Nationwide Investigation of Respiratory Problemsin Sheep Lambs and Goat Kids in Greece
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Visits to Farms
2.2. Data Management and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Findings
3.2. Predictors
3.3. Importance for Farmers
3.4. Administration of Pharmaceuticals and Vaccines to Newborns
4. Discussion
4.1. Preamble
4.2. Predictors
4.3. Importance for Farmers
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacasta, D.; González, J.M.; Navarro, T.; Saura, F.; Acín, C.; Vasileiou, N.G.C. Significance of respiratory diseases in the health management of sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 181, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, T.; Ramos, J.J.; Ruíz de Arcaute, M.; González, J.M. Predisposing factors inducing ovine respiratory complex in intensive-reared lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 181, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, E.; Cazeau, G.; Jarrige, N.; Calavas, D. Antibiotic use in domestic ruminants in France: Results from surveys of practices among farmers and veterinarians. Bull. Epidémiol. Santé Anim. Aliment. 2012, 53, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Karakus, F. Weaning stress in lambs. J. Int. Sci. Publ. Agric. Food 2014, 2, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Tadich, N.; Gallo, C.; Brito, M.L.; Broom, D.M. Effects of weaning and 48 h transport by road and ferry on some blood indicators of welfare in lambs. Livest. Sci. 2009, 121, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.R.; Karring, H. A determination and comparison of urease activity in feces and fresh manure from pig and cattle in relation to ammonia production and pH changes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.J.C.; Pines, M.K.; Latter, M.; Muller, T.; Petherick, J.C.; Norman, S.T.; Gaughan, J.B. Physiological and behavioral responses of sheep to gaseous ammonia. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, J.; Abecia, J.A.; Cannas, A.; Delgadillo, J.A.; Lacasta, D.; Voigt, K.; Chemineau, P. Managing sheep and goats for sustainable high yield production. Animal 2021, 15, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, S. Respiratory disease in sheep 1. Differential diagnosis and epidemiology. Practice 2008, 30, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.M.; Lacasta, D.; Ferrer, L.M.; Figueras, L.; Abadie, G.; De las Heras, M. Mannheimia haemolytica and Bibersteinia trehalosi serotypes isolated from lambs with ovine respiratory complex in Spain. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2013, 64, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McAuliffe, L.; Hatchell, F.M.; Ayling, R.D.; King, A.I.M.; Nicholas, A.J. Detection of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae in Pasteurella-vaccinated sheep flocks with respiratory disease in England. Vet. Rec. 2003, 153, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.M.; Bello, J.M.; Rodríguez, M.; Navarro, R.; Lacasta, D.; Fernández, A.; De las Heras, M. Lamb feedlot production in Spain: Most relevant health issues. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 142, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, R.A.J.; Ayling, R.D.; Loria, G.R. Ovine mycoplasmal infections. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 76, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Rural Development and Food, Hellenic Republic. Greek Agriculture—Animal Production; Ministry of Rural Development and Food, General Directorate for Animal Production: Athens, Greece, 2021.
- Angelopoulou, K.; Brellou, G.D.; Vlemmas, I. Detection of Maedi-Visna Virus in the Kidneys of Naturally Infected Sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 134, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogianni, A.I.; Bossis, I.; Ekateriniadou, L.V.; Gelasakis, A.I. Etiology, epizootiology and control of maedi-visna in dairy sheep: A review. Animals 2020, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogianni, A.I.; Stavropoulos, I.; Chaintoutis, S.C.; Bossis, I.; Gelasakis, A.I. Serological, molecular and culture-based diagnosis of lentiviral infections in small ruminants. Viruses 2021, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianou, D.T. Mapping the Small Ruminant Industry in Greece: Health Management and Diseases of Animals, Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Therapeutics, Reproductive Performance, Production Outcomes, Veterinary Public Health, Socio-Demographic Characteristics of the Farmers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Thessaly, Volos, Greece, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on the welfare risks related to the farming of sheep for wool, meat and milk production. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3933–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianou, D.T.; Michael, C.K.; Fthenakis, G.C. Data on mapping 444 dairy small ruminant farms during a countrywide investigation performed in Greece. Animals 2023, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianou, D.T.; Chatziprodromidou, I.P.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Michael, C.K.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Politis, A.P.; Kordalis, N.G.; Billinis, C.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Papadopoulos, E.; et al. A detailed questionnaire for the evaluation of health management in dairy sheep and goats. Animals 2020, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, E.I.; Lianou, D.T.; Papadopoulos, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Long-term climatic changes in small ruminant farms in Greece and potential associations with animal health. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, E.I.; Arsenopoulos, K.V.; Michael, C.K.; Lianou, D.T.; Petinaki, E.; Papadopoulos, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Gastrointestinal helminth infections in dogs in sheep and goat farms in Greece: Prevalence, involvement of wild canid predators and use of anthelmintics. Animals 2024, 14, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohoo, I.; Martin, W.; Stryhn, H. Veterinary Epidemiologic Research, 3rd ed.; VER Inc.: Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 2014; 865p. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, R.; O’Grady, L.; Green, M. Stability selection for mixed effect models with large numbers of predictor variables: A simulation study. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 206, 105714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariner, J.C. Manual on Participatory Epidemiology—Method for the Collection of Action-Oriented Epidemiological Intelligence; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2001; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Catley, A.; Alders, R.G.; Wood, J.L.N. Participatory epidemiology: Approaches, methods, experiences. Vet. J. 2012, 191, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alders, R.G.; Ali, S.N.; Ameri, A.A.; Bagnol, B.; Cooper, T.L.; Gozali, A.; Hidayat, M.M.; Rukambile, E.; Wong, J.T.; Catley, A. Participatory epidemiology: Principles, practice, utility, and lessons learnt. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 532763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemneh, T.; Tewodros, A. Sheep and goats pasteurellosis: Isolation, identification, biochemical characterization and prevalence determination in Fogera Woreda, Ethiopia. J. Cell Anim. Biol. 2016, 10, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkiri, D.; Elmejdoub, S.; Bamouh, Z.; Fihri, Q.F.; El-Harrak, M. Comparative protection of small ruminants against Mannheimia haemolytica infection by inactivated bacterin and toxoid vaccines. Vet. World 2023, 16, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Engelen, E.; Heuvelink, A.; Dijkman, R.; Van Den Brom, R.; Snijders-Van De Burgwal, N. Pasteurellosis: Sheep versus goats. Anim. Sci. Proc. 2023, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijheid, M. Health effects of residence near hazardous waste landfill sites: A review of epidemiologic literature. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108 (Suppl. S1), 101–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Takahashi, K.; Pan, G.; Chan, C.C.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Hoshuyama, T.; Chuang, K.J.; Lin, R.T.; Hwang, J.S. Respiratory symptoms among residents of a heavy-industry province in China: Prevalence and risk factors. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, D.; Milani, S.; Lazzarino, A.I.; Perucci, C.A.; Forastiere, F. Systematic review of epidemiological studies on health effects associated with management of solid waste. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.; Dominici, F.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.; Wang, Y.; Di, Q.; Christiania, D.C. Risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome among older adults living near construction and manufacturing sites. Epidemiology 2020, 31, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiou, O.S.; Kotsios, V.S.; Lampropoulos, I.; Zidros, T.; Zarogiannis, S.G.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. PM2.5 pollution strongly predicted COVID-19 incidence in four high-polluted urbanized Italian cities during the pre-lockdown and lockdown periods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, N.; Pantazopoulos, I.; Mermiri, M.; Mavrovounis, G.; Kalantzis, G.; Saharidis, G.; Gourgoulianis, K. Effect of PM2.5 levels on respiratory pediatric ED visits in a semi-urban Greek peninsula. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliou, D.S.; Kotsiou, O.S.; Gourgoulianis, K. Estimates of COVID-19 risk factors among social strata and predictors for a vulnerability to the infection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, S.; Benedetti, M.; Comba, P.; Lagravinese, D.; Martucci, V.; Martuzzi, M.; Morleo, D.; Trinca, S.; Viviano, G. Case-control study on cancer risk associated to residence in the neighbourhood of a petrochemical plant. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Bae, S.; Lim, J.A.; Kim, G.B.; Yu, S.D.; Kim, Y.; Lim, H.L.; Son, B.S.; Paek, D.; et al. Health effects of environmental pollution in population living near industrial complex areas in Korea. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2018, 33, e2018004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergadi, E.; Rouva, G.; Angeli, M.; Galanakis, E. Infectious diseases associated with desert dust outbreaks: A systematic review. Int. J. Envriron. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IQAir. Explore Your Air Quality—Greece Site. 2023. Available online: https://www.iqair.com (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- World Health Organization. Communicable Diseases Following Natural Disasters. 2006. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/communicable-diseases-following-natural-disasters (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- CleanAir in Greece. A Blog About Breathing Clean Air in Greece. 2022. Available online: https://cleanairingreece.org (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Sargison, N. Sheep Flock Health—A Planned Approach; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2008; p. 465. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Gao, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, X. Ammonia exposure induced cilia dysfunction of nasal mucosa in the piglets. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1705387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.E.; Berriatua, E.; Morgan, K.L. The relationship between abnormalities detected in live lambs on farms and those detected at post mortem meat inspection. Epidemiol. Infect. 1997, 118, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzón, J. Influence of the Respiratory Problems in the Principal Production Parametres of Lambs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- McRae, K.M.; Baird, H.J.; Dodds, K.G.; Bixley, M.J.; Clarke, S.K. Incidence and heritability of ovine pneumonia, and the relationship with production traits in New Zealand sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 145, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, B.C.; Muir, P.D.; Smith, N.B. Does the age and sex affect meat quality in older lambs. N. Z. J. Anim. Sci. Prod. 2019, 79, 98–99. [Google Scholar]

| Management System Applied in Farms | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Intensive or Semi-Intensive (n = 222) | Semi-Extensive or Extensive (n = 222) | ||
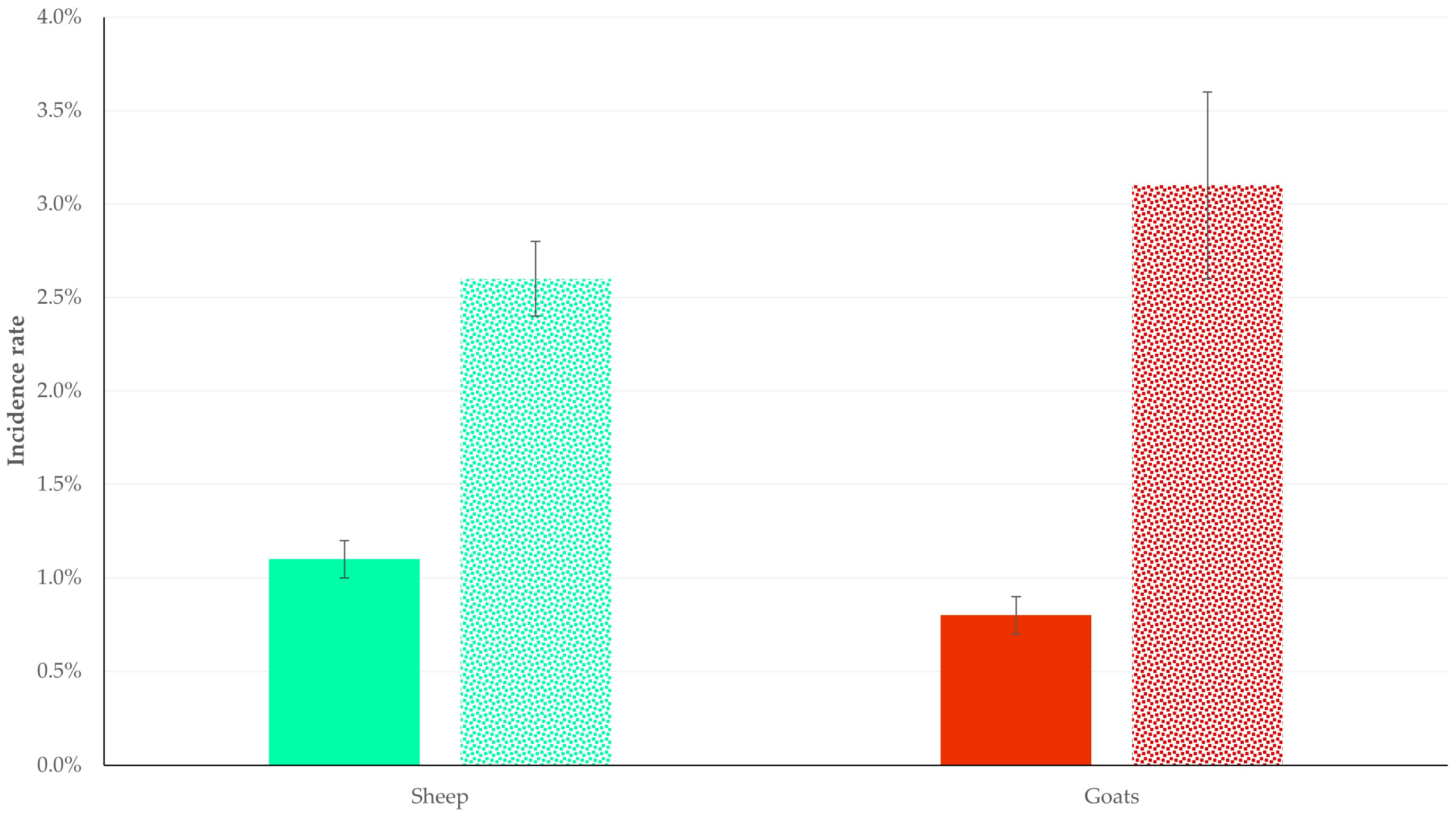
| Sheep farms (n = 325) | median 0.0% (IQR: 0.8% 2) mean 1.5% (s.e.: 0.3% 3) range: 0.0–21.4% | median 0.0% (IQR: 0.6%) mean 1.1% (s.e.: 0.2%) range: 0.0–20.0% | 0.62 |
| Goat farms (n = 119) | median 0.0% (IQR: 0.0%) mean 1.6% (s.e.: 0.8%) range: 0.0–26.7% | median 0.0% (IQR: 0.0%) mean 0.8% (s.e.: 0.2%) range: 0.0–12.5% | 0.63 |
| p value | 0.36 | 0.12 | |
| Variables | Relative Risk (±s.e. 1) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Sheep Farms | ||
| Availability of separate barn for lambs | ||
| Yes (0.0% (0.5%) 2) | reference | - |
| No (0.0% (2.4%)) | 1.014 ± 1.004 | 0.0008 |
| Proximity of the farm to industrial sites | ||
| Yes (0.0% (2.2%)) | 1.013 ± 1.005 | 0.008 |
| No (0.0% (0.5%)) | reference | - |
| Goat Farms | ||
| Proximity of the farm to industrial sites | ||
| Yes (0.3% (6.7%)) | 1.040 ± 1.009 | <0.0001 |
| No (0.0% (0.0%)) | reference | - |
| Routine administration of antibiotics to kids | ||
| Yes (0.0% (3.6%)) | 1.017 ± 1.009 | 0.010 |
| No (0.0% (0.0%)) | reference | - |
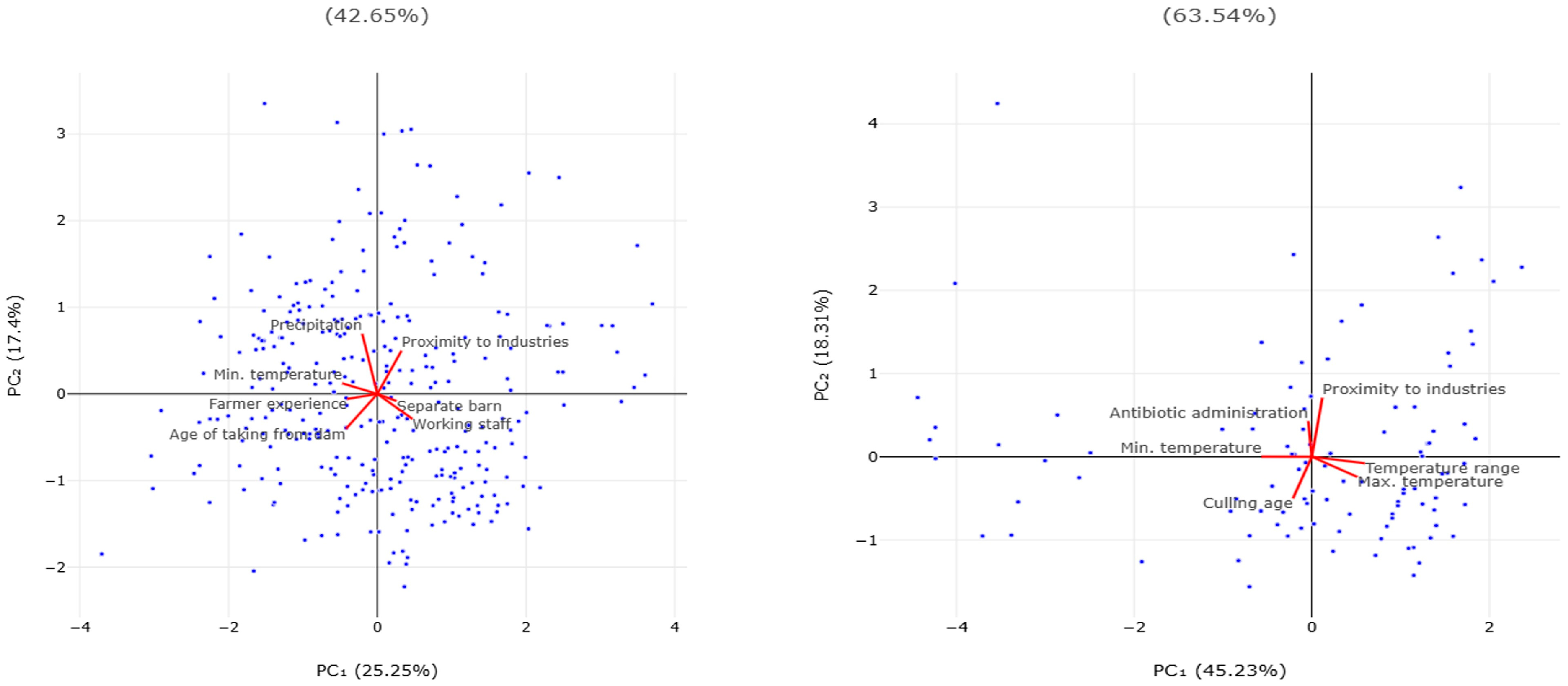
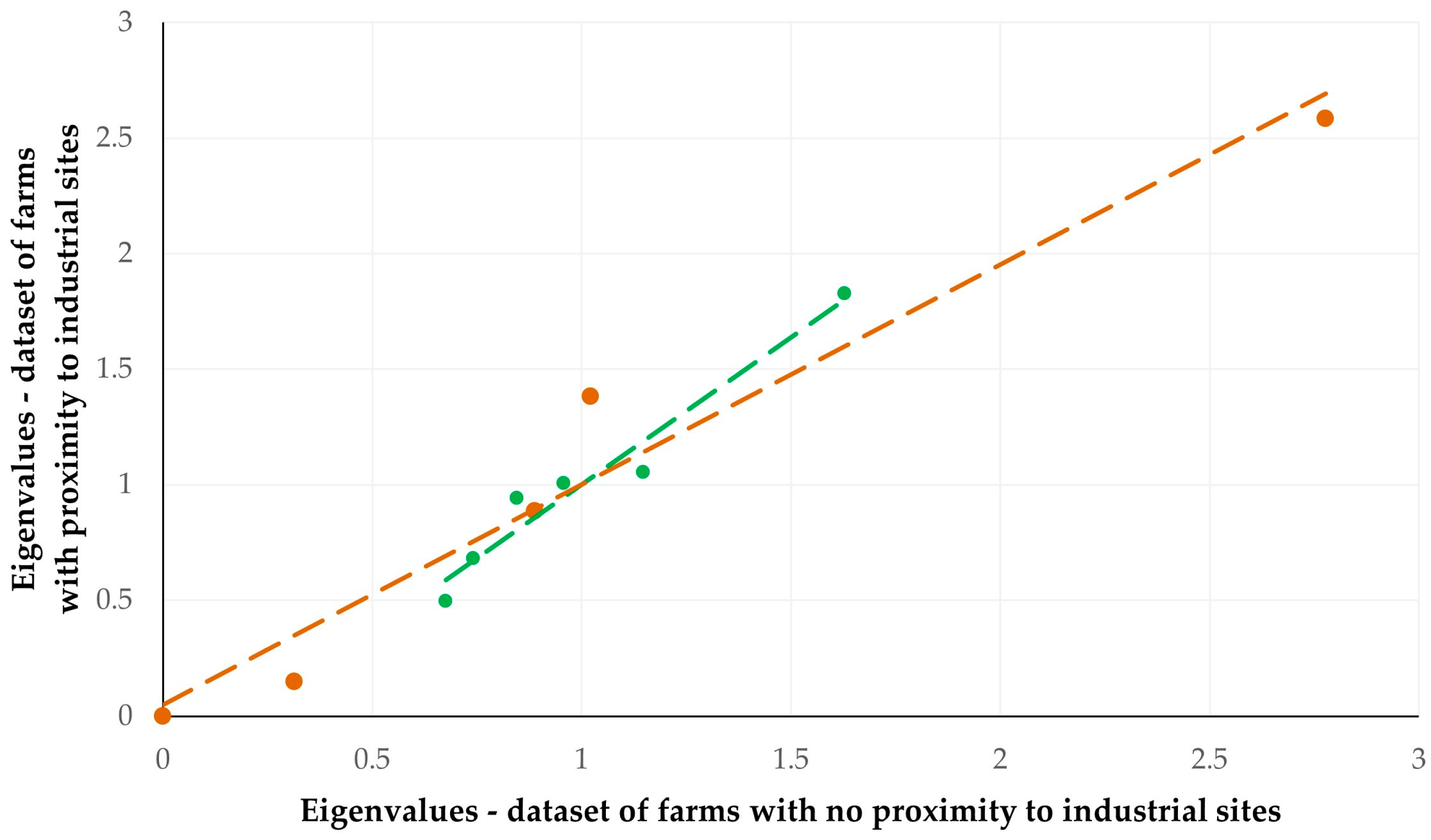
| Sheep Flocks | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | PC1 1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | |||||
| Eigenvalue | 1.767 | 1.218 | 0.985 | 0.832 | 0.787 | 0.732 | 0.678 | |||||
| % of variance | 25.25 | 17.41 | 14.08 | 11.88 | 11.25 | 10.46 | 9.69 | |||||
| Cumulative variance (%) | 25.25 | 42.65 | 56.73 | 68.62 | 79.85 | 90.31 | 100.0 | |||||
| Goat Herds | ||||||||||||
| Parameter | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | ||||||
| Eigenvalue | 2.714 | 1.098 | 0.988 | 0.863 | 0.337 | 0.000 | ||||||
| % of variance | 45.23 | 18.31 | 16.47 | 14.38 | 5.63 | 0.000 | ||||||
| Cumulative variance (%) | 45.23 | 63.54 | 80.00 | 94.38 | 100 | 100 | ||||||
| Health Problems 1 | Sheep Flocks (n = 325) | Goat Herds (n = 119) |
|---|---|---|
| diarrhea | 233 (71.7%) | 83 (69.7%) |
| Pneumonia | 89 (27.4%) | 27 (22.7%) |
| Contagious ecthyma | 25 (7.7%) | 4 (3.4%) |
| Clostridial infections | 24 (7.4%) | 12 (10.1%) |
| Coliform infections | 12 (3.7%) | 11 (9.2%) |
| Selenium deficiency | 10 (3.1%) | <1% |
| Endoparasitic infections | 8 (2.5%) | 11 (9.2%) |
| Routine Administration of Antibiotics Performed | No Routine Administration of Antibiotics Performed | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep farms | 0.0% (2.6%) 1 | 0.0% (0.0%) | 0.0001 |
| Goat farms | 0.0% (3.6%) | 0.0% (0.0%) | 0.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsarou, E.I.; Michael, C.K.; Lianou, D.T.; Liagka, D.V.; Vaitsi, G.A.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Fthenakis, G.C. Nationwide Investigation of Respiratory Problemsin Sheep Lambs and Goat Kids in Greece. Animals 2025, 15, 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213155
Katsarou EI, Michael CK, Lianou DT, Liagka DV, Vaitsi GA, Mavrogianni VS, Fthenakis GC. Nationwide Investigation of Respiratory Problemsin Sheep Lambs and Goat Kids in Greece. Animals. 2025; 15(21):3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213155
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsarou, Eleni I., Charalambia K. Michael, Dafni T. Lianou, Dimitra V. Liagka, Georgia A. Vaitsi, Vasia S. Mavrogianni, and George C. Fthenakis. 2025. "Nationwide Investigation of Respiratory Problemsin Sheep Lambs and Goat Kids in Greece" Animals 15, no. 21: 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213155
APA StyleKatsarou, E. I., Michael, C. K., Lianou, D. T., Liagka, D. V., Vaitsi, G. A., Mavrogianni, V. S., & Fthenakis, G. C. (2025). Nationwide Investigation of Respiratory Problemsin Sheep Lambs and Goat Kids in Greece. Animals, 15(21), 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213155









