Mathematical Methods Applied to the Problem of Dairy Cow Replacements: A Scoping Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Questions
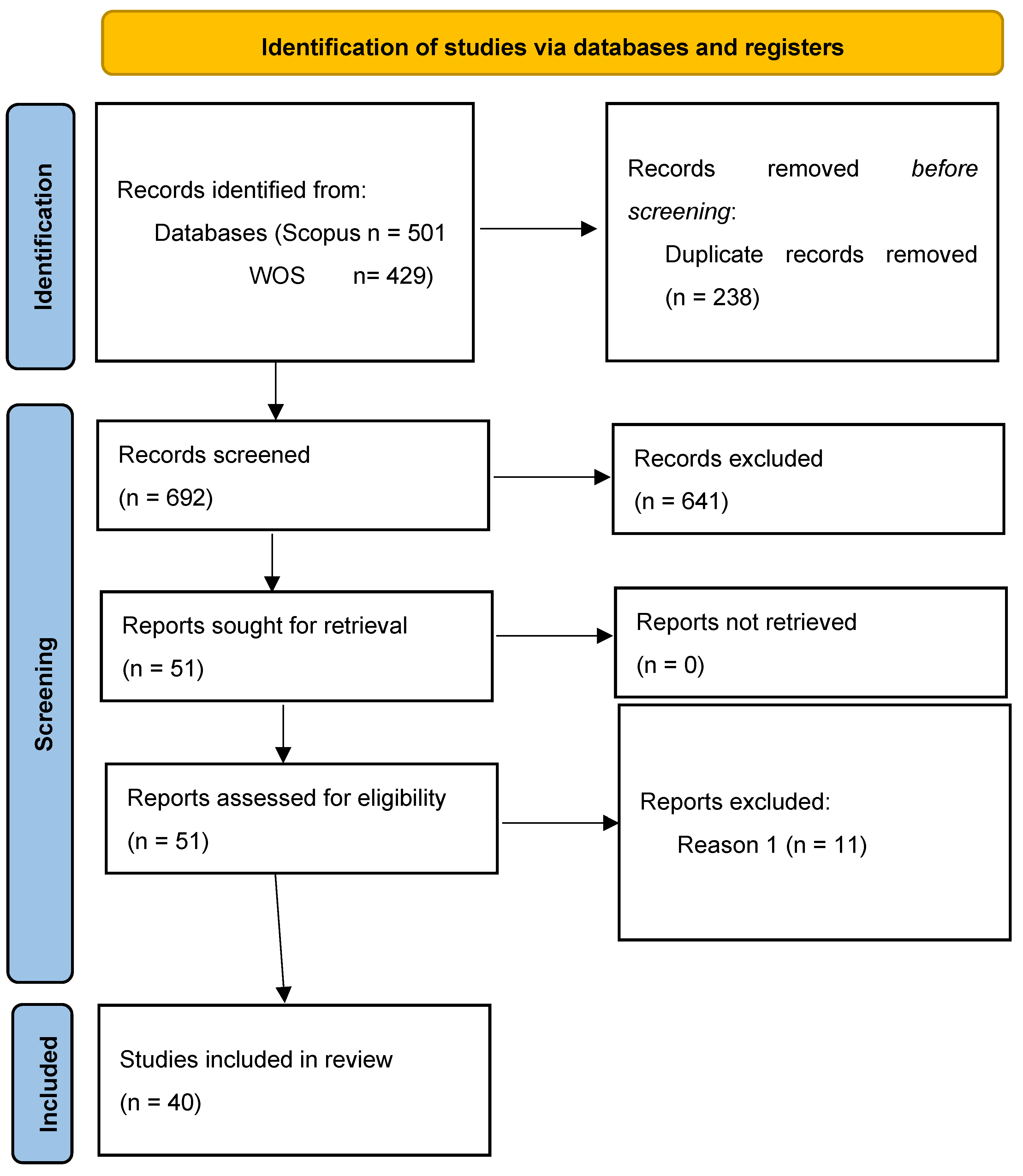
2.2. Identify Relevant Studies
2.3. Selection Criteria
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identify Relevant Studies and Selection Criteria
3.2. Chart the Data
3.3. Results Related to Specific Research Questions
3.4. Gaps in the Literature and Future Outlook
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demeter, R.M.; Kristensen, A.R.; Dijkstra, J.; Oude Lansink, A.G.J.M.; Meuwissen, M.P.M.; van Arendonk, J.A.M. A Multi-Level Hierarchic Markov Process with Bayesian Updating for Herd Optimization and Simulation in Dairy Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5938–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, A.S.; Mehrabani-Yeganeh, H.; Moradi, M.; Sanders, A.H.; De Vries, A. Determining the Optimum Replacement Policy for Holstein Dairy Herds in Iran. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Haijema, R.; Hogeveen, H.; Steeneveld, W.; Mourits, M.C.M. Economic Impacts of Constrained Replacement Heifer Supply in Dairy Herds. Agric. Syst. 2024, 217, 103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graesboll, K.; Kirkeby, C.; Nielsen, S.S.; Halasa, T.; Toft, N.; Christiansen, L.E. A Robust Statistical Model to Predict the Future Value of the Milk Production of Dairy Cows Using Herd Recording Data. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebusch, S.; Hoop, D.; von Rohr, P.; Pausch, H.; Gazzarin, C. Enhancing Culling Decisions in Swiss Dairy Farming: Introducing a Tool for Improved Replacement Choices. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, V.E. A Large Markovian Linear Program to Optimize Replacement Policies and Dairy Herd Net Income for Diets and Nitrogen Excretion. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, A.-M.; Nousiainen, J.I.; Jauhiainen, L. Optimal Replacement Policy and Economic Value of Dairy Cows with Diverse Health Status and Production Capacity. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Heuwieser, W. Culling Policies in Dairy Herds. A Review. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A-Physiol. Pathol. Clin. Med. 1999, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schryen, G.; Sperling, M. Literature Reviews in Operations Research: A New Taxonomy and a Meta Review. Comput. Oper. Res. 2023, 157, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stygar, A.; Makulska, J. Application of Mathematical Modelling in Beef Herd Management—A Review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2010, 10, 333–348. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, A. Economics of Delayed Replacement When Cow Performance Is Seasonal. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehenbauer, T.W.; Oltjen, J.W. Dairy Cow Culling Strategies: Making Economical Culling Decisions. In Proceedings of the Journal of Dairy Science; American Dairy Science Association: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998; Volume 81, pp. 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Delorenzo, M.A.; Spreen, T.H.; Bryan, G.R.; Beede, D.K.; Vanarendonk, J.A.M. Optimizing Model—Insemination, Replacement, Seasonal Production, and Cash Flow. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benari, Y.; Amir, I.; Sharar, S. Operational Replacement Decision-Model for Dairy Herds. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, B.L. Recursive Stochastic-Programming Applied to Dairy-Cow Replacement. Agric. Syst. 1990, 34, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.D.; Kudahl, A.B.; Ostergaard, S.; Nielsen, L.R. Gross Margin Losses Due to Salmonella Dublin Infection in Danish Dairy Cattle Herds Estimated by Simulation Modelling. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 111, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A.; Kinsel, M.L.; Kirkpatrick, M.A. Characterizing Biosecurity, Health, and Culling during Dairy Herd Expansions. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, T.; Kristensen, E.S. Analysis and Simulation Modelling of the Production in Danish Organic and Conventional Dairy Herds. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1998, 54, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.A.; Herbert, W.A. Preliminary Model to Investigate Culling and Replacement Policy in Dairy Herds. Agric. Syst. 1979, 4, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.A. Replacement Policy in Dairy Herds on Farms Where Heifers Compete with Cows for Grassland: Part 2-Experimentation. Agric. Syst. 1982, 8, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozzi, P.; Wilton, J.W.; Burnside, E.B.; Pfeiffer, W.C. Beef-Production from a Dairy Farm—A Linear-Programming Simulation Approach. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1984, 11, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benari, Y.; Gal, S. Optimal Replacement Policy for Multicomponet Systems—An Aplication to a Dairy-Herd. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1986, 23, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkhuisen, A.A.; Stelwagen, J. An Economic Comparison of 4 Insemination and Culling Policies in Dairy Herds, by Method of Stochastic Simulation. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1988, 18, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, A.R.; Thysen, I. Ranking of Dairy-Cows for Replacement—Alternative Methods Tested by Stochastic Simulation. Acta Agric. Scand. 1991, 41, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, A.R. Optimal Replacement in the Dairy-Herd—A Multicomponent System. Agric. Syst. 1992, 39, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalvingh, A.W.; Vanarendonk, J.A.M.; Dijkhuizen, A.A. Dynamic Probabilistic Simulation of Dairy-Herd Management-Practices. 1. Model Description and Outcome of Different Seasonal Calving Patterns. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1993, 37, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalvingh, A.W.; Vanarendonk, J.A.M.; Dijkhuizen, A.A.; Renkema, J.A. Dynamic Probabilistic Simulation of Dairy-Herd Management-Practices. 2. Comparison of Strategies in Order to Change a Herds Calving Pattern. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1993, 37, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, A.R. A Survey of Markov Decision Programming Techniques Applied to the Animal Replacement-Problem. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 1994, 21, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalvingh, A.W.; Dijkhuizen, A.A.; Vanarendonk, J.A.M. Optimizing the Herd Calving Pattern with Linear-Programming and Dynamic Probabilistic Simulation. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, S.M.; Sorensen, J.T.; Kristensen, A.R. Technical and Economic-Effects of Culling and Reproduction Strategies in Dairy-Cattle Herds Estimated by Stochastic Simulation. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. A-Anim. Sci. 1995, 45, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostergaard, S.; Sorensen, J.T.; Hindhede, J.; Kristensen, A.R. Technical and Economic Effects of Feeding One vs. Multiple Total Mixed Estimated by Stochastic Simulation under Different Dairy herd and Management Characteristics. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1996, 45, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, D.A.; DeLorenzo, M.A. Evaluation of a Stochastic Dynamic Replacement and Insemination model for Dairy Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaizier, J.C.B.; King, G.J.; Dekkers, J.C.M.; Lissemore, K. Modeling the Relationship between Reproductive Performance and Net-Revenue in Dairy Herds. Agric. Syst. 1998, 56, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, C.M.; Rehman, T. A Linear Programming Formulation of the Markovian Decision Process to Modelling the Dairy Replacement Problem. Agric. Syst. 1998, 58, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostergaard, S.; Sorensen, J.T.; Kristensen, A.R. A Stochastic Model Simulating the Feeding-Health-Production Complex in a dairy Herd. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala-Schultz, P.J.; Gröhn, Y.T.; Allore, H.G. Optimizing Replacement Decisions for Finnish Dairy Herds. Acta Vet. Scand. 2000, 41, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala-Schultz, P.J.; Gröhn, Y.T.; Allore, H.G. Optimizing Breeding Decisions for Finnish Dairy Herds. Acta Vet. Scand. 2000, 41, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, B.; Herrero, M.; van Arendonk, J.A.M. Interactions between Optimal Replacement Policies and Feeding strategies in Dairy Herds. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2001, 69, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala-Schultz, P.J.; Gröhn, Y.T. Comparison of Economically Optimized Culling Recommendations and Actual Decisions of Finnish Ayrshire Cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2001, 49, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, D.; Tauer, L.W.; Bennett, G.; Gonzalez, R.N.; Hertl, J.A.; Schukken, Y.H.; Schulte, H.F.; Welcome, F.L.; Groehn, Y.T. The Cost of Generic Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows as Estimated by using Dynamic Programming. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, K.; Ibi, T.; Kahi, A.K.; Hirooka, H. Optimal Culling Strategy in Relation to Biological and Economic and Annualized Net Revenue in the Japanese Black Cow-Calf System. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 149, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, A.S.; Cabrera, V.E. The Effect of Reproductive Performance on the Dairy Cattle Herd Value Assessed by Integrating a Daily Dynamic Programming Model with a Daily Markov Chain Model. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6160–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, V.E. A Simple Formulation and Solution to the Replacement Problem: A Tool to Assess the Economic Cow Value, the Value of a New, and the Cost of a Pregnancy Loss. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4683–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Hirooka, H. Effects of Sex Control and Twinning on Economic Optimization of Culling in Japanese Black Cow-Calf Production Systems. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinfar, S.; Kalantari, A.S.; Cabrera, V.; Weigel, K. Short Communication: Prediction of Retention Pay-off Using a machine Learning Algorithm. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2949–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, A.S.; Cabrera, V.E. Stochastic Economic Evaluation of Dairy Farm Reproductive Performance. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 95, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Suarez, M.; Armengol, E.; Calsamiglia, S.; Castillejos, L. Using Decision Trees to Extract Patterns for Dairy Culling Management. IFIP Adv. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2018, 519, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plà, L.M.; Sandars, D.L.; Higgins, A.J. A Perspective on Operational Research Prospects for Agriculture. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2014, 65, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, G.H. Deterministic and Stochastic Inventory Models in Production Systems: A Review of the Literature. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2023, 7, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzetto, A.M.; Bishop, G.; Styles, D.; Arndt, C.; Brook, R.; Chadwick, D. Comparing the Environmental Efficiency of Milk and Beef Production through Life Cycle Assessment of Interconnected Cattle Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, N.; Garnett, T.; Lorimer, J. Dairy Intensification: Drivers, Impacts and Alternatives. Ambio 2020, 49, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, A. Symposium Review: Why Revisit Dairy Cattle Productive Lifespan? J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3838–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rueden, L.; Mayer, S.; Sifa, R.; Bauckhage, C.; Garcke, J. Combining Machine Learning and Simulation to a Hybrid Modelling Approach: Current and Future Directions. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Berthold, M.R., Feelders, A., Krempl, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12080 LNCS, pp. 548–560. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncali, C.E.; Fainekos, G.; Ito, H.; Kapinski, J. Simulation-Based Adversarial Test Generation for Autonomous Vehicles with Machine Learning Components. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Proceedings, Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1555–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Plà-Aragonès, L.M. The Evolution of DSS in the Pig Industry and Future Perspectives. In EURO Working Group on DSS: A Tour of the DSS Developments Over the Last 30 Years; Papathanasiou, J., Zaraté, P., de Sousa, J.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 299–323. ISBN 978-3-030-70377-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, V.E.; Fricke, P.M. Economics of Twin Pregnancies in Dairy Cattle. Animals 2021, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, V.E.; Fadul-Pacheco, L. Future of Dairy Farming from the Dairy Brain Perspective: Data Integration, Analytics, and Applications. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 121, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, L.O.; Greenwood, P.L.; Halachmi, I. Advancements in Sensor Technology and Decision Support Intelligent Tools to Assist Smart Livestock Farming. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.K.J.; Behdinan, K. Dimensionality Reduction in Surrogate Modeling: A Review of Combined Methods. Data Sci. Eng. 2022, 7, 402–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, R.; Allen, J.K.; Mistree, F. Managing Computational Complexity Using Surrogate Models: A Critical Review. Res. Eng. Des. 2020, 31, 275–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoverde-Molina, M.; Luján-Mora, S. Cybersecurity in Smart Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review. Comput. Secur. 2025, 150, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Publication Number in Paper New | Title | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Preliminary model to investigate culling and replacement policy in dairy herds | [20] |
| 2 | Replacement policy in dairy herds on farms where heifers compete with cows for grassland. 2. Experimentation | [21] |
| 3 | Operational replacement decision model for dairy herds | [14] |
| 4 | Beef production from a dairy farm a linear programming simulation approach | [22] |
| 5 | Optimal replacement policy for multicomponent systems: An application to a dairy herd | [23] |
| 6 | An economic comparison of 4 insemination and culling policies in dairy herds, by method of stochastic simulation | [24] |
| 7 | Recursive stochastic programming applied to dairy cow replacement | [15] |
| 8 | Ranking of dairy cows for replacement | [25] |
| 9 | Optimizing model-insemination, replacement, seasonal production, and cash flow | [13] |
| 10 | Optimal replacement in the dairy herd a multi component system | [26] |
| 11 | Dynamic probabilistic simulation of dairy herd management practices. i. model description and outcome of different seasonal calving patterns | [27] |
| 12 | Dynamic probabilistic simulation of dairy herd management practices. ii. comparison of strategies in order to change a herds calving pattern | [28] |
| 13 | A survey of markov decision programming techniques applied to the animal replacement problem | [29] |
| 14 | Optimizing the herd calving pattern with linear programming and dynamic probabilistic simulation | [30] |
| 15 | Technical and economic effects of culling and reproduction strategies in dairy cattle herds estimated by stochastic simulation | [31] |
| 16 | Technical and economic effects of feeding one vs. multiple total mixed rations estimated by stochastic simulation under different dairy herd and management characteristics | [32] |
| 17 | Evaluation of a stochastic dynamic replacement and insemination model for dairy cattle | [33] |
| 18 | Modeling the relationship between reproductive performance and net-revenue in dairy herds | [34] |
| 19 | A linear programming formulation of the Markovian decision process approach to modelling the dairy replacement problem | [35] |
| 20 | A stochastic model simulating the feeding-health-production complex in a dairy herd | [36] |
| 21 | Optimizing replacement decisions for Finnish dairy herds | [37] |
| 22 | Optimizing breeding decisions for Finnish dairy herds | [38] |
| 23 | Interactions between optimal replacement policies and feeding strategies in dairy herds | [39] |
| 24 | Comparison of economically optimized culling recommendations and actual culling decisions of Finnish Ayrshire cows | [40] |
| 25 | Economics of delayed replacement when cow performance is seasonal | [11] |
| 26 | The cost of generic clinical mastitis in dairy cows as estimated by using dynamic programming | [41] |
| 27 | Optimal replacement policy and economic value of dairy cows with diverse health status and production capacity | [7] |
| 28 | Determining the optimum replacement policy for Holstein dairy herds in Iran | [2] |
| 29 | A large Markovian linear program to optimize replacement policies and dairy herd net income for diets and nitrogen excretion | [6] |
| 30 | A multi-level hierarchic Markov process with Bayesian updating for herd optimization and simulation in dairy cattle | [1] |
| 31 | Optimal culling strategy in relation to biological and economic efficiency and annualized net revenue in the Japanese Black cow calf production system | [42] |
| 32 | The effect of reproductive performance on the dairy cattle herd value assessed by integrating a daily dynamic programming model with a daily Markov chain model | [43] |
| 33 | A simple formulation and solution to the replacement problem: A practical tool to assess the economic cow value, the value of a new pregnancy, and the cost of a pregnancy loss | [44] |
| 34 | Effects of sex control and twinning on economic optimization of culling cows in Japanese Black cow calf production systems | [45] |
| 35 | Short communication: Prediction of retention pay-off using a machine learning algorithm | [46] |
| 36 | Stochastic economic evaluation of dairy farm reproductive performance | [47] |
| 37 | A robust statistical model to predict the future value of the milk production of dairy cows using herd recording data | [4] |
| 38 | Using decision trees to extract patterns for dairy culling management | [48] |
| 39 | Enhancing culling decisions in swiss dairy farms: introducing a tool for improved replacement choices | [5] |
| 40 | Economic impacts of constrained replacement heifer supply in dairy herds | [3] |
| Application | Methodology | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimization | Simulation | Other | ||||||
| Paper Number | Herd | Individual | Markov Chains | Markov Decision Process | Linear Programming | Deterministic | Stochastic | |
| 1 | X | X | X | |||||
| 2 | X | X | ||||||
| 3 | X | X | ||||||
| 4 | X | X | ||||||
| 5 | X | X | X | |||||
| 6 | X | X | ||||||
| 7 | X | Recursive Stochastic Programming | ||||||
| 8 | X | X | X | |||||
| 9 | X | X | ||||||
| 10 | X | X | X | |||||
| 11 | X | X | ||||||
| 12 | X | X | X | |||||
| 13 | X | X | X | |||||
| 14 | X | X | X | |||||
| 15 | X | X | X | |||||
| 16 | X | X | ||||||
| 17 | X | X | ||||||
| 18 | X | X | X | |||||
| 19 | X | X | X | |||||
| 20 | X | X | ||||||
| 21 | X | X | ||||||
| 22 | X | X | ||||||
| 23 | X | X | ||||||
| 24 | X | X | ||||||
| 25 | X | X | X | |||||
| 26 | X | X | X | |||||
| 27 | X | X | Logistic regression | |||||
| 28 | X | X | ||||||
| 29 | X | X | ||||||
| 30 | X | Multilevel Markov hierarchical process | ||||||
| 31 | X | X | ||||||
| 32 | X | X | X | |||||
| 33 | X | X | X | |||||
| 34 | X | X | ||||||
| 35 | X | X | ML decision trees | |||||
| 36 | X | X | ||||||
| 37 | X | Exponential smoothing, linear regression, and logistic function | ||||||
| 38 | X | Decision trees | ||||||
| 39 | X | X | ||||||
| 40 | X | X | X | |||||
| Response Variables | Economic Indicator | Main Production Type | Type of Extensive Production | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number Publication in Paper | Milk Production | Diseases | Other | Benefit | Income | Cost | Other | Beef | Milk | Grazing | Barn |
| 1 | X | Genetic improvement in performance per cow. | X | X | X | ||||||
| 2 | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| 3 | Present net value (NPV) | X | |||||||||
| 4 | Beef production. Replacement rate. Breed. | X | X | ||||||||
| 5 | Expected value of keeping a cow in the herd | X | |||||||||
| 6 | X | Interval between calvings, the rate of discarding, and the rate of detection of estrus and conception. | X | X | |||||||
| 7 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 8 | X | X | |||||||||
| 9 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 10 | X | ||||||||||
| 11 | X | X | |||||||||
| 12 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 13 | Optimal replacement policies, and herd statistics. | Present net value (NPV) | X | ||||||||
| 14 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 15 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 16 | X | X | |||||||||
| 17 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 18 | X | X | |||||||||
| 19 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 20 | X | Food intake, food utilization, conception, slaughter, involuntary elimination, and death. | X | X | |||||||
| 21 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 22 | X | The replacement rate, the structure of the herd. | X | X | |||||||
| 23 | X | Average herd lifespan, calving interval, replacement rate, feed intake, and body weight change. | X | X | X | ||||||
| 24 | X | Risk of discarding, open days (pregnancy), lactation stage (days in milk), and month of delivery. | X | X | |||||||
| 25 | X | X | |||||||||
| 26 | mastitis | X | X | X | |||||||
| 27 | X | X | |||||||||
| 28 | X | Retention value (RPO). | X | X | |||||||
| 29 | X | Herd structure, replacement policy, dry matter intake (DMI), and nitrogen excretion (N). | X | X | |||||||
| 30 | X | Productive herd life. Interval between calvings. Annual discard rate. Proportion of voluntary discards. Feed intake capacity. Energy requirement. Forage and concentrate intake. Monthly Revenue and Costs. Monthly and lifetime net income. | X | X | X | ||||||
| 31 | Biological efficiency (BE), the live weight of discarded cows and their calves, metabolizable energy consumption (ME), and economic costs and revenues. | Economic efficiency (EE) and annualized net income (AN). | X | ||||||||
| 32 | Retention value (RPO) | X | X | ||||||||
| 33 | X | The value of a new pregnancy, the cost of a pregnancy loss, the pregnancy rate, the discard rate, and the structure of the herd. | Present net value (NPV) | X | |||||||
| 34 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 35 | Retention value (RPO) | X | X | ||||||||
| 36 | X | Feed costs, calf sales revenues, discard costs, reproductive costs, herd structure (parity, days in milk, days open), and pregnancy and discard rates. | X | X | |||||||
| 37 | X | Somatic cell count, survival, and correlation structures between these herd-level measures. | X | ||||||||
| 38 | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 39 | X | Expected lifespan of the cow. Average monthly income per cow. Average monthly costs per cow. State transitions (lactation, month in milk, month of pregnancy). Lactation curves (milk production, protein and fat content). | X | Cow value | X | X | |||||
| 40 | X | X | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palma, O.; Plà-Aragonés, L.M.; Mac Cawley, A.; Albornoz, V.M. Mathematical Methods Applied to the Problem of Dairy Cow Replacements: A Scoping Review. Animals 2025, 15, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070970
Palma O, Plà-Aragonés LM, Mac Cawley A, Albornoz VM. Mathematical Methods Applied to the Problem of Dairy Cow Replacements: A Scoping Review. Animals. 2025; 15(7):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070970
Chicago/Turabian StylePalma, Osvaldo, Lluis M. Plà-Aragonés, Alejandro Mac Cawley, and Víctor M. Albornoz. 2025. "Mathematical Methods Applied to the Problem of Dairy Cow Replacements: A Scoping Review" Animals 15, no. 7: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070970
APA StylePalma, O., Plà-Aragonés, L. M., Mac Cawley, A., & Albornoz, V. M. (2025). Mathematical Methods Applied to the Problem of Dairy Cow Replacements: A Scoping Review. Animals, 15(7), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070970








