Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis Modulates Immunity, Serum Metabolome, and Intestinal Homeostasis in Cats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Treatments
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Serum Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Immune Cytokine Analysis
2.5. Fecal Microbiome Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Serum Metabolomics
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Fecal Scores
3.3. Immunoglobulin Parameters
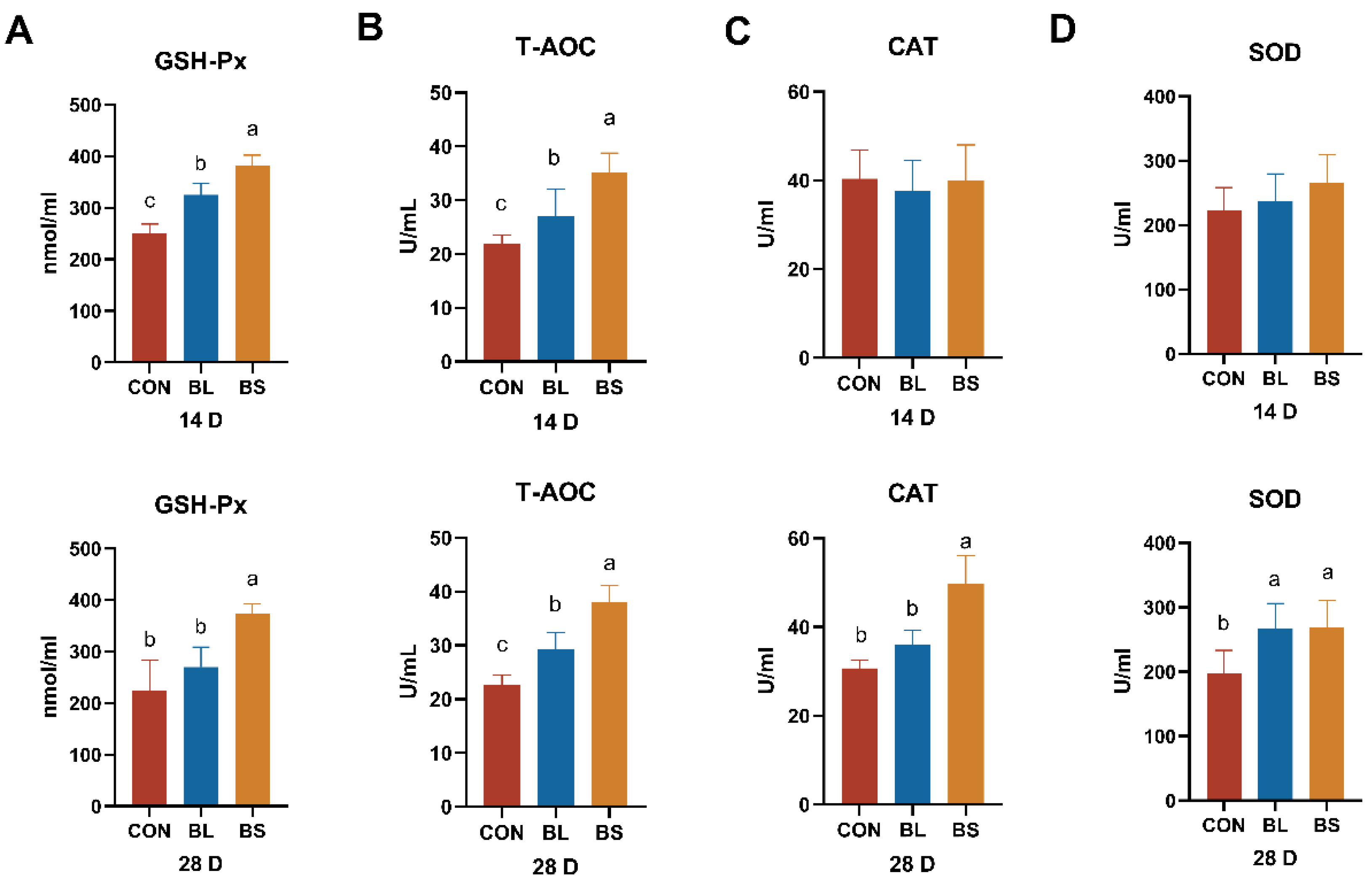
3.4. Antioxidant Parameters
3.5. Inflammatory Factors
3.6. Gut Barrier Function Parameters
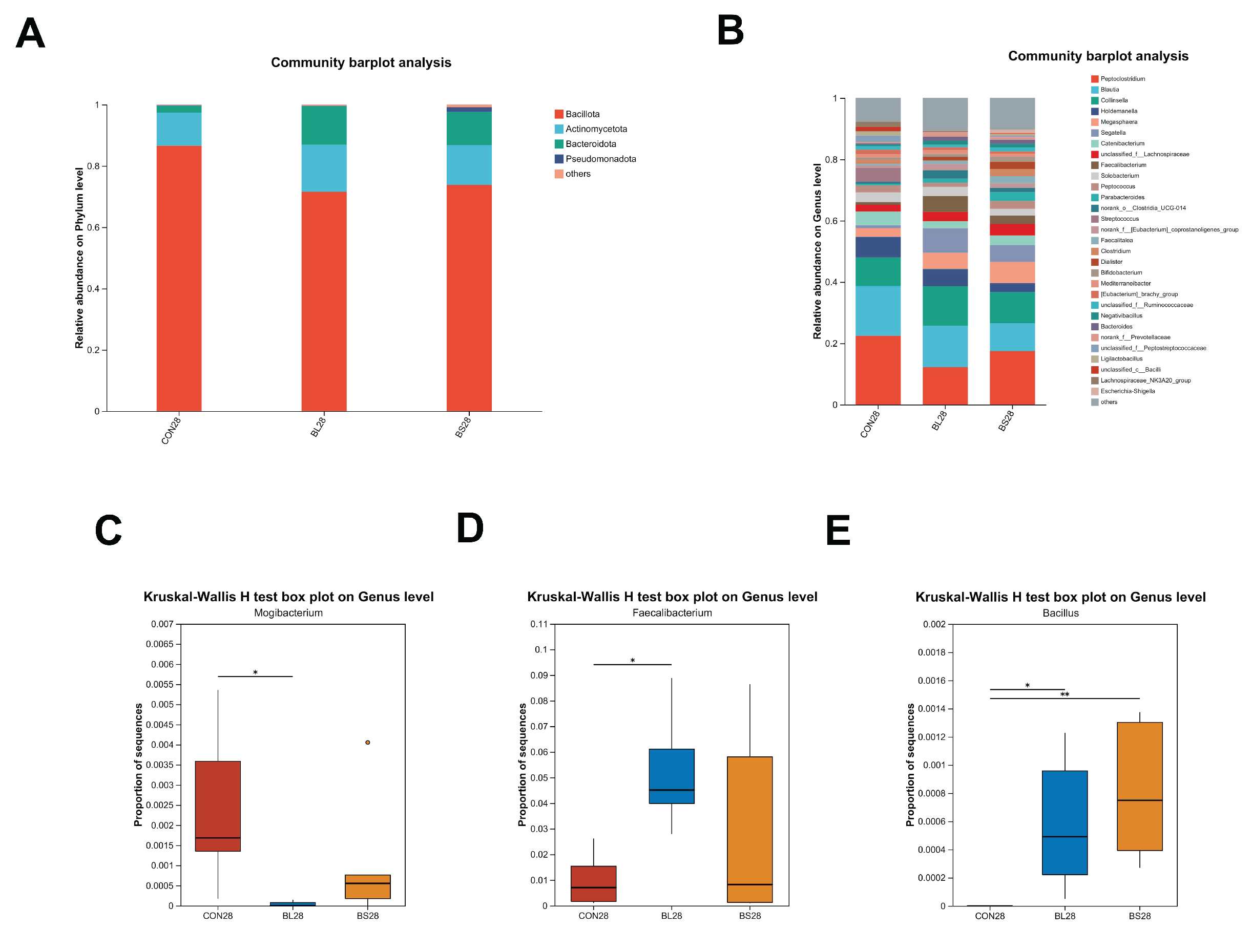
3.7. Fecal Microbiota Composition
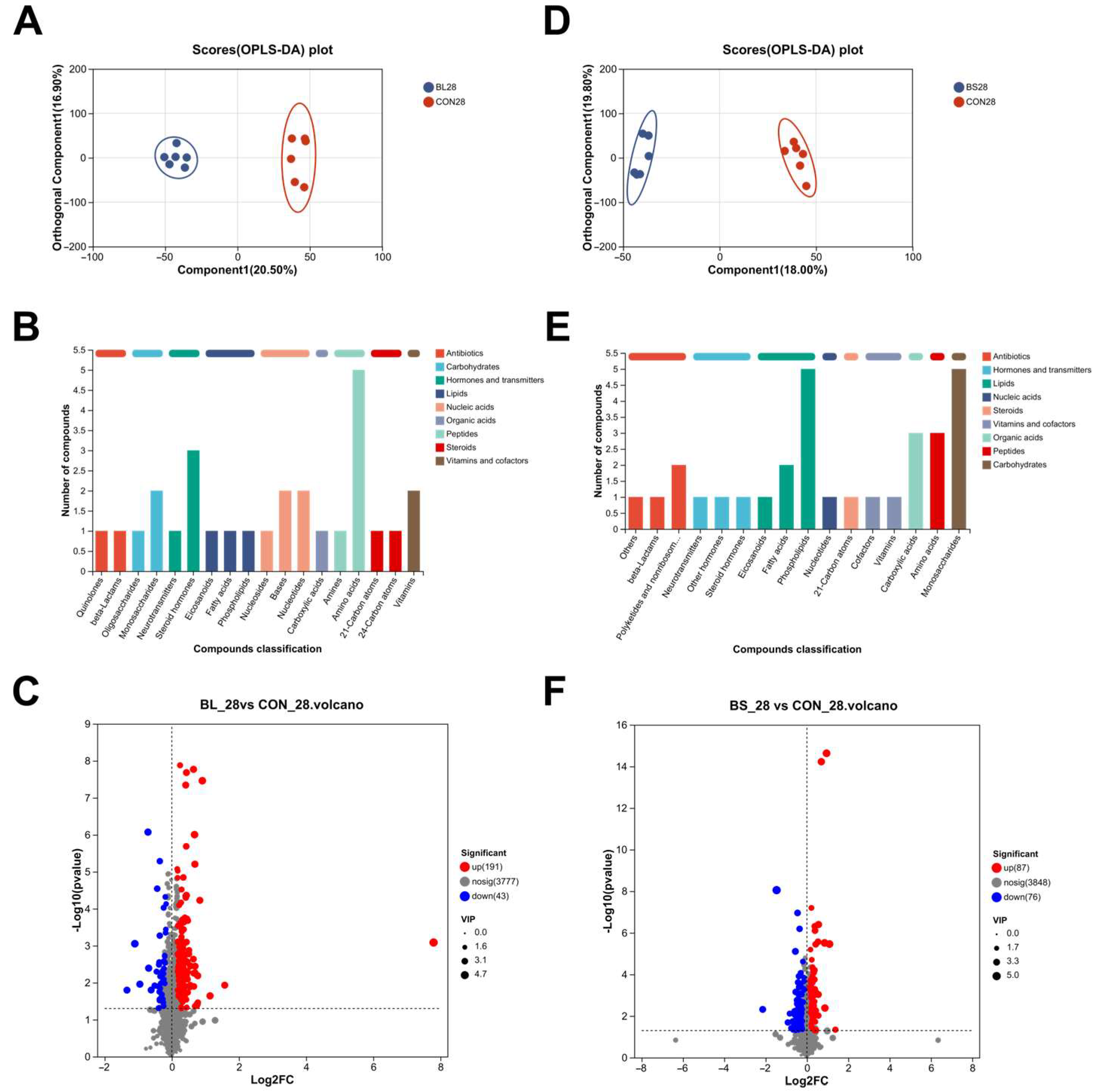
3.8. Serum Metabolomics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BL | Bacillus licheniformis |
| BS | Bacillus subtilis |
| B. licheniformis | Bacillus licheniformis |
| B. subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| AOPP | Advanced oxidation protein products |
| d-ROMS | Diacron-reactive oxygen metabolites |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| T-AOC | Total antioxidant capacity |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| DLA | D-lactic acid |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL | Interleukin |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinate Analysis |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal projections to latent structures-discriminant analysis |
| VIP | variable importance in projection |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| ADFI | Average daily feed intake |
| ASVs | Amplicon sequence variants |
| B. lactis | Bifidobacterium lactis |
References
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandri, G.; Argentini, C.; Milani, C.; Turroni, F.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Sinderen, D.V.; Ventura, M. Catching a glimpse of the bacterial gut community of companion animals: A canine and feline perspective. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1708–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y. Probiotics and cat health: A review of progress and prospects. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Goh, T.W.; Kang, M.G.; Choi, H.J.; Yeo, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Huh, C.S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, Y. Perspectives and advances in probiotics and the gut microbiome in companion animals. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2022, 64, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jergens, A.E. Feline idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizard, I.R.; Jones, S.W. The microbiota regulates immunity and immunologic diseases in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ali, I.; Lei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Effect of a multistrain probiotic on feline gut health through the fecal microbiota and its metabolite SCFAs. Metabolites 2023, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.A.H.; Ahmed, A.E.M.; Kovács, B.; Pál, K. The Significance of Probiotics in Aquaculture: A Review of Research Trend and Latest Scientific Findings. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Meng, C.; Hao, Z.; Liu, H. Bacillus licheniformis reshapes the gut microbiota to alleviate the subhealth. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Spore resistance properties. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenspach, K.; Sung, C.-H.; Ceron, J.J.; Peres Rubio, C.; Bourgois-Mochel, A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Yuan, L.; Kundu, D.; Colom Comas, J.; Rea, K. Effect of the probiotic bacillus subtilis DE-CA9TM on fecal scores, serum oxidative stress markers and fecal and serum metabolome in healthy dogs. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, A.P.; Netto, M.V.T.; Murakami, F.Y.; de Brito, C.B.M.; de Oliveira, S.G.; Maiorka, A. Digestibility and fecal characteristics of dogs fed with Bacillus subtilis in diet. Cienc. Rural 2010, 40, 2169–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Dai, Z.; Cao, G.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C. Protective effects of Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, gut barrier functions, immunity and serum metabolome in lipopolysaccharide-challenged weaned piglets. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1140564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carciofi, A.C.; de-Oliveira, L.D.; Valério, A.G.; Borges, L.L.; de Carvalho, F.M.; Brunetto, M.A.; Vasconcellos, R.S. Comparison of micronized whole soybeans to common protein sources in dry dog and cat diets. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2009, 151, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, E.B.; Benini, A. Relationship between number of bacteria and their probiotic effects. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2008, 20, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Goldenberg, J.Z.; Humphrey, C.; El Dib, R.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C. A review of dose-responses of probiotics in human studies. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, F.; Hou, Q.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Metagenomic analysis revealed beneficial effects of probiotics in improving the composition and function of the gut microbiota in dogs with diarrhoea. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Henderson, C.; Summers, S.; Suchodolski, J.; Lappin, M.R. Effect of enterococcus faecium strain SF68 on gastrointestinal signs and fecal microbiome in cats administered amoxicillin-clavulanate. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2017, 32, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cui, Z.; Qin, S.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, C. Effects of Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, diarrhea incidence, antioxidant capacity, immune function, and fecal microflora in weaned piglets. Animals 2022, 12, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, E.C.; Frangione, B. Immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Med. 1969, 20, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Aschermann, S.; Biburger, M.; Nimmerjahn, F. The pro and anti-Inflammatory activities of immunoglobulin G. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69 (Suppl. S1), i92–i96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Lan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, G.; Yang, C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immunity, short chain fatty acid production, antioxidant capacity, and cecal microflora in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zha, J.; Qiao, X.; Chai, T.; Wu, B. Benefit of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis BYS2 on growth performance, immune response, and disease resistance of broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nie, G. Effects of an exopolysaccharide from lactococcus lactis Z-2 on innate immune response, antioxidant activity, and disease resistance against aeromonas hydrophila in Cyprinus carpio L. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassier-Chauvat, C.; Marceau, F.; Farci, S.; Ouchane, S.; Chauvat, F. The glutathione system: A journey from cyanobacteria to higher eukaryotes. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Li, Y.L.; Yu, D.Y.; Rajput, I.R.; Li, W.F. Influence of dietary inclusion of Bacillus licheniformis on laying performance, egg quality, antioxidant enzyme activities, and intestinal barrier function of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Supplemental Effects of probiotic Bacillus subtilis fmbJ on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.L.; Bowers, W.J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and the Roles It plays in homeostatic and degenerative processes within the central nervous system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; He, L.; Bao, C.; Yan, X.; Ao, J. The role of TNF-α in osteoporosis, bone repair and inflammatory bone diseases: A review. Tissue Cell 2024, 89, 102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNγ: Signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.Y.; Selmi, C.; Gershwin, M.E. The regulatory, inflammatory, and T cell programming roles of interleukin-2 (IL-2). J. Autoimmun. 2008, 31, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Tao, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhan, X. Positive effects of a clostridium butyricum-based compound probiotic on growth performance, immune responses, intestinal morphology, hypothalamic neurotransmitters, and colonic microbiota in weaned piglets. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HS, R.; Halami, P.M. The combined effect of potential probiotic Bacillus licheniformis MCC 2514 and bifidobacterium breve NCIM 5671 towards anti-inflammatory activity on HT-29 cell lines. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yang, C. Bacillus licheniformis alleviates clostridium perfringens-induced intestinal injury in mice model by modulating inflammation, apoptosis, and cecal microbial-metabolic responses. Animals 2025, 15, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Kleniewska, P.; Pawliczak, R. Antioxidative activity of probiotics. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-J.; Wang, X.-Q. Deoxynivalenol induces intestinal injury: Insights from oxidative stress and intestinal stem cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 48676–48685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Luo, R.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Shen, L.; Cao, S.; et al. Protective effects of Bacillus subtilis HH2 against oral enterotoxigenic escherichia coli in beagles. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Dong, H.; Chang, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Ge, S.; Wang, P.; et al. Bifidobacterium lactis and lactobacillus plantarum enhance immune function and antioxidant capacity in cats through modulation of the gut microbiota. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handl, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Massive parallel 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals highly diverse fecal bacterial and fungal communities in healthy dogs and cats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, L.E.; Burke, K.F.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Characterization of fecal microbiota in cats using universal 16S rRNA gene and group-specific primers for lactobacillus and bifidobacterium spp. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, M.; Martín, R.; Torres-Maravilla, E.; Chadi, S.; González-Dávila, P.; Sokol, H.; Langella, P.; Chain, F.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Butyrate mediates anti-inflammatory effects of faecalibacterium prausnitzii in intestinal fpithelial cells through Dact3. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1826748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, H.M.; Jonkers, D.; Venema, K.; Vanhoutvin, S.; Troost, F.J.; Brummer, R.-J. Review Article: The role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Mei, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Jin, Q. Compound Bacillus alleviates diarrhea by regulating gut microbes, metabolites, and inflammatory responses in pet cats. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-J.; He, Y.; Chen, C.; Shi, J.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multiomics analysis revealed colorectal cancer pathogenesis. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 2100–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, P.M.; Swanson, O.R.; Kang, Y.; Mioto, J.C.; Menton, J.F.; Vinay, E.; Millette, M.; Kelly, M.R.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of Bacillus subtilis ATCC PTA-122264 on apparent total tract macronutrient digestibility and fecal characteristics, metabolites, and microbiota of healthy adult dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 103, skaf038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Wheeler, M.D.; Li, X.; Froh, M.; Schemmer, P.; Yin, M.; Bunzendaul, H.; Bradford, B.; Lemasters, J.J. L-Glycine: A novel antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory, and cytoprotective agent. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrat, F.; Boengler, K.; Schulz, R.; de Groot, H. Glycine, a simple physiological compound protecting by yet puzzling mechanism(s) against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: Current knowledge. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.-L. Amino acid metabolism in intestinal bacteria: Links between gut ecology and host health. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.; Bassot, A.; Bulteau, A.-L.; Pirola, L.; Morio, B. Glycine metabolism and its alterations in obesity and metabolic diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Fecal State | Score |
|---|---|
| Hard and dry, particles are discharged, friable in lumps | 5 |
| Feces’ surface shows a segmented texture and leaves little residue when picked up | 4 |
| The surface of the feces is moist and log-like, and picking up will leave residue | 3 |
| Feces are piled, not fully liquid, hard to pick up, and leave residues when lifted | 2 |
| Liquid and difficult to pick up | 1 |
| Item | Groups 2 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | BL | BS | ||
| ADFI, g/d | 51.73 ± 15.35 | 53.51 ± 16.60 | 51.05 ± 13.09 | 0.318 |
| D1 Body weight, kg | 3.40 ± 0.12 | 3.68 ± 0.93 | 3.71 ± 0.70 | 0.783 |
| D7 Body weight, kg | 3.40 ± 0.15 | 3.70 ± 0.87 | 3.69 ± 0.76 | 0.792 |
| D14 Body weight, kg | 3.45 ± 0.15 | 3.68 ± 0.93 | 3.71 ± 0.70 | 0.841 |
| D21 Body weight, kg | 3.47 ± 0.18 | 3.77 ± 0.81 | 3.76 ± 0.68 | 0.736 |
| D28 Body weight, kg | 3.49 ± 0.18 | 3.74 ± 0.94 | 3.71 ± 0.56 | 0.837 |
| Item | Groups 2 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | BL | BS | ||
| D1 | 3.33 ± 1.03 | 3.67 ± 0.52 | 3.83 ± 0.75 | 0.554 |
| D2 | 3.33 ± 1.03 | 4.17 ± 0.41 | 4.33 ± 0.82 | 0.098 |
| D3 | 3.50 ± 0.84 b | 4.17 ± 0.41 ab | 4.50 ± 0.55 a | 0.041 |
| D4 | 3.33 ± 0.82 b | 4.50 ± 0.55 a | 4.17 ± 0.75 ab | 0.035 |
| D5 | 3.33 ± 0.82 b | 4.33 ± 0.52 a | 4.33 ± 0.82 a | 0.048 |
| D6 | 3.50 ± 0.55 | 3.83 ± 0.75 | 4.33 ± 0.82 | 0.161 |
| D7 | 3.33 ± 0.82 b | 3.33 ± 0.52 b | 4.67 ± 0.52 a | 0.003 |
| D14 | 3.33 ± 0.82 b | 3.50 ± 0.55 b | 4.67 ± 0.82 a | 0.013 |
| D21 | 3.50 ± 0.55 b | 4.00 ± 0.89 ab | 4.67 ± 0.82 a | 0.057 |
| D28 | 4.00 ± 0.63 | 4.00 ± 0.63 | 4.50 ± 0.84 | 0.391 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, T.; Kang, J.; Xu, Z.; Wu, P.; Niu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, C. Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis Modulates Immunity, Serum Metabolome, and Intestinal Homeostasis in Cats. Animals 2025, 15, 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202971
Zhang M, Xu H, Zhang T, Kang J, Xu Z, Wu P, Niu Y, Shi Y, Zhong Y, Yang C. Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis Modulates Immunity, Serum Metabolome, and Intestinal Homeostasis in Cats. Animals. 2025; 15(20):2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202971
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Meiting, Haocheng Xu, Tianfeng Zhang, Jia Kang, Zhihao Xu, Peng Wu, Yu Niu, Yonghao Shi, Yifan Zhong, and Caimei Yang. 2025. "Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis Modulates Immunity, Serum Metabolome, and Intestinal Homeostasis in Cats" Animals 15, no. 20: 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202971
APA StyleZhang, M., Xu, H., Zhang, T., Kang, J., Xu, Z., Wu, P., Niu, Y., Shi, Y., Zhong, Y., & Yang, C. (2025). Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis Modulates Immunity, Serum Metabolome, and Intestinal Homeostasis in Cats. Animals, 15(20), 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202971






