Silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus) Aquaculture: Advances, Bottlenecks, and Future Strategies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biological Characteristics of P. argenteus
3. Germplasm Resource Characteristics of P. argenteus
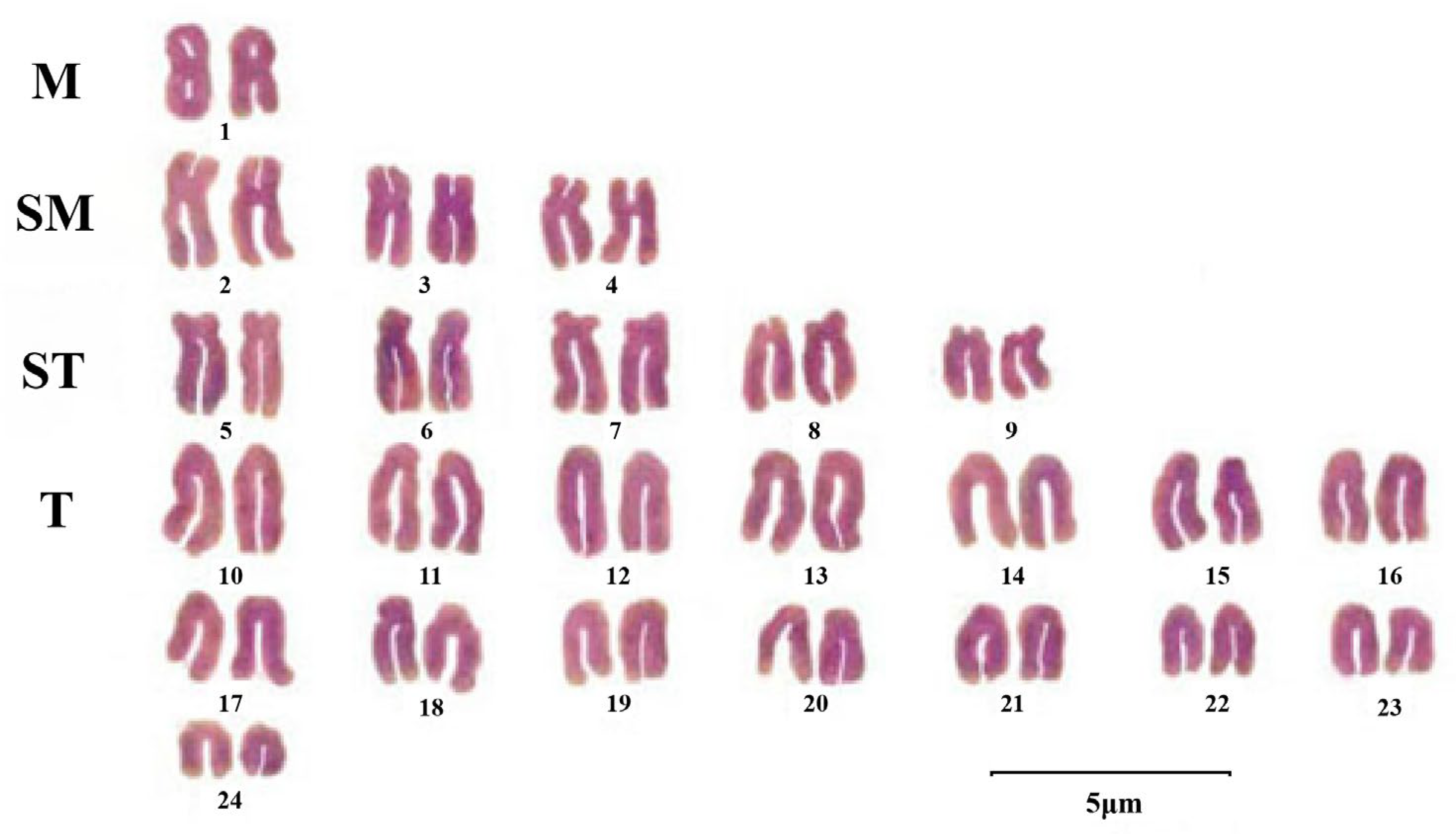
3.1. Cytogenetics
3.2. Biochemical Genetics
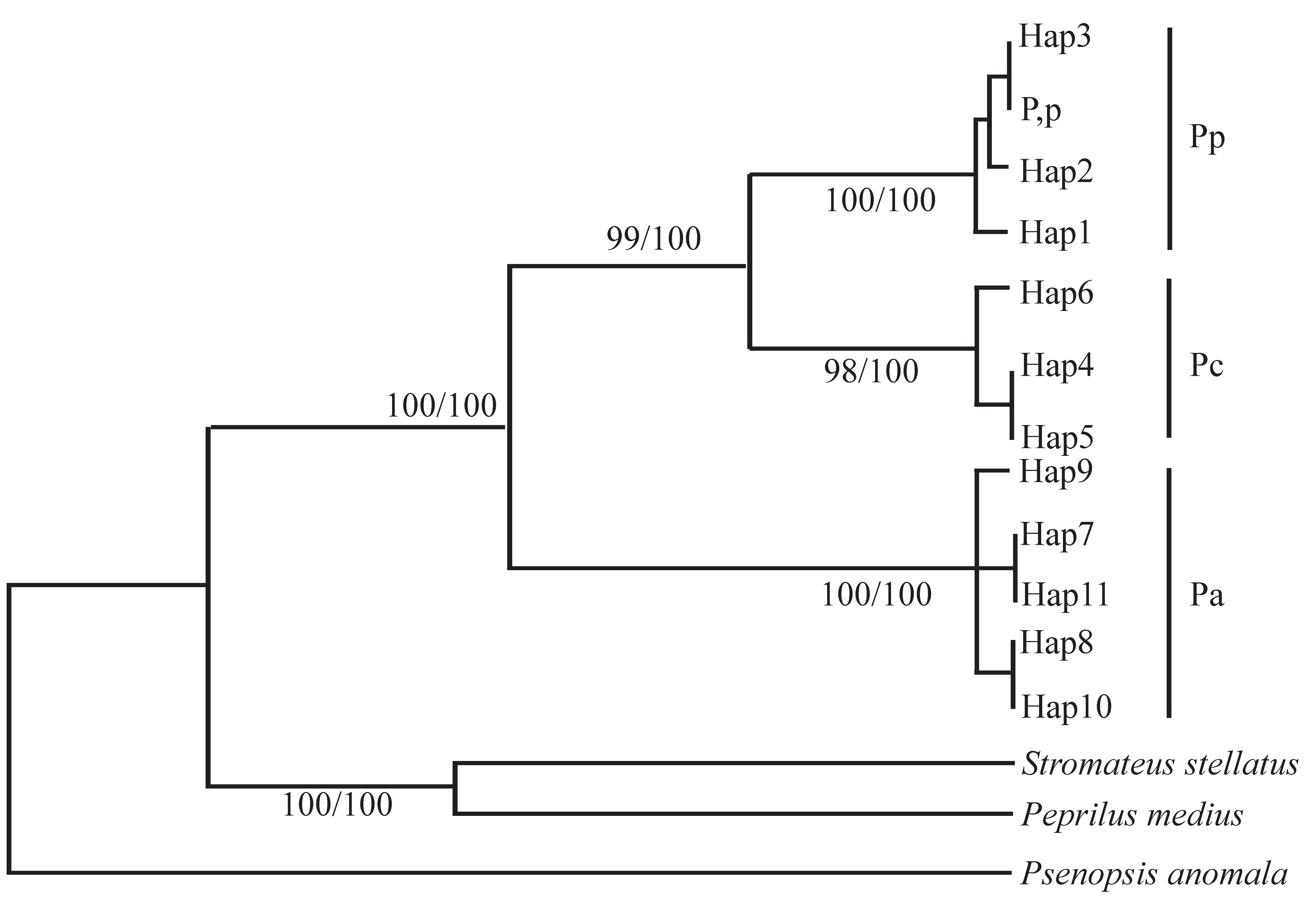
3.3. Molecular Genetics and Genomics
4. Development Process of Artificial Breeding Technology
4.1. Overseas Research Progress
4.2. Domestic Research Progress
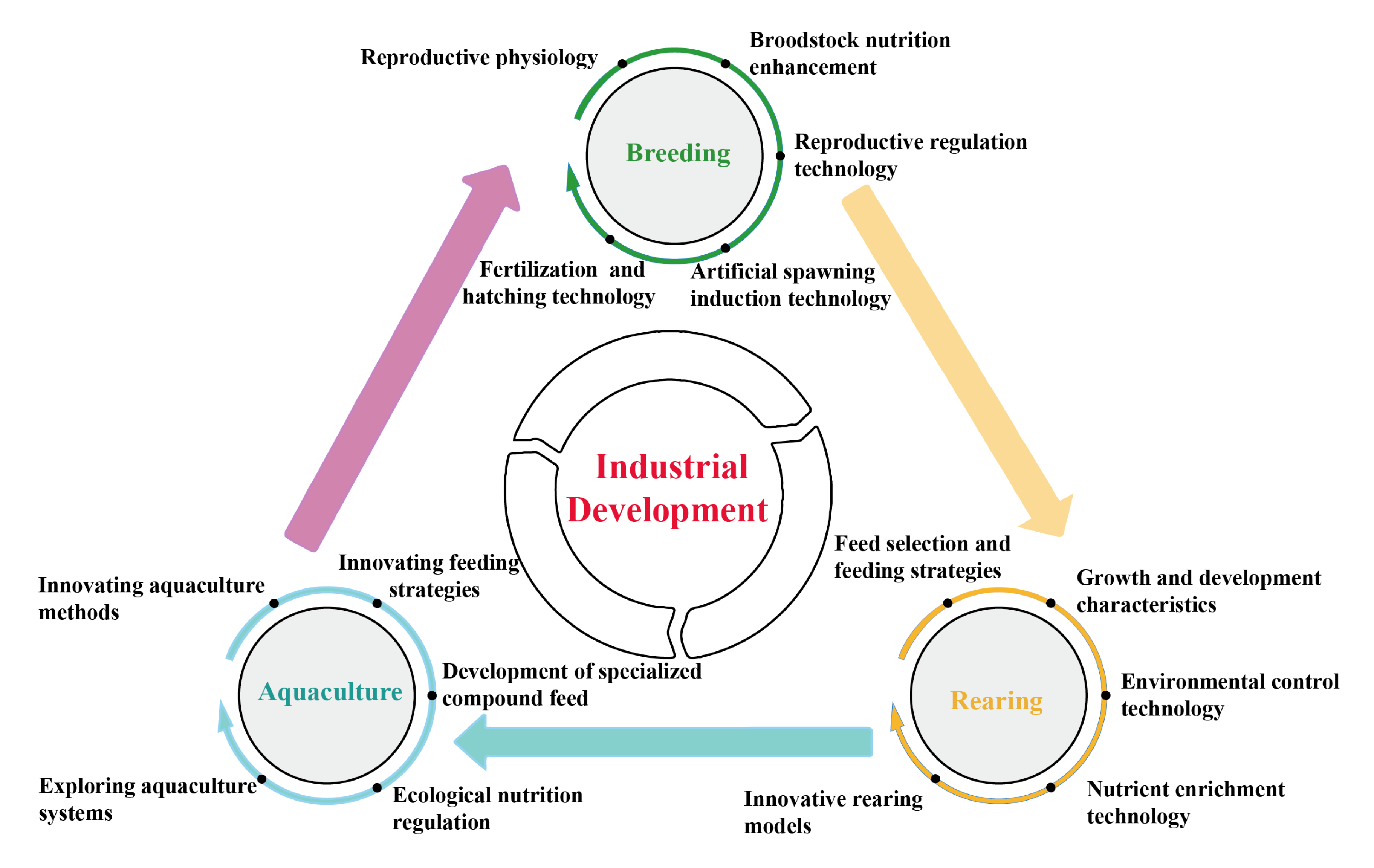
5. Current Status of Industrial Technology Development in P. argenteus
5.1. Broodstock Cultivation Techniques
5.2. Artificial Breeding and Larval Rearing Technology
5.3. Nutritional Physiology and Feed Development
5.4. Environmental Physiology and Stress Adaptation Mechanisms
5.5. Disease Control and Prevention
5.6. Innovation and Development of Aquaculture System
6. Bottlenecks in Industrial Development
6.1. Unique Biological Characteristics Lead to Great Difficulties in Aquaculture
6.2. Lack of Stable Supply of High-Quality Broodstock
6.3. Slow Growth Rates and Suboptimal Harvest Size
6.3.1. Overall Small Size of Farmed P. argenteus
6.3.2. Prevalence of Precocious Maturation
6.3.3. High Difficulty in Genetic Improvement of Germplasm
6.4. Lagging Development of Specialized Compound Feeds
6.5. Inadequate System for Integrated Disease Control
6.6. Lack of Standardized Aquaculture Protocols
7. Core Recommendations for Industrial Development
7.1. Elucidate the Mechanisms Underlying Specific Biological Traits and Develop Targeted Aquaculture Techniques
7.2. Establishment of a Superior Germplasm Resources Base
7.2.1. Systematic Collection and Conservation of Germplasm
7.2.2. Construction of Aquatic Original and Improved Strain Breeding Farms
7.3. Seedling Industry Innovation and Breeding of High-Yield New Varieties
7.3.1. Deciphering the Mechanism of Key Economic Traits
7.3.2. Creation of Intensive and High-Yield New Varieties
7.4. Development of Efficient Artificial Compound Feeds
7.4.1. Building a Comprehensive Nutritional Requirement Database
7.4.2. Development of Commercial Series of Compound Feeds
7.5. Establishment of a Precision Disease Prevention and Control System
7.5.1. Analysis of Pathogenic Mechanisms of Aquatic Pathogens
7.5.2. Establishment of an Integrated Prevention and Control Technology System
7.6. Establishment of a Standardized Aquaculture Technology System
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Status of Farming and Promotion by Major Domestic Enterprises (or Aquaculture Platforms)
- Xiangshan Harbor Aquatic Seed Co., Ltd. (Ningbo, China).
- 2.
- Ningbo Yuanfang Technology Co., Ltd. (Ningbo, China).
- 3.
- Guoxin 101
- 4.
- Donghai No.1
References
- Zhao, F.; Shi, Z.; Zhuang, P. Advance on reproductive biology and artificial breeding technology of silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. Mar. Sci. 2010, 34, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.; Ni, H.; Li, L.; Zheng, C. On the change of the ovary in annual cycle of silver pomfret Stromateoides argenteus from the East China Sea. J. Fish. China 1989, 13, 316–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Fisheries and Fishing Administration; Ministry of Agriculture, China. China Fisheries Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, W. Research progresses of resource biology of important marine pelagic food fishes in China. J. Fish. China 2014, 38, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z. Breeding Theory and Culture Technology of Silver Pomfret; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, D. Morphological and molecular functional evidence of the pharyngeal sac in the digestive tract of silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ni, J.; Hou, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S.; Xu, W. Morphology, histological structure characteristics and digestive enzyme activities of the digestive tract of Pampus argenteus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 643–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Du, C.; Gao, X.; Ni, J.; Wang, Y.; Hou, C.; Zhu, J.; Tang, D. Changes in the histology and digestive enzyme activity during digestive system development of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadzie, B.S.; Abou-Seedo, F.; Al-Qattan, E. The food and feeding habits of the silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen), in Kuwait waters. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2000, 16, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Feeding ecology of Pampus argenteus in the southern waters of the Yellow Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2013, 34, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Shi, Z.; Lian, S.; Peng, S. Alternations in the liver metabolome, skin and serum antioxidant function of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) is induced by jellyfish feeding. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lian, S.; Yue, Y.; Gao, Q.; Peng, S. Dietary jellyfish affect digestive enzyme activities and gut microbiota of Pampus argenteus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhuang, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, C. Medusa consumption and prey selection of silver pomfret Pampus argenteus juveniles. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Wang, J. Feeding habits of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) in East China Sea based on stable isotope techniques. Chin. J. Ecol. 2011, 30, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, L.; Ling, J. Advances on the studies of reproductive biology and artificial breeding technology in silver pomfret Pampus argenteus. Mar. Fish. 2005, 27, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Qin, C.; Yu, C.; Hu, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y. Determination of the timing of early gonadal differentiation in silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 261, 107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Peng, S. On the karyotype in Pampus argenteus. Mar. Fish. 2018, 40, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, X.; Zou, J. Advances in karyotype and chromosome banding studies of marine fish in China. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2007, 26, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K. Chromosome Samples Preparation and Karyotype Analysis of Pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Prog. Fish. Sci. 2017, 38, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Gao, Q.; Shi, Z. Differential expression of 4 kinds of isozyme in different tissues of Pampus argenteus. Mar. Fish. 2017, 39, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Zhao, F.; Meng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhuang, P.; Zhao, Y. Phylogenetic relationships of Pampus inferred from mitochondrial cytochrome b sequences. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2009, 30, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, L.; Shi, Z.; Ma, C. Sequence variation and molecular phylogeny of mitochondrial COI gene segments from three pomfret species. J. Fish. Sci. China 2008, 3, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Hou, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, H. Genetic diversity of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) populations from the China Sea based on mitochondrial DNA control region sequences. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2009, 37, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Hou, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, F. Genetic diversity of three wild silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) populations based on COI gene sequences. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2009, 18, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Dong, Y.; Zhuang, P.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z. Genetic diversity of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) in the Southern Yellow and East China Seas. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Genetic Diversity of Pampus argenteus Different Generations and Screening of Genes Related to Growth Performance. Master’s Thesis, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Peng, S.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Z. Bioinformatic analysis of SSR markers based on RNA-seq of Pampus argenteus. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Herrera-Ulloa, A.; Loh, K.; Xu, K. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the silver pomfret Pampus argenteus. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Two high quality chromosome-scale genome assemblies of female and male silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mito, S. On the egg development and prelarval stages of silver pomfret with reference to its spawning in the Seto Inland Sea. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1967, 33, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadzie, S.; Abou-Seedo, F.; Al-Shallal, T. The onset of spawning in the silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen), in Kuwait waters and its implications for management. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 1998, 5, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadzie, S.; Abou-Seedo, F.; Al-Shallal, T. Reproductive biology of the silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen), in Kuwait waters. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2000, 16, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatar, S.; Lone, K.; Abu-Rezq, T.; Yousef, A. Spawning frequency, fecundity, egg weight and spawning type of silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen) (Stromateidae), in Kuwait waters. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2004, 20, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdul-Elah, K.; Almatar, S.; Abu-Rezq, T.; James, C. Development of hatchery technology for the silver pomfret Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen): Effect of microalgal species on larval survival. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.; Almatar, S. Potential of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) as a new candidate species for aquaculture. Ichthyol. Res. 2008, 47, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad Hossain, M.; Almatar, S.M.; James, C.M. Optimum dietary protein level for juvenile silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2010, 41, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Almatar, S.; James, C.; Al-Yaqout, A.; Yaseen, S. Seasonal variation in fatty acid composition of silver pomfrets, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen), in Kuwait waters. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, I.; Al-Marzouk, A.; James, C.; Almatar, S.; Al-Gharabally, H.; Qasem, J. Outbreak of natural Streptococcosis in hatchery produced silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus Euphrasen) larvae in Kuwait. Aquaculture 2012, 330, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdul-Elah, K.; Hossain, M.; Akatsu, S. Recent advances in artificial breeding and larval rearing of silver pomfret Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen 1788) in Kuwait. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5808–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, L.; Gao, L.; Yu, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, B.; Fu, R. Feeding habits and growth characteristics of larva and juvenile of Pampus argenteus under artificial rearing condition. Mar. Fish. Res. 2007, 28, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Yin, F. Observation of embryonic, larval and juvenile development in Pampus argenteus offspring. J. Fish. Sci. China 2011, 18, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesh, A.S.; El-Nahla, A.M.; Aly, S.M.; Badran, M.F. Role of vitamin E supplementation on the reproductive and growth performance, hormonal profile and biochemical parameters of female hybrid red tilapia. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 40, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, H. Artificial insemination and incubation of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) from Zhoushan fishing ground. Fish. Mod. 2009, 36, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Shi, Z.; Wang, J. Effects of different diets on weight gain, hepatic lipase and antioxidant enzyme of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Wang, J. Selection of diet for culture of juvenile silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Gao, Q.; Shi, Z.; Wang, J. Effects of Dietary Substitution of Fish Oil by Soybean Oil on the Serum Lysozyme Activity and Tissue Antioxidant Capacity in Juvenile Silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Prog. Fish. Sci. 2017, 38, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, M.; Yan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Xu, S.; Yan, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y. Effects of supplemental medusa (Rhopilema esculentum) on intestinal microbiota and metabolites in silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). J. Fish Biol. 2025, 106, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Gao, Q.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Yin, F.; Zhang, Y. Effect of dietary n − 3 LC-PUFAs on plasma vitellogenin, sex steroids, and ovarian steroidogenesis during vitellogenesis in female silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) broodstock. Aquaculture 2015, 444, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J. Changes intissue antioxidant levels in silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) during vitellogenesis and the response to dietary n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Fish. Sci. China 2016, 23, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J. Dietary n-3 LC-PUFA s affect lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and fatty acid synthase (FAS) activities and mRNA expression during vitellogenesis and ovarian fatty acid composition of female silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) broodstock. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Le, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xu, S.; He, S.; Yan, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y. The effect of Schizochytrium sp. on growth, fatty acid profile and gut microbiota of silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Wang, J. Effects of increasing dietary vitamin C on serum lysozyme activity and antioxidant ability of tissues in Pampus argenteus. South China Fish. Sci. 2013, 9, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Xiao, C.; Min, M.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Shi, Z. Effects of probiotics dietary supplementation on growth performance; innate immunity and digestive enzymes of silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2016, 50, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ding, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Dietary effects of vitamin C on antioxidant capacity, intestinal microbiota and the resistance of pathogenic bacteria in cultured Silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Q.; Shi, Z. Effects of acute temperature stress on antioxidant enzyme activities and immune indexes of juvenile Pampus argenteus. Mar. Fish. 2015, 37, 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Xie, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Z. Effect of acute temperature stress on metabolic enzymes, ion enzymes and concentration of ion in serum of juvenile Pampus argenteus. South China Fish. Sci. 2016, 12, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Xie, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Q. Effects of Temperature Stress on Activities of Digestive Enzymes and Serum Biochemical Indices of Pampus argenteus Juveniles. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2016, 37, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Hu, J.; Lin, Z. Effects of body weight, temperature, and daily ti me periods on oxygen consumption rate of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Aquac. Res. 2025, 2025, 1513694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q. Effects of salinity on serum osmolality, catalase and gill ion-regulatory enzyme activities in silver pomfret. J. Fish. China 2013, 37, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Peng, S.; Shi, Z. Effects of low salinity stress on the antioxidant enzyme activities in juvenile Pampus argenteus liver and the APTase activities in its gill and kidney. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1059. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z. The effects of salinity on Na+/K+-atpase activity and plasma osmoregulatory hormone concentration in silver pomfret Pampus argenteus. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2013, 44, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Sun, P.; Yin, F.; Wang, J. Effects of breeding density on the growth and tissues biochemical indices of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Lin, S.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Yin, F. Effects of rearing density on growth rate and digestive enzyme activity of juvenile Pampus argenteus. Mar. Fish. 2013, 35, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Zhu, X.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, D. Effects of breeding density on the growth, metabolic enzyme activity and related gene expression level of juvenile Pampus argenteus. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2020, 39, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Wang, J. Effect of transportation stress on serum cortisol, glucose, tissue glycogen and lactate of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). J. Fish. China 2011, 35, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Yin, F.; Sun, P. Survival of Juvenile Silver Pomfret, Pampus argenteus, Kept in Transport Conmditions in Different Densities and Temperatures. Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2012, 64, 20653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jacques, K.; Gu, W.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S. Immune response of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) to Amyloodinium ocellatum infection. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 2111–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Xu, S.; Guo, C. Study on tolerance, tissue damage and oxidative stress of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) under copper sulfate, formaldehyde and freshwater stress. Aquaculture 2025, 599, 742134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Jiang, L.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Investigating the interplay between Cryptocaryon irritans ectoparasite infection and the immune responses of the head kidney in silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, X.; Yue, X.; Cui, H.; Huang, W.; Ma, R.; Jiang, J.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Outbreak of Cryptocaryon irritans infection in silver pomfret Pampus argenteus cultured in China. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2023, 154, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y. Histopathology, immunoenzyme activity and transcriptome analysis of immune response in silver pomfret infected by cryptokaryon (Cryptorchidism irritant). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 136, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Li, X.; Yue, X.; Gouife, M.; Huang, K.; Chen, S.; Ma, R.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, S.; Jin, S. Transcriptome profiling and differential expression analysis of the immune-related genes during the acute phase of infection with Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae in silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 131, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Yan, K.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, D. Immune response of silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) to Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae: Virulence factors might induce immune escape by damaging phagosome. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lei, J.; Huang, B.; Liang, Y. The development state and prospect of land-based industrial mariculture in China. Fish. Mod. 2015, 42, 1–5+10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Gao, Q.; Qin, G.; Peng, S.; Xie, N.; Shi, Z. Effects of Antarctic krill meal replacing fish meal on growth performance, gonadal index, amino acid and fatty acid composition in muscle of large size Pampus argenteus. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 931, 4877–4884. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Shi, Z. Effects of Antarctic krill powder on growth, non-specific immunity and antioxidant functions of Pampus argenteus juveniles. Mar. Fish. 2019, 41, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
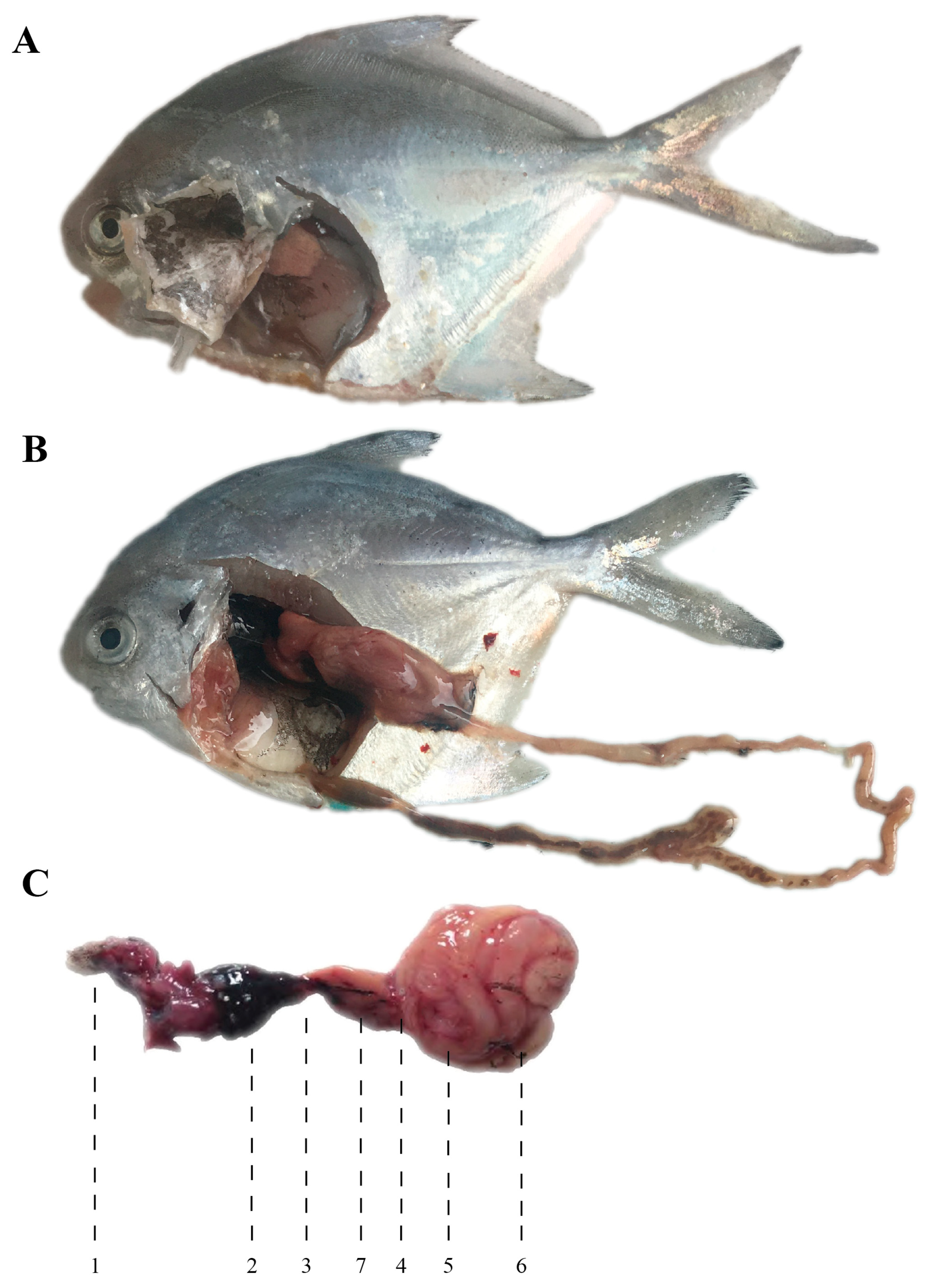


| Region | Specific Areas/Countries |
|---|---|
| Domestic (China) | Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea |
| International | Coastal waters from North Korea to Japan |
| Bay of Bengal (India) | |
| Persian Gulf (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia) |
| Environmental Factor | Optimal Range | Tolerance Range |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 25–28 | 14–32 |
| Salinity (‰) | 20–25 | 10–36 |
| Isozyme | Spleen | Liver | Muscle | Heart | Kidney | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EST | 1 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 30 |
| LDH | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 16 |
| GDH | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| ADH | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Total | 5 | 18 | 12 | 15 | 11 | 61 |
| Country | Research Period | Key Achievements | Larval Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 1960s | First artificial insemination and detailed description of embryonic and larval development [30] | / |
| Kuwait | before 2010 | Identified spawning season, fecundity, and reproductive characteristics; improved larval rearing survival from 1.5% to 3.6–4.2%; first successful production from cultured broodstock | 3–4% (offspring); 3.6–4.2% (38-day larvae) [31,32,33,34,35] |
| Kuwait | after 2010 | Continued research on broodstock nutrition and management; examined fertilization rate and larval survival | <50% cumulative survival within 24 days post-hatching [36,37,38,39] |
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Hormone Regimen | 2-injection protocol: HCG + LRH-A + DOM (in physiological saline) |
| Injection Protocol | First injection: 20% of total dose; second injection: remaining 80% after 12 h |
| Injection Site | Base of the pectoral fin |
| Female-to-Male Ratio | 1:1 (dry fertilization) |
| Water Quality for Fertilization | Temperature: 14–18 °C, Salinity: 28–33, Dissolved oxygen: ≥6 mg/L, Light: ≤500 lx |
| Water Quality for Larval Rearing | Temperature: 18–24 °C, Salinity: 28–34, Dissolved oxygen: >5 mg/L, Light: 500–2000 lx |
| Fry Density | 15,000–20,000 individuals/m3 |
| Water Exchange (Post-Fry) | 50% daily from day 6–25; 100–140% daily from day 26 onward |
| Feed Protocol | Rotifers (15–20 individuals/mL), Artemia nauplii (3–7 individuals/mL), copepods (1–3 individuals/mL), compound feed (5–10 particles/mL) |
| Dietary Treatment | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Four Diets (fresh fish meat; fresh fish meat mixed with formulated feed; fresh fish meat mixed with formulated feed and solen meat; fresh fish meat mixed with formulated feed, solen meat and copepods) | Supplementation with copepods promoted growth [44,45] |
| 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55% protein diets | The optimal protein content is 46–50% [36] |
| Four Diets (100% fish oil; 70% fish oil and 30% soybean oil; 30% fish oil and 70% soybean oil; 100% soybean oil) | Replacing fish oil with soybean oil (18–24% n-3 LC-PUFA, balanced n-3/n-6 ratio of 1–2) promoted healthy growth [46] |
| Adding Jellyfish to the Diet | Increased liver amino acids, amines, and unsaturated fatty acids [11,47] |
| n-3 LC-PUFA levels during vitellogenesis | Enhanced antioxidant capacity, lipid metabolism regulation [48,49,50] |
| Schizochytrium Supplementation | Accelerated growth, improved unsaturated fatty acids [51] |
| Vitamin C and Probiotics | Positive effects on growth and immunity [52,53,54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, G.; Li, B.; Ke, Q.; Tao, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, S. Silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus) Aquaculture: Advances, Bottlenecks, and Future Strategies. Animals 2025, 15, 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223347
Qiao G, Li B, Ke Q, Tao S, Xu W, Wang Y, Peng S. Silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus) Aquaculture: Advances, Bottlenecks, and Future Strategies. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223347
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Guangde, Bingfei Li, Qiaozhen Ke, Shunshun Tao, Wantu Xu, Yabing Wang, and Shiming Peng. 2025. "Silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus) Aquaculture: Advances, Bottlenecks, and Future Strategies" Animals 15, no. 22: 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223347
APA StyleQiao, G., Li, B., Ke, Q., Tao, S., Xu, W., Wang, Y., & Peng, S. (2025). Silver Pomfret (Pampus argenteus) Aquaculture: Advances, Bottlenecks, and Future Strategies. Animals, 15(22), 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223347





