Bacterial Composition Across Bat Species: A Human Health Perspective
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
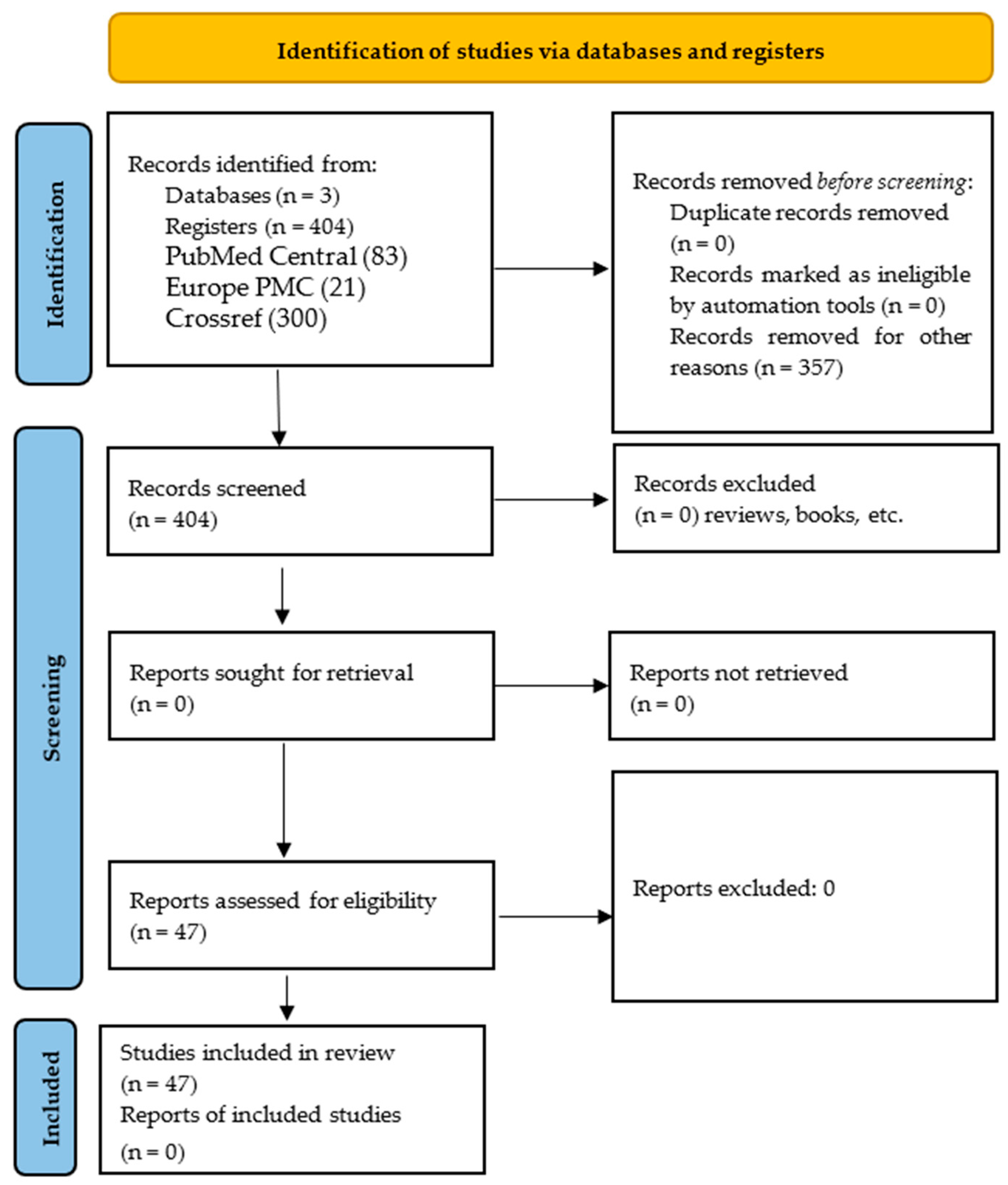
2. Materials and Methods
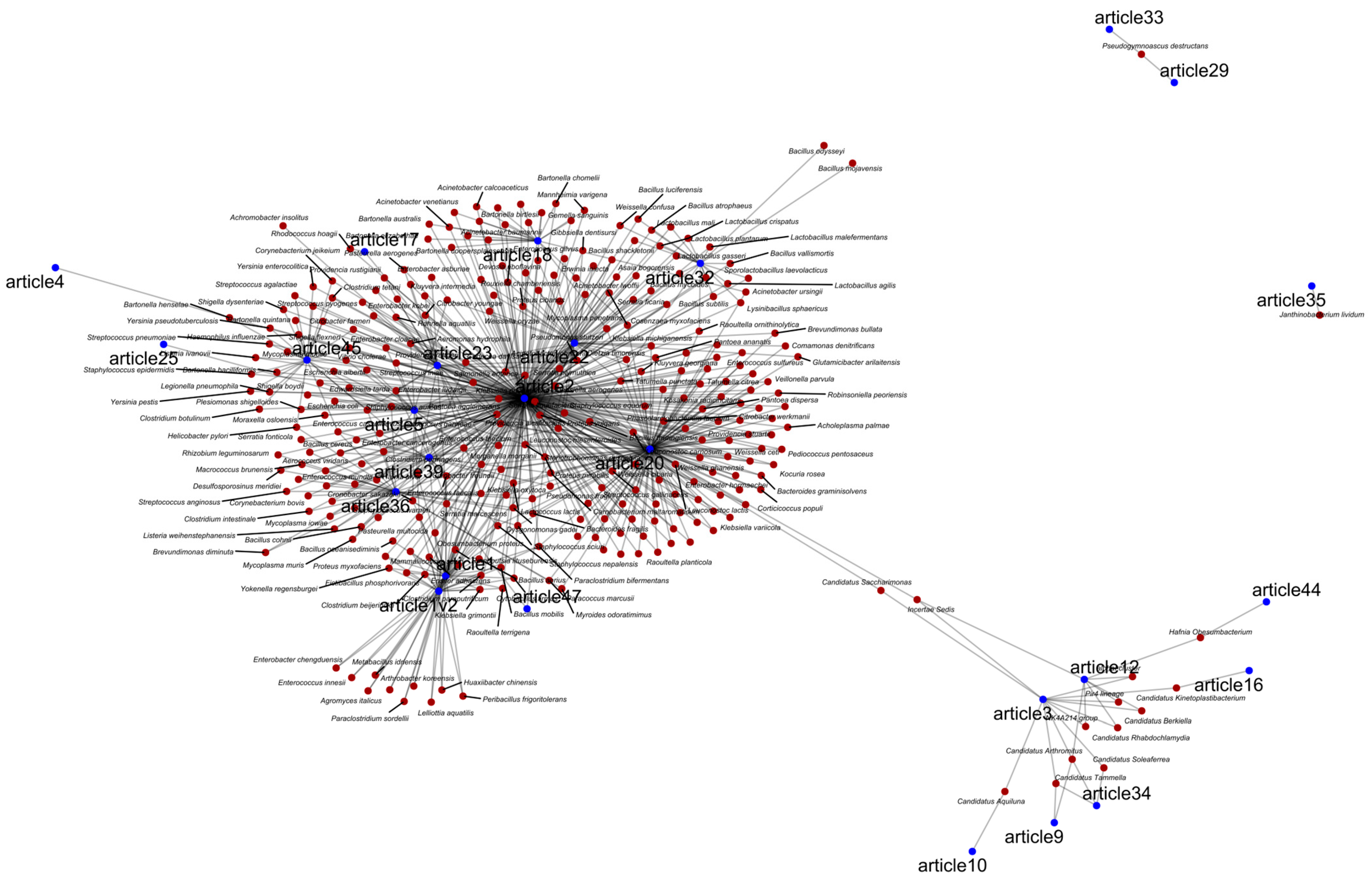
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Trends in Bat Microbiome Studies
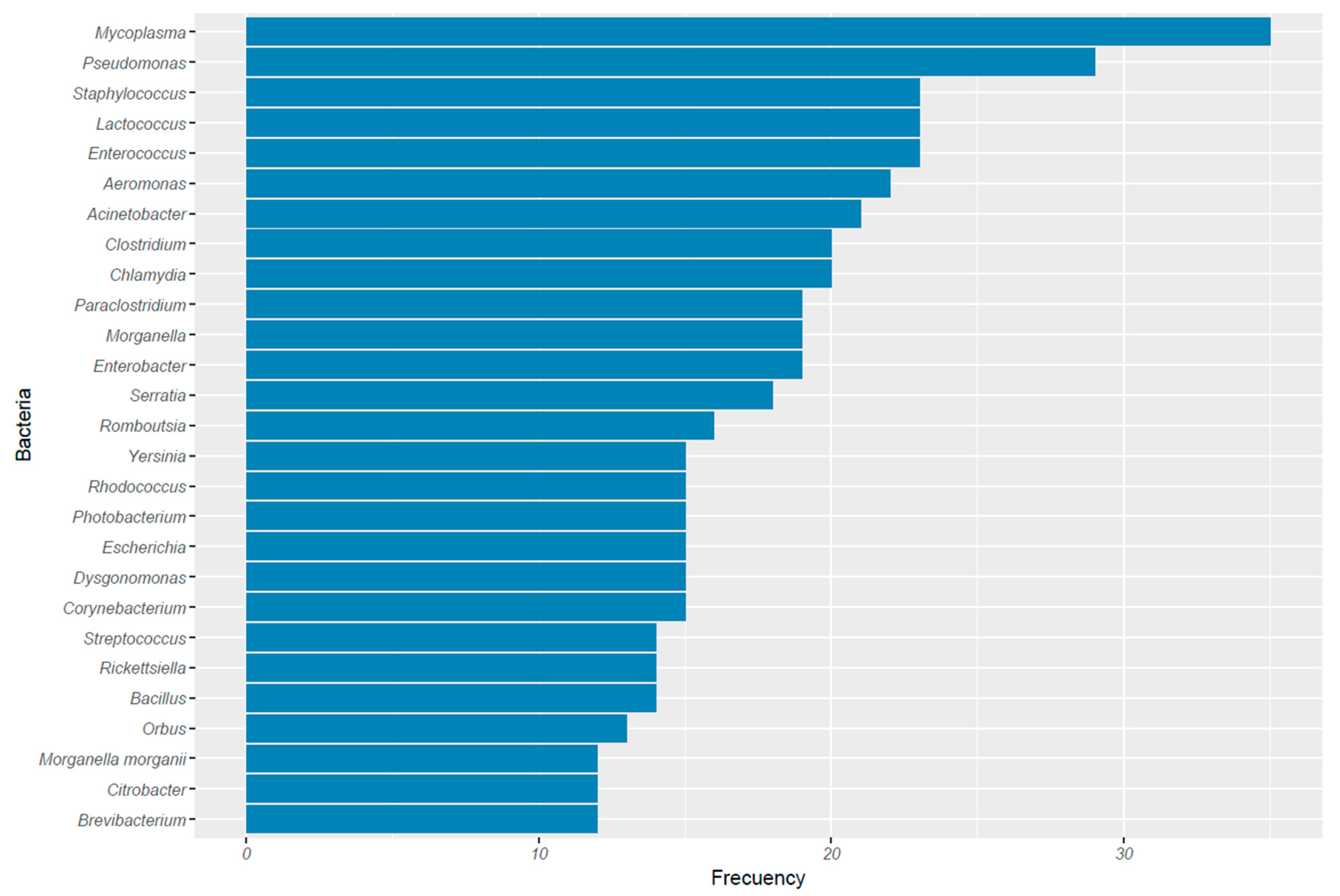
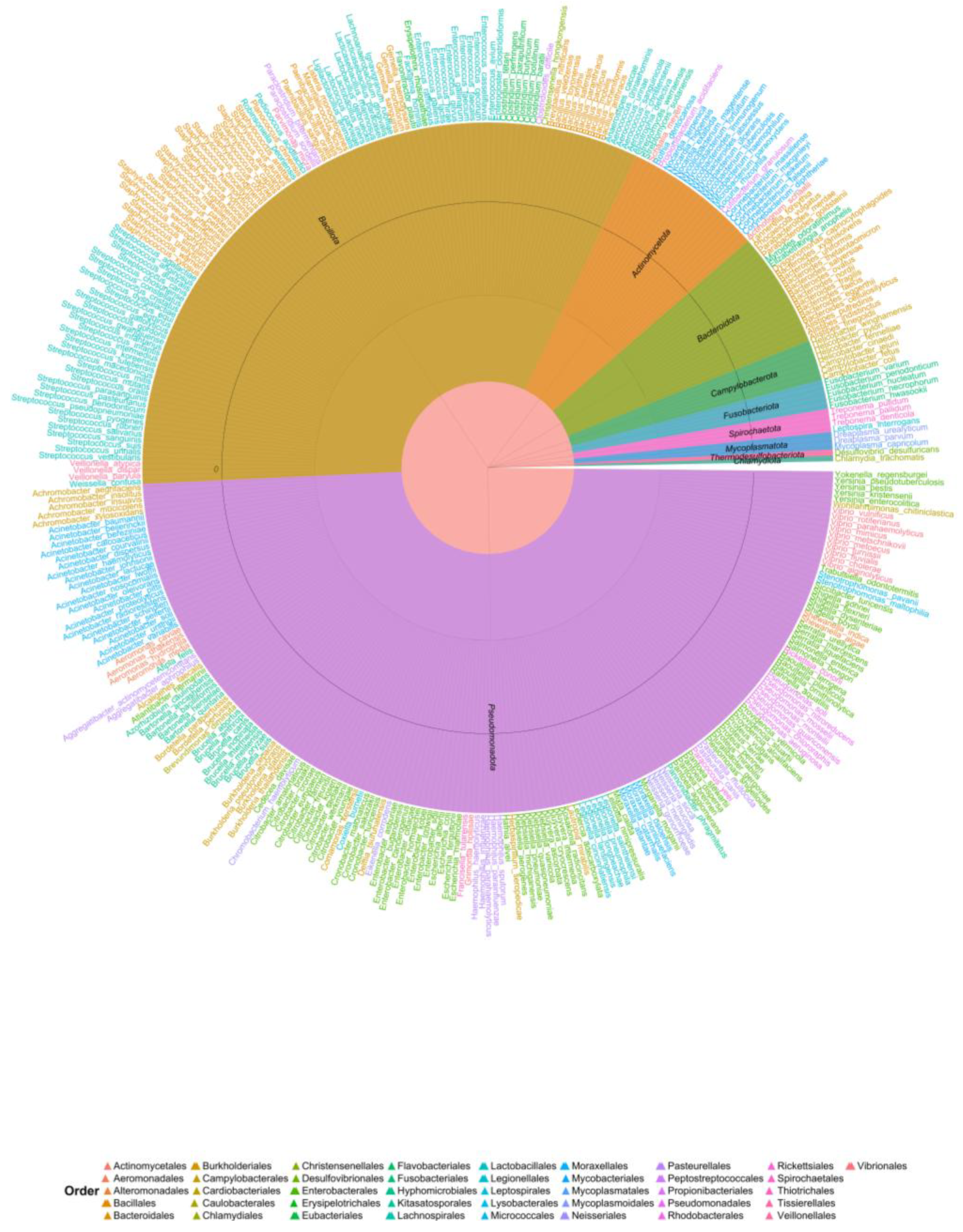
3.2. Bacteria Associated with Bats
3.3. Bias in Current Bat Microbiome Research
3.4. High-Throughput Sequencing Approaches in Bat Microbiome Studies
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgin, C.J.; Colella, J.P.; Kahn, P.L.; Upham, N.S. How many species of mammals are there? J. Mammal. 2018, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, N.B.; Cirranello, A.L. Bat Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Database. 2024. Available online: https://batnames.org (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Teeling, E.C.; Jones, G.; Rossiter, S.J. Phylogeny, Genes, and Hearing: Implications for the Evolution of Echolocation in Bats. Bat Bioacoust. 2016, 54, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumrungsri, S.; Lang, D.; Harrower, C.; Sripaoraya, E.; Kitpipit, K.; Racey, P.A. The Dawn Bat, Eonycteris spelaea Dobson (Chiroptera: Pteropodidae) Feeds Mainly on Pollen of Economically Important Food Plants in Thailand. Acta Chiropt. 2013, 15, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccucci, M.; Lanza, B. Bats and insect pest control: A review. Vespertilio 2014, 17, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez, E.A.; Ferrarezzi, H. Systematic patterns and evolution of feeding habits in Chiroptera (Archonta: Mammalia). J. Comp. Biol. 1996, 1, 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, H.L.; Jackson, E.W.; Webala, P.W.; Babyesiza, W.S.; Kerbis Peterhans, J.C.; Demos, T.C.; Patterson, B.D.; Gilbert, J.A. Ecology and Host Identity Outweigh Evolutionary History in Shaping the Bat Microbiome. Msystems 2019, 4, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodny, O.; Weinberg, M.; Reshef, L.; Harten, L.; Hefetz, A.; Gophna, U.; Feldman, M.W.; Yovel, Y. Coordinated change at the colony level in fruit bat fur microbiomes through time. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 3, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux-Labonté, V.; Tromas, N.; Shapiro, B.J.; Lapointe, F.-J. Environment and host species shape the skin microbiome of captive neotropical bats. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.S.; Hathaway, J.J.; Kimble, J.C.; Buecher, D.C.; Valdez, E.W.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Young, J.M.; Read, K.J.; Northup, D.E. Skin and fur bacterial diversity and community structure on American southwestern bats: Effects of habitat, geography and bat traits. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Altan, E.; Reyes, G.; Halstead, B.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E. Virome of Bat Guano from Nine Northern California Roosts. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, C.; Nitsche, A.; Kurth, A. Update on Potentially Zoonotic Viruses of European Bats. Vaccines 2021, 9, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; Smith, C.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, H.; Crameri, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bats Are Natural Reservoirs of SARS-Like Coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memish, Z.A.; Mishra, N.; Olival, K.J.; Fagbo, S.F.; Kapoor, V.; Epstein, J.H.; Alhakeem, R.; Durosinloun, A.; Al Asmari, M.; Islam, A.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in Bats, Saudi Arabia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardmeier, I.; Aeberhard, N.; Qi, W.; Schoenbaechler, K.; Kraettli, H.; Hatt, J.-M.; Fraefel, C.; Kubacki, J. Metagenomic analysis of fecal and tissue samples from 18 endemic bat species in Switzerland revealed a diverse virus composition including potentially zoonotic viruses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Li, S.; Yount, B.; Smith, A.; Sturges, L.; Olsen, J.C.; Nagel, J.; Johnson, J.B.; Agnihothram, S.; Gates, J.E.; et al. Evidence Supporting a Zoonotic Origin of Human Coronavirus Strain NL63. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12816–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.A.; Hassan, S.S.; Olival, K.J.; Mohamed, M.; Chang, L.-Y.; Hassan, L.; Saad, N.M.; Shohaimi, S.A.; Mamat, Z.C.; Naim, M.; et al. Characterization of Nipah Virus from Naturally Infected Pteropus vampyrus Bats, Malaysia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.M.; Kumulungui, B.; Pourrut, X.; Rouquet, P.; Hassanin, A.; Yaba, P.; Délicat, A.; Paweska, J.T.; Gonzalez, J.-P.; Swanepoel, R. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 2005, 438, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Victoria, J.G.; Wang, C.; Jones, M.; Fellers, G.M.; Kunz, T.H.; Delwart, E. Bat Guano Virome: Predominance of Dietary Viruses from Insects and Plants plus Novel Mammalian Viruses. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6955–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühldorfer, K. Bats and Bacterial Pathogens: A Review. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veikkolainen, V.; Vesterinen, E.J.; Lilley, T.M.; Pulliainen, A.T. Bats as Reservoir Hosts of Human Bacterial Pathogen, Bartonella mayotimonensis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Estók, P.; Kováts, D.; Flaisz, B.; Takács, N.; Szőke, K.; Krawczyk, A.; Kontschán, J.; Gyuranecz, M.; Fedák, A.; et al. Screening of bat faeces for arthropod-borne apicomplexan protozoa: Babesia canis and Besnoitia besnoiti-like sequences from Chiroptera. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.T.; Thomas, N.J.; Hunter, D.B. Parasitic Diseases of Wild Birds; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dimkić, I.; Fira, D.; Janakiev, T.; Kabić, J.; Stupar, M.; Nenadić, M.; Unković, N.; Grbić, M.L. The microbiome of bat guano: For what is this knowledge important? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, C.; Brinkmann, A.; Radonić, A.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Mühldorfer, K.; Nitsche, A.; Wibbelt, G.; Kurth, A. The virome of German bats: Comparing virus discovery approaches. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, V.F.S.; Rocha, P.A.; Silva, M.A.D.; Beltrão-Mendes, R.; Ramos, R.A.N.; Giannelli, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Estrela, P.C.; Alves, L.C. Survey on helminths and protozoa of free-living Neotropical bats from Northeastern Brazil. Acta Trop. 2018, 185, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvin, J.; Lanong, S.; Syiem, D.; De Mandal, S.; Kayang, H.; Kumar, N.S.; Kiran, G.S. Culture-dependent and metagenomic analysis of lesser horseshoe bats’ gut microbiome revealing unique bacterial diversity and signatures of potential human pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, L.; Masulli, M.; De Laurenzi, V.; Allocati, N. An overview of bats microbiota and its implication in transmissible diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1012189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingala, M.R.; Simmons, N.B.; Wultsch, C.; Krampis, K.; Speer, K.A.; Perkins, S.L. Comparing Microbiome Sampling Methods in a Wild Mammal: Fecal and Intestinal Samples Record Different Signals of Host Ecology, Evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingala, M.R.; Simmons, N.B.; Perkins, S.L. Bats Are an Untapped System for Understanding Microbiome Evolution in Mammals. Msphere 2018, 3, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.J. rentrez: An R package for the NCBI eUtils API. PeerJ Prepr. 2017, 5, e3179v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, N. europepmc: R Interface to the Europe PubMed Central RESTful Web Service; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain, S.; Zhu, H.; Jahn, N.; Boettiger, C.; Ram, K. rcrossref: Client for Various “CrossRef” “APIs”; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Piacentini, M. DB Browser for SQLite. 2024. Available online: https://sqlitebrowser.org/ (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Science Engineering Foundation Publications Output: U.S. Trends and International Comparisons. Sci. Eng. Indic. 2023. Available online: https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsb202333/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Tenaillon, O.; Skurnik, D.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. The population genetics of commensal Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, N.; Páez-Triana, L.; Ramírez, A.L.; Muñoz, M.; Goméz, M.; Medina, J.E.; Urbano, P.; Barragán, K.; Ariza, C.; Martínez, D.; et al. Microbial community dynamics in blood, faeces and oral secretions of neotropical bats in Casanare, Colombia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ScienceDirect. Topics: Medicine and Dentistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/ (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Gerbáčová, K.; Maliničová, L.; Kisková, J.; Maslišová, V.; Uhrin, M.; Pristaš, P. The Faecal Microbiome of Building-Dwelling Insectivorous Bats (Myotis myotis and Rhinolophus hipposideros) also Contains Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Representatives. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandžurová, A.; Bačkor, P.; Javorský, P.; Pristaš, P. Staphylococcus nepalensis in the guano of bats (Mammalia). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important Reservoir Hosts of Emerging Viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, A.T.; Ahn, M.; Goh, G.; Anderson, D.E.; Wang, L.-F. Lessons from the host defences of bats, a unique viral reservoir. Nature 2021, 589, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, G.S.; Adams, D.M. Recurrent evolution of extreme longevity in bats. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 20180860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, F.; Stawski, C. Hibernation and Torpor in Tropical and Subtropical Bats in Relation to Energetics, Extinctions, and the Evolution of Endothermy. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2011, 51, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Holderied, M.W. Bat echolocation calls: Adaptation and convergent evolution. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Parsons, S.; Walker, M.; Zhang, S. Bats respond to polarity of a magnetic field. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 2901–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutterer, R.; Ivanova, T.; Meyer-Cords, C.; Rodrigues, L. Bat Migrations in Europe: A Review of Banding Data and Literature; Federal Agency for Nature Conservation: Bonn, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, I.; Wang, L.-F. Bats and their virome: An important source of emerging viruses capable of infecting humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plowright, R.K.; E Field, H.; Smith, C.; Divljan, A.; Palmer, C.; Tabor, G.; Daszak, P.; E Foley, J. Reproduction and nutritional stress are risk factors for Hendra virus infection in little red flying foxes (Pteropus scapulatus). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.; Racey, P. Bats as bushmeat in Madagascar. Madag. Conserv. Dev. 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodré, M.M.; Gama, A.R.D.; Almeida, M.F.D. Updated list of bat species positive for rabies in Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2010, 52, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.; Free, T.; Martin, J. Metagenomics: Preventing future pandemics. Biotechniques 2021, 70, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L.; Sims, A.C.; Debbink, K.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Graham, R.L.; Scobey, T.; Plante, J.A.; Royal, S.R.; et al. SARS-like WIV1-CoV poised for human emergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3048–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, N.; de Jong, A.E.; Li, Y.; Trubl, G.; Xue, Y.; Dove, N.C. Metagenomic tools in microbial ecology research. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 67, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.; Vrbanac, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Aksenov, A.; Callewaert, C.; Debelius, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Kosciolek, T.; McCall, L.-I.; McDonald, D.; et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, T.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Li, S. Investigating the gut bacteria structure and function of hibernating bats through 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing and culturomics. MSystems 2025, 10, e01463–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morni, M.A.; William-Dee, J.; Jinggong, E.R.; Sabaruddin, N.A.-S.; Azhar, N.A.A.; Iman, M.A.; Larsen, P.A.; Seelan, J.S.S.; Bilung, L.M.; Khan, F.A.A. Gut microbiome community profiling of Bornean bats with different feeding guilds. Anim. Microbiome 2025, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.J.; Suski, C.D.; O’Keefe, J.M. Molecular epidemiology of Eimeria spp. parasites and the faecal microbiome of Indiana bats (Myotis sodalis): A non-invasive, multiplex metabarcode survey of an endangered species. Microb. Genom. 2025, 11, 001358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Giacchino, I.; Blanda, V.; Gucciardi, F.; Scibetta, S.; La Russa, F.; Lastra, A.; Purpari, G.; Grasso, R.; Spena, M.T.; et al. Zoonotic Bacteria and Vector-Borne Protozoa in Troglophilus Bat Colonies in Sicily (Southern Italy): A Biomolecular Survey. Animals 2025, 15, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poosakkannu, A.; Xu, Y.; Suominen, K.M.; Meierhofer, M.B.; Sørensen, I.H.; Madsen, J.J.; Plaquin, B.; Guillemain, M.; Joyeux, E.; Keišs, O.; et al. Pathogenic bacterial taxa constitute a substantial portion of fecal microbiota in common migratory bats and birds in Europe. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e01948-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, D.W.; Meyer, M.; Kümmerle, C.; A Alvarado-Barrantes, K.; Wilhelm, K.; Sommer, S.; Tschapka, M.; Risely, A. Delayed feeding disrupts diurnal oscillations in the gut microbiome of a neotropical bat in captivity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2025, 101, fiaf012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisnik, M.; Walker, D.M. Bat Cutaneous Microbial Assemblage Functional Redundancy Across a Host-Mediated Disturbance. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano-Hernández, H.D.; Montes-Carreto, L.M.; Guerrero, J.A.; Martinez-Romero, E. The fecal microbiota of the mouse-eared bat (Myotis velifer) with new records of microbial taxa for bats. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0314847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insuk, C.; Cheeptham, N.; Lausen, C.; Xu, J. DNA metabarcoding analyses reveal fine-scale microbiome structures on Western Canadian bat wings. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e00376-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Leng, H.; Li, A.; Dai, W.; Huang, L.; Feng, J.; Sun, K. Microbiota diversity and anti-Pseudogymnoascus destructans bacteria isolated from Myotis pilosus skin during late hibernation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e00693-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canata, D.A.M.; Benfato, M.S.; Pereira, F.D.; Pereira, M.J.R.; Hackenhaar, F.S.; Mann, M.B.; Frazzon, A.P.G.; Rampelotto, P.H. Comparative Analysis of the Gut Microbiota of Bat Species with Different Feeding Habits. Biology 2024, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraci, Ö.; Antonatou-Papaioannou, A.; Jünemann, S.; Schneeberger, K.; Schulze, M.; Scheffler, I.; Caspers, B.A. Bats, Bacteria, and Bat Smell V.2.0: Repeatable Sex-Specific Differences in Scent Organ Microbiota. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Leng, H.; Li, J.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Sun, K.; Feng, J. The role of host traits and geography in shaping the gut microbiome of insectivorous bats. Msphere 2024, 9, e00087-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, I.V.; Mazanko, M.S.; Kulaeva, E.D.; Golovin, S.N.; Malinovkin, A.V.; Aleshukina, I.S.; Aleshukina, A.V.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Tverdokhlebova, T.I.; Chikindas, M.L.; et al. Gut microbiota of bats: Pro-mutagenic properties and possible frontiers in preventing emerging disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.R.; Ikeda, P.; Lee, D.A.B.; Amaral, R.B.D.; Carvalho, L.A.L.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Torres, J.M.; de Mello, V.V.C.; Rice, G.K.; Cer, R.Z.; et al. Characterization of the bacterial microbiome of non-hematophagous bats and associated ectoparasites from Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1261156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, R.; Jones, C.; Ledezma-Campos, P.; Czirják, G.Á.; Sommer, S.; Gillespie, T.R.; Vicente-Santos, A. Gut microbial shifts in vampire bats linked to immunity due to changed diet in human disturbed landscapes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, N.; Muñoz, M.; Castillo-Castañeda, A.; Hernandez, C.; Urbano, P.; Shaban, M.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A.; Ramírez, J.D. Characterizing the blood microbiota of omnivorous and frugivorous bats (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae) in Casanare, eastern Colombia. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, Z.; Leng, H.; Jin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, K.; Feng, J. Seasonal assembly of skin microbiota driven by neutral and selective processes in the greater horseshoe bat. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 4695–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, T.S.; Weinberg, M.; Moreno, K.R.; Czirják, G.Á.; Yovel, Y. In sickness and in health: The dynamics of the fruit bat gut microbiota under a bacterial antigen challenge and its association with the immune response. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1152107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd-Yusof, N.S.; Abdul-Latiff, M.A.B.; Mohd-Ridwan, A.R.; Badrulisham, A.S.; Othman, N.; Yaakop, S.; Md-Nor, S.; Md-Zain, B.M. First report on metabarcoding analysis of gut microbiome in Island Flying Fox (Pteropus hypomelanus) in island populations of Malaysia. Biodivers. Data J. 2022, 10, e69631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Q.; Lv, X.; Pu, J.; Zhu, W.; Lu, S.; Jin, D.; Liu, L.; Shi, Z.; et al. The Threat of Potentially Pathogenic Bacteria in the Feces of Bats. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01802-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Spena, M.T.; Fisichella, V.; Mascetti, A.; Colnaghi, M.; Grasso, M.; Piraino, C.; Sciurba, F.; Grasso, R. Cultivable Bacteria Associated with the Microbiota of Troglophile Bats. Animals 2022, 12, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisnik, M.; Grinath, J.B.; Munafo, J.P.; Walker, D.M. Functional Redundancy in Bat Microbial Assemblage in the Presence of the White Nose Pathogen. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, K.; Barbon, A.; Gibbon, M.J.; Lloyd, D.H.; Loeffler, A.; Feil, E.J. Staphylococcus aureus lineages associated with a free-ranging population of the fruit bat Pteropus livingstonii retained over 25 years in captivity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Agudelo, J.D.; Ramírez-Chaves, H.E.; Ossa-López, P.A.; Rivera-Páez, F.A. Bacteria related to tick-borne pathogen assemblages in Ornithodoros cf. hasei (Acari: Argasidae) and blood of the wild mammal hosts in the Orinoquia region, Colombia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 87, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Hamm, P.S.; Hathaway, J.J.M.; Winter, A.S.; A Caimi, N.; Buecher, D.C.; Valdez, E.W.; E Northup, D. Great diversity of KSα sequences from bat-associated microbiota suggests novel sources of uncharacterized natural products. FEMS Microbes 2022, 3, xtac012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, R.; Schmid, D.W.; Wasimuddin; Brändel, S.D.; Rasche, A.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C.; Tschapka, M.; Sommer, S. Interaction between MHC diversity and constitution, gut microbiota and Astrovirus infections in a neotropical bat. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 3342–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, A.; Dai, W.; Leng, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, L.; Sun, K.; Feng, J. Skin Microbiota Variation Among Bat Species in China and Their Potential Defense Against Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 808788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víquez-R, L.; Speer, K.; Wilhelm, K.; Simmons, N.; Medellín, R.A.; Sommer, S.; Tschapka, M. A Faithful Gut: Core Features of Gastrointestinal Microbiota of Long-Distance Migratory Bats Remain Stable despite Dietary Shifts Driving Differences in Specific Bacterial Taxa. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01525-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua, O.; Nyholm, L.; Morris, E.; Chaverri, G.; Montalvo, L.G.H.; Flores-Martinez, J.J.; Lin, A.; Razgour, O.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Alberdi, A. The role of the gut microbiota in the dietary niche expansion of fishing bats. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, I.V.; Popov, I.V.; Krikunova, A.A.; Lipilkina, T.A.; Derezina, T.N.; Chikindas, M.L.; Venema, K.; Ermakov, A.M. Gut Microbiota Composition of Insectivorous Synanthropic and Fructivorous Zoo Bats: A Direct Metagenomic Comparison. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Li, Z.; Dai, W.; Parise, K.L.; Leng, H.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, K.; Hoyt, J.R.; Feng, J. Bacterial community dynamics on bats and the implications for pathogen resistance. Env. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 1484–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Liu, B.; Wu, H.; Feng, J.; Jiang, T. Seasonal Dietary Shifts Alter the Gut Microbiota of Avivorous Bats: Implication for Adaptation to Energy Harvest and Nutritional Utilization. Msphere 2021, 6, e0046721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, H.L.; Gilbert, J.A.; Dick, C.W. Associations between Afrotropical bats, eukaryotic parasites, and microbial symbionts. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, C.; Schoeman, M.C.; Sanko, T.J.; Bezuidenhout, C.; Mienie, C.M.S.; Preiser, W.; Vosloo, D. Wastewater treatment works change the intestinal microbiomes of insectivorous bats. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corduneanu, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Sándor, A.D.; Hornok, S.; Malmberg, M.; Viso, N.P.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E. The heart microbiome of insectivorous bats from Central and South Eastern Europe. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux-Labonté, V.; Dorville, N.A.S.-Y.; Willis, C.K.R.; Lapointe, F.-J. Antifungal Potential of the Skin Microbiota of Hibernating Big Brown Bats (Eptesicus fuscus) Infected With the Causal Agent of White-Nose Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edenborough, K.M.; Mu, A.; Mühldorfer, K.; Lechner, J.; Lander, A.; Bokelmann, M.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Radonic, A.; Kurth, A. Microbiomes in the insectivorous bat species Mops condylurus rapidly converge in captivity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0223629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaona, O.; Cerqueda-García, D.; Moya, A.; Neri-Barrios, X.; Falcón, L.I. Geographical separation and physiology drive differentiation of microbial communities of two discrete populations of the bat Leptonycteris yerbabuenae. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisnik, M.; Bowers, O.; Moore, A.J.; Jones, B.F.; Campbell, J.R.; Walker, D.M. The cutaneous microbiota of bats has in vitro antifungal activity against the white nose pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiz193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ange-Stark, M.; Parise, K.L.; Cheng, T.L.; Hoyt, J.R.; Langwig, K.E.; Frick, W.F.; Kilpatrick, A.M.; Gillece, J.; MacManes, M.D.; Foster, J.T. White-nose syndrome restructures bat skin microbiomes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02715-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato-Bailón, L.; García-Ulloa, M.; Santos, A.; Guixé, D.; Camprodon, J.; Florensa-Rius, X.; Molleda, R.; Manzano, R.; Ribas, M.P.; Espunyes, J.; et al. The fecal bacterial microbiome of the Kuhl’s pipistrelle bat (Pipistrellus kuhlii) reflects landscape anthropogenic pressure. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-L.; Gao, Y.-Z.; Ge, X.-Y.; Shi, Z.-L.; Zhou, N.-Y. Special Features of Bat Microbiota Differ from Those of Terrestrial Mammals. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, A.; Sun, D.; Li, Z.; Xiao, G.; Feng, J. Changes in the gut microbiota during Asian particolored bat (Vespertilio sinensis) development. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Junker, K.; Wood, S.; Ueckermann, E.A.; Venter, G.J.; van der Mescht, L.; Heyne, H.; Jacobs, D.S. Compositional turnover in ecto-and endoparasite assemblages of an African bat, Miniopterus natalensis (Chiroptera, Miniopteridae): Effects of hierarchical scale and host sex. Parasitology 2020, 147, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
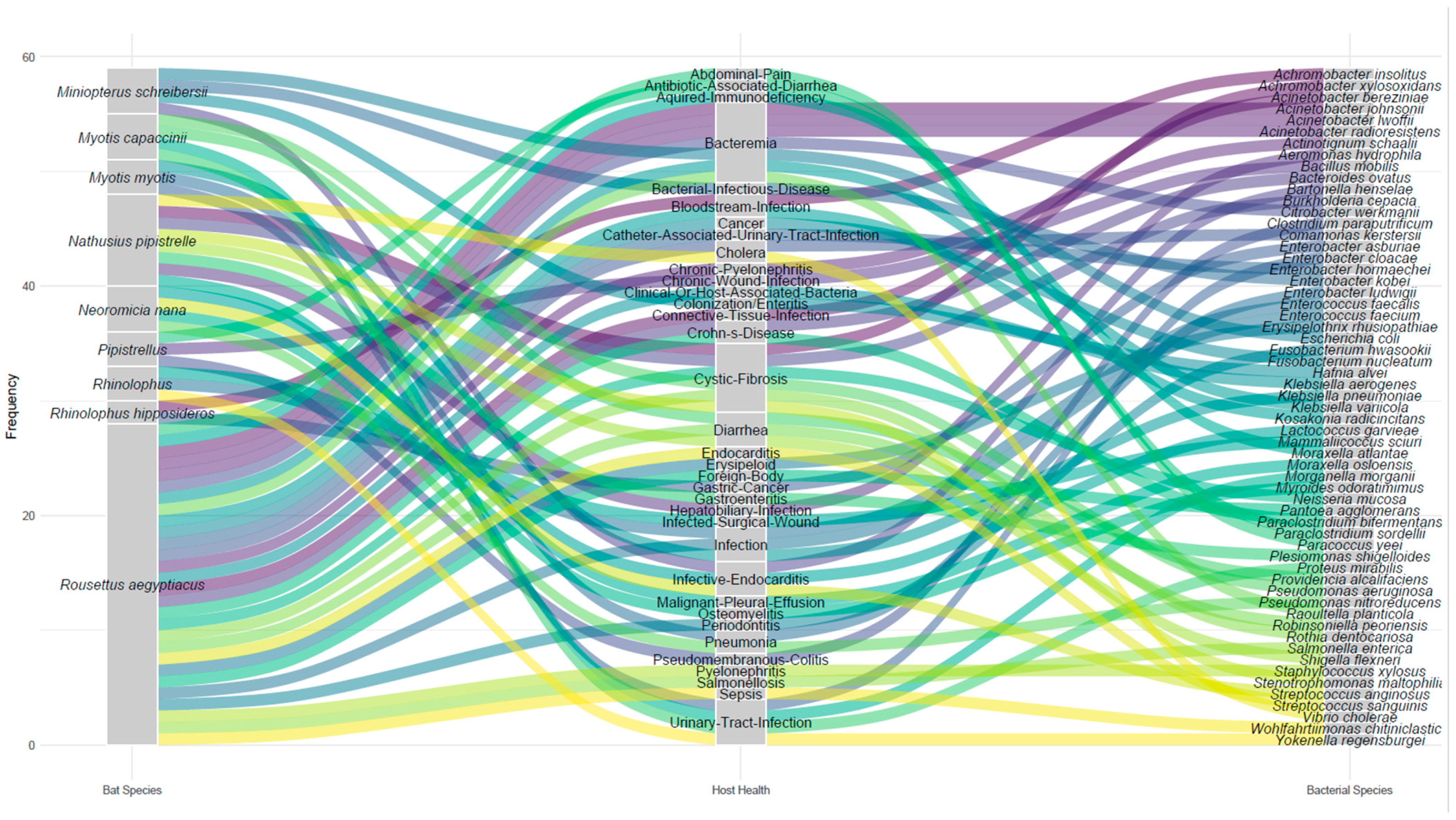
| Bacteria | Disease * |
|---|---|
| Corynebacterium jeikeium Jackman et al., 1988 | Bacteremia, endocarditis, infections in immunocompromised patients |
| Enterococcus faecalis (Andrewes and Horder 1906) Schleifer and Kilpper-Bälz 1984 | Urinary tract infections, endocarditis, sepsis |
| Enterococcus faecium (Orla-Jensen 1919) Schleifer and Kilpper-Bälz 1984 | Resistant nosocomial infections (VRE) |
| Moraxella osloensis Bøvre and Henriksen 1967 (Approved Lists 1980) | Opportunistic infections (otitis, bacteremia) |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus (Fairbrother 1940) Shaw et al. 1951 (Approved Lists 1980) | Urinary tract infection (common in young women) |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis Freney et al., 1988 | Skin infections, endocarditis |
| Streptococcus suis Hasegawa et al., 2024 | Meningitis, sepsis (zoonosis from pigs) |
| Campylobacter jejuni (Jones et al., 1931) Steele and Owen 1988 | Gastroenteritis, Guillain-Barré syndrome |
| Pasteurella canis Mutters et al., 1985 | Infections from dog bites |
| Chromobacterium haemolyticum Han et al., 2008 | Rare systemic infections, sepsis |
| Elizabethkingia anophelis (Kämpfer et al., 2011) García-López et al., 2020 | Nosocomial infections, neonatal meningitis |
| Ralstonia pickeettii (Ralston et al., 1973) Yabuuchi et al., 1996 | Opportunistic nosocomial infections |
| Myroides odoratimimus (Vancanneyt et al., 1996) García-López et al., 2020 | Wound infections, urinary tract infections, pneumonia |
| Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (Klinger 1912) Nørskov-Lauritsen and Kilian 2006 | Aggressive periodontitis, endocarditis |
| Haemophilus parainfluenzae Rivers 1922 (Approved Lists 1980) | Opportunistic respiratory infections |
| Veillonella parvula (Veillon and Zuber 1898) Prévot 1933 (Approved Lists 1980) | Endocarditis, polymicrobial infections |
| Bacteroides fragilis (Veillon and Zuber 1898) Castellani and Chalmers 1919 (Approved Lists 1980) | Intra-abdominal abscesses, bacteremia |
| Propionibacterium acnes McDowell et al., 2016 | Acne, prosthetic device infections |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum Gharbia and Shah 1992 | Periodontitis, abscesses, associated with colorectal cancer |
| Parabacteroides distasonis (Eggerth and Gagnon 1933) Sakamoto and Benno 2006 | Intestinal and opportunistic infections |
| Treponema denticola (ex Flügge 1886) Chan et al., 1993 | Advanced periodontal disease |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae (Schroeter 1886) Trevisan 1887 (Approved Lists 1980) | Pneumonia (including classical lobar pneumonia), urinary tract infections, sepsis, liver abscesses |
| Acinetobacter baumannii Bouvet and Grimont 1986 | Nosocomial pneumonia, wound infections, sepsis, meningitis (especially in ICU) |
| Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach 1884 (Approved Lists 1980) | Skin infections, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, pneumonia, food poisoning, sepsis |
| Streptococcus pyogenes Rosenbach 1884 (Approved Lists 1980) | Pharyngitis, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever, necrotizing fasciitis, impetigo, toxic shock syndrome |
| Streptococcus agalactiae Lehmann and Neumann 1896 (Approved Lists 1980) | Neonatal sepsis and meningitis, urinary tract infections, chorioamnionitis in pregnant women |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae (Klein 1884) Chester 1901 (Approved Lists 1980) | Neumonía, meningitis, otitis media, sinusitis, bacteriemia |
| Moraxella catarrhalis (Frosch and Kolle 1896) Henriksen and Bøvre 1968 (Approved Lists 1980) | Otitis media, sinusitis, respiratory infections (bronchitis, exacerbated COPD) |
| Escherichia coli (Migula 1895) Castellani and Chalmers 1919 (Approved Lists 1980) | Urinary tract infections, gastroenteritis (EHEC, ETEC), sepsis, neonatal meningitis |
| Yersinia enterocolitica (Schleifstein and Coleman 1939) Neubauer et al., 2000 | Gastroenteritis, pseudoapendicitis, adenitis mesentérica |
| Proteus mirabilis Hauser 1885 (Approved Lists 1980) | Urinary tract infections, kidney stone formation (due to urease), bacteremia |
| Providencia stuartii (Buttiaux et al., 1954) Ewing 1962 (Approved Lists 1980) | Catheter-associated urinary tract infections, nosocomial infections in immunocompromised patients |
| Serratia marcescens Bizio 1823 (Approved Lists 1980) | Nosocomial infections: respiratory, urinary, sepsis, wound infections |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Schroeter 1872) Migula 1900 (Approved Lists 1980) | Pulmonary infections (cystic fibrosis, ICU), burns, external otitis, ocular infections |
| Clostridioides difficile (Hall and O’Toole 1935) Lawson et al., 2016 | Pseudomembranous colitis (after antibiotics), antibiotic-associated diarrhea, toxic megacolon |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae Somerson et al., 1963 | Atypical pneumonia, bronchitis, pharyngitis, extrapulmonary complications (rash, hemolytic anemia) |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Hugh 1981 ex Hugh and Ryschenkow 1961) Palleroni and Bradbury 1993 | Respiratory, urinary tract, and bloodstream infections (mainly in immunocompromised patients) |
| Aeromonas hydrophila (Chester 1901) Stanier 1943 (Approved Lists 1980) | Diarrhea, wound infections (especially in freshwater), sepsis in immunosuppressed |
| Vibrio vulnificus (Reichelt et al., 1979) Farmer 1980 | Wound infections (necrotizing), fulminant septicemia from shellfish consumption, gastroenteritis |
| Pasteurella multocida (Lehmann and Neumann 1899) Rosenbusch and Merchant 1939 (Approved Lists 1980) | Cellulitis and animal bite infections (dogs/cats), chronic respiratory infections |
| Bartonella henselae (Regnery et al., 1992) Brenner et al., 1993 | Cat scratch disease (lymphadenopathy), bacillary angiomatosis (in immunocompromised) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soto-López, J.D.; Fernández-Soto, P.; Muro, A. Bacterial Composition Across Bat Species: A Human Health Perspective. Animals 2025, 15, 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213126
Soto-López JD, Fernández-Soto P, Muro A. Bacterial Composition Across Bat Species: A Human Health Perspective. Animals. 2025; 15(21):3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213126
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoto-López, Julio David, Pedro Fernández-Soto, and Antonio Muro. 2025. "Bacterial Composition Across Bat Species: A Human Health Perspective" Animals 15, no. 21: 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213126
APA StyleSoto-López, J. D., Fernández-Soto, P., & Muro, A. (2025). Bacterial Composition Across Bat Species: A Human Health Perspective. Animals, 15(21), 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213126






