Chinese Named Entity Recognition for Dairy Cow Diseases by Fusion of Multi-Semantic Features Using Self-Attention-Based Deep Learning
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
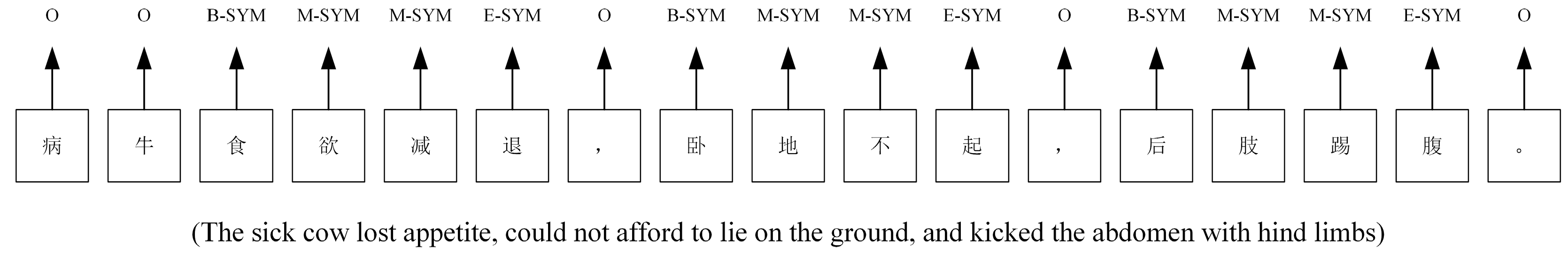
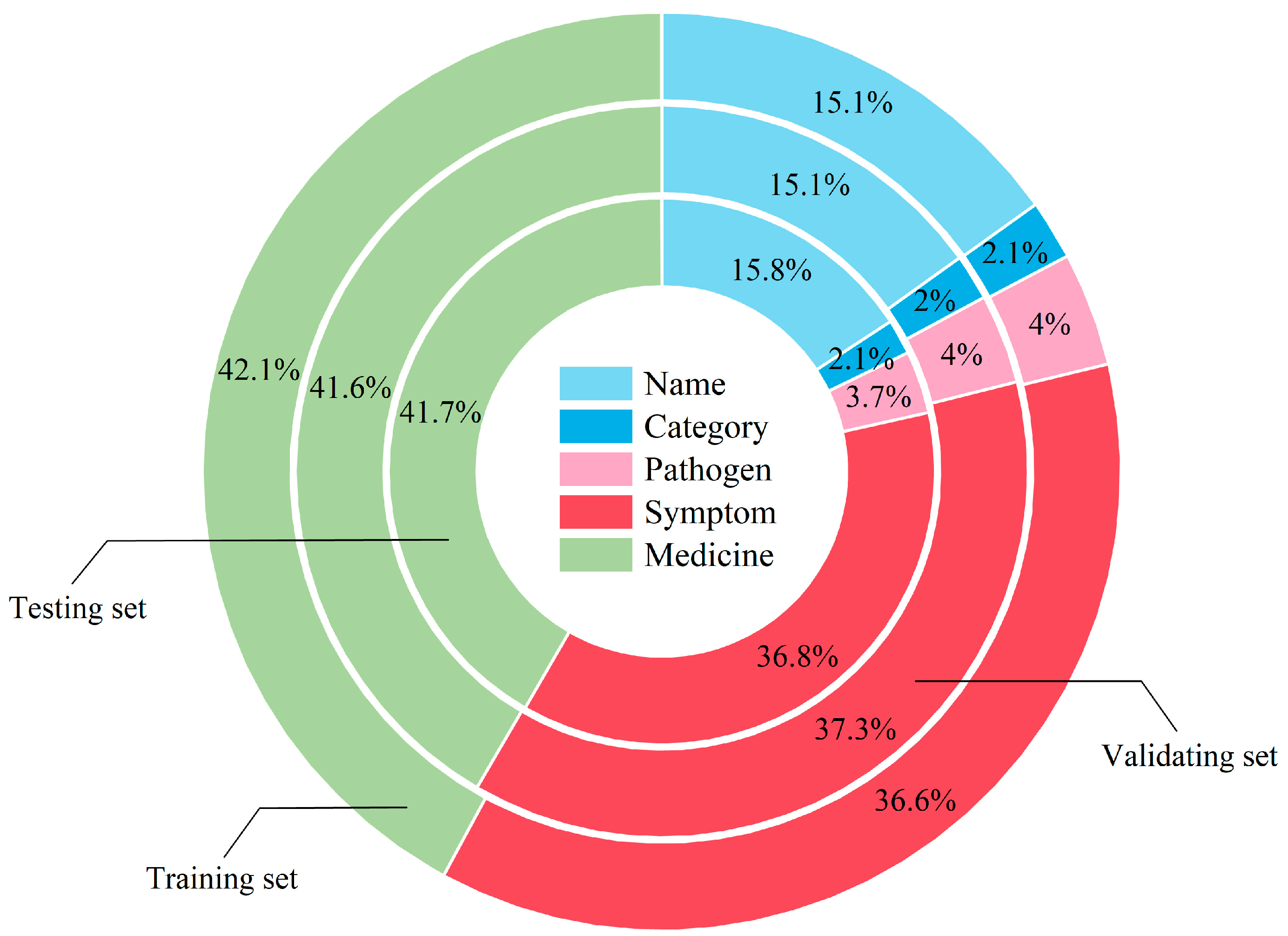
2.1. Dataset
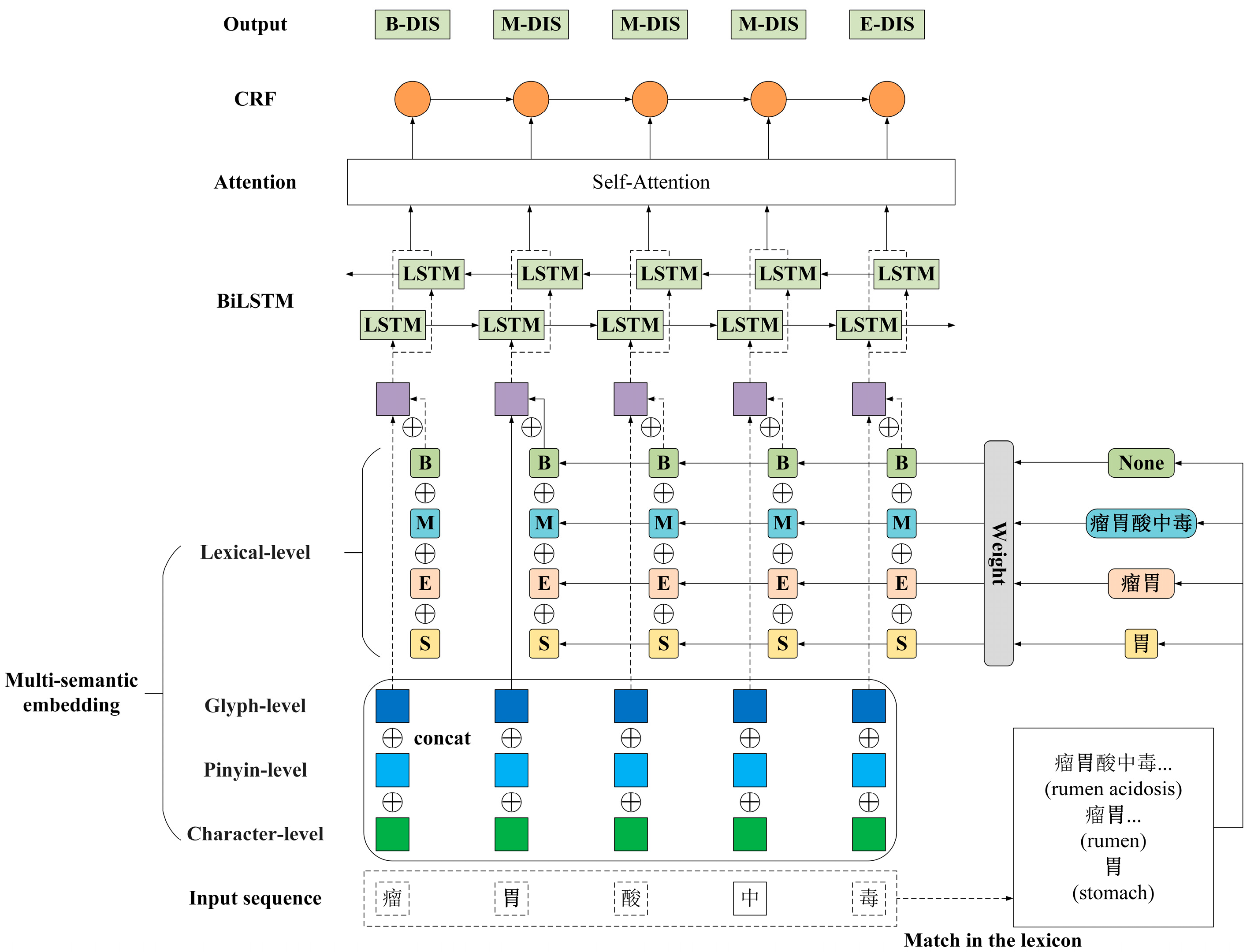
2.2. Model
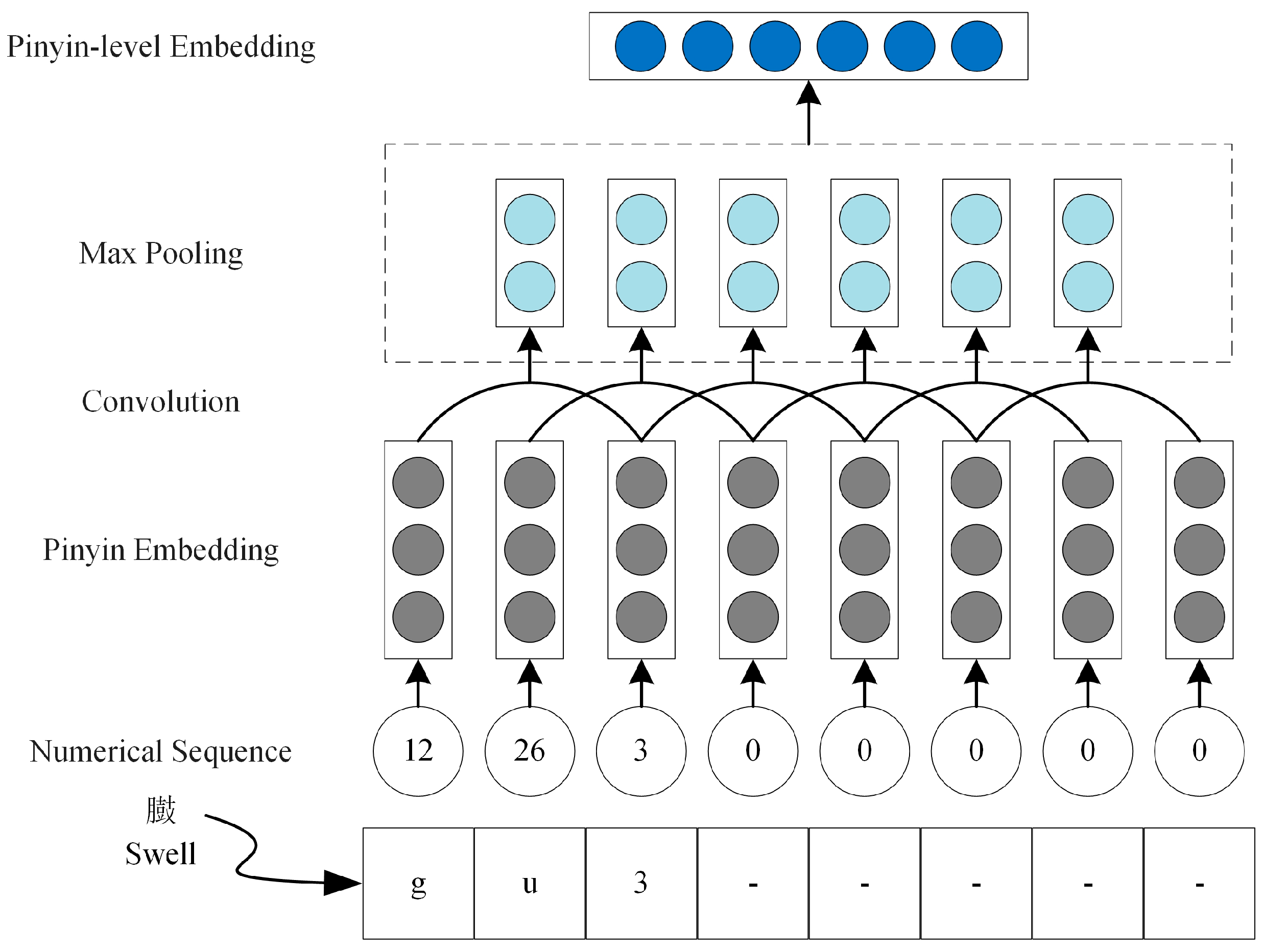
2.2.1. Multi-Semantic Embedding Layer
2.2.2. Bi-LSTM Layer
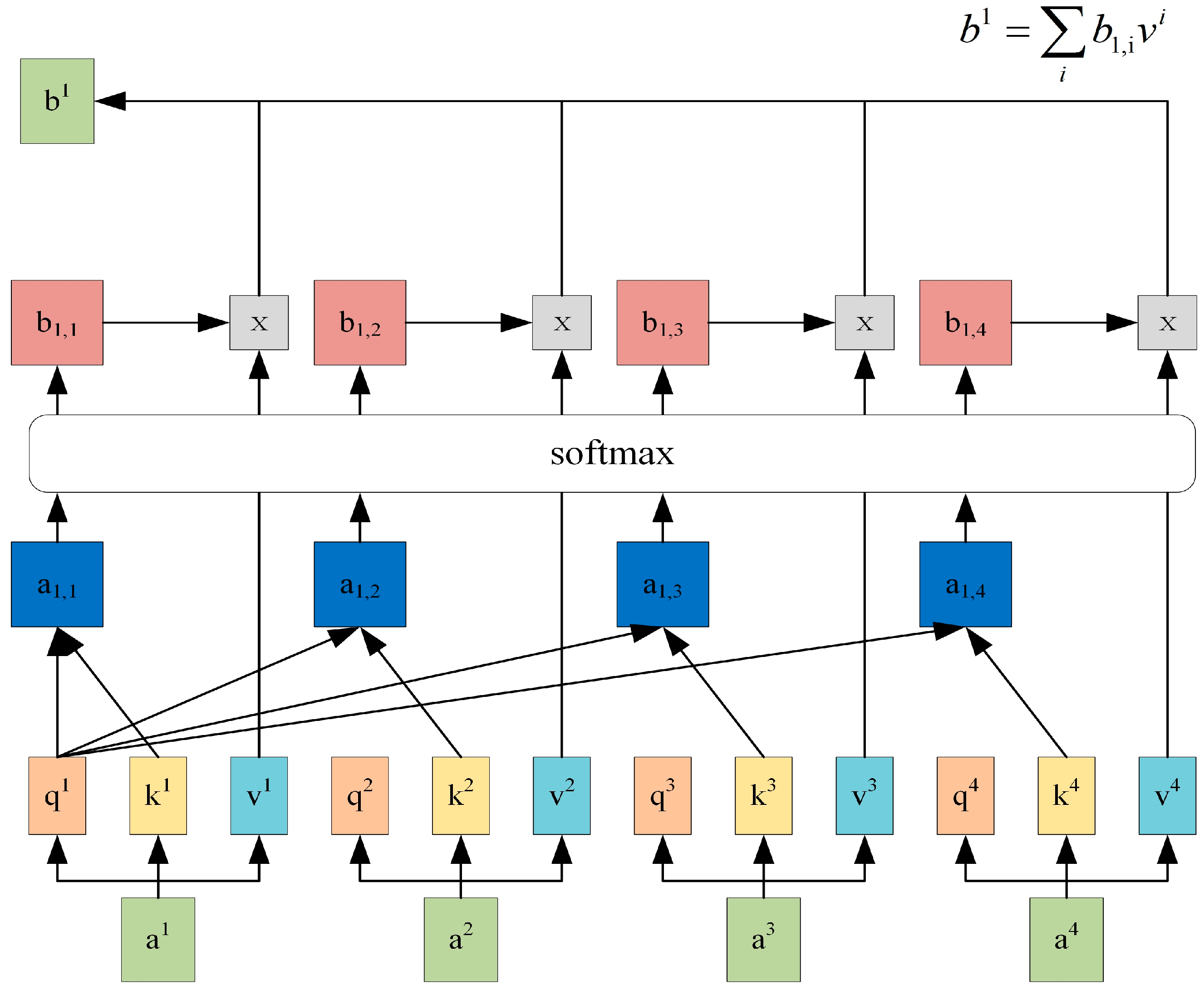
2.2.3. Self-Attention Layer
2.2.4. CRF Layer
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.3.1. Parameters
2.3.2. Models
3. Results
3.1. Recognition Performances of Different Models
3.1.1. Comparison with Baselines
3.1.2. Comparison with Related Works
3.2. Ablation Study
3.2.1. Pinyin-Level Embedding
3.2.2. Glyph-Level Embedding
3.2.3. Self-Attention Mechanism
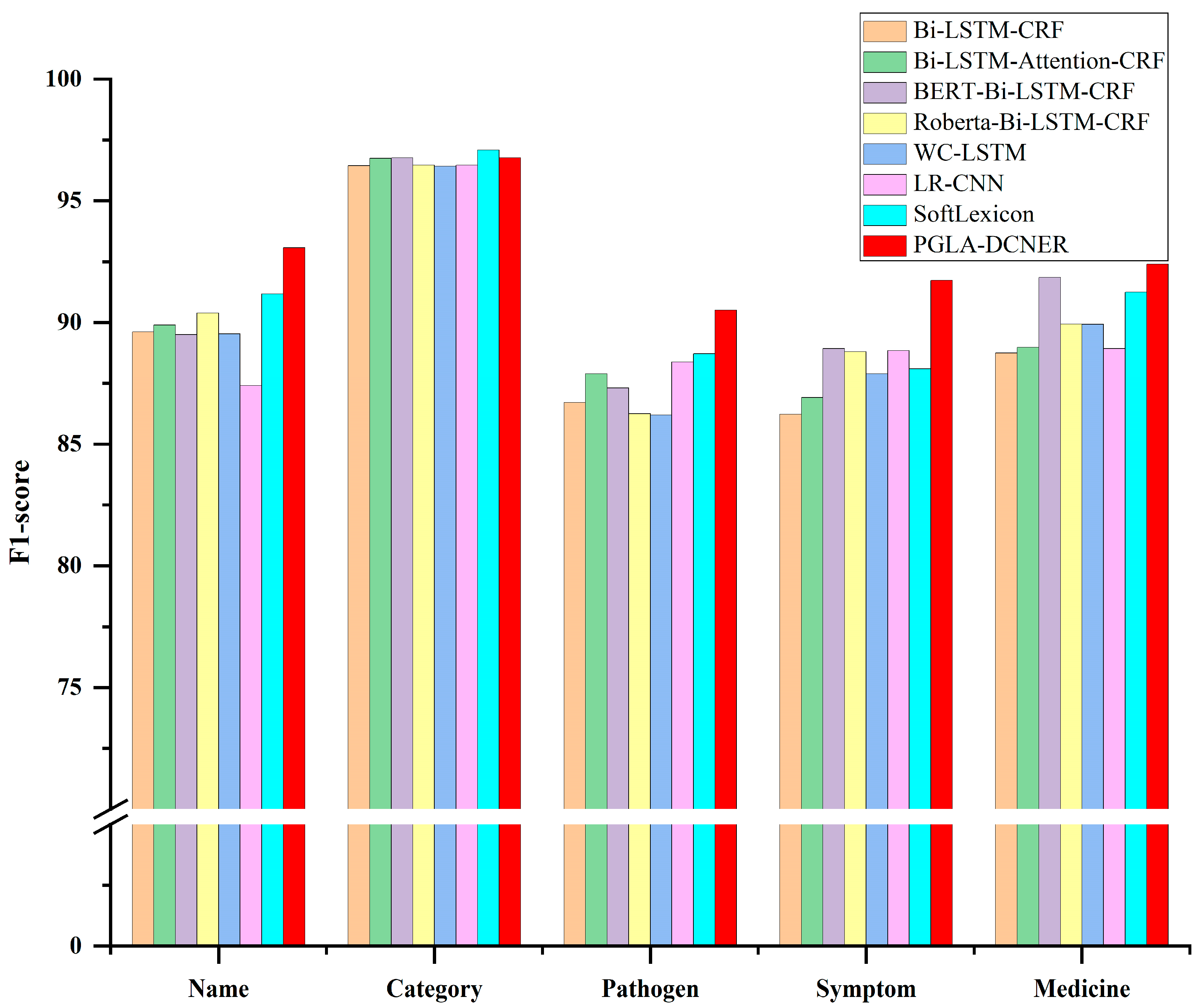
3.3. Performance on Different Entity Types
3.4. Computation Performances of Different Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance Analysis of Baselines and Related Works
4.2. Effects of Each Component of Our Model
4.3. Performance Analysis on Different Entity Types
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Sun, J.; Guan, M.; Sun, S.; Shi, G.; Zhu, C. A New Method for Non-Destructive Identification and Tracking of Multi-Object Behaviors in Beef Cattle Based on Deep Learning. Animals 2024, 14, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Shi, G.; Zhu, C. Dynamic Serpentine Convolution with Attention Mechanism Enhancement for Beef Cattle Behavior Recognition. Animals 2024, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.; Alabi, J.; Roy, R.S.; Weikum, G. UNIQORN: Unified question answering over RDF knowledge graphs and natural language text. J. Web Semant. 2024, 83, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, M.; Song, C.; Wu, L. Nanjing Yunjin intelligent question-answering system based on knowledge graphs and retrieval augmented generation technology. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xiaohui, A.; Du, H.; Qiu, B. Diagnosis of dairy cow diseases by knowledge-driven deep learning based on the text reports of illness state. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Song, L. Research on knowledge graph-driven equipment fault diagnosis method for intelligent manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 4649–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Xie, Z. Explainable fraud detection of financial statement data driven by two-layer knowledge graph. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 246, 123126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Yan, C.; Liu, W.; Lin, X. Research on medical insurance anti-gang fraud model based on the knowledge graph. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 134, 108627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Y. Semantic relatedness algorithm for keyword sets of geographic metadata. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 47, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; So, C.H.; Kang, J. BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, U.; Khushi, M.; Reddy, V.; Rajendran, S.; Razzak, I.; Kim, J. Bioalbert: A simple and effective pre-trained language model for biomedical named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Ji, L. Chinese named entity recognition method for the finance domain based on enhanced features and pretrained language models. Inf. Sci. 2023, 625, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, J.; Ji, L. Chinese nested entity recognition method for the finance domain based on heterogeneous graph network. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bat, T.; Xiang, H.; Dai, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z. Recognition of Cotton Pests and Diseases Named Entities Based on RoBERTA Multi⁃feature Fusion. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2024, 53, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Li, D.; Lin, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, Z. Named entity recognition of Chinese crop diseases and pests based on RoBERTa-wwm with adversarial training. Agronomy 2023, 13, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengliev, D.B.; Barakhnin, V.B.; Atakhanov, M.; Ibragimov, B.B.; Eshkulov, M.; Saidov, B. Developing rule-based and gazetteer lists for named entity recognition in Uzbek language: Geographical names. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE XVI International Scientific and Technical Conference Actual Problems of Electronic Instrument Engineering (APEIE), Samara, Russia, 25–27 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.T.; Lin, J.R.; Leng, S.; Li, J.L.; Hu, Z.Z. Rule-based information extraction for mechanical-electrical-plumbing-specific semantic web. Automat. Constr. 2022, 135, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsri, J. CRF-Named Entity Recognition Model for Ancient Isan Medicine Texts. In Proceedings of the 2024 12th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 22–25 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Okgetheng, B.; Malema, G. Named Entity Recognition for Setswana Language: A conditional Random Fields (CRF) Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 19–21 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, R.; Tsai, C.T.; Tsereteli, K.; Kambadur, P.; Yang, Y. A semi-Markov structured support vector machine model for high-precision named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Chinese NER using lattice LSTM. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.02023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Peng, M.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X. Simplify the usage of lexicon in Chinese NER. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.05969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, H.; Qiu, X.; Huang, X. FLAT: Chinese NER using flat-lattice transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nie, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, M.; Geissen, V.; Ritsema, C.J.; Zhang, H. Lexicon and attention-based named entity recognition for kiwifruit diseases and pests: A Deep learning approach. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1053449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Mou, C.; Xiong, K.; Ren, J. Chinese clinical named entity recognition with radical-level feature and self-attention mechanism. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 98, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, S.; Tang, Z.; Bai, Z.; Diao, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, L. CG-ANER: Enhanced contextual embeddings and glyph features-based agricultural named entity recognition. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Wang, T.; Deng, J.; Cheng, L. Improving Chinese named entity recognition by interactive fusion of contextual representation and glyph representation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, C.; Zhou, S.; Shang, X.; Wang, Y. An RG-FLAT-CRF model for named entity recognition of Chinese electronic clinical records. Electronics 2022, 11, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Ren, H.; Gao, D.; Fang, A. Chinese Clinical Named Entity Recognition from Electronic Medical Records Based on Multisemantic Features by Using Robustly Optimized Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers Pretraining Approach Whole Word Masking and Convolutional Neural Networks: Model Development and Validation. JMIR Med. Inform. 2023, 11, e44597. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Song, X.; Feng, Z. MECT: Multi-metadata embedding based cross-transformer for Chinese named entity recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.05418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, T.Y. Dictionary Enhancement and Radical Perception for Sheep Disease Named Entity Recognition. Comput. Digital. Eng. 2024, 52, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yang, L.; Wang, S. Handbook of Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Dairy Cow Diseases, 1st ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 74–514. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Comprehensive Diagnosis and Treatment of Dairy Cow Diseases, 1st ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 27–315. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Diagnosis and Treatment Technologies of Dairy Cow Diseases, 1st ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 5–257. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, T. Diagnosis and Treatment Graph of Dairy Cow Diseases, 1st ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, J. Rebhun’s Diseases of Dairy Cattle, 2nd ed.; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 39–590. [Google Scholar]
- Baidu Baike. Available online: https://baike.baidu.com (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Agricultural Knowledge Service System. Available online: http://agri.nais.net.cn (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Qian, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ouyang, D.; Dong, S.; Huang, L. Agricultural text named entity recognition based on the Bi-LSTM-CRF model. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Computer Information Science and Artificial Intelligence (CISAI 2022), Tokyo, Japan, 22–24 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1310.4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, Y.; Ao, X.; He, Q.; Li, J. Chinesebert: Chinese pretraining enhanced by glyph and pinyin information. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehanobish, A.; Song, C.H. Using Chinese glyphs for named entity recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xue, C.; Su, X.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Named entity recognition for Chinese construction documents based on conditional random field. Front. Eng. Manag. 2023, 10, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viterbi, A. Error bounds for convolutional codes and an asymptotically optimum decoding algorithm. IEEE. Trans. Inform. Theory 1967, 13, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Xia, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Luo, H.; Ma, J. Research on power entity recognition technology base on Bi-LSTM-CRF. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Power, Electronics and Computer Applications (ICPECA), Mumbai, India, 3–5 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Ma, X. Attention in character-based Bi-LSTM-CRF for Chinese named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, Chengdu, China, 12–15 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Huang, H.; Lai, Q.; Li, M.; Guan, L. Naming entity recognition of citrus pests and diseases based on the BERT-Bi-LSTM-CRF model. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Mu, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L. Named entity recognition of Traditional Chinese Medicine cases based on RoBERTa-Bi-LSTM-CRF. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Istanbul, Turkey, 5–10 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xu, T.; Xu, Q.; Song, J.; Zu, Y. An encoding strategy based word-character LSTM for Chinese NER. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, T.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.G.; Huang, X. CNN-Based Chinese NER with Lexicon Rethinking. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Qi, G.J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J. Interleaved group convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Dimension of character vectors | 50 |
| Dimension of word vectors | 50 |
| Dimension of hidden layer in Bi-LSTM | 300 |
| Number of layers in Bi-LSTM | 1 |
| Dimension of hidden layer in attention | 600 |
| Number of heads in attention | 10 |
| Dropout rate | 0.5 |
| Learning rate | 0.002 |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Max. epoch | 80 |
| Optimization algorithm | Adam |
| Model | Encoder | External Features | Attention Mechanism | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lexicon | Pinyin | Glyph | ||||
| baselines | SoftLexicon(CNN) | CNN | √ | × | × | × |
| SoftLexicon(Transformer) | Transformer | √ | × | × | × | |
| SoftLexicon(Bi-LSTM) | Bi-LSTM | √ | × | × | × | |
| ablation models | +pinyin | Bi-LSTM | √ | √ | × | × |
| +glyph | Bi-LSTM | √ | × | √ | × | |
| +attention | Bi-LSTM | √ | × | × | √ | |
| +pinyin+glyph | Bi-LSTM | √ | √ | √ | × | |
| +pinyin+attention | Bi-LSTM | √ | √ | × | √ | |
| +glyph+attention | Bi-LSTM | √ | × | √ | √ | |
| our model | PGLA-DCNER | Bi-LSTM | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| related works | Bi-LSTM-CRF | Bi-LSTM | × | × | × | × |
| Bi-LSTM-Attention-CRF | Bi-LSTM | × | × | × | √ | |
| BERT-Bi-LSTM-CRF | Bi-LSTM | × | × | × | × | |
| RoBERTa-Bi-LSTM-CRF | Bi-LSTM | × | × | × | × | |
| WC-LSTM | Bi-LSTM | √ | × | × | × | |
| LR-CNN | CNN | √ | × | × | × | |
| FLAT | Transformer | √ | × | × | × | |
| MECT | Transformer | √ | × | √ | × | |
| Models | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baselines | SoftLexicon (CNN) | 75.53 | 86.18 | 80.50 |
| SoftLexicon (Transformer) | 83.41 | 88.65 | 85.95 | |
| SoftLexicon (Bi-LSTM) | 85.76 | 93.88 | 89.64 | |
| character-based models | Bi-LSTM-CRF | 84.70 | 90.94 | 87.71 |
| Bi-LSTM-Attention-CRF | 84.69 | 92.07 | 88.23 | |
| BERT-Bi-LSTM-CRF | 87.48 | 92.29 | 89.82 | |
| RoBERTa-Bi-LSTM-CRF | 86.33 | 92.65 | 89.38 | |
| ensemble models | WC-LSTM | 88.03 | 89.54 | 88.78 |
| LR-CNN | 84.54 | 93.44 | 88.77 | |
| FLAT | 86.86 | 94.56 | 90.54 | |
| MECT | 86.21 | 95.35 | 90.55 | |
| our model | PGLA-DCNER | 91.93 | 92.42 | 92.18 |
| Models | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | SoftLexicon | 85.76 | 93.88 | 89.64 |
| ablation models | +pinyin | 88.58 | 92.96 | 90.72 |
| +glyph | 86.49 | 93.83 | 90.01 | |
| +attention | 89.66 | 91.28 | 90.47 | |
| +pinyin+glyph | 88.81 | 93.44 | 91.06 | |
| +pinyin+attention | 89.55 | 92.55 | 91.02 | |
| +glyph+attention | 88.56 | 93.03 | 90.74 | |
| our model | +pinyin+glyph+attention | 91.93 | 92.42 | 92.18 |
| Models | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Radical_CNN | 91.12 | 92.34 | 91.73 |
| 2 | Tianzige_CNN | 90.16 | 92.58 | 91.36 |
| 3 | GLYNN | 91.93 | 92.42 | 92.18 |
| Models | Training Time (s/iter) | Inference Speed (s/iter) | Memory Usage (G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SoftLexicon | 129.64 | 17.75 | 14.58 |
| Bi-LSTM-CRF | 126.09 | 17.41 | 14.28 |
| Bi-LSTM-Attention-CRF | 129.00 | 17.68 | 14.27 |
| BERT-Bi-LSTM-CRF | 367 | 31 | 6.43 |
| RoBERTa-Bi-LSTM-CRF | 349 | 36 | 6.44 |
| WC-LSTM | 186.62 | 32.83 | 9.92 |
| LR-CNN | 196.71 | 23.24 | 6.42 |
| FLAT | 120.3 | 12.85 | 10.89 |
| MECT | 106 | 10.25 | 4.63 |
| PGLA-DCNER | 130.41 | 17.85 | 16.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Du, H.; Shen, W. Chinese Named Entity Recognition for Dairy Cow Diseases by Fusion of Multi-Semantic Features Using Self-Attention-Based Deep Learning. Animals 2025, 15, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060822
Lou Y, Gao M, Zhang S, Yang H, Wang S, He Y, Yang J, Yang W, Du H, Shen W. Chinese Named Entity Recognition for Dairy Cow Diseases by Fusion of Multi-Semantic Features Using Self-Attention-Based Deep Learning. Animals. 2025; 15(6):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060822
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Yongjun, Meng Gao, Shuo Zhang, Hongjun Yang, Sicong Wang, Yongqiang He, Jing Yang, Wenxia Yang, Haitao Du, and Weizheng Shen. 2025. "Chinese Named Entity Recognition for Dairy Cow Diseases by Fusion of Multi-Semantic Features Using Self-Attention-Based Deep Learning" Animals 15, no. 6: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060822
APA StyleLou, Y., Gao, M., Zhang, S., Yang, H., Wang, S., He, Y., Yang, J., Yang, W., Du, H., & Shen, W. (2025). Chinese Named Entity Recognition for Dairy Cow Diseases by Fusion of Multi-Semantic Features Using Self-Attention-Based Deep Learning. Animals, 15(6), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060822






