First Histological Study of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Associated Lymphoid Structures of a Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
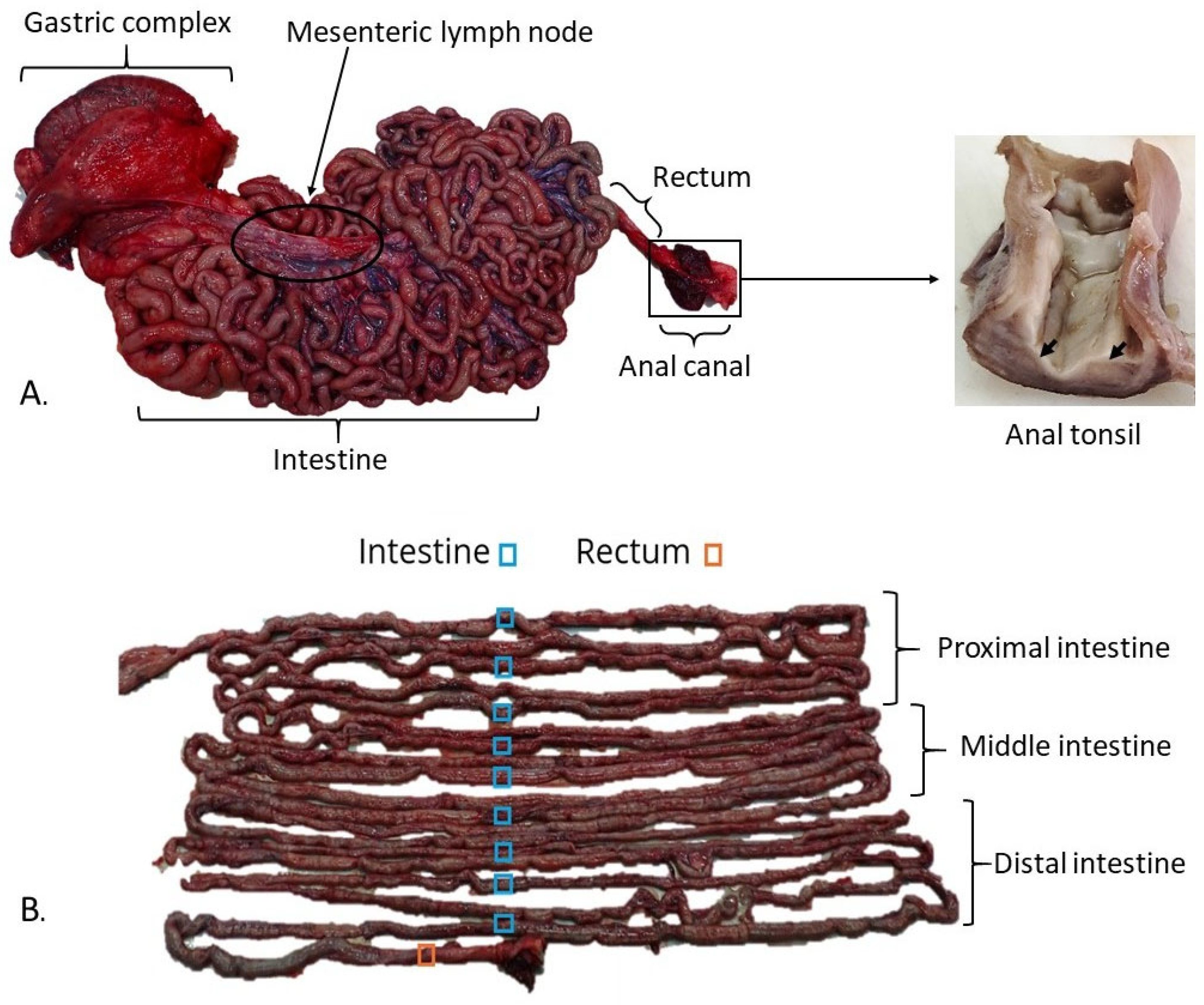
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Measurement of Histological Layer Thickness in the GIT
2.4. Evaluation and Quantification of Cell Types in the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) and Lymph Nodes (LNs)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
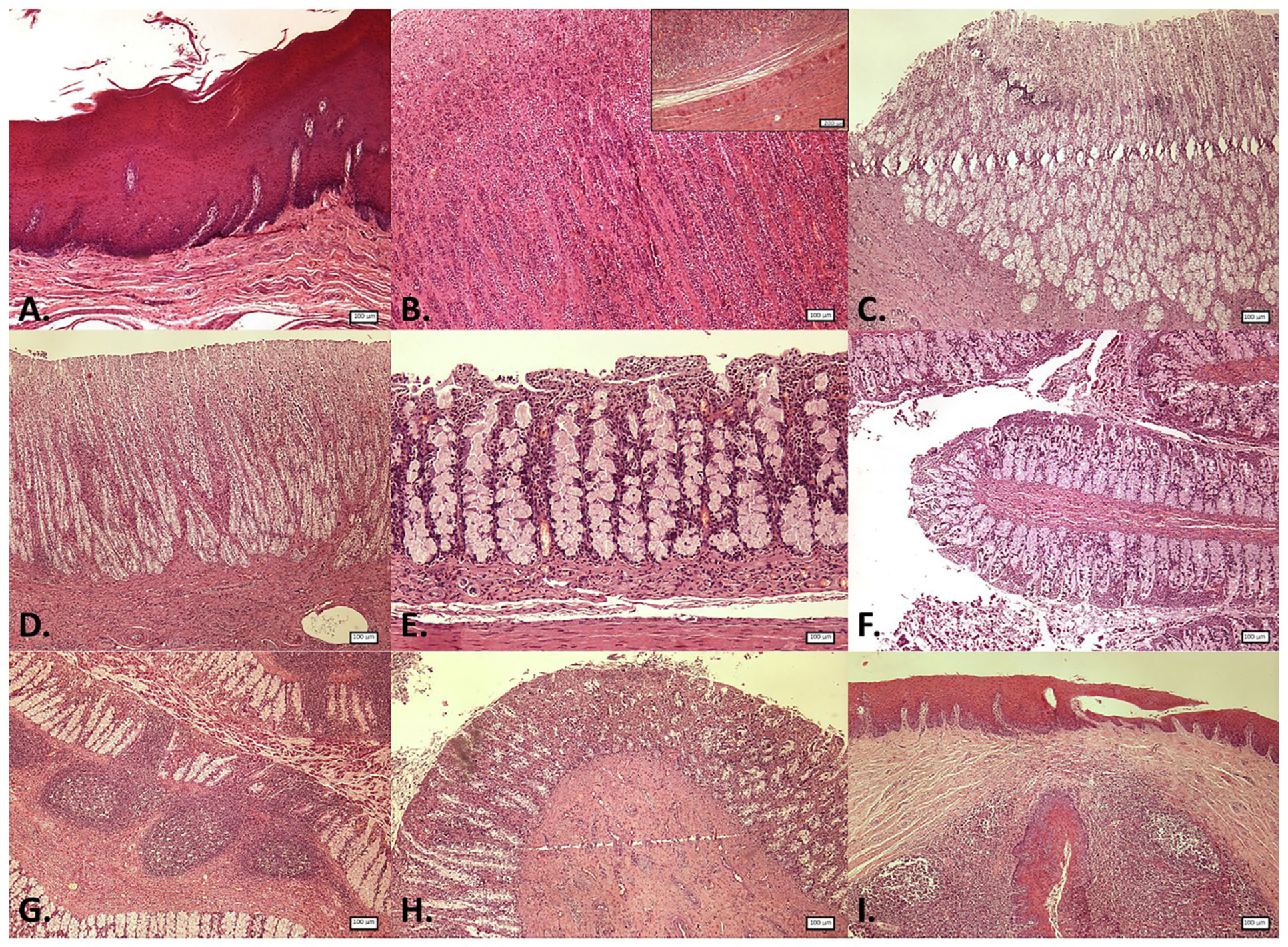
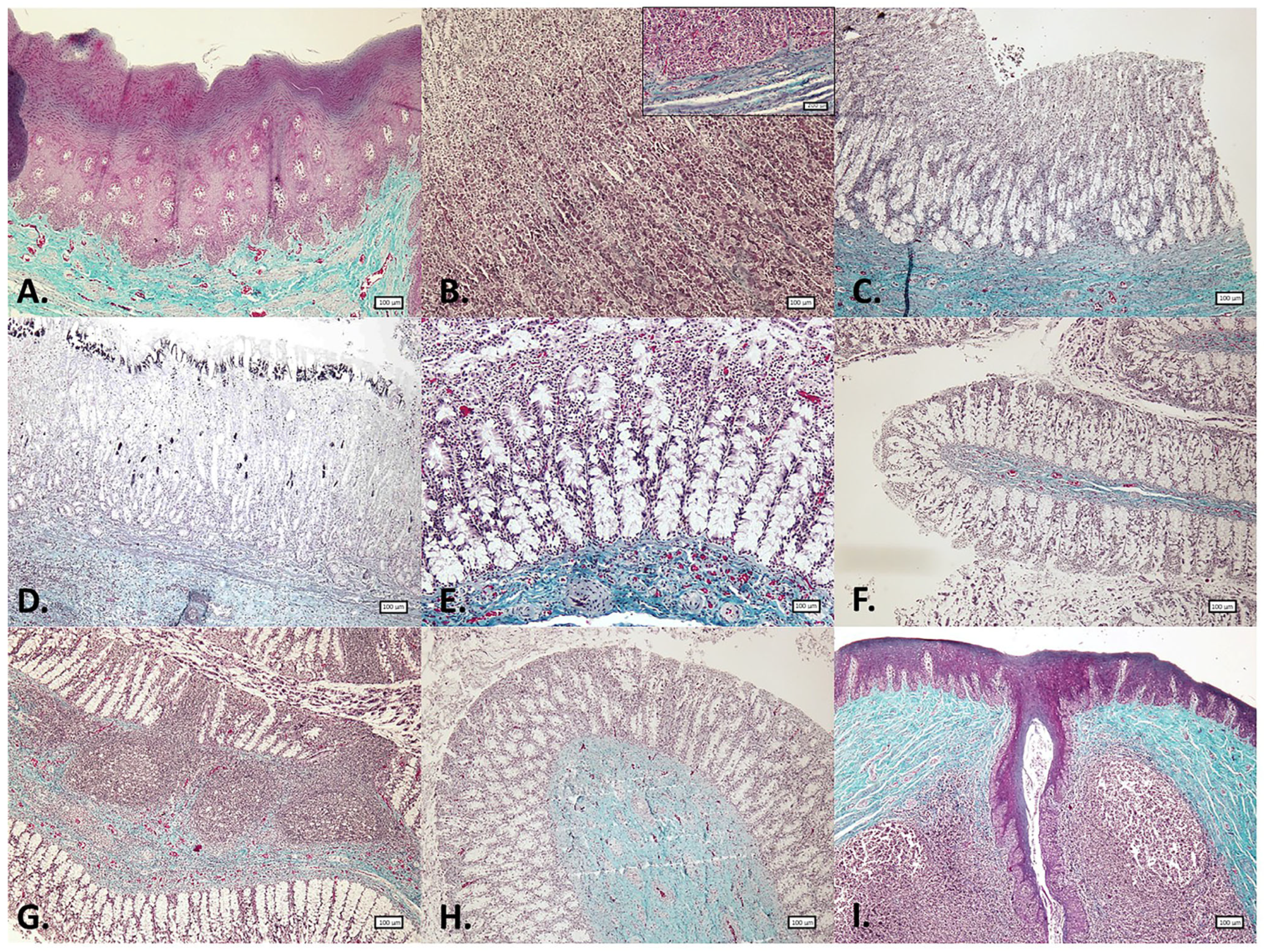
3.1. Histological Structure of the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)
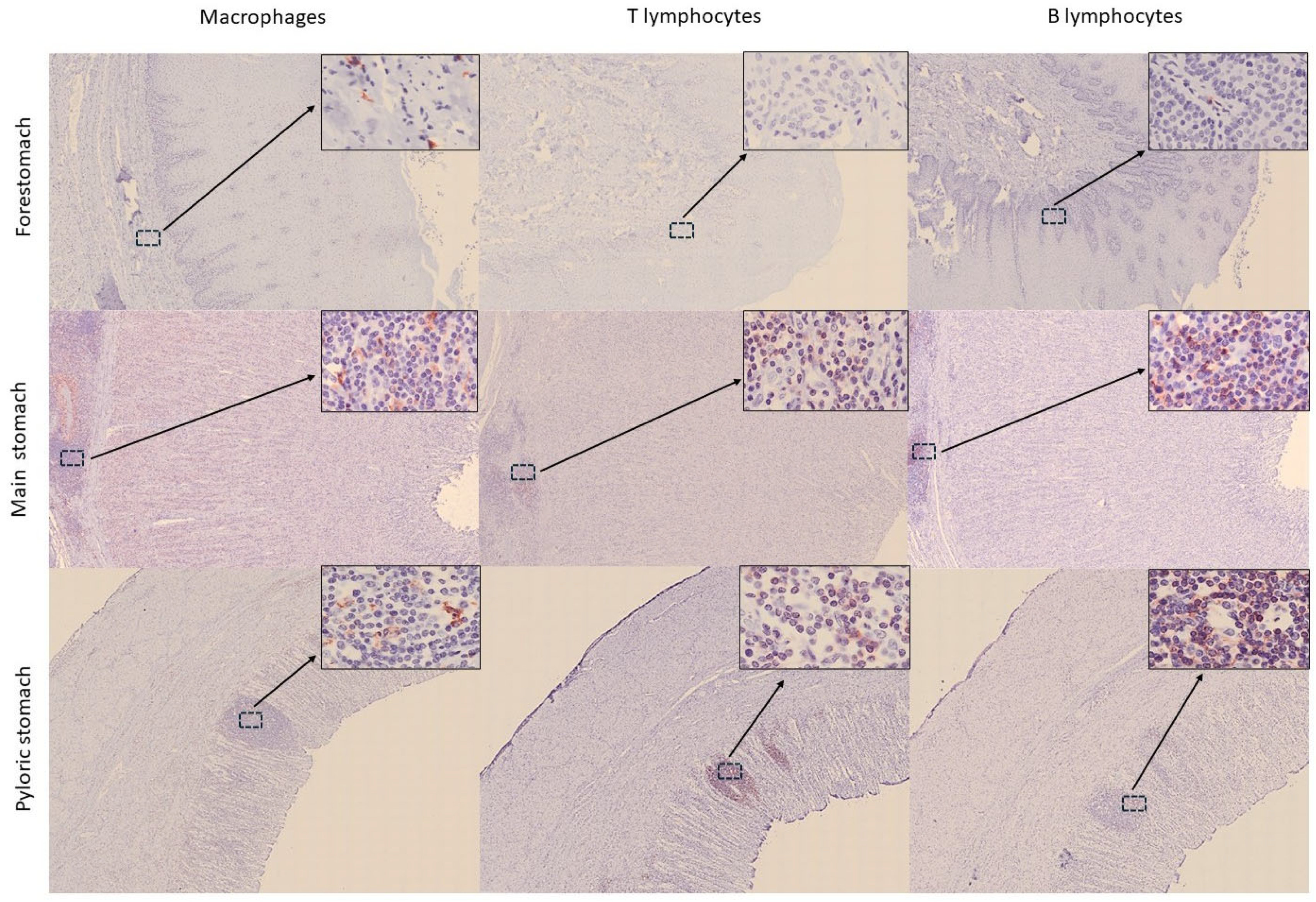
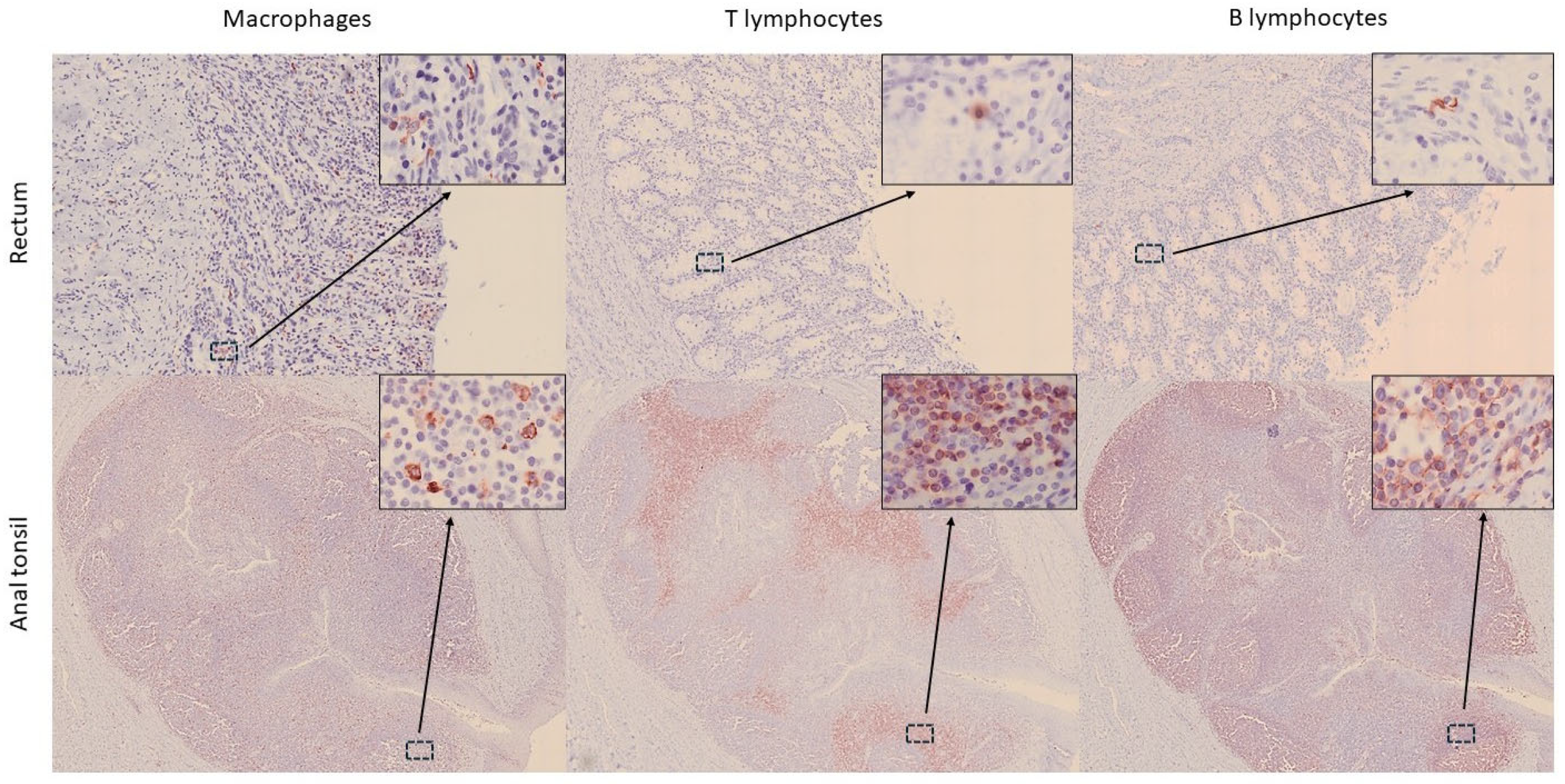
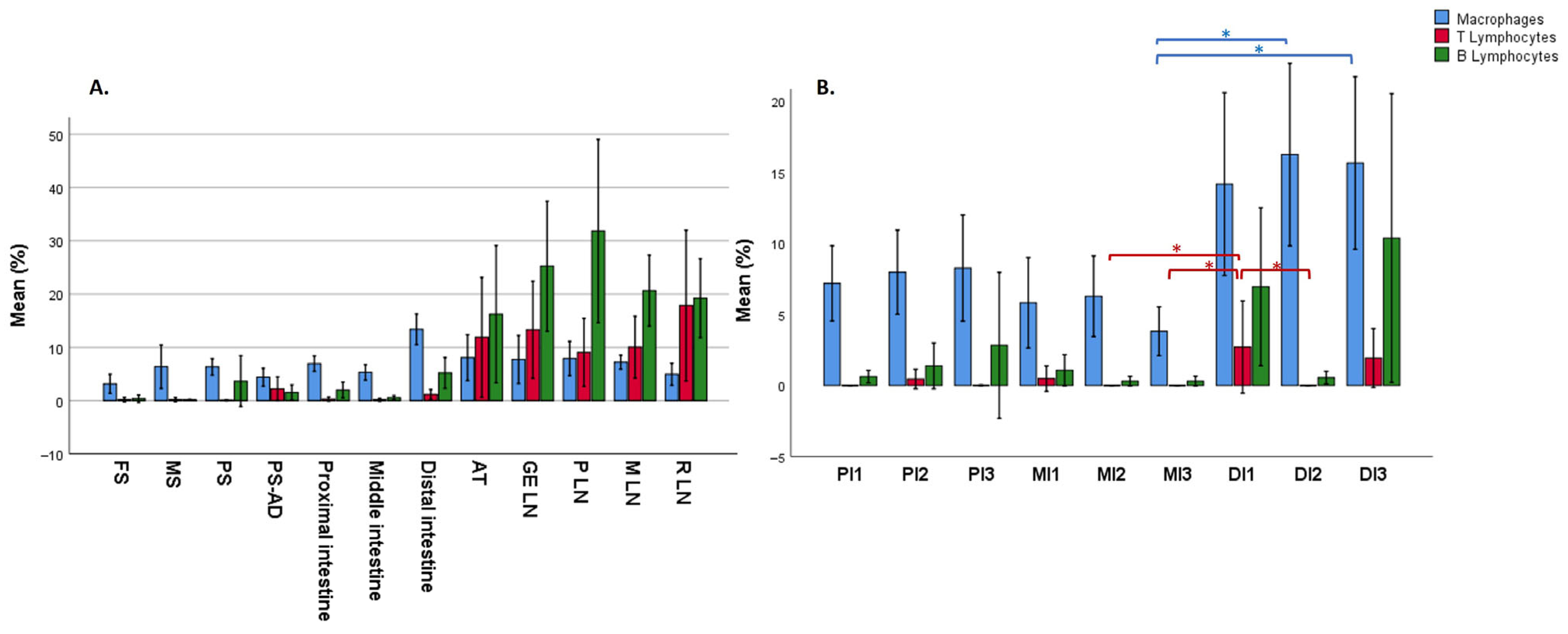
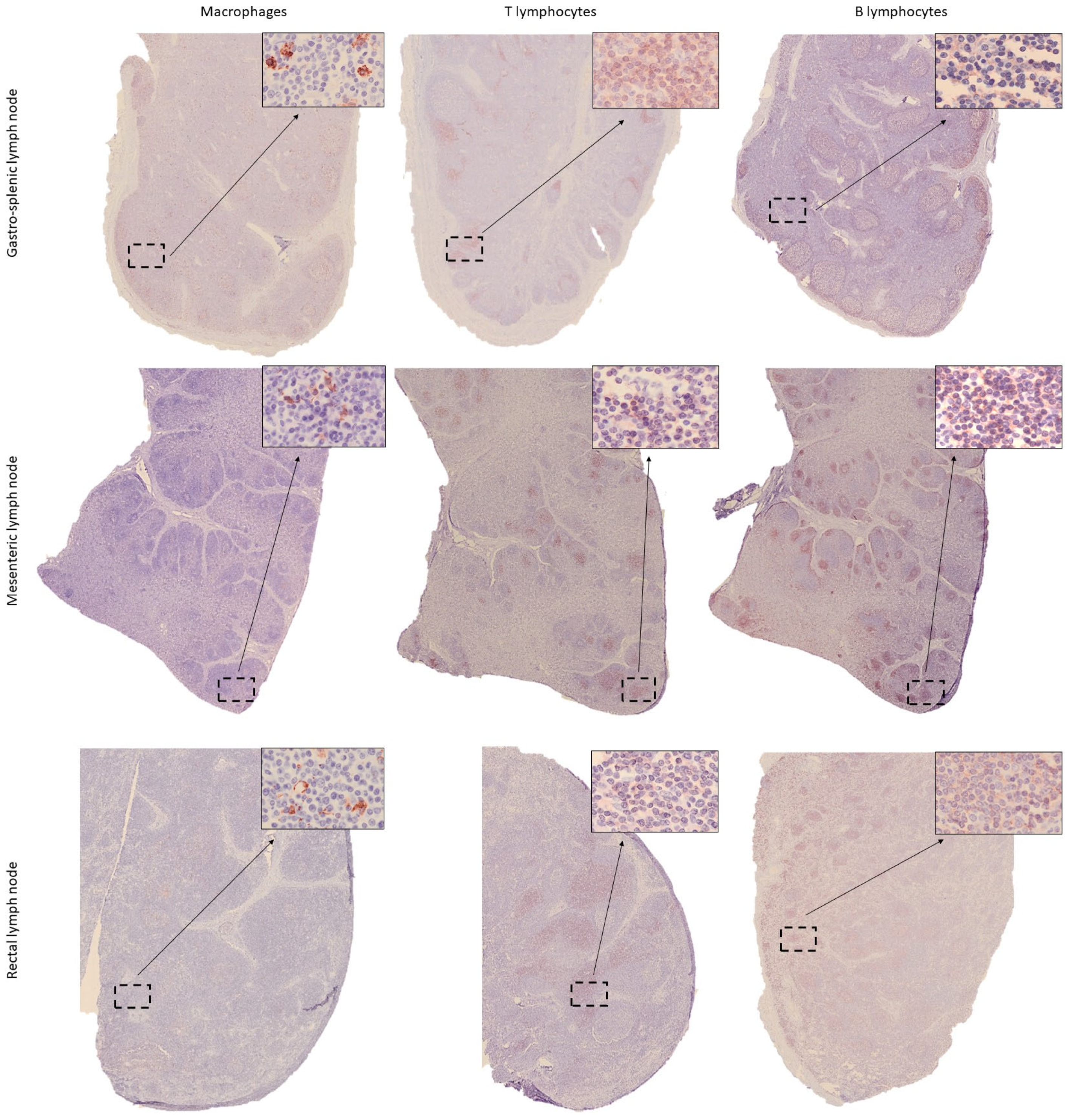
3.2. Distribution of Immune Cells Within Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT) and Associated Lymphoid Tissue
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BL | B lymphocytes |
| TL | T lymphocytes |
| GALT | Gut-associated lymphoid tissue |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| IBA1 | Ionized calcium-binding molecule 1 |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LN | Lymph node |
References
- Cozzi, B.; Huggenberger, S.; Oelschläger, H. Anatomy of Dolphins: Insights into Body Structure and Function, 1st ed.; Academic press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 344–359. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorucci, L. Determinación de Los Principales Datos de Referencia Para el Examen del Tracto Gastrointestinal en Delfines Mulares (Tursiops truncatus) Clínicamente Sanos Bajo el Cuidado Humano. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Las Palmas, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorucci, L.; Grande, F.; Flanagan, C.; Silva, J.; Urbani, N.; Sampayo, J.; Marcelli, R. Reference baseline data for gastric cytology in healthy bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) under human care. Aquat. Mamm. 2015, 41, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, S.A.; Lowenstine, L.J. Gross and microscopic anatomy. In CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine, 1st ed.; Dierauf, L.A., Gulland, F.M.D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 129–164. [Google Scholar]
- Huggenberger, S.; Oelschläger, H.; Cozzi, B. Atlas of the Anatomy of Dolphins and Whales, 1st ed.; Academic press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 363–479. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero Cansino, M.J.; Jaber Mohamad, J.R.; Fernández Rodríguez, A. Atlas de Histología de Peces y Cetáceos, 1st ed.; Vicerrectorado de Planificación y Calidad de la Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria: Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, España, 2005; pp. 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, J.G. Gastrointestinal tract. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Perrin, W.F., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.J.; Johnson, F.R.; Young, B.A. The small intestine of dolphins (Tursiops, Delphinus, Stenella). In Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals, 1st ed.; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 297–331. [Google Scholar]
- Gerussi, T.; Graïc, J.M.; Orekhova, K.; Cozzi, B.; Grandis, A. Vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract of the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus, Montagu 1821). J. Anat. 2023, 244, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shil, S.K.; Zahangir, M.M.; Das, B.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Yadav, S.K.; Kibria, M.M.; Siddiki, A.Z. Macro and microanatomy of some organs of a juvenile male Ganges River dolphin (Platanista gangetica spp. gangetica). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2022, 52, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, D.F.; Smith, T.L. Morphology of the lymphoid organs of the bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncates. J. Anat. 1999, 194, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemark, M.; Pitcher, M.J.; Dionisi, C.; Spencer, J. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue: A microbiota-driven hub of B cell immunity. Trends Immunol. 2024, 45, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-Villagómez, D.; Van Kaer, L. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes: Sentinels of the mucosal barrier. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, T.A.; Felten, S.Y.; Olschowka, J.A.; Felten, D.L. A microscopic investigation of the lymphoid organs of the beluga, Delphinapterus Leucas. J. Morphol. 1993, 215, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.M.O.; Guimarães, J.P.; Vergara-Parente, J.E.; Carvalho, V.L.; Carolina, A.; Meirelles, O.; Marmontel, M.; Oliveira, B.S.S.P.; Santos, S.M.; Becegato, E.Z.; et al. Morphology of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in odontocetes. Micros. Res. Tech. 2016, 79, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.S.; Turner, J.P.; Cowan, D.F. Involution of lymphoid organs in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the western Gulf of Mexico: Implications for life in an aquatic environment. Anat. Rec. 2005, 282A, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuković, S.; Lucić, H.; Gomerčić, H.; Duras-Gomerčić, M.; Gomerčić, T.; Škrtić, D.; Vurković, S. Morphology of the lymph nodes in bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) from the Adriatic Sea. Acta Vet. Hung. 2005, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moskov, M.; Schiwatschewa, T.; Bonev, S. Comparative histological study of lymph nodes in mammals. Lymph nodes of the dolphin. Anat. Anz. 1969, 124, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.C.; Gardner, M.D. Comparative microscopic anatomy of selected marine mammals. In Mammals of the Sea: Biology and Medicine, 1st ed.; Ridgway, S.H., Ed.; Charles C. Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1972; pp. 298–418. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, F.; Gatta, C.; De Girolamo, P.; Cozzi, B.; Giurisato, M.; Lucini, C.; Varricchio, E. Expression and immunohistochemical detection of leptinlike peptide in the gastrointestinal tract of the South American sea lion (Otaria flavescens) and the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frappier, B.L. Digestive system. In Dellmann’s Textbook of Veterinary Histology, 6th ed.; Eurell, J.A., Frappier, B.L., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, TN, USA, 2006; pp. 170–211. [Google Scholar]
- Junqueira, L.C.; Carneiro, J. Junqueira & Carneiro. Histología Básica. Texto y Atlas, 13th ed.; Editorial Médica Panamericana: City of Mexico, Mexico, 2022; pp. 308–329. [Google Scholar]
- Tostado-Marcos, C.; Diz, M.J.O.; Martín-Orti, R.; Loureiro, J.P.; Melopeceres-Diego, I.; Tendillo-Domínguez, E.; Pérez-Lloret, P.; Santos-Álvarez, I.; González-Soriano, J. Nature or nurture: Is the digestive system of the Pontoporia blainvillei influenced or determined by its diet? Animals 2024, 14, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buendía Martín, A.J.; Durán Flórez, E.; Gázquez Ortiz, A.; Gómez Cabrera, S.; Méndez Sánchez, A.; Navarro Cámara, J.A. Aparato digestivo. In Tratado de Histología Veterinaria, 1st ed.; Gázquez Ortiz, A., Blanco Rodríguez, A., Eds.; Masson: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; pp. 239–280. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F.M.D.O.E.; Guimarães, J.P.; Vergara-parente, J.E.; Carvalho, V.L.; De Meirelles, A.C.O.; Marmontel, M.; Ferrão, J.S.P.; Miglino, M.A. Morphological análisis of lymph nodes in odontocetes from northand northeast coast of Brazil. Anat. Rec. 2014, 297, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primary Antibody (Dilution) | Cell Type Detected | Clone No. | Source | Secondary Antibody (Dilution) | Catalogue No. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBA1 1 (1:1000) | Macrophages | Polyclonal 019-19741 | FLUJIFILM-Wako Chemicals Europe GmbH, Neuss, Germany | Goat anti-rabbit (1:200) | BA-1000-1.5 | Vector Laboratories, Newark, CA, USA |
| CD3 (1:500) | T lymphocytes | Monoclonal NCL-L-CD3-565 | Novacastra, Leica Biosystem, Newcastle, UK | Horse anti-mouse (1:200) | BA-2000-1.5 | Vector Laboratories, Newark, CA, USA |
| CD20 (1:400) | B lymphocytes | Polyclonal PA5-16701 | ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA | Goat anti-rabbit (1:200) | BA-1000-1.5 | Vector Laboratories, Newark, CA, USA |
| Structure | Mucosa | Submucosa | Muscularis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forestomach (FS) | Stratified keratinized epithelium. Muscularis mucosae highly developed. Absence of glands. Thickness: 937 microns (µm). | No glands. Submucosal plexus. Thickness: 252 µm. | Layers difficult to differentiate. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 1430 µm. |
| Main stomach (MS) | Simple columnar epithelium. Gastric pits with secretory cells. Muscularis mucosae less developed than in FS. Thickness: 3180 µm. | No glands. Submucosal plexus. Thickness: 403 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 913 µm (inner) and 432 µm (outer). |
| Pyloric stomach (PS) | Simple columnar epithelium. Pyloric glands. Muscularis mucosae. Thickness: 1260 µm. | No glands. Submucosal plexus. Thickness: 292 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 774 µm (inner) and 212 µm (outer). |
| Duodenal ampulla (DA) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae poorly developed. No folds. Thickness: 1140 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 639 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 712 µm (inner) and 512 µm (outer). |
| Proximal intestine 1 (PI1) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Numerous folds. Thickness: 272 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 135 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 245 µm (inner) and 61.8 µm (outer). |
| Proximal intestine 2 (PI2) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Numerous folds. Thickness: 461 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 97.6 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 629 µm (inner) and 162 µm (outer). |
| Proximal intestine 3 (PI3) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Numerous folds. Thickness: 361 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 96.8 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 629 µm (inner) and 191 µm (outer). |
| Middle intestine 1 (MI1) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Numerous folds. Thickness: 351 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 63.9 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 522.464 µm (inner) and 130 µm (outer). |
| Middle intestine 2 (MI2) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Few folds. Thickness: 423 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 96.3 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 456 µm (inner) and 91.4 µm (outer). |
| Middle intestine 3 (MI3) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Few folds. Thickness: 373 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 111 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 408 µm (inner) and 124 µm (outer). |
| Distal intestine 1 (DI1) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Few folds. Thickness: 328 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 142 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 359 µm (inner) and 112 µm (outer). |
| Distal intestine 2 (DI2) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Few folds. Thickness: 364 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 142 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 373 µm (inner) and 90.3 µm (outer). |
| Distal intestine 3 (DI3) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. Muscularis mucosae very poorly developed. No villi. Few folds. Thickness: 344 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Thickness: 143 µm. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 518 µm (inner) and 103 µm (outer). |
| Rectum (R) | Simple columnar epithelium. Mucous glands. No muscularis mucosae. Wide folds. Thickness: 737 µm. | No glands. Submucosal plexus present. | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 808 µm (inner) and 353 µm (outer). |
| Anal canal (AC) | Stratified keratinized epithelium. Crypts with stratified keratinized epithelium. No glands. No muscularis mucosae. Thickness: 3400 µm. | No glands. No submucosal plexus. Large lymphoid aggregates (anal tonsil). | Inner and outer layers easily distinguishable. Myenteric plexus. Thickness: 854 µm (inner) and 544 µm (outer). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Maroto, D.; Balseiro, A.; Barroso, P.; Molpeceres-Diego, I.; Fernández, A.; García Marín, J.F.; García-Álvarez, N. First Histological Study of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Associated Lymphoid Structures of a Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). Animals 2025, 15, 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223277
Pérez-Maroto D, Balseiro A, Barroso P, Molpeceres-Diego I, Fernández A, García Marín JF, García-Álvarez N. First Histological Study of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Associated Lymphoid Structures of a Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). Animals. 2025; 15(22):3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223277
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Maroto, Diego, Ana Balseiro, Patricia Barroso, Ignacio Molpeceres-Diego, Antonio Fernández, Juan Francisco García Marín, and Natalia García-Álvarez. 2025. "First Histological Study of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Associated Lymphoid Structures of a Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena)" Animals 15, no. 22: 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223277
APA StylePérez-Maroto, D., Balseiro, A., Barroso, P., Molpeceres-Diego, I., Fernández, A., García Marín, J. F., & García-Álvarez, N. (2025). First Histological Study of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Associated Lymphoid Structures of a Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). Animals, 15(22), 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223277






