Baicalin Mitigates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Pulmonary and Vascular Injury via NLRP3/COX-2 Inhibition in Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Bacteria and Culture Conditions
2.3. Animals
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Immunohistochemical Assays for IL-1β, IL-18, COX-2, and NLRP3
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and MMPBSA
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
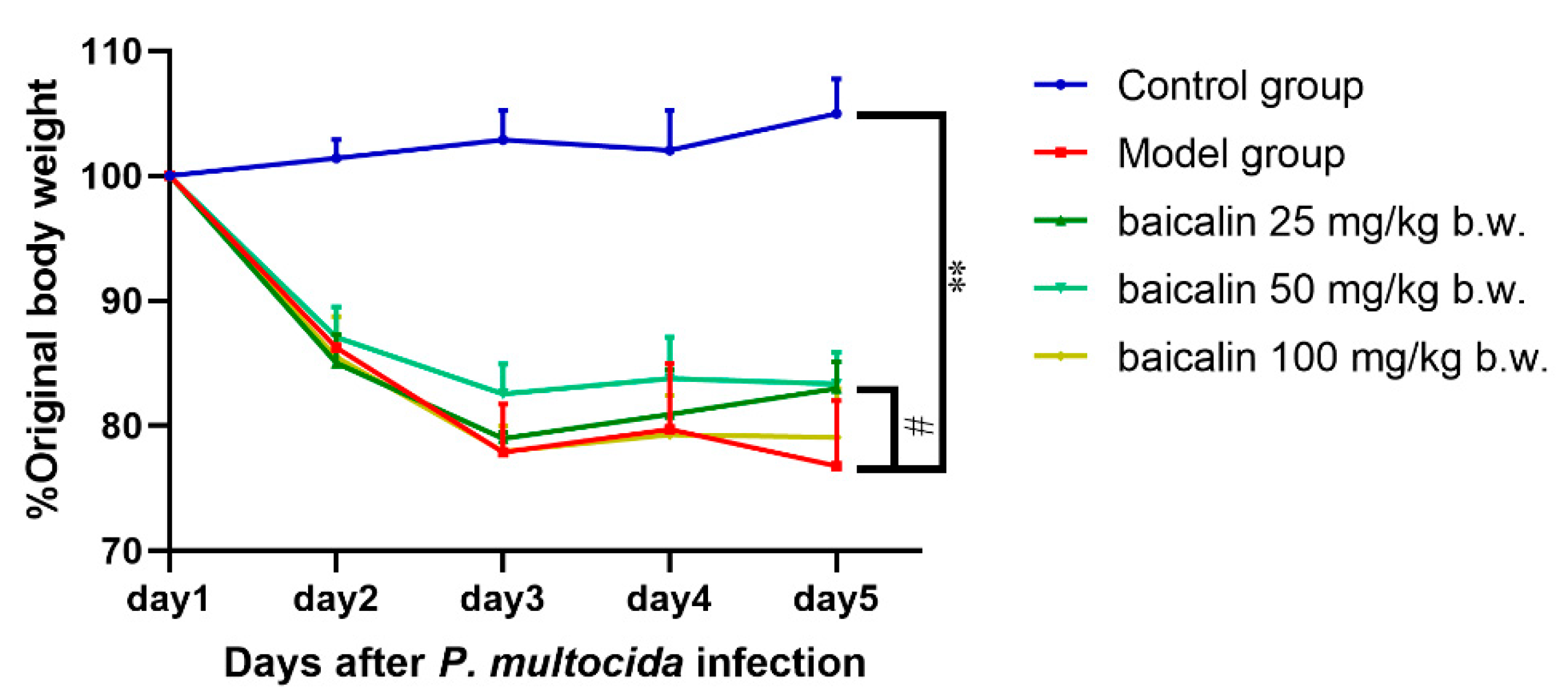
3.1. Altered Mental Status
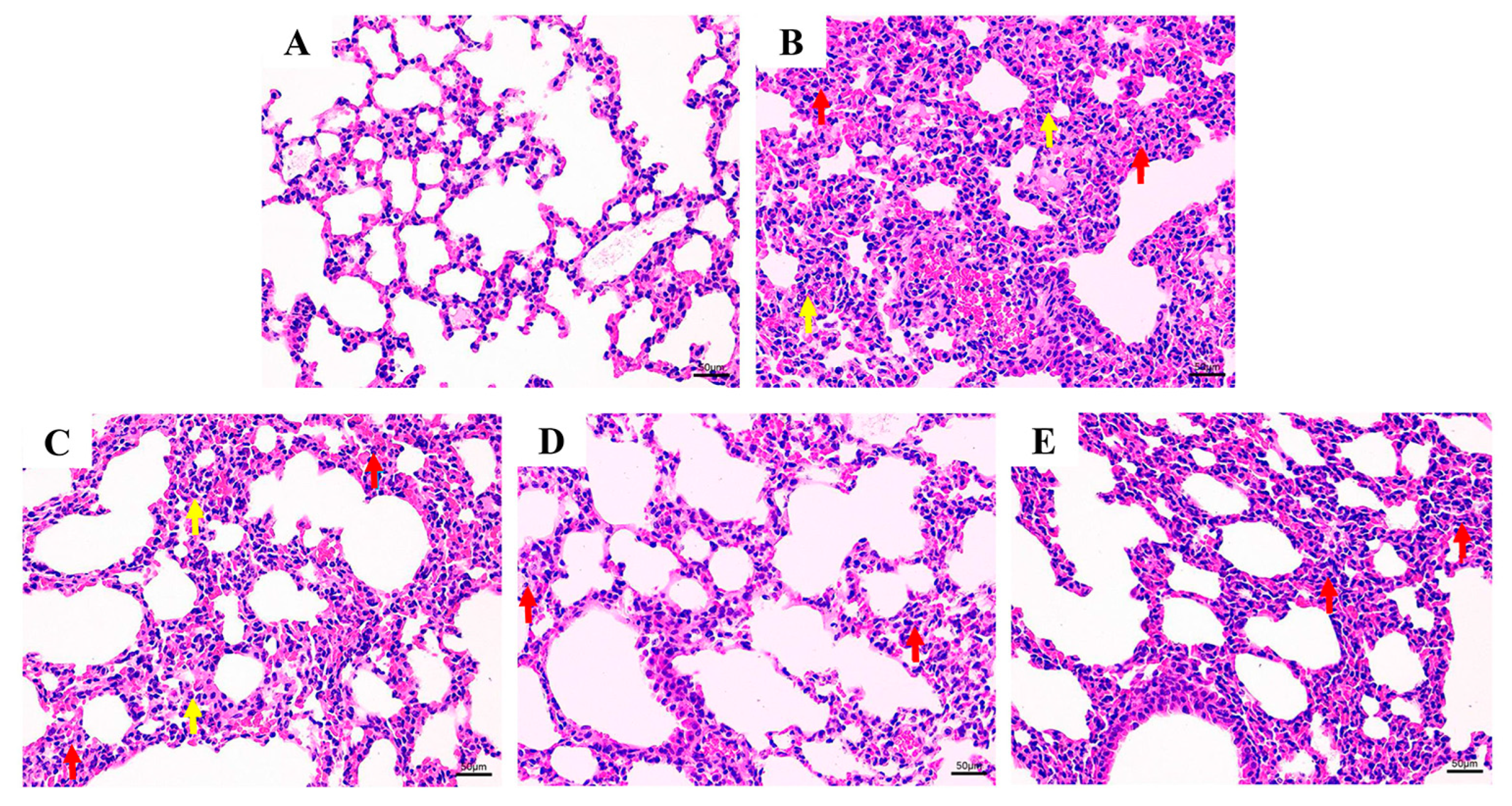
3.2. Histological Evaluation
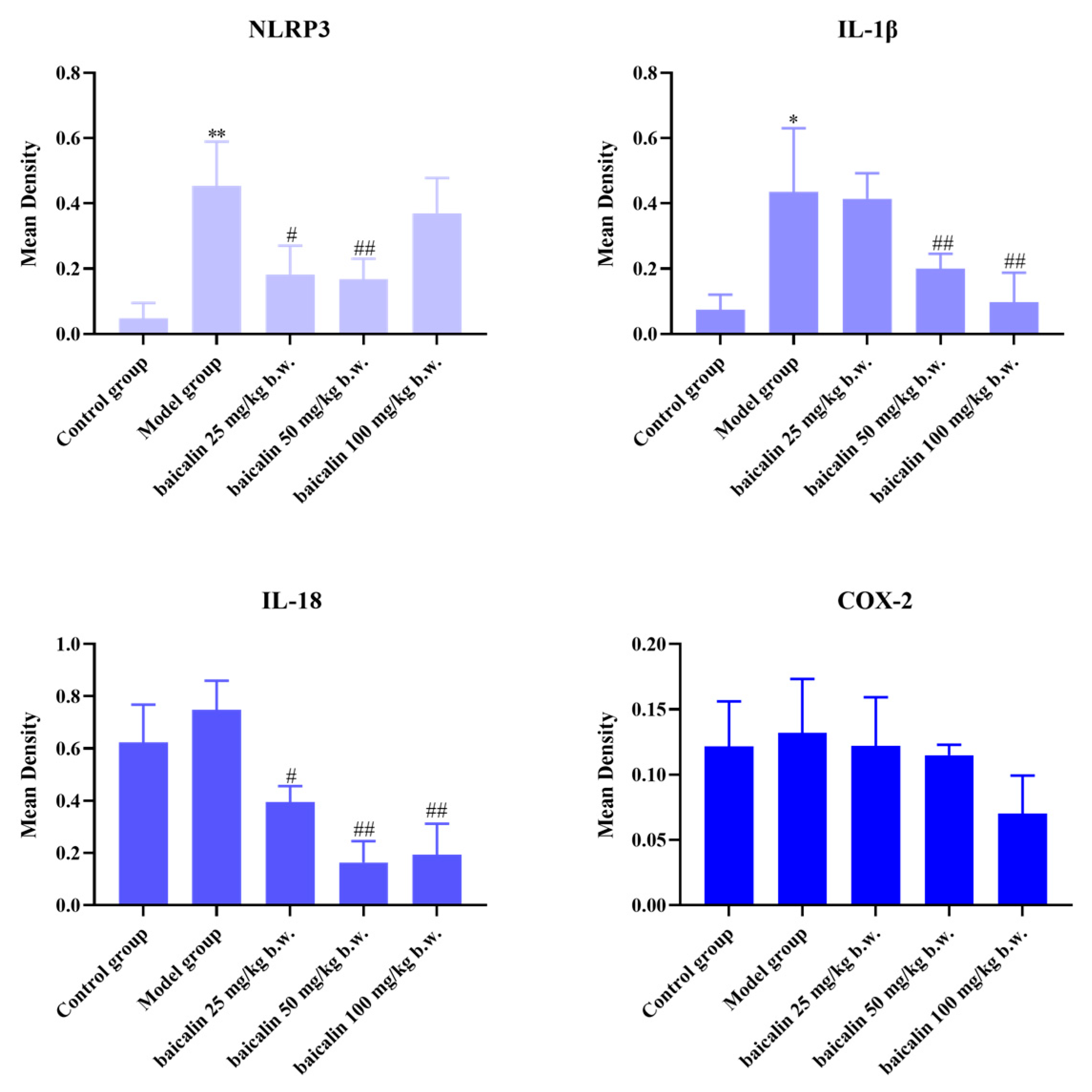
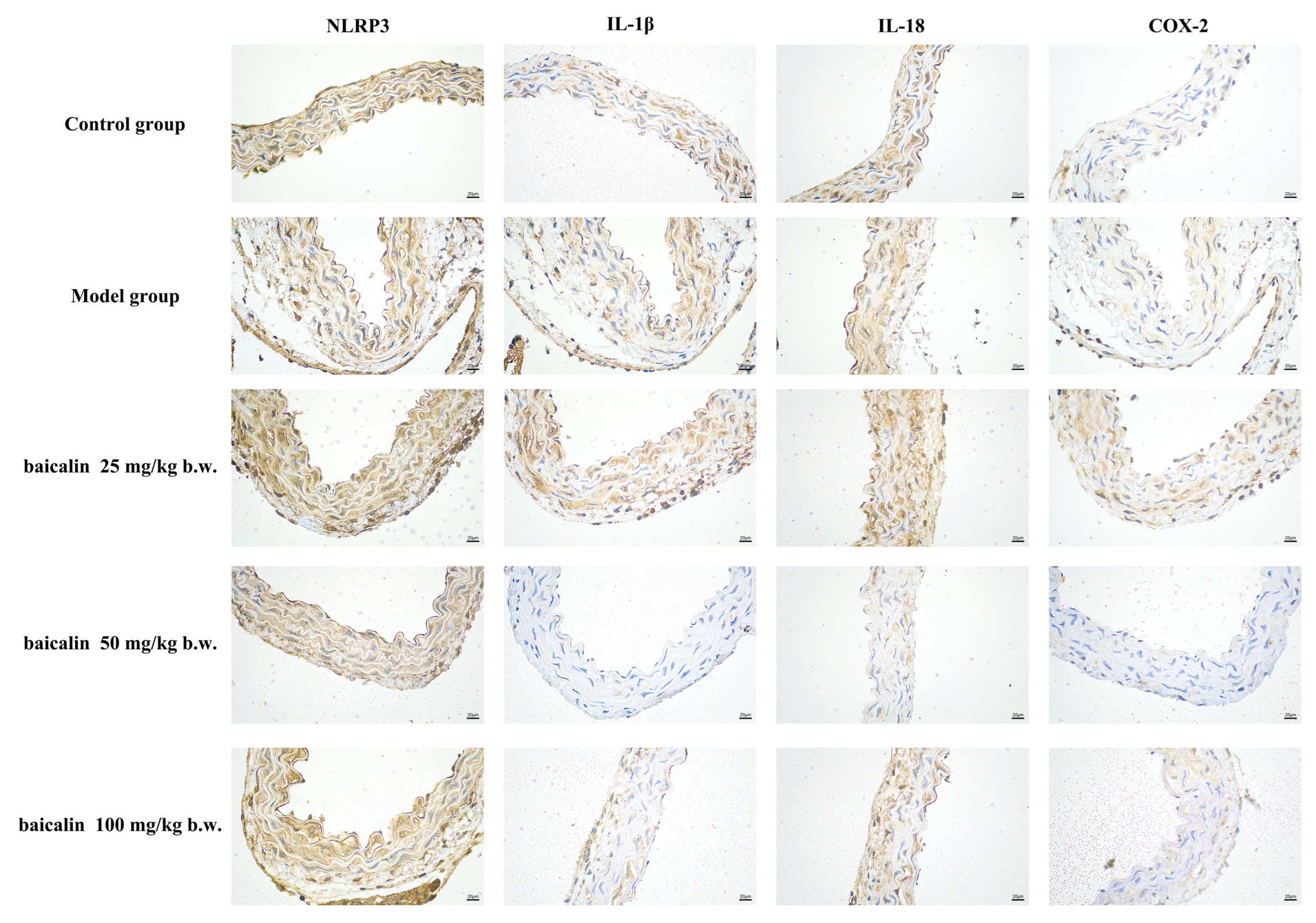
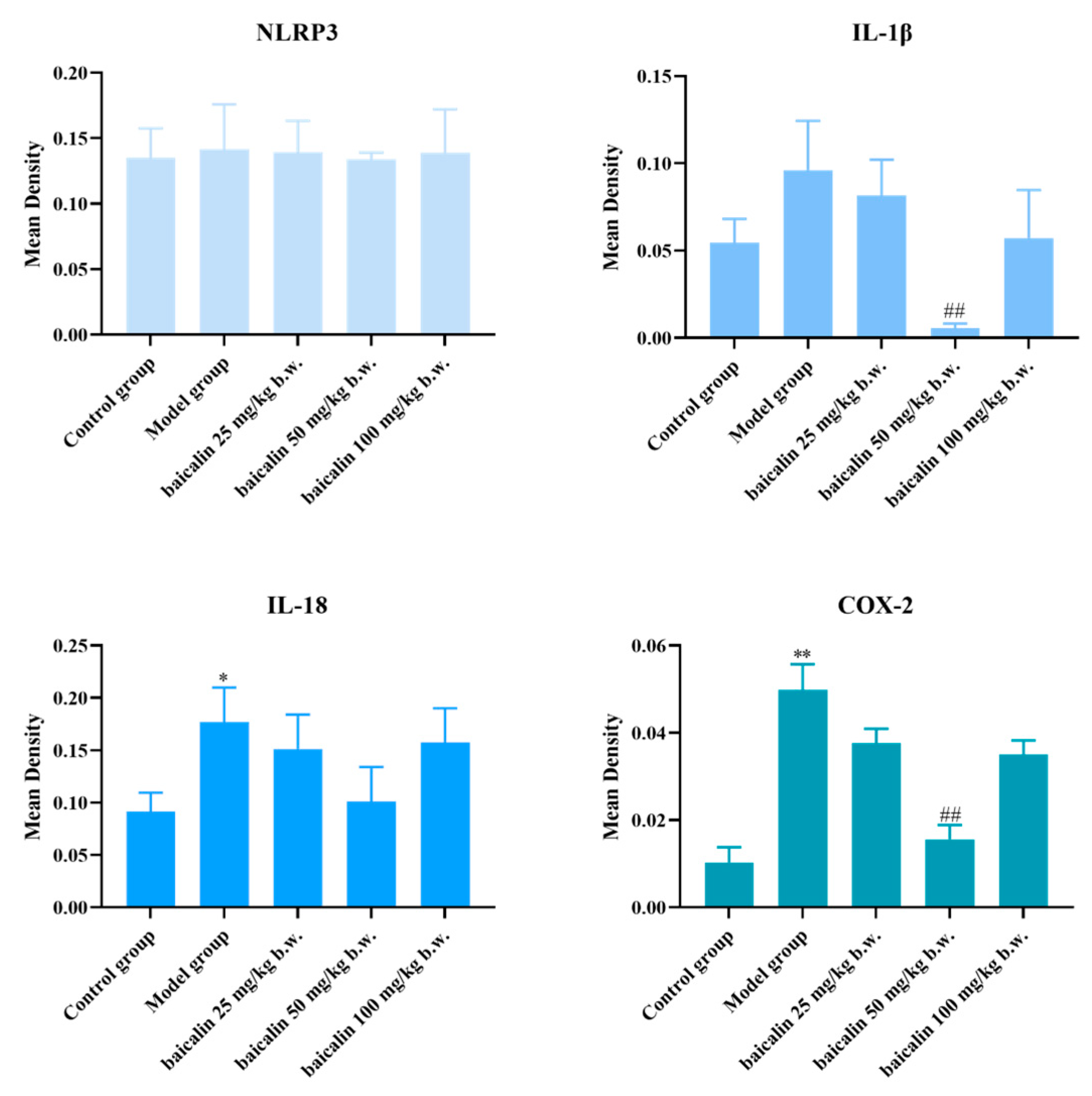
3.3. Expression of IL-1β, IL-18, COX-2, and NLRP3
3.4. Analysis of Molecular Docking Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF3 | AlphaFold3 |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| GLY | glycine |
| HIS | histidine |
| ILE | isoleucine |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-18 | interleukin-18 |
| LYS | lysine |
| NLRP3 | NOD, LRR, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| P. multocida | Pasteurella multocida |
| THR | threonine |
| VAL | valine |
References
- El-Demerdash, A.S.; Mowafy, R.E.; Fahmy, H.A.; Matter, A.A.; Samir, M. Pathognomonic features of isolates among various avian species in Sharkia Governorate, Egypt. World J. Microb. Biot. 2023, 39, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, M.; Baloni, S.; Thakor, J.C.; Kumar, P.; Thomas, P.; Nagaleekar, V.K.; Dhama, K.; Singh, R.; Singh, K.P.; Mani, S.; et al. Pathology, virulence-associated gene profiling, antimicrobial susceptibility, and pathogenicity of untypeable capsular serotypes of Pasteurella multocida isolated from slaughtered pigs of India. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovad112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K.; Goyal, S.M.; Joo, H.S. Retrospective analysis of etiologic agents associated with respiratory diseases in pigs. Can. Vet. J. 2003, 44, 735–737. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Yu, X.X.; He, D.X.; Ku, X.G.; Hong, B.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, H.F.; He, Q.G. Investigation and analysis of etiology associated with porcine respiratory disease complex in China from 2017 to 2021. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 960033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoheer, R.; Abd Wahid, M.E.; Zakaria, H.A.; Jonet, M.A.B.; Al-shaibani, M.M.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Addis, S.N.K. Spatial, temporal, and demographic patterns in the prevalence of hemorrhagic septicemia in 41 countries in 2005–2019: A systematic analysis with special focus on the potential development of a new-generation vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihunie, F.B.; Syoum, A.; Dubie, T. Seroprevalence of Pasteurella multocida Serotype A2 in Cattle, Afar Region, Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Int. 2025, 2025, 6610210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tarabili, R.M.; Enany, M.E.; Alenzi, A.M.; Almessiry, B.K.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Ghobashy, M.O.I.; Abdelrahman, N.A.; Youssef, F.M.; Algammal, A.M. Unveiling resistance patterns, kmt1 sequence analyses, virulence traits, and antibiotic resistance genes of multidrug-resistant Pasteurella multocida retrieved from poultry and rabbits. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Tariq, M.H.A.; Yaqoob, M.; Haq, M.U.; Zahra, R. Molecular epidemiology and characterization of antibiotic resistance of Pasteurella multocida isolated from livestock population of Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2025, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsi, Z.E.; Allen, J.; Meza, A. More than a case of cellulitis: Pasteurella multocida bacteremia. Cureus 2023, 15, e36096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Integrative and conjugative elements of Pasteurella multocida: Prevalence and signatures in population evolution. Virulence 2024, 15, 2359467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcakavak, G.; Karatas, O.; Tuzcu, N.; Tuzcu, M. Determination of apoptosis, necroptosis and autophagy markers by real-time PCR in naturally infected Pneumonic pasteurellosis caused by Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica in cattle. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.P.; Luo, J.Q.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A.; Steegborn, C.; Xu, S.W.; Jin, Z.G. SIRT6 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human pulmonary lung microvascular endothelial cells. Inflammation 2024, 47, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.X.; Morés, M.A.Z.; Rebellato, R.; Kich, J.D.; Cantao, M.E.; Klein, C.S.; Guedes, R.M.C.; Coldebella, A.; de Barcellos, D.E.S.N.; Morés, N. Pathogenic variability among type A isolates from Brazilian pig farms. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Bi, H.; Yang, J.; Shang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, D.; Huang, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, F.; Hua, L.; et al. Pasteurella multocida infection induces blood-brain barrier disruption by decreasing tight junctions and adherens junctions between neighbored brain microvascular endothelial cells. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallman, T.R.; Perlaza-Jimenez, L.; Wang, X.; Korman, T.M.; Kotsanas, D.; Gibson, J.S.; Turni, C.; Harper, M.; Boyce, J.D. Pathogenomic analysis and characterization of Pasteurella multocida strains recovered from human infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0380523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Gu, Q.B.; Li, B.R.; Abi, K.; Yang, F.L. High prevalence of virulence genes and multi-drug resistance in Pasteurella multocida from goats in Sichuan, China. Vet. J. 2025, 311, 106344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschbach, C.L.; Raabis, S.M.; Ollivett, T.L. Effect of antibiotic treatment in preweaned Holstein calves after experimental bacterial challenge with Pasteurella multocida. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11359–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Mao, W.; Cao, J.S.; Hao, P.G.; Su, J.G.; Yin, K.W.; Gu, K.R.; Zhao, H.X. Chinese medicine monomers inhibit biofilm formation in multidrug-resistant P. isolated from cattle respiratory infections. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.L.; Zeng, M.N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jia, J.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liang, S.L.; Zheng, X.K.; Feng, W.S. Zingibroside R1 isolated from achyranthes bidentata blume ameliorates LPS/D-GalN-induced liver injury by regulating succinic acid metabolism via the gut microbiota. Phytother. Res. 2025, 39, 4520–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.F.; Hu, X.J. Flavonoid Glycosides from the bulbs of Lilium speciosum var. gloriosoides and their potential antiviral activity against RSV. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2019, 55, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yu, Z.P.; Yang, P.; Chen, X.H. Baicalin maintains articular cartilage homeostasis and alleviates osteoarthritis by activating FOXO1. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.Y.; Cheng, W.T.; Cheng, H.C.; Chou, W.C.; Chen, H.I.; Ou, H.C.; Tsai, K.L. Baicalin enhances chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in breast cancer cells via upregulation of oxidative stress-mediated mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.W.; Liang, Y.Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.C.; Zhou, C.Z.; Wan, X.H. Antiviral properties of baicalin: A concise review. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2021, 31, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Jiang, C.X.; Peng, L.; Li, Z.M.; Wang, J.T.; Liao, X.W.; Guo, W.Y. Discovery of metal complexes with antibacterial properties in aqueous extracts of and a study of the antibacterial properties of the baicalin-manganese complex. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 6506–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Kao, T.C.; Hu, S.H.; Li, Y.B.; Feng, W.Y.; Guo, X.C.; Zeng, J.H.; Ma, X. Protective role of baicalin in the dynamic progression of lung injury to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2023, 114, 154777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.N.; Li, Y. Pharmacological effects of baicalin in lung diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1188202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Wu, M.Y.; Ding, J.R.; Tan, W.; Jiang, H.B. Baicalin alleviates acute lung injury in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawi, Z.W.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Abd-alhameed, E.K.; Althagafy, H.S.; Jaber, F.A.; Harakeh, S.; Hassanein, E.H.M. Baicalin and lung diseases. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Zhu, Z.J.; Ling, Z.X.; Zeng, F.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, J.G. Baicalin relieves LPS-induced lung inflammation via the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Molecules 2023, 28, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.M.; Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.Z. Baicalin exerts protective effects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the crosstalk between the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis and NF-κB pathway in CX3CL1-knockout mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cui, H.R.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Y.F.; Huang, T.X.; Xue, B.; Guo, W.B.; Huang, Z.F.; et al. Baicalin ameliorates multidrug-resistant induced pulmonary inflammation in rat via arginine biosynthesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.F.; Tang, Y.H.; Dan, R.T.; Xie, M.H.; Zhang, T.C.; Li, P.; He, F.; Li, N.Z.; Peng, Y.Y. Pasteurella multocida activates apoptosis via the FAK-AKT-FOXO1 axis to cause pulmonary integrity loss, bacteremia, and eventually a cytokine storm. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.R.; Wang, L.Y.; Jiang, X.P.; Han, W.T.; Guo, P.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.L.; Xiong, J.L.; Wu, Z.Y.; Qiu, Y.S. Protective effects of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on Pasteurella multocida-induced vascular inflammatory injury in mice. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 11, 1515977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Lu, Q.R.; Hu, S.Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.R.; Yang, X.Z.; Wang, X. Daucosterol confers protection against T-2 toxin induced blood-brain barrier toxicity through the PGC-1α-mediated defensive response and in vivo. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.R.; Hu, S.Y.; Guo, P.; Zhu, X.H.; Ren, Z.C.; Wu, Q.H.; Wang, X. PPAR-γ with its anti-fibrotic action could serve as an effective therapeutic target in T-2 toxin-induced cardiac fibrosis of rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Wang, S.Y.; Dong, H.Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Bi, Y.; Chen, L.X.; Naseem, A.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; et al. Harnessing natural products for myocardial infarction therapy: Mechanistic insights and translational opportunities. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 217, 107802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.Y.; Jiang, J.M.; Li, X.B.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, X.M.; Li, C.R.; Chen, Q.L.; Man, C.R.G.; Du, L.; Wang, F.Y.; et al. Activation of MyD88-dependent TLR signaling modulates immune response of the mouse heart during infection. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.C.; Yu, L.J.; Qiu, J.M.; Shen, B.Y.; Wang, D.; Soromou, L.W.; Feng, H.H. Linalool attenuates lung inflammation induced by Pasteurella multocida via activating Nrf-2 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, K.C.; Lin, L.S.; Zhao, X.K.; Pan, Z.H.; Zhou, Z.L. Differences in pathogenicity and virulence-associated gene expression among strains with high and low virulence in a lung tissue model. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 140, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.B.; Yao, Y.C.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, W.M.; Wu, Z.Y. A review on the application of traditional to modern approaches of chinese herbal veterinary medicines: Current status and challenges. J. Food Biochem. 2024, 2024, 5801408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Li, X.Q.; He, X.F.; Wang, Z.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Sun, L.M.; Ma, Y.; Deng, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, N. Baicalin liposomes ameliorate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by modulating the inflammatory response. Brain Res. 2025, 1859, 149642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Wei, W.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huo, J.H.; Wang, W.M. The mechanism of baicalin in improving pulmonary inflammatory response and injury and regulating intestinal flora in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia mice. Cell. Signal. 2025, 126, 111530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.R.; Wang, N.; Wen, D.F.; Guo, P.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.L.; Ye, C.; Wu, Z.Y.; Qiu, Y.S. Baicalin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammatory injury via suppressing PARP1-mediated NF-κB and NLRP3 signalling pathway. Toxicon 2024, 239, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, B.B.; Xiao, Y.; Ren, M.X.; Wang, P.Y.; Fu, S.L.; Qiu, Y.S. Baicalin Weakens the Porcine ExPEC-Induced Inflammatory Response in 3D4/21 Cells by Inhibiting the Expression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathways and Reducing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Manan, A.; Kim, J.; Choi, S. NLRP3 inflammasome: A key player in the pathogenesis of life-style disorders. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebe, A.; Hoss, F.; Latz, E. NLRP3 Inflammasome and the IL-1 Pathway in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1722–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendler, M.; van den Brandt, C.; Glaubitz, J.; Wilden, A.; Golchert, J.; Weiss, F.U.; Homuth, G.; Chama, L.L.D.; Mishra, N.; Mahajan, U.M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome regulates development of systemic inflammatory response and compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndromes in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.D.; Du, H.H.; Lei, G.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Feng, S.W.; Ye, C.; Li, N.Z.; Peng, Y.Y. NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β secretion in macrophages infected with. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 231, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.R.; Yin, H.; Xu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, X.P.; Peng, L.C.; Peng, Y.Y.; Fang, R.D. RACK1 mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation during infection. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakoso, Y.A.; Susilo, A.; Widyarini, S. The standardization and efficacy of fermented Crescentia cujete (L.) in combination with enrofloxacin against artificially induced Pneumonic pasteurellosis in rat models. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 3404–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacominelli-Stuffler, R.; Marruchella, G.; Storelli, M.M.; Sabatucci, A.; Angelucci, C.B.; Maccarrone, M. 5-Lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the lungs of pigs naturally affected by enzootic pneumonia and porcine pleuropneumonia. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.F.; Chou, J.C.; Ka, S.M.; Tasi, Y.L.; Chen, A.; Wu, S.H.; Chiu, H.W.; Wong, W.T.; Wang, Y.F.; Tsai, C.L.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome-Derived IL-1β Production. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Liu, D.; Chen, L.Y.; Liu, Y. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 attenuates primary dysmenorrhea in mice via the NF-κB/COX-2/PG pathway. J. Inflamm. 2020, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Z.R.; Xu, J.D.; Tang, K.S.; Chen, F.E. Structural modification based on the diclofenac scaffold: Achieving reduced colitis side effects through COX-2/NLRP3 selective inhibition. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 268, 116257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.; Xue, Y.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Ye, C.; Fu, S.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Baicalin Mitigates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Pulmonary and Vascular Injury via NLRP3/COX-2 Inhibition in Mice. Animals 2025, 15, 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203055
Zhang D, Zhao C, Xue Y, Lu Q, Liu Y, Xiong J, Ye C, Fu S, Wu Z, Qiu Y, et al. Baicalin Mitigates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Pulmonary and Vascular Injury via NLRP3/COX-2 Inhibition in Mice. Animals. 2025; 15(20):3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203055
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dan, Chengzhuo Zhao, Yunda Xue, Qirong Lu, Yu Liu, Jianglin Xiong, Chun Ye, Shulin Fu, Zhongyuan Wu, Yinsheng Qiu, and et al. 2025. "Baicalin Mitigates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Pulmonary and Vascular Injury via NLRP3/COX-2 Inhibition in Mice" Animals 15, no. 20: 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203055
APA StyleZhang, D., Zhao, C., Xue, Y., Lu, Q., Liu, Y., Xiong, J., Ye, C., Fu, S., Wu, Z., Qiu, Y., & Guo, P. (2025). Baicalin Mitigates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Pulmonary and Vascular Injury via NLRP3/COX-2 Inhibition in Mice. Animals, 15(20), 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203055




