Simple Summary
This study presents the first epidemiological survey of tick-borne spotted fever pathogens (SFGR) in yaks from Jiulong County, Southwest China. By analyzing 585 ticks collected across pastoral and semi-agricultural zones through morphological and molecular methods, we identified four tick species, predominantly Rhipicephalus microplus (52.65%). Strikingly, 63.93% of ticks carried SFGR pathogens, with Rickettsia raoultii as the dominant species. Infection rates were significantly higher in semi-agricultural areas (70.60%) than in pastoral zones (45.10%), revealing elevated disease risks in human-modified landscapes. These findings provide critical insights into SFGR ecology at human–animal interfaces and underscore the urgency of surveillance in transitional ecosystems.
Abstract
This study investigated tick species and spotted fever group rickettsiae (SFGR) infection rates in ticks from yaks in Jiulong County, Sichuan Province, China. Firstly, ticks collected from yaks were meticulously classified through morphological identification. Subsequently, the total DNA of ticks was extracted, and specific partial sequences of their ITS-2 region, as well as the ompA and ompB genes of SFGR, were amplified using PCR. The positive PCR products were sequenced and compared thoroughly against the NCBI database. A phylogenetic analysis was conducted for ITS-2, ompA, and ompB to determine the species of tick and the SFGR. The results revealed that a total of 585 ticks were collected, with the most abundant species being R. microplus, which accounted for 52.65% (308/585) of the total and was followed by I. ovatus (32.99%, 193/585), I. acutitarsus (8.89%, 52/585), and D. everestianus (5.50%, 32/585). Furthermore, SFGR was detected in 63.93% (374/585) of the ticks. Notably, the infection rate of SFGR in semi-agricultural and pastoral areas was significantly higher at 70.60%, compared to 45.10% in pastoral areas (p < 0.01). Overall, this study marks the first investigation into the prevalence of SFGR in Jiulong County and highlights the high infection rate of SFGR in ticks, with R. raoultii being the predominant species.
1. Introduction
Ticks are significant obligate blood-feeding ectoparasites that attach to the body surface of various hosts, including mammals, birds, and reptiles. They function critically as natural reservoirs and transmission vectors for a wide array of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, many of which can infect humans and animals, leading to numerous zoonotic diseases. In recent years, with global warming and the continuous expansion of human activities, the incidence of tick-borne diseases has been increasing. Therefore, understanding the distribution of tick populations and their pathogen carriage is vital for the prevention and control of tick-borne diseases, which helps ensure the health of animals and humans and improves the overall level of public health safety [1].
Spotted fever group rickettsiae (SFGR) are obligate intracellular bacteria primarily transmitted through tick bites, causing a range of diseases in humans such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever and Mediterranean spotted fever [2]. The disease typically presents with sudden fever, accompanied by headache and malaise, and skin manifestations such as rashes and eschars. Clinical symptoms can vary widely. While most patients experience mild symptoms, a minority may develop severe symptoms that can be life-threatening [3,4,5,6]. For example, Rickettsia raoultii was first detected in 1999 in Haemaphysalis concinna and Hyalomma asiaticum collected from the former Soviet Union border region [7]. In 2008, R. raoultii was identified as a new Rickettsia based on genomic and serological characteristics [8]. In 2012, R. raoultii was first detected in Dermacentor silvarum in Xinjiang, China. R. raoultii has a wide geographic distribution, with reports of its detection in different tick species in Germany, France, and other European countries, as well as in South Korea, Mongolia, and other Asian countries [9,10,11,12]. In China, there have been several reports of human infections with R. raoultii following tick bites. For instance, in 2012, R. raoultii was detected in two patients in Mudanjiang, China. The Rickettsiae isolated from these two patients were homologous to those found in D. silvarum ticks collected from the patients’ surrounding environments [13]. From 2015 to 2016, Chinese scholars detected R. raoultii in patient samples from Shandong, Henan, and Inner Mongolia (26/1295), successfully isolating R. raoultii from these samples [14].
Jiulong County, located in the western part of Sichuan Province and southeast of the Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, covers an area of 6770 square kilometers and has a continental plateau climate. The county is characterized by its extensive grasslands (approximately 334,400 hectares), which account for 49.40% of the total area, making it a typical semi-agricultural and semi-pastoral region. Yaks (Bos grunniens) are the primary economic animals in Jiulong County, with a population of approximate 59,436 as of December 2020. Currently, there are no reports on the ticks or the prevalence of SFGR in this area. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the tick species infesting yaks in Jiulong County and assess their infection status with SFGR. The findings would provide valuable scientific evidence for ensuring the health of local residents, enhancing public health levels, and supporting the sustainable development of animal husbandry in this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Southwest Minzu University (approval NO. AECSWU2020-12).
2.2. Sample Collection and Ticks Morphological Classification
Ticks were collected from the body surface of yaks in Tanggu (coordinate: 30.417778, 101.283333), Sanyanlong (coordinate: 28.7869156, 101.2811314), and Xia’er (coordinate: 29.0068878, 101.5157275), townships in Jiulong County, Sichuan Province, China from May to September 2020. In each township, ticks were gathered from 2 to 5 villages. The collection focused on the ears, face, and neck of each yak, and the ticks were then placed into tubes with moist cotton. After morphological classification, all ticks were stored in 75% ethanol at 4 °C. The feeding ticks were identified based on their morphological characteristics, such as false head base, basal process, whisker limb, scutellum, margin stack, stomatal plate, foot and anal groove, using standard taxonomic keys [15] under a stereo microscope. This morphological identification was then complemented with the molecular method to accurately determine the species.
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Phylogenetic Analysis
All ticks were sectioned longitudinally and homogenized in ddH2O. The homogenates were then centrifuged for 5 min at 8000× g. The total DNA was extracted from all samples using the TIAN amp Genomic DNA Kit (TIANGEN Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China, Cat. No. DP304) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted DNA was subsequently stored at −20 °C for tick molecular identification and detection of SFGR spp. Primer sequences are listed in Table 1.
To identify the species of ticks, a partial sequence of the ribosomal ITS-2 gene, approximately 750–1800 nucleotides (nt) in length, was amplified using primers (ITS2-F and ITS2-R), as described by Lv et al., 2014 [16]. In addition, all samples were subjected to PCR assays targeting the ompA gene of Rickettsia (347 bp), as described by Li et al., 2016 [17]. All samples that tested positive for ompA were further analyzed, targeting ompB (418 bp) [18]. PCR was performed in a total reaction volume of 25 μL, including 1 μL of template DNA or 1 μL of PCR product, 1 μL of each primer (10 μM), 12.5 μL of PCR Supermix (TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China, Cat. No. AS111), and 9.5 µL of distilled wateR. After an initial denaturation for 3 min at 95 °C, 40 cycles of denaturation for 30 s at 94 °C, annealing for 30 s at 55 °C, and elongation for 30 s at 72 °C were performed, followed by a final extension step at 72 °C for 7 min. The sequences were analyzed and compared using the DNASTAR v.7.1.0 software. Nucleotide sequences were examined using the BLAST tool (BLAST+2.16.0), following the methods described by Sayers et al., 2021 [19], so as to compare them with sequences deposited in GenBank. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the Neighbor-Joining method in MEGA 6 software, based on the ITS-2, ompA and ompB genes, respectively. The evolutionary distance was calculated using the Kimura 2-parameter method, with 1000 bootstrap replicates.

Table 1.
Primer sequences used for tick and Rickettsia spp. identification.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used for tick and Rickettsia spp. identification.
| Species | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Target Gene | Product (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tick | ITS2-F: ACATTGCGGCCTTGGGTCTT ITS2-R: TCGCCTGATCTGAGGTCGAC | ITS-2 | 750–1800 | [16] |
| Rickettsia spp. | 190.70-38s1: AAAACCGCTTTATTCACC 190.602-384r1: GGCAACAAGTTACCTCCT | ompA | 347 | [17] |
| ompB4F:GTTTAATACGTGCTGCTAACCAA ompB4R: GGTTTGGCCCATATACCATAAG | ompB | 418 | [20] |
2.4. Statistical Analysis
A Pearson Chi-square (χ2) test using SPSS 19.0 (IBM, New York, NY, USA) was conducted to determine the prevalence of Rickettsia spp. among different sampling locations and tick species, with significant differences (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Tick Species and Quantities
A total of 585 ticks were collected from three townships in Jiulong County (Xia’er, n = 256; Sanyanlong, n = 176; Tanggu, n = 153). Four species of ticks comprising three genera were preliminary identified (Figure 1), namely Rhipicephalus microplus (R. microplus) (n = 308), Ixodes ovatus (I. ovatus) (n = 193), Ixodes acutitarsus (I. acutitarsus) (n = 52), and Dermacentor everestianus (D. everestianus) (n = 32). R. microplus (52.65%) was the predominant and most prevalent species.

Figure 1.
Morphological characteristics of ticks collected from yaks in Jiulong County. (A) Dorsal surface of R. microplus (male). (B) Dorsal surface of I. ovatus (female). (C) Dorsal surface of I. acutitarsus (female). (D) Dorsal surface of D. everestianus (male). Bar = 3 mm.
3.2. Tick Molecular Identification
After sequencing the ITS-2 gene of the ticks, nine unique sequences were obtained through splicing and pairwise comparison. Among these, four sequences were identified as I. ovatus (named I. ovatus Jiulong 1–4), three as I. acutitarsus (I. acutitarsus Jiulong 1–3), and the remaining two as R. microplus (R. microplus Jiulong 1) and D. everestianus (D. everestianus Jiulong 1). I. ovatus Jiulong 1–4 clustered closely with the Ixodes ovatus isolate from Yunnan (KU664537), exhibiting the closest genetic relationship with a similarity of 99.07–99.16%. I. acutitarsus Jiulong 1–3 clustered with the I. acutitarsus isolate from Yunnan (KU664535), showing the closest genetic relationship and a similarity of 87.47–94.54%. R. microplus Jiulong 1 had the closest genetic relationship with the R. microplus isolates from Xiangxi (MK224585) and Jishou (MK224571) in Hunan, with a 100.00% similarity. D. everestianus Jiulong 1 was most closely related to the D. everestianus isolate from Lanzhou, Gansu (JQ737111), also with a 100.00% similarity. The sequences are available in the Supplementary Material.
3.3. Rickettsia spp. Detection
Out of the 585 tick samples, 374 tested positives for SFGR, resulting in a positive rate of 63.93%. SFGR was detected in ticks from all three towns, with strikingly high positive rates varying from 45.10% to 74.61%, as detailed in Table 2 and Figure 2. Among the three survey sites, Xia’er Town had the highest infection rate at 74.61%, followed by Sanyanlong (64.77%) and Tanggu Town (45.10%). The positive rate in pure pastoral areas was 45.10%, while in semi-agricultural and pastoral areas, it was 70.60%. The χ2 test showed that the infection rate in semi-agricultural and pastoral areas (marked with “**” in Table 2) was significantly higher than in pure pastoral areas (p < 0.01).

Table 2.
The infection rates of SFGR in ticks from different regions.
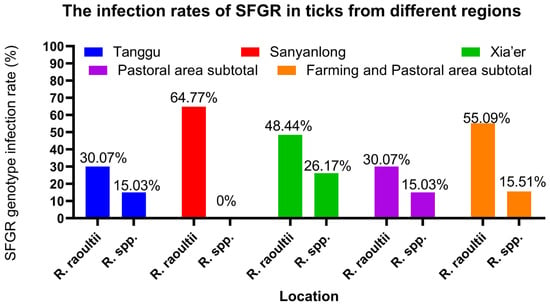
Figure 2.
The infection rates of SFGR in ticks from different regions.
Based on the ompA and ompB genes, the 374 Rickettsia-positive tick samples were identified with R. raoultii and Rickettsia spp. (MZ420228). R. raoultii was the predominant species, accounting for 75.94% (284/374). In this study, the SFGR positive rates in I. acutitarsus, I. ovatus, R. microplus, and D. everestianus ticks were 67.31% (35/52), 63.73% (123/193), 63.64% (196/308), and 62.50% (20/32), respectively, (Table 3) with no significant difference i (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Infection rates of SFGR in different tick species.
3.4. Phylogenetic Analyses of Rickettsia
The ompA and ompB genes of Rickettsia were sequenced and compared. A total of four unique sequences of ompA and five unique sequences of ompB were obtained and deposited in GenBank with accession numbers as follows: ompA, MZ420226 to MZ420229; ompB, MZ344986 to MZ344990. For the ompA gene, sequences (MZ420226 and MZ420227) were clustered with R. raoultii isolates WYG 68 (JQ792162), WYG 91 (JQ792163), LYG 419 (JQ792150), and LYG 575 (JQ792153) from Tibet, showing sequence identities of 100% and 99.20%, respectively. The sequence (MZ420228) showed 99.59% identity to Rickettsia sp. isolated from Beijing (KY469282). Sequence MZ420229 was clustered with Rickettsia sp. isolated from Yunnan (MF134885) and Candidatus Rickettsia longicornii from Yanbian in Jilin (MN026548), with a sequence identity of 100%. For the ompB gene, sequence MZ344990 was clustered with Rickettsia spp. isolated CNH 17-7 (MK236551) and 5-15 (MN631235) from Korea, forming a clade with the closest phylogenetic relationship, but the highest similarity of 99.47% with Rickettsia sp. CNH 17-7 (MK236551) from Korea. Sequences MZ344986 to MZ344989 were clustered with R. raoultii strains LYG 419 (JQ792103), LYG 538 (JQ792104), LYG 155 (JQ792102), and LYG 624 (JQ792105) from Tibet, sharing 96.97–99.39% nucleotide identity with the R. raoultii LYG 419 (JQ792103) strain from Tibet (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
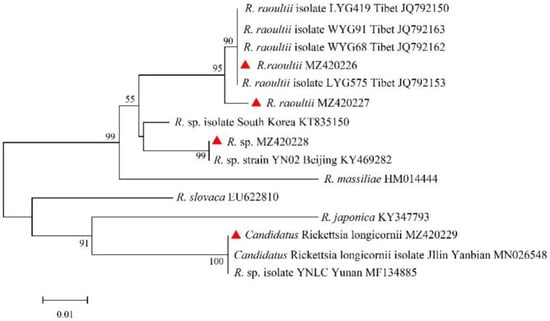
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of SFGR based on the ompA gene.
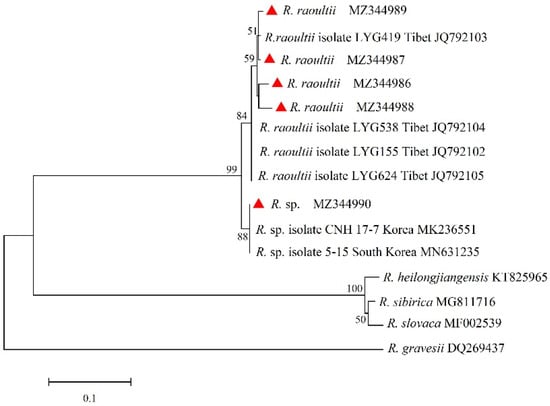
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree of SFGR based on the ompB gene.
4. Discussion
Four tick species were identified in this study through morphological and molecular methods: I. ovatus, I. acutitarsus, R. microplus, and D. everestianus [21]. R. microplus was the most abundant species, accounting for 52.65% (308/585) of the total ticks collected, making it the dominant tick species in Jiulong County. D. everestianus and I. acutitarsus were only identified in yaks from Tanggu and Xia’er towns, accounting for 5.47% (32/585) and 8.89% (52/585) of the total tick population, respectively. These findings are likely related to the specific living characteristics and survival environments of each tick species, which are closely tied to local altitude and ecological conditions. For instance, D. everestianus has been previously reported only in northwestern China and Nepal at altitudes of 2600 m to 4700 m. In contrast, I. acutitarsus primarily inhabits mixed forest areas at altitudes of 1600 m to 2700 m, including regions in Southwest China, Chinese Taiwan, Nepal, Burma, Japan, and India [22]. In this study, Tanggu town, located in the northwest of Jiulong County, is a typical alpine pure pastoral area with an altitude ranging from 3050 m to 5424 m, which is suitable for the survival of D. everestianus. Xia’er town has an average altitude of 2700 m, with a mountain warm temperate and alpine sub-cold climate, which provides an ideal environment for the survival of I. acutitarsus.
For SFGR identification, according to Fournier’s criteria, the ompA gene is a specific protein gene for SFGR [23]. If the ompA gene is detected, it can be identified as SFGR. If not, SFGR must meet two of the following four criteria: (1) 16S rRNA homology > 98.80%; (2) gltA homology > 92.70%; (3) ompB homology > 85.80%; and (4) geneD homology > 82.20%. Thus, in this study, the ompA and ompB genes were used as target genes to detect SFGR infection in ticks from Jiulong County.
Additionally, in the study, it was revealed that R. raoultii accounted for a high proportion of SFGR. The SFGR infection rates in I. ovatus, I. acutitarsus, R. microplus, and D. everestianus ranged from 62.50% to 67.31%, with no significant differences, indicating that these four ticks are dominant SFGR-carrying species in Jiulong County. The R. raoultii infection rate in D. everestianus was significantly higher than previously reported by our laboratory (47.60%) [24]. Notably, the infection rate in semi-agricultural areas (70.60%) was significantly higher than in pure pastoral areas (45.10%) in Jiulong County, as reported in our previous findings in Shiqu County, Ganzi Prefecture, which may be related to differences in vegetation types between agricultural and pastoral areas [24].
Notably, in recent years, Japanese Spotted Fever (JSF) has emerged as the predominant tick-borne Rickettsial disease in China. JSF is a disease caused by R. japonica. In China, since its first discovery in Hainan Province in 1989, the epidemic range and number of infections have expanded significantly [25]. Currently, human cases of Japanese Spotted Fever have been reported in 14 provinces. Between 2021 and 2024, the number of reported cases nearly doubled [26]. In 2021, the first JSF case resulting in death—due to multiple organ failure and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)—was reported in Zigui County, Hubei Province [27]. Rather, the regions where R. japonica was detected were mainly the humid mountainous areas of central and eastern China, and the infections exhibited a clear seasonal trend, with cases primarily occurring from April to November and peaking in autumn. Additionally, the study found that the high-risk population for JSF mainly consists of rural residents aged over 55. However, in this study, R. japonica was not detected in ticks. Collectively, given the high infection rates of R. raoultii in I. ovatus, I. acutitarsus, R. microplus, and D. everestianus in Jiulong County, it is crucial to investigate whether local residents are infected with R. raoultii.
In addition, there are still some limitations in this study: especially, the methods of collection and the host species are important factors that affect the results of tick species identification. The reasons are as follows: firstly, the developmental stages of one-host ticks, such as the tiny Ixodes ticks, occur entirely on a single host; secondly, over 90% of a tick’s life cycle is spent in a non-parasitic stage, with ticks typically inhabiting environments like grasslands and forests; thirdly, two-host and three-host ticks, such as I. ovatus, I. acutitarsus, and D. everestianus, drop off after feeding at each developmental stage and then seek a new host for the next stage. Future work should involve flagging methods or increase the variety of hosts by collecting ticks from the surfaces of sheep, horses, dogs, plateau pikas, plateau marmots, etc. Moreover, expanding the collection areas beyond both pure pastoral and semi-agricultural-pastoral areas in Jiulong County would likely yield a more comprehensive understanding of the types and distribution of ticks in the area.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study represents the first systematic investigation of tick species infesting yaks and their infectious status with SFGR in Jiulong County, Sichuan Province, China. The results indicate that I. acutitarsus, I. ovatus, R. microplus, and D. everestianus are important vectors of R. raoultii in this area. The high prevalence of SFGR in ticks in Jiulong County greatly increases the risk of human infection. In the future, more research should focus on strengthening the surveillance of ticks and the epidemiological study of R. raoultii. This is essential for understanding the potential transmission risks and for developing effective prevention and control strategies to protect both human and animal health.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15070975/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.H., C.W. and L.D.; formal analysis, R.J., K.Z., Y.L. and Q.J.; investigation, L.Z. and C.X.; writing—original draft preparation, C.W. and L.D; writing—review and editing, L.H.; project administration, L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD1801302, 2022YFD1800903) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Southwest Minzu University (2024CXTD14).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Southwest Minzu University (approval NO. AECSWU2020-12).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from farm owners.
Data Availability Statement
Available from the corresponding author on reasonable request, subject to compliance with institutional review board protocols.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fernández-Ruiz, N.; Estrada-Peña, A. Towards New Horizons: Climate Trends in Europe Increase the Environmental Suitability for Permanent Populations of Hyalomma marginatum (Ixodidae). Pathogens 2021, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yin, T.; Ma, W.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of tick-borne SFGR in China from 2000 to 2022. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Siddiqui, C.; Sharma, P.; Kataria, J.; Singh, S.; Sood, V.; Singhai, M. A Case Series on Spotted Fever and Typhus Fever Seropositivity at National Center for Disease Control and Epidemiological Perspective. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 24, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Probert, W.S.; Haw, M.P.; Nichol, A.C.; Glaser, C.A.; Park, S.Y.; Campbell, L.E.; Trivedi, K.K.; Romo, H.; Saunders, M.E.M.; Kjemtrup, A.M.; et al. Newly Recognized Spotted Fever Group Rickettsia as Cause of Severe Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever-Like Illness, Northern California, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Qiu, Y.; Ando, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Nagasaka, A. The case of Mediterranean spotted fever of the traveler returned from Zambia. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102347. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Hernández, G.; Paddock, C.D.; Walker, D.H.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Calleja-López, J.R.T.; Rivera-Rosas, C.N.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R. Rocky Mountain spotted fever is a neglected tropical disease in Latin America. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012276. [Google Scholar]
- Rydkina, E.; Roux, V.; Rudakov, N.; Gafarova, M.; Tarasevich, I.; Raoult, D. New Rickettsiae in ticks collected in territories of the former soviet union. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 811–814. [Google Scholar]
- Mediannikov, O.; Matsumoto, K.; Samoylenko, I.; Drancourt, M.; Roux, V.; Rydkina, E.; Davoust, B.; Tarasevich, I.; Brouqui, P.; Fournier, P.E. Rickettsia raoultii sp. nov. a spotted fever group rickettsia associated with Dermacentor ticks in Europe and Russia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58 Pt 7, 1635–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Shen, H.; Xie, J.R.; Luo, J.; Tian, M.Y. First report on the occurrence of Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia raoultii in Dermacentor silvarum in China. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Borawski, K.; Dunaj, J.; Pancewicz, S.; Król, M.; Czupryna, P.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A. Tick-borne rickettsioses in Europe—A review. Prz. Epidemiol. 2019, 73, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.G.; Kwon, O.D.; Kwak, D. High Prevalence of Rickettsia raoultii and Associated Pathogens in Canine Ticks, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2530–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelet, L.; Joncour, G.; Devillers, E.; Torina, A.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.I.; Moutailler, S. Tick species, tick-borne pathogens and symbionts in an insular environment off the coast of Western France. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Zheng, Y.C.; Ma, L.; Huo, Q.B.; Ni, X.B.; Jiang, B.G.; Chu, Y.L.; Jiang, R.R.; Jiang, J.F.; Cao, W.C. Human infections with Rickettsia raoultii, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, P.H.; Huang, Y.; Du, J.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.D.; Tang, F.; Fu, F.X.; Li, X.M.; Cui, X.M.; et al. Isolation and Identification of Rickettsia raoultii in Human Cases: A Surveillance Study in 3 Medical Centers in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2018, 66, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.F.; Jiang, Z.J. Economic insect fauna of China. Fasc 1991, 39, 127–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, X.M.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.D.; Hu, J.G.; Fan, Y.D.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.H.; Liu, W.; et al. Human Infection with Novel Spotted Fever Group Rickettsia Genotype, China, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2153–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdad, M.Y.; Abdallah, R.A.; Karkouri, K.E.; Beye, M.; Stenos, J.; Owen, H.; Unsworth, N.; Robertson, I.; Blacksell, S.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. Rickettsia gravesii sp. nov.: A novel spotted fever group rickettsia in Western Australian Amblyomma triguttatum triguttatum ticks. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3156–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Rapp, B.A.; Wheeler, D.L. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteo, J.A.; Portillo, A.; Santibáñez, S.; Blanco, J.R.; Pérez-Martínez, L.; Ibarra, V. Cluster of cases of human Rickettsia felis infection from Southern Europe (Spain) diagnosed by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2669–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ma, R.; Yue, C.; Liu, J.; Yue, B.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Ayala, J.E.; Bunker, D.E.; et al. A snapshot of climate drivers and temporal variation of Ixodes ovatus abundance from a giant panda living in the wild. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 20, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, W.; Yuan, X.; Li, J. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages based on geodetector: Jiarong Tibetan in Western Sichuan, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11700. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, P.E.; Dumler, J.S.; Greub, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Raoult, D. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new rickettsia isolates and description of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5456–5465. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Ta, Y.; Hao, L. High prevalence of spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks collected from yaks (Bos grunniens) in Shiqu county, eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 968793. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Lin, J.; Gong, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ye, X.; Gu, S.; Pang, W.; Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Hou, J.; et al. Detection of spotted fever group Rickettsiae in ticks from Zhejiang Province, China. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 65, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Qin, T. The increasing prevalence of Japanese spotted fever in China: A dominant rickettsial threat. J. Infect. 2025, 90, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Gong, P.; Wang, W.; Zhao, N.; Jin, X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, X.; Wen, B.; et al. Clinical Forms of Japanese Spotted Fever from Case-Series Study, Zigui County, Hubei Province, China, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 202–206. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).