Effect of Temperature on the Early Development of Paralichthys olivaceus Otoliths
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Processing of Samples
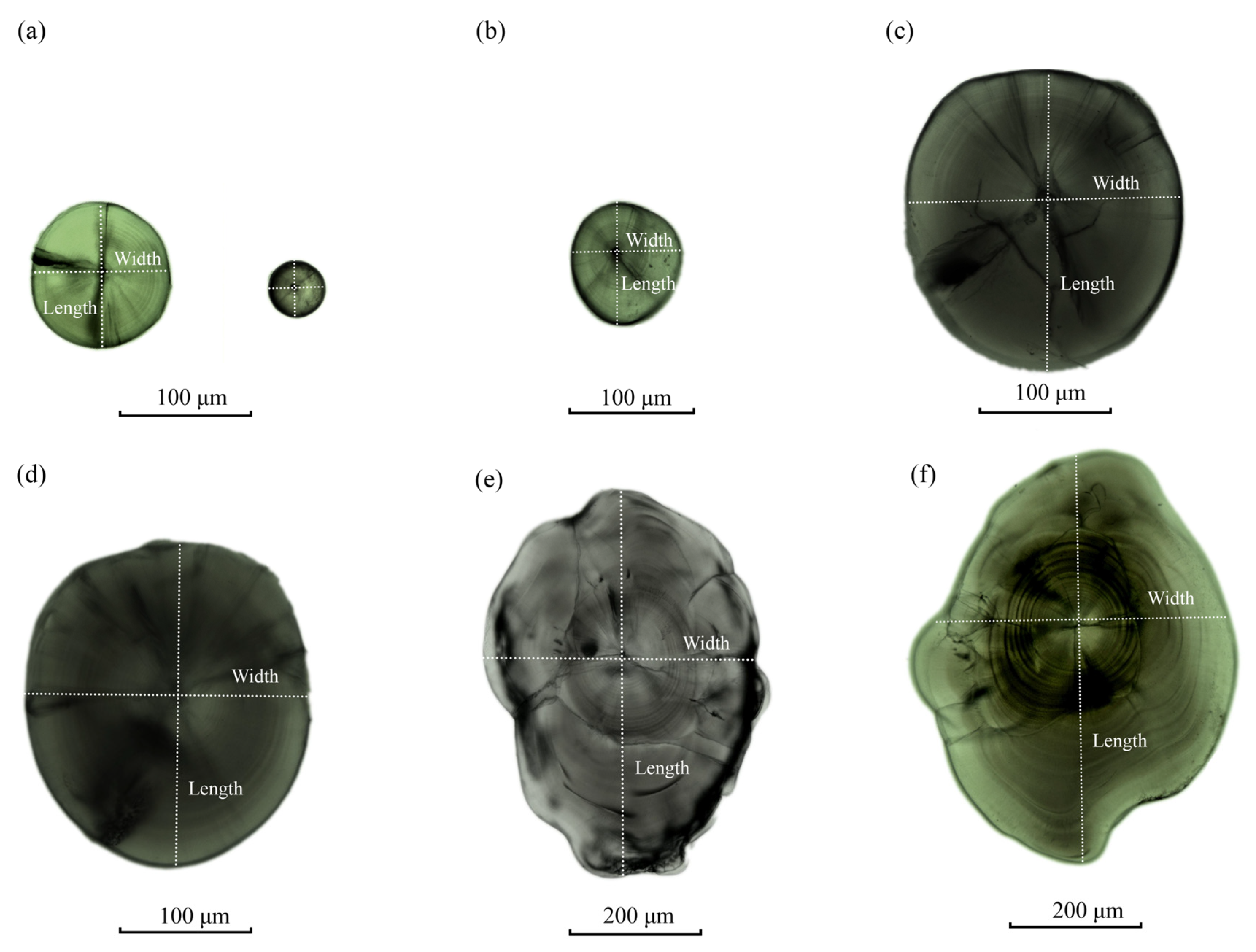
2.3. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
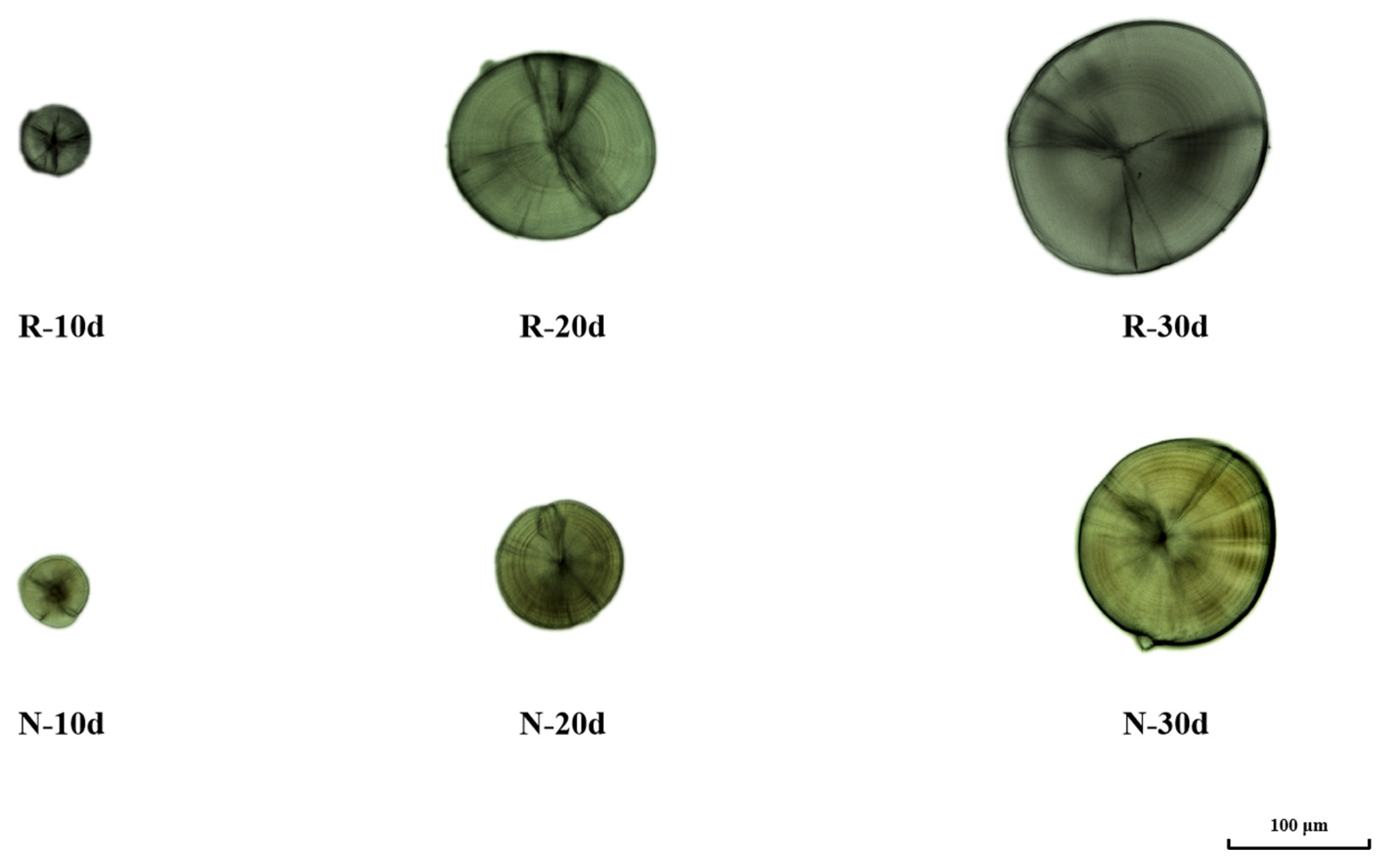
3.1. Effect of Temperature on the Microstructure of Otoliths
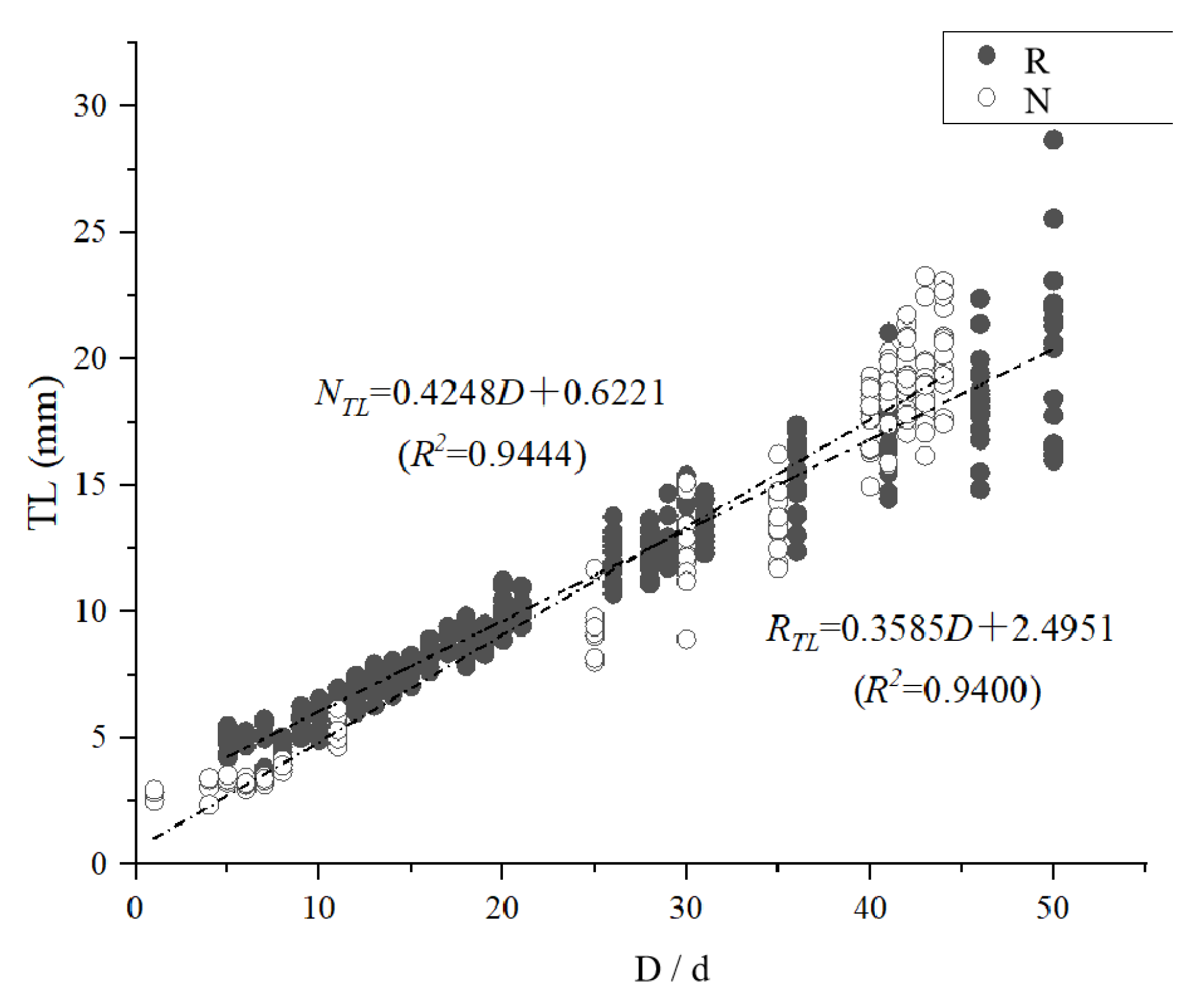
3.2. Temperature Effects on the Growth of Juvenile Fish
3.3. Effect of Temperature on the Time of Otolith Formation and Morphological Changes
3.4. Effect of Temperature on Otolith Growth and Development and Microstructure
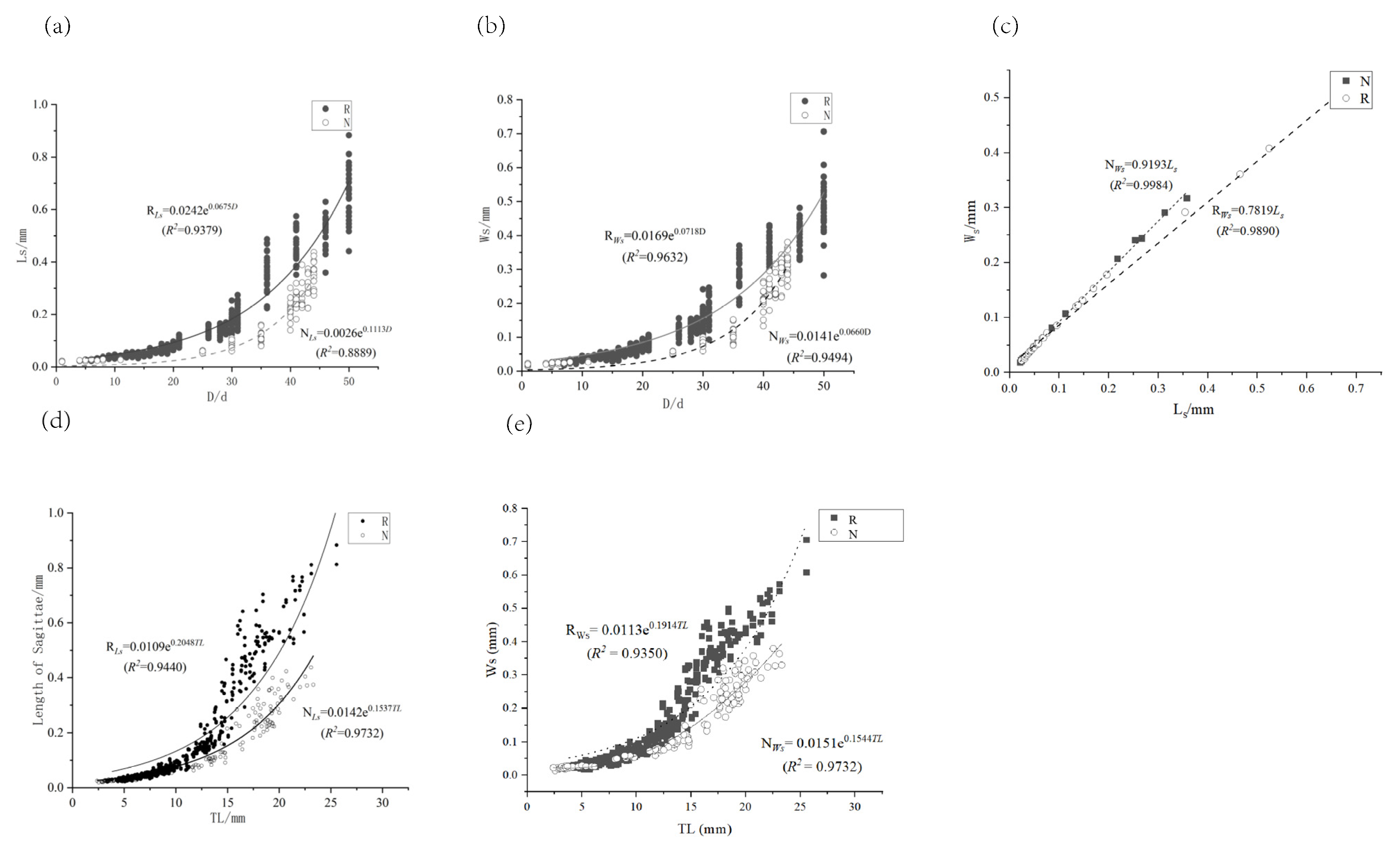
3.4.1. Effects of Different Temperature Modes on the Growth of Sagittal Otoliths
3.4.2. Effect of Different Temperature Patterns on Lapillus Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermann, T.W.; Duponchelle, F.; Castello, L.; Limburg, K.E.; Pereira, L.A.; Hauser, M. Harnessing the potential for otolith microchemistry to foster the conservation of Amazonian fishes. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2021, 31, 1206–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzhans, W.W.; Gerringer, M.E. Otoliths of the deepest-living fishes. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2023, 198, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, E.C. Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: Pathways, mechanisms and applications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 188, 263–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kikko, T.; Ishizaki, D.; Yodo, T.; Aino, S.; Kuwamura, K.; Okamoto, H.; Nemoto, M.; Yoneda, K.; Oue, N.; Sakai, A.; et al. Daily growth increments in otoliths of wild-caught honmoroko Gnathopogon caerulescens. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark Barkalow, S.L.; Brandenburg, M.A.; Platania, S.P. Otoliths Reveal Spawning Ecology and Early Life History of Sympatric Catostomids. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2020, 40, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloumi, N.; Doubleday, Z.A.; Gillanders, B.M. The effects of temperature and salinity on otolith chemistry of King George whiting. Fish. Res. 2017, 196, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Dou, S. Temperature and salinity effects on strontium and barium incorporation into otoliths of flounder Paralichthys olivaceus at early life stages. Fish. Res. 2021, 239, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.J.; Rowe, D.; Thorpe, J.E. Daily growth increments in the otoliths of Atlantic salmon parr, Salmo salar L., and the influence of environmental factors on their periodicity. J. Fish Biol. 1991, 39, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofelio, C.; Moyano, M.; Sswat, M.; Rioual, F.; Moullec, F.; Aguirre-Velarde, A.; Peck, M. Temperature and prey density drive growth and otolith formation of the world’s most valuable fish stock. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.A.; Hurst, T.P. Growth Rate, Ration, and Temperature Effects on Otolith Elemental Incorporation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fey, D.P.; Greszkiewicz, M. Effects of temperature on somatic growth, otolith growth, and uncoupling in the otolith to fish size relationship of larval northern pike, Esox lucius L. Fish. Res. 2021, 236, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladakis, G.; Kourkouta, C.; Somarakis, S.; Koumoundouros, G. Developmental Temperature Shapes the Otolith Morphology of Metamorphosing and Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758). Fishes 2022, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schismenou, E.; Palmer, M.; Giannoulaki, M.; Alvarez, I.; Tsiaras, K.; Triantafyllou, G.; Somarakis, S. Seasonal changes in otolith increment width trajectories and the effect of temperature on the daily growth rate of young sardines. Fish. Oceanogr. 2016, 25, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidoghli, A.; Won, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Farris, N.W.; Bai, S.C. Nutrition and Feeding of Olive Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus: A Review. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, O.; Watanabe, Y. Geographical dispersal and optimum release size of hatchery-reared Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus released in Ishikari Bay, Hokkaido, Japan. J. Sea Res. 1998, 40, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Paek, J.; Kim, D. Economic effectiveness of the olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) fry releasing program in Korea. Ocean Polar Res. 2010, 32, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Lv, Z.; Tang, X.; Yu, M. A comprehevensive, metabolomic and lipidomic analysis reveals the effect of temperature on flounder (paralichtys olivaceus). J. Therm. Biol. 2022, 104, 103203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Ferreira, S.; Ré, P.; Teodósio, M.A.; Santos, A.M.; Batista, H.; Baylina, N.; Garrido, S. Effect of Temperature on the Daily Increment Deposition in the Otoliths of European Sardine Sardina pilchardus (Walbaum, 1792) Larvae. Oceans 2021, 2, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidabadi, F.; Abdoli, A.; Tajbakhsh, F.; Nejat, F.; Avigliano, E. Unravelling the stock structure of the Persian brown trout by otolith and scale shape. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 96, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuset, V.M.; Otero-Ferrer, J.L.; Siliprandi, C.; Manjabacas, A.; Marti-Puig, P.; Lombarte, A. Paradox of otolith shape indices: Routine but overestimated use. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 78, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimori, A.; Khajooei, A.; Motamedi, M.; Hesni, M.A. Characteristics of sagittae morphology in sixteen marine fish species collected from the Persian Gulf: Demonstration of the phylogenetic influence on otolith shape. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 29, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, M.; Okamura, A.; Yamada, Y.; Hayasaka, S.; Tsukamoto, K. Evaluation of optimum temperature for the early larval growth of Japanese eel in captivity. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, J.; Sheng, X.; Chi, H.; Zhan, W. Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals Differential Immune Response to Hirame Novirhabdovirus (HIRRV) Infection in the Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) under Different Temperature. Biology 2023, 12, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Chu, Z. Effect of temperature on the growth, feeding performance, gonadal development, and nutritive compositions in the muscle of fry stream groupers, Acrossocheilus fasciatus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2024, 55, e13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S. Peptidomic analysis of digested products of surimi gels with different degrees of cross-linking: In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and absorption. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, S.S.; Sawant, P.B.; Chadha, N.K.; Prasad, K.P.; Muralidhar, A.P.; Syamala, K.; Xavier, K.A.M. Duration of stunting impacts compensatory growth and carcass quality of farmed milkfish, Chanos chanos (Forsskal, 1775) under field conditions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasburger, W.W.; Nicolls, D.; Hinds, C.M.; McNeel, K.W. The utility of juvenile sablefish otoliths in reconstructing life history and growth in the Gulf of Alaska. Fish. Res. 2023, 268, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Togoshi, S.; Yasue, N.; Takasuka, A. Seasonal variability in the otolith and somatic size relationship of Japanese anchovy larvae: Counter effects of somatic growth and temperature. Fish. Res. 2024, 275, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaszek, B.; Nowosielski, A.; Dbrowski, J.; Górecka, K.; Keszka, S.; Strzelczak, A. Fish size effect on sagittal otolith outer shape variability in round goby Neogobius melanostomus (Pallas 1814). J. Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 1520–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, K.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Song, Z.B. Otolith Microstructure Character Analysis between Wild-caught and Hatchery-breeding Myxocyprinus asiaticus. Sichuan J. Zool. 2017, 36, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.M.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, W.; Han, Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Xiao, Z.G.; Chen, W.Q.; Liu, P. Temperature Regulation Marking on Otolith in Release Populations of Chum Salmon. Chin. J. Fish. 2022, 35, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.B.; Chang, J.B.; Cao, W.X.; Xia, L.Q. Otolith microstructure of hatchery-reared and wild juveniles of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2003, 27, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommel, A.Y.; Pourfaraj, V.; Brauner, C.J.; McAdam, D.S.O. Evaluation of otolith microstructures for ageing of larval white sturgeon. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 78, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Gao, Q.; Dong, Y.; Dong, S. Effects of constant and diel cyclic temperatures on the liver and intestinal phospholipid fatty acid composition in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss during seawater acclimation. BMC Zool. 2021, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Bai, B. A review of molecular tagging measurement technique. Measurement 2021, 171, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeppky, A.R.; McDougall, C.A.; Anderson, W.G. Identification of Hatchery-Reared Lake Sturgeon Using Natural Elemental Signatures and Elemental Marking of Fin Rays. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2020, 40, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriel, C.; Permingeat, C.; Ventura, J.; Avellanal-Zaballa, E.; Bañuelos, J.; García-Moreno, I.; Gómez, A.M.; Lopez, J.C. BODIPYs as Chemically Stable Fluorescent Tags for Synthetic Glycosylation Strategies towards Fluorescently Labeled Saccharides. Chem.-Eur. J. 2020, 26, 5388–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, M.A.; Buckmeier, D.L.; Hamel, M.J.; Koch, J.D. Creating a Digital Repository of Calcified Structures from Known-Age Fishes, a Century in the Making. Fisheries 2022, 47, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, Q.; Jacquin, L.; Riem, L.; Pitout, M.; Perrault, A.; Cousseau, M.; Laffaille, P.; Jean, S. Intraspecific variability of responses to combined metal contamination and immune challenge among wild fish populations. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznar, M.; Stolarski, J.; Sikora, A.; Mazur, M.; Olesiak-Bańska, J.; Brach, K.; Ożyhar, A.; Dobryszycki, P. Fish Otolith Matrix Macromolecule-64 (OMM-64) and Its Role in Calcium Carbonate Biomineralization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 5808–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Time | Group | Average | T | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–30 d | N | 0.1848 | 2.274 | 0.598 |
| R | 0.2734 | |||
| 35–50 d | N | 0.5863 | 0.863 | 0.039 * |
| R | 0.3679 |
| Group | Time | Average | T | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ls | N | 0–30 d | 0.0017 | −13.827 | 0.182 |
| 35–50 d | 0.0162 | ||||
| R | 0–30 d | 0.0030 | −21.308 | 0.047 * | |
| 35–50 d | 0.0262 | ||||
| Ws | N | 0–30 d | 0.0016 | −15.490 | 0.321 |
| 35–50 d | 0.0147 | ||||
| R | 0–30 d | 0.0029 | −17.348 | 0.015 * | |
| 35–50 d | 0.0187 |
| Group | Time | Average | T | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ll | N | 0–30 d | 0.0056 | −11.847 | 0.614 |
| 35–50 d | 0.0043 | ||||
| R | 0–30 d | 0.0022 | −21.308 | 0.627 | |
| 35–50 d | 0.0284 | ||||
| Wl | N | 0–30 d | 0.0014 | −11.91 | 0.485 |
| 35–50 d | 0.0045 | ||||
| R | 0–30 d | 0.0019 | −17.348 | 0.009 ** | |
| 35–50 d | 0.0058 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, G.; Tang, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Yu, S.; Si, F. Effect of Temperature on the Early Development of Paralichthys olivaceus Otoliths. Animals 2025, 15, 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060814
Meng G, Tang J, Wang Q, Sun Z, Yu S, Si F. Effect of Temperature on the Early Development of Paralichthys olivaceus Otoliths. Animals. 2025; 15(6):814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060814
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Gao, Jiabao Tang, Qinglin Wang, Zhaohui Sun, Shanshan Yu, and Fei Si. 2025. "Effect of Temperature on the Early Development of Paralichthys olivaceus Otoliths" Animals 15, no. 6: 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060814
APA StyleMeng, G., Tang, J., Wang, Q., Sun, Z., Yu, S., & Si, F. (2025). Effect of Temperature on the Early Development of Paralichthys olivaceus Otoliths. Animals, 15(6), 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060814






