Are Reusable Dry Electrodes an Alternative to Gelled Electrodes for Canine Surface Electromyography?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pre-Study Evaluation
2.2. Animal Selection
2.3. Clinical Evaluation
- Collection of medical history;
- General health inspection;
- Standing inspection to assess muscle asymmetry, musculoskeletal deformities, and even weight distribution across limbs;
- Gait inspection with special attention to signs of lameness;
- Palpation of limb joints to confirm absence of crepitus, edoema, instability, or pain;
- Palpation of the spine and surrounding musculature, including careful manipulation of the cervical spine through its full range of motion (ROM) to ensure absence of pain;
- Proprioceptive testing and spinal reflexes on all four limbs;
- Specific orthopedic tests, such as the drawer test and tibial thrust.
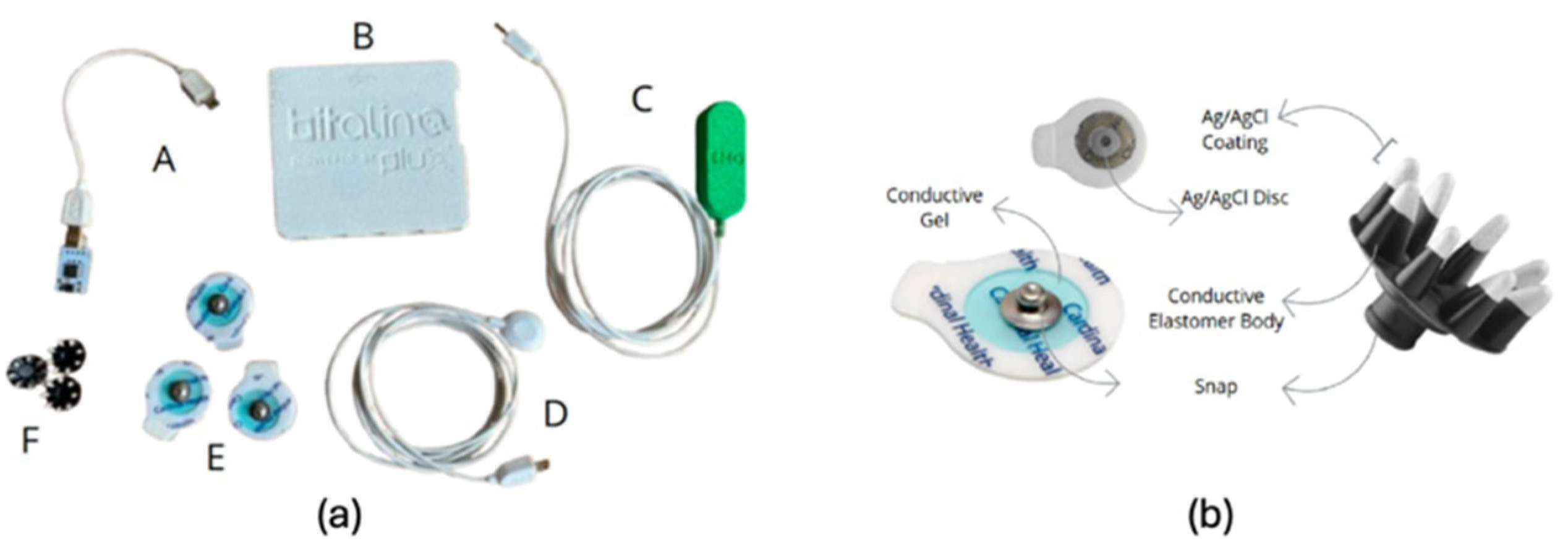
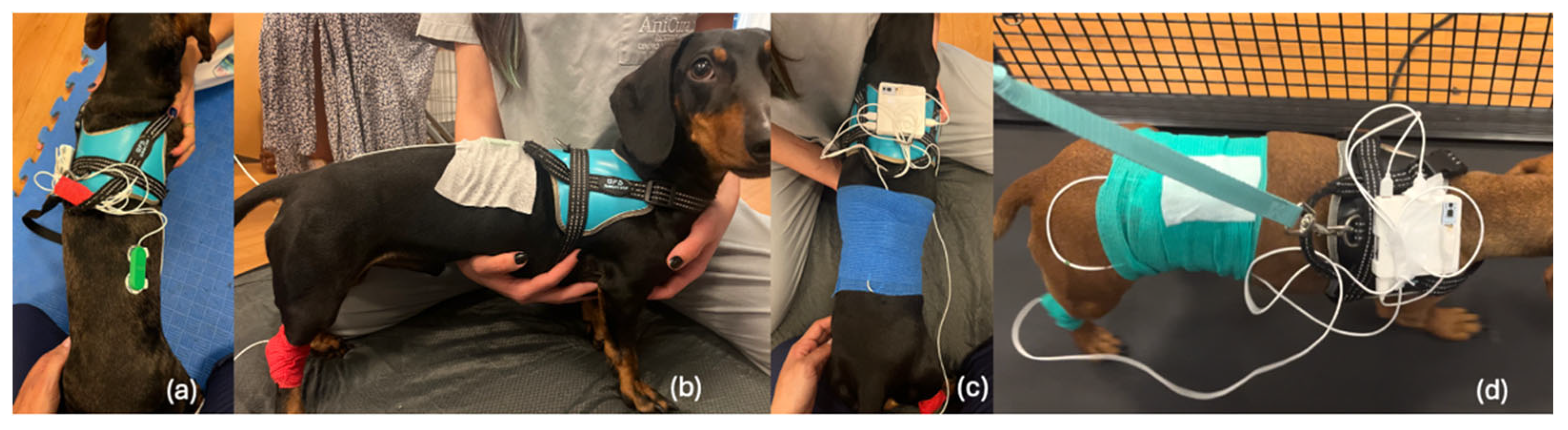
2.4. Data Acquisition Setup
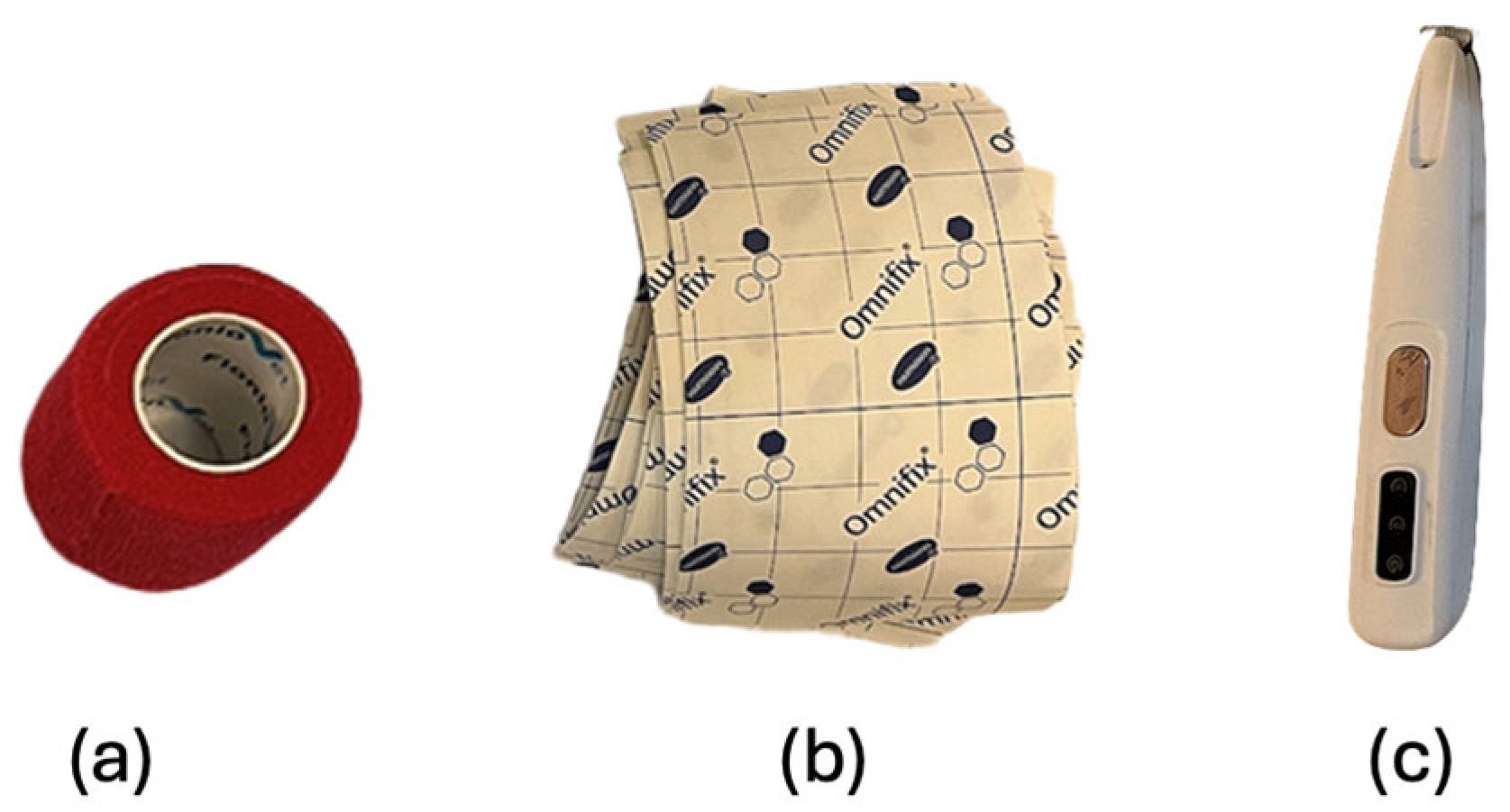
2.5. Skin Preparation and Exercise
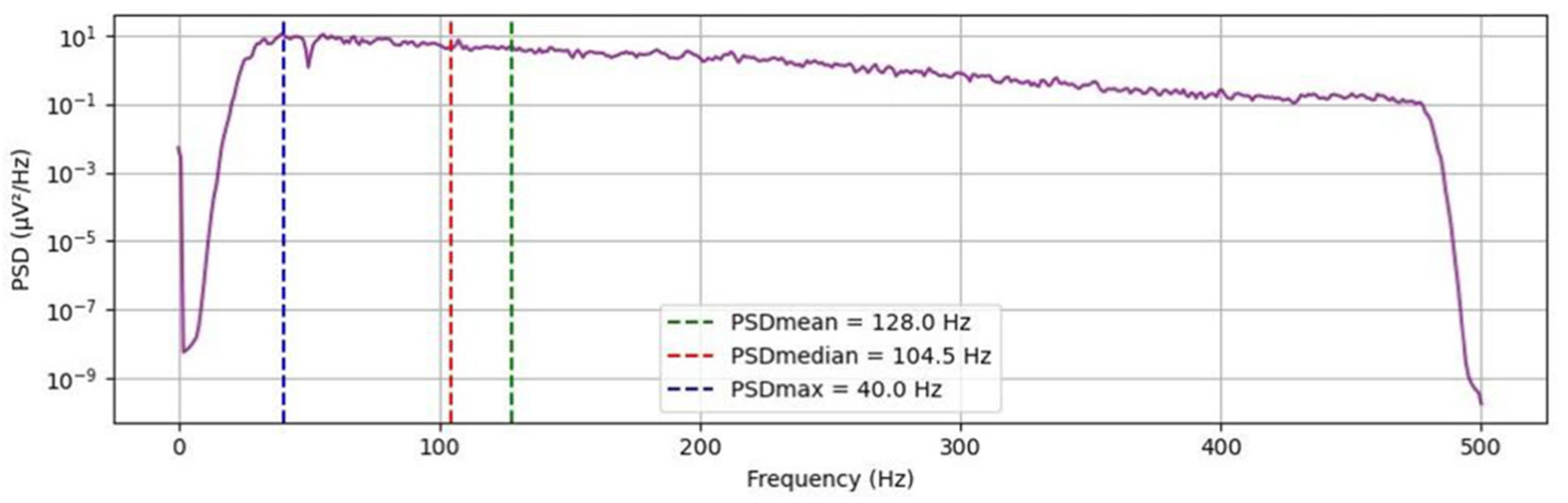
2.6. Signal Processing
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| sEMG | Surface electromyography |
| ISNCSCI | International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury AIS—American Spinal Cord Association Impairment Scale |
| GRASSP | Graded redefined Assessment of strength, sensibility and Prehension |
| SCI | Spinal cord injury |
| CEDE | Consensus for Experimental Design in Electromyography |
| IVDD | Intervertebral disk disease |
| Ag/AgCl | Silver/silver chloride |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| Hz | Hertz |
| Env | Envelope |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| PSD | Power spectral density |
| PSDmean | Mean power spectral density |
| PSDmax | Maximum power spectral density |
| PSDmedian | Median power spectral density |
| CE | Conductive elastomer |
References
- Merletti, R.; Muceli, S. Tutorial. Surface EMG Detection in Space and Time: Best Practices. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 49, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekins, G.D.; So, Y.; Quan, D. American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine Evidenced-Based Review: Use of Surface Electromyography in the Diagnosis and Study of Neuromuscular Disorders. Muscle Nerve 2008, 38, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cram, J.R. The History of Surface Electromyography. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2003, 28, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermens, H.J.; Freriks, B.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Rau, G. Development of Recommendations for SEMG Sensors and Sensor Placement Procedures. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2000, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Guo, A.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances in Flexible Noninvasive Electrodes for Surface Electromyography Acquisition. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Song, C.; Li, Z. The Application of Surface Electromyography Technology in Evaluating Paraspinal Muscle Function. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ayyad, M.; Owida, H.A.; De Fazio, R.; Al-Naami, B.; Visconti, P. Electromyography Monitoring Systems in Rehabilitation: A Review of Clinical Applications, Wearable Devices and Signal Acquisition Methodologies. Electronics 2023, 12, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcan, V.; Zinnuroğlu, M. Current Developments in Surface Electromyography. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 53, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besomi, M.; Hodges, P.W.; Van Dieën, J.; Carson, R.G.; Clancy, E.A.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Holobar, A.; Hug, F.; Kiernan, M.C.; Lowery, M.; et al. Consensus for Experimental Design in Electromyography (CEDE) Project: Electrode Selection Matrix. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 48, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besomi, M.; Hodges, P.W.; Clancy, E.A.; Van Dieën, J.; Hug, F.; Lowery, M.; Merletti, R.; Søgaard, K.; Wrigley, T.; Besier, T.; et al. Consensus for Experimental Design in Electromyography (CEDE) Project: Amplitude Normalization Matrix. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 53, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathlean, T.J.H.; Ramachandran, A.K.; Sim, S.; Whittle, I.R. The Clinical Utility and Reliability of Surface Electromyography in Individuals with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2024, 129, 110877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.D.; Yarossi, M.B.; Pierce, D.N.; Garbarini, E.L.; Forrest, G.F. Reliability of Surface EMG as an Assessment Tool for Trunk Activity and Potential to Determine Neurorecovery in SCI. Spinal Cord 2015, 53, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbinot, G.; Li, G.; Wiest, M.J.; Pakosh, M.; Furlan, J.C.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Zariffa, J. Properties of the Surface Electromyogram Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: A Scoping Review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, N.; Busha, I.; Morgan, A.; Mattathil, C.; Levy Pinto, A.; Spyridakos, F.; Sokolovskiy, I.; Tahirbegi, B.; Chapman, C.; Cuttaz, E.; et al. Surface Electromyography Using Dry Polymeric Electrodes. APL Bioeng. 2023, 7, 036115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.J. Dry Epidermal Electrodes Can Provide Long-Term High Fidelity Electromyography for Limited Dynamic Lower Limb Movements. Sensors 2020, 20, 4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, S.; Zsoldos, R.R. Surface Electromyography in Animal Biomechanics: A Systematic Review. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2016, 28, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Bockay, A.; Liptak, T.; Ledecky, V.; Kuricova, M. Practical Use of Electromyography in Veterinary Medicine—A Review. Vet. Med. 2022, 67, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, I.H.; Parmentier, J.I.M.; Rovel, T.; van Dieen, J.; Serra Bragança, F.M. Towards Standardisation of Surface Electromyography Measurements in the Horse: Bipolar Electrode Location. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2024, 76, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, N.; Sims, C.; Fenn, J.; Williams, K.; Griffith, E.; Early, P.J.; Mariani, C.L.; Munana, K.R.; Guevar, J.; Olby, N.J. A Randomized, Blinded, Prospective Clinical Trial of Postoperative Rehabilitation in Dogs after Surgical Decompression of Acute Thoracolumbar Intervertebral Disc Herniation. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Valdes, E.; Enoka, R.M.; Holobar, A.; McGill, K.; Farina, D.; Besomi, M.; Hug, F.; Falla, D.; Carson, R.G.; Clancy, E.A.; et al. Consensus for Experimental Design in Electromyography (CEDE) Project: Single Motor Unit Matrix. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2023, 68, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besomi, M.; Devecchi, V.; Falla, D.; McGill, K.; Kiernan, M.C.; Merletti, R.; van Dieën, J.H.; Tucker, K.; Clancy, E.A.; Søgaard, K.; et al. Consensus for Experimental Design in Electromyography (CEDE) Project: Checklist for Reporting and Critically Appraising Studies Using EMG (CEDE-Check). J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2024, 76, 102874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Pereira, D.; Gaspar, G.B.; Dos Santos, M.C.; Plácido da Silva, H.; Requicha, J.F. Surface Electromyography: A Pilot Study in Canine Spinal Muscles. MethodsX 2024, 13, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockstahler, B.; Kräutler, C.; Holler, P.; Kotschwar, A.; Vobornik, A.; Peham, C. Pelvic Limb Kinematics and Surface Electromyography of the Vastus Lateralis, Biceps Femoris, and Gluteus Medius Muscle in Dogs with Hip Osteoarthritis. Vet. Surg. 2012, 41, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockstahler, B.B.; Gesky, R.; Mueller, M.; Thalhammer, J.G.; Peham, C.; Podbregar, I. Correlation of Surface Electromyography of the Vastus Lateralis Muscle in Dogs at a Walk with Joint Kinematics and Ground Reaction Forces. Vet. Surg. 2009, 38, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, R.R.; Rahal, S.C.; Kano, W.T.; Mesquita, L.R.; Hormaza, J.M. Analysis of Time Series of Surface Electromyography and Accelerometry in Dogs. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 74, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, H.; Millis, D.; Levine, D. Surface Electromyography of the Vastus Lateralis, Biceps Femoris, and Gluteus Medius in Dogs During Stance, Walking, Trotting, and Selected Therapeutic Exercises. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, F.; Galisteo, A.M.; Garrido-Castro, J.L.; Vivo, J. Surface Electromyography of the Longissimus and Gluteus Medius Muscles in Greyhounds Walking and Trotting on Ground Flat, Up, and Downhill. Animals 2020, 10, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergknut, N. Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Dogs; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fenn, J.; Olby, N.J. Canine Spinal Cord Injury Consortium (CANSORT-SCI) Classification of Intervertebral Disc Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 579025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzeid, J.; Grapes, N.; Khan, S.; De Decker, S.; Freeman, P. Comparison of Clinical Features of Intervertebral Disc Extrusions in English Cocker Spaniels, French Bulldogs and Dachshunds. Animals 2025, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.A.; Carrera-Justiz, S.; Repac, J.A. Surface Electromyography of the Vastus Lateralis and Gluteus Medius Muscles in Post-Operative T3–L3 Hemilaminectomy Dogs: A Prospective Controlled Observational Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1431843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millis, D.; Levine, D. Canine Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy, 2nd ed.; Saunders: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4377-0309-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, C.; da Costa, R. Practical Guide to Canine and Feline Neurology, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-119-94611-3. [Google Scholar]
- Radostits, O.M.; Mayhew, I.G.; Houston, D.M. (Eds.) Veterinary Clinical Examination and Diagnosis; W.B. Saunders: London, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-0-7020-2476-4. [Google Scholar]
- Pinello, K.; Geraz, H.; Salgueiro, H.; Cabral, E.; Vieira, E.; Mendonça, M.; Severo, M.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Ribeiro, J. Socio-Geographic and Demographic Analysis of the Official National Registry Data of Dogs’ Population in Portugal in 2023. Data from SIAC. Vet. J. 2025, 312, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.G.; McMillan, K.M.; Church, D.B.; Brodbelt, D.C. Dog Breeds and Conformations in the UK in 2019: VetCompass Canine Demography and Some Consequent Welfare Implications. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergknut, N.; Egenvall, A.; Hagman, R.; Gustås, P.; Hazewinkel, H.A.W.; Meij, B.P.; Lagerstedt, A.-S. Incidence of Intervertebral Disk Degeneration–Related Diseases and Associated Mortality Rates in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 240, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.A.; Dickinson, P.J.; Mansour, T.; Sturges, B.K.; Aguilar, M.; Young, A.E.; Korff, C.; Lind, J.; Ettinger, C.L.; Varon, S.; et al. FGF4 Retrogene on CFA12 Is Responsible for Chondrodystrophy and Intervertebral Disc Disease in Dogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11476–11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batcher, K.; Dickinson, P.; Giuffrida, M.; Sturges, B.; Vernau, K.; Knipe, M.; Rasouliha, S.H.; Drögemüller, C.; Leeb, T.; Maciejczyk, K.; et al. Phenotypic Effects of FGF4 Retrogenes on Intervertebral Disc Disease in Dogs. Genes 2019, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunanen, V.L.J.; Jokinen, T.S.; Hytönen, M.K.; Junnila, J.J.T.; Lappalainen, A.K. Evaluation of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Young Adult Asymptomatic Dachshunds with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Radiography. Acta Vet. Scand. 2023, 65, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.M.A.; Seath, I.J.; O’Neill, D.G.; De Decker, S.; Volk, H.A. DachsLife 2015: An Investigation of Lifestyle Associations with the Risk of Intervertebral Disc Disease in Dachshunds. Canine Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, Â.; Gouveia, D.; Cardoso, A.; Carvalho, C.; Coelho, T.; Silva, C.; Viegas, I.; Gamboa, Ó.; Ferreira, A. A Controlled Clinical Study of Intensive Neurorehabilitation in Post-Surgical Dogs with Severe Acute Intervertebral Disc Extrusion. Animals 2021, 11, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, J.S.; Griffiths, I.R. Age Related Changes in the Motor Nerve Conduction Velocity in Dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 1977, 23, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verga, S.A.; Pandeya, S.R.; Kowal, J.B.; Cochran, R.J.; Lim, S.; Sabol, J.C.; Coates, J.R.; Rutkove, S.B. Electrical Impedance Myography in Healthy Dogs: Normative Values, Repeatability, and the Impact of Age. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1025528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Peri, E.; Vullings, R.; Rabotti, C.; Van Dijk, J.P.; Mischi, M. Comparative Review of the Algorithms for Removal of Electrocardiographic Interference from Trunk Electromyography. Sensors 2020, 20, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, P. The Abc of Emg; Noraxon Inc.: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Galiana-Merino, J.J.; Ruiz-Fernandez, D.; Martinez-Espla, J.J. Power Line Interference Filtering on Surface Electromyography Based on the Stationary Wavelet Packet Transform. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2013, 111, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzecha, K.; Krakós, M.; Więcek, B.; Chudzik, P.; Tatar, K.; Lisowski, G.; Mosorov, V.; Sankowski, D. Processing of EMG Signals with High Impact of Power Line and Cardiac Interferences. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, M.; Bouyer, L.; Roy, J.-S.; Campeau-Lecours, A. Reducing Noise, Artifacts and Interference in Single-Channel EMG Signals: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, E.A.; Morin, E.L.; Merletti, R. Sampling, Noise-Reduction and Amplitude Estimation Issues in Surface Electromyography. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2002, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, S.; Duan, Y.Y. Towards Conductive-Gel-Free Electrodes: Understanding the Wet Electrode, Semi-Dry Electrode and Dry Electrode-Skin Interface Impedance Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Fitting. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Animal | Age (Years) | Sex | Reproductive Status | Body Type | Coat Type | Weight (kg) | Body Condition Score (1 to 9) | Included/Excluded | Reason for Exclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH1 | 2 | male | intact | standard | long | 7 | 4 | included | |
| SH2 | 6 | female | OVH | mini | smooth | 6.8 | 6 | included | |
| SH3 * | 1 | male | intact | standard | smooth | 8.2 | 5 | excluded | Pain at L4–L6 |
| SH4 | 5 | female | intact | mini | smooth | 5 | 5 | included | |
| SH5 | 2 | male | intact | standard | smooth | 11 | 5 | included | |
| SH6 | 3 | female | OVH | standard | wire | 9 | 7 | included | |
| SH7 | 3 | male | intact | standard | smooth | 6.7 | 4 | included | |
| SH8 | 3 | male | intact | standard | smooth | 9 | 6 | included | |
| SH9 | 2 | male | spayed | standard | smooth | 7.25 | 5 | included | |
| SH10 | 5 | male | intact | mini | wire | 5.8 | 5 | included | |
| SH11 | 5 | male | spayed | Kanichen | smooth | 3.5 | 4 | included | |
| SH12 | 2 | female | OVH | mini | smooth | 4.5 | 4 | included | |
| SH13 | 1 | male | intact | standard | smooth | 7.2 | 4 | included | |
| Mean | 3 | 7 | 5 | ||||||
| Standard deviation | 1.7 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| Median | 3 | 7 | 5 |
| Properties | Dry Electrode | Wet Electrode |
|---|---|---|
| Model and Manufacturer | SoftPulse® Flex, Datwyler, Switzerland | Kendall™H124SG, UK |
| Diameter | 13 mm | 24 mm |
| Material | Dry conductive elastomer and contact area with an Ag/AgCl-based coating | Wet conductive and adhesive hydrogel with a polymeric Ag/AgCl coating |
| Inter-electrode Spacing | Fixed | Fixed |
| Inter-electrode Distance | approximately 2 cm | approximately 1 cm |
| Number of Electrodes | 2 | 2 |
| Recording Montage | Bipolar | Bipolar |
| Active vs. Passive Electrode | Passive | Passive |
| Grounding | Medial aspect of the tarsus | Medial aspect of the tarsus |
| Anatomical Location on the Muscle | 0.5 cm lateral to the spinous processes of T12-L2 vertebra, overlying the longissimus dorsi muscle | 0.5 cm lateral to the spinous processes of T12-L2 vertebra, overlying the longissimus dorsi muscle |
| Electrode Orientation | Parallel to muscle fibers | Parallel to muscle fibers |
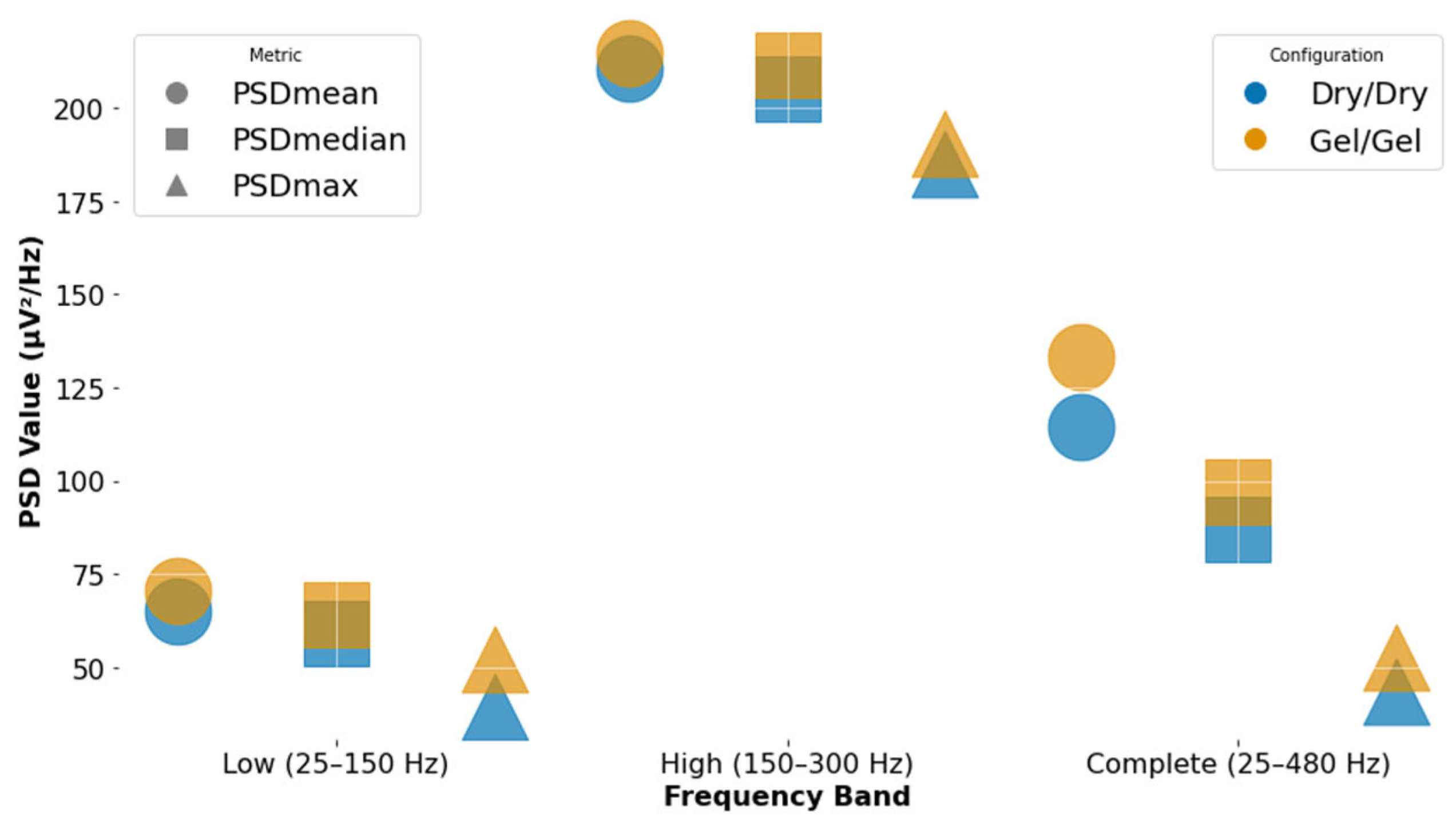
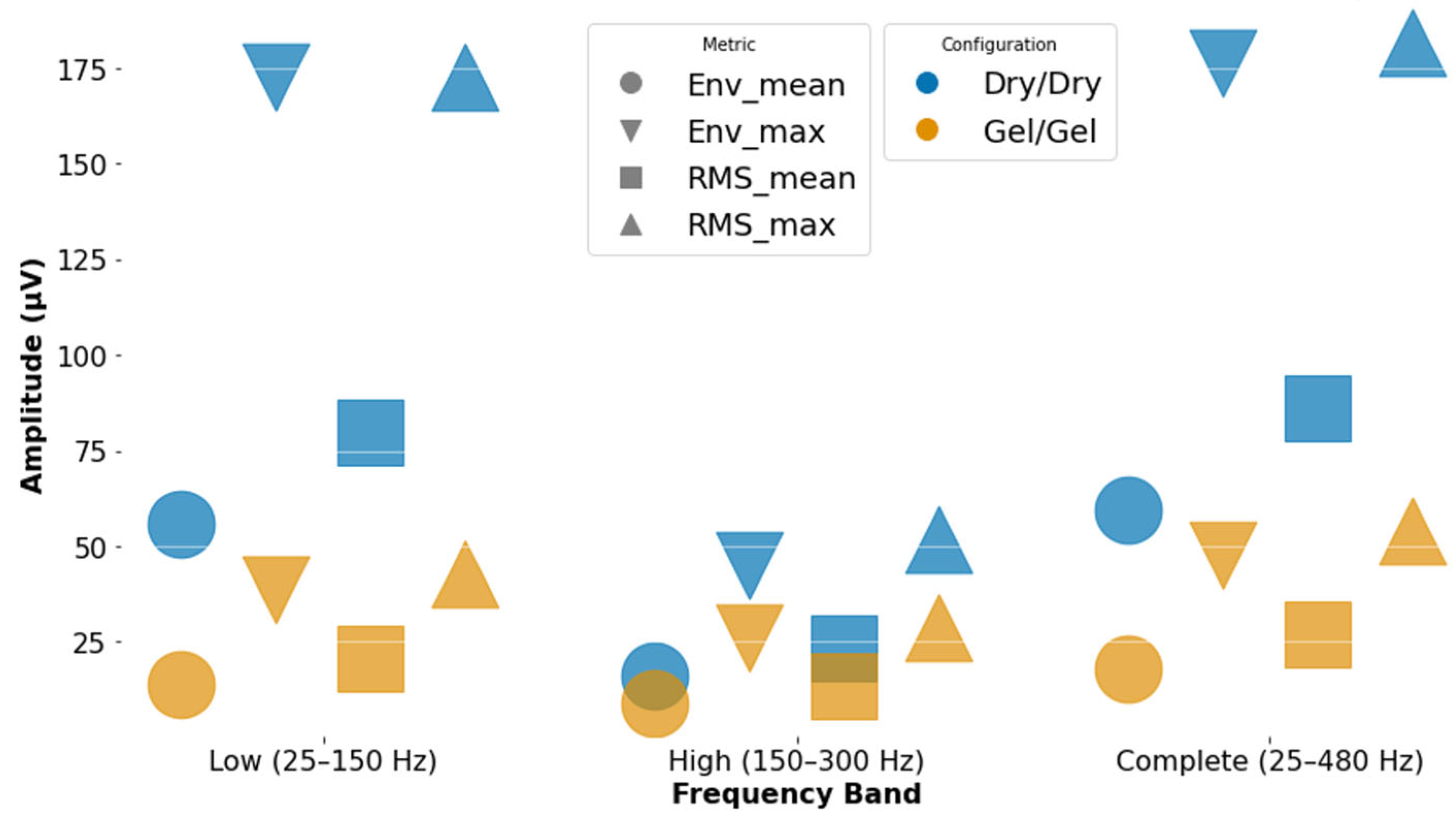
| Frequency Band | Configuration | Env Max | Ret Max | PSDmean | PSDmedian | PSDmax | Mean RMS | Max RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (25–150 Hz) | Dry | 172.72 | 609.76 | 64.88 | 58.86 | 39.51 | 79.59 | 172.46 |
| Low (25–150 Hz) | Gel | 38.70 | 178.46 | 70.30 | 64.19 | 52.29 | 20.78 | 42.70 |
| Complete (25–480 Hz) | Dry | 176.37 | 792.33 | 114.26 | 87.18 | 43.59 | 85.85 | 181.87 |
| Complete (25–480 Hz) | Gel | 47.93 | 269.01 | 133.24 | 97.21 | 52.65 | 26.87 | 53.85 |
| High (150–300 Hz) | Dry | 44.86 | 285.22 | 210.43 | 205.17 | 185.1 | 23.51 | 51.77 |
| High (150–300 Hz) | Gel | 25.92 | 142.02 | 214.97 | 211.74 | 190.7 | 13.62 | 28.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, A.M.; Brás, I.; Caldeira, L.; Caldeira, J.; Peham, C.; Plácido da Silva, H.; Requicha, J.F. Are Reusable Dry Electrodes an Alternative to Gelled Electrodes for Canine Surface Electromyography? Animals 2025, 15, 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202959
Ribeiro AM, Brás I, Caldeira L, Caldeira J, Peham C, Plácido da Silva H, Requicha JF. Are Reusable Dry Electrodes an Alternative to Gelled Electrodes for Canine Surface Electromyography? Animals. 2025; 15(20):2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202959
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Ana M., I. Brás, L. Caldeira, J. Caldeira, C. Peham, H. Plácido da Silva, and João F. Requicha. 2025. "Are Reusable Dry Electrodes an Alternative to Gelled Electrodes for Canine Surface Electromyography?" Animals 15, no. 20: 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202959
APA StyleRibeiro, A. M., Brás, I., Caldeira, L., Caldeira, J., Peham, C., Plácido da Silva, H., & Requicha, J. F. (2025). Are Reusable Dry Electrodes an Alternative to Gelled Electrodes for Canine Surface Electromyography? Animals, 15(20), 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202959







