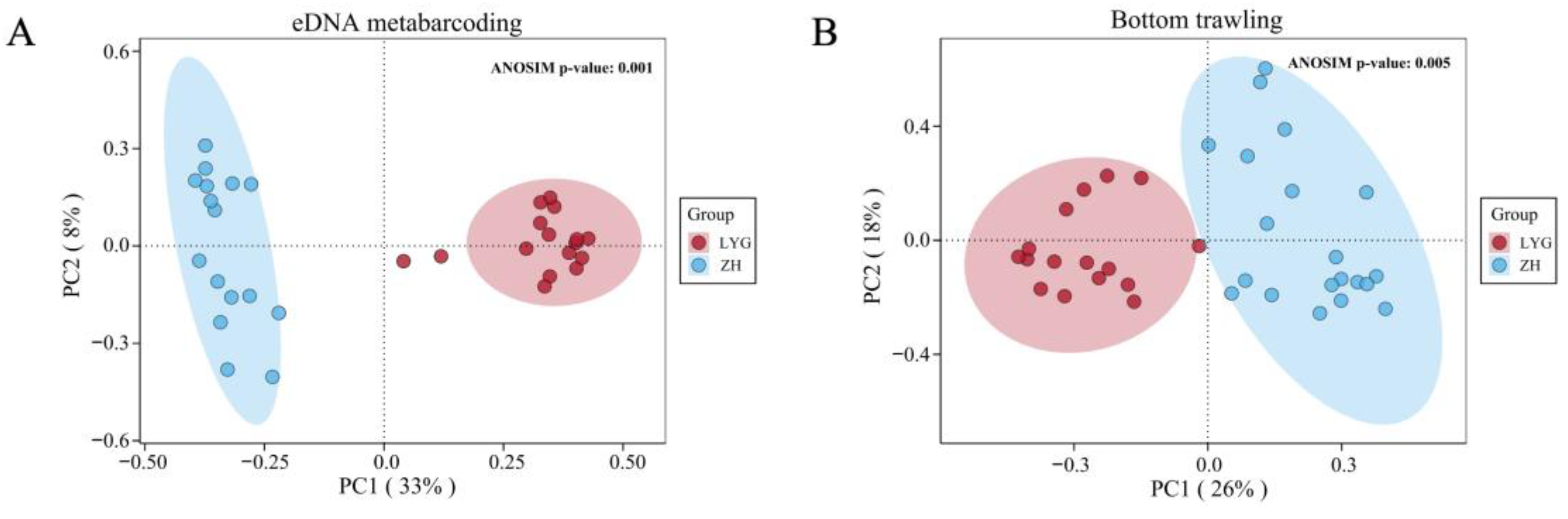
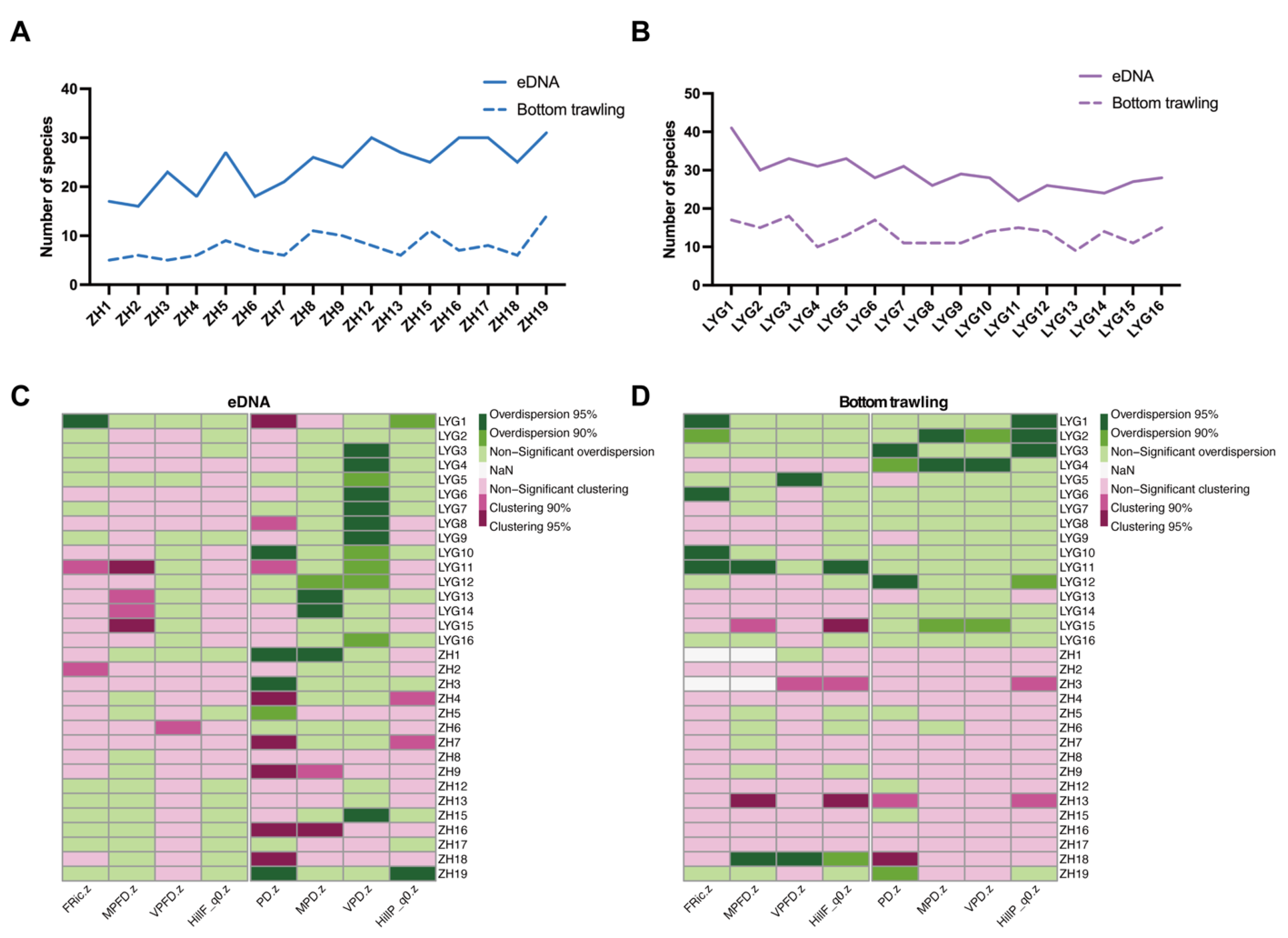
3.2. Alpha and Beta Diversity of Fish Communities in the Yellow Sea
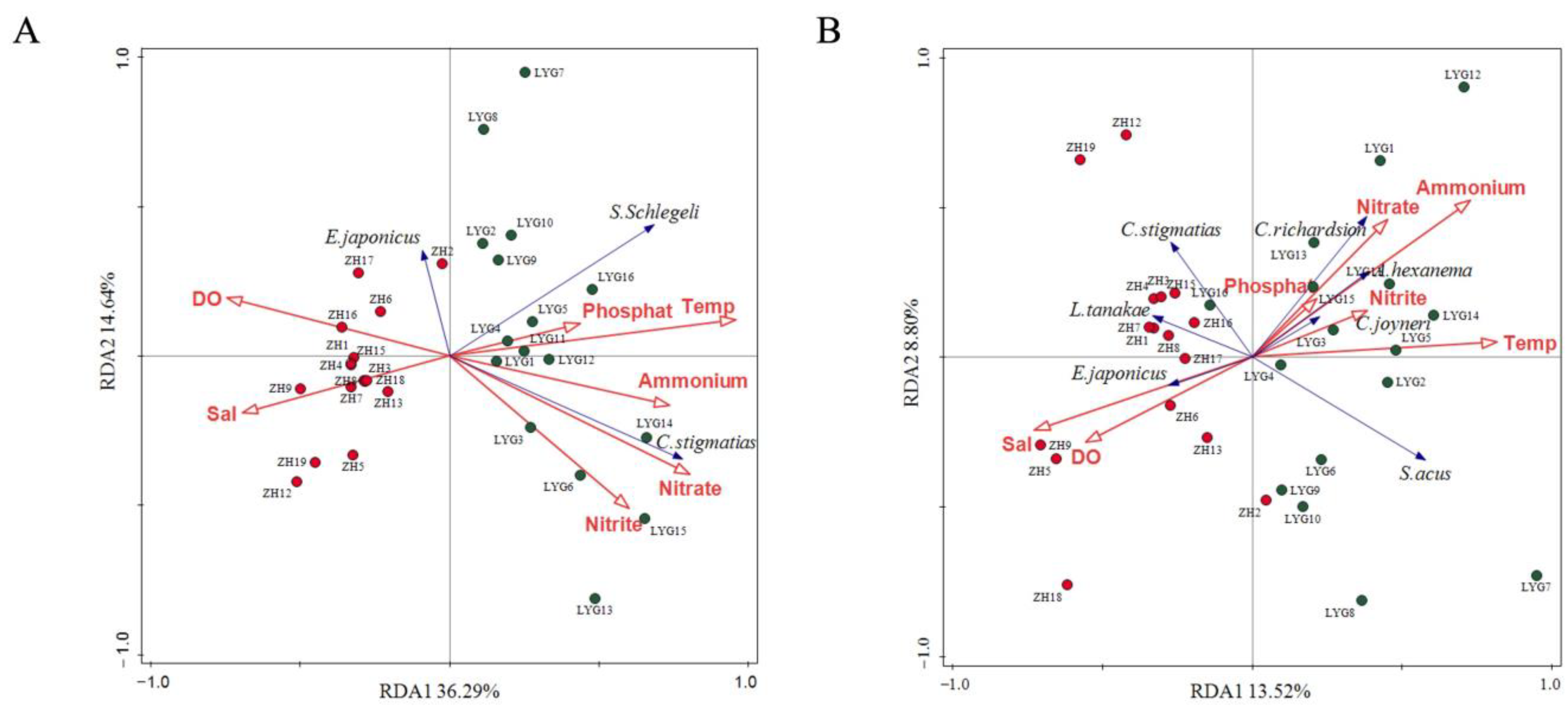
3.3. Relationship Between Fish Community Composition and Environmental Factors
3.4. Spread and Variation of Taxonomic, Phylogenetic, and Functional Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. eDNA Metabarcoding as a Promising Tool for Assessing Fish Biodiversity in the Yellow Sea
4.2. Characteristics of Fish Community Structure in the Yellow Sea
4.3. Effects of Environmental Factors on Fish Community Structure in the Yellow Sea
4.4. Fine-Scale Diversity Patterns
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Pellissier, L.; Zhang, X. Holistic Impact Evaluation of Human Activities on the Coastal Fish Biodiversity in the Chinese Coastal Environment. Environ. Sci Technol 2022, 56, 6574–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Chen, J.; Ruan, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, M.; Liu, L. eDNA metabarcoding as a promising conservation tool for monitoring fish diversity in a coastal wetland of the Pearl River Estuary compared to bottom trawling. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 702, 134704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. A comprehensive and comparative evaluation of primers for metabarcoding eDNA from fish. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guri, G.; Shelton, A.; Kelly, R.; Yoccoz, N.; Johansen, T.; Præbel, K.; Hanebrekke, T.; Ray, J.; Fall, J.; Westgaard, J.-I. Predicting trawl catches using environmental DNA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 81, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, S.; Mercado-Silva, N.; Hubert, W.; Beard, T.; Dave, G.; Kubecka, J.; Graeb, B.; Lester, N.; Porath, M.; Winfield, I. Standard Methods for Sampling Freshwater Fishes: Opportunities for International Collaboration. Fisheries 2017, 42, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osathanunkul, M.; Suwannapoom, C. Sustainable fisheries management through reliable restocking and stock enhancement evaluation with environmental DNA. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creer, S.; Deiner, K.; Frey, S.; Porazinska, D.; Taberlet, P.; Thomas, W.; Potter, C.; Bik, H. The ecologist’s field guide to sequence-based identification of biodiversity. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.; Chadderton, W.; Mahon, A.; Renshaw, M.; Corush, J.; Budny, M.; Mysorekar, S.; Lodge, D. Detection of Asian carp DNA as part of a Great Lakes basin-wide surveillance program. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, K.; Murakami, H.; Yoon, S.; Minami, K.; Osada, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Kasai, A.; Miyashita, K.; Minamoto, T.; et al. Estimating fish population abundance by integrating quantitative data on environmental DNA and hydrodynamic modelling. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, A.O.; Ramón-Laca, A.; Wells, A.; Clemons, J.; Chu, D.; Feist, B.E.; Kelly, R.P.; Parker-Stetter, S.L.; Thomas, R.; Nichols, K.M.; et al. Environmental DNA provides quantitative estimates of Pacific hake abundance and distribution in the open ocean. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 20212613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boivin-Delisle, D.; Laporte, M.; Burton, F.; Dion, R.; Normandeau, E.; Bernatchez, L. Using environmental DNA for biomonitoring of freshwater fish communities: Comparison with established gillnet surveys in a boreal hydroelectric impoundment. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Lin, L.; Ye, S. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of fish communities in a small hydropower dam reservoir: A comparison between the eDNA approach and established fishing methods. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2022, 37, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeglédi, I.; Sály, P.; Specziár, A.; Preiszner, B.; Szalóky, Z.; Maroda, Á.; Pont, D.; Meulenbroek, P.; Valentini, A.; Erős, T. Congruency between two traditional and eDNA-based sampling methods in characterising taxonomic and trait-based structure of fish communities and community-environment relationships in lentic environment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.M.; Câmara, P.; Ogaki, M.B.; Pinto, O.H.B.; Lirio, J.M.; Coria, S.H.; Vieira, R.; Carvalho-Silva, M.; Amorim, E.T.; Convey, P.; et al. Green algae (Viridiplantae) in sediments from three lakes on Vega Island, Antarctica, assessed using DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylemans, J.; Gleeson, D.M.; Hardy, C.M.; Furlan, E. Toward an ecoregion scale evaluation of eDNA metabarcoding primers: A case study for the freshwater fish biodiversity of the Murray-Darling Basin (Australia). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 8697–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.; Berger, C.; García-Machado, E.; Côté, G.; Morissette, O.; Bernatchez, L. Cage transplant experiment shows weak transport effect on relative abundance of fish community composition as revealed by eDNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. eDNA metabarcoding revealed differential structures of aquatic communities in a dynamic freshwater ecosystem shaped by habitat heterogeneity. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Machado, E.; Laporte, M.; Normandeau, E.; Hernández, C.; Côté, G.; Paradis, Y.; Mingelbier, M.; Bernatchez, L. Fish community shifts along a strong fluvial environmental gradient revealed by eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2021, 4, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Yoshizawa, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Li, Y.; Xian, W.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Variation and Assessment of Fish Resources in the Yangtze Estuary Based on Environmental DNA. Water 2020, 12, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.T.; Wang, R.L.; Li, H.T.; Liu, L.; Kuang, T.X.; Li, M.; Zou, K.S. Effects of sampling strategies and DNA extraction methods on eDNA metabarcoding: A case study of estuarine fish diversity monitoring. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathon, L.; Marques, V.; Mouillot, D.; Albouy, C.; Andrello, M.; Baletaud, F.; Borrero-Perez, G.; Dejean, T.; Edgar, G.; Grondin, J.; et al. Cross-ocean patterns and processes in fish biodiversity on coral reefs through the lens of eDNA metabarcoding. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.i.; Doi, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Hanahara, N.; Sado, T. Environmental DNA metabarcoding for biodiversity monitoring of a highly diverse tropical fish community in a coral reef lagoon: Estimation of species richness and detection of habitat segregation. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.; Gillanders, B.; Jones, A.; Young, J.; Waycott, M. A muddy time capsule: Using sediment environmental DNA for the long-term monitoring of coastal vegetated ecosystems. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, S.; Bourdages, H.; Laporte, M.; Mérot, C.; Normandeau, E.; Audet, C.; Bernatchez, L. Comparing environmental metabarcoding and trawling survey of demersal fish communities in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, L.; Polanowski, A.M.; Clarke, L.J.; Kitchener, J.A.; Deagle, B.E. Capturing open ocean biodiversity: Comparing environmental DNA metabarcoding to the continuous plankton recorder. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3140–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestel, J.H.; Field, D.L.; Bateman, P.W.; White, N.E.; Allentoft, M.E.; Hopkins, A.J.M.; Gibberd, M.; Nevill, P. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in agricultural systems: Current uses, limitations and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, E.; Coppola, E.; Pires, R.; Parmegiani, A.; Casiraghi, M.; Galli, P.; Bruno, A. A species-specific qPCR assay provides novel insight into range expansion of the Mediterranean monk seal (Monachus monachus) by means of eDNA analysis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2022, 31, 1175–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, A.; Matechou, E.; Griffin, J.; Diana, A.; Griffiths, R.A. Optimising sampling and analysis protocols in environmental DNA studies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Bonin, A.; Zinger, L.; Coissac, E. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Keck, F.; Blackman, R.C.; Bossart, R.; Brantschen, J.; Couton, M.; Hürlemann, S.; Kirschner, D.; Locher, N.; Zhang, H.; Altermatt, F. Meta-analysis shows both congruence and complementarity of DNA and eDNA metabarcoding to traditional methods for biological community assessment. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 1820–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merten, V.; Bayer, T.; Reusch, T.; Puebla, O.; Fuss, J.; Stefanschitz, J.; Lischka, A.; Hauss, H.; Neitzel, P.; Piatkowski, U.; et al. An Integrative Assessment Combining Deep-Sea Net Sampling, in situ Observations and Environmental DNA Analysis Identifies Cabo Verde as a Cephalopod Biodiversity Hotspot in the Atlantic Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 760108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraija-Fernandez, N.; Bouquieaux, M.C.; Rey, A.; Mendibil, I.; Cotano, U.; Irigoien, X.; Santos Mokoroa, M.; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N. Marine water environmental DNA metabarcoding provides a comprehensive fish diversity assessment and reveals spatial patterns in a large oceanic area. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 7560–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckle, M.; Adolf, J.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Dunton, K.; Hinks, G.; VanMorter, S. Trawl and eDNA assessment of marine fish diversity, seasonality, and relative abundance in coastal New Jersey, USA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Xiong, P.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, M. Comparison of environmental DNA metabarcoding and bottom trawling for detecting seasonal fish communities and habitat preference in a highly disturbed estuary. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouy, C.; Guilhaumon, F.; Villéger, S.; Mouchet, M.; Mercier, L.; Culioli, J.-M.; Tomasini, J.; Le Loc’h, F.; Mouillot, D. Predicting trophic guild and diet overlap from functional traits: Statistics, opportunities and limitations for marine ecology. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 436, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, K.; Cianciaruso, M.; Loyola, R.; Brito, D.; Armour, K.; Diniz-Filho, J.A. Understanding global patterns of mammalian functional and phylogenetic diversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violle, C.; Navas, M.-L.; Vile, D.; Kazakou, E.; Fortunel, C.; Hummel, I.; Garnier, E. Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos. Oikos 2007, 116, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Dai, F.Q.; Jin, X.S.; Yang, D.T. Variations in fish community structure and diversity in the sections of the central and southern Yellow Sea. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 377–389. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P.; Bian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, X.; Jin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Community structure of fishery organisms in offshore waters of the North Yellow Sea. J. Fish. China 2024, 48, 049314-1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.X.; Ma, L. Fishes of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Sun, R.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, J. Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas-Annelida: Polychaeta (Zhou:Spionidae, Paraonidae 67 spp.); Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhan, A.; Dong, C.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. Environmental DNA captures native and non-native fish community variations across the lentic and lotic systems of a megacity. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk0097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Osugi, T.; Inagawa, T.; Okitsu, J.; Sakamoto, S.; Minamoto, T. Monitoring of multiple fish species by quantitative environmental DNA metabarcoding surveys over two summer seasons. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2024, 24, e13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollive, S.; Peterfreund, G.L.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Bittinger, K.; Sinha, R.; Hoffmann, C.; Nabel, C.S.; Hill, D.A.; Artis, D.; Bachman, M.A.; et al. A tool kit for quantifying eukaryotic rRNA gene sequences from human microbiome samples. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Pruitt, K.D.; Sherry, S.T.; Yankie, L.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I. GenBank 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D141–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M.; et al. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an accurate and automatic annotation pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Computing 2022, 1, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. Taking stock of global fisheries. Science 2024, 385, 824–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanski, R.; Trenkel, V.; Lorance, P.; Valentini, A.; Dejean, T.; Pellissier, L.; Eme, D.; Albouy, C. Disentangling the components of coastal fish biodiversity in southern Brittany by applying an environmental DNA approach. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 920–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, P.; Rozanski, R.; Marques, V.; Joost, S.; Deschez, M.; Trenkel, V.; Lorance, P.; Valentini, A.; Polanco, A.; Pellissier, L.; et al. Environmental DNA complements scientific trawling in surveys of marine fish biodiversity. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 2150–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprieur, F.; Albouy, C.; De Bortoli, J.; Cowman, P.F.; Bellwood, D.R.; Mouillot, D. Quantifying phylogenetic beta diversity: Distinguishing between ‘true’ turnover of lineages and phylogenetic diversity gradients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z. Characters of underwater topography and geomorphology in inner lingdingyang firth of the Pearl River (Zhujiang River) estuary. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2005, 25, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Stat, M.; John, J.; DiBattista, J.D.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M.; Harvey, E.S. Combined use of eDNA metabarcoding and video surveillance for the assessment of fish biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.; Carl, H.; Krag, M.; Knudsen, S.; Xing, Y.; Holm-Hansen, T.; Moller, P.; Thomsen, P. Seawater environmental DNA reflects seasonality of a coastal fish community. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Turner, C.; Jerde, C.; Renshaw, M.; Chadderton, W.; Lodge, D. Environmental Conditions Influence eDNA Persistence in Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilliod, D.; Goldberg, C.; Arkle, R.; Waits, L. Factors influencing detection of eDNA from a stream-dwelling amphibian. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troth, C.R.; Sweet, M.J.; Nightingale, J.; Burian, A. Seasonality, DNA degradation and spatial heterogeneity as drivers of eDNA detection dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shan, X.J.; Wang, W.J.; Ding, X.S.; Dai, F.Q.; LV, D.; Wu, H.H. Studying the Retention Time of Fenneropenaeus chinensis eDNA in Water. Progrees Fish. Sci. 2020, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylemans, J.; Gleeson, D.; Lintermans, M.; Hardy, C.; Beitzel, M.; Gilligan, D.; Furlan, E. Monitoring riverine fish communities through eDNA metabarcoding: Determining optimal sampling strategies along an altitudinal and biodiversity gradient. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2018, 2, e30457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, N.G.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Carvalho, D.C.; Deiner, K.; Præbel, K.; Coscia, I.; McDevitt, A.D.; Mariani, S. Space-time dynamics in monitoring neotropical fish communities using eDNA metabarcoding. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 754, 142096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Rosabal, M.; Bernatchez, L. Estimating fish abundance and biomass from eDNA concentrations: Variability among capture methods and environmental conditions. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Inui, R.; Akamatsu, Y.; Kanno, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA analysis for estimating the abundance and biomass of stream fish. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 62, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, T.; McKelvey, K.; Young, M.; Sepulveda, A.; Shepard, B.; Jane, S.; Whiteley, A.; Lowe, W.; Schwartz, M. Understanding environmental DNA detection probabilities: A case study using a stream-dwelling char Salvelinus fontinalis. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 194, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, A.O.; Gold, Z.J.; Jensen, A.J.; D’Agnese, E.; Andruszkiewicz Allan, E.; Van Cise, A.; Gallego, R.; Ramón-Laca, A.; Garber-Yonts, M.; Parsons, K.; et al. Toward quantitative metabarcoding. Ecology 2023, 104, e3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledger, K.J.; Hicks, M.B.R.; Hurst, T.P.; Larson, W.; Baetscher, D.S. Validation of Environmental DNA for Estimating Proportional and Absolute Biomass. Environ. DNA 2024, 6, e70030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.Q.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.L. Variations of fishery resource structure in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2020, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.D.; Jin, X.S.; Liang, Z.L. Changes of demersal fish community structure in the Yellow Sea during the autumn. J. Fish. Sci. China 2003, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, Q.S. Study on trophic level of important resources species at high troph levels in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2004, 22, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, A.S.; Isbell, F.; Seidl, R. β-Diversity, Community Assembly, and Ecosystem Functioning. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, T.; Pitz, K.J.; Chavez, F.P.; Yorke, C.E.; Miller, R.J. Environmental DNA reveals the fine-grained and hierarchical spatial structure of kelp forest fish communities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espínola, L.; Abrial, E.; Rabuffetti, A.; Simões, N.; Amsler, M.; Blettler, M.; Eurich, M.; Paira, A. Discrimination of hydrologic variations for spatial distribution of fish assemblage in a large subtropical temperate river. Ecohydrology 2019, 13, e2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, J.; Margulies, D.; Scholey, V. Temperature and dissolved oxygen requirements for survival of yellowfin tuna, Thunnus albacares, larvae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.-J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 404, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Flecker, A. Deforesting the Riverscape: The Effects of Wood on Fish Diversity in a Venezuelan Piedmont Stream. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 120, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Xu, B.D.; Ji, Y.P.; Ren, Y.P. Fish community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in Haizhou Bay and adjacent waters of East China in winter. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2013, 24, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.D.; Wang, J.W.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.T.; Guan, C.T.; Huang, B. Effect of Dissolved Oxygen on Physiological Functions and Mechanism in Fish. Open J. Fish. Res. 2020, 7, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountrey, A.N.; Coulson, P.G.; Meeuwig, J.J.; Meekan, M. Water temperature and fish growth: Otoliths predict growth patterns of a marine fish in a changing climate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.B.; Zhu, H.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.J.; Lu, Z.H.; Cui, G.C.; Dai, Q. Quantitative distribution of juvenile Engraulis japonicus and the rela tionship with environmental factors along the Zhejiang coast. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.L.; Ren, Y.P.; Xu, B.D. Spatiotemporal variation in the distribution and abundance of Chaeturichthys stigmatias in the Yellow River estuary and adjacent waters. J. Fish. Sci. China 2015, 22, 791–798. [Google Scholar]
- Malone, T.; Newton, A. The Globalization of Cultural Eutrophication in the Coastal Ocean: Causes and Consequences. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, A.; Marques, V.; Fopp, F.; Juhel, J.-B.; Borrero-Perez, G.; Cheutin, M.-C.; Dejean, T.; González Corredor, J.; Acosta-Chaparro, A.; Hocdé, R.; et al. Comparing environmental DNA metabarcoding and underwater visual census to monitor tropical reef fishes. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglieri, G.; Baillie, C.; Mariani, S.; Cattano, C.; Calò, A.; Turco, G.; Spatafora, D.; Di Franco, A.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Guidetti, P.; et al. Environmental DNA effectively captures functional diversity of coastal fish communities. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, E.; Loiseau, N.; Valentini, A.; Arnal, V.; Boissery, P.; Dejean, T.; Deter, J.; Guellati, N.; Holon, F.; Juhel, J.B.; et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals and unpacks a biodiversity conservation paradox in Mediterranean marine reserves. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20210112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. Unraveling Fish Community Diversity and Structure in the Yellow Sea: Evidence from Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Bottom Trawling. Animals 2025, 15, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091283
Zhang J, Cui X, Lin L, Liu Y, Ye J, Zhang W, Li H. Unraveling Fish Community Diversity and Structure in the Yellow Sea: Evidence from Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Bottom Trawling. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091283
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinyong, Xiaoyu Cui, Lin Lin, Yuan Liu, Jinqing Ye, Weiyue Zhang, and Hongjun Li. 2025. "Unraveling Fish Community Diversity and Structure in the Yellow Sea: Evidence from Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Bottom Trawling" Animals 15, no. 9: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091283
APA StyleZhang, J., Cui, X., Lin, L., Liu, Y., Ye, J., Zhang, W., & Li, H. (2025). Unraveling Fish Community Diversity and Structure in the Yellow Sea: Evidence from Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Bottom Trawling. Animals, 15(9), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091283



