Ferulic Acid Alleviates Intestinal Inflammatory Damage in Mice, Associated with Ameliorating Intestinal Barrier Damage and Gut Microbiota
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal and Experimental Design
2.2. Body Weight and Organ Index
2.3. Serum D-LA and DAO Were Detected in Mice
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Determination of Intestinal NO Content
2.7. Determination of Intestinal Oxidative Stress Related Indexes
2.8. Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.9. Gut Microbiota 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protective Effect of FA on LPS-Induced Intestinal Inflammatory Damage in Mice
3.2. FA Alleviates Intestinal Tissue Damage in Mice with Intestinal Inflammatory Damage
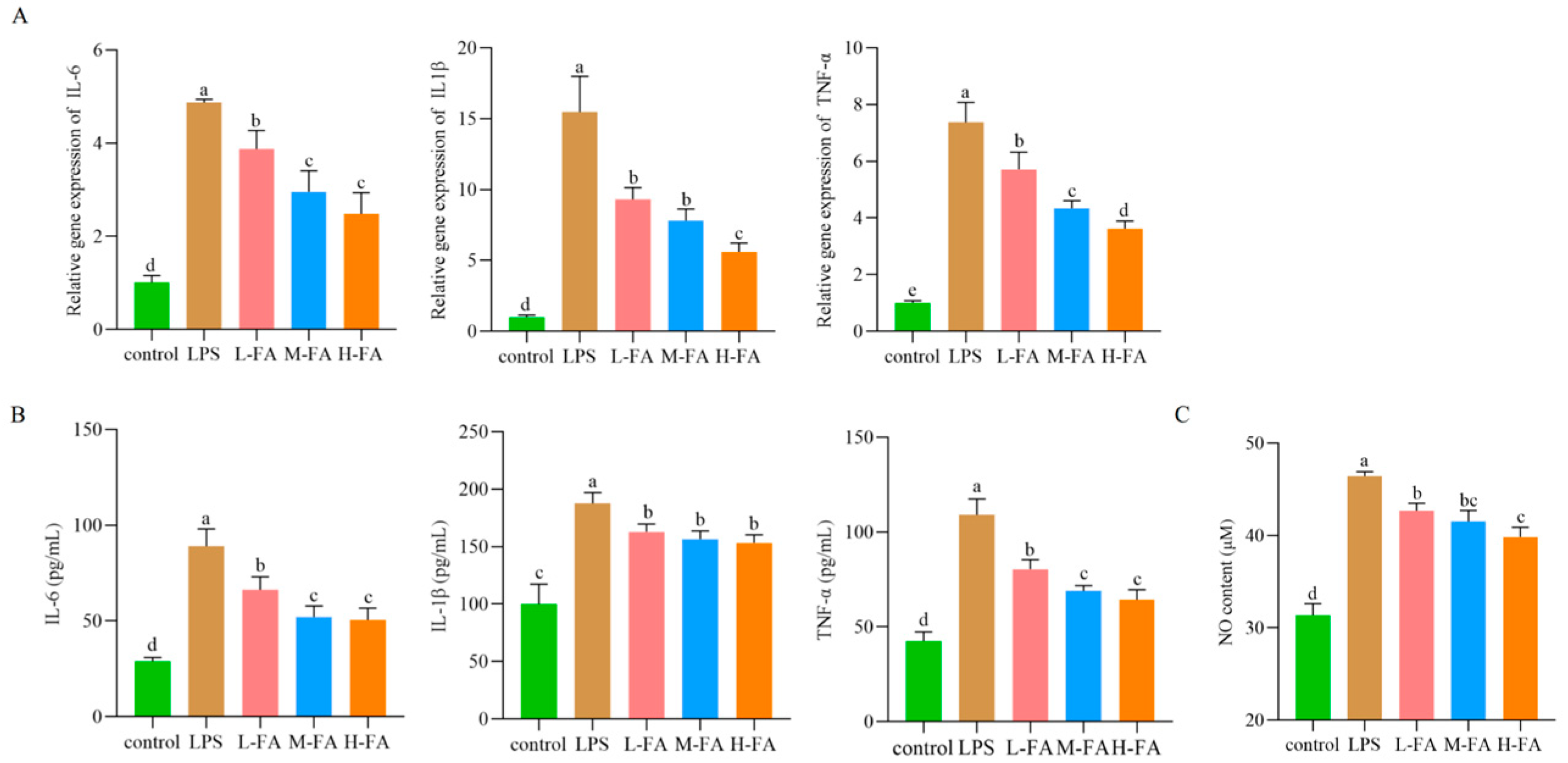
3.3. FA Improved the Level of Intestinal Inflammatory Factors in Mice with Intestinal Inflammatory Damage
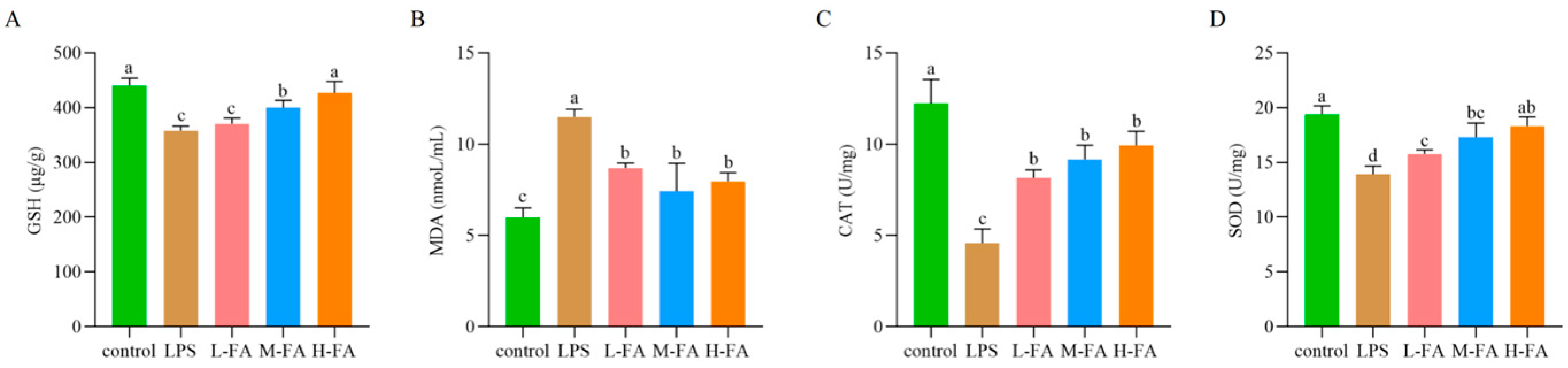
3.4. FA Improves Intestinal Oxidative Stress in Mice with Intestinal Inflammatory Damage
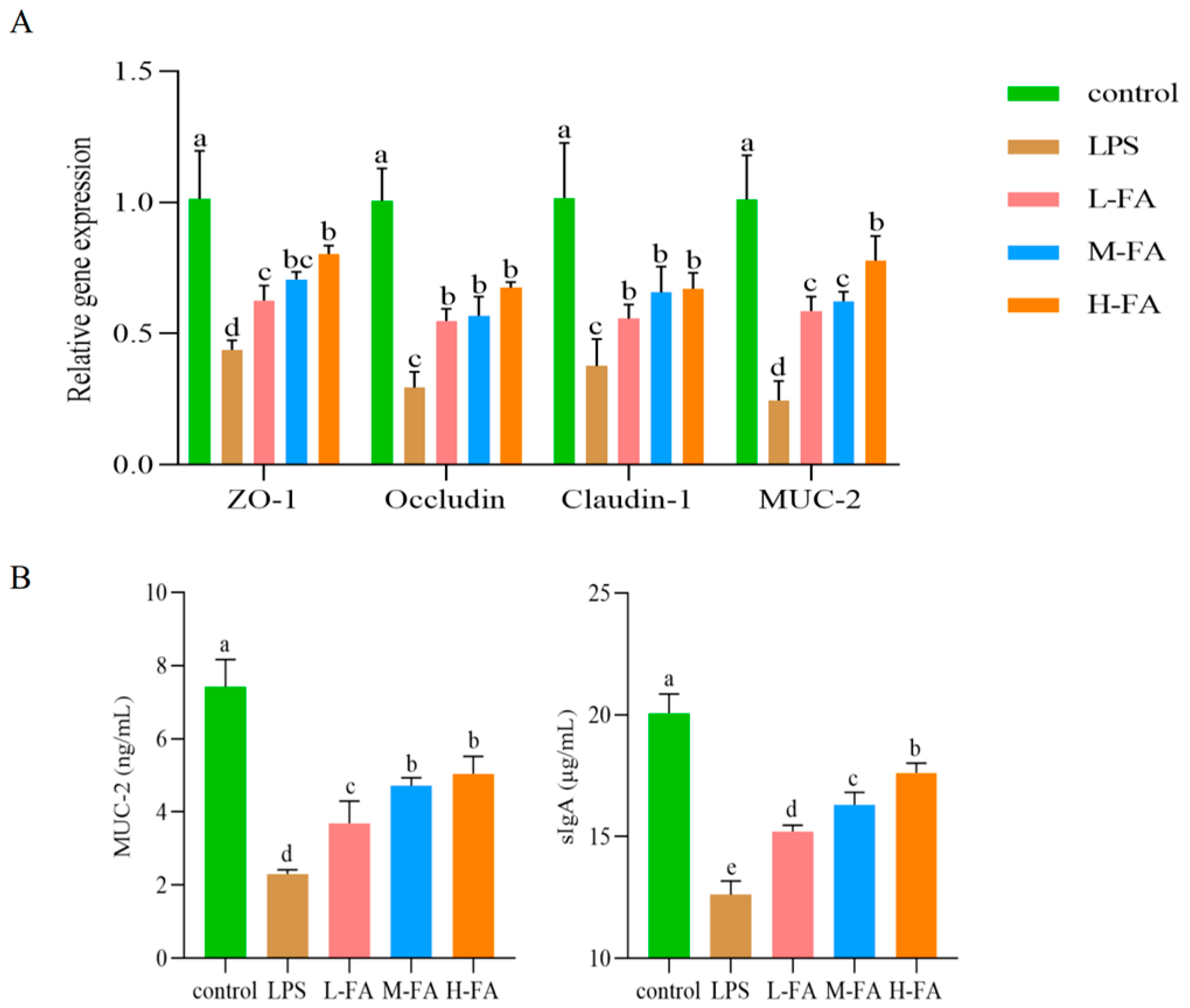
3.5. FA Improves Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Mice with Enteritis
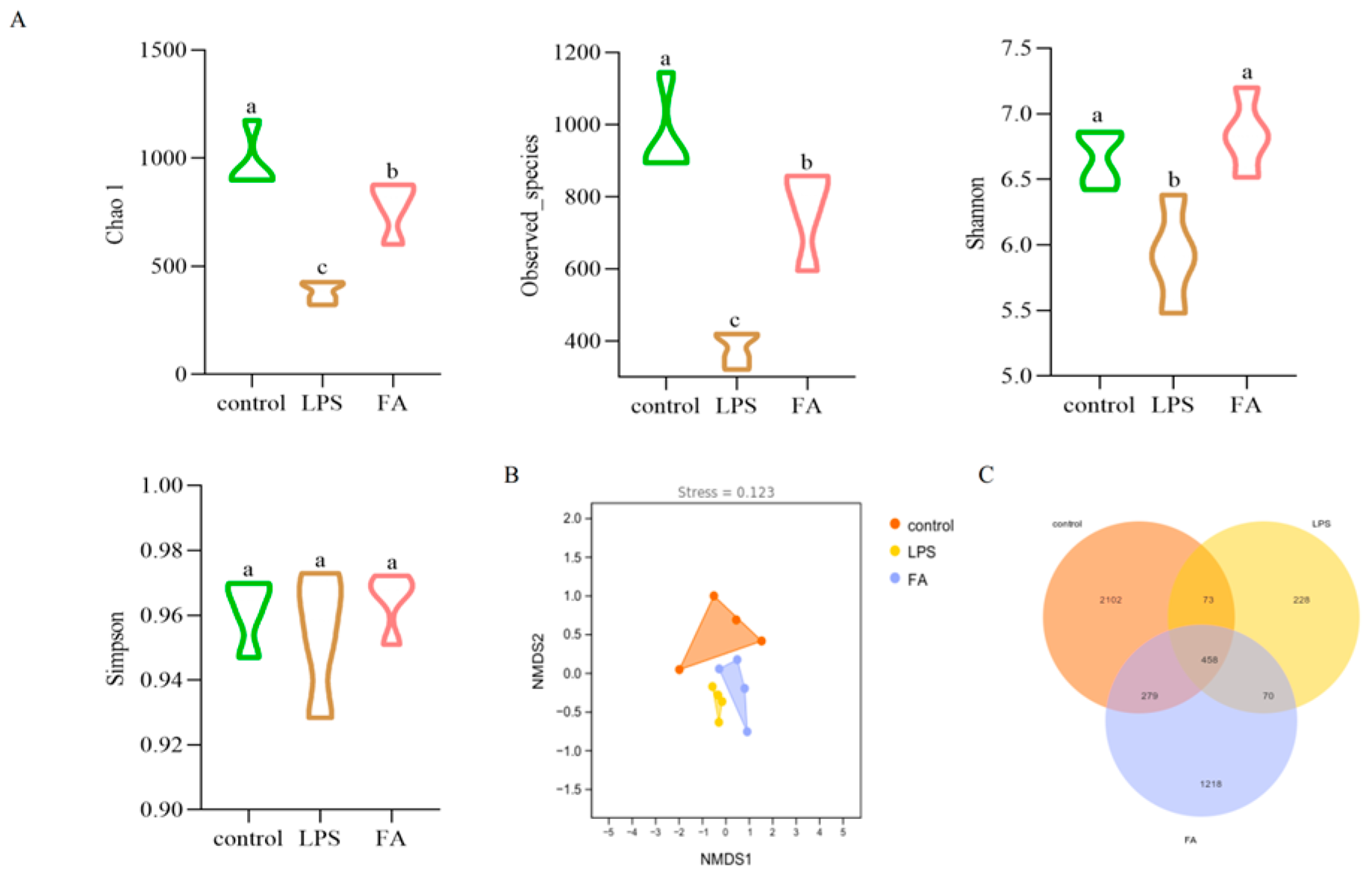
3.6. FA Regulates Gut Microbiota in Mice with Enteritis
3.6.1. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analysis of Gut Microbitoa
3.6.2. Gut Microbiota Composition
3.6.3. Statistical Analysis of Gut Microbiota Diversity and Predictive Analysis of Potential Functions
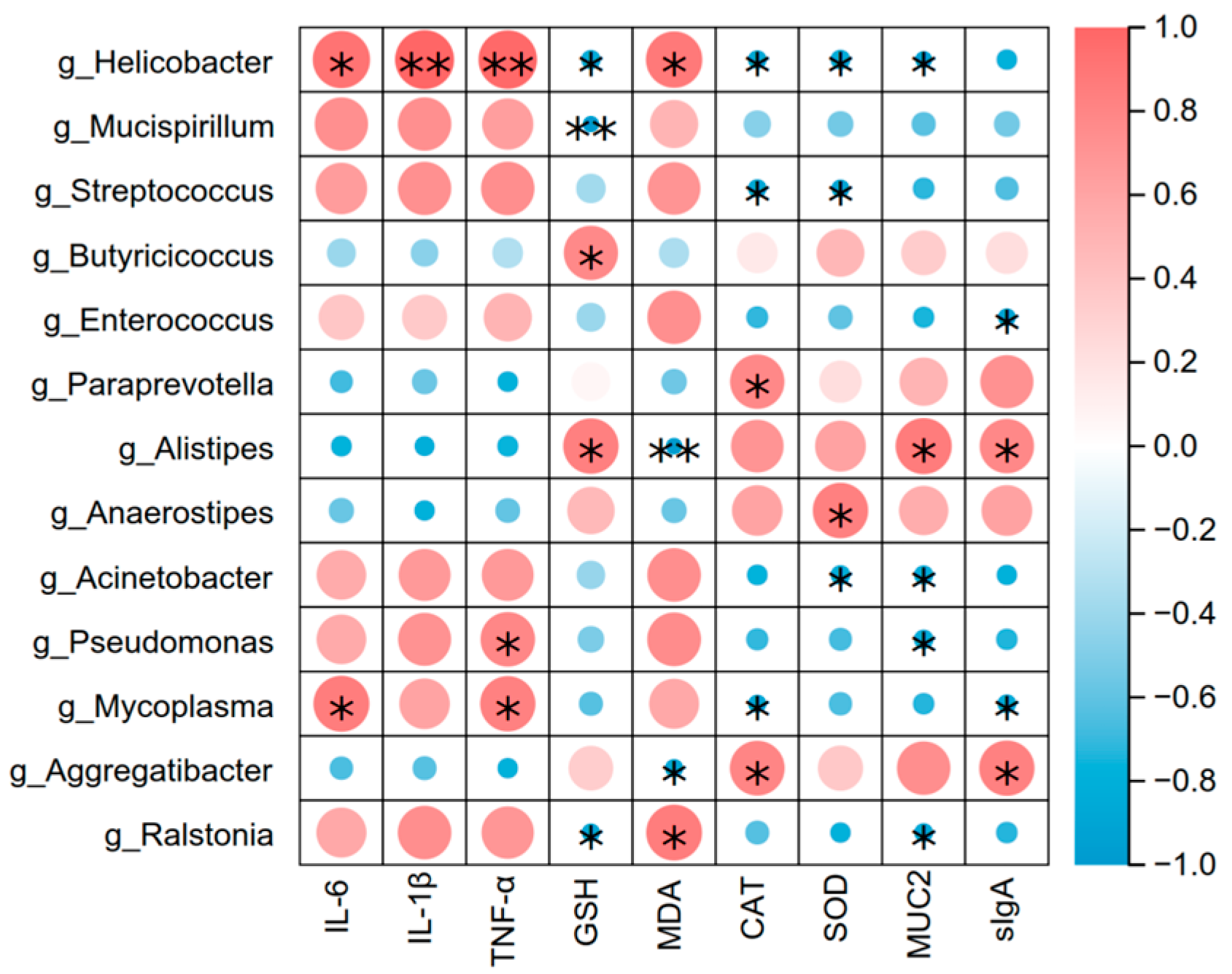
3.7. Correlation of Gut Microbiota (At the Genus Level) with Intestinal Inflammation, Oxidation Index and Barrier-Related Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, D.; Dong, Y.; Che, D.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Han, R.; Jiang, H. Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharide alleviates LPS-induced intestinal inflammation in piglets by gut microbiota and hyodeoxycholic acid regulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307 Pt 1, 141467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Lu, W.-H.; Qiao, W.-T.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, B.-Y.; Li, H.-X.; Li, J.-L. The highly pathogenic strain of porcine deltacoronavirus disrupts the intestinal barrier and causes diarrhea in newborn piglets. Virulence 2025, 16, 2446742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fan, L.; Yin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Jia, X.; Dong, F.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, D.; et al. Ginseng exosomes modulate M1/M2 polarisation by activating autophagy and target IKK/IκB/NF-κB to alleviate inflammatory bowel disease. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Mi, X.; Qiu, L.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, J.; Wu, Q.; Wei, H. Ripened Pu-erh Tea Extract Promotes Gut Microbiota Resilience against Dextran Sulfate Sodium Induced Colitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2190–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, P.; Li, P.; Fu, Y.; Tan, G.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, J.; Huang, P. Modulation of Acute Intestinal Inflammation by Dandelion Polysaccharides: An In-Depth Analysis of Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Gut Microbiota Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Iliopoulos, D.; Macpherson, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Ali, R.A.R.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fiocchi, C. Environmental triggers in IBD: A review of progress and evidence. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, I. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Drives and Implies Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetes Mellitus and Related Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Huang, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, J.; Guo, S.; Xiao, H.; Fan, W.; Tang, Z. Kumquat pomace removal of free polyphenol alleviates induced acute enteritis and restores gut microbiota in dextran sodium sulphate-treated mice. Food Front. 2024, 5, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, D.; Duan, B.; Mo, G.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Ye, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, P.; et al. Metabolomics integrated network pharmacology reveals the mechanism of Ma-Mu-Ran Antidiarrheal Capsules on acute enteritis mice. Anal. Biochem. 2023, 668, 115116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, T.; Poonia, N.; Subudhi, R.N.; Arora, V. Therapeutic potential and underlying mechanisms of phytoconstituents: Emphasizing on resveratol, curcumin, quercetin, berberine, and hesperidin in ulcerative colitis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 6579–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pruthi, V. Potential applications of ferulic acid from natural sources. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, D.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y. Ferulic acid alleviates cardiac injury by inhibiting avermectin-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 287, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Z.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q. The Antioxidant Properties, Metabolism, Application and Mechanism of Ferulic Acid in Medicine, Food, Cosmetics, Livestock and Poultry. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Q. Ferulic Acid Inhibits Arsenic-Induced Colon Injury by Improving Intestinal Barrier Function. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 4821–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Geng, Y.; Wang, P.; Cai, M.; Neng, J.; Hu, J.; Xia, D.; Cao, W.; Yang, K.; Sun, P. Ferulic acid improves intestinal barrier function through altering gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet-induced mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3767–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekhtiar, M.; Ghasemi-Dehnoo, M.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Bagheri, N. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Ferulic Acid and Quinic Acid on Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2025, 39, e70169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Dehnoo, M.; Amini-Khoei, H.; Lorigooini, Z.; AnjomShoa, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Ferulic acid ameliorates ulcerative colitis in a rat model via the inhibition of two LPS-TLR4-NF-κB and NF-κB-INOS-NO signaling pathways and thus alleviating the inflammatory, oxidative and apoptotic conditions in the colon tissue. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lin, H.; Shen, W.; Cao, W.; Qin, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhong, S.; Huang, H. The Preventive Effect of Low-Molecular Weight Oyster Peptides on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Microbiota Communities. Foods 2024, 13, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, G.; Cao, H.; Guo, X. Quercetin Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Duodenal Inflammation through Modulating Autophagy, Programmed Cell Death and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Chicken Embryos. Animals 2022, 12, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Du, L.; Ma, Q.; Li, J.; Gan, L.; Bi, S. Protective effect of ginsenosides Rgl and Re on LPS-induced intestinal barrier damage. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 44, 527–535+557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, N.; Wu, X.; Cao, G.; Qiao, H.; Wang, J.; Hao, R. The preventive effect of Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute colitis in mice by modulating gut microbial communities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, H.; Han, H.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.; Liu, C.; Tian, X.; Hou, R. Ameliorative effect of Berberidis radix polysaccharide selenium nanoparticles against carbon tetrachloride induced oxidative stress and inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1058480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanović, O.; Altirriba, J.; Rigo, D.; Spiljar, M.; Evrard, E.; Roska, B.; Fabbiano, S.; Zamboni, N.; Maechler, P.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; et al. Dietary excess regulates absorption and surface of gut epithelium through intestinal PPARα. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Yang, F.; Chen, P.; Zuo, H.; Liang, Y.; Xian, M.; Tang, N.; Wang, G. A Novel Polysaccharide Separated from Panax Notoginseng Residue Ameliorates Restraint Stress- and Lipopolysaccharide-induced Enteritis in Mice. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Yu, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T. Trans-anethole exerts protective effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute jejunal inflammation of broilers via repressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Guan, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, X. p-hydroxy benzaldehyde attenuates intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction caused by colitis via activating the HNF-1β/SLC26A3 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1448863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Liu, W.; Han, J. Xylitol attenuates diabetes induced intestinal permeability changes and inflammatory injury by improving intestinal tight junction protein expression and mucus secretion in rats. CyTA—J. Food 2024, 22, 2303447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Shu, G.; Du, H.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhang, W.; Lv, C.; Xu, F.; Li, H.; Ouyang, P.; et al. Effects of Dietary Ferulic Acid on Intestinal Health and Ileal Microbiota of Tianfu Broilers Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide. Molecules 2023, 28, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; Li, B.; Cui, S. Taurine Alleviates Experimental Colitis by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibiting Inflammatory Response through TLR4/NF-κB Signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 12119–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yu, B.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.; Mao, X.; Luo, J.; Yan, H.; He, J. Effect of β-Glucan Supplementation on Growth Performance and Intestinal Epithelium Functions in Weaned Pigs Challenged by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Tang, K.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z. Anti-inflammatory Effects of the Fucoidan from Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Mar. Biotechnol. 2025, 27, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Pathomechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Potential Antioxidant Therapies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4535194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adwas, A.A.; Elsayed, A.; Azab, A.E.; Quwaydir, F.A. Oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms in human body. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 1, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, J.; Ai, G.; Xiong, P.; Song, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zou, Z.; Chen, X. Mechanisms of the effects of turpiniae folium extract on growth performance, immunity, antioxidant activity and intestinal barrier function in LPS-challenged broilers. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Yin, F.; Li, D.; Zhou, D. Evaluation of oyster peptide-chitosan oligosaccharide-iron complex (OPCFe) complex as a novel approach for iron supplementation: Effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and gut microbiota in vivo. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Almutairi, M.H.; Nawaz, S.; Dong, S. Effect of Morchella esculenta polysaccharides on the rectal microbiota of mice challenged with lipopolysaccharides. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1446924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Wang, W.-Z.; Chu, S.; Liu, X.-X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Tan, C.; Zhu, F.; Deng, S.-J.; Dong, Y.-L.; et al. Compound sophorae decoction enhances intestinal barrier function of dextran sodium sulfate induced colitis via regulating notch signaling pathway in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, A.; Zeng, X.; Hou, C.; Liu, H.; Qiao, S. Lactobacillus reuteri I5007 modulates tight junction protein expression in IPEC-J2 cells with LPS stimulation and in newborn piglets under normal conditions. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, W.; Gong, S.; Li, Y.; Xia, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, J. Effects of dietary protein on gut development, microbial compositions and mucin expressions in mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Yang, Y.; Gu, P.; Li, K.; Adelijiang, W.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D. The secretion of sIgA and dendritic cells activation in the intestinal of cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice are regulated by Alhagi honey polysaccharides. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 103, 154232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, K.L.; Rodriguez, T.R.; McAdams, Z.L.; Coghill, L.M.; Ericsson, A.C.; Franklin, C.L. Failure of colonization following gut microbiota transfer exacerbates DSS-induced colitis. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2447815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Shi, B.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z. Relieving Effect of Artemisia ordosica Krasch Extract on DSS-Induced Colitis by Regulating Immunity, Antioxidant Function, Gut Microbiota, and Bile Acid Metabolism in Mice. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wan, F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. Caffeic acid modulates intestinal microbiota, alleviates inflammatory response, and enhances barrier function in a piglet model challenged with lipopolysaccharide. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Shahinozzaman; Subedi, U.; Fan, S.; Ogedengbe, O.; Obanda, D.N. The Vegetable ‘Kale’ Protects against Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Acute Inflammation through Moderating the Ratio of Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory LPS-Producing Bacterial Taxa and Augmenting the Gut Barrier in C57BL6 Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alioui, Y.; Ullah, H.; Ali, S.; Rahman, M.U.; Elkharti, M.; Farooqui, N.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Ilyas, M.; Alsholi, D.M.; Siddiqi, N.Z.; et al. Polysaccharides derived from golden mushroom (Cantharellus cibarius Fr.) modulate gut microbiota and enhance intestinal barrier function to ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1498625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Hu, X.; Guan, S.; Cai, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, W.; Marzorati, M.; Li, B.; et al. Capilliposide A alleviates DSS-induced colitis by regulating the intestinal flora and its metabolites of origin. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 146, 113858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Meng, D.; Lai, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Huang, X.; Gao, X. Rosa roxburghii fermented juice mitigates LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulation of intestinal flora and metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1447735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.-Y. The major roles of intestinal microbiota and TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway in acute intestinal inflammation in mice, and the improvement effect by Hippophae rhamnoides polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, K.; Deng, S.; Liu, Y. Sodium humate alleviates LPS-induced intestinal barrier injury by improving intestinal immune function and regulating gut microbiota. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 161, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Carroll-Portillo, A.; Lin, H. Desulfovibrio in the Gut: The Enemy within? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shao, X. Thinned peach polyphenols alleviate obesity in high fat mice by affecting gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Accession Number | Primer | Size (Base) |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | NM_007393.5 | F: ACTGCCGCATCCTCTTCCTC R: AACCGCTCGTTGCCAATAGTG | 80 |
| IL-6 | NM_001314054.1 | F: CGGAGAGGAGACTTCACAGAGG R: TTCCACGATTTCCCAGAGAACATG | 102 |
| IL-1β | NM_008361.4 | F: TCGCAGCAGCACATCAACAAG R: TCCACGGGAAAGACACAGGTAG | 94 |
| TNF-α | NM_001278601.1 | F: ACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAGG R: TGAGAAGAGGCTGAGACATAGGC | 86 |
| ZO-1 | NM_001163574.2 | F: AGGAGGTAGAACGAGGCATCATC R: CCCGCTGTCTTTGGAAGTGTG | 85 |
| Occludin | NM_001360536.1 | F: GGCGGCTATGGAGGCTATGG R: CTAAGGAAGCGATGAAGCAGAAGG | 106 |
| Claudin-1 | NM_016674.4 | F: CCTGGCTTCTCTGGGATGGATC R: CTGAGCGGTCACGATGTTGTC | 97 |
| MUC2 | NM_023566.4 | F: GAGCACATCACCTACCACATCATC R: AATCCAGCCAGCCAGTCCAC | 89 |
| Days | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 20.79 ± 0.87 | 21.34 ± 0.81 | 22.23 ± 0.80 | 21.90 ± 1.30 | 22.16 ± 0.83 | 22.36 ± 1.05 | 22.57 ± 1.12 | 22.34 ± 1.15 |
| LPS | 20.80 ± 1.39 | 21.18 ± 1.18 | 21.49 ± 1.19 | 21.90 ± 1.17 | 22.09 ± 1.12 | 21.74 ± 1.06 | 21.94 ± 1.21 | 20.84 ± 1.11 |
| L-FA | 20.40 ± 1.05 | 20.98 ± 0.84 | 21.15 ± 1.39 | 21.28 ± 0.66 | 21.61 ± 0.82 | 21.93 ± 0.82 | 21.85 ± 0.77 | 20.98 ± 0.81 |
| M-FA | 20.92 ± 0.83 | 21.48 ± 0.92 | 21.96 ± 1.11 | 21.63 ± 0.85 | 21.82 ± 0.68 | 22.53 ± 0.84 | 22.79 ± 0.68 | 21.95 ± 0.50 |
| H-FA | 20.82 ± 1.51 | 20.99 ± 1.29 | 21.30 ± 0.67 | 21.35 ± 1.30 | 21.81 ± 1.13 | 21.91 ± 1.06 | 21.96 ± 0.69 | 21.20 ± 0.89 |
| Organ Index | Heart Index | Liver Index | Lung Index | Spleen Index | Kidney Index | Thymus Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| control | 5.91 ± 0.69b | 44.47 ± 2.12c | 3.24 ± 0.62b | 6.64 ± 0.85b | 13.57 ± 0.90b | 1.63 ± 0.34b |
| LPS | 7.18 ± 1.09a | 52.21 ± 2.20a | 5.37 ± 0.66a | 7.62 ± 0.60a | 15.48 ± 1.15a | 2.06 ± 0.27a |
| L-FA | 6.76 ± 0.83a | 49.15 ± 1.34b | 5.04 ± 0.39ab | 7.02 ± 0.53a | 15.39 ± 1.11a | 1.73 ± 0.23ab |
| M-FA | 6.89 ± 0.71a | 48.39 ± 2.17b | 4.79 ± 0.55ab | 7.24 ± 0.42a | 15.38 ± 0.90a | 1.71 ± 0.27ab |
| H-FA | 6.80 ± 0.71a | 48.61 ± 2.03b | 5.05 ± 0.45ab | 7.08 ± 0.60a | 15.51 ± 0.80a | 1.78 ± 0.48ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Li, J.; Zuo, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, B.; Hu, R.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Intestinal Inflammatory Damage in Mice, Associated with Ameliorating Intestinal Barrier Damage and Gut Microbiota. Animals 2025, 15, 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182698
Huang H, Li J, Zuo J, Qiu Y, Li B, Hu R, Bai Y, Zhang J. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Intestinal Inflammatory Damage in Mice, Associated with Ameliorating Intestinal Barrier Damage and Gut Microbiota. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182698
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Huan, Jiehang Li, Jingru Zuo, Yanhua Qiu, Bing Li, Rongbin Hu, Yubin Bai, and Jiyu Zhang. 2025. "Ferulic Acid Alleviates Intestinal Inflammatory Damage in Mice, Associated with Ameliorating Intestinal Barrier Damage and Gut Microbiota" Animals 15, no. 18: 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182698
APA StyleHuang, H., Li, J., Zuo, J., Qiu, Y., Li, B., Hu, R., Bai, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). Ferulic Acid Alleviates Intestinal Inflammatory Damage in Mice, Associated with Ameliorating Intestinal Barrier Damage and Gut Microbiota. Animals, 15(18), 2698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182698





