Pasture Heterogeneity Improves Donkey Welfare: Effects of Structural Variation, Species Diversity, and Sward Height on Herd Emotional States
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Assess how overall field-level habitat heterogeneity influences herd emotional state;
- Examine how individual components of habitat heterogeneity are associated with variation in emotional states.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Animals and Management
2.3. Habitat Assessment
2.3.1. Structural Variation
2.3.2. Species Abundance, Species Richness, and Sward Height
2.4. Donkey Welfare Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Habitat Heterogeneity and Donkey Emotional State
2.5.2. Components of Habitat Heterogeneity
3. Results
3.1. Scoring and Inter-Observer Agreement
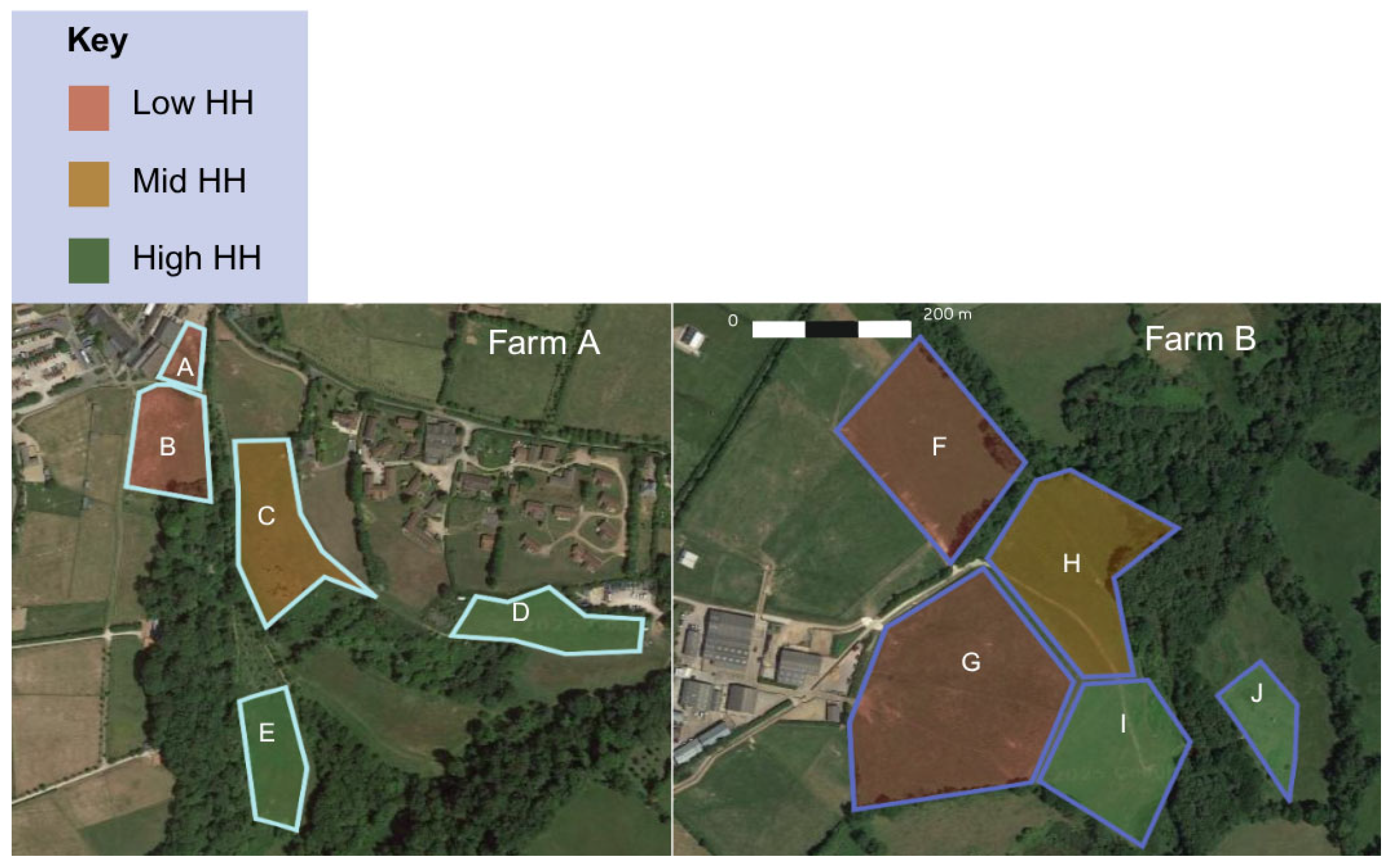
3.2. Habitat Heterogeneity Categorisation
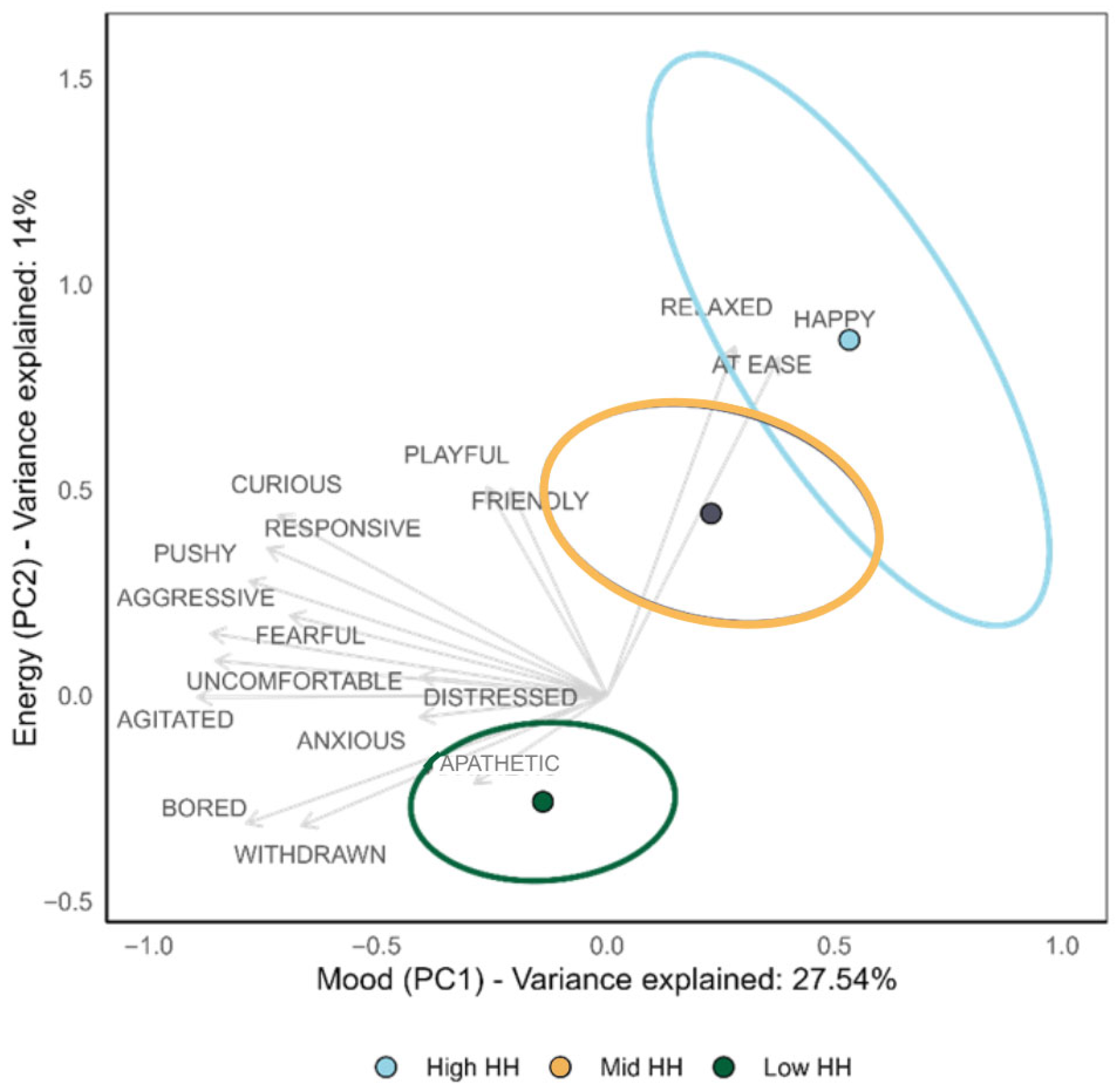
3.3. Habitat Heterogeneity and Donkey Emotional State
Multivariate Testing for QBA Scores
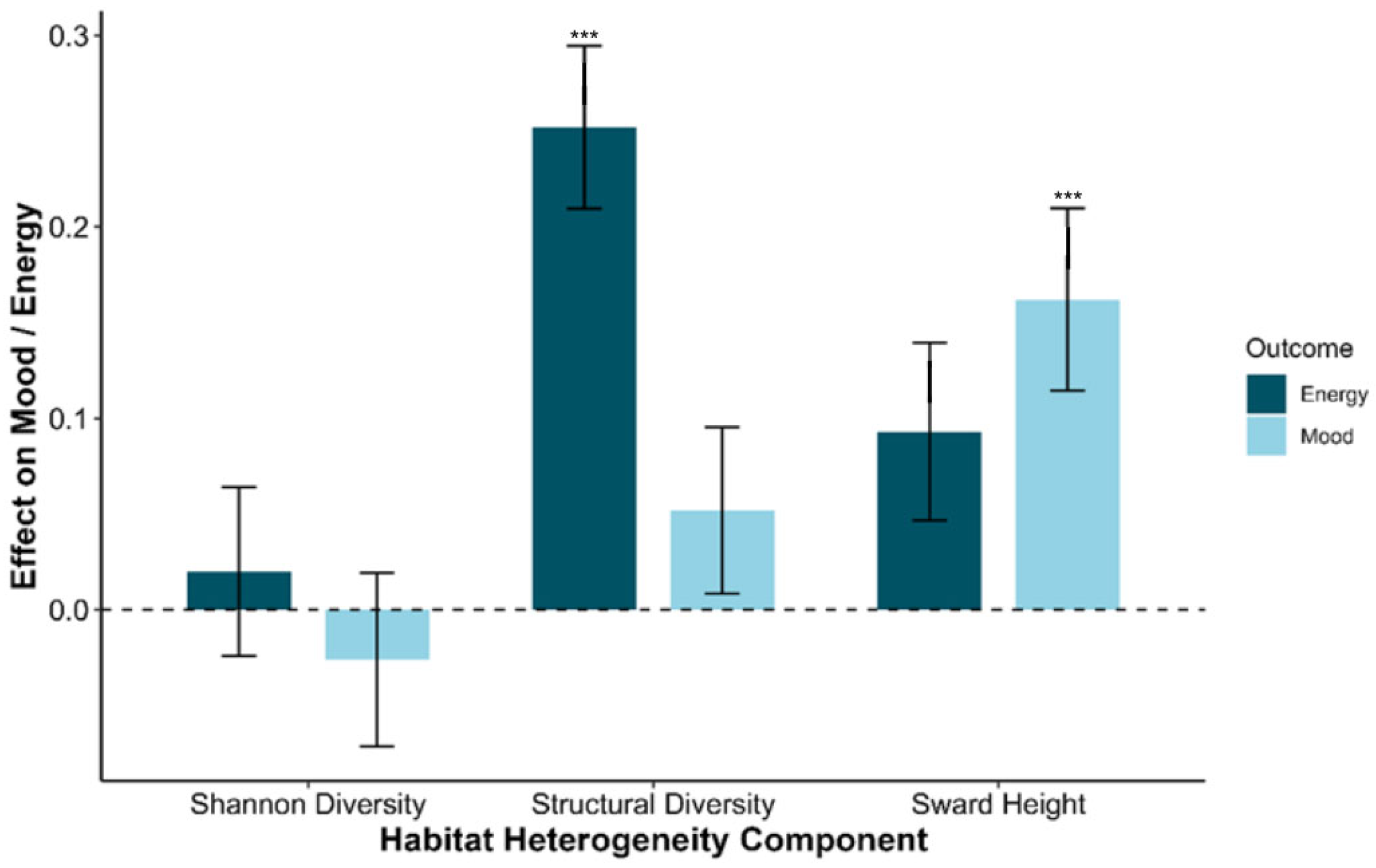
3.4. Components of Habitat Heterogeneity
3.5. Effect of Farm and Herd
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruet, A.; Arnould, C.; Levray, J.; Lemarchand, J.; Mach, N.; Moisan, M.-P.; Foury, A.; Briant, C.; Lansade, L. Effects of a temporary period on pasture on the welfare state of horses housed in individual boxes. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 228, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koknaroglu, H.; Akunal, T. Animal welfare: An animal science approach. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, S.S.; Shepherdson, D.; Lewis, K.; Prado, N.; Brown, J.L.; Lee, B.; Wielebnowski, N. Supporting Zoo Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus) Welfare and Herd Dynamics with a More Complex and Expanded Habitat. Animals 2021, 11, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, C.E.; Miller, L.J.; Schulte, B.A. Examination of enrichment using space and food for African elephants (Loxodonta africana) at the San Diego Zoo Safari Park. Anim. Welf. 2018, 27, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousing, T.; Wemelsfelder, F. Qualitative assessment of social behaviour of dairy cows housed in loose housing systems. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2006, 101, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, K.; Fukuizumi, H.; Kawamura, A.; Kase, C.; Uetake, K. Effects of browsing enrichment associated with the temperature–humidity index and landscaping trees in giraffes (Giraffa camelopardalis reticulata). J. Therm. Biol. 2022, 104, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, A.; Mantino, A.; Annecchini, F.; Cappucci, A.; Casarosa, L.; Turini, L.; Foggi, G.; Mele, M. Outcomes of a comparison between pastoral and silvopastoral management on beef cattle productivity, animal welfare and pasture depletion in a Mediterranean extensive farm. Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 97, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, G.H.M.; Liestøl, S.H.O.; Bøe, K.E. Effects of enrichment items on activity and social interactions in domestic horses (Equus caballus). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 129, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Rose, P.E. Assessing the impact of environmental enrichment on behavior in understudied armadillo species: A case study. Zoo. Biol. 2024, 43, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laméris, D.W.; Verspeek, J.; Depoortere, A.; Plessers, L.; Salas, M. Effects of Enclosure and Environmental Enrichment on the Behaviour of Ring-Tailed Lemurs (Lemur catta). J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2021, 2, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, C.S.; Cipreste, C.F.; Pizzutto, C.S.; Young, R.J. Review of the Effects of Enclosure Complexity and Design on the Behaviour and Physiology of Zoo Animals. Animals 2023, 13, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.W.; Zharkikh, T.; Ladewig, J.; Yasinetskaya, N. Social behaviour in stallion groups (Equus przewalskii and Equus caballus) kept under natural and domestic conditions. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2002, 76, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neindre, P.; Guémené, D.; Arnould, C.; Leterrier, C.; Faure, J.M.; Prunier, A. Space, Environmental Design and Behaviour: Effect of Space and Environment on Animal Welfare. 2004. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2016-10/ia_standards_oie_2003_2073_3l_en.pdf#page=143 (accessed on 23 November 2025).
- Villalba, J.J.; Manteca, X.; Vercoe, P.E.; Maloney, S.K.; Blache, D. Integrating Nutrition and Animal Welfare in Extensive Systems. In Nutrition and the Welfare of Farm Animals; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 135–163. [Google Scholar]
- Clancy, C.L.; Kubasiewicz, L.M.; Raw, Z.; Cooke, F. Science and Knowledge of Free-Roaming Donkeys—A Critical Review. J. Wildl. Manag. 2021, 85, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Statistical Database Crops and Livestock Products; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023; Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Cox, R.; Burden, F.; Proudman, C.J.; Trawford, A.F.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Demographics, management and health of donkeys in the UK. Vet. Rec. 2010, 166, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, T.; King, M.; Perkins, E.; McGowan, C.; Chubbock, S.; Hannelly, E.; Rogers, J.; Pinchbeck, G. An Exploration of Environmentally Sustainable Practices Associated with Alternative Grazing Management System Use for Horses, Ponies, Donkeys and Mules in the UK. Animals 2022, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, F.J.; Toribio, R.E.; Perez-Ecija, A. Metabolic and Endocrine Insights in Donkeys. Animals 2024, 14, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.; Boocock, H. Managing obesity and metabolic disease in donkeys. Practice 2025, 47, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.B.; De Blas Giral, I.; Thiemann, A.K.; Vázquez Bringas, F.J. Demography, preventative healthcare and reason for relinquishment of donkeys to an equine charity in the UK (2013–2015). Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, P.J.; Protos, P.; Houpt, K.A.; Van Soest, P. Chewing behaviour in the domestic donkey (Equus asinus) fed fibrous forage. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1998, 60, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G.; Pearson, R.A. A Review of the Factors Affecting the Survival of Donkeys in Semi-arid Regions of Sub-Saharan Africa. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2005, 37, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinder, M.I.; Krausman, P.R.; Hoffmann, R.S. Equus asinus. Mamm. Species 2006, 794, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, F.; Thiemann, A. Donkeys Are Different. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosyns, E.; Degezelle, T.; Demeulenaere, E.; Hoffmann, M. Feeding ecology of Konik horses and donkeys in Belgian coastal dunes and its implication for nature management. Belg. J. Zool. 2001, 131, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Couto, M.; Santos, A.S.; Laborda, J.; Nóvoa, M.; Ferreira, L.; de Carvalho, L.M. Grazing behaviour of Miranda donkeys in a natural mountain pasture and parasitic level changes. Livest. Sci. 2016, 186, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.A.; Archibald, R.F.; Muirhead, R.H. The effect of forage quality and level of feeding on digestibility and gastrointestinal transit time of oat straw and alfalfa given to ponies and donkeys. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 85, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.J. Some Factors Affecting the Digestible Energy Requirements and Dry Matter Intake of Mature Donkeys and a Comparison with Normal Husbandry Practices. 2010. Available online: https://era.ed.ac.uk/handle/1842/4817 (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Robin, C.A.; Ireland, J.L.; Wylie, C.E.; Collins, S.N.; Verheyen, K.L.P.; Newton, J.R. Prevalence of and risk factors for equine obesity in Great Britain based on owner-reported body condition scores. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, A.; Fernandez, E.B.; Rickards, K.; Harrison, A. Assessing quality of life and welfare of donkeys in the UK. Practice 2018, 40, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, M.; Herzon, I.; Särkijärvi, S.; Schreurs, C.; Myllymäki, M. Horse Welfare and Natural Values on Semi-Natural and Extensive Pastures in Finland: Synergies and Trade-Offs. Land 2017, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, J.A.; Tallowin, J.R.; Feber, R.E.; Asteraki, E.; Atkinson, P.; Fuller, R.; Brown, V. The management of lowland neutral grasslands in Britain: Effects of agricultural practices on birds and their food resources. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farruggia, A.; Pomiès, D.; Coppa, M.; Ferlay, A.; Verdier-Metz, I.; Le Morvan, A.; Bethier, A.; Pompanon, F.; Troquier, O.; Martin, B. Animal performances, pasture biodiversity and dairy product quality: How it works in contrasted mountain grazing systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 185, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, J.; Brose, U.; Grimm, V.; Tielbörger, K.; Wichmann, M.C.; Schwager, M.; Jeltsch, F. Animal species diversity driven by habitat heterogeneity/diversity: The importance of keystone structures. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, S.M. Review: Grazing preferences in sheep and cattle: Implications for production, the environment and animal welfare. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 90, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, R.; Provenza, F.; Kreuter, U.; Steffens, T.; Barnes, M. Multi-paddock grazing on rangelands: Why the perceptual dichotomy between research results and rancher experience? J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, G.; Cannas, A.; Gregorini, P. A review on the effects of part-time grazing herbaceous pastures on feeding behaviour and intake of cattle, sheep and horses. Livest. Sci. 2022, 263, 104982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigarelli, C.; Zuliani, A.; Battini, M.; Mattiello, S.; Bovolenta, S. Welfare Assessment on Pasture: A Review on Animal-Based Measures for Ruminants. Animals 2020, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.; Seganfreddo, S.; Galardi, M.; Mutinelli, F.; Normando, S.; Contalbrigo, L. Donkey behaviour and cognition: A literature review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 244, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minero, M.; Dalla Costa, E.; Dai, F.; Murray, L.A.M.; Canali, E.; Wemelsfelder, F. Use of Qualitative Behaviour Assessment as an indicator of welfare in donkeys. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 174, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoot, I.; Callebaut, J.; Demeulenaere, E.; Vandenberghe, C.; Hoffmann, M. Foraging behaviour of donkeys grazing in a coastal dune area in temperate climate conditions. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 92, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Met Office. Exeter Airport: Monthly Climate Average. 2024 National Meteorological Library and Archive, Met Office, UK. © Crown Copyright 2024. Available online: https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/research/climate/maps-and-data/location-specific-long-term-averages (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Cooke, A.S.; Mullan, S.M.; Morten, C.; Hockenhull, J.; Lee, M.R.F.; Cardenas, L.M.; Rivero, M.J. V-QBA vs. QBA—How Do Video and Live Analysis Compare for Qualitative Behaviour Assessment? Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 832239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, F.; De Rosa, G.; Grasso, F.; Wemelsfelder, F. Qualitative behaviour assessment of dairy buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 141, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyttens, F.A.M.; de Graaf, S.; Heerkens, J.L.T.; Jacobs, L.; Nalon, E.; Ott, S.; Stadig, L.; Van Laer, E.; Ampe, B. Observer bias in animal behaviour research: Can we believe what we score, if we score what we believe? Anim. Behav. 2014, 90, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, K.M.D.; Donald, R.D.; Lawrence, A.B.; Wemelsfelder, F. Qualitative Behavioural Assessment of emotionality in pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucougaray, G.; Bonis, A.; Bouzillé, J.-B. Effects of grazing by horses and/or cattle on the diversity of coastal grasslands in western France. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 116, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrage, N.; Şahin Demirbağ, N.; Hofmann, M.; Isselstein, J. Vegetation height of patch more important for phytodiversity than that of paddock. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, A.; Sayer, E.J.; Saiz, H.; Yuan, Z.; Ali, A. Species co-occurrence shapes spatial variability in plant diversity–biomass relationships in natural rangelands under different grazing intensities. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4390–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, C.; Lerer, A.; Anokwa, Y.; Tseng, C.; Brunette, W.; Borriello, G. Open Data Kit: Tools to Build Information Services for Developing Regions. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies and Development, London, UK, 13–16 December 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2022. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 23 November 2025).
- Wark, J.D.; Wierzal, N.K.; Cronin, K.A. Mapping Shade Availability and Use in Zoo Environments: A Tool for Evaluating Thermal Comfort. Animals 2020, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Louis, A.; Côté, S.D. Foraging behaviour at multiple temporal scales in a wild alpine equid. Oecologia 2011, 169, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleurance, G.; Edouard, N.; Collas, C.; Duncan, P.; Farruggia, A.; Baumont, R.; Lecomte, T.; Dumont, B. How do horses graze pastures and affect the diversity of grassland ecosystems? EAAP Sci. Ser. 2012, 132, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Tuñon, G.; Kennedy, E.; Horan, B.; Hennessy, D.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Kemp, P.; Brennan, A.; O’Donovan, M. Effect of grazing severity on perennial ryegrass herbage production and sward structural characteristics throughout an entire grazing season. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.F.; Parsons, A.J.; Cosgrove, G.P.; Barker, D.J.; Marotti, D.M.; Venning, K.J.; Rutter, S.M.; Hill, J.; Thompson, A.N. Impacts of Spatial Patterns in Pasture on Animal Grazing Behavior, Intake, and Performance. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süss, K.; Schwabe, A. Sheep versus donkey grazing or mixed treatment: Results from a 4-year field experiment in Armerio-Festucetum trachyphyllae sand vegetation. Phytocoenologia 2007, 37, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.; Nota, G.; Viterbi, R.; Mainetti, A.; Enri, S.R.; Lonati, M.; Lombardi, G.; Pittarello, M. Foraging behaviour of donkeys in encroached pastures in Gran Paradiso National Park, Italy. Agrofor. Syst. 2025, 99, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, J.; Fernàndez-Martínez, J.; Araus, J.L. Managing abandoned Mediterranean mountain landscapes: The effects of donkey grazing on biomass control and floral diversity in pastures. Catena 2023, 233, 107503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoot, I.; Vandenberghe, C.; Bauwens, D.; Hoffmann, M. Grazing behaviour of free-ranging donkeys and Shetland ponies in different reproductive states. J. Ethol. 2005, 23, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, D.; Komainda, M.; Tonn, B.; Harbers, J.; Grinnell, N.A.; Isselstein, J. The Effect of Grazing Intensity and Sward Heterogeneity on the Movement Behavior of Suckler Cows on Semi-natural Grassland. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 639096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, B.; Schall, P.; Bässler, C. Achieving structural heterogeneity and high multi-taxon biodiversity in managed forest ecosystems: A European review. Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 34, 3327–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
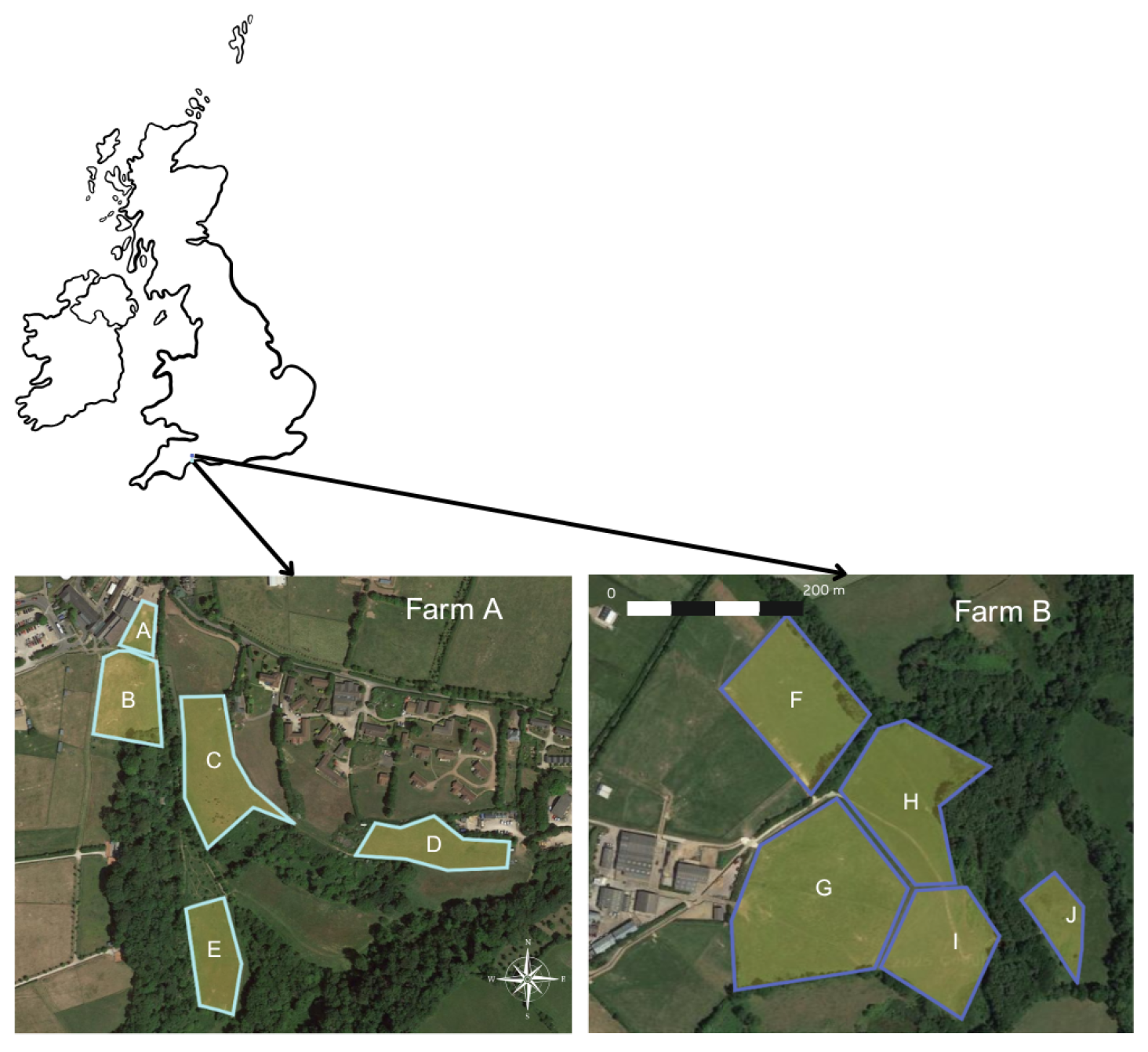
| Field | Donkeys Grazed | Browse Access | Area (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | End of July | No | 1538 |
| B | Early May | No | 6604 |
| C | End of August | Minimal | 9943 |
| D | Mid-May | Yes | 6433 |
| E | Early June | Yes | 6240 |
| F | Mid-June, Mid-July | Yes | 17,908 |
| G | Early June, Late July and August | Yes | 31,426 |
| H | Late May | Yes | 17,570 |
| I | Late May, Late June | Yes | 14,462 |
| J | Mid July | Yes | 5406 |
| Herd | Farm | Herd Size | Age Range (Average) | Breed | Sex | Median Weight (kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Miniature | Mare | Gelding | |||||
| 1 | A | 53 | 3–21 (14.3) | 49 | 4 | 34 | 19 | 187.00 |
| 2 | B | 90 | 5–25 (14.7) | 86 | 4 | 46 | 44 | 193.05 |
| 3 | B | 72 | 6–24 (14.9) | 72 | 0 | 34 | 38 | 196.71 |
| Low HH | Mid HH | High HH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural variation | 1.80 (1.76–1.84) | 2.74 (2.64–2.84) | 3.16 (3.09–3.23) |
| Sward height (cm) | 12.25 (11.69–12.81) | 7.40 (6.98–7.82) | 19.98 (18.99–20.97) |
| Shannon’s diversity | 1.10 (1.08–1.12) | 1.27 (1.22–1.32) | 1.24 (1.19–1.29) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fitts, J.; Kubasiewicz, L.M.; Norris, S.L.; Worth, S.; Watson, T.; Angell, R.L.; Steer, M.D.; Lintott, P. Pasture Heterogeneity Improves Donkey Welfare: Effects of Structural Variation, Species Diversity, and Sward Height on Herd Emotional States. Animals 2025, 15, 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233421
Fitts J, Kubasiewicz LM, Norris SL, Worth S, Watson T, Angell RL, Steer MD, Lintott P. Pasture Heterogeneity Improves Donkey Welfare: Effects of Structural Variation, Species Diversity, and Sward Height on Herd Emotional States. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233421
Chicago/Turabian StyleFitts, Jessie, Laura M. Kubasiewicz, Stuart L. Norris, Sarah Worth, Tamlin Watson, Ruth L. Angell, Mark D. Steer, and Paul Lintott. 2025. "Pasture Heterogeneity Improves Donkey Welfare: Effects of Structural Variation, Species Diversity, and Sward Height on Herd Emotional States" Animals 15, no. 23: 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233421
APA StyleFitts, J., Kubasiewicz, L. M., Norris, S. L., Worth, S., Watson, T., Angell, R. L., Steer, M. D., & Lintott, P. (2025). Pasture Heterogeneity Improves Donkey Welfare: Effects of Structural Variation, Species Diversity, and Sward Height on Herd Emotional States. Animals, 15(23), 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233421






