Gut Microbiome of Two Rodent Species (Niviventer confucianus and Apodemus agrarius) from Two Regions Exhibit Different Structures and Assembly Mechanisms
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and CYTB Gene Sequencing
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing, Sequence Processing, and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Multiple Regression on (Dis)Similarity Matrices (MRMs)
3. Results
3.1. Species Identification
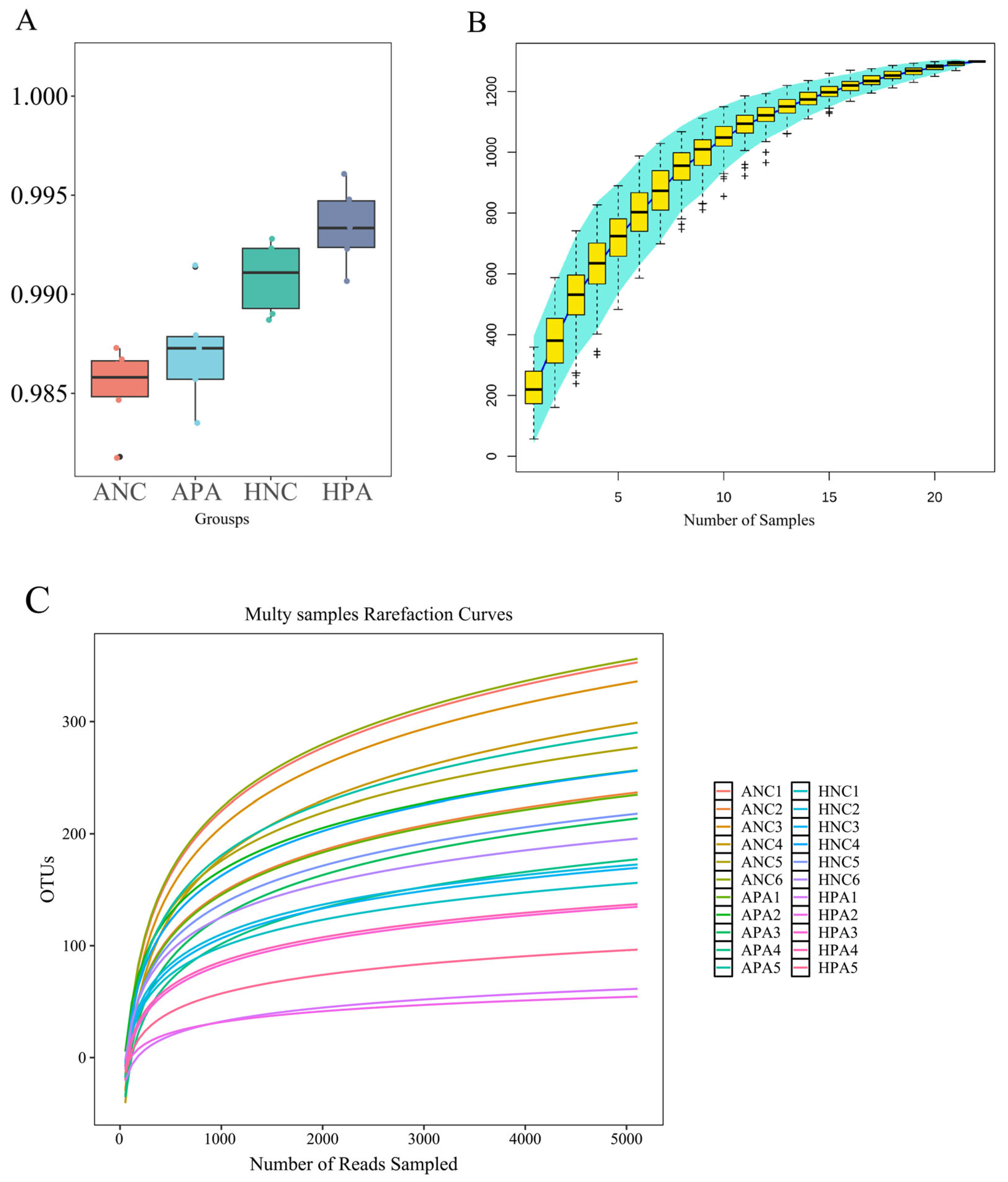
3.2. Data Statistics
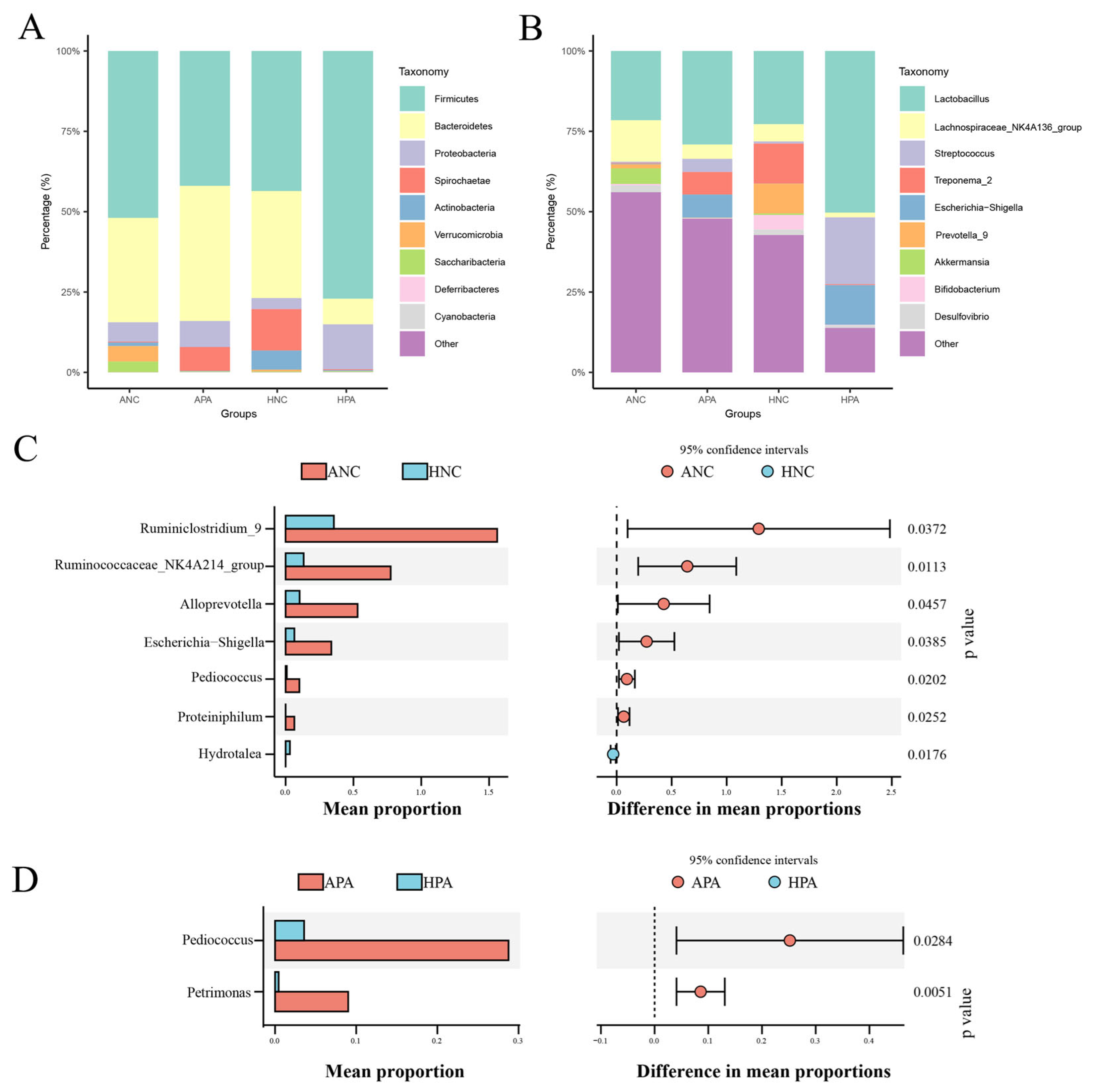
3.3. Composition and Differences in the Gut Microbiome
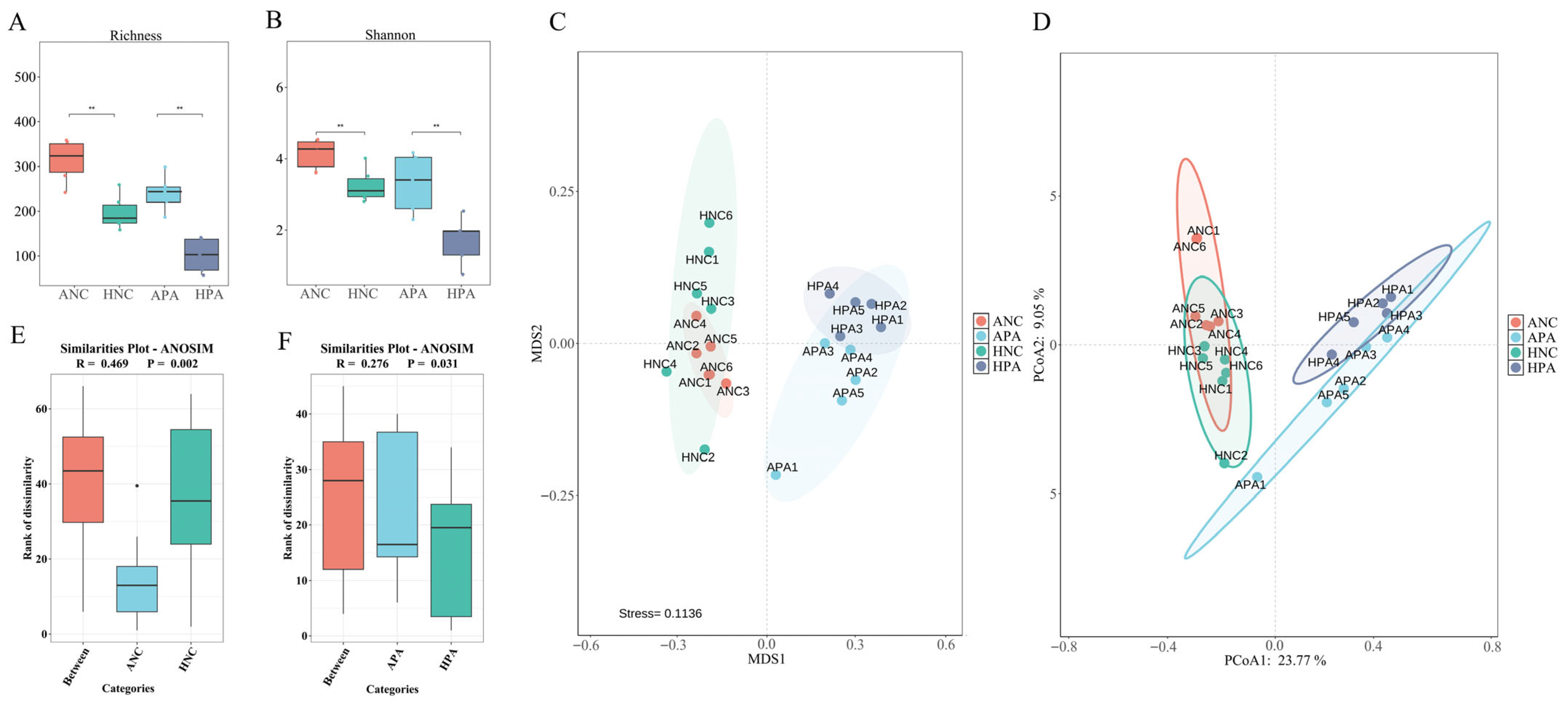
3.4. Alpha and Beta Analyses
3.5. MRMs Analysis
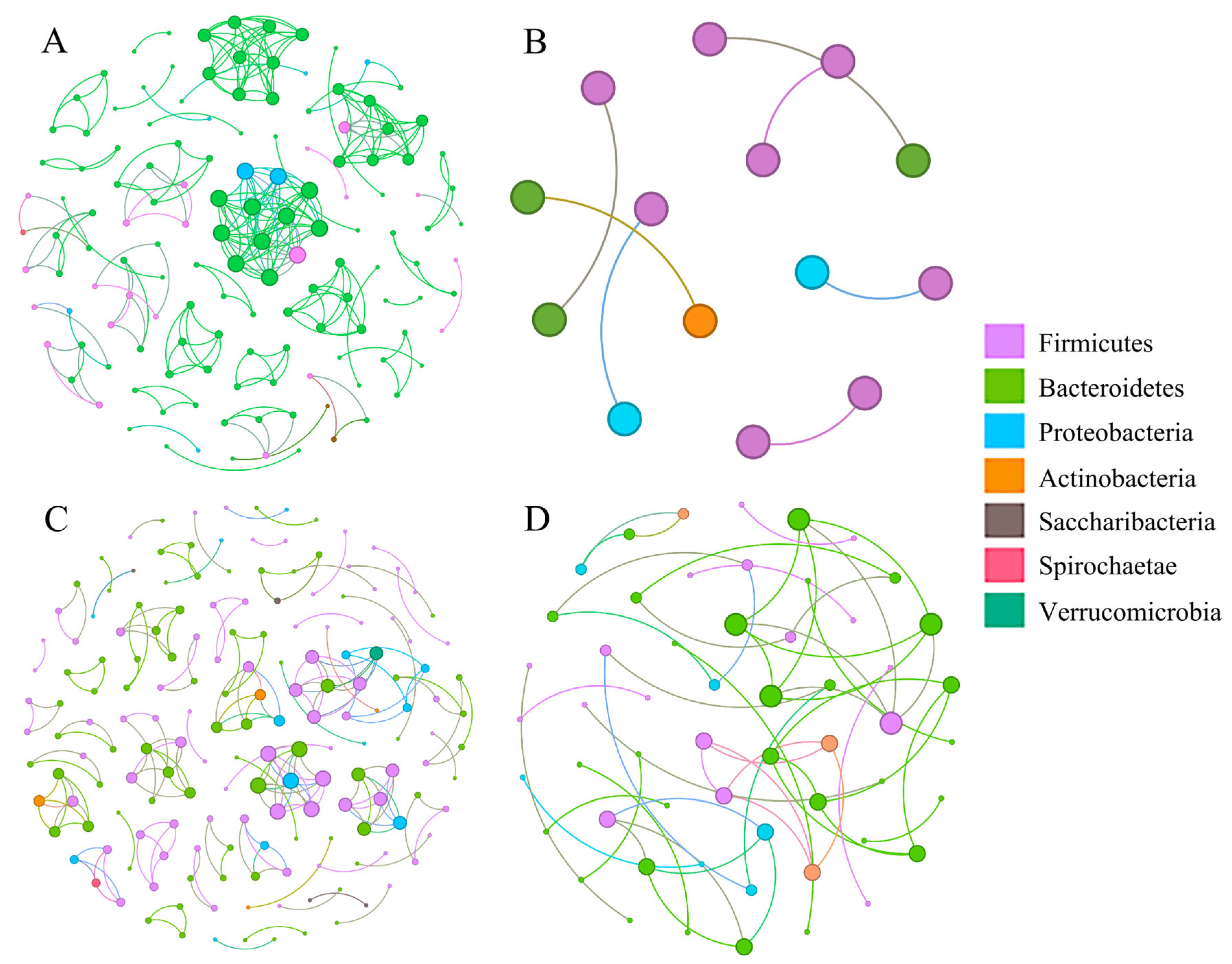
3.6. Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network and Community Assemblages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, H. Comparative analysis of the gut microbiome of ungulate species from Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shi, M.; Zhang, B.; Hu, X.; Xu, S.; Ding, J.; Liu, S.; Hu, D.; Rubenstein, D. Characterization of intestinal microbiota and fecal cortisol, T3, and IgA in forest musk deer (Moschus berezovskii) from birth to weaning. Integr. Zool. 2021, 16, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H. Captive environments reshape the compositions of carbohydrate active enzymes and virulence factors in wolf gut microbiome. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yun, C.; Pang, Y.; Qiao, J. The impact of the gut microbiota on the reproductive and metabolic endocrine system. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1894070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Yi, X. The potential of olfaction loss to induce cognitive impairment and anxiety behavior in mice via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1595742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X. High-tannin food enhances spatial memory and scatter-hoarding in rodents via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microbiome 2024, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; Ochman, H.; Hammer, T.J. Evolutionary and ecological consequences of gut microbial communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2019, 50, 451–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, L.; Kemp, J.A.; Baptista, B.G.; Ribeiro, M.; Lima, L.S.; Mafra, D. Production of Toxins by the Gut Microbiota: The Role of Dietary Protein. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, Z.; Zhang, X.; Khakisahneh, S.; Degen, A.; Wang, D. The microbiota-gut-kidney axis mediates host osmoregulation in a small desert mammal. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulo, A.; Allen, B.E.; Troitsky, T.; Husby, A.; Firth, J.A.; Coulson, T.; Knowles, S.C.L. Social networks strongly predict the gut microbiota of wild mice. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, A.; Ramírez-Barahona, S.; Holekamp, E.; Theis, R. Host phylogeny and host ecology structure the mammalian gut microbiota at different taxonomic scales. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wei, Q.; Pang, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Dou, H.; et al. Microcystin exposure alters gut microbiota composition in fish: An in-Situ analysis of post-bloom effects in Hulun Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363 Pt 2, 125174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Shang, Y.; Mei, X.; Zhou, S.; Wei, Q.; Sun, G.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H. Convergent evolution of the gut microbiome in marine carnivores. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnenbrink, M.; Wang, J.; Hardouin, E.A.; Künzel, S.; Metzler, D.; Baines, J.F. The role of biogeography in shaping diversity of the intestinal microbiota in house mice. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Yi, X. The influence of species identity and geographic locations on gut microbiota of small rodents. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 983660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Gu, C.; Yin, B.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W. Geographical distribution and species variation of gut microbiota in small rodents from the agro-pastoral transition ecotone in northern China. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, S.C.L.; Eccles, R.M.; Baltrūnaitė, L. Species identity dominates over environment in shaping the microbiota of small mammals. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.B.; Martínez-Mota, R.; Stapleton, T.E.; Klure, D.M.; Greenhalgh, R.; Orr, T.J.; Dale, C.; Kohl, K.D.; Dearing, M.D. Microbiome stability and structure is governed by host phylogeny over diet and geography in woodrats (Neotoma spp.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2108787118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kong, L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Motokawa, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Molecular phylogeographic analyses and species delimitations reveal that Leopoldamys edwardsi (Rodentia: Muridae) is a species complex. Integr. Zool. 2019, 14, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Qiao, X.; Xi, J.; Lu, H.; et al. EasyAmplicon: An easy-to-use, open-source, reproducible, and community-based pipeline for amplicon data analysis in microbiome research. iMeta 2023, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, Q.; Dong, Y.; Mei, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, G.; et al. High-altitude drives the convergent evolution of alpha diversity and indicator microbiota in the gut microbiomes of ungulates. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 953234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffron, S.; Rehrauer, H.; Pernthaler, J.; von Mering, C. A global network of coexisting microbes from environmental and whole-genome sequence data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zang, Y.; Xue, S.; Xin, J.; Liu, L.; Tang, X.; Chen, J. Exploring the structure and assembly of seagrass microbial communities in rhizosphere and phyllosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0243724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, W.; Huang, S.; Peng, C.; Li, D.; Li, G. Network Analysis Indicates Microbial Assemblage Differences in Life Stages of Cladophora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0211222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.S.; Shi, P. Critical complex network structures in animal gastrointestinal tract microbiomes. Anim. Microbiome 2024, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; McMinn, A.; Wang, M. Community organization and network complexity and stability: Contrasting strategies of prokaryotic versus eukaryotic microbiomes in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Msphere 2024, 9, e0039524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Kohl, K.D.; Yin, B.; Wei, W.; Wan, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Z. Dietary shifts influenced by livestock grazing shape the gut microbiota composition and co-occurrence networks in a local rodent species. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, A.H.; Suzuki, T.A.; Lin, D.; Lacey, E.A.; Wasser, S.K.; Nachman, M.W. Dispersal limitation promotes the diversification of the mammalian gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13768–13773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Huang, R.; Xu, H.; Jiao, C. Seasonality overwhelms aquacultural activity in determining the composition and assembly of the bacterial community in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, E.; Stagaman, K.; Spaan, S.; Combrink, J.; Sharpton, J.; Beechler, R.; Jolles, E. Diet and gut microbiome enterotype are associated at the population level in African buffalo. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, X.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Y. Environment and host species identity shape gut microbiota diversity in sympatric herbivorous mammals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1300–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Sim, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, D.M. Lifestyle and geographic insights into the distinct gut microbiota in elderly women from two different geographic locations. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2016, 35, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Cai, L.; Lv, L.; Li, L. Pediococcus pentosaceus, a future additive or probiotic candidate. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.C.; Kuniyoshi, T.M.; Azevedo, P.O.; Vitolo, M.; Oliveira, R.P. Pediococcus spp.: An important genus of lactic acid bacteria and pediocin producers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Xiao, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y. Pediococcus pentosaceus CECT 8330 protects DSS-induced colitis and regulates the intestinal microbiota and immune responses in mice. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xia, J.; Lv, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Bian, X.; Ye, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Effects of Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05 on immunity and metabolism in germ-free rats. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5077–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Hu, G.; Zhang, M.; Sun, L.; Su, L.; Zhao, L.; Jin, Y. Supplemental Clostridium butyricum modulates skeletal muscle development and meat quality by shaping the gut microbiota of lambs. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Shi, L.; Bao, M.Y.; Yu, F.L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.X.; Lin, J.C.; Jia, W.; et al. Dietary ellagic acid therapy for CNS autoimmunity: Targeting on Alloprevotella rava and propionate metabolism. Microbiome 2024, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Díaz, J.; Manzano, M.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Giron, M.D.; Salto, R.; López-Pedrosa, J.M.; Santos-Fandila, A.; Garcia-Corcoles, M.T.; Rueda, R.; Gil, Á. Intake of slow-digesting carbohydrates is related to changes in the microbiome and its functional pathways in growing rats with obesity induced by diet. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 992682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.-L.; Pan, Y.-R.; Liu, J.; Butler, D. Alkaline environments benefit microbial K-strategists to efficiently utilize protein substrate and promote valorization of protein waste into short-chain fatty acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wu, X.; Dou, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Sha, W.; Sun, G.; Ma, S.; et al. Comparative analyses of the gut microbiome of two fox species, the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) and corsac fox (Vulpes corsac), that occupy different ecological niches. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Song, P.; Jiang, F.; Cai, Z.; Gu, H.; Gao, H.; Li, B.; Liang, C.; Qin, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Large-scale metagenomic assembly provide new insights into the genetic evolution of gut microbiomes in plateau ungulates. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factors | ANC/HNC | APA/HPA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha Diversity | Beta Diversity | Alpha Diversity | Beta Diversity | |||||
| R2 | p | R2 | p | R2 | p | R2 | p | |
| Weight | 0.056 | 0.054 | 0.020 | 0.265 | 0.008 | 0.694 | 0.002 | 0.835 |
| Gender | 0.011 | 0.343 | 0.022 | 0.266 | 0.004 | 0.615 | 0.003 | 0.702 |
| Geographic location | 0.196 | 0.009 | 0.166 | 0.0002 | 0.154 | 0.011 | 0.064 | 0.021 |
| Altitude | 0.196 | 0.010 | 0.166 | 0.001 | 0.154 | 0.012 | 0.064 | 0.019 |
| Temperature | 0.196 | 0.011 | 0.166 | 0.0009 | 0.154 | 0.011 | 0.064 | 0.017 |
| Phylogenetic branch length | 0.029 | 0.099 | 0.007 | 0.534 | 0.005 | 0.634 | 0.043 | 0.254 |
| Properties | APA | HPA | ANC | HNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 139 | 14 | 172 | 55 |
| Edges | 253 | 7 | 197 | 53 |
| Modularity | 0.888 | 0.857 | 0.960 | 0.909 |
| Network density | 0.026 | 0.077 | 0.013 | 0.036 |
| Positive proportions | 90.909% | 85.714% | 97.462% | 100% |
| Negative proportions | 9.091% | 14.285% | 2.538% | 0 |
| Average Degree | 3.640 | 1.000 | 2.291 | 1.927 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Gao, Q.; Han, J.; Song, Q.; Yan, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Gut Microbiome of Two Rodent Species (Niviventer confucianus and Apodemus agrarius) from Two Regions Exhibit Different Structures and Assembly Mechanisms. Animals 2025, 15, 3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213187
Li H, Gao Q, Han J, Song Q, Yan F, Xu Y, Zhang C, Wang X, Li Y. Gut Microbiome of Two Rodent Species (Niviventer confucianus and Apodemus agrarius) from Two Regions Exhibit Different Structures and Assembly Mechanisms. Animals. 2025; 15(21):3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213187
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haotian, Qian Gao, Jiawen Han, Qiuyue Song, Fangheng Yan, Yunzhao Xu, Chuansheng Zhang, Xin Wang, and Yuchun Li. 2025. "Gut Microbiome of Two Rodent Species (Niviventer confucianus and Apodemus agrarius) from Two Regions Exhibit Different Structures and Assembly Mechanisms" Animals 15, no. 21: 3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213187
APA StyleLi, H., Gao, Q., Han, J., Song, Q., Yan, F., Xu, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, X., & Li, Y. (2025). Gut Microbiome of Two Rodent Species (Niviventer confucianus and Apodemus agrarius) from Two Regions Exhibit Different Structures and Assembly Mechanisms. Animals, 15(21), 3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213187






