Dietary Differentiation Mitigates Interspecific Interference Competition Between Sympatric Pallas’s Cats (Otocolobus manul) and Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
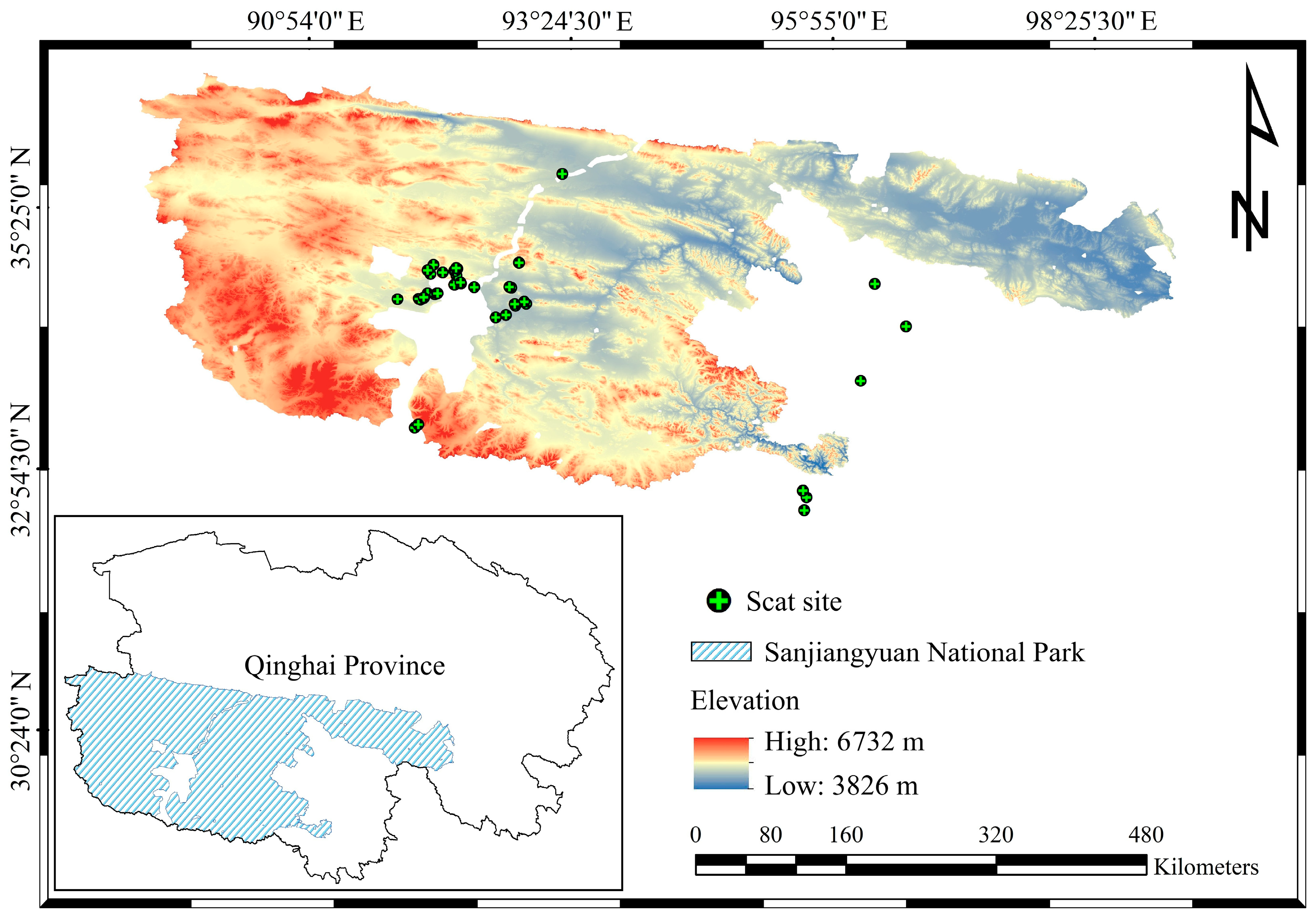
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Fecal Sample Collection
2.3. Fecal DNA Extraction, Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
- (1)
- This study utilized relative read abundance (RRA%) to quantitatively describe the proportion of sequence abundance for each prey taxonomic group in fecal samples following weighted averaging. The calculation formula is as follows:In this formula, the parameter S denotes the total number of fecal samples collected for the target species, T represents the total number of prey species identified, and ni,k signifies the number of sequences attributed to prey species i within fecal sample k. The cumulative relative read abundance (RRA) for each prey species across all fecal samples of a given target species equals 100%.
- (2)
- To further investigate the dietary differences between the two small carnivores, this study employed the Levins index (B) and the Pianka overlap index (Ojk). These indices were applied to evaluate the dietary niche breadth of the Pallas’s cat and the red fox [33], as well as the extent of dietary overlap between them [34,35], based on the relative abundance of food composition at the species level.In the above formula, parameter B denotes niche breadth, while Pj signifies the proportion of food item j. The value of B ranges from 0 to infinity. Ojk represents the Pianka overlap index, where Pij and Pik indicate the relative abundance of food item i in the diets of species j and k, respectively. The range of Ojk values extends from 0 to 1. According to the evaluation criteria, an Ojk value of 0 implies no dietary overlap, whereas an Ojk value of 1 suggests complete dietary overlap. An Ojk value exceeding 0.3 is deemed to signify significant overlap, and an Ojk value surpassing 0.6 is considered to reflect pronounced overlap.
3. Results
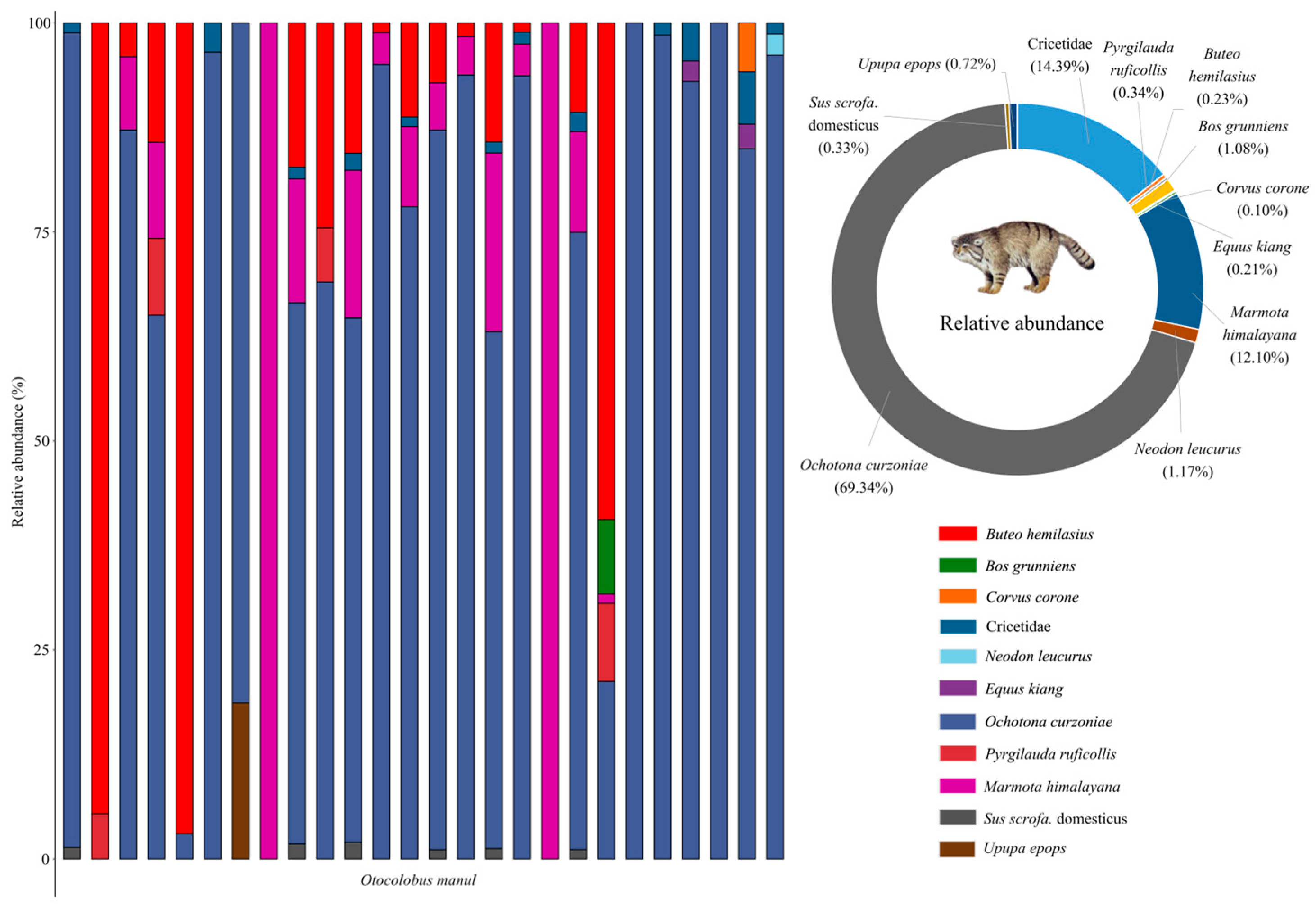
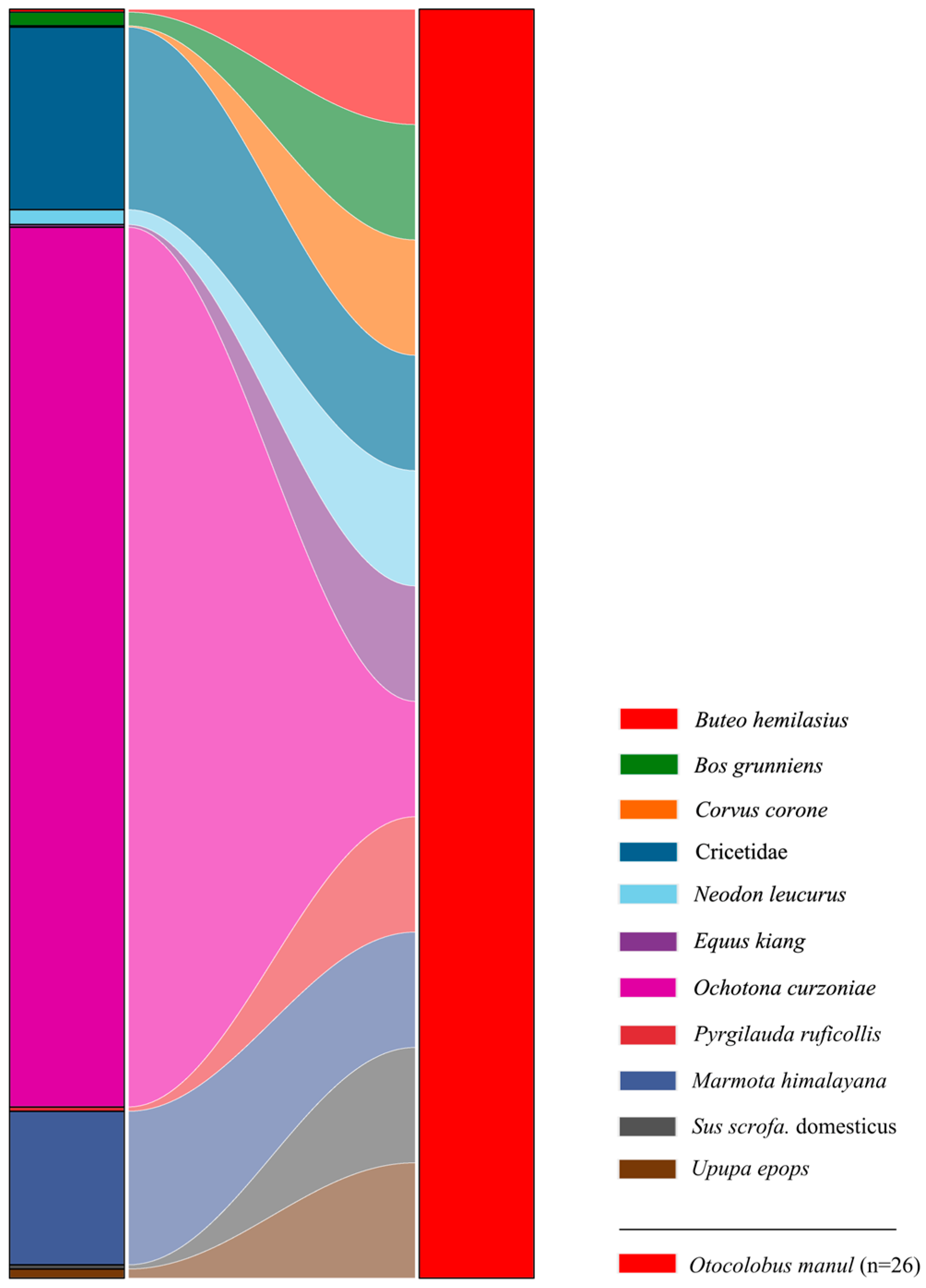
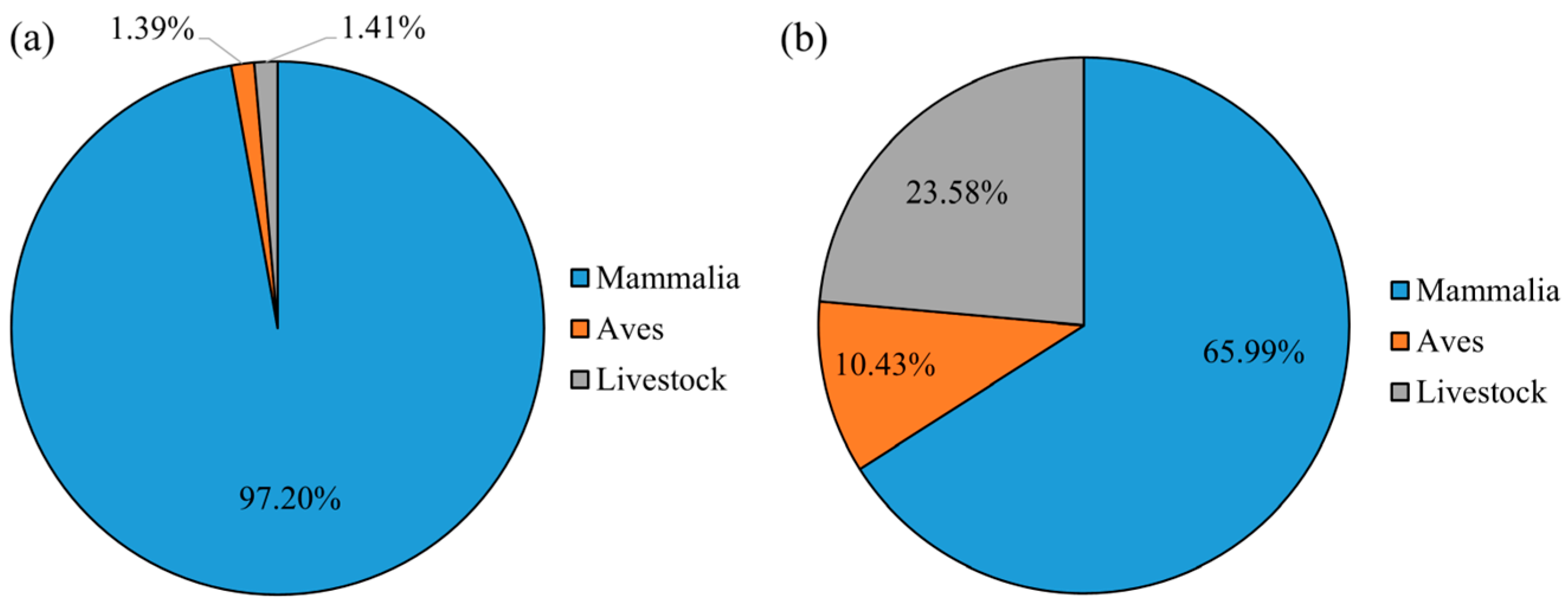
3.1. Dietary Composition of Pallas’s Cats
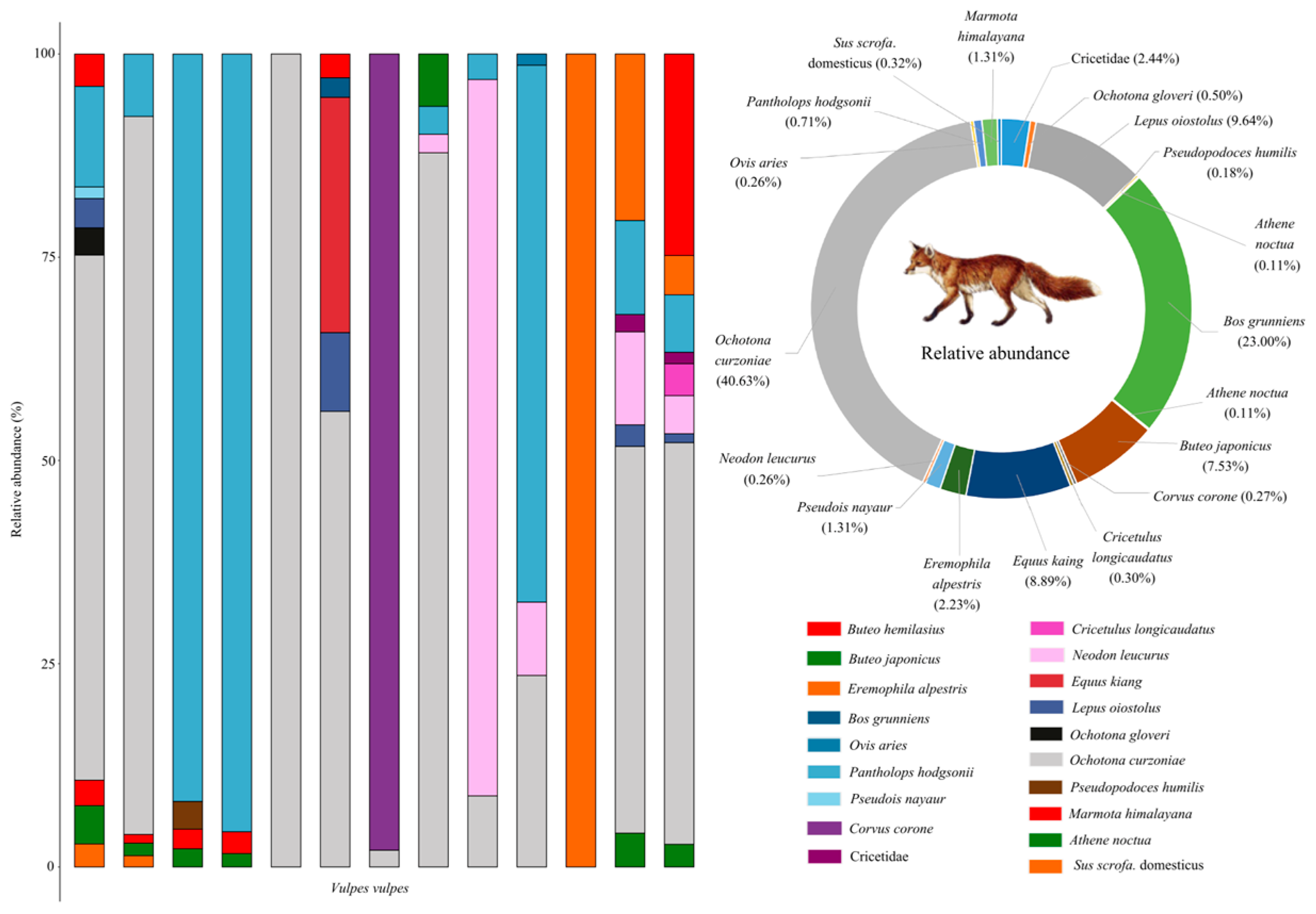
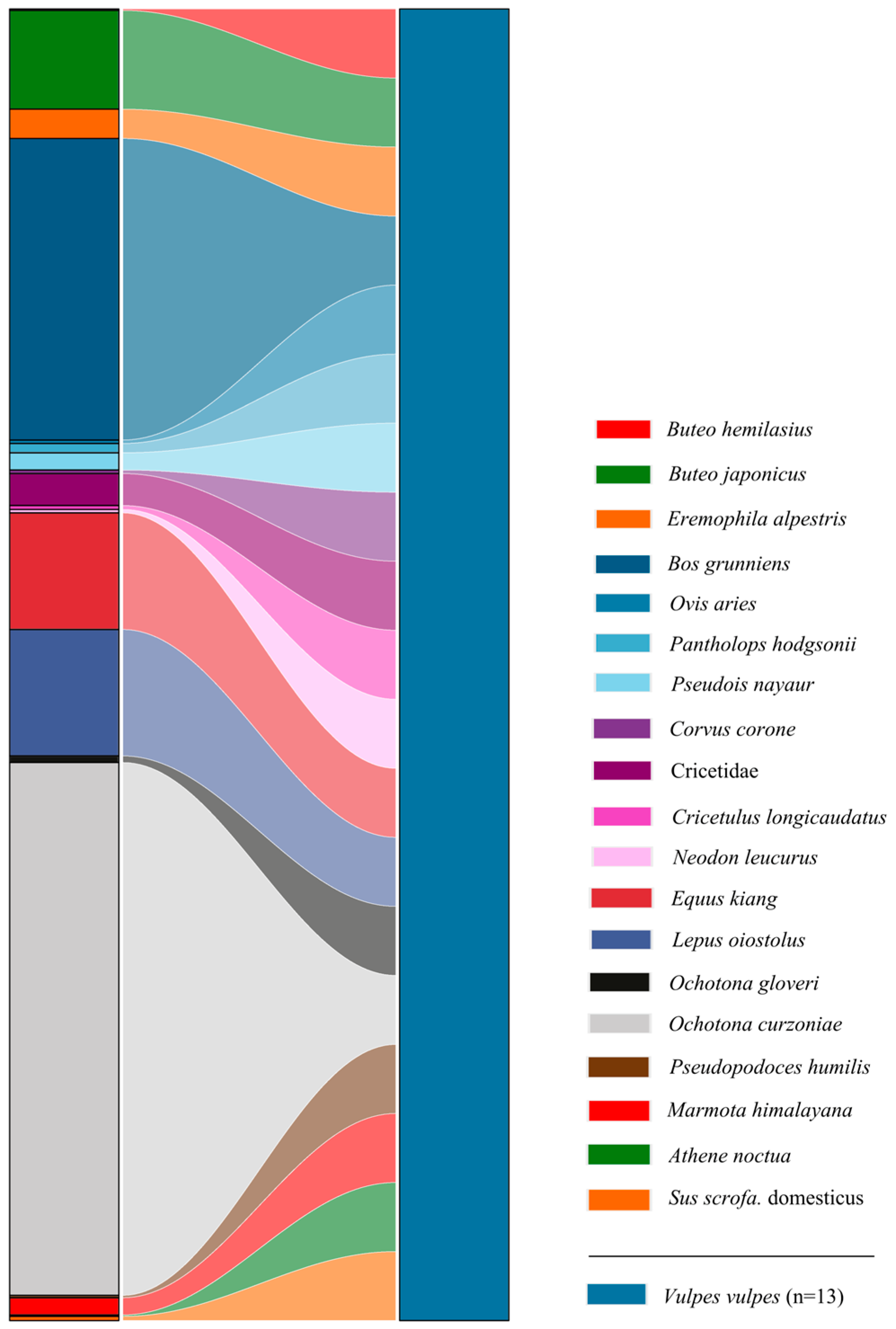
3.2. Dietary Composition of Red Foxes
3.3. Dietary Breadth and Overlap Between Pallas’s Cats and Red Foxes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ripple, W.J.; Estes, J.A.; Beschta, R.L.; Wilmers, C.C.; Ritchie, E.G.; Hebblewhite, M.; Berger, J.; Elmhagen, B.; Letnic, M.; Nelson, M.P.; et al. Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science 2014, 343, 1241484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descalzo, E.; Torres, J.A.; Ferreras, P.; Díaz-Ruiz, F. Methodological improvements for detecting and identifying scats of an expanding mesocarnivore in south-western Europe. Mamm. Biol. 2020, 101, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.G.; Elmhagen, B.; Glen, A.S.; Letnic, M.; Ludwig, G.; Mcdonald, R.A. Ecosystem restoration with teeth: What role for predators? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.G.; Johnson, C.N. Predator interactions, mesopredator release and biodiversity conservation. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanszki, J.; Heltai, M.; Kövér, G.; Zalewski, A. Non-linear relationship between body size of terrestrial carnivores and their trophic niche breadth and overlap. Basic. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 38, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnell, J.D.C.; Strand, O. Interference interactions, co-existence and conservation of mammalian carnivores. Divers. Distrib. 2000, 6, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadio, E.; Buskirk, S.W. Diet, morphology, and Interspecific killing in carnivora. Am. Nat. 2006, 167, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokheral, C.P.; Wegge, P. Coexisting large carnivores: Spatial relationships of tigers and leopards and their prey in a prey-rich area in lowland Nepal. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Wang, T.M.; Smith, J.L.D.; Feng, R.N.; Feng, L.M.; Mou, P.; Ge, J.P. Coexistence of two sympatric flagship carnivores in the human-dominated forest landscapes of Northeast Asia. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 34, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pereira, R.; Araújo, M.S.; Souza, F.L.; Travis, I. Competition and resource breadth shape niche variation and overlap in multiple trophic dimensions. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20190369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manlick, P.J.; Pauli, J.N. Human disturbance increases trophic niche overlap in terrestrial carnivore communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26842–26848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibold, M.A. The niche concept revisited: Mechanistic models and community context. Ecology 1995, 76, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshal, J.P.; Bleich, V.C.; Andrew, N.G. Evidence for interspecific competition between feral ass Equus asinus and mountain sheep Ovis canadensis in a desert environment. Wild Biol. 2008, 14, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, A.I.; Barabás, G.; Bimler, M.D.; Mayfield, M.M.; Miller, T.E. The evolution of niche overlap and competitive differences. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, R.; Seuaturien, N.; Intanajitjuy, P.; Inrueang, P.; Prempree, K. The effects of prey depletion on dietary niches of sympatric apex predators in Southeast Asia. Integr. Zool. 2021, 16, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.L.; Raposo, D.; Almeida, J.D.; Jesus, H.; Oliveira, M.A.; Fernandes, C.R.; Mackenzie, D.I.; Santos-Reis, M. An integrated assessment of niche partitioning reveals mechanisms of coexistence between mesocarnivores. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 54, e03116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrim, F.; Mahmood, T.; Max, T.; Nadeem, M.S.; Qasim, S.; Andleeb, S. Assessment of bias in morphological identification of carnivore scats confirmed with molecular scatology in north-eastern Himalayan region of Pakistan. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamler, J.F.; Stenkewitz, Z.; Klare, U.; Jacobsen, N.F.; Macdonald, D.W. Resource partitioning among cape foxes, bat-eared foxes, and black-backed jackals in South Africa. J. Wildl. Manag. 2002, 76, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, E.; Riboldi, L.; Costa, E.; Delfoco, C.; Frignani, E.; Meriggi, A. Niche partitioning between sympatric wild canids: The case of the golden jackal (Canis aureus) and the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in north-eastern Italy. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompanon, F.; Deagle, B.E.; Symondson, W.O.C.; Brown, D.S.; Jarman, S.N.; Taberlet, P. Who is eating what: Diet assessment using next generation sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1931–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J.; García-Robledo, C.; Uriarte, M.; Erickson, D.L. DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porazinska, D.L.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Esquivel, A.; Powers, T.O.; Sung, W.; Thomas, W.K. Ecometagenetics confirm high tropical rainforest nematode diversity. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 5521–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Shokralla, S.; Zhou, X.; Singer, G.A.C.; Baird, D.J.; Voolstra, C.R. Environmental barcoding: A next-generation sequencing approach for biomonitoring applications using river benthos. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Cheng, C.; Xiao, L.Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, J.D.; Yao, M. Food webs reveal coexistence mechanisms and community organization in carnivores. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, C.E.; Jevit, M.; Hussain, S.; Muhammad, G.; Munkhtsog, B.; Munkhtsog, B.; Zhang, Y.G.; Li, D.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Farrington, J.D.; et al. Regional comparison of snow leopard (Panthera uncia) diet using DNA Metabarcoding. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 797–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sai, Q.G.W.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhao, H.X.; Lian, X.M. Spatiotemporal overlap among sympatric Pallas’s cat (Otocolobus manul), Tibetan fox (Vulpes ferrilata) and red fox (V. vulpes) in the source region of the Yangtze River. Biodiv Sci. 2022, 30, 21365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, T.W. Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science 1974, 185, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.B.; Tang, R.M.; Li, J.J.; Tang, H.C.; Guo, Z.X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of landscape pattern and vegetation ecological quality in Sanjiangyuan National Park. Sustainability 2025, 17, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.D.; Tian, J.L.; Ren, Y.H.; Li, J.S.; Zhu, Y.P. Functional zoning and space management of Three-River-Source National Park. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 2069–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, J.J.; Song, P.F.; Qin, W.; Wang, H.J.; Cai, Z.Y.; Gao, H.M.; Liu, D.X.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.Z. Identifying priority reserves favors the sustainable development of wild ungulates and the construction of Sanjiangyuan National Park. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.L. Spatial and temporal variations and significance identification of ecosystem services in the Sanjiangyuan National Park, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, T.; Shehzad, W.; Viari, A.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P.; Coissac, É. ecoPrimers: Inference of new DNA barcode markers from whole genome sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlbert, S.H. The measurement of niche overlap and some relatives. Ecology 1978, 59, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka, E.R. The structure of lizard communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. S 1973, 4, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.Q.; Tao, L.; Li, J.; Fan, R.H.; Chen, S.D.; Fu, C.K.; Wang, Q.; Tang, K.Y. DNA metabarcoding dietary analysis of six sympatric small mammals at the Lanjunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Biodiv Sci. 2023, 31, 22474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Cardinale, B.J.; France, K.E.; Mcintyre, P.B.; Thébault, E.; Loreau, M. The functional role of biodiversity in ecosystems: Incorporating trophic complexity. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Harwood, J.D. Advances in molecular ecology: Tracking trophic links through predator–prey food-webs. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severud, W.J.; Windels, S.K.; Belant, J.L.; Bruggink, J.G. The role of forage availability on diet choice and body condition in American beavers (Castor canadensis). Mamm. Biol. 2013, 78, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.Y.; Shao, X.N.; Long, Y.; Bu, H.L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.J.; Li, S.; Wang, R.J.; Yao, M. Molecular analysis of vertebrates and plants in scats of leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis) in southwest China. J. Mammal. 2016, 97, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.N.; Lu, Q.; Xiong, M.Y.; Bu, H.L.; Shi, X.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Zhao, J.D.; Li, S.; Yao, M. Prey partitioning and livestock consumption in the world’s richest large carnivore assemblage. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.L.; Yang, H.T.; Smith, J.L.D.; Feng, L.M.; Wang, T.M.; Ge, J.P. Prey selection of Amur tigers in relation to the spatiotemporal overlap with prey across the Sino-Russian border. Wildl. Biol. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B.; Woo, D.; Choi, T.Y. Composition of the insect diet in feces of yellow-throated marten, Martes flavigula, in Jirisan National Park, South Korea. J. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 38, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmeros, M.; Mikkelsen, D.M.G.; Nrgaard, L.S.; Pertoldi, C.; Chriél, M. The diet of feral raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and native badger (Meles meles) and red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in Denmark. Mammal. Res. 2018, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, Z.H.; Liu, Z.S.; Teng, L.W. Food habits by red fox (Vulpes vulpes), a review. J. Econ. Animal. 2014, 18, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, W.; Li, J.; Hacker, C.E.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.Q.; Xue, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.G. Different coexistence patterns between apex carnivores and mesocarnivores based on temporal, spatial, and dietary niche partitioning analysis in Qilian Mountain National Park, China. eLife 2024, 13, RP90559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Li, F.J.; Díaz-Sacco, J.J.; Shi, K. Dietary and temporal partitioning facilitates coexistence of sympatric carnivores in the Everest region. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, V.; Golla, T.R.; Sharma, V.; Kumar, B.K.; Gaur, A. Kleptoparasitic interaction between Snow Leopard Panthera uncia and Red Fox Vulpes vulpes suggested by circumstantial evidence in Pin Valley National Park, India. J. Threat. Taxa. 2022, 14, 21928–21935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomarest, F.; Caro, T.M. Interspecific killing among mammalian carnivores. Am. Nat. 1999, 153, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet, P.C. Prey use strategies of sympatric wolves and coyotes in Riding Mountain National Park, Manitoba. J. Mammal. 1992, 73, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.O. Hypothetical relationships between the San Joaquin kit fox, California grizzly bear, and gray wolf on the pre-European California landscape. Endang Species Update 2007, 24, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.Y.; Qin, W.; Gao, H.M.; Wu, T.; Chi, X.W.; Yang, J.D.; Miao, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Song, P.F.; Lian, X.M.; et al. Species diversity and fauna of mammals in Sanjiangyuan National Park. Acta Theriol. Sinica. 2019, 39, 410–420. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Duo, L.A.; Li, S.; Wang, T.M. Competition and coexistence among terrestrial mammalian carnivores. Biodiv Sci. 2021, 29, 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- du Preez, B.; Purdon, J.; Trethowan, P.; Macdonald, D.W.; Loveridge, A.J. Dietary niche differentiation facilitates coexistence of two large carnivores. J. Zool. 2017, 302, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Schaller, G.B.; Zhen, S. Status and conservation of the plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Mammal. Res. 2019, 64, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X. Population density and spatial distribution of plateau pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2003, 21, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
| Primer Pair | Sequences | Target Region |
|---|---|---|
| F_12SV5 | 5′-TAGAACAGGCTCCTCTAG-3′ | 12S |
| R_12SV5 | 5′-TTAGATACCCCACTATGC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Hou, L.; Zou, Y.; Lian, X. Dietary Differentiation Mitigates Interspecific Interference Competition Between Sympatric Pallas’s Cats (Otocolobus manul) and Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Animals 2025, 15, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091267
Wang D, Li Q, Gao J, Hou L, Zou Y, Lian X. Dietary Differentiation Mitigates Interspecific Interference Competition Between Sympatric Pallas’s Cats (Otocolobus manul) and Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Animals. 2025; 15(9):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091267
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dong, Quanbang Li, Jingyu Gao, Luyi Hou, Yanjun Zou, and Xinming Lian. 2025. "Dietary Differentiation Mitigates Interspecific Interference Competition Between Sympatric Pallas’s Cats (Otocolobus manul) and Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes)" Animals 15, no. 9: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091267
APA StyleWang, D., Li, Q., Gao, J., Hou, L., Zou, Y., & Lian, X. (2025). Dietary Differentiation Mitigates Interspecific Interference Competition Between Sympatric Pallas’s Cats (Otocolobus manul) and Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Animals, 15(9), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091267






