Diversity and Distribution of Deep-Sea Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea Based on Visual and Acoustic Surveys
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
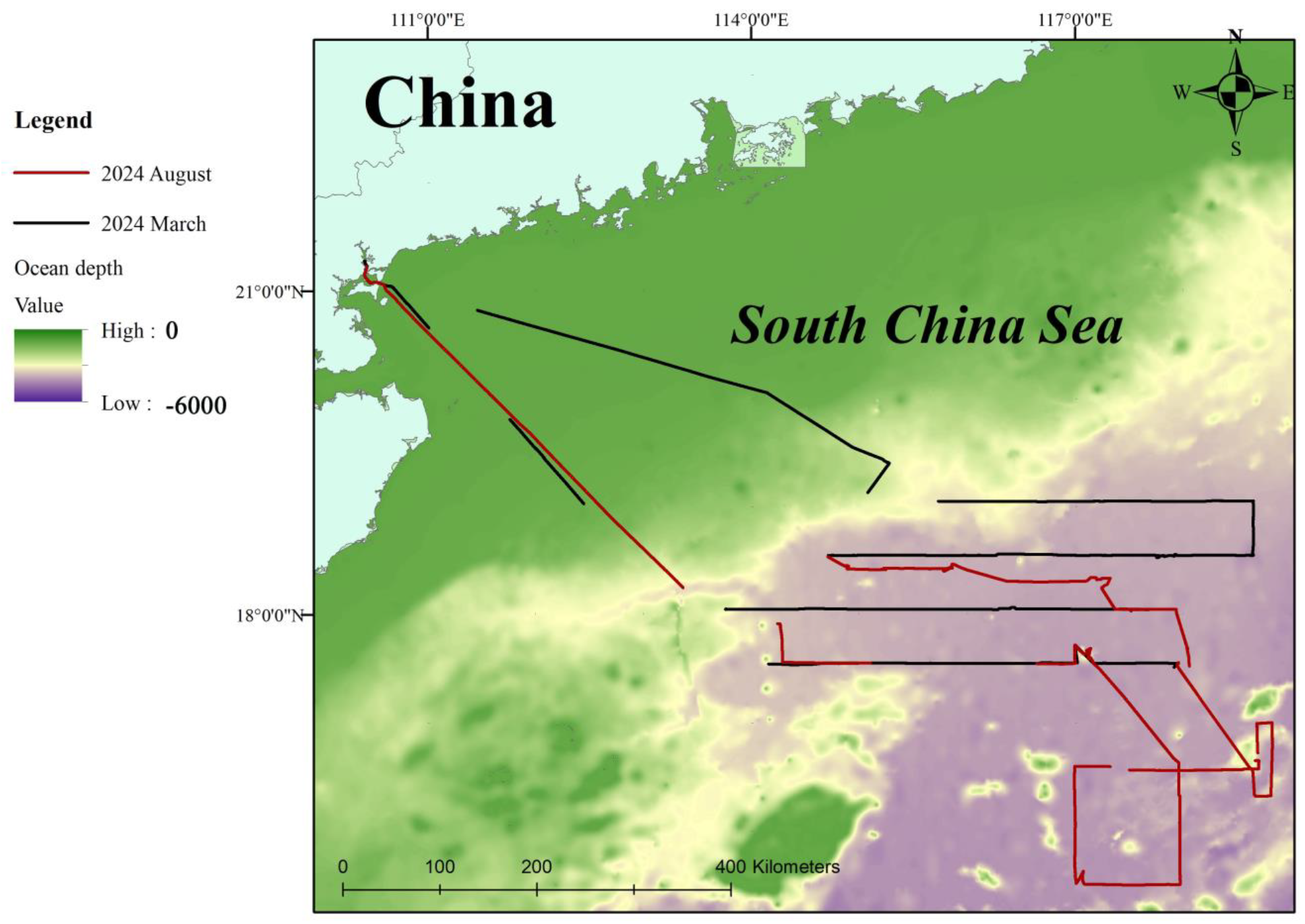
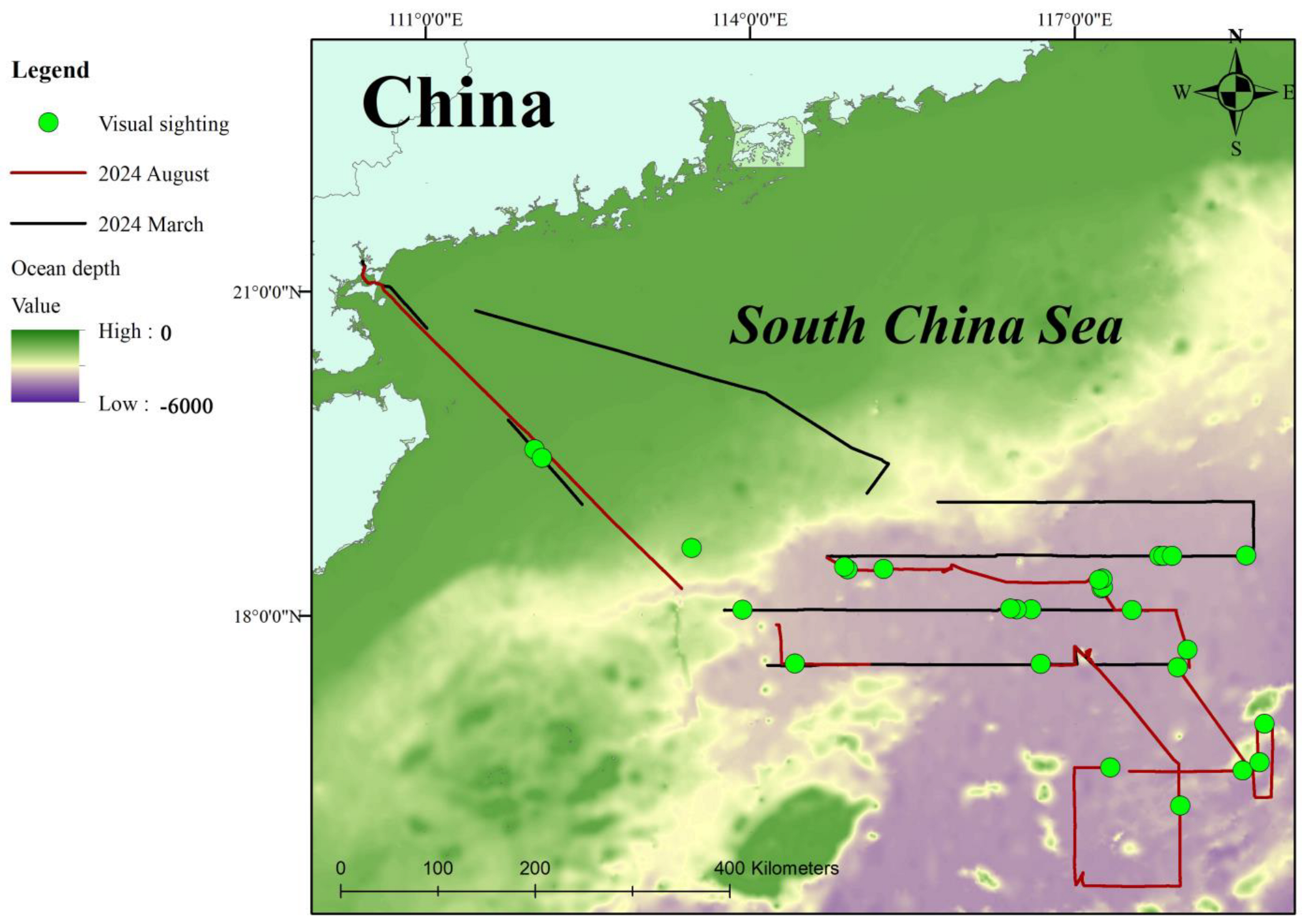
2.1. Survey Area
2.2. Visual Survey
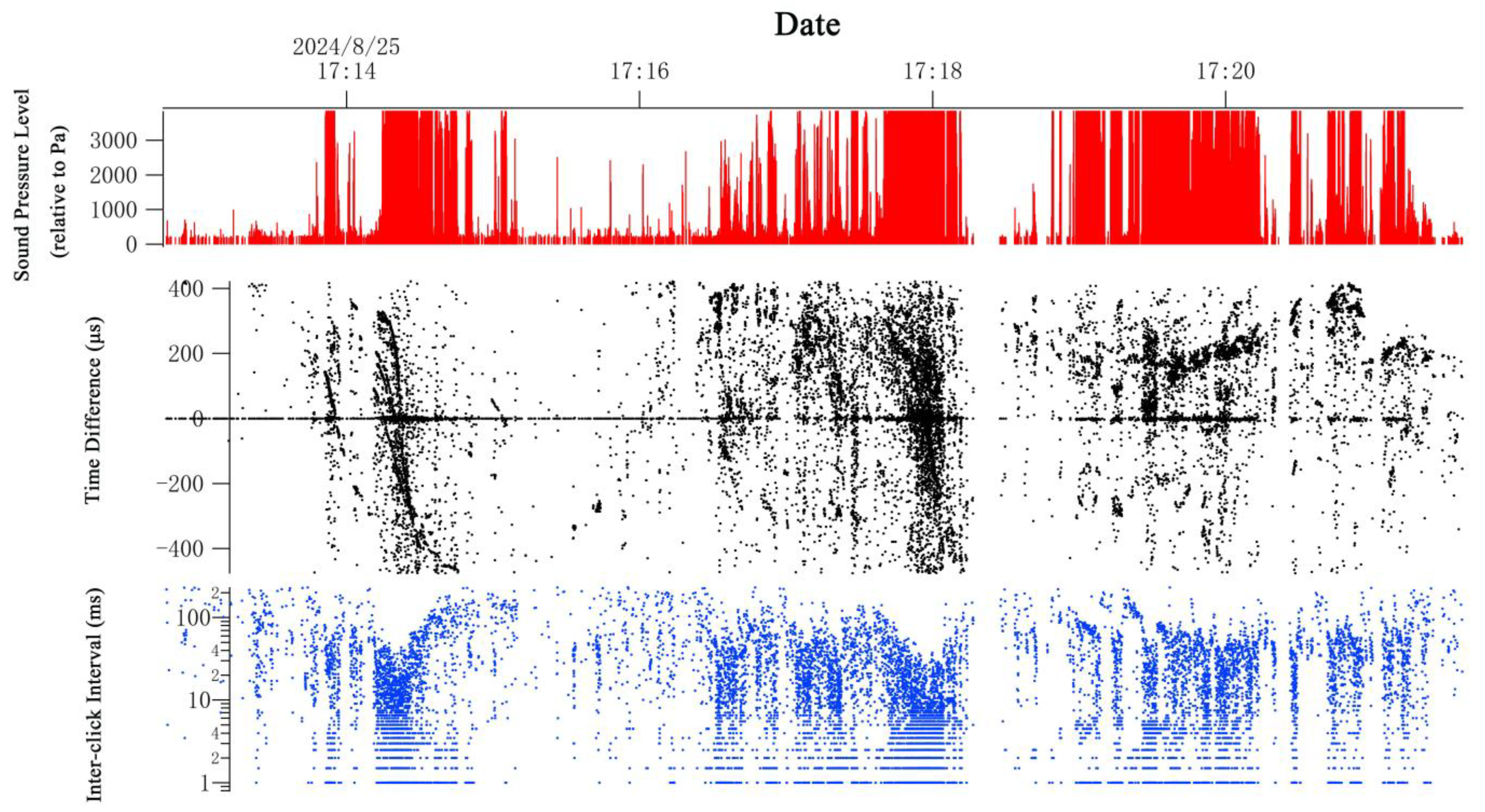
2.3. Passive Acoustic Survey
2.4. Acoustic Data Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Visual Sightings of Cetaceans
3.2. Acoustic Survey Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Cetacean Diversity in the Deep-Sea Area of the Northern South China Sea
4.2. Comparison Between the Visual and Acoustic Surveys
4.3. Threats
4.3.1. Fishing Activities
4.3.2. Shipping
4.3.3. Oil and Gas Extraction
4.4. Conservation and Management
- Prioritize comprehensive cetacean surveys in the South China Sea to document population size, distribution patterns, conservation status, and anthropogenic threats, particularly for large-bodied species or mass aggregations.
- Strengthen conservation management frameworks by addressing impacts from fisheries, maritime traffic, and oil resource extraction. Current impact assessments remain inadequate. Consequently, enacting dedicated legislation for cetacean protection will empower law enforcement against violations.
- Promote sustainable fisheries practices critical for long-term cetacean survival. This reduces bycatch and entanglement (e.g., from drift nets and purse seines, which are primary causes of non-natural mortality), while safeguarding prey resources and restoring fish stocks.
- Intensify conservation outreach to deepen understanding among government agencies and public stakeholders regarding urgent threats and the imperative for immediate protection measures.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GPS | Global positioning system |
| ICI | Inter-click interval |
| SPL | Sound pressure level |
| TD | Time difference |
References
- Kalinkat, G.; Cabral, J.S.; Darwall, W.; Ficetola, G.F.; Fisher, J.L.; Giling, D.P.; Gosselin, M.; Grossart, H.; Jähnig, S.C.; Jeschke, J.M. Flagship Umbrella Species Needed for the Conservation of Overlooked Aquatic Biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Sciara, G.N.; Hoyt, E.; Reeves, R.; Ardron, J.; Marsh, H.; Vongraven, D.; Barr, B. Place-based Approaches to Marine Mammal Conservation. Aquatic Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2016, 26, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.E. Marine Mammals as Ecosystem Sentinels. J. Mammal. 2008, 89, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschner, K.; Tittensor, D.P.; Ready, J.; Gerrodette, T.; Worm, B. Current and Future Patterns of Global Marine Mammal Biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, J.; Altman, I.; Dunphy-Daly, M.M.; Campbell, C.; Jasny, M.; Read, A.J. The Marine Mammal Protection Act at 40: Status, Recovery, and Future of U.S. Marine Mammals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1286, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, S.; Alfaro-Shigueto, J.; Arnould, J.; Avila, I.; Bengtson Nash, S.; Campbell, E.; Carter, M.; Collins, T.; Currey, R.; Domit, C. Marine Mammal Conservation: Over the Horizon. Endang. Species Res. 2021, 44, 291–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, H.; Thompson, P. Using Marine Mammal Habitat Modelling to Identify Priority Conservation Zones Within a Marine Protected Area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 378, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, A.M.; Slooten, E.; Dawson, S.; Barker, R.J.; Rayment, W.; du Fresne, S.; Bräger, S. First Evidence That Marine Protected Areas Can Work for Marine Mammals. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompa, S.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Ceballos, G. Global Distribution and Conservation of Marine Mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13600–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W. Role of Marine Mammals in Aquatic Ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 158, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.R.; Glover, A.G.; Treude, T.; Higgs, N.D.; Amon, D.J. Whale-fall Ecosystems: Recent Insights into Ecology, Paleoecology, and Evolution. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 571–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lei, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. Review of the Impact of Whale Fall on Biodiversity in Deep-sea Ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 885572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.R.; Baco, A.R. Ecology of Whale Falls at the Deep-Sea Floor. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review; Gibson, R.N., Atkinson, R.J.A., Gordon, J.D.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Volume 41, pp. 311–354. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, J.; Estes, J.A.; Morissette, L.; Smith, C.; Costa, D.; McCarthy, J.; Nation, J.; Nicol, S.; Pershing, A.; Smetacek, V. Whales as Marine Ecosystem Engineers. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, J.; McCarthy, J.J. The Whale Pump: Marine Mammals Enhance Primary Productivity in a Coastal Basin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, S.; Jack, L.; Shatova, O.; Leichter, J.; Barr, D.; Frew, R.; Gault-Ringold, M. Seabirds and Marine Mammals Redistribute Bioavailable Iron in the Southern Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 510, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mézo, P.K.; Galbraith, E.D. The Fecal Iron Pump: Global Impact of Animals on the Iron Stoichiometry of Marine Sinking Particles. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodstock, M.S.; Kiszka, J.J.; Ramírez-León, M.R.; Sutton, T.T.; Fennel, K.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y. Cetacean-mediated Vertical Nitrogen Transport in the Oceanic Realm. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.; Jeanniard-du-Dot, T.; Authier, M.; Chouvelon, T.; Spitz, J. Composition of Cetacean Communities Worldwide Shapes Their Contribution to Ocean Nutrient Cycling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.; Ballard, G.; Blight, L.K.; Ackley, S.; Emslie, S.D.; Lescroël, A.; Olmastroni, S.; Townsend, S.E.; Tynan, C.T.; Wilson, P. Impacts of Cetaceans on the Structure of Southern Ocean Food Webs. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2010, 26, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.; Kahru, M.; Mitchell, B. Cetacean Biomass, Prey Consumption, and Primary Production Requirements in the California Current Ecosystem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 371, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Chinese Cetaceans; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Lin, M.; Li, S. Species Diversity and Spatiotemporal Patterns Based on Cetacean Stranding Records in China, 1950–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, M.; Turvey, S.T.; Li, S. An Interview-based Investigation of Marine Megafauna Bycatch in the Northern South China Sea. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 286, 110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Kang, H.; Seim, I.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Dong, L.; Lin, M.; Song, Y.; Ouyang, M. The First Genetically Confirmed Live Sighting of the Deraniyagala’s Beaked Whale (Mesoplodon hotaula), with Insights into the Diversity, Phylogeny, and Past Demographic History. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2025, 41, 13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lin, W.; Lin, M.; Caruso, F.; Rosso, M.; Zhang, P.; Dong, L.; Dai, L.; Li, S. Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus) in the Northern South China Sea: Evidence of a Nursing Ground? Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2022, 184, 103767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lin, W.; Lin, M.; Dong, L.; Li, S. Short-finned Pilot Whales in the South China Sea: Insights into Regional Distribution, Movement Pattern, and Habitat Characteristics. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2024, 40, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, M.; Caruso, F.; Rosso, M.; Tang, X.; Dong, L.; Lin, W.; Borroni, A.; Bocconcelli, A.; Dai, L. A Pioneering Survey of Deep-Diving and Offshore Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea. Integr. Zool. 2021, 16, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Lin, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Lin, W.; Lin, M.; Dong, L.; Kang, H. Distribution Pattern of Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea Based on Visual Surveys and Environmental DNA Metabarcoding. Conserv. Biol. 2025, e70060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; White, M. South China Sea: Its Importance for Shipping, Trade, Energy and Fisheries. Asia-Pac. J. Ocean Law Policy 2017, 2, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, M.; Caruso, F.; Dong, L.; Lin, W.; Rosso, M.; Bocconcelli, A. Cetaceans Under Threat in South China Sea. Science 2020, 368, 1074–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, O.; Matthews, J.; Gillespie, D.; Lacey, C.; Moscrop, A.; Ouamari, N.E. A Visual and Acoustic Survey for Harbour Porpoises Off North-west Africa: Further Evidence of a Discrete Population. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 29, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.E.; Dahlheim, M.E.; Stafford, K.M.; Fox, C.G.; Braham, H.W.; Mcdonald, M.A.; Thomason, J. Acoustic and Visual Detection of Large Whales in the Eastern North Pacific Ocean. NOAA Tech. Memo. NMFS-AFSC 1999, 107, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, P.; Wall, C.C.; Allen, J.B.; Wells, R.S.; Gowans, S.; Forys, E.A. Dolphin Distribution on the West Florida Shelf Using Visual Surveys and Passive Acoustic Monitoring. Aquat. Mamm. 2015, 41, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.W.; Brown, M.W.; Corkeron, P. Visual and Acoustic Surveys for North Atlantic Right Whales, Eubalaena Glacialis. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2001, 26, 837–854. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, J.; Taylor, B.L. Estimates of Sperm Whale Abundance in the Northeastern Temperate Pacific from a Combined Acoustic and Visual Survey. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2005, 21, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Akamatsu, T.; Dong, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Kimura, S. Widespread Passive Acoustic Detection of Yangtze Finless Porpoise Using Miniature Stereo Acoustic Data-loggers: A Review. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Wei, Z.; Naito, Y. A Passive Acoustical Survey Method of Finless Porpoises. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kimura, S.; Akamatsu, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Dong, S.; Arai, N. Comparison of Stationary Acoustic Monitoring and Visual Observation of Finless Porpoises. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Fu, B.; Xie, L.; Yan, L. Acoustic Deterrent of Pantropical Spotted Dolphins (Stenella attenuata) from Light-falling Net Fisheries in the South China Sea. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 348–354. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Xie, B.; Zhang, P.; Song, Z.; Li, M.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Y. A Field Trial to Study the Effects of Stenella attenuata Deterrent on the Catch of a Light-falling Net Fishery. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Q.; Leatherwood, S. A Survey on the Incidental Catches of Small Cetaceans in Coastal Waters of China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1999, 10, 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson, T.A.; Weir, C.R.; Anderson, R.C.; Ballance, L.T.; Kenney, R.D.; Kiszka, J.J. Global Distribution Ofrisso’s Dolphin Grampus griseus: A Review and Critical Evaluation. Mamm. Rev. 2014, 44, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin-Yi, Y.; Ching-Yi, L.; Wen-Jyh, Y.; Lien-Siang, C. Distribution of Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the East-central Coastal Waters of Taiwan Based on Whale-Watching Records. Taiwania 2019, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.E.; Lien, R. Pilot Whales Follow Internal Solitary Waves in the South China Sea. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2007, 23, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lin, M.; Li, S. Sperm Whales in the Waters Off China: A Glimpse of the Past and Present. Water Biol. Secur. 2023, 2, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Z.; Yongsong, C.; Zuozhi, C.; Peng, Z.; Kui, Z.; Jiangtao, F.; Guobao, C.; Yancong, C.; Mingshuai, S. Advances in Pelagic Fishery Resources Survey and Assessment in Open South China Sea. South China Fish. Sci. 2018, 14, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Nong, Z.; Chen, M.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Mei, Z. The First Baleen Whale Marine Protected Area Proposed for Bryde’s Whales in the Beibu Gulf, China. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2024, 40, 13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, L.; Jefferson, T.A.; Zhou, K.; Yang, G. Coastal Bryde’s Whales’ (Balaenoptera edeni) Foraging Area Near Weizhou Island in the Beibu Gulf. Aquat. Mamm. 2019, 45, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, S.; Wu, H.; Mei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, W.; Deng, K.; Yang, C.; Chen, M. Occurrence of Bryde’s Whales, Balaenoptera edeni, in the Northern Beibu Gulf, China. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2019, 35, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, F.; Liao, B.; Xiao, B.; Li, M.; He, L.; Bai, L.; Chen, B. A Young Eden’s Whale (Balaenoptera edeni edeni) Wandering in a Busy International Container Port. Aquat. Mamm. 2023, 49, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goold, J.C.; Jones, S.E. Time and Frequency Domain Characteristics of Sperm Whale Clicks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 98, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møhl, B.; Wahlberg, M.; Madsen, P.T.; Heerfordt, A.; Lund, A. The Monopulsed Nature of Sperm Whale Clicks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møhl, B.; Wahlberg, M.; Madsen, P.T.; Miller, L.A.; Surlykke, A. Sperm Whale Clicks: Directionality and Source Level Revisited. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.W.L.; Pawloski, J.L.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Blonz, M.; Gisner, R.C. Echolocation Signals and Transmission Beam Pattern of a False Killer Whale (Pseudorca crassidens). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 98, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Simonis, A.; Oleson, E.; Baird, R.; Roch, M.; Wiggins, S. False Killer Whale and Short-finned Pilot Whale Acoustic Identification. Endang. Species Res. 2015, 28, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Kerr, I.; Payne, R. Echolocation Clicks of Two Free-ranging, Oceanic Delphinids with Different Food Preferences: False Killer Whales Pseudorca crassidens and Risso’s Dolphins Grampus griseus. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskesen, I.G.; Wahlberg, M.; Simon, M.; Larsen, O.N. Comparison of Echolocation Clicks from Geographically Sympatric Killer Whales and Long-finned Pilot whales L. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; McDonald, M.A.; Simonis, A.E.; Solsona Berga, A.; Merkens, K.P.B.; Oleson, E.M.; Roch, M.A.; Wiggins, S.M.; Rankin, S.; Yack, T.M. Species-Specific Beaked Whale Echolocation Signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Roch, M.A.; Brownell, R.L., Jr.; Simonis, A.E.; McDonald, M.A.; Solsona-Berga, A.; Oleson, E.M.; Wiggins, S.M.; Hildebrand, J.A. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Beaked Whale Echolocation Signals in the North Pacific. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Song, Y.; Lin, W.; Liu, M.; Lin, M.; Li, S. Echolocation Signals Recorded in the Presence of Deraniyagala’s Beaked Whales (Mesoplodon hotaula) in the Western Pacific (South China Sea) Indicate Species-specificity and Intraspecific Variation. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2025, 41, 13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin-Mouy, H.; Mouy, X.; Pilkington, J.; Küsel, E.; Nichol, L.; Doniol-Valcroze, T.; Lee, L. Acoustic and Visual Cetacean Surveys Reveal Year-round Spatial and Temporal Distributions for Multiple Species in Northern British Columbia, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaila, U.R.; Cheung, W.W.L. Boom or Bust: The Future of Fish in the South China Sea. Available online: https://www.admcf.org/research-admcf/boom-or-bust-the-future-of-fish-in-the-south-china-sea/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Pauly, D.; Liang, C. The Fisheries of the South China Sea: Major Trends Since 1950. Mar. Policy. 2020, 121, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, L.; Cashion, T.; Alava, J.J.; Cheung, W.W.; Sumaila, U.R. Status, Trends, and the Future of Fisheries in the East and South China Seas. 2019. Available online: https://www.admcf.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Sink-or-Swim-Full-Report_171121.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Teh, L.S.L.; Witter, A.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Sumaila, U.R.; Yin, X. What Is at Stake? Status and Threats to South China Sea Marine Fisheries. Ambio 2017, 46, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y. Climate-induced Small Pelagic Fish Blooms in an Overexploited Marine Ecosystem of the South China Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, D. Fisheries management in the South China Sea. In Security and International Politics in the South China Sea: Towards a Cooperative Management Regime; Bateman, S., Emmers, R., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 77–95. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.W.L. The Sonar of Dolphins; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Dudzinski, K.M.; Thomas, J.A.; Gregg, J.D. Communication in Marine Mammals. Encycl. Mar. Mamm. 2009, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayigh, L.S. Cetacean Acoustic Communication. In Biocommunication of Animals; Tembrock, G., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, W.J.; Greene, C.R., Jr.; Malme, D.H.; Thomson, D.H. Marine Mammals and Noise; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Erbe, C.; Marley, S.A.; Schoeman, R.P.; Smith, J.N.; Trigg, L.E.; Embling, C.B. The Effects of Ship Noise on Marine Mammals—A Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, W.D.; Insley, S.J.; Hilliard, R.C.; de Jong, T.; Pine, M.K. Potential Impacts of Shipping Noise on Marine Mammals in the Western Canadian Arctic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middel, H.; Verones, F. Making Marine Noise Pollution Impacts Heard: The Case of Cetaceans in the North Sea Within Life Cycle Impact Assessment. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervo, O.M.; Blackwell, S.B.; Ditlevsen, S.; Garde, E.; Hansen, R.G.; Samson, A.L.; Conrad, A.S.; Heide-Jørgensen, M.P. Stuck in a Corner: Anthropogenic Noise Threatens Narwhals in Their Once Pristine Arctic Habitat. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoop, J.M.; Moore, M.J.; Barco, S.G.; Cole, T.V.N.; Daoust, P.; Henry, A.G.; McAlpine, D.F.; McLellan, W.A.; Wimmer, T.; Solow, A.R. Assessment of Management to Mitigate Anthropogenic Effects on Large Whales. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lair, S.; Martineau, L.N.; Measures, L. Causes of Mortality in St. Lawrence Estuary Beluga (Delphinapterus leuca) from 1983 to 2012. Can. Sci. Advis. Secr. Ott. Can. 2014, 14, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Metelitsa, A.; Kupfer, J. Oil and Gas Resources and Transit Issues in the South China Sea; Asia Society: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P.; Lin, L.; Lv, Y.; Liang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, H.; Yan, B.; Ji, Z.; Wang, L. Potential and Distribution of Natural Gas Hydrate Resources in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delefosse, M.; Rahbek, M.L.; Roesen, L.; Clausen, K.T. Marine Mammal Sightings Around Oil and Gas Installations in the Central North Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2018, 98, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, R.C.; Costa, D.P.; DeBruyn, T.D.; O’Shea, T.J.; Wells, R.S.; Williams, T.M. Overview of Effects of Oil Spills on Marine Mammals. In Handbook of Oil Spill Science and Technology; Wang, Z., Fingas, M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 455–475. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, J.; Dragoset, W. A Brief Overview of Seismic Air-gun Arrays. Lead. Edge 2000, 19, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoset, B. Introduction to Air Guns and Air-gun Arrays. Lead. Edge 2000, 19, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Gillespie, D.; Potter, J.; Frantzis, A.; Simmonds, M.P.; Swift, R.; Thompson, D. A Review of the Effects of Seismic Surveys on Marine Mammals. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2003, 37, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilgart, L.S. A Brief Review of Known Effects of Noise on Marine Mammals. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affatati, A.; Camerlenghi, A. Effects of Marine Seismic Surveys on Free-ranging Fauna: A Systematic Literature Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1222523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.O.; Johnson, M.P.; Madsen, P.T.; Biassoni, N.; Quero, M.; Tyack, P.L. Using At-Sea Experiments to Study the Effects of Airguns on the Foraging Behavior of Sperm Whales in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2009, 56, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, R.A.; Noad, M.J.; McCauley, R.D.; Scott-Hayward, L.; Kniest, E.; Slade, R.; Paton, D.; Cato, D.H. Determining the Behavioural Dose–response Relationship of Marine Mammals to Air Gun Noise and Source Proximity. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 2878–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, R.; Sullivan, L.; Smith, C.; Collier, T.; Hall, A.; Brosnan, T.; Rowles, T.; Schwacke, L. The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Marine Mammal Injury Assessment. Endang. Species Res. 2017, 33, 95–106. [Google Scholar]


| Date (Year-Month-Day) | Time (Hour-Minute) | Species | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Group Size (Number of Individuals) | Depth (m) | Sea State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-03-26 | 09:14 | Bryde’s whale (Balaenoptera brydei) | 112.003 | 19.534 | 1 | 120 | 2 |
| 2024-03-26 | 10:23 | Unidentified | 112.071 | 19.454 | 1 | 200 | 2 |
| 2024-03-28 | 09:24 | Pantropical spotted dolphin Stenella attenuata | 116.683 | 17.551 | 40 | 4000 | 1 |
| 2024-03-29 | 15:20 | Common dolphin (Delphinus delphis) | 116.597 | 18.054 | 50 | 3600 | 1 |
| 2024-03-29 | 16:19 | Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) | 116.462 | 18.054 | 70 | 3750 | 1 |
| 2024-03-29 | 17:11 | Striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) Pantropical spotted dolphin Spinner dolphin (Stenella longirostris) | 116.403 | 18.062 | 90 | 3900 | 1 |
| 2024-03-30 | 16:20 | Unidentified | 113.927 | 18.052 | 1 | 3800 | 1 |
| 2024-04-01 | 07:50 | Pilot whale (Globicephala spp.) | 117.779 | 18.550 | 200 | 3840 | 2 |
| 2024-04-01 | 09:20 | Risso’s dolphin | 117.818 | 18.548 | 20 | 3840 | 1 |
| 2024-04-01 | 10:24 | Sperm whale | 117.899 | 18.550 | 4 | 3840 | 1 |
| 2024-04-01 | 16:41 | Striped dolphin | 118.584 | 18.551 | 1 | 3740 | 1 |
| 2024-08-15 | 12:07 | Unidentified | 114.410 | 17.557 | 1 | 3500 | 4 |
| 2024-08-17 | 09:53 | Unidentified | 117.975 | 16.243 | 4 | 3500 | 2 |
| 2024-08-18 | 17:58 | Unidentified | 117.329 | 16.594 | 5 | 4000 | 2 |
| 2024-08-19 | 15:22 | Unidentified | 118.553 | 16.568 | 1 | 2200 | 2 |
| 2024-08-19 | 17:24 | Unidentified | 118.708 | 16.642 | 7 | 2200 | 2 |
| 2024-08-20 | 09:57 | Unidentified | 118.752 | 16.999 | 3 | 2300 | 3 |
| 2024-08-21 | 17:21 | Spinner dolphin | 117.950 | 17.522 | 75 | 2900 | |
| 2024-08-22 | 08:23 | Beak whale | 118.039 | 17.682 | 4 | 3900 | 1 |
| 2024-08-22 | 14:32 | Pantropical spotted dolphin Spinner dolphin | 117.528 | 18.046 | 250 | 3900 | 2 |
| 2024-08-22 | 18:40 | Unidentified | 117.248 | 18.249 | 1 | 3900 | 1 |
| 2024-08-22 | 19:00 | Unidentified | 117.260 | 18.258 | 1 | 3900 | 2 |
| 2024-08-23 | 07:27 | Pantropical spotted dolphin | 117.253 | 18.338 | 32 | 3800 | 2 |
| 2024-08-23 | 07:48 | Striped dolphin | 117.224 | 18.327 | 25 | 3900 | 2 |
| 2024-08-24 | 11:37 | Beak whale | 115.230 | 18.429 | 4 | 3700 | 2 |
| 2024-08-24 | 15:20 | Pantropical spotted dolphin | 114.899 | 18.424 | 120 | 3650 | 2 |
| 2024-08-24 | 16:35 | Pantropical spotted dolphin Bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops aduncus) | 114.867 | 18.449 | 200 | 3650 | 2 |
| 2014-08-25 | 17:02 | Bottlenose dolphin | 113.456 | 18.621 | 150 | 1500 | 2 |
| Event | Date (Year-Month-Day) | Time (Hour-Minute-Second) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2024-03-28 | 3:29:50 | 17.550 | 116.006 |
| 2 | 2024-03-28 | 4:21:30 | 17.550 | 116.104 |
| 3 | 2024-03-28 | 7:50:55 | 17.550 | 116.495 |
| 4 | 2024-03-28 | 9:26:30 | 17.553 | 116.687 |
| 5 | 2024-03-28 | 13:28:45 | 17.717 | 117.000 |
| 6 | 2024-03-28 | 14:34:45 | 17.636 | 117.085 |
| 7 | 2024-03-29 | 2:30:00 | 17.589 | 117.951 |
| 8 | 2024-03-29 | 16:26:00 | 18.054 | 116.462 |
| 9 | 2024-03-29 | 17:12:00 | 18.062 | 116.403 |
| 10 | 2024-03-31 | 1:32:00 | 18.353 | 114.334 |
| 11 | 2024-03-31 | 23:22:00 | 18.561 | 116.658 |
| 12 | 2024-04-01 | 2:15:00 | 18.551 | 117.045 |
| 13 | 2024-04-01 | 8:30:00 | 18.530 | 117.765 |
| 14 | 2024-04-01 | 9:30:00 | 18.544 | 117.826 |
| 15 | 2024-04-01 | 10:36:00 | 18.544 | 117.911 |
| 16 | 2024-04-01 | 11:51:00 | 18.550 | 117.944 |
| 17 | 2024-04-01 | 16:48:00 | 18.551 | 118.584 |
| 18 | 2024-04-01 | 22:57:00 | 19.051 | 115.888 |
| 19 | 2024-04-01 | 23:29:00 | 19.050 | 115.832 |
| 20 | 2024-04-03 | 12:32:00 | 19.551 | 114.939 |
| 21 | 2024-04-03 | 15:10:00 | 19.746 | 114.633 |
| 22 | 2024-04-03 | 18:52:00 | 20.014 | 114.209 |
| 23 | 2024-08-15 | 19:18:00 | 17.552 | 115.187 |
| 24 | 2024-08-15 | 21:38:15 | 17.559 | 115.387 |
| 25 | 2024-08-16 | 1:03:30 | 17.534 | 115.976 |
| 26 | 2024-08-16 | 2:04:00 | 17.516 | 116.140 |
| 27 | 2024-08-16 | 3:37:10 | 17.516 | 116.299 |
| 28 | 2024-08-16 | 3:50:00 | 17.502 | 116.376 |
| 29 | 2024-08-16 | 21:55:00 | 17.283 | 117.413 |
| 30 | 2024-08-17 | 1:31:50 | 16.874 | 117.750 |
| 31 | 2024-08-17 | 1:34:10 | 16.870 | 117.753 |
| 32 | 2024-08-19 | 13:06:00 | 16.564 | 118.268 |
| 33 | 2024-08-19 | 18:15:00 | 16.650 | 118.669 |
| 34 | 2024-08-19 | 21:52:00 | 16.689 | 118.686 |
| 35 | 2024-08-20 | 14:54:00 | 17.242 | 118.148 |
| 36 | 2024-08-21 | 17:40:00 | 17.557 | 117.96 |
| 37 | 2024-08-21 | 20:55:00 | 17.523 | 118.06 |
| 38 | 2024-08-21 | 23:30:00 | 17.523 | 118.06 |
| 39 | 2024-08-22 | 14:40:00 | 18.038 | 117.521 |
| 40 | 2024-08-22 | 15:29:00 | 18.048 | 117.498 |
| 41 | 2024-08-22 | 19:35:00 | 18.258 | 117.259 |
| 42 | 2024-08-23 | 3:30:00 | 18.278 | 117.3 |
| 43 | 2024-08-23 | 7:35:00 | 18.33 | 117.244 |
| 44 | 2024-08-23 | 8:06:30 | 18.333 | 117.2 |
| 45 | 2024-08-23 | 20:30:00 | 18.446 | 115.852 |
| 46 | 2024-08-24 | 0:00:00 | 18.405 | 115.781 |
| 47 | 2024-08-24 | 2:00:00 | 18.418 | 115.79 |
| 48 | 2024-08-24 | 12:35:00 | 18.418 | 115.247 |
| 49 | 2024-08-24 | 15:26:44 | 18.424 | 114.888 |
| 50 | 2024-08-24 | 16:39:00 | 18.443 | 114.899 |
| 51 | 2024-08-24 | 20:35:00 | 18.536 | 114.71 |
| 52 | 2024-08-25 | 17:12:00 | 18.625 | 113.442 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Long, X.; Lu, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhen, Z.; Li, K.; Gutang, Q.; et al. Diversity and Distribution of Deep-Sea Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea Based on Visual and Acoustic Surveys. Animals 2025, 15, 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192802
Fang L, Wang X, Chen Y, Wang Y, Long X, Lu W, Zhao H, Zhen Z, Li K, Gutang Q, et al. Diversity and Distribution of Deep-Sea Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea Based on Visual and Acoustic Surveys. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192802
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Liang, Xinxing Wang, Yujian Chen, Yuezhong Wang, Xinrui Long, Wentao Lu, Hancheng Zhao, Zhao Zhen, Kunhuan Li, Qilin Gutang, and et al. 2025. "Diversity and Distribution of Deep-Sea Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea Based on Visual and Acoustic Surveys" Animals 15, no. 19: 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192802
APA StyleFang, L., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Long, X., Lu, W., Zhao, H., Zhen, Z., Li, K., Gutang, Q., & Chen, T. (2025). Diversity and Distribution of Deep-Sea Cetaceans in the Northern South China Sea Based on Visual and Acoustic Surveys. Animals, 15(19), 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192802






