Preliminary Multi-Omics Insights into Green Alternatives to Antibiotics: Effects of Pulsatilla chinensis, Acer truncatum, and Clostridium butyricum on Gut Health and Metabolic Regulation in Chickens
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model Treatment and Sample Collection
2.2. Biometric Measurements and Sample Collection
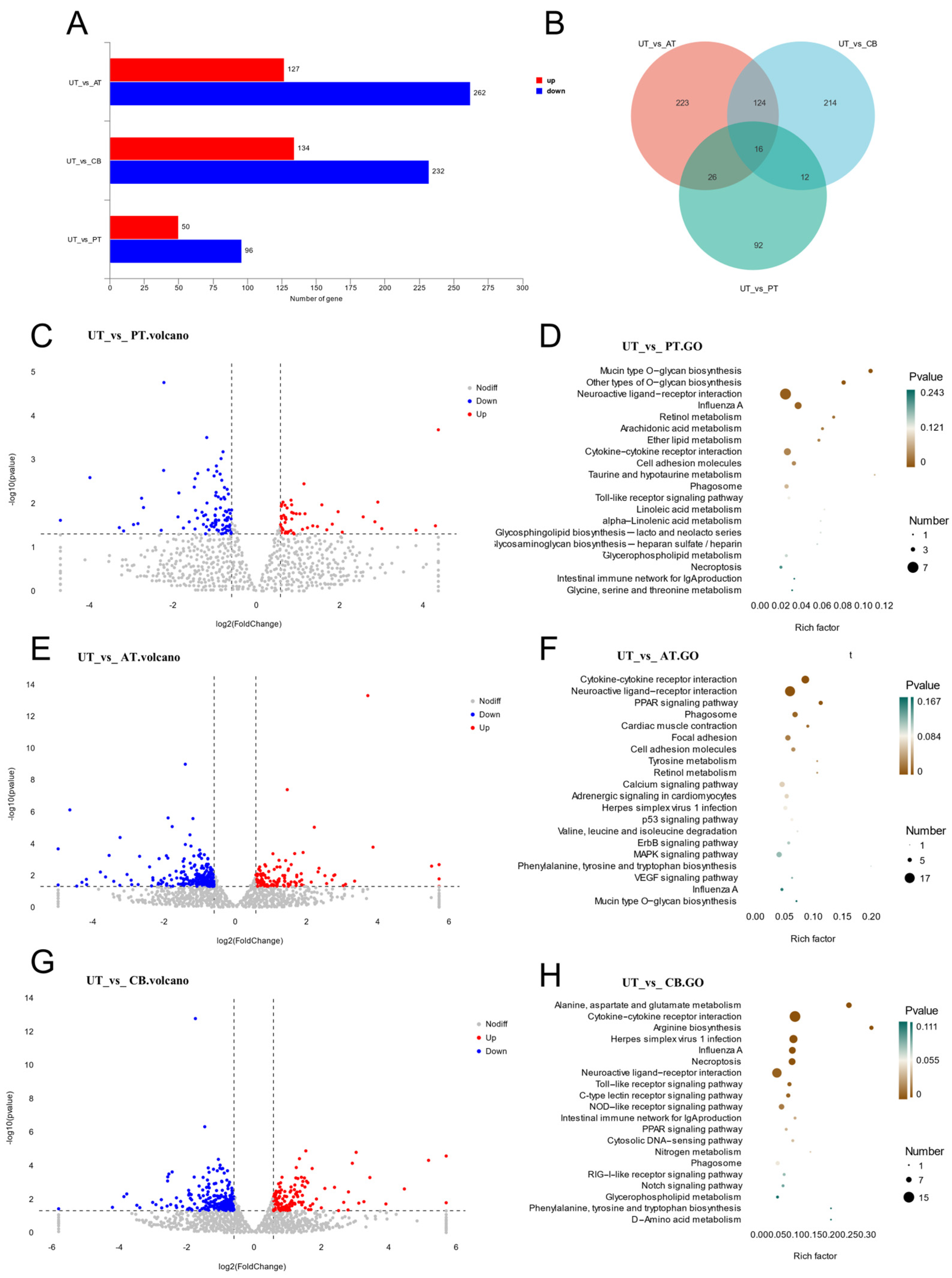
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis
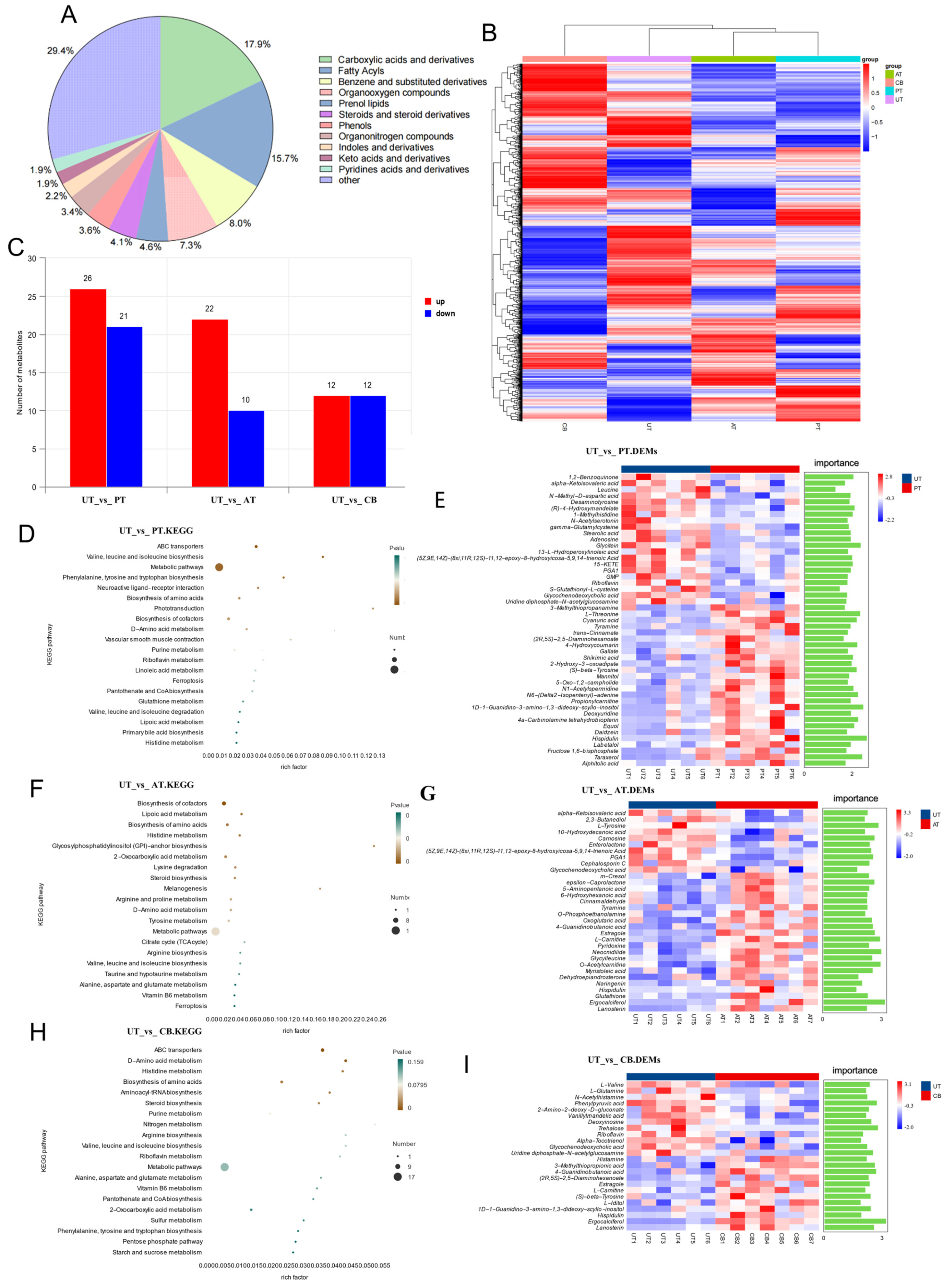
2.4. LC-MS Non-Targeted Metabolic Analysis
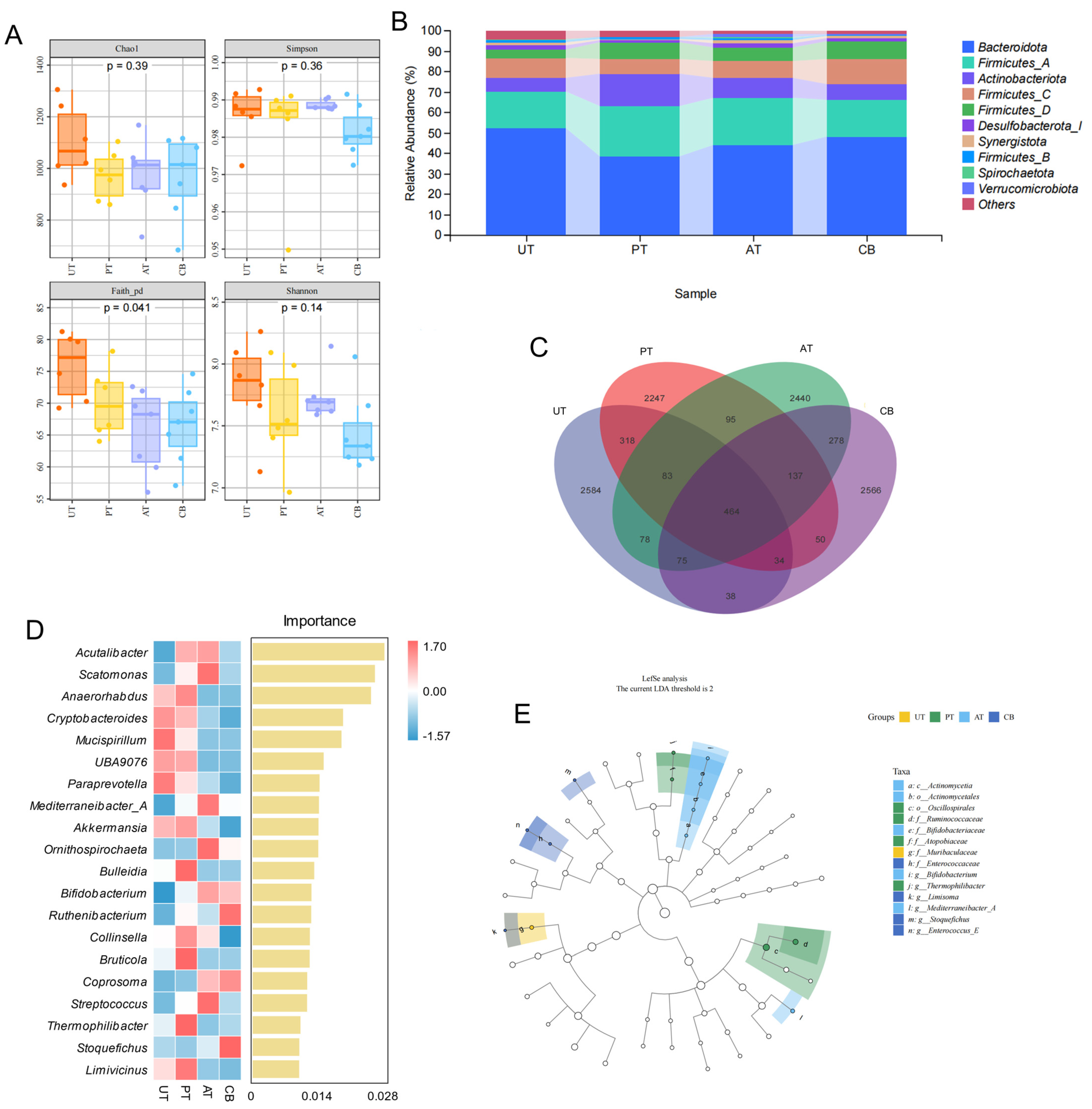
2.5. 16 S rRNA Sequencing
2.6. GO and KEGG Annotation and Enrichment
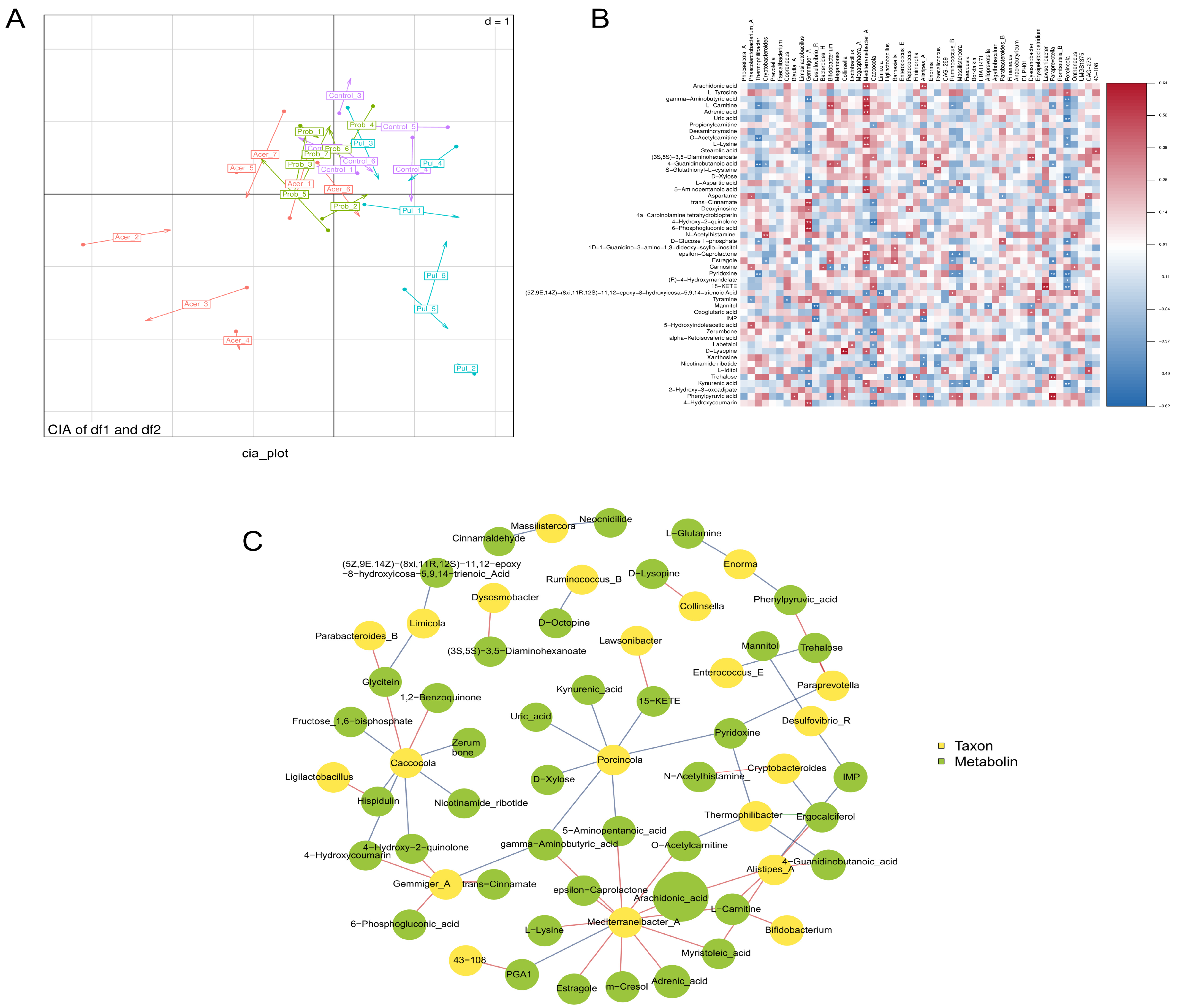
2.7. Association Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cecal Transcriptome Analysis
3.2. Cecal Metabolomic Analysis
3.3. Cecal Microbial Community Structure and Function Analysis
3.4. Association Between 16S and Metabolome
3.5. Association Between Transcriptome and Metabolome
3.6. Growth Performance Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Sang, R.; Li, N.; Du, S.; Kong, X.; Tai, M.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Y. A new approach to overcoming antibiotic-resistant bacteria: Traditional Chinese medicine therapy based on the gut microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1119037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ding, X.-J.; Lu, B.-Q.; Ji, C.-J.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.-R.; Yang, S.-L. Three New Triterpenoids from Pulsatilla chinensis (Bunge) Regel and Their Cytotoxic Activities. Heterocycles 2011, 83, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ren, Z.; Duan, L.; Du, Z.; Su, K.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Chinese herbal medicine on Performance and Nutrient apparent digestibility of broilers. Feed. Res. 2010, 6, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S. The Effects of Baitouweng Powder on Laying Performance, Immune Function, and Intestinal Microbiota of Laying Hens in the Late Laying Period. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Treatment for Sheep Diarrhea. J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2021, 7, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Gu, R.; Long, C. Acer truncatum Bunge: A comprehensive review on ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gu, R.; Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Long, C. Protective effects of extracts from Acer truncatum leaves on SLS-induced HaCaT cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1068849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Effects of Acer truncatum Leaves on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Intestinal Microbiota in Piglets. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liang, S.; Qin, K.; Jia, B.; Ren, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, X. Acer truncatum leaves extract modulates gut microbiota, improves antioxidant capacity, and alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassir, N.; Benamar, S.; La Scola, B. Clostridium butyricum: From beneficial to a new emerging pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Deng, W.; Wei, F.; Ma, H.; Fu, C.; Wang, G.; Li, S. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on Growth Performance, Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Function of Broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 777456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ling, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Peng, N.; Zhao, S. Protease or Clostridium butyricum addition to a low-protein diet improves broiler growth performance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 7917–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Ju, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Sun, S. Clostridium butyricum Ameliorates Salmonella Enteritis Induced Inflammation by Enhancing and Improving Immunity of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier at the Intestinal Mucosal Level. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Kou, S.; Chen, C.; Raza, S.H.A.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.-J.; Nie, C. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on growth performance, metabonomics and intestinal microbial differences of weaned piglets. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, A.; Mottawea, W.; Mehdi, Y.; Hammami, R. Bacteriocinogenic probiotics as an integrated alternative to antibiotics in chicken production—Why and how? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8744–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, A.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Genome Sequence Archive Family: Toward Explosive Data Growth and Diverse Data Types. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners. Database Resources of the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D18–D32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuralkar, P.; Kuralkar, S.V. Role of herbal products in animal production—An updated review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Yan, W.; Ma, Y.; Fang, J. The impact of probiotics on gut health via alternation of immune status of monogastric animals. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Al-Hejin, A.M.; Abujamel, T.S.; Ghetas, A.M.; Yacoub, H.A. Chicken β-defensin-1 peptide as a candidate anticoccidial agent in broiler chickens. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 3108–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, H.; Dong, W.; Yang, G.; Li, L. Effects of dietary supplementation with itaconic acid on the growth performance, nutrient digestibility, slaughter variables, blood biochemical parameters, and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, R.; Zeng, M.; Li, X.; Shi, J. Polysaccharides from Chinese herbal medicine for anti-diabetes recent advances. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Guo, K.; Liu, L.; Tian, W.; Xie, X.; Wen, S.; Wen, C. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic data reveal the flavonoid biosynthesis metabolic pathway in Perilla frutescens (L.) leaves. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, X.D.; Tang, P.Y.; Li, H.M.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J.J.; Tang, Y. Advances of antitumor drug discovery in traditional Chinese medicine and natural active products by using multi-active components combination. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 1778–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Guevarra, R.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.H. Role of Probiotics in Human Gut Microbiome-Associated Diseases. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Probiotics and immune health. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 27, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.F.; Nyachoti, M. Using probiotics to improve swine gut health and nutrient utilization. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.S.; Deng, W.; Liu, H.W. Effects of chlorogenic acid-enriched extract from Eucommia ulmoides leaf on performance, meat quality, oxidative stability, and fatty acid profile of meat in heat-stressed broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimon, S.; Angkanaporn, K.; Nuengjamnong, C. Microencapsulation of Lactobacillus plantarum MB001 and its probiotic effect on growth performance, cecal microbiome and gut integrity of broiler chickens in a tropical climate. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 36, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.; Ali, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Kebzhai, F.; Li, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Tibetan chickens on the growth performance and gut microbiota of broiler. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1171074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zeng, N.; Chen, Y.; Fu, G.; Wang, B. Effects of Acer truncatum leaves on performance, egg quality and antioxidant indices of Taihang chicken. China Feed. 2022, 5, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. ; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and Their Role as Members of the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wei, S.; Tian, J.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, D. Changes in gut microbiota affect DNA methylation levels and development of chicken muscle tissue. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasova, T.; Kollarcikova, M.; Crhanova, M.; Karasova, D.; Cejkova, D.; Sebkova, A.; Matiasovicova, J.; Faldynova, M.; Sisak, F.; Babak, V.; et al. Gut Anaerobes Capable of Chicken Caecum Colonisation. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.L.; Ma, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.S.; Cheng, X.H.; Jia, Y.Q.; Peng, X.T.; Yao, W.L.; Ji, P.; Hu, J.J.; et al. Metabolomics analysis of Pulsatilla decoction on treatment of wetness-heat-induced diarrhea in rats based on UPLC-Q/TOF-MS/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Q.; Ji, H.; Yu, H. Acer truncatum leaves reduce lipid accumulation and improve liver and intestine health of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fed with high-fat diet. Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Ramírez, F.; Torrecillas, S.; Betancor, M.B.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Caballero, M.J.; Montero, D. Effects of dietary arachidonic acid in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) distal intestine lipid classes and gut health. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. T cell receptor signaling pathway and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction affect the rehabilitation process after respiratory syncytial virus infection. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebessa, E.; Bello, S.F.; Guo, L.; Tuli, M.D.; Hanotte, O.; Nie, Q. MicroRNA expression profile of chicken jejunum in different time points Eimeria maxima infection. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1331532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, S.; Olajide, J.S.; Qu, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, K.; et al. Clostridium butyricum Supplement Can Ameliorate the Intestinal Barrier Roles in Broiler Chickens Experimentally Infected with Clostridium perfringens. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 737481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Aspartic Acid in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.M.; Deng, X.T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.P.; Ge, X.X.; Miao, L. Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshkian, Z.; Mirhoseini, S.Z.; Ghovvati, S. Identification of hub genes involved in apparent metabolizable energy of chickens. Anim. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, X.; Tian, K.; Yan, S.; Xu, C.; Tian, Y.; Xiao, C.; Jia, X.; Shi, J.; Bai, Y.; et al. Dynamic Expression Profile of Follicles at Different Stages in High- and Low-Production Laying Hens. Genes 2023, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.A.; Su, W.; Chapman, N.M.; Chi, H. Lipid metabolism in T cell signaling and function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Leissing, T.M.; Chowdhury, R.; Hopkinson, R.J.; Schofield, C.J. 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Oxygenases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 585–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, A.; Alberts, P.; Mari, S.; Tong, J.; Murchie, R.; Maspero, E.; Safi, F.; Moran, M.F.; Polo, S.; Rotin, D. Tyrosine phosphorylation of NEDD4 activates its ubiquitin ligase activity. Sci. Signal 2014, 7, ra95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Ejima, A.; Abe, S.; Shimba, A. Control of immunity and allergy by steroid hormones. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.; Pang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Zheng, W. Research progress of renal injury induced by Chinese herbal medicine and its related components toxicity mechanism. Med. Her. 2021, 40, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zheng, W.; Chen, B.; Gao, Y. Research methods and progress of liver injury induced by Chinese herbal medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Liver Dis. 2024, 34, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Dang, J.; Sheng, Y. Effects of Supplemented Shenling Baizhu Powder combined with probiotics on digestion and immune function of lambs. J. Shandong Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2024, 45, 17–20. [Google Scholar]

| Ingredient | Content (%) | Nutritional Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Corn | 55.0 | Dry Matter (DM) |
| Soybean Meal | 30.0 | Crude Protein (CP) |
| Fish Meal | 5.0 | Crude Fat (EE) |
| Wheat Bran | 5.0 | Crude Ash |
| Limestone | 1.5 | Neutral Detergent Fiber (NDF) |
| Dicalcium Phosphate | 1.0 | Acid Detergent Fiber (ADF) |
| NaCl | 0.3 | Metabolizable Energy (ME) |
| Fat | 1.2 | |
| Compound Premix | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Qin, S.; Liang, C.; Zhao, A.; He, K. Preliminary Multi-Omics Insights into Green Alternatives to Antibiotics: Effects of Pulsatilla chinensis, Acer truncatum, and Clostridium butyricum on Gut Health and Metabolic Regulation in Chickens. Animals 2025, 15, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091262
Sun L, Wang Z, Qin S, Liang C, Zhao A, He K. Preliminary Multi-Omics Insights into Green Alternatives to Antibiotics: Effects of Pulsatilla chinensis, Acer truncatum, and Clostridium butyricum on Gut Health and Metabolic Regulation in Chickens. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091262
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lin, Zhijun Wang, Shidi Qin, Chunhong Liang, Ayong Zhao, and Ke He. 2025. "Preliminary Multi-Omics Insights into Green Alternatives to Antibiotics: Effects of Pulsatilla chinensis, Acer truncatum, and Clostridium butyricum on Gut Health and Metabolic Regulation in Chickens" Animals 15, no. 9: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091262
APA StyleSun, L., Wang, Z., Qin, S., Liang, C., Zhao, A., & He, K. (2025). Preliminary Multi-Omics Insights into Green Alternatives to Antibiotics: Effects of Pulsatilla chinensis, Acer truncatum, and Clostridium butyricum on Gut Health and Metabolic Regulation in Chickens. Animals, 15(9), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091262









