Weight Gain and Tenderness in Nelore Cattle: Genetic Association and a Potential Pleiotropic Role of Transcription Factors and Genes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.1. Estimation of (co)Variance Components
2.2.2. GWAS Analysis
2.2.3. Pós-GWAS Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of Genetic Parameters
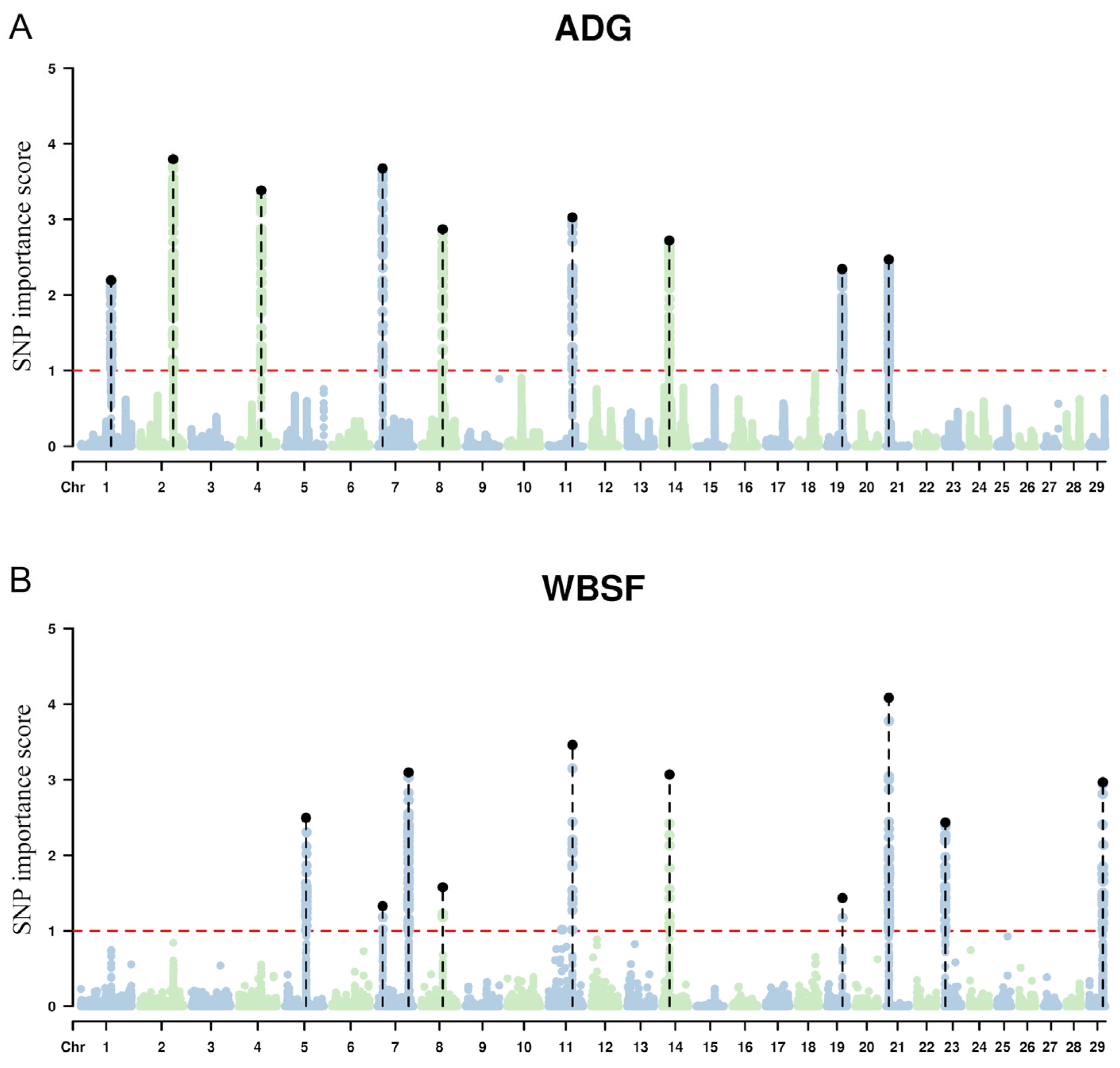
3.2. GWAS
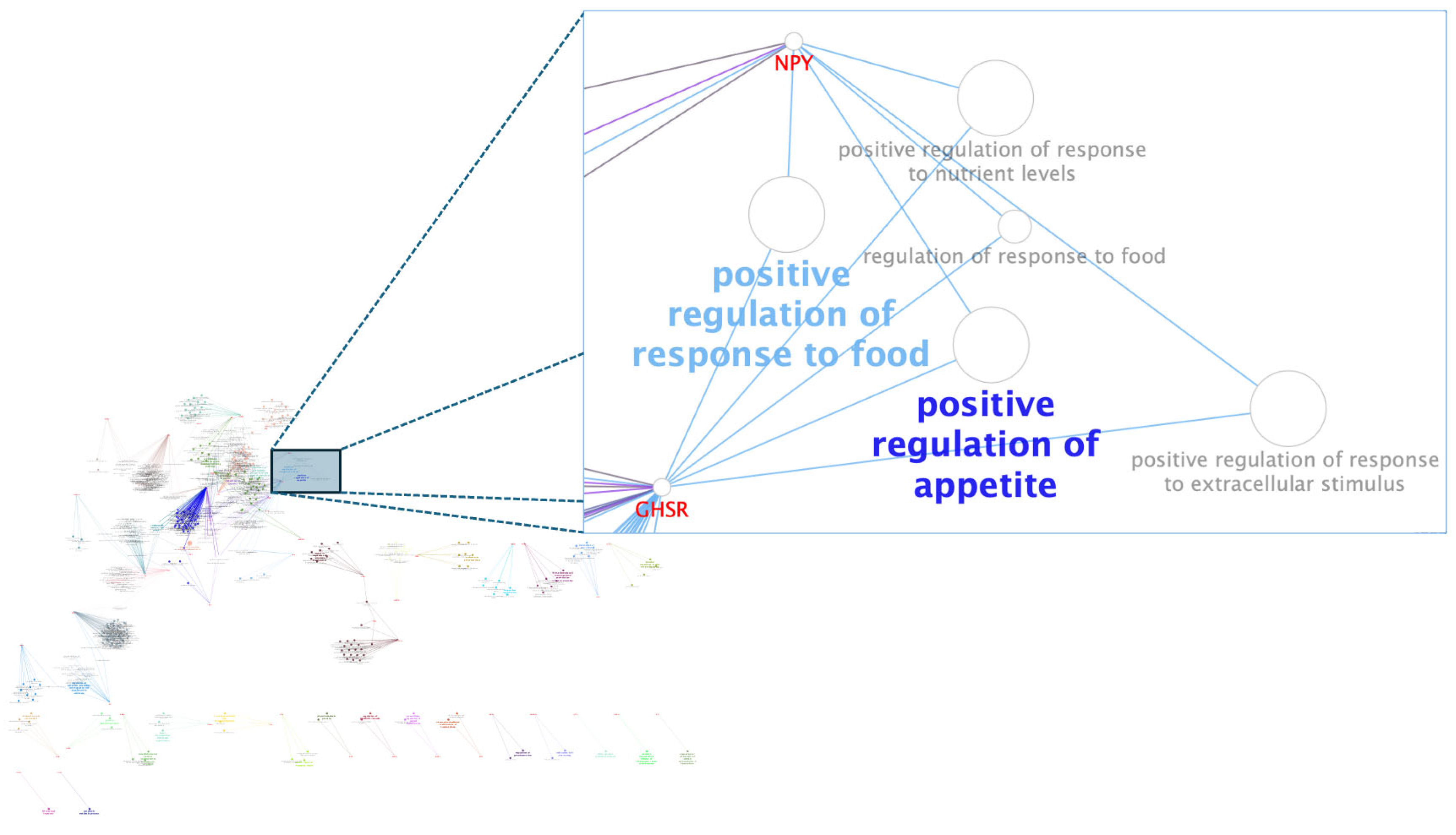
3.3. Pós-GWAS
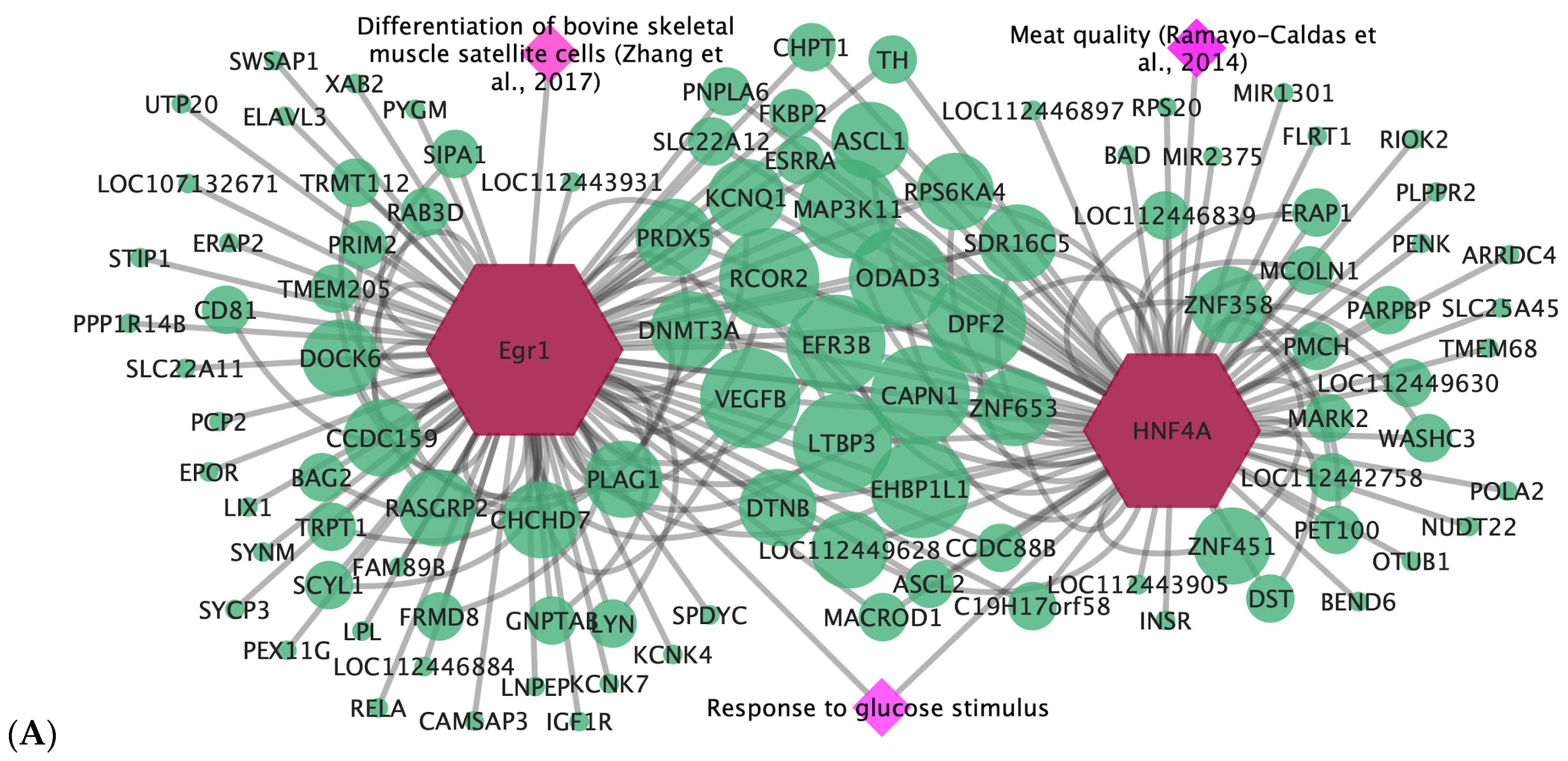
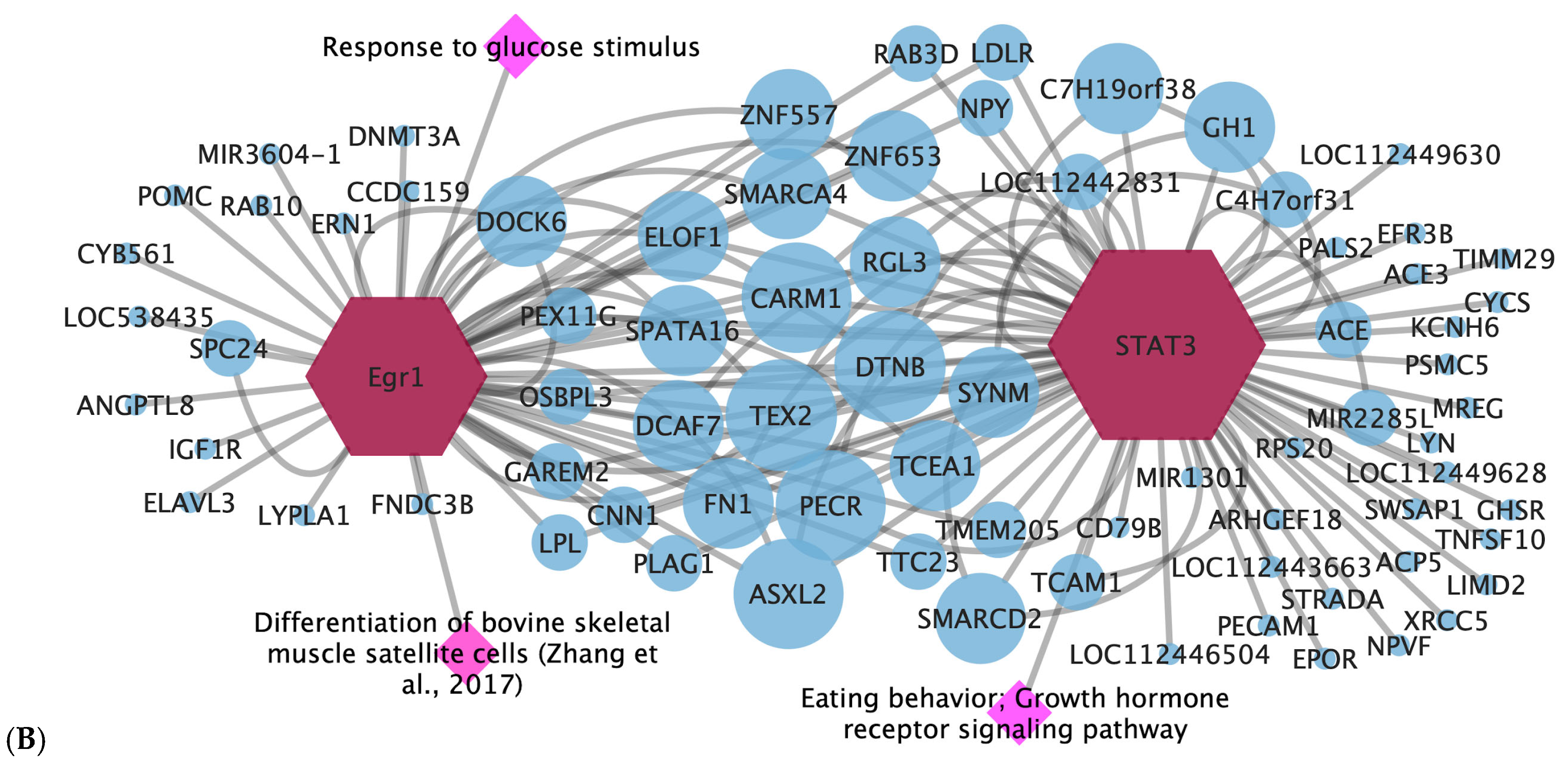
3.4. Gene-Transcription Factor
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimation of Genetic Parameters
4.2. Pós-GWAS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Production—Beef. Available online: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/production/commodity/0111000 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Pereira, M.d.A.; Bungenstab, D.J.; Euclides, V.P.B.; Malafaia, G.C.; Biscola, P.H.N.; Menezes, G.R.O.; de Abreu, U.G.P.; Laura, V.A.; Nogueira, É.; Mauro, R.d.A.; et al. From Traditionally Extensive to Sustainably Intensive: A Review on the Path to a Sustainable and Inclusive Beef Farming in Brazil. Animals 2024, 14, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.S.C.; Baldi, F.; Sainz, R.D.; Utembergue, B.L.; Chiaia, H.L.J.; Magnabosco, C.U.; Manicardi, F.R.; Araujo, F.R.C.; Guedes, C.F.; Margarido, R.C.; et al. Growth Performance, and Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in Progeny of Poll Nellore, Angus and Brahman Sires under Tropical Conditions. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2015, 55, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardulo, L.A.L.; Silveira, A.C.; Vianello, F. Analytical Aspects for Tropical Meat Quality Assessment. In Food Quality, Safety and Technology; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, A.F.B.; de Camargo, G.M.F.; Fernandes, G.A.; Gordo, D.G.M.; Tonussi, R.L.; Costa, R.B.; Espigolan, R.; Silva, R.M.d.O.; Bresolin, T.; de Andrade, W.B.F.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Meat Quality Traits in Nellore Cattle. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nadai Bonin, M.; Pedrosa, V.B.; da Luz e Silva, S.; Bünger, L.; Ross, D.; da Costa Gomes, R.; de Almeida Santana, M.H.; de Córdova Cucco, D.; de Rezende, F.M.; Ítavo, L.C.V.; et al. Genetic Parameters Associated with Meat Quality of Nellore Cattle at Different Anatomical Points of Longissimus: Brazilian Standards. Meat Sci. 2021, 171, 108281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naserkheil, M.; Lee, D.H.; Mehrban, H. Improving the Accuracy of Genomic Evaluation for Linear Body Measurement Traits Using Single-Step Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction in Hanwoo Beef Cattle. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryce, J.E.; Hayes, B.J.; Goddard, M.E. Novel Strategies to Minimize Progeny Inbreeding While Maximizing Genetic Gain Using Genomic Information. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Luo, H.; Zhao, B.; Tian, K.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, X.; Tian, Y.; Di, J.; Xu, X.; et al. The Effect of Integrating Genomic Information into Genetic Evaluations of Chinese Merino Sheep. Animals 2020, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonussi, R.L.; Espigolan, R.; Gordo, D.G.M.; Magalhães, A.F.B.; Venturini, G.C.; Baldi, F.; de Oliveira, H.N.; Chardulo, L.A.L.; Tonhati, H.; de Albuquerque, L.G. Genetic Association of Growth Traits with Carcass and Meat Traits in Nellore Cattle. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 18713–18719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakado, A.P.N.; Costa, R.B.; de Camargo, G.M.F.; Irano, N.; Bresolin, T.; Takada, L.; Carvalho, C.V.D.; Oliveira, H.N.; Carvalheiro, R.; Baldi, F.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Growth Traits in Nelore Cattle. Animal 2018, 12, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, L.M.; Mota, L.F.M.; Schmidt, P.I.; Frezarim, G.B.; Fonseca, L.F.S.; Magalhães, A.F.B.; Silva, D.A.; Carvalheiro, R.; Chardulo, L.A.L.; de Albuquerque, L.G. Genome-Wide Scans Identify Biological and Metabolic Pathways Regulating Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in Beef Cattle. Meat Sci. 2024, 209, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.N.; dos Santos, T.C.F.; Verardo, L.L.; Magalhães, A.F.B.; dos Santos Silva, D.B. Identification and Functional Annotation of Candidate Genes and Transcription Factors Associated with Reproductive Traits to Nelore Bulls: New Insights from GWAS and Post-GWAS Analysis. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2025, 57, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verardo, L.L.; e Silva, F.F.; Machado, M.A.; do Carmo Panetto, J.C.; de Lima Reis Faza, D.R.; Otto, P.I.; de Almeida Regitano, L.C.; da Silva, L.O.C.; do Egito, A.A.; do Socorro Maués Albuquerque, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Analyses Reveal the Genetic Architecture and Candidate Genes of Indicine, Taurine, Synthetic Crossbreds, and Locally Adapted Cattle in Brazil. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 702822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littiere, T.O.; Castro, G.H.F.; Rodriguez, M.d.P.R.; Bonafé, C.M.; Magalhães, A.F.B.; Faleiros, R.R.; Vieira, J.I.G.; Santos, C.G.; Verardo, L.L. Identification and Functional Annotation of Genes Related to Horses’ Performance: From GWAS to Post-GWAS. Animals 2020, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.F.; Braga Magalhães, A.F.; Verardo, L.L.; Santos, G.C.; Silva Fernandes, A.A.; Gomes Vieira, J.I.; Irano, N.; dos Santos, D.B. Functional Analysis of Litter Size and Number of Teats in Pigs: From GWAS to Post-GWAS. Theriogenology 2022, 193, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, C.G.; Sousa, M.F.; Vieira, J.I.G.; de Morais, L.R.; Fernandes, A.A.S.; de Oliveira Littiere, T.; Itajara Otto, P.; Machado, M.A.; Silva, M.V.G.B.; Bonafé, C.M.; et al. Candidate Genes for Tick Resistance in Cattle: A Systematic Review Combining Post-GWAS Analyses with Sequencing Data. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2022, 50, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.I.G.; Braga, L.G.; Chud, T.C.S.; Ferreira, P.H.; Guimarães, S.E.F.; Martins, M.F.; do Carmo Panetto, J.C.; Machado, M.A.; Silva, D.B.d.S.; Bonafé, C.M.; et al. Resequencing of Brazilian Locally Adapted Cattle Breeds Revealed Variants in Candidate Genes and Transcription Factors for Meat Fatty Acid Profile. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2024, 141, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargolzaei, M.; Chesnais, J.P.; Schenkel, F.S. A New Approach for Efficient Genotype Imputation Using Information from Relatives. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L.F.M.; Carvajal, A.B.; Silva Neto, J.B.; Díaz, C.; Carabaño, M.J.; Baldi, F.; Munari, D.P. Assessment of Inbreeding Coefficients and Inbreeding Depression on Complex Traits from Genomic and Pedigree Data in Nelore Cattle. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L.F.M.; Arikawa, L.M.; Valente, J.P.S.; Fonseca, L.F.S.; Mercadante, M.E.Z.; Cyrillo, J.N.S.G.; Oliveira, H.N.; Albuquerque, L.G. Variable Selection Strategies for Genomic Prediction of Growth and Carcass Related Traits in Experimental Nellore Cattle Herds under Different Selection Criteria. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Legarra, A.; Aguilar, I.; Misztal, I. 331 Efficient Quality Control Methods for Genomic and Pedigree Data Used in Routine Genomic Evaluation. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misztal, I.; Tsuruta, S.; Lourenco, D.; Masuda, Y. Manual for BLUPF90 Family of Programs; University of Georgia: Athens, GA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.J. Boa: An Package for MCMC Output Convergence Assessment and Posterior Inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geweke, J. Evaluating the Accuracy of Sampling-Based Approaches to the Calculation of Posterior Moments; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.K.; Narasimhan, B.; Hastie, T. Elastic Net Regularization Paths for All Generalized Linear Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2023, 106, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L.F.M.; Giannuzzi, D.; Pegolo, S.; Trevisi, E.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Cecchinato, A. Integrating On-Farm and Genomic Information Improves the Predictive Ability of Milk Infrared Prediction of Blood Indicators of Metabolic Disorders in Dairy Cows. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2023, 55, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandelin, A. JASPAR: An Open-Access Database for Eukaryotic Transcription Factor Binding Profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D91–D94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, H.; Varré, J.-S. Efficient and Accurate P-Value Computation for Position Weight Matrices. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2007, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maere, S.; Heymans, K.; Kuiper, M. BiNGO: A Cytoscape Plugin to Assess Overrepresentation of Gene Ontology Categories in Biological Networks. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3448–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.-H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape Plug-in to Decipher Functionally Grouped Gene Ontology and Pathway Annotation Networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, R.; Ren, S.-G.; Wawrowsky, K.; Melmed, S. STAT3 Upregulation in Pituitary Somatotroph Adenomas Induces Growth Hormone Hypersecretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, S.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Yan, Y. Transcription Factor EGR1 Promotes Differentiation of Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells by Regulating MyoG Gene Expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Fortes, M.R.S.; Hudson, N.J.; Porto-Neto, L.R.; Bolormaa, S.; Barendse, W.; Kelly, M.; Moore, S.S.; Goddard, M.E.; Lehnert, S.A.; et al. A Marker-Derived Gene Network Reveals the Regulatory Role of PPARGC1A, HNF4G, and FOXP3 in Intramuscular Fat Deposition of Beef Cattle1. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 2832–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureano, M.M.M.; Boligon, A.A.; Costa, R.B.; Forni, S.; Severo, J.L.P.; Albuquerque, L.G. Estimativas de Herdabilidade e Tendências Genéticas Para Características de Crescimento e Reprodutivas Em Bovinos Da Raça Nelore: Estimates of Heritability and Genetic Trends for Growth and Reproduction Traits in Nelore Cattle. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2011, 63, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, F.L.B.; Roso, V.M.; de Araújo, C.V.; Filho, J.C.R. Genetic Parameters and Response to Selection for Post-Weaning Weight Gain, Visual Scores and Carcass Traits in Hereford and Hereford×Nellore Cattle. Livest. Sci. 2011, 137, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A.F.B.; Schenkel, F.S.; Garcia, D.A.; Gordo, D.G.M.; Tonussi, R.L.; Espigolan, R.; Silva, R.M.d.O.; Braz, C.U.; Fernandes Júnior, G.A.; Baldi, F.; et al. Genomic Selection for Meat Quality Traits in Nelore Cattle. Meat Sci. 2019, 148, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, L.M.; Mota, L.F.M.; Schmidt, P.I.; Salatta, B.M.; Nasner, S.L.C.; Silva Neto, J.B.D.; Fonseca, L.F.S.; Magalhães, A.F.B.; Silva, D.A.; Carvalheiro, R.; et al. Genetic Parameter Estimates for Carcass and Meat Quality Traits and Their Genetic Associations with Sexual Precocity Indicator Traits in Nellore Cattle. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbossa, P.L.M.; Poleti, M.D.; Martins, T.d.S.; Mueller, L.F.; Muñoz, J.A.; Rocha, H.C.; do Barco, A.G.V.; Gemelli, J.L.; de Amorim, T.R.; Ferrinho, A.M.; et al. A Condição Sexual de Bovinos Cruzados Altera o Proteoma Muscular e Influencia a Maciez Da Carne. In Novos Desafios da Pesquisa em Nutrição e Produção Animal; Editora 5D: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NCBI. MYBPC1 Myosin Binding Protein C1. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/4604 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Tong, B.; Muramatsu, Y.; Ohta, T.; Kose, H.; Yamashiro, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamada, T. Association of the Expression Level of the MYBPC1 Gene in Skeletal Muscle with Marbling Trait in Japanese Black Beef Cattle. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2015, 15, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Blecker, C.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Chen, L. Validation of Protein Biological Markers of Lamb Meat Quality Characteristics Based on the Different Muscle Types. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, S.M.; Mendonça, F.S.; Costa, P.T.; De Conto, L.; Corrêa, G.F.; Schwengber, E.B.; Vaz, R.Z.; Silveira, I.D.B. Beef: Consumer Front of the Animal Welfare—Review. Rev. Electrónica Vet. 2017, 18, 051708. [Google Scholar]
- Boissy, A.; Fisher, A.D.; Bouix, J.; Hinch, G.N.; Le Neindre, P. Genetics of Fear in Ruminant Livestock. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 93, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.P.; Kalra, P.S. NPY and Cohorts in Regulating Appetite, Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Beneficial Effects of Gene Therapy. Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.-R.; Shin, S.-C.; Heo, J.-P. Association Analysis between SNP Marker in Neuopeptide Y (NPY) Gene and Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in Korean Cattle. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2011, 31, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vanLieshout, T.L.; Stouth, D.W.; Hartel, N.G.; Vasam, G.; Ng, S.Y.; Webb, E.K.; Rebalka, I.A.; Mikhail, A.I.; Graham, N.A.; Menzies, K.J.; et al. The CARM1 Transcriptome and Arginine Methylproteome Mediate Skeletal Muscle Integrative Biology. Mol. Metab. 2022, 64, 101555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.F.; Coutinho, L.L.; Herring, K.L.; Gallagher, D.S.; Brenneman, R.A.; Burney, N.; Sanders, J.O.; Turner, J.W.; Smith, S.B.; Miller, R.K.; et al. Candidate Gene Analysis of GH1 for Effects on Growth and Carcass Composition of Cattle. Anim. Genet. 1998, 29, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curi, R.A.; Palmieri, D.A.; Suguisawa, L.; de Oliveira, H.N.; Silveira, A.C.; Lopes, C.R. Growth and Carcass Traits Associated with GH1/Alu I and POU1F1/Hinf I Gene Polymorphisms in Zebu and Crossbred Beef Cattle. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2006, 29, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Curi, R.A.; Chardulo, L.A.L.; Giusti, J.; Silveira, A.C.; Martins, C.L.; de Oliveira, H.N. Assessment of GH1, CAPN1 and CAST Polymorphisms as Markers of Carcass and Meat Traits in Bos indicus and Bos taurus–Bos indicus Cross Beef Cattle. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bruce, H.; Yang, T.; Charagu, P.; Kemp, R.A.; Boddicker, N.; Miar, Y.; Wang, Z.; Plastow, G. Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS) Identify QTL on SSC2 and SSC17 Affecting Loin Peak Shear Force in Crossbred Commercial Pigs. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, B.T.; Casas, E.; Heaton, M.P.; Cullen, N.G.; Hyndman, D.L.; Morris, C.A.; Crawford, A.M.; Wheeler, T.L.; Koohmaraie, M.; Keele, J.W.; et al. Evaluation of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in CAPN1 for Association with Meat Tenderness in Cattle1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Miao, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Zhu, B.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies the PLAG1-OXR1 Region on BTA14 for Carcass Meat Yield in Cattle. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Traits | n | GC | Mean | Min | Max | r | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADG (kg/dia) | 6077 | 737 | 0.63 ± 0.09 | 0.37 | 1.05 | 0.0009 ± 0.00001 | 0.004 ± 0.0008 | 0.23 ± 0.025 | −0.17 |
| WBSF (kgf) | 5555 | 715 | 6.27 ± 1.96 | 1.60 | 12.84 | 0.28 ± 0.047 | 2.03 ± 0.25 | 0.13 ± 0.039 |
| BTA | n SNP | Region (Mb) | Size (Mb) | Importance Score (%) | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85 | 94.37–95.17 | 0.8 | 1.87 (1.02–2.20) | SPATA16 (spermatogenesis associated 16), ECT2 (epithelial cell transforming 2), NCEH1 (neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1), TNFSF10 (TNF superfamily member 10), GHSR (growth hormone secretagogue receptor), FNDC3B (fibronectin type III domain containing 3B) |
| 2 | 97 | 103.50–104.42 | 0.92 | 2.50 (1.02–3.80) | FN1 (fibronectin 1), MIR2285L (microRNA mir-2285l), MREG (melanoregulin), LOC112443663 (small nucleolar RNA SNORA40), TMEM169 (transmembrane protein 169), PECR (peroxisomal trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase), XRCC5 (X-ray repair cross complementing 5), MARCHF4 (membrane associated ring-CH-type finger 4), SMARCAL1 (SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a like 1), RPL37A (ribosomal protein L37a) |
| 4 | 109 | 70.52–71.56 | 1.04 | 2.15 (1.01–3.38) | NPVF (Neuropeptide VF precursor), C4H7orf31 (chromosome 4 C7orf31 homolog), CYCS (Cytochrome c, somatic), OSBPL3 (Oxysterol binding protein like 3), LOC112446504 (U6atac minor spliceosomal RNA), LOC100299757 (EP300-interacting inhibitor of differentiation 1), GSDME (Gasdermin E), PALS2 (protein associated with LIN7 2, MAGUK p55 family member), NPY (Neuropeptide Y) |
| 7 | 119 | 15.28–16.25 | 0.97 | 2.24 (1.03–3.67) | QTRT1 (Queuine tRNA-Ribosyltransferase Catalytic Subunit 1), DNM2 (Dynamin 2), MIR3604-1 (MicroRNA 3604-1), TMED1 (Transmembrane P24 Trafficking Protein 1), C7H19orf38 (Chromosome 7 C19orf38 Homolog), CARM1 (Coactivator Associated Arginine Methyltransferase 1), YIPF2 (Yip1 Domain Family Member 2), TIMM29 (Translocase Of Inner Mitochondrial Membrane 29), SMARCA4 (SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin Dependent Regulator Of Chromatin, Subfamily A, Member 4), LOC112447661 (U6 spliceosomal RNA), LDLR (Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor), SPC24 (SPC24 Component Of NDC80 Kinetochore Complex), KANK2 (KN Motif And Ankyrin Repeat Domains 2), DOCK6 (Dedicator Of Cytokinesis 6), ANGPTL8 (Angiopoietin Like 8), RAB3D (RAB3D, Member RAS Oncogene Family), TMEM205 (Transmembrane Protein 205), CCDC159 (Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 159), PLPPR2 (Phospholipid Phosphatase Related 2), SWSAP1 (SWIM-Type Zinc Finger 7 Associated Protein 1), EPOR (Erythropoietin Receptor), RGL3 (Ral Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Stimulator Like 3), ODAD3 (Outer Dynein Arm Docking Complex Subunit 3), PRKCSH (Glucosidase II Beta Subunit), ELAVL3 (ELAV Like RNA-Binding Protein 3), ZNF653 (Zinc Finger Protein 653), ECSIT (ECSIT Signaling Integrator), CNN1 (Calponin 1), ELOF1 (Transcription Elongation Factor 1), ACP5 (Acid Phosphatase 5, Tartrate Resistant), LOC538435 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1), ZNF557 (Zinc Finger Protein 557), LOC508834 (RNA-binding protein S1, serine-rich domain-like), INSR (Insulin Receptor), ARHGEF18 (Rho/Rac Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 18), PEX11G (PEX11 Gamma) |
| 8 | 103 | 66.64–67.06 | 0.42 | 2.12 (1.01–2.87) | LPL (lipoprotein lipase) |
| 11 | 71 | 73.40–74.12 | 0.72 | 2.17 (1.03–3.03) | GAREM2 (GRB2 associated regulator of MAPK1 subtype 2), RAB10 (RAB10, member RAS oncogene family), KIF3C (kinesin family member 3C), ASXL2 (ASXL transcriptional regulator 2), DTNB (dystrobrevin beta), DNMT3A (DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha), MIR1301 (microRNA 1301), POMC (proopiomelanocortin), EFR3B (EFR3 homolog B, plasma membrane associated) |
| 14 | 215 | 22.08–23.24 | 1.16 | 2.32 (1.02–2.72) | TCEA1 (transcription elongation factor A1), LYPLA1 (lysophospholipase 1), MRPL15 (mitochondrial ribosomal protein L15), SOX17 (SRY-box transcription factor 17), RP1 (RP1, axonemal microtubule associated), XKR4 (XK related 4), TMEM68 (transmembrane protein 68), TGS1 (trimethylguanosine synthase 1), LYN (LYN proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase), RPS20 (ribosomal protein S20), LOC112449628 (small nucleolar RNA U54), LOC112449630 (U1 spliceosomal RNA), MOS (MOS proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase), PLAG1 (PLAG1 zinc finger) |
| 19 | 193 | 47.59–48.55 | 0.96 | 1.79 (1.01–2.34) | TANC2 (tetratricopeptide repeat, ankyrin repeat and coiled-coil containing 2), CYB561 (cytochrome b561), ACE (angiotensin I converting enzyme), ACE3 (angiotensin I converting enzyme 3), KCNH6 (potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 6), DCAF7 (DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 7), TACO1 (translation activator of cytochrome c oxidase I), MAP3K3 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3), LIMD2 (LIM domain containing 2), STRADA (STE20 related adaptor alpha), CCDC47 (coiled-coil domain containing 47), DDX42 (DEAD-box helicase 42), FTSJ3 (FtsJ RNA methyltransferase homolog 3), PSMC5 (proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 5), SMARCD2 (SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily D, member 2), TCAM1 (testicular cell adhesion molecule 1), GH1 (growth hormone 1), CD79B (CD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta), SCN4A (sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 4), LOC616254 (intercellular adhesion molecule 2), LOC100140873 (intercellular adhesion molecule 2), ERN1 (endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1), LOC112442810 (small nucleolar RNA SNORD104), LOC112442831 (small nucleolar RNA SNORA76), TEX2 (testis expressed 2), PECAM1 (platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1) |
| 21 | 88 | 7.37–7.85 | 0.48 | 1.96 (1.02–2.47) | LRRC28 (Leucine Rich Repeat Containing 28), TTC23 (Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 23), SYNM (Synemin, Intermediate Filament Protein), IGF1R (Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor) |
| BTA | n SNP | Region (Mb) | Size (Mb) | Importance Score (%) | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 36 | 65.08–66.99 | 1.91 | 1.50 (1.01–2.50) | ANO4 (Anoctamin 4), SLC5A8 (Solute Carrier Family 5 Member 8), UTP20 (UTP20 Small Subunit Processome Component), ARL1 (ADP Ribosylation Factor Like GTPase 1), SPIC (Spi-C Transcription Factor), MYBPC1 (Myosin Binding Protein C1), CHPT1 (Choline Phosphotransferase 1), SYCP3 (Synaptonemal Complex Protein 3), GNPTAB (N-Acetylglucosamine-1-Phosphate Transferase Subunits Alpha And Beta), WASHC3 (WASH Complex Subunit 3), NUP37 (Nucleoporin 37), PARPBP (PARP1 Binding Protein), PMCH (Pro-Melanin Concentrating Hormone), LOC112446897 (U6 spliceosomal RNA), LOC112446839 (U6 spliceosomal RNA), PAH (Phenylalanine Hydroxylase), ASCL1 (Achaete-Scute Family bHLH Transcription Factor 1), LOC112446884 (U1 spliceosomal RNA) |
| 7 | 3 | 15.77–16.38 | 0.61 | 1.18 (1.02–1.33) | DOCK6 (Dedicator Of Cytokinesis 6), RAB3D (RAB3D, Member RAS Oncogene Family), TMEM205 (Transmembrane Protein 205), CCDC159 (Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 159), PLPPR2 (Phospholipid Phosphatase Related 2), SWSAP1 (SWIM-Type Zinc Finger 7 Associated Protein 1), EPOR (Erythropoietin Receptor), RGL3 (Ral Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Stimulator Like 3), ODAD3 (Outer Dynein Arm Docking Complex Subunit 3), PRKCSH (Glucosidase II Beta Subunit), ELAVL3 (ELAV Like RNA-Binding Protein 3), ZNF653 (Zinc Finger Protein 653), ECSIT (ECSIT Signaling Integrator), LOC508834 (RNA-binding protein S1, serine-rich domain-like), INSR (Insulin Receptor), ARHGEF18 (Rho/Rac Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 18), PEX11G (PEX11 Gamma), ZNF358 (Zinc Finger Protein 358), MCOLN1 (Mucolipin TRP Cation Channel 1), PNPLA6 (Patatin Like Phospholipase Domain Containing 6), CAMSAP3 (Calmodulin Regulated Spectrin Associated Protein Family Member 3), XAB2 (XPA Binding Protein 2), PET100 (PET100 Cytochrome C Oxidase Chaperone), PCP2 (Purkinje Cell Protein 2) |
| 7 | 61 | 95.68–96.41 | 1.22 | 1.84 (1.01–3.11) | PCSK1 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 1), CAST (Calpastatin), ERAP1 (Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1), ERAP2 (Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 2), LNPEP (Leucyl And Cystinyl Aminopeptidase), LOC107132671 (FUN14 domain-containing protein 1-like), LIX1 (Lix1 Homolog), RIOK2 (RIO Kinase 2) |
| 8 | 4 | 66.93–67.11 | 0.18 | 1.29 (1.18–1.58) | LPL (Lipoprotein Lipase) |
| 11 | 15 | 73.94–74.32 | 0.37 | 1.90 (1.02–3.46) | DTNB (dystrobrevin beta), DNMT3A (DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha), MIR1301 (microRNA 1301), POMC (proopiomelanocortin), EFR3B (EFR3 homolog B), DNAJC27 (DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C27), ADCY3 (adenylate cyclase 3) |
| 14 | 12 | 23.14–23.67 | 0.53 | 1.75 (1.05–3.07) | TMEM68 (Transmembrane Protein 68), TGS1 (Trimethylguanosine Synthase 1), LYN (LYN Proto-Oncogene, Src Family Tyrosine Kinase), RPS20 (Ribosomal Protein S20), LOC112449628, LOC112449630, MOS (MOS Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase), PLAG1 (PLAG1 Zinc Finger), CHCHD7 (Coiled-Coil-Helix-Coiled-Coil-Helix Domain Containing 7), SDR16C5 (Short Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase Family 16C Member 5), SDR16C6 (Short Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase Family 16C Member 6), PENK (Proenkephalin) |
| 19 | 2 | 48.99–49.38 | 0.39 | 1.31 (1.17–1.44) | KPNA2 (Karyopherin Subunit Alpha 2), C19H17orf58 (Chromosome 19 C17orf58 Homolog), BPTF (Bromodomain PHD Finger Transcription Factor), PITPNC1 (Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Protein Cytoplasmic 1), LOC112442758 (5S ribosomal RNA) |
| 21 | 45 | 7.20–8.95 | 1.75 | 1.82 (1.03–4.08) | LRRC28 (Leucine Rich Repeat Containing 28), TTC23 (Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 23), SYNM (Synemin), IGF1R (Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor), FAM169B (Family With Sequence Similarity 169 Member B), ARRDC4 (Arrestin Domain Containing 4) |
| 23 | 26 | 2.34–3.53 | 1.19 | 1.70 (1.01–2.44) | PRIM2 (DNA Primase Subunit 2), LOC112443931, RAB23 (RAB23, Member RAS Oncogene Family), BAG2 (BAG Cochaperone 2), ZNF451 (Zinc Finger Protein 451), BEND6 (BEN Domain Containing 6), LOC112443905 (small nucleolar RNA SNORA18), MIR2375 (MicroRNA 2375), MIR2285J-2 (MicroRNA 2285j-2), DST (Dystonin) |
| 29 | 27 | 42.24–43.76 | 2.52 | 1.67 (1.03–2.97) | MARK2 (Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 2), RCOR2 (REST Corepressor 2), NAA40 (N-Alpha-Acetyltransferase 40, NatD Catalytic Subunit), COX8A (Cytochrome C Oxidase Subunit 8A), OTUB1 (OTU Deubiquitinase, Ubiquitin Aldehyde Binding 1), MACROD1 (Macrodomain Containing 1), FLRT1 (Fibronectin Leucine Rich Transmembrane Protein 1), STIP1 (Stress Induced Phosphoprotein 1), FERMT3 (Fermitin Family Member 3), TRPT1 (tRNA 2′-Phosphotransferase 1), NUDT22 (Nudix Hydrolase 22), DNAJC4 (DnaJ Heat Shock Protein Family (Hsp40) Member C4), VEGFB (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor B), FKBP2 (FKBP Prolyl Isomerase 2), PPP1R14B (Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Inhibitor Subunit 14B), BAD (BCL2 Associated Agonist Of Cell Death), GPR137 (G Protein-Coupled Receptor 137), KCNK4 (Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 4), ESRRA (Estrogen Related Receptor Alpha), TRMT112 (tRNA Methyltransferase 112), PRDX5 (Peroxiredoxin 5), CCDC88B (Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 88B), RPS6KA4 (Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase A4), SLC22A11 (Solute Carrier Family 22 Member 11), SLC22A12 (Solute Carrier Family 22 Member 12), NRXN2 (Neurexin 2), RASGRP2 (RAS Guanyl Releasing Protein 2), PYGM (Glycogen Phosphorylase, Muscle Associated), SPDYC (Speedy/RINGO Cell Cycle Regulator Family Member C), CAPN1 (Calpain 1), MIR2407 (MicroRNA 2407), SLC22A20 (Solute Carrier Family 22 Member 20), POLA2 (DNA Polymerase Alpha 2, Accessory Subunit), CDC42EP2 (CDC42 Effector Protein 2), DPF2 (Double PHD Fingers 2), TIGD3 (Tigger Transposable Element Derived 3), SLC25A45 (Solute Carrier Family 25 Member 45), FRMD8 (FERM Domain Containing 8), SCYL1 (SCY1 Like Pseudokinase 1), LTBP3 (Latent Transforming Growth Factor Beta Binding Protein 3), ZNRD2 (Zinc Ribbon Domain Containing 2), FAM89B (Family With Sequence Similarity 89 Member B), EHBP1L1 (EH Domain Binding Protein 1 Like 1), KCNK7 (Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 7), MAP3K11 (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 11), PCNX3 (Pecanex 3), SIPA1 (Signal-Induced Proliferation-Associated 1), RELA (RELA Proto-Oncogene, NF-KB Subunit) |
| 29 | 21 | 48.85–49.71 | 0.86 | 1.38 (1.06–1.74) | KCNQ1 (Potassium Voltage-Gated Channel Subfamily Q Member 1), TRPM5 (Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily M Member 5), TSSC4 (Tumor Suppressing Subtransferable Candidate 4), CD81 (CD81 Molecule), TSPAN32 (Tetraspanin 32), ASCL2 (Achaete-Scute Family bHLH Transcription Factor 2), TH (Tyrosine Hydroxylase), INS (Insulin), IGF2 (Insulin Like Growth Factor 2), LSP1 (Lymphocyte Specific Protein 1), TNNI2 (Troponin I2, Fast Skeletal Type), CTSD (Cathepsin D) |
| TF | Trait | Biological Process | Literature Evidence * |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAT3 | ADG | Eating behavior; growth hormone receptor signaling pathway | Growth hormone secretion [34] |
| Egr1 | ADG and WBSF | Response to hormone stimulus; response to glucose stimulus | Differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells [35] |
| HNF4A | WBSF | Response to glucose stimulus; glucose homeostasis; carbohydrate homeostasis | Associated with carcass quality [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borges, E.R.P.d.S.; Mota, L.F.M.; Verardo, L.L.; Albuquerque, L.G.d.; Duarte, M.R.; Santos, G.C.; Pereira, A.S.; Carvalho, L.M.P.d.; Carvalho, L.S.; Almeida, E.A.R.; et al. Weight Gain and Tenderness in Nelore Cattle: Genetic Association and a Potential Pleiotropic Role of Transcription Factors and Genes. Animals 2025, 15, 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192874
Borges ERPdS, Mota LFM, Verardo LL, Albuquerque LGd, Duarte MR, Santos GC, Pereira AS, Carvalho LMPd, Carvalho LS, Almeida EAR, et al. Weight Gain and Tenderness in Nelore Cattle: Genetic Association and a Potential Pleiotropic Role of Transcription Factors and Genes. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192874
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorges, Elora R. P. de S., Lucio F. M. Mota, Lucas L. Verardo, Lucia G. de Albuquerque, Marcela R. Duarte, Geovana C. Santos, Alice S. Pereira, Lorena M. P. de Carvalho, Lilia S. Carvalho, Emily A. R. Almeida, and et al. 2025. "Weight Gain and Tenderness in Nelore Cattle: Genetic Association and a Potential Pleiotropic Role of Transcription Factors and Genes" Animals 15, no. 19: 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192874
APA StyleBorges, E. R. P. d. S., Mota, L. F. M., Verardo, L. L., Albuquerque, L. G. d., Duarte, M. R., Santos, G. C., Pereira, A. S., Carvalho, L. M. P. d., Carvalho, L. S., Almeida, E. A. R., & Magalhães, A. F. B. (2025). Weight Gain and Tenderness in Nelore Cattle: Genetic Association and a Potential Pleiotropic Role of Transcription Factors and Genes. Animals, 15(19), 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192874







