Enhancing Genomic Prediction Accuracy with a Single-Step Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction Model Integrating Genome-Wide Association Study Results
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulated Data
2.2. Real Data
2.3. Single-Step GBLUP Model with Pseudo QTNs and a Weighted G Matrix
2.4. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS)
2.5. Single Step Genome-Wide Association Assisted BLUP (ssGWABLUP)
2.6. Pseudo QTNs Selection
2.7. Benchmarking
2.8. Validation of Genomic Predictions
3. Results
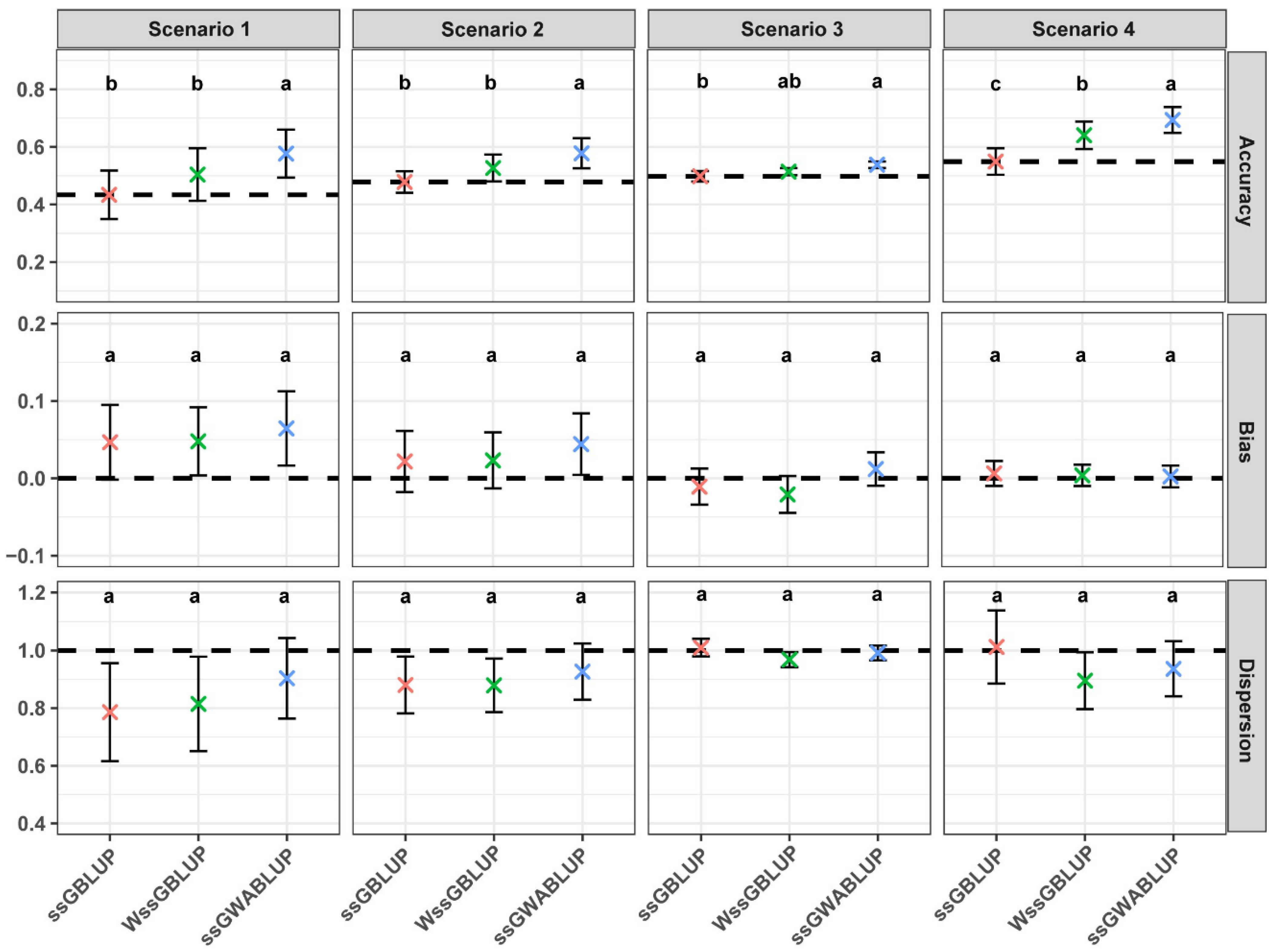
3.1. Comparison of Performance Between ssGWABLUP and WssGBLUP
3.2. Impact of Genetic Complexity on pQTN Selection and Effectiveness
3.3. Performance Evaluation of the ssGWABLUP_QTNs
3.4. Performance on Pig Dataset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meuwissen, T.H.E.; Hayes, B.J.; Goddard, M.E. Prediction of Total Genetic Value Using Genome-Wide Dense Marker Maps. Genetics 2001, 157, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misztal, I.; Lourenco, D.; Legarra, A. Current status of genomic evaluation. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J. Dairy. Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, M.; Charlier, C.; Hayes, B. Harnessing genomic information for livestock improvement. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desta, Z.A.; Ortiz, R. Genomic selection: Genome-wide prediction in plant improvement. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Shi, J.; García-Closas, M. Developing and evaluating polygenic risk prediction models for stratified disease prevention. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaniuc, B.; Price, A.L. Dissecting the genetics of complex traits using summary association statistics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, O.F.; Lund, M.S. Genomic prediction when some animals are not genotyped. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2010, 42, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, I.; Misztal, I.; Johnson, D.L.; Legarra, A.; Tsuruta, S.; Lawlor, T.J. Hot topic: A unified approach to utilize phenotypic, full pedigree, and genomic information for genetic evaluation of Holstein final score1. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daetwyler, H.D.; Swan, A.A.; van der Werf, J.H.J.; Hayes, B.J. Accuracy of pedigree and genomic predictions of carcass and novel meat quality traits in multi-breed sheep data assessed by cross-validation. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2012, 44, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, R.L.; Leeds, T.D.; Gao, G.; Parsons, J.E.; Martin, K.E.; Evenhuis, J.P.; Fragomeni, B.O.; Wiens, G.D.; Palti, Y. Genomic selection models double the accuracy of predicted breeding values for bacterial cold water disease resistance compared to a traditional pedigree-based model in rainbow trout aquaculture. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2017, 49, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andonov, S.; Lourenco, D.A.L.; Fragomeni, B.O.; Masuda, Y.; Pocrnic, I.; Tsuruta, S.; Misztal, I. Accuracy of breeding values in small genotyped populations using different sources of external information—A simulation study. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daetwyler, H.D.; Villanueva, B.; Woolliams, J.A. Accuracy of Predicting the Genetic Risk of Disease Using a Genome-Wide Approach. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, J.M.S.; Piepho, H.-P.; Silva, F.F.e. Quantitative genetics theory for genomic selection and efficiency of breeding value prediction in open-pollinated populations. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habier, D.; Fernando, R.L.; Dekkers, J.C.M. The Impact of Genetic Relationship Information on Genome-Assisted Breeding Values. Genetics 2007, 177, 2389–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, T.; Eikje, L.S.; Gjuvsland, A.B. GWABLUP: Genome-wide association assisted best linear unbiased prediction of genetic values. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2024, 56, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ober, U.; Erbe, M.; Zhang, H.; Gao, N.; He, J.; Li, J.; Simianer, H. Improving the Accuracy of Whole Genome Prediction for Complex Traits Using the Results of Genome Wide Association Studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X. KAML: Improving genomic prediction accuracy of complex traits using machine learning determined parameters. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, B.F.; Riser, M.; Hay, E.H.A.; Fragomeni, B.d.O. Alternative SNP weighting for multi-step and single-step genomic BLUP in the presence of causative variants. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2023, 140, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lourenco, D.; Aguilar, I.; Legarra, A.; Misztal, I. Weighting Strategies for Single-Step Genomic BLUP: An Iterative Approach for Accurate Calculation of GEBV and GWAS. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Misztal, I.; Aguilar, I.; Legarra, A.; Muir, W.M. Genome-wide association mapping including phenotypes from relatives without genotypes. Genet. Res. 2012, 94, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; Christensen, O.F.; Janss, L.; Lund, M.S. Comparison of genomic predictions using genomic relationship matrices built with different weighting factors to account for locus-specific variances. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6547–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Maltecca, C.; VanRaden, P.M.; O’Connell, J.R.; Ma, L.; Jiang, J. SLEMM: Million-scale genomic predictions with window-based SNP weighting. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brøndum, R.F.; Su, G.; Janss, L.; Sahana, G.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Boichard, D.; Lund, M.S. Quantitative trait loci markers derived from whole genome sequence data increases the reliability of genomic prediction. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4107–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRaden, P.M.; Tooker, M.E.; O’Connell, J.R.; Cole, J.B.; Bickhart, D.M. Selecting sequence variants to improve genomic predictions for dairy cattle. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2017, 49, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.S.; Bovenhuis, H.; van Son, M.; Nordbø, Ø.; Grindflek, E.H.; Knol, E.F.; Bastiaansen, J.W.M. Using markers with large effect in genetic and genomic predictions1. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; de Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Gould, B.A.; Stinchcombe, J.R. Identifying the genes underlying quantitative traits: A rationale for the QTN programme. AoB Plants 2014, 6, plu004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargolzaei, M.; Schenkel, F.S. QMSim: A large-scale genome simulator for livestock. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, M.A.; Hickey, J.M.; Forni, S. A Common Dataset for Genomic Analysis of Livestock Populations. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2012, 2, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Sul, J.H.; Service, S.K.; Zaitlen, N.A.; Kong, S.Y.; Freimer, N.B.; Sabatti, C.; Eskin, E. Variance component model to account for sample structure in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, D.; Legarra, A.; Tsuruta, S.; Masuda, Y.; Aguilar, I.; Misztal, I. Single-Step Genomic Evaluations from Theory to Practice: Using SNP Chips and Sequence Data in BLUPF90. Genes 2020, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teissier, M.; Larroque, H.; Robert-Granié, C. Weighted single-step genomic BLUP improves accuracy of genomic breeding values for protein content in French dairy goats: A quantitative trait influenced by a major gene. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X. hibayes: An R Package to Fit Individual-Level, Summary-Level and Single-Step Bayesian Regression Models for Genomic Prediction and Genome-Wide Association Studies. BioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Breen, E.J.; MacLeod, I.M.; Ho, P.N.; Haile-Mariam, M.; Pryce, J.E.; Thomas, C.D.; Daetwyler, H.D.; Goddard, M.E. BayesR3 enables fast MCMC blocked processing for largescale multi-trait genomic prediction and QTN mapping analysis. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Golden, B.L.; Garrick, D.J. Computational strategies for alternative single-step Bayesian regression models with large numbers of genotyped and non-genotyped animals. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2016, 48, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; An, L.; Li, B.; Qiao, L.; Liu, W. Efficient weighting methods for genomic best linear-unbiased prediction (BLUP) adapted to the genetic architectures of quantitative traits. Heredity 2021, 126, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, I.; Fritz, S.; Boichard, D. QTL fine mapping with Bayes C(π): A simulation study. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2013, 45, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, V.; Lehermeier, C.; Albrecht, T.; Auinger, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Schön, C.C. Genome-wide prediction of traits with different genetic architecture through efficient variable selection. Genetics 2013, 195, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, N.R.; Yang, J.; Hayes, B.J.; Price, A.L.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. Pitfalls of predicting complex traits from SNPs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, M.E.; Hayes, B.J. Mapping genes for complex traits in domestic animals and their use in breeding programmes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visscher, P.M.; Brown, M.A.; McCarthy, M.I.; Yang, J. Five Years of GWAS Discovery. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemoto, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Kojima, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Watanabe, T. Impact of QTL minor allele frequency on genomic evaluation using real genotype data and simulated phenotypes in Japanese Black cattle. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, D.; Tang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; et al. Longitudinal genome-wide association studies of milk production traits in Holstein cattle using whole-genome sequence data imputed from medium-density chip data. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 2535–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, L.M.; Mota, L.F.M.; Schmidt, P.I.; Frezarim, G.B.; Fonseca, L.F.S.; Magalhães, A.F.B.; Silva, D.A.; Carvalheiro, R.; Chardulo, L.A.L.; Albuquerque, L.G.d. Genome-wide scans identify biological and metabolic pathways regulating carcass and meat quality traits in beef cattle. Meat Sci. 2024, 209, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, E.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Meta-analysis methods for genome-wide association studies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, S.D.; Schnabel, R.D.; Murdoch, B.M.; Matukumalli, L.K.; Aerts, J.; Coppieters, W.; Crews, D.; Neto, E.D.; Gill, C.A.; Gao, C.; et al. Whole genome linkage disequilibrium maps in cattle. BMC Genet. 2007, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roos, A.P.W.; Hayes, B.J.; Spelman, R.J.; Goddard, M.E. Linkage Disequilibrium and Persistence of Phase in Holstein–Friesian, Jersey and Angus Cattle. Genetics 2008, 179, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Model | Equation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| ssGBLUP | Standard single-step GBLUP model using a matrix. | |
| ssGBLUP_pQTNs | Extends ssGBLUP by including pQTNs as fixed covariates. | |
| ssGWABLUP | Incorporates SNP weights derived from GWAS results into the matrix. | |
| ssGWABLUP_pQTNs | Combines marker weighting from GWAS and inclusion of pQTNs as covariates. |
| Scenario | Time (s) | Memory (Gb) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WssGBLUP | ssGWABLUP | WssGBLUP | ssGWABLUP | |
| Scenario 1 | 50.25 | 9.66 | 4.32 | 2.36 |
| Scenario 2 | 46.67 | 10.58 | 4.32 | 2.34 |
| Scenario 3 | 54.28 | 12.08 | 4.32 | 2.35 |
| Scenario 4 | 43.30 | 12.10 | 4.32 | 2.37 |
| Scenario | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | 6.90 | 1.73 |
| Scenario 2 | 5.30 | 1.25 |
| Scenario 3 | 2.78 | 1.09 |
| Scenario 4 | 5.90 | 0.74 |
| Traits | ssGBLUP | ssGBLUP_pQTNs | ssGWABLUP | ssGWABLUP_pQTNs | ssBayesR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.283 ± 0.047 b | 0.288 ± 0.049 ab | 0.291 ± 0.049 a | 0.297 ± 0.048 a | 0.269 ± 0.040 c |
| T2 | 0.717 ± 0.040 c | 0.728 ± 0.041 b | 0.730 ± 0.038 ab | 0.741 ± 0.034 a | 0.727 ± 0.040 b |
| T3 | 0.545 ± 0.025 b | 0.581 ± 0.029 a | 0.579 ± 0.026 a | 0.587 ± 0.028 a | 0.585 ± 0.029 a |
| T4 | 0.603 ± 0.048 b | 0.613 ± 0.056 b | 0.628 ± 0.048 a | 0.630 ± 0.055 a | 0.625 ± 0.047 a |
| T5 | 0.535 ± 0.033 c | 0.549 ± 0.036 b | 0.550 ± 0.035 b | 0.573 ± 0.034 a | 0.569 ± 0.034 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Z.; Wang, W.; Huang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Qiao, L.; Liu, J.; Pan, Y.; Yang, K.; et al. Enhancing Genomic Prediction Accuracy with a Single-Step Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction Model Integrating Genome-Wide Association Study Results. Animals 2025, 15, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091268
Pang Z, Wang W, Huang P, Zhang H, Zhang S, Yang P, Qiao L, Liu J, Pan Y, Yang K, et al. Enhancing Genomic Prediction Accuracy with a Single-Step Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction Model Integrating Genome-Wide Association Study Results. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091268
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Zhixu, Wannian Wang, Pu Huang, Hongzhi Zhang, Siying Zhang, Pengkun Yang, Liying Qiao, Jianhua Liu, Yangyang Pan, Kaijie Yang, and et al. 2025. "Enhancing Genomic Prediction Accuracy with a Single-Step Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction Model Integrating Genome-Wide Association Study Results" Animals 15, no. 9: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091268
APA StylePang, Z., Wang, W., Huang, P., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Yang, P., Qiao, L., Liu, J., Pan, Y., Yang, K., & Liu, W. (2025). Enhancing Genomic Prediction Accuracy with a Single-Step Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction Model Integrating Genome-Wide Association Study Results. Animals, 15(9), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091268





