Toxoplasmosis in Sheep Caused by Toxoplasma gondii Clonal Type I
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information on Samples and Sources
2.2. Detection of T. gondii Antibodies in Sheep
2.3. T. gondii Nucleic Acid Detection in Sheep
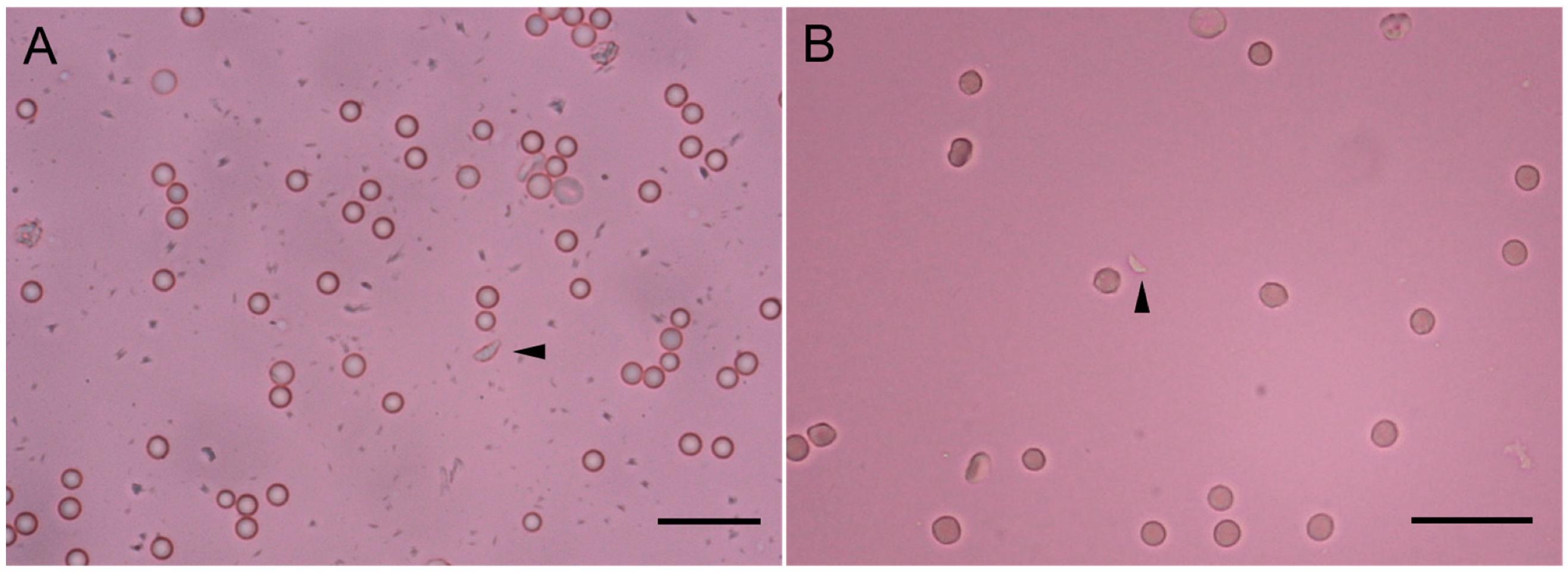
2.4. Morphological Observation of T. gondii Parasites in Sheep Tissues
2.5. Isolation Viable T. gondii from Tissues of Sheep
2.6. Cell Cultivation and Genotyping
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Investigation of Ovine Toxoplasmosis in Sheep
3.2. Assessment of Pathological Lesions, and T. gondii Antigen Distribution
3.3. Isolation of the T. gondii Strain from Sheep Tissues or Blood
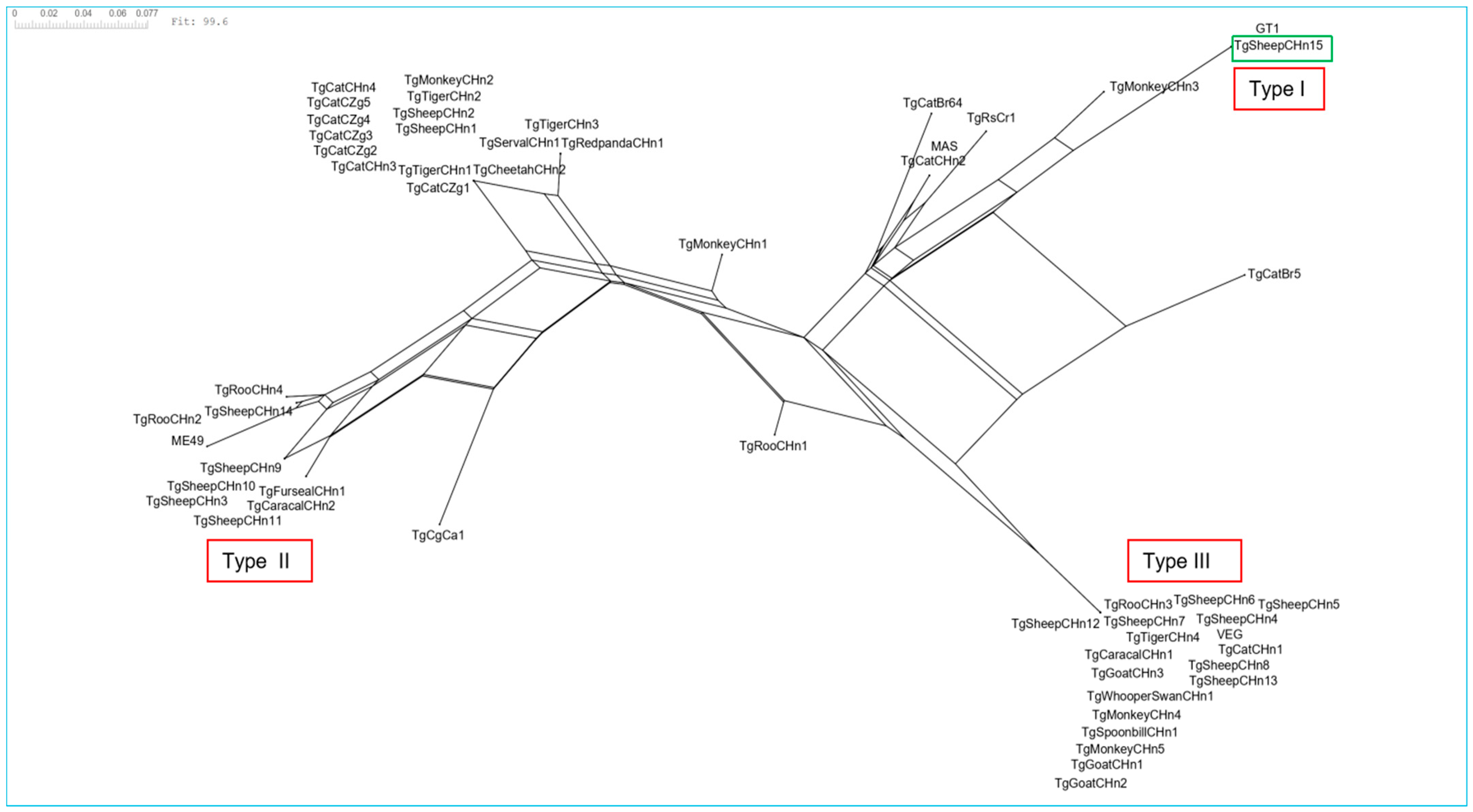
3.4. Genotypes of TgSheepCHn15
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPI | days post-inoculation |
| MAT | modified agglutination test |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2022; pp. 1–542. [Google Scholar]
- Klauck, V.; Pazinato, R.; Radavelli, W.M.; Custódio, E.; Bianchi, A.E.; Camillo, G.; Cezar, A.S.; Vogel, F.F.; Tonin, A.A.; Ferreira, R.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection in dairy ewes: Vertical transmission and influence on milk production and reproductive performance. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Innes, E.A.; Bartley, P.M.; Buxton, D.; Katzer, F. Ovine toxoplasmosis. Parasitology 2009, 136, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hide, G. Role of vertical transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in prevalence of infection. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.; Murata, F.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.; Kwok, O.; Su, C. Economic and public health importance of Toxoplasma gondii infections in sheep: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 286, 109195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Mouse pathogenicity of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from a goat. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1980, 41, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sabin, A.B. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in children. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1941, 116, 801–807. [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Schoch, A.E.; Bernet, D.; Doherr, M.G.; Gottstein, B.; Frey, C.F. Toxoplasma gondii in Switzerland: A serosurvey based on meat juice analysis of slaughtered pigs, wild boar, sheep and cattle. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 472–478. [Google Scholar]
- Račka, K.; Bártová, E.; Budíková, M.; Vodrážka, P. Survey of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in meat juice of wild boar (Sus scrofa) in several districts of the Czech Republic. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Desmonts, G. Serological responses of equids fed Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Equine Vet. J. 1987, 19, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Sundar, N.; Hill, D.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Bandini, L.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Majumdar, D.; Su, C. High prevalence and abundant atypical genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from lambs destined for human consumption in the USA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 999–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Su, R.; Jian, F.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Toxoplasma gondii in lambs of China: Heart juice serology, isolation and genotyping. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 322, 108563. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in sheep—The last 20 years. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schares, G.; Herrmann, D.C.; Beckert, A.; Schares, S.; Hosseininejad, M.; Pantchev, N.; Globokar Vrhovec, M.; Conraths, F.J. Characterization of a repetitive DNA fragment in Hammondia hammondi and its utility for the specific differentiation of H. hammondi from Toxoplasma gondii by PCR. Mol. Cell Probes. 2008, 22, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Oocyst shedding by cats fed isolated bradyzoites and comparison of infectivity of bradyzoites of the VEG strain Toxoplasma gondii to cats and mice. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Xin, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y. Low prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in sheep and isolation of a viable strain from edible mutton from central China. Pathogens 2023, 12, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2009, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shwab, E.K.; Jiang, T.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. The ROP18 and ROP5 gene allele types are highly predictive of virulence in mice across globally distributed strains of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, D.; Huson, D.H. NeighborNet: Improved algorithms and implementation. Front. Bioinform. 2023, 3, 1178600. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L. Seroprevalence, isolation, genotyping, and pathogenicity of Toxoplasma gondii strains from sheep in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Lin, R.Q.; Zhang, D.L.; Song, H.Q.; Su, C.; Zhu, X.Q. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from China. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Amouei, A.; Sarvi, S.; Mizani, A.; Hashemi-Soteh, M.B.; Salehi, S.; Javidnia, J.; Hosseini, S.A.; Amuei, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Shabanzade, S.; et al. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in meat-producing animals in Iran. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Su, C.; Cortés, J.A.; Sundar, N.; Gómez-Marín, J.E.; Polo, L.J.; Zambrano, L.; Mora, L.E.; Lora, F.; Jimenez, J.; et al. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in cats from Colombia, South America and genetic characterization of T. gondii isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 141, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Ferreira, L.R.; Martins, J.; McLeod, R. Oral oocyst-induced mouse model of toxoplasmosis: Effect of infection with Toxoplasma gondii strains of different genotypes, dose, and mouse strains (transgenic, out-bred, in-bred) on pathogenesis and mortality. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shen, W.; Wu, P.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Yue, W. How food consumption trends change the direction of sheep breeding in China. Animals 2024, 14, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, H.; Xin, S.; Jiang, N. Comparative immunological response and pathobiology of mice inoculated with Toxoplasma gondii isolated from different hosts. J. Parasitol. 2021, 107, 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Thulliez, P.; Weigel, R.M.; Andrews, C.D.; Lind, P.; Powell, E.C. Sensitivity and specifcity of various serologic tests for detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in naturally infected sows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, S.; Jiang, N.; Yang, L.; Zhu, N.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, C.; Yang, Y. Isolation, genotyping and virulence determination of a Toxoplasma gondii strain from non-human primate from China. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 919–925. [Google Scholar]
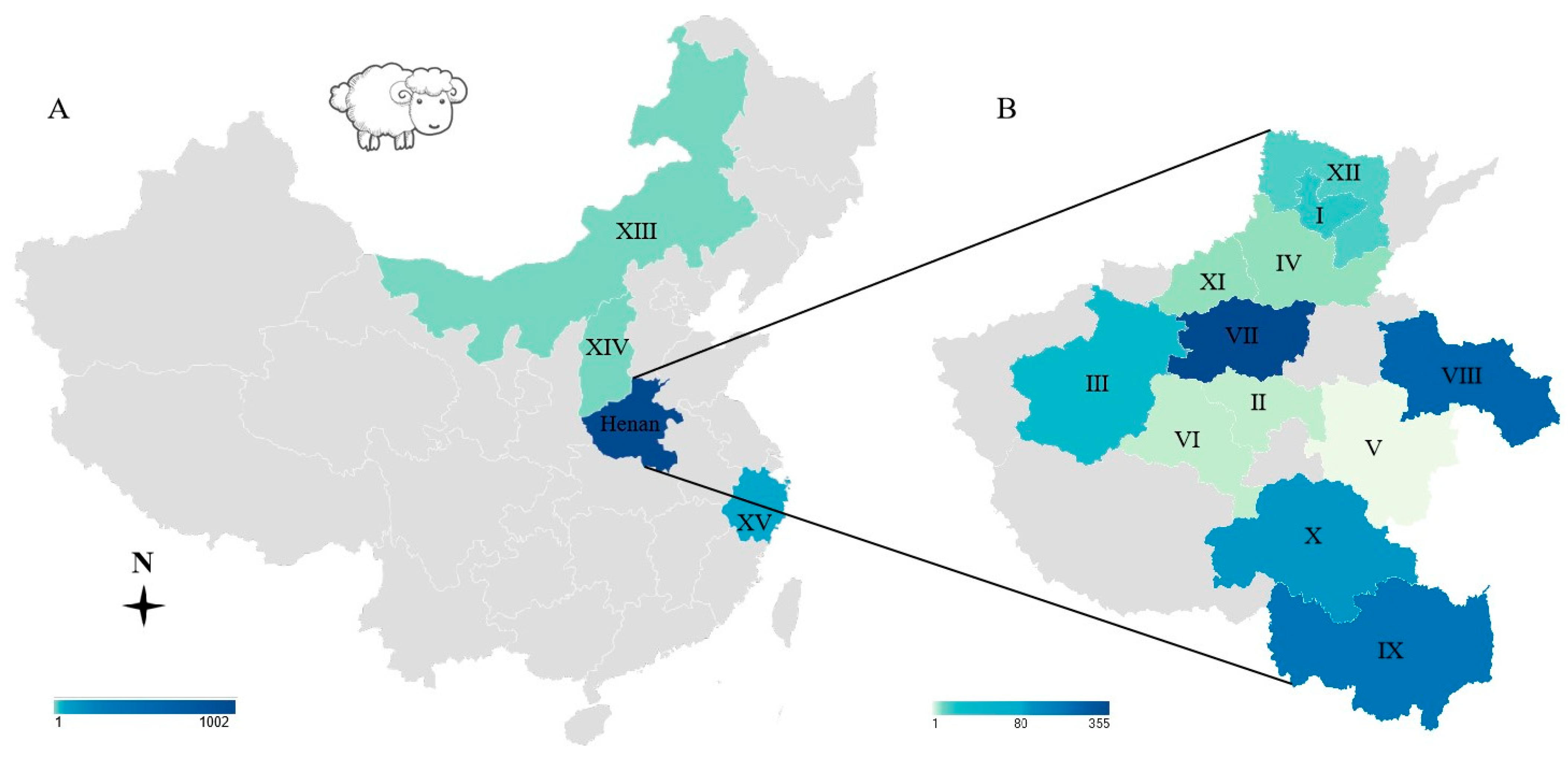

| Provinces | Location a | Source | Sample Received Date | No. of Samples | Positive /Test by MAT b | Positive/Test by PCR c, Positive Tissues | Positive /Test by IHC d | Isolation by Mice e | Mice Group Tox# f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Mongolia | XIII | Vet | 12 Dec 2018 | 1 lamb | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | ||
| Shanxi | XIV | Vet | 14 Jan 2019 | 1 lamb | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | ||
| Henan n = 1002 | I: Hebi | Vet | 6 May 2019 | 8 ewe sera, 11 aborted feuses | 0/19 | 0/11 | 0/11 | ||
| II: Xuchang | Sh | 15 May 2019 | 2 lambs | 2/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 | 5-306, 307 | |
| III: Luoyang | Vet | 14 Sep 2021 | 2 lambs | 0/1 | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/1 | 35-40 | |
| Vet | 15 Sep 2021 | 2 lambs | 2/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 | ||||
| Sh | 15 Jun 2023 | 35 lamb hearts | 1/35 | 2/35 | 0/35 | 0/3 | 35-81-35-83 | ||
| IV: Xinxiang | Vet | 11 Oct 2021 | 1 ewe | 0/1 | 1/1, Li, Lu, Bl | 1/1, LN | 1/1 TgSheepCHn15 | 35-43-35-50, 35-53, 55, 56, 58 | |
| 3 Dec 2021 | 2 aborted fetus, placenta | 0/2 | 2/2, Pl, H, Li, Lu, Um | 0/2 | |||||
| 19 Dec 2021 | 3 aborted fetus, 1 placenta | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | |||||
| 14 Mar 2022 | 1 aborted fetus, 1 placenta | 0/1 | 1/1, Pl | 0/1 | |||||
| 25 Mar 2024 | 1 ewe | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | |||||
| V: Zhoukou | Vet | 23 Sep 2021 | 1 lamb | 1/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 35-41, 42 | |
| VI: Pingdingshan | Vet | 12 Nov 2021 | 2 lambs | 0/2 | 1/2, H, Sk | 0/2 | |||
| VII: Zhengzhou | Vet | 9 Dec 2021 | 1 lamb | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | |||
| Sh | 30 May 2023 | 41 lamb hearts | 3/41 | 5/41 | 0/41 | 0/8, 3 hearts pool | 35-71-35-78 | ||
| Farm | 2 May 2021 | 313 ewe sera | 0/313 | nd | nd | ||||
| VIII: Shangqiu | Vet | 22 Mar 2022 | 9 ewe sera, 1 ram serum | 0/10 | nd | nd | |||
| Sh | 2 Apr 2023 | 242 ewe sera | 5/242 | nd | nd | ||||
| Vet | 26 May 2022 | 1 lamb | 0/1 | 1/1, Bi, Bla | 0/1 | ||||
| Vet | 16 Jan 2024 | 1 lamb | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | ||||
| IX: Xinyang | Farm | 16 Mar 2022 | 45 lamb sera | 12/45 | nd | nd | |||
| 29 Mar 2022 | 15 lamb sera | 1/15 | nd | nd | |||||
| 22 Apr 2022 | 29 lamb sera | 0/29 | nd | nd | |||||
| 18 May 2022 | 30 lamb sera | 2/30 | nd | nd | |||||
| 18 Jun 2022 | 30 lamb sera | 29/30 | nd | nd | |||||
| 29 Sep 2022 | 31 lamb sera | 8/31 | nd | nd | |||||
| 11 Oct 2022 | 35 lamb sera | 0/35 | nd | nd | |||||
| X: Zhumadian | Vet | 13 Sep 2021 | 1 lamb, 2 sera | 0/3 | 1/1, Lu, Di | 1/1, Lu | |||
| 26 Sep 2021 | 31 ewe sera | 3/31 | nd | nd | |||||
| 16 Dec 2021 | 50 ewe sera | 6/50 | nd | nd | |||||
| 16 Nov 2023 | 2 lambs | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 | |||||
| XI: Jiaozuo | Sh | 21 Nov 2023 | 8 lamb hearts | 0/8 | 0/8 | 0/8 | 0/6 | 35-84-35-89 | |
| XII: Anyang | Vet | 23 Jan 2024 | 1 ewe, 2 aborted fetuses | 0/3 | 2/3, H, Li, Lu, Ki, Sk, T, Br/ewe; Li, Lu, Ki, Sk, T, Br 1/2 fetuses | 0/3 | |||
| Sh | 30 Apr 2024 | 10 lambs | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | ||||
| Zhejiang | XV | Vet | 4 Aug 2022 | 30 lamb blood | 0/30 | 11/30 | nd | 0/2 | 35-64,65 |
| 10 Dec 2023 | 1 lamb | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | |||||
| Overall prevlence | Tissues from 134 sheep Sera or blood from 901 sheep | 7.2% (75/1035) | 16.4% (27/164) | 1.5% (2/134) | 2/24 | ||||
| Variable | Number of Samples | Seropositivity (n/%) | Odds ratio (95% Confidence Internal) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling sites | Farm | 528 | 52/9.8 | 3.248 (1.669–6.318) | 0.0003 * |
| Veterinary clinic | 169 | 12/7.1 | 2.272 (0.9809–5.263) | 0.0498 * | |
| Slaughterhouse | 338 | 11/3.3 | 1 | ||
| Age (y) | <1 | 378 | 61/16.1 | 8.838 (4.869–16.04) | <0.0001 * |
| ≥1 | 657 | 14/2.1 | 1 | ||
| Location | Henan | 1002 | 75/7.5 | - | - |
| Inner Mongolia | 1 | 0/1 | - | - | |
| Shanxi | 1 | 0/1 | - | - | |
| Zhejiang | 31 | 0/31 | - | - |
| Group# a | Mouse# b | Serum MAT Titer/DPI | Survival Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35-43 | 629 | Tachyzoites were observed in lungs/15 | 15 |
| 35-46 | 643 | Tachyzoites were observed in lungs/19 | 19 |
| 35-45 | 639 | ≥1:100 (liver juice)/13 | 13 |
| 35-48 | 654 | ≥1:200/30 | 32 |
| 35-49 | 659 | ≥1:200/30 | ≥116 |
| 35-55 | 689 | ≥1:200/30 | ≥102 |
| 35-56 | 912 | ≥1:200/30 | ≥81 |
| 35-58 | 947 | ≥1:200/52 | 214 |
| 35-58 | 948 | ≥1:200/52 | ≥278 |
| Mean ± SEM | 97 ± 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Quan, K.; Guo, B.; Jiang, Y. Toxoplasmosis in Sheep Caused by Toxoplasma gondii Clonal Type I. Animals 2025, 15, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081074
Yang Y, Ma Y, Quan K, Guo B, Jiang Y. Toxoplasmosis in Sheep Caused by Toxoplasma gondii Clonal Type I. Animals. 2025; 15(8):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081074
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yurong, Yiheng Ma, Kai Quan, Bingyan Guo, and Yibao Jiang. 2025. "Toxoplasmosis in Sheep Caused by Toxoplasma gondii Clonal Type I" Animals 15, no. 8: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081074
APA StyleYang, Y., Ma, Y., Quan, K., Guo, B., & Jiang, Y. (2025). Toxoplasmosis in Sheep Caused by Toxoplasma gondii Clonal Type I. Animals, 15(8), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081074







