Ecological and Functional Changes in the Hindgut Microbiome of Holstein Cows at High Altitudes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
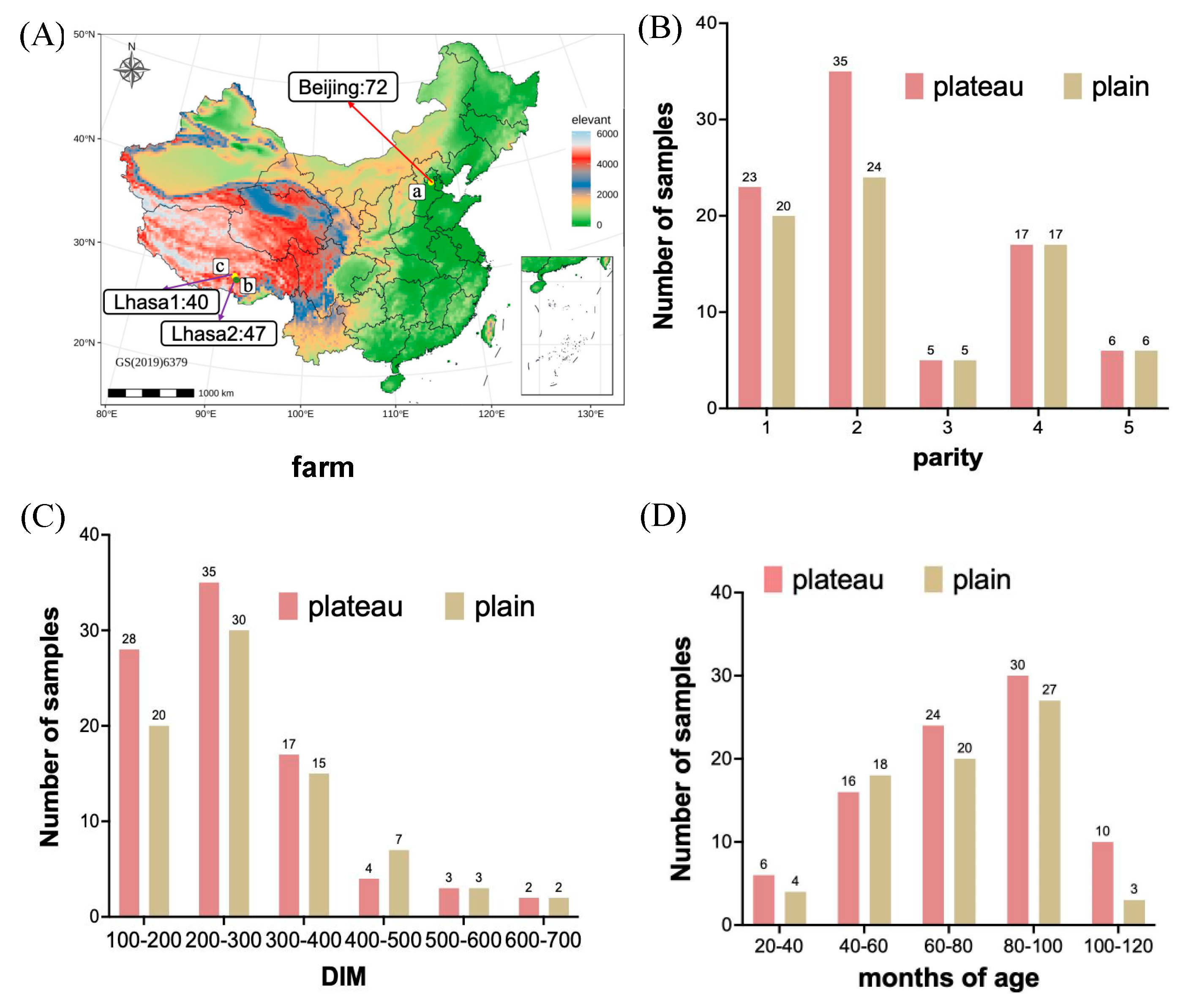
2.1. Animal Selection and Fecal Sample Collection
2.2. Microbial DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Quality Control of 16s Data
2.4. Species Community and Diversity Analysis
2.5. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
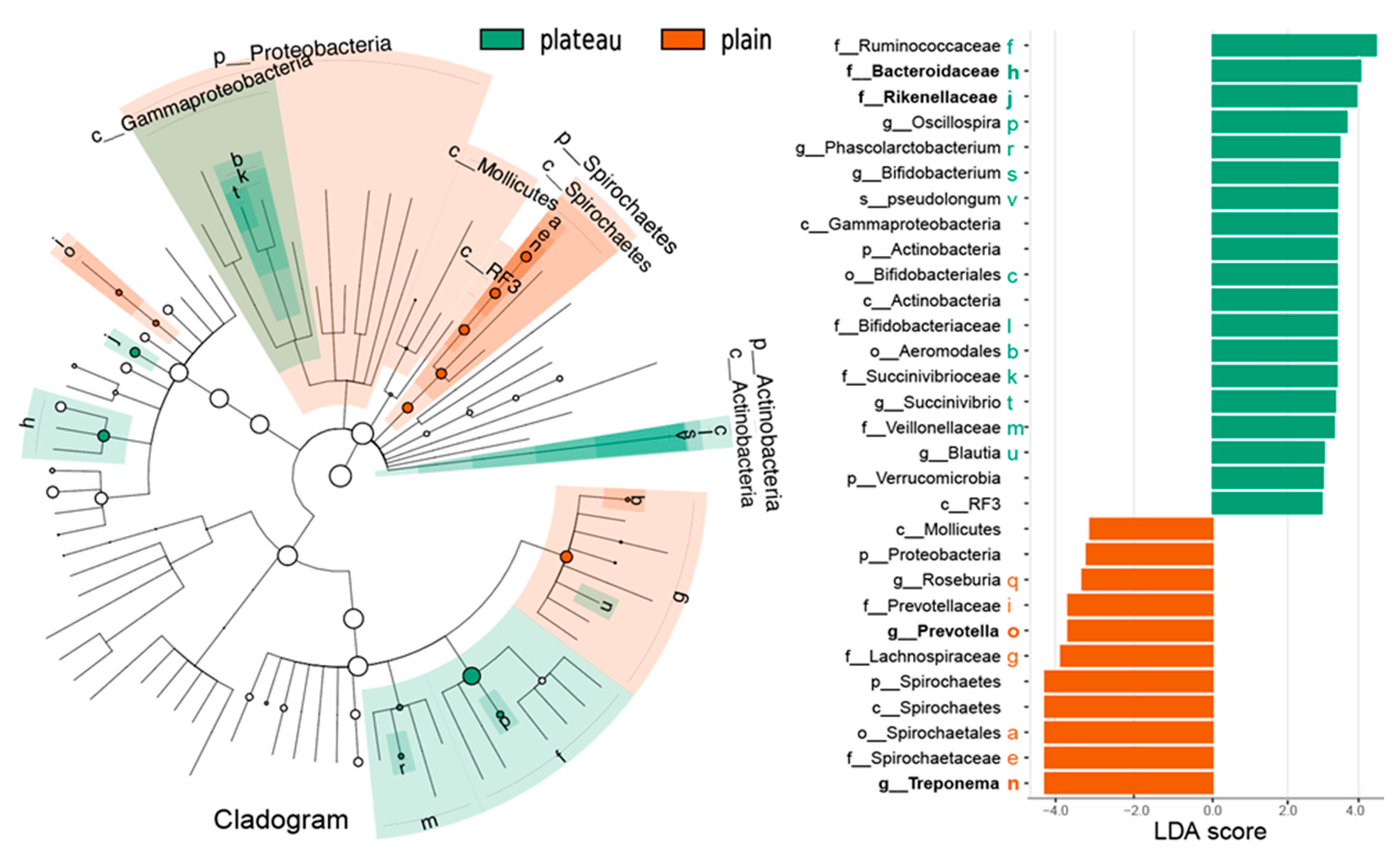
2.6. LEfSe Analysis
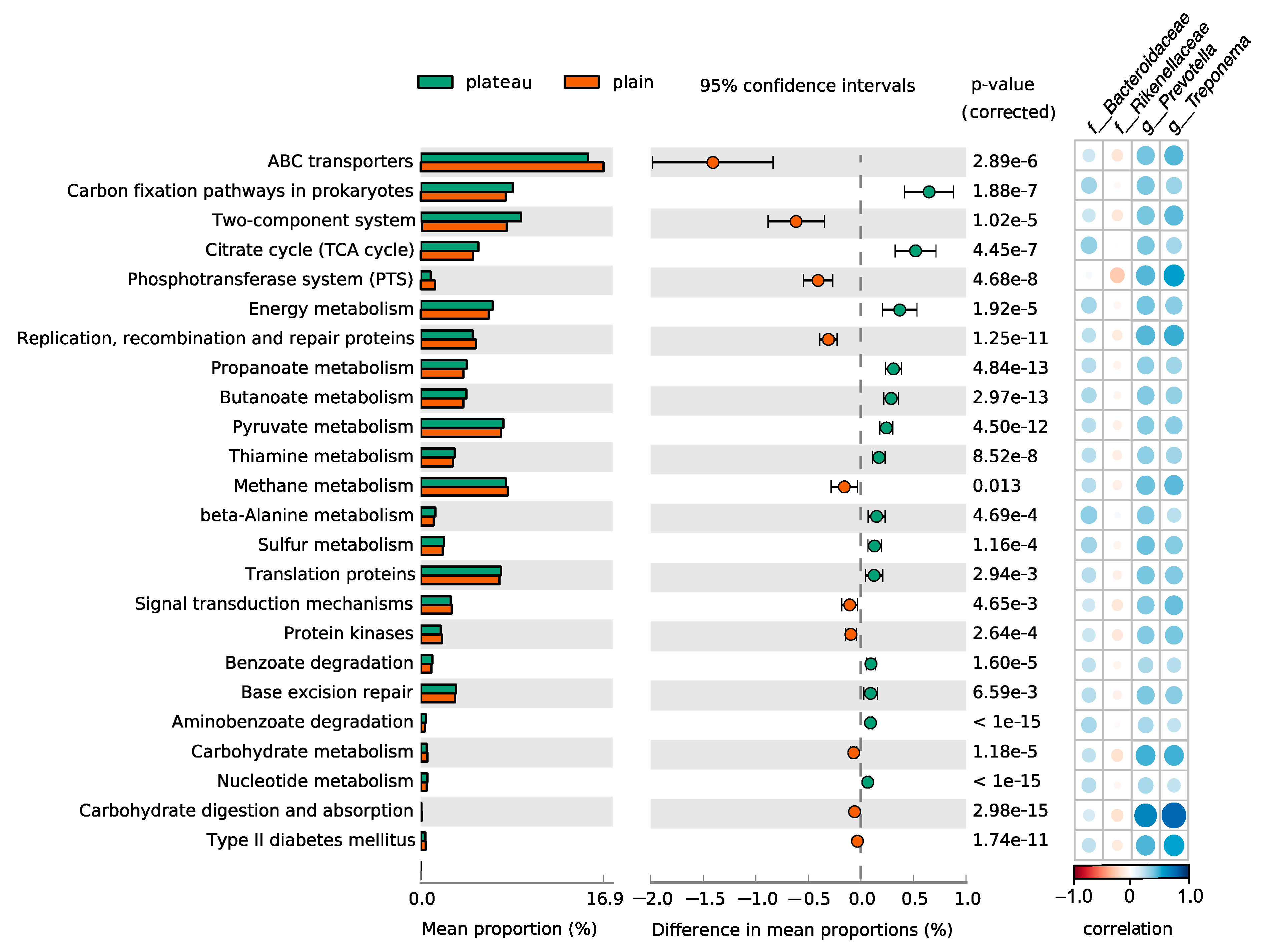
2.7. Functional Prediction of Microbial Pathway Abundances by PICRUSt2
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
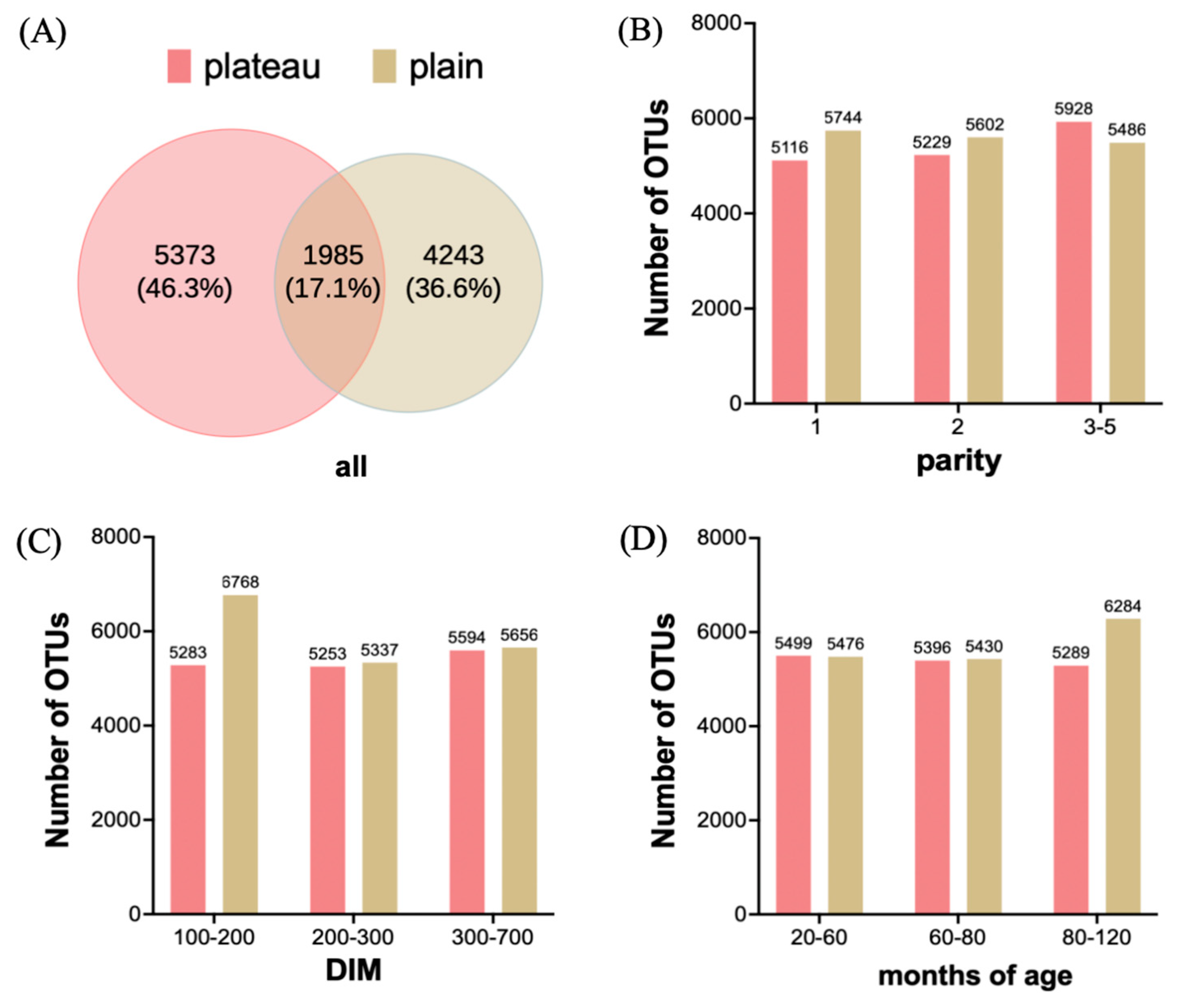
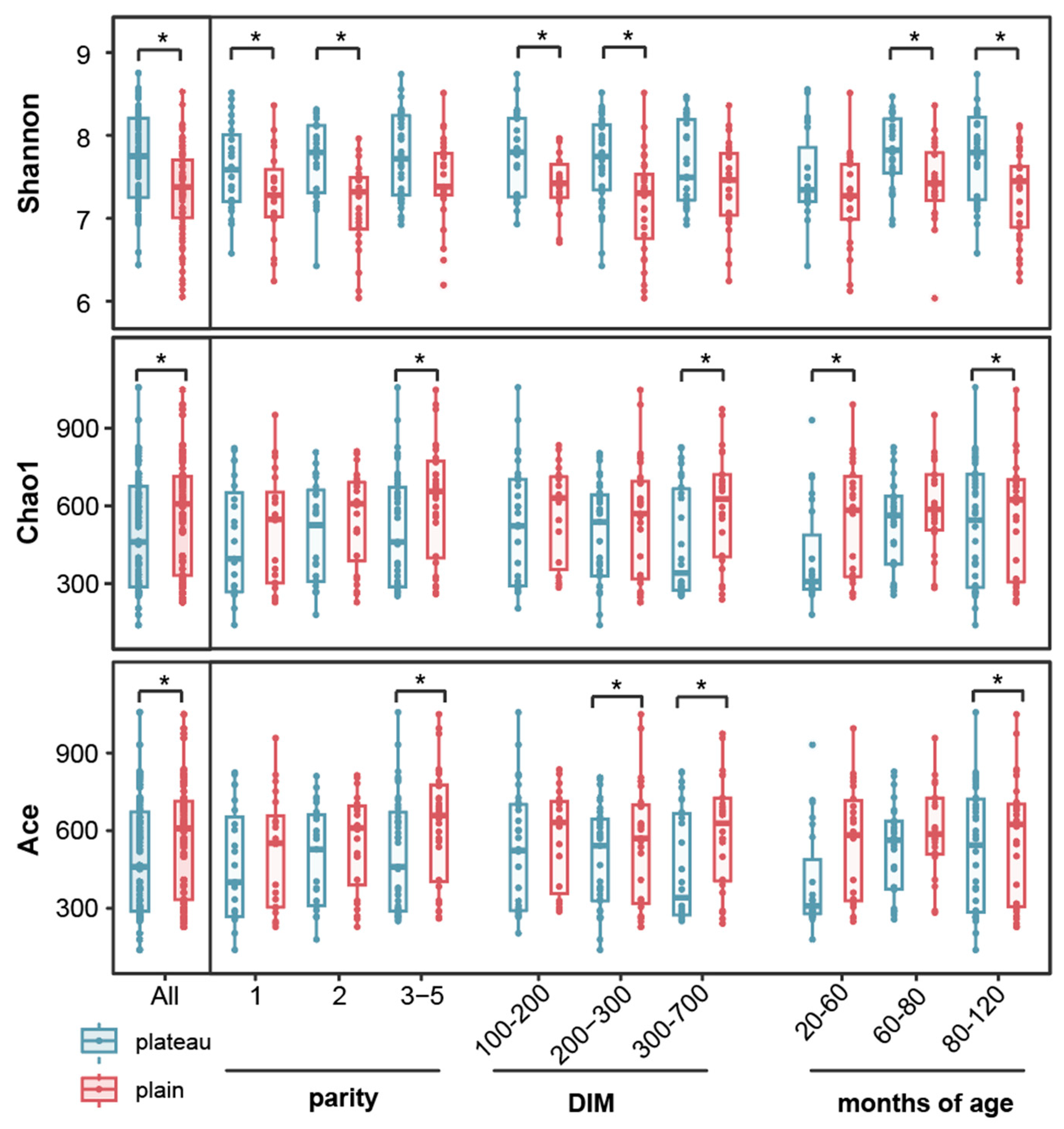
3.1. Hindgut Bacterial Community Diversity in OTU Richness Between the Plateau and Plain Holstein Cows
3.2. Hindgut Bacterial Community Diversity in OTU Abundance Between the Plateau and Plain Holstein Cows
3.3. Hindgut Bacterial Community Diversity in the Structure Between the Plateau and Plain Holstein Cows
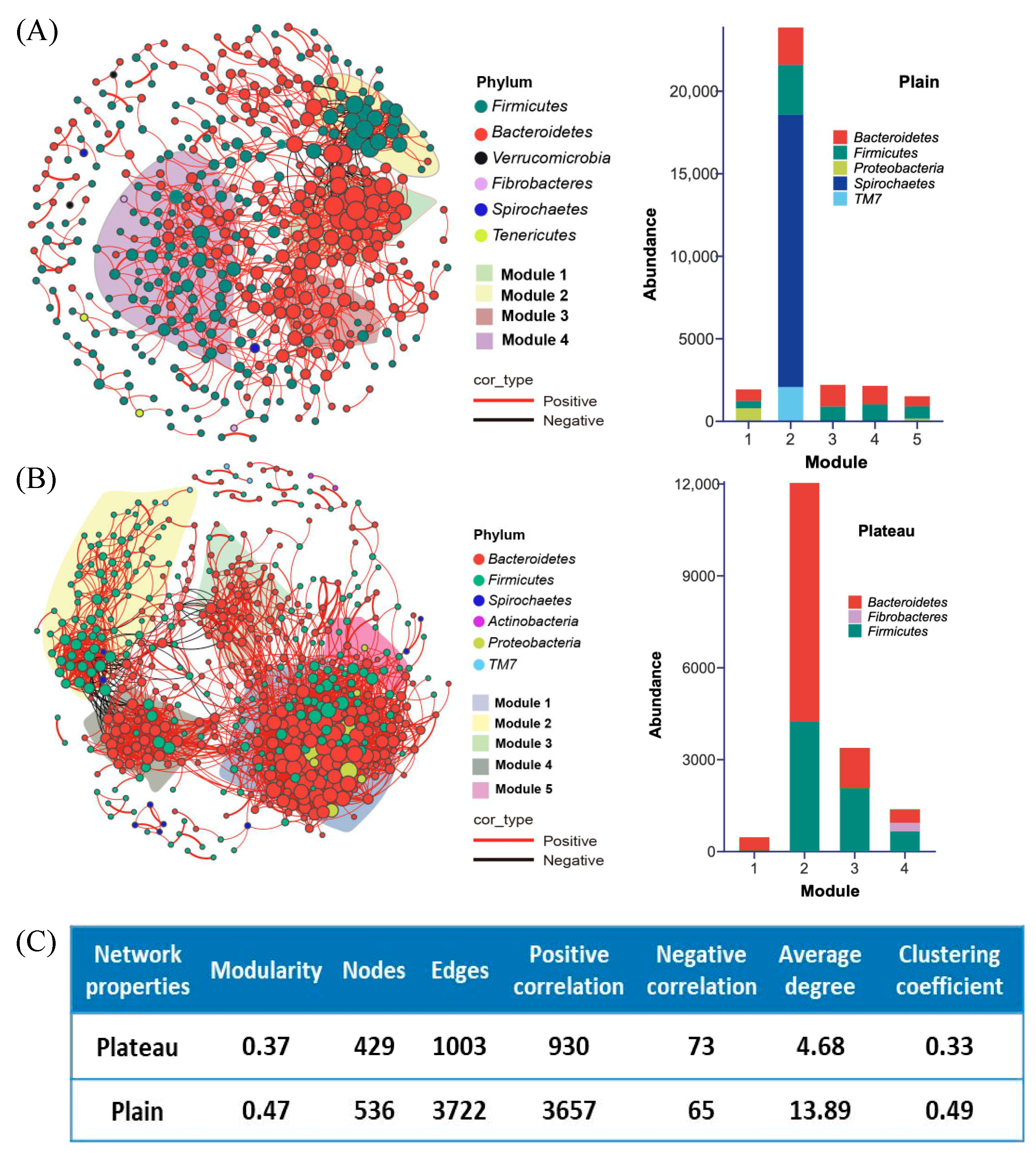
3.4. Hindgut Bacterial Community Diversity in the Co-Occurrence Network Between the Plateau and Plain Holstein Cows
3.5. Different Bacteria Identified with the Relative Abundance of Hindgut Bacteria Between the Plateau and Plain Holstein Cows
3.6. Different Function Pathways in Hindgut Microbiota Between the Plateau and Plain Holstein Cows
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Z. The system of physico-geographical regions of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 1996, 39, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Ran, Y.; Wan, W.; Luo, W.; Chen, W.; Xu, F.; Li, X. 100 years of lake evolution over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3951–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, C.; Han, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, G.; Qi, X.; Du, P.; Liu, L. Tibetan Plateau yak milk: A comprehensive review of nutritional values, health benefits, and processing technology. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, E.; Horan, B.; Evans, R.; Berry, D. Milk production and fertility performance of Holstein, Friesian, and Jersey purebred cows and their respective crosses in seasonal-calving commercial farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5681–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utama, D.; Lee, S.; Baek, K.; Chung, W.; Chung, I.; Kim, D.; Kim, G.; Lee, S. Blood profile and meat quality of Holstein-Friesian steers finished on total mixed ration or flaxseed oil-supplemented pellet mixed with reed canary grass haylage. Animal 2018, 12, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neary, J.M.; Gould, D.H.; Garry, F.B.; Knight, A.P.; Dargatz, D.A.; Holt, T.N. An investigation into beef calf mortality on five high-altitude ranches that selected sires with low pulmonary arterial pressures for over 20 years. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J. Comparative physiology of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension: Historical clues from brisket disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Dong, S. Effect of strategic feed supplementation on productive and reproductive performance in yak cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 1999, 38, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Farhan, S.B. Precipitation bias variability versus various gauges under different climatic conditions over the Third Pole Environment (TPE) region. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Tian, X.; Du, W. Dynamic of aboveground biomass and soil moisture as affected by short-term grazing exclusion on eastern alpine meadow of Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 76, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qiao, G.; Shao, T.; Yu, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y. A comparative study at two different altitudes with two dietary nutrition levels on rumen fermentation and energy metabolism in Chinese Holstein cows. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 97, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Amalfitano, N.; Sturaro, E.; Schiavon, S.; Tagliapietra, F.; Bittante, G.; Carafa, I.; Franciosi, E.; Gallo, L. Effects of summer transhumance of dairy cows to alpine pastures on body condition, milk yield and composition, and cheese making efficiency. Animals 2019, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Koga, R.; Fukatsu, T. Host plant specialization governed by facultative symbiont. Science 2004, 303, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, K.R.; Leigh, S.R.; Kent, A.; Mackie, R.I.; Yeoman, C.J.; Stumpf, R.M.; Wilson, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; White, B.A.; Garber, P.A. The role of gut microbes in satisfying the nutritional demands of adult and juvenile wild, black howler monkeys (Alouatta pigra). Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2014, 155, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sparks, J.B.; Karyala, S.V.; Settlage, R.; Luo, X.M. Host adaptive immunity alters gut microbiota. ISME J. 2015, 9, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, R. Metabolomics of a superorganism. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 259s–266s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.E.; Hume, I.D. Contributions of microbes in vertebrate gastrointestinal tract to production and conservation of nutrients. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 393–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauss, M.; Hume, I.D.; Hummel, J. Evolutionary adaptations of ruminants and their potential relevance for modern production systems. Animal 2010, 4, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Sukhchuluun, G.; Bo, T.-B.; Chi, Q.-S.; Yang, J.-J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.-H. Huddling remodels gut microbiota to reduce energy requirements in a small mammal species during cold exposure. Microbiome 2018, 6, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, K.; Mishra, K.P.; Ganju, L.; Kumar, B.; Singh, S.B. High-Altitude-Induced alterations in Gut-Immune Axis: A review. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 37, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.W.; Gillum, T.L.; Lee, B.J.; Romano, P.A.; Schall, Z.J.; Hamilton, A.M.; Kuennen, M.R. Prolonged treadmill running in normobaric hypoxia causes gastrointestinal barrier permeability and elevates circulating levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Beasley, D.E.; Heděnec, P.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Lin, Q.; Li, X. Diet Diversity Is Associated with Beta but not Alpha Diversity of Pika Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhou, J. Convergent evolution of rumen microbiomes in high-altitude mammals. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Miao, Z.-Y.; Su, J.-P.; Wasser, S.K. Shift of maternal gut microbiota of tibetan antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii) During the Periparturition Period. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tian, J.; Cidan, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, K.; Basang, W. Influence of Varied Environment Conditions on the Gut Microbiota of Yaks. Animals 2024, 14, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Effects of altitude on the gut microbiome and metabolomics of Sanhe heifers. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1076011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, F. Living the high life: Could gut microbiota matter for adaptation to high altitude? Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 2119–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sande, C.J.; Njunge, J.M.; Mwongeli Ngoi, J.; Mutunga, M.N.; Chege, T.; Gicheru, E.T.; Gardiner, E.M.; Gwela, A.; Green, C.A.; Drysdale, S.B.; et al. Airway response to respiratory syncytial virus has incidental antibacterial effects. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Walters, W.A.; Gonzalez, A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R. Using QIIME to analyze 16S rRNA gene sequences from microbial communities. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2011, 10, 10.17.11–10.17.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; McDonald, D.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Kopylova, E.; Morton, J.T.; Zech Xu, Z.; Kightley, E.P.; Thompson, L.R.; Hyde, E.R.; Gonzalez, A. Deblur rapidly resolves single-nucleotide community sequence patterns. MSystems 2017, 2, e00191-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.R.; Anderson, S.R.; Den Uyl, P.A.; Patin, N.V.; Lim, S.J.; Sanderson, G.; Goodwin, K.D. Tourmaline: A containerized workflow for rapid and iterable amplicon sequence analysis using QIIME 2 and Snakemake. GigaScience 2022, 11, giac066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.H.; Yu, G.; Cai, P. ggVennDiagram: An Intuitive, Easy-to-Use, and Highly Customizable R Package to Generate Venn Diagram. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 706907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginestet, C. 2011. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 174, pp. 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Vogtmann, E.; Graubard, B.I.; Gail, M.H.; Abnet, C.C.; Shi, J. fast.adonis: A computationally efficient non-parametric multivariate analysis of microbiome data for large-scale studies. Bioinform. Adv. 2022, 2, vbac044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, J. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities in fermentative hydrogen production system using PICRUSt. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 3716–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Hao, W.; Yin, W.; Ai, S.; Han, J.; Wang, R.; Duan, Z. Depicting fecal microbiota characteristic in yak, cattle, yak-cattle hybrid and tibetan sheep in different eco-regions of qinghai-tibetan plateau. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00021–e00022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-J.H.; Zegarra-Ruiz, D.F.; Diehl, G.E. Intestinal microbes in autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 597966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, H.F.; Zhou, Z.; Gomes, M.S.; Peixoto, P.M.; Bonsaglia, E.C.; Canisso, I.F.; Weimer, B.C.; Lima, F.S. Rumen and lower gut microbiomes relationship with feed efficiency and production traits throughout the lactation of Holstein dairy cows. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Nelson, C.D.; Driver, J.D.; Elzo, M.A.; Peñagaricano, F.; Jeong, K.C. Host genetics exerts lifelong effects upon hindgut microbiota and its association with bovine growth and immunity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2306–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Vinitchaikul, P.; Deng, M.; Zhang, G.; Sun, L.; Gou, X.; Mao, H.; Yang, S. Host and altitude factors affect rumen bacteria in cattle. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C.; Wells, W.G.; Smith, C.J. Characterization of the primary starch utilization operon in the obligate anaerobe Bacteroides fragilis: Regulation by carbon source and oxygen. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 4663–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, N.J.; Brown, J.M.; Murray, R.D.; Getty, B.; Birtles, R.J.; Hart, C.A.; Carter, S.D. Characterization of novel bovine gastrointestinal tract Treponema isolates and comparison with bovine digital dermatitis treponemes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, T.; Chang, S.; Wang, H.; Hou, F. Rumen bacterial diversity of Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) associated with different forage types on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolini, M.; Barabási, A.-L. Predicting perturbation patterns from the topology of biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6375–E6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.E.; Kent, A.D.; Brisson, V.L.; Gaudin, A.C. Agricultural management and plant selection interactively affect rhizosphere microbial community structure and nitrogen cycling. Microbiome 2019, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Zhu, Y.G.; Wang, J.T.; Singh, B.; Han, L.L.; Shen, J.P.; Li, P.P.; Wang, G.B.; Wu, C.F.; Ge, A.H. Host selection shapes crop microbiome assembly and network complexity. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Gao, C.; Gao, Z.; Rahman, M.A.U.; He, Y.; Cao, B.; Su, H. Temporal dynamics in rumen bacterial community composition of finishing steers during an adaptation period of three months. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Zhou, S.; Luo, R.; Gesang, Z.; Suolang, S. Metagenomic insights into the diversity of carbohydrate-degrading enzymes in the yak fecal microbial community. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Carrión, V.J. Importance of Bacteroidetes in host-microbe interactions and ecosystem functioning. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Wanapat, M.; Yan, T.; Hou, F. Altitude influences microbial diversity and herbage fermentation in the rumen of yaks. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.Y.; Sun, H.Z.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, J.X.; Guan, L.L. Multi-omics reveals that the rumen microbiome and its metabolome together with the host metabolome contribute to individualized dairy cow performance. Microbiome 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Sun, H.; Wu, X.; Guan, L.; Liu, J. Assessment of rumen bacteria in dairy cows with varied milk protein yield. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5031–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Kim, S.; Ramos, S.; Mamuad, L.; Son, A.; Yu, Z.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S. Holstein and Jersey steers differ in rumen microbiota and enteric methane emissions even fed the same total mixed ration. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 601061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, I.; Wallace, R.J.; Moraïs, S. The rumen microbiome: Balancing food security and environmental impacts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Corn silage | 62.5 |
| Wheat grass | 20.83 |
| Alfalfa hay | 8.33 |
| Oat | 0.92 |
| Wheat bran | 0.75 |
| Distillers’ dried grains with solubles | 0.67 |
| Corn | 4.37 |
| Soybean meal | 0.5 |
| Cottonseed meal | 0.42 |
| Premix 1 | 0.63 |
| NaCl | 0.08 |
| Total | 100 |
| Phylum | Genus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Plateau (%) | Plain (%) | Average (%) | Taxa | Plateau (%) | Plain (%) | Average (%) |
| Firmicutes | 63.43 | 52.75 | 58.09 | 5-7N15 | 23.61 | 15.76 | 19.69 |
| Bacteroidetes | 33.59 | 33.79 | 33.69 | Treponema | 3.74 | 34.1 | 18.92 |
| Spirochaetes | 0.83 | 10.47 | 5.65 | CF231 | 23.67 | 11.44 | 17.56 |
| TM7 | 0.96 | 0.76 | 0.86 | Oscillospira | 12.56 | 4.94 | 8.75 |
| Proteobacteria | 0.06 | 0.96 | 0.51 | Ruminococcus | 9.52 | 5.85 | 7.69 |
| Tenericutes | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.47 | Clostridium | 9.26 | 4.69 | 6.98 |
| Actinobacteria | 0.04 | 0.61 | 0.33 | [Clostridium] | 7.72 | 5.65 | 6.69 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.17 | Prevotella | 2.78 | 9.72 | 6.25 |
| Cyanobacteria | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.14 | Paludibacter | 4.39 | 3.42 | 3.91 |
| Fibrobacteres | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.1 | Roseburia | 2.79 | 4.44 | 3.62 |
| Module | Plateau | Plain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | OTU | Degree | Phylum | OTU | Degree | |
| 1 | Bacteroidetes | o_Bacteroidales | 16 | Bacteroidetes | g_5-7N15 | 87 |
| Bacteroidetes | f_Rikenellaceae | 12 | Bacteroidetes | g_Prevotella | 81 | |
| Bacteroidetes | g_5-7N15 | 7 | Proteobacteria | g_Succinivibrio | 75 | |
| 2 | Firmicutes | g_[Clostridium] | 27 | Firmicutes | f_Ruminococcaceae | 28 |
| Bacteroidetes | f_p-2534-18B5 | 22 | Bacteroidetes | f_S24-7 | 19 | |
| Firmicutes | f_Ruminococcaceae | 20 | Bacteroidetes | g_CF231 | 16 | |
| 3 | Bacteroidetes | g_5-7N15 | 32 | Bacteroidetes | o_Bacteroidales | 27 |
| Bacteroidetes | f_Bacteroidaceae | 15 | Bacteroidetes | f_S24-7 | 15 | |
| Bacteroidetes | o_Bacteroidales | 13 | Firmicutes | f_Ruminococcaceae | 3 | |
| 4 | Firmicutes | f_Ruminococcaceae | 18 | Firmicutes | g_Phascolarctobacterium | 33 |
| Bacteroidetes | o_Bacteroidales | 9 | Bacteroidetes | g_RF16 | 31 | |
| Firmicutes | o_Clostridiales | 9 | Bacteroidetes | g_CF231 | 29 | |
| 5 | Firmicutes | f_Ruminococcaceae | 42 | |||
| Firmicutes | f_Lachnospiraceae | 25 | ||||
| Firmicutes | g_Oscillospira | 19 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Lu, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Hou, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. Ecological and Functional Changes in the Hindgut Microbiome of Holstein Cows at High Altitudes. Animals 2025, 15, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020218
Chen G, Lu H, Huang S, Zhang C, Ma X, Li B, Hou L, Xu Q, Wang Y. Ecological and Functional Changes in the Hindgut Microbiome of Holstein Cows at High Altitudes. Animals. 2025; 15(2):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020218
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Gong, Haibo Lu, Shangzhen Huang, Congcong Zhang, Xiaojuan Ma, Bin Li, Lingling Hou, Qing Xu, and Yachun Wang. 2025. "Ecological and Functional Changes in the Hindgut Microbiome of Holstein Cows at High Altitudes" Animals 15, no. 2: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020218
APA StyleChen, G., Lu, H., Huang, S., Zhang, C., Ma, X., Li, B., Hou, L., Xu, Q., & Wang, Y. (2025). Ecological and Functional Changes in the Hindgut Microbiome of Holstein Cows at High Altitudes. Animals, 15(2), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020218







