Cetacean Habitat Use and Occurrence in Fort-de-France Bay (Martinique)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
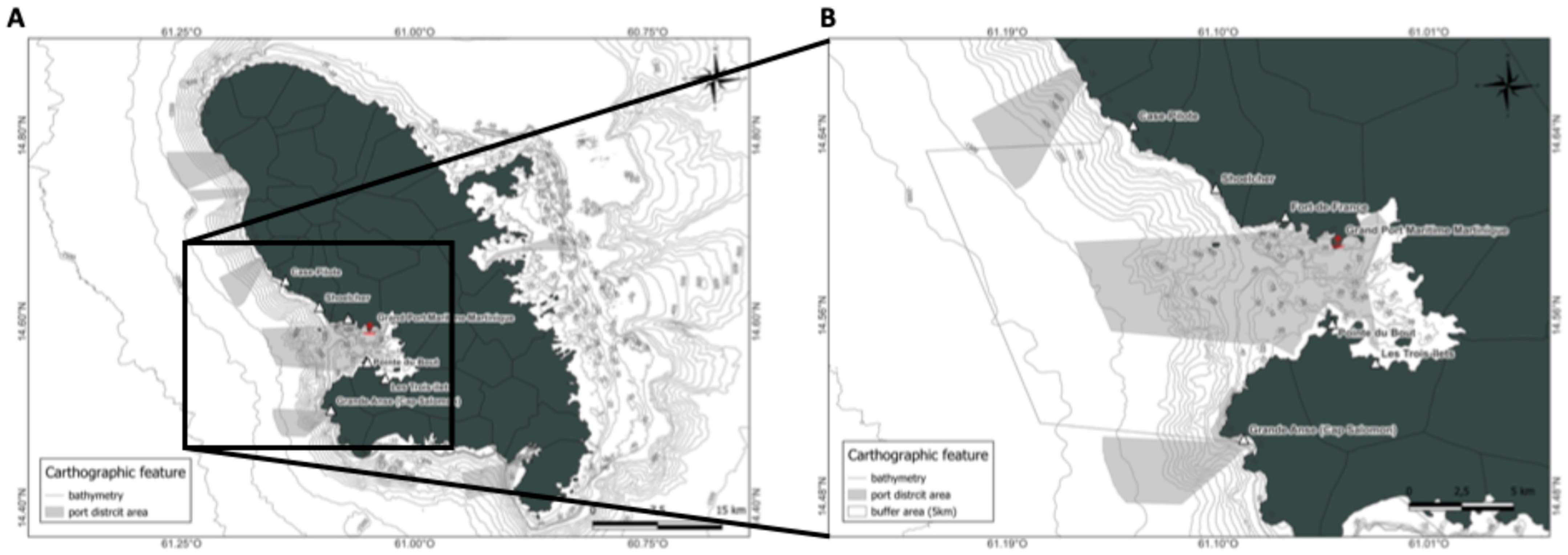
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Period
2.2.1. Historical Database
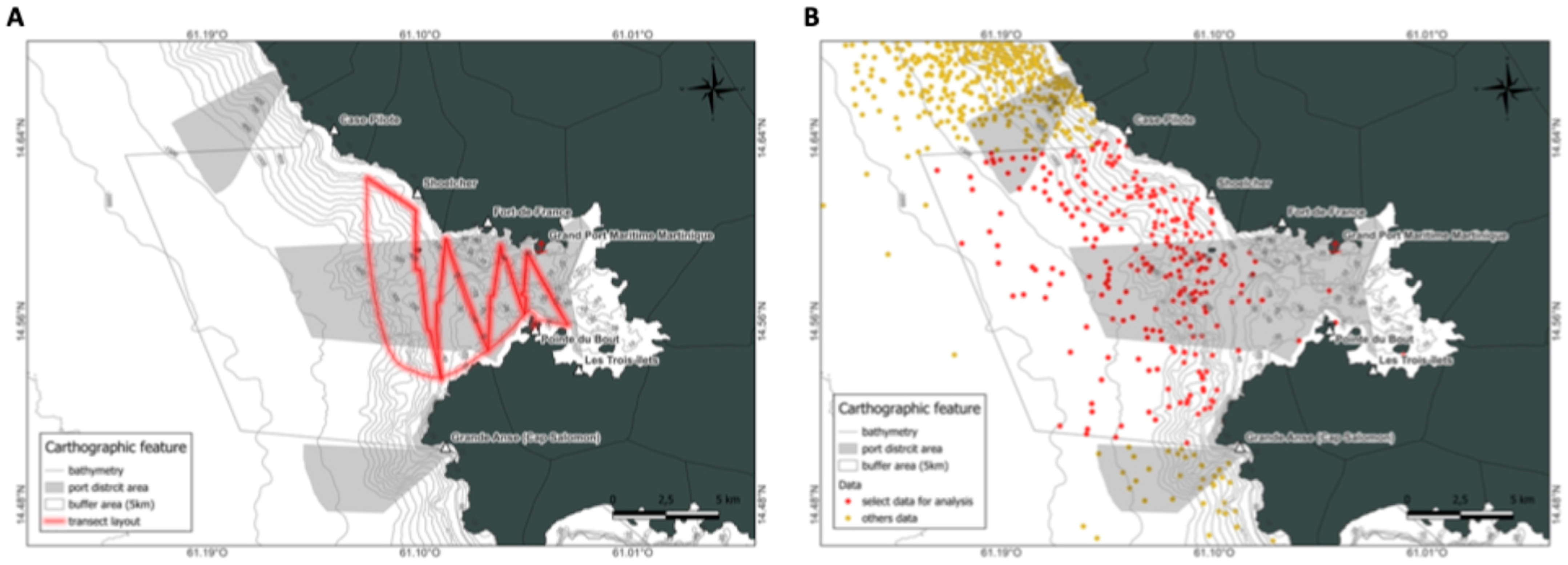
2.2.2. Field Database
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Spatial Analysis
3. Results
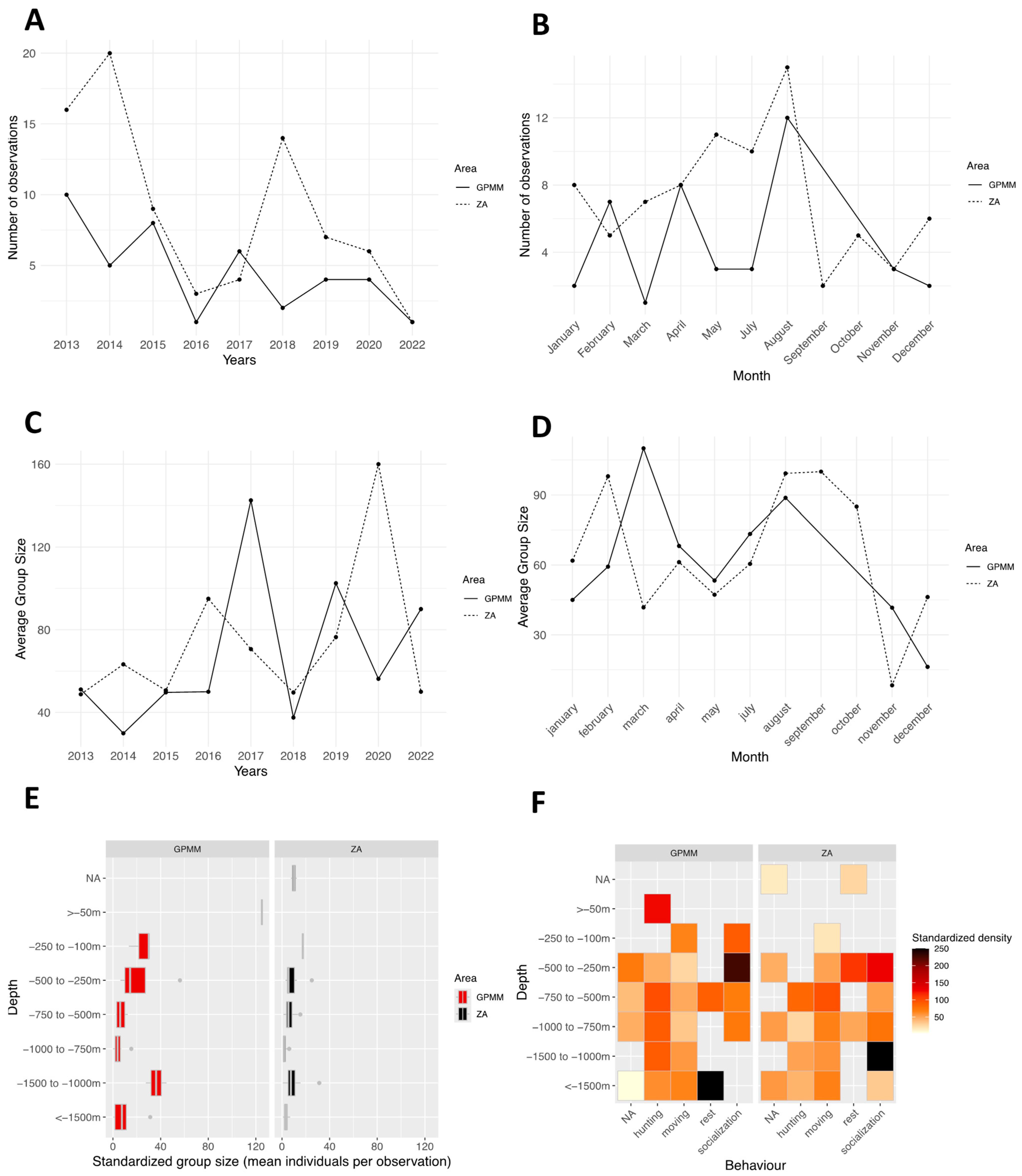
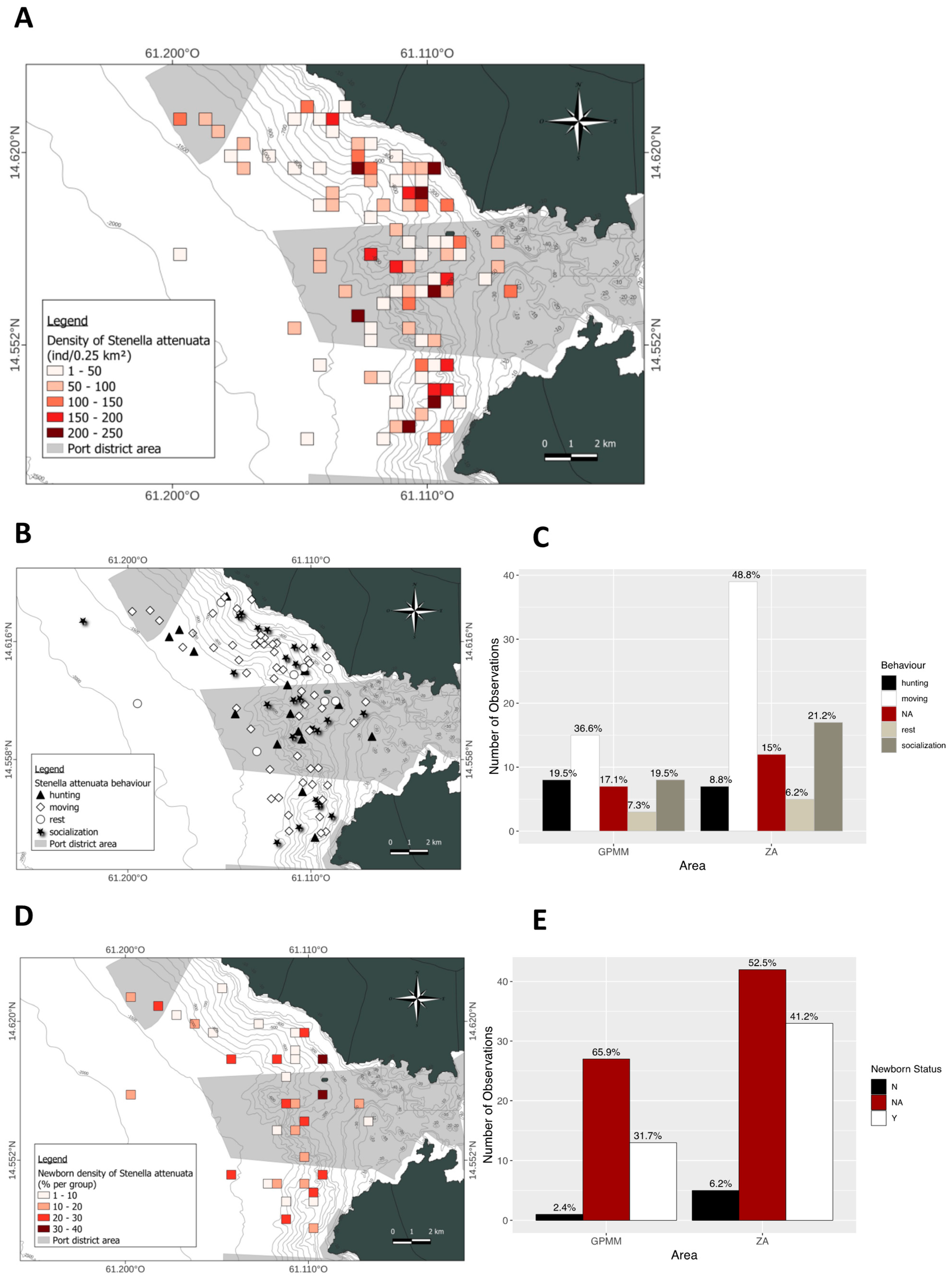
3.1. Stenella attenuata
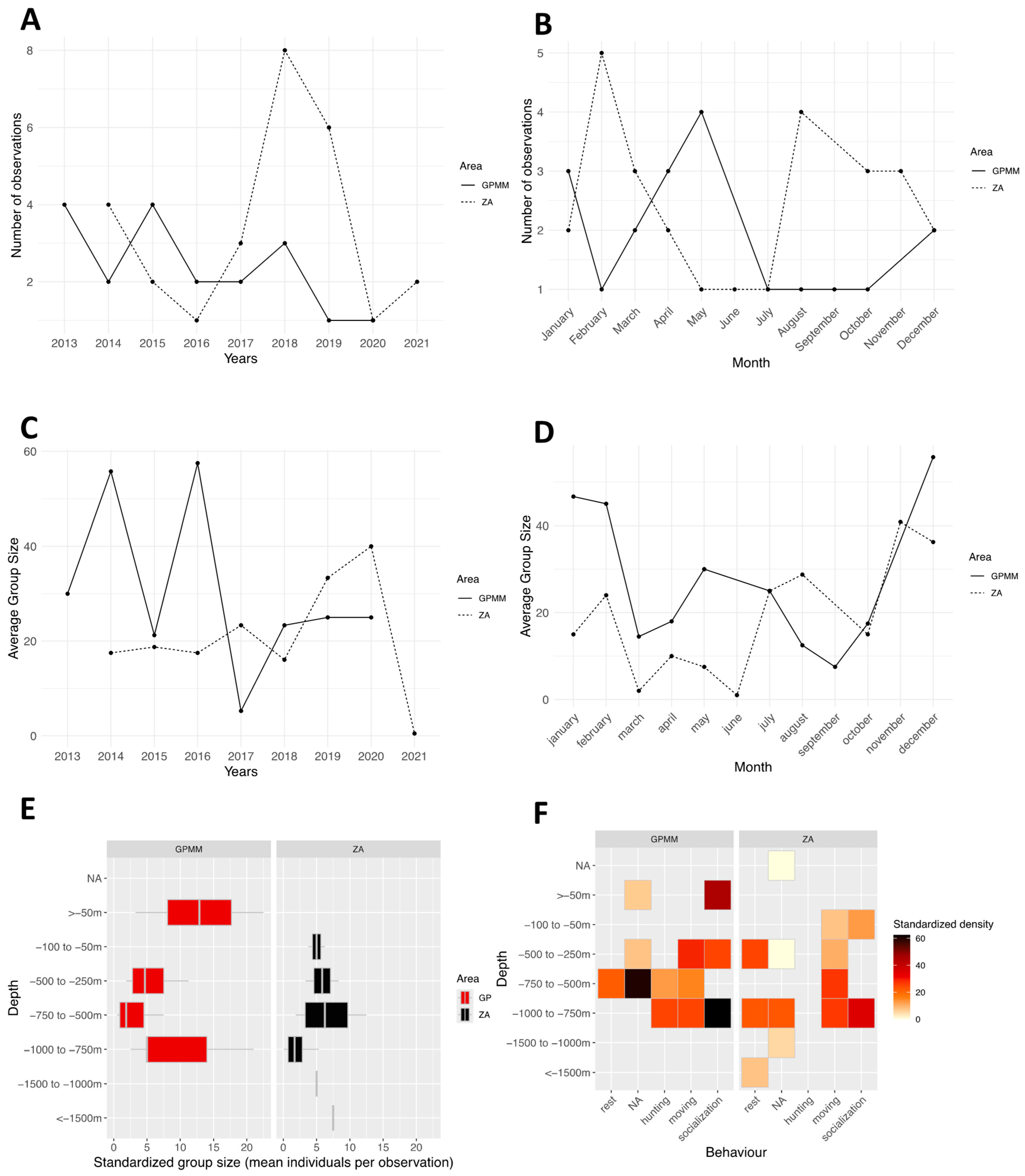
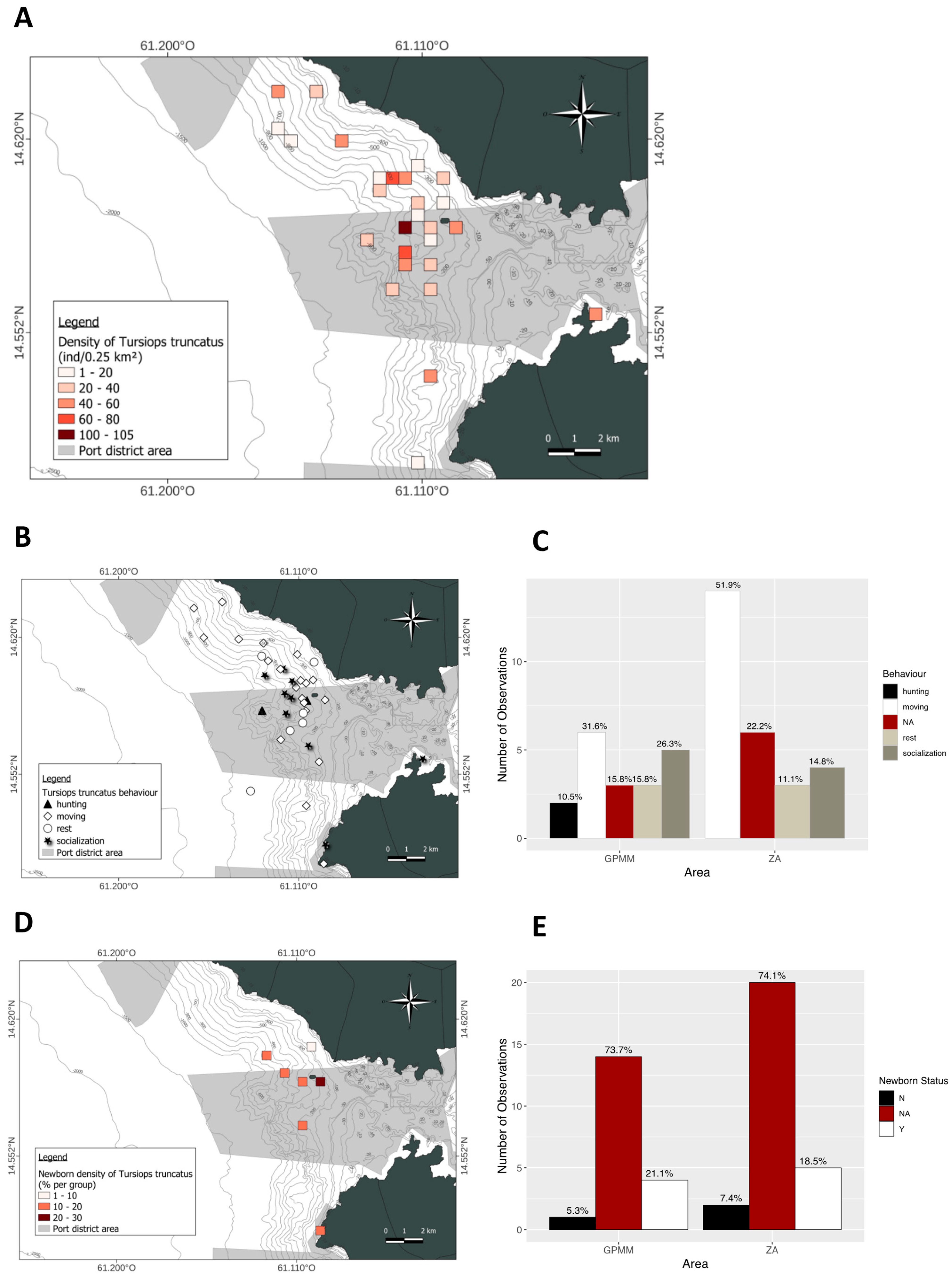
3.2. Tursiops truncatus
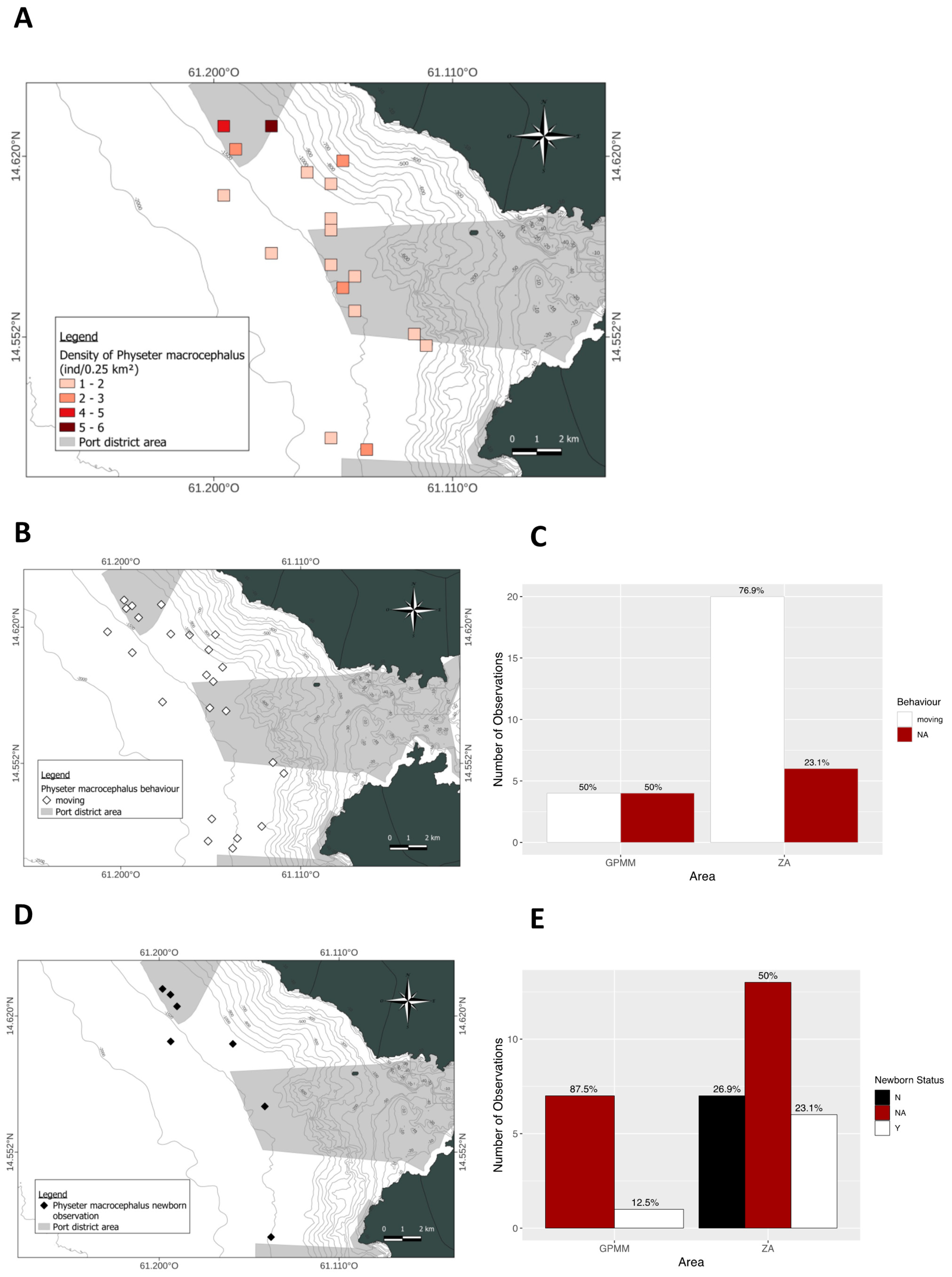
3.3. Physeter macrocephalus
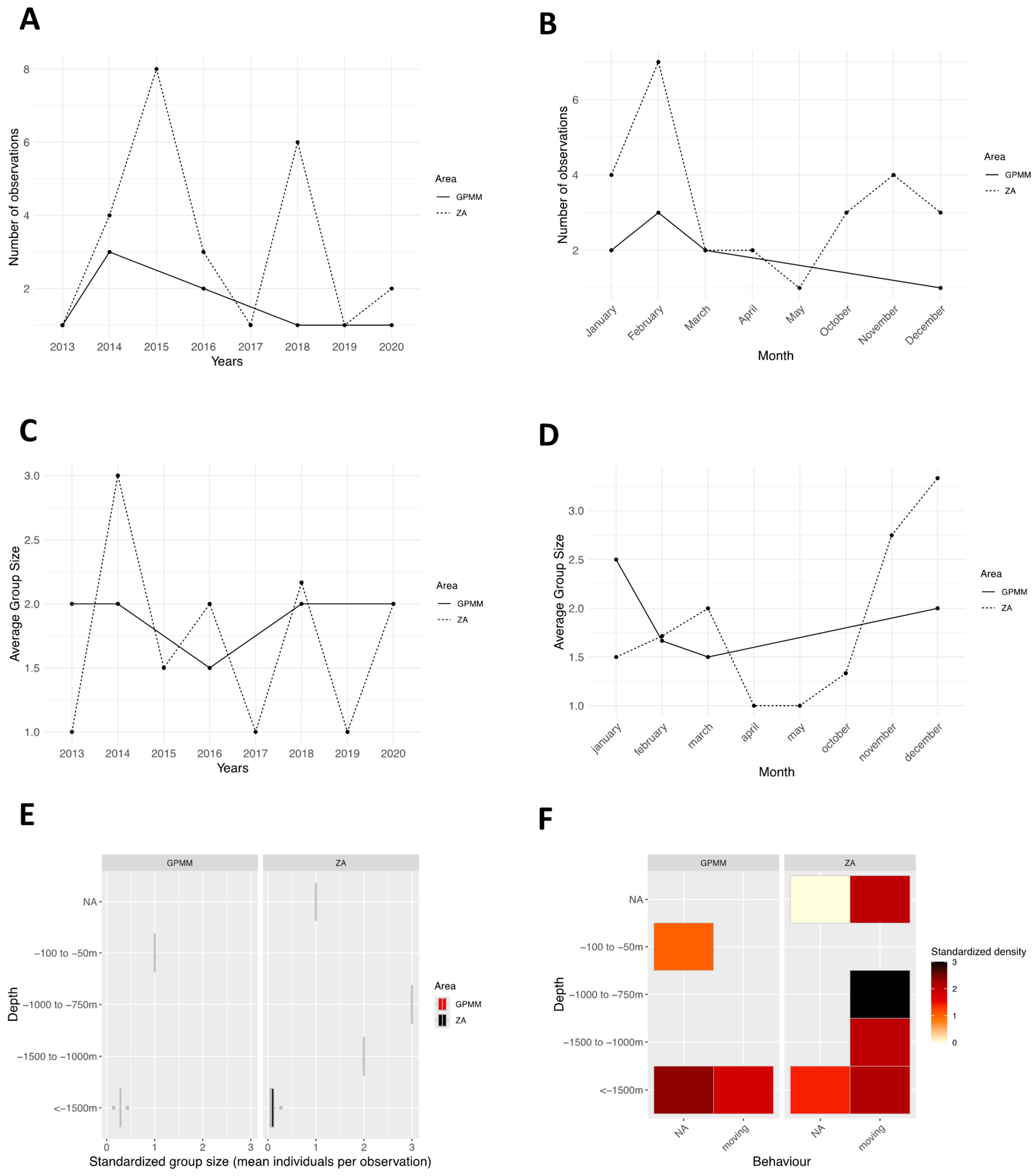
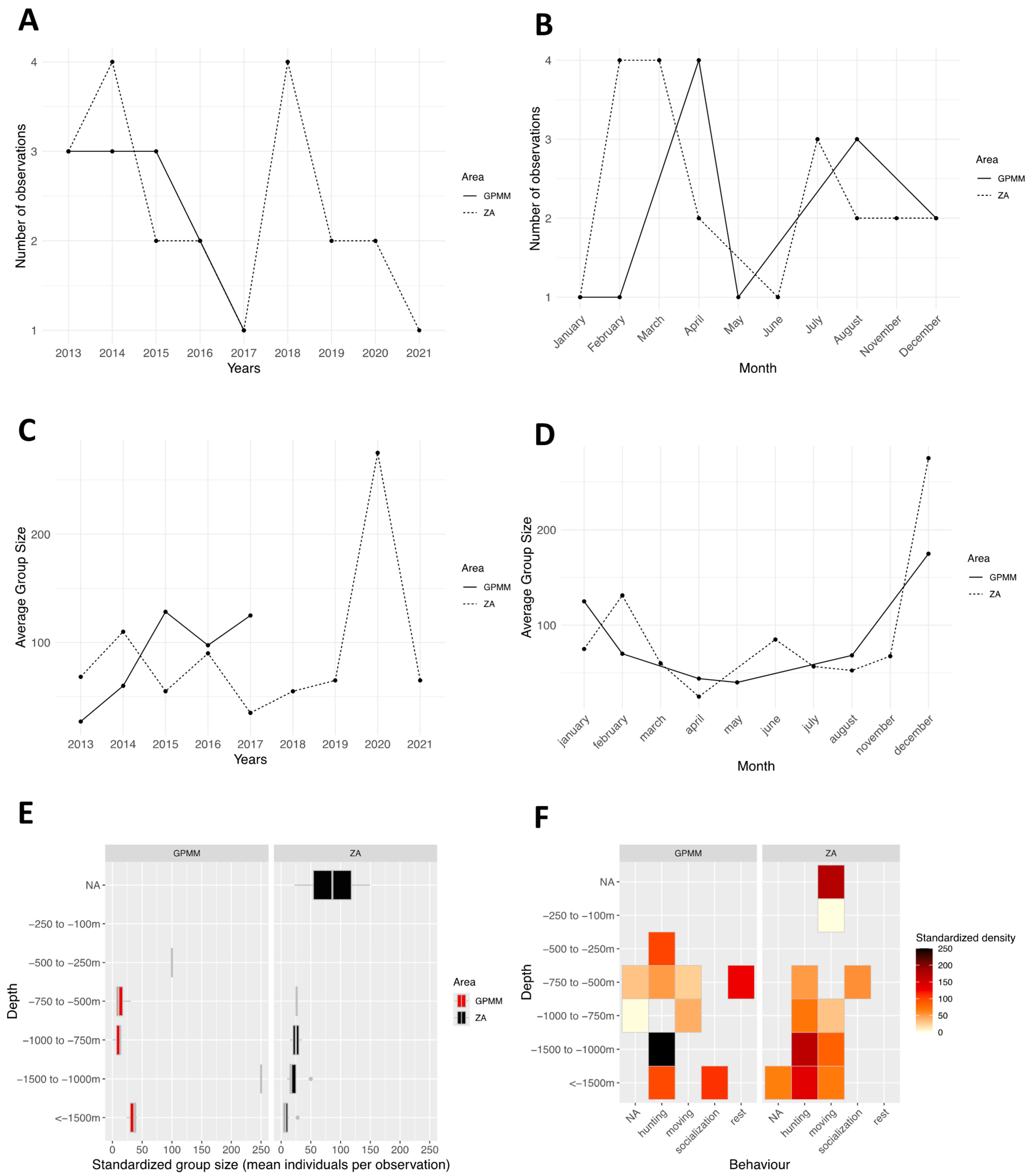
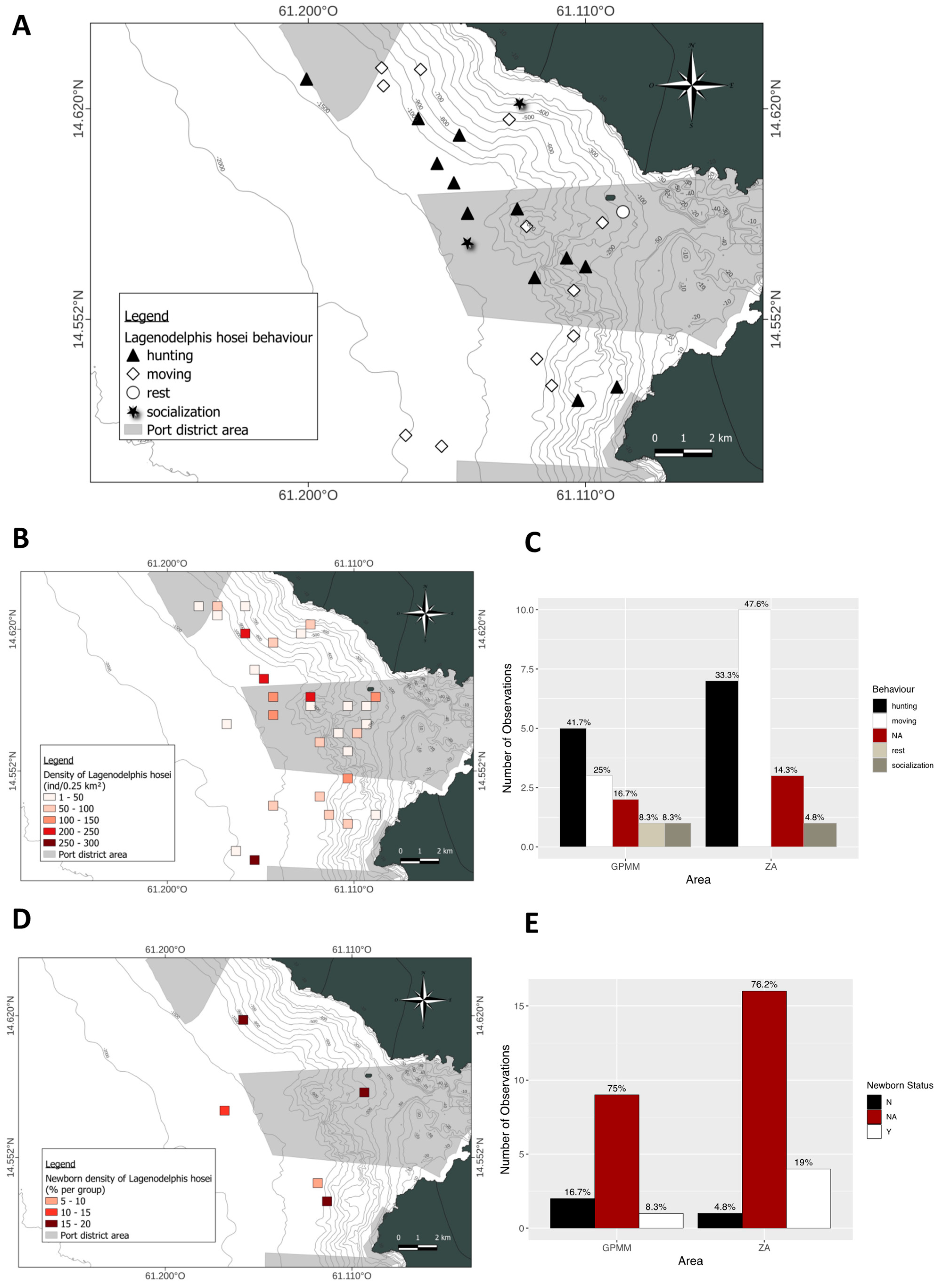
3.4. Lagenodelphis hosei
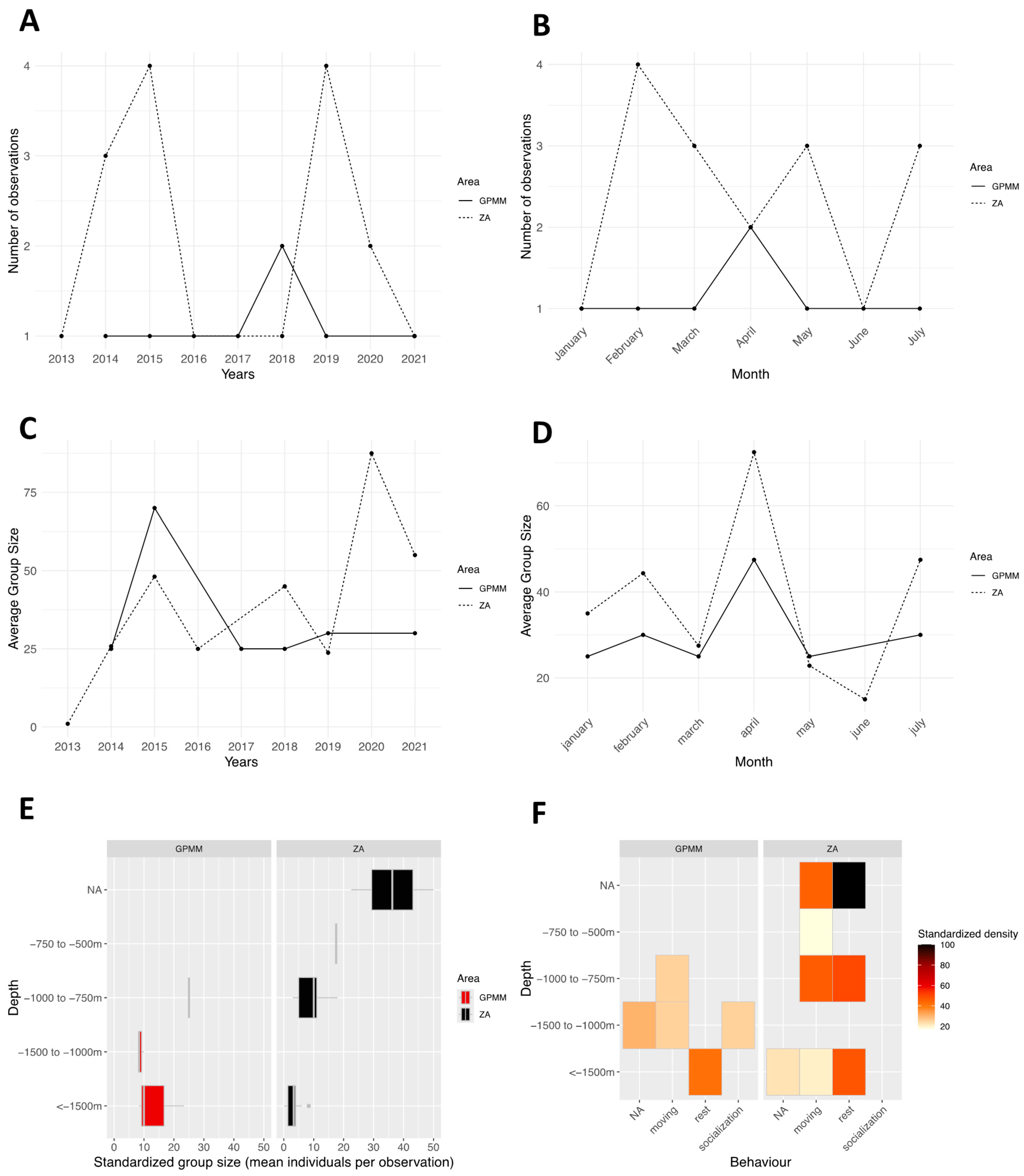
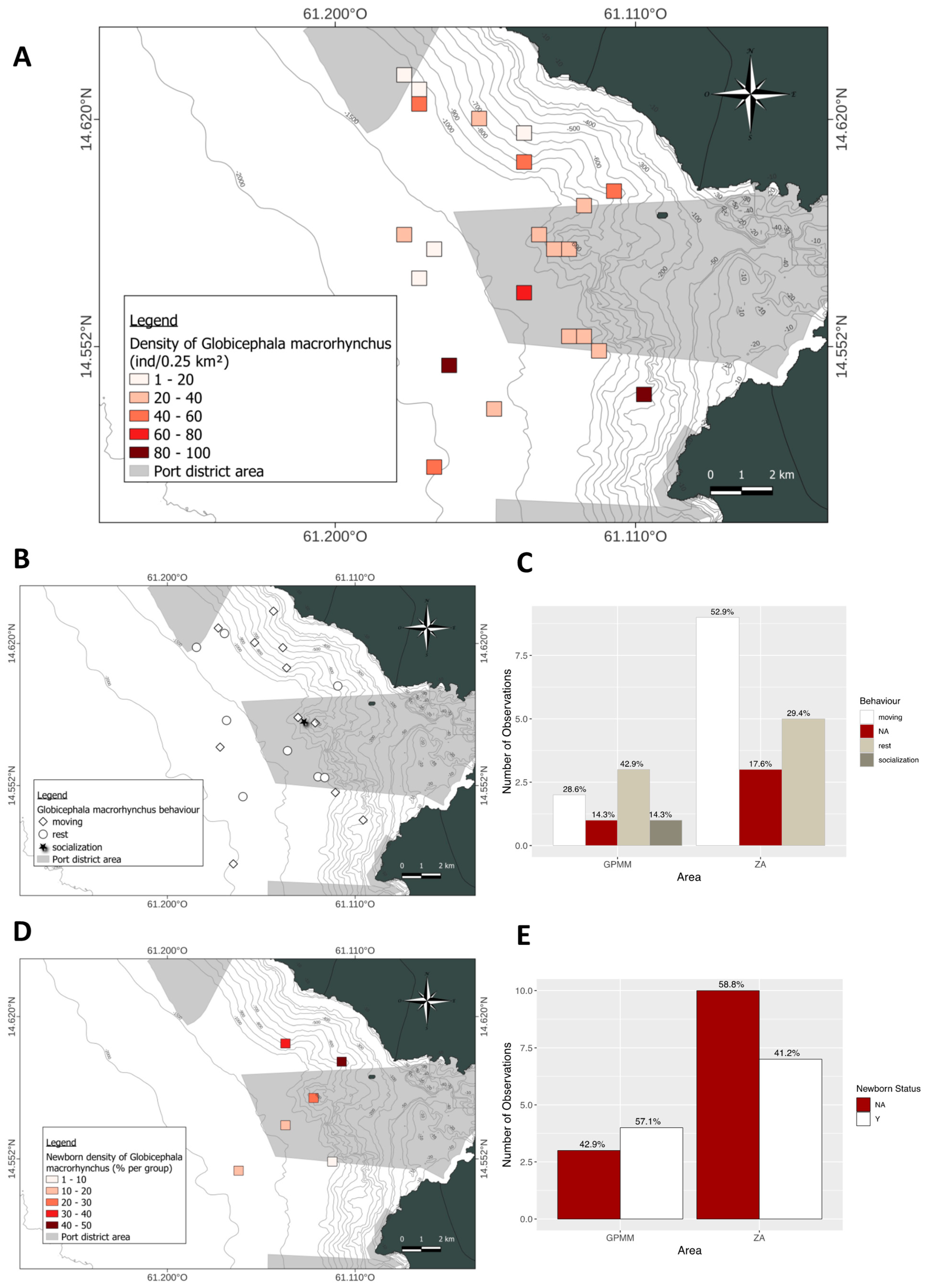
3.5. Globicephala macrorhynchus
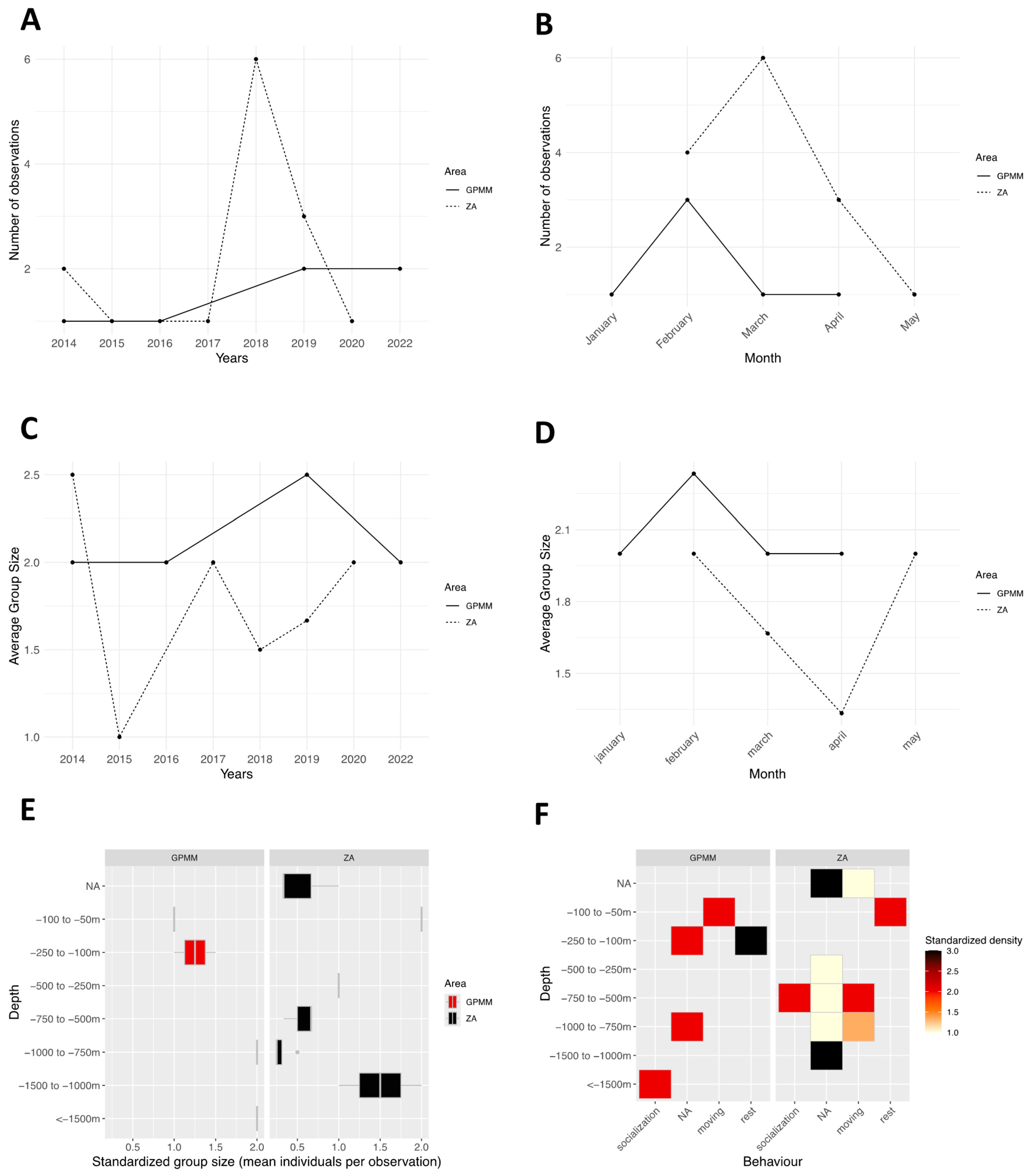
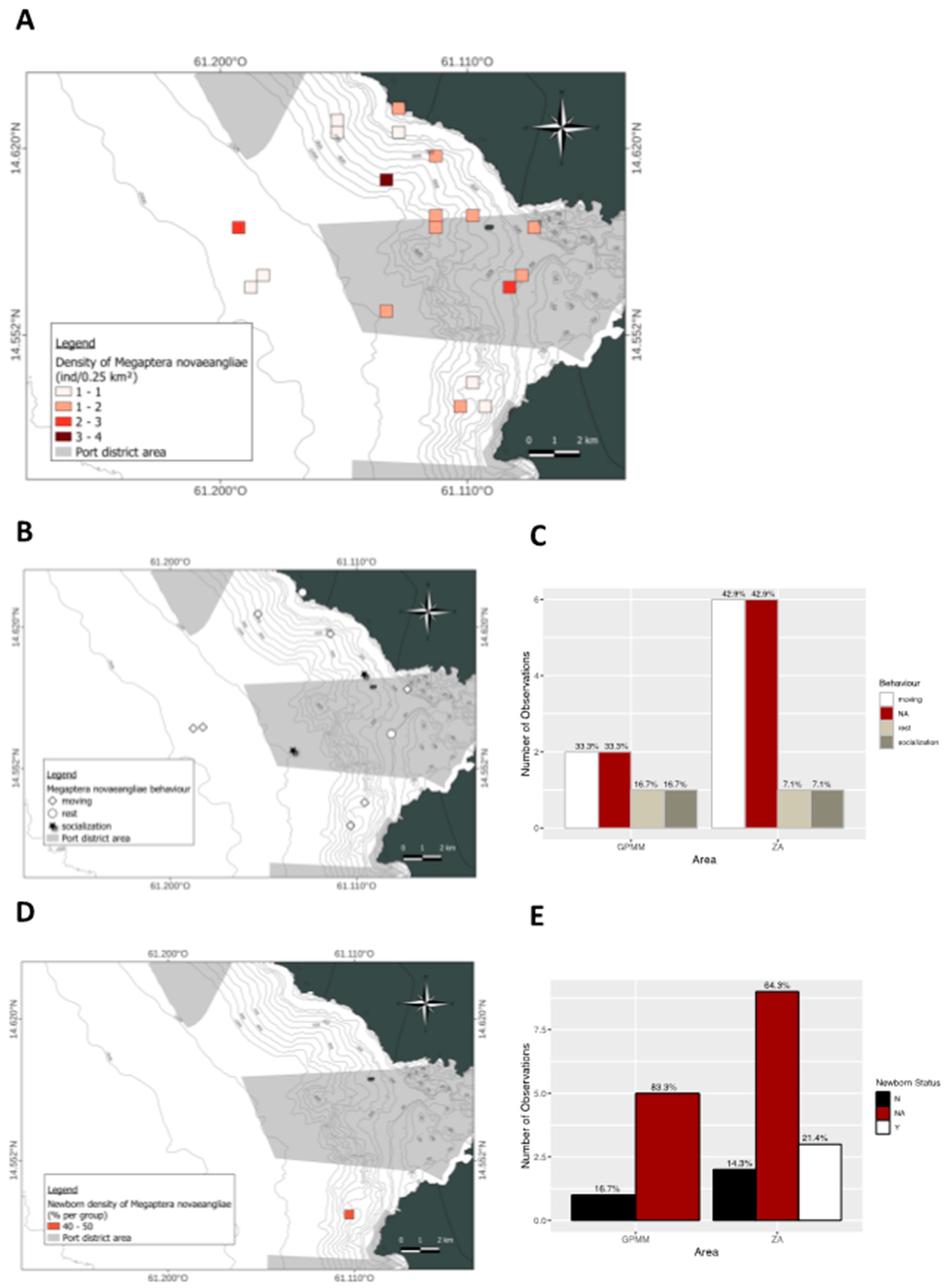
3.6. Megaptera novaeangliae
4. Discussion
4.1. Groupe Size
4.2. Behaviors
4.3. Influence of Marine Traffic
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooker, S.K.; Gerber, L.R. Marine reserves as a tool for ecosystem-based management: The potential importance of megafauna. Bioscience 2004, 54, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez Rosales, S.; Josephson, E.; Palka, D.; Garrison, L. Detection of habitat shifts of cetacean species: A comparison between 2010 and 2017 habitat suitability conditions in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 877580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, S.E.; Cope, J.M. Dynamics of cetacean mixed species groups: A review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 678173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, H. Sperm Whales: Social Evolution in the Ocean; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barco, S.G.; Swingle, W.M.; McLellan, W.A.; Harris, R.N.; Pabst, D.A. Local abundance and distribution of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the nearshore waters of Virginia Beach, Virginia. Mar. Mammal Sci. 1999, 15, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, S.; Meynecke, J.O.; Franklin, T.; Franklin, W.; Chauvenet, A.L.M. Humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) behaviour determines habitat use in two Australian bays. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 72, 1251–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, F.; Hewitt, J.E.; Torres, L.G.; Mouton, T.L.; Brough, T.; Goetz, K.T.; Lundquist, C.J.; MacDiarmid, A.B.; Ellis, J.; Constantine, R. Cetacean conservation planning in a global diversity hotspot: Dealing with uncertainty and data deficiencies. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebke, A.; Samarra, F.; Derous, D. Climate change and cetacean health: Impacts and future directions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 377, 20210249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D.; Slooten, E.; Currey, R.J. Unsustainable dolphin-watching tourism in Fiordland, New Zealand. Tour. Mar. Environ. 2006, 3, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, A.; Sagarminaga, R.; de Stephanis, R.; Urquiola, E.; Hammond, P.S. Habitat preference modelling as a conservation tool: Proposals for marine protected areas for cetaceans in southern Spanish waters. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.P.; Breed, G.A.; Robinson, P.W. New insights into pelagic migrations: Implications for ecology and conservation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2020, 51, 91–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez Rosales, S.; Palka, D.L.; Garrison, L.P.; Josephson, E.A. Environmental predictors of habitat suitability and occurrence of cetaceans in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigada, S.; Pavan, G.; Borg, J.A.; Galil, B.S.; Vallini, C. Biodiversity impacts of ship movement, noise, grounding and anchoring. In Maritime Traffic Effects on Biodiversity in the Mediterranean Sea: Review of Impacts, Priority Areas and Mitigation Measures; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 9–56. [Google Scholar]
- Marley, S.A.; Salgado Kent, C.P.; Erbe, C.; Parnum, I.M. Effects of vessel traffic and underwater noise on the movement, behaviour and vocalisations of bottlenose dolphins in an urbanised estuary. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacek, D.P.; Thorne, L.H.; Johnston, D.W.; Tyack, P.L. Responses of cetaceans to anthropogenic noise. Mammal Rev. 2007, 37, 81–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Wright, A.J.; Ashe, E. Marine mammals and noise: A review of the implications of disturbance on welfare. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 58–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bejder, L.; Samuels, A.; Whitehead, H.; Gales, N. Interpreting short-term behavioural responses to disturbance within a longitudinal perspective. Anim. Behav. 2006, 72, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Pierce, G.J.; Law, R.J.; Bersuder, P.; Jepson, P.D.; Learmonth, J.A.; Addink, M.; Dabin, W.; Santos, M.B.; Deaville, R.; et al. Assessing the effect of persistent organic pollutants on reproductive activity in common dolphins and harbour porpoises. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 2010, 42, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Baini, M.; Simmonds, M.P. Cetaceans as ocean health indicators of marine litter impact at global scale. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 586627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, F.; Panigada, S. Collisions of vessels with cetaceans—The underestimated threat. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 531–547. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, P.D.; Law, R.J. Persistent pollutants, persistent threats: Polychlorinated biphenyls remain a major threat to marine apex predators. Science 2016, 352, 1388–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laist, D.W.; Knowlton, A.R.; Pendleton, D. Collisions between ships and whales. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2001, 17, 35–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.R.; Hosegood, P.; Wynn, R.B.; De Boer, M.N.; Butler-Cowdry, S.; Embling, C.B. Seascape ecology of cetacean habitat. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106256. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, M.F.; Cole, T.V.N.; Clapham, P.J.; Mate, B.R. North Atlantic right whale habitat in the lower Bay of Fundy and on the Scotian Shelf. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 264, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkeron, P.J.; Connor, R.C.; Foroughirad, V.; Genov, T.; Wells, R.S. Why do dolphins carry sponges? Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20182800. [Google Scholar]
- Rolland, R.M.; Parks, S.E.; Hunt, K.E.; Castellote, M.; Corkeron, P.J.; Nowacek, D.P.; Kraus, S.D. Evidence that ship noise increases stress in right whales. Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 2363–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoop, J.M.; Moore, M.J.; Fahlman, A.; Bocconcelli, A.; George, C.; Jackson, K.; Zoodsma, B. Behavioral impacts of disentanglement of a right whale under sedation and the energetic cost of entanglement. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2015, 31, 1864–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, M.A.; Klinck, H.; Baumann-Pickering, S.; Mellinger, D.K.; Qui, S.; Soldevilla, M.S.; Hildebrand, J.A. Classification of odontocete echolocation clicks from the Gulf of Mexico. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.D.; Methion, S.; Covelo, P. Effects of coastal tourism on common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in a marine protected area. Aquat. Conserv. 2018, 28, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, R.; Rinaldi, C.; Salinas, M. Cetacean diversity in the Bay of Fort-de-France, Martinique: Preliminary observations. Caribb. J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 10, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.; Madsen, P.T.; Beedholm, K. Ocean noise: Technological progress and new challenges. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 730, 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, K.; Croxall, J.P.; Briggs, D.R. Marine ecosystems and environmental change: Antarctic perspectives. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 025003. [Google Scholar]
- Sanctuaire Agoa. Charte du Sanctuaire Agoa Pour la Protection des Mammifères Marins Dans les Antilles Françaises; Office Français de la Biodiversité: Vincennes, France, 2012; Available online: https://sanctuaire-agoa.fr/sites/default/files/2021-03/Charte_Agoa_2012.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- May Collado, L.J.; Forcada, J. Small scale estimation of relative abundance for the coastal spotted dolphins (Stenella attenuata graffmani) in Costa Rica: The effect of habitat and seasonality. Rev. De Biol. Trop. 2012, 60 (Suppl. 2), 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G.; Fortuna, C.M.; Reeves, R.R. Ecology and conservation of common bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus in the Mediterranean Sea. Mammal Rev. 2008, 39, 92–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejder, L.; Samuels, A.; Whitehead, H.; Gales, N.; Mann, J.; Connor, R.; Kruetzen, M. Decline in relative abundance of bottlenose dolphins exposed to long-term disturbance. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.S.; Zerbini, A.N.; Vasquez, O.V. Local and migratory movements of humpback whales in the western South Atlantic Ocean. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2014, 13, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Tezanos-Pinto, G. Population Structure, Abundance and Reproductive Parameters of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Bay of Islands. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Auckland, Northland, New Zealand, 2009; pp. 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.J.; van der Schaar, M.; Dunn, J.; Bennett, C.; Curé, C.; Barlow, J.; McDonald, M.A.; Parsons, E.C.M. The impact of underwater noise on marine mammals. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 137, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ketten, D.R. The impacts of noise on cetaceans and marine mammals: The role of anatomy and physiology. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Barber Meyer, S.M.; Olson, G.L.; Currie, J.J. Pantropical spotted dolphin (Stenella attenuata attenuata) abundance estimates in Maui Nui, Hawai‘i reveal small stock structure, long term site fidelity and year round presence. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 1, e939263. [Google Scholar]
- Courtin, B.; Millon, C.; Feunteun, A.; Safi, M.; Duporge, N.; Bolaños Jiménez, J.; Barragán Barrera, D.C.; Bouveret, L.; de Montgolfier, B. Site fidelity and population parameters of pantropical spotted dolphins in the Eastern Caribbean through photographic identification. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 939263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowans, S.; Würsig, B.; Karczmarski, L. The social structure and strategies of delphinids: Predictions based on an ecological framework. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2007, 53, 195–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stensland, E.; Berggren, P. Behavioural changes in female Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins in response to boat-based tourism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacek, S.M.; Wells, R.S.; Solow, A.R. Short-term effects of boat traffic on bottlenose dolphins, Tursiops truncatus, in Sarasota Bay, Florida. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2001, 17, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulau, V.; Gannier, A.; Kiszka, J. Diving and feeding behaviour of sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 857–865. [Google Scholar]
- Bernier, L.; Prieto González, R.; Hassall, C.; Teillard, V.; Bernus, J. Characterizing Fraser’s dolphin (Lagenodelphis hosei) in the Lesser Antilles: Distribution, movements, and co-occurrence with other cetacean species to inform conservation strategies in the Caribbean. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2025, 41, e70039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hern, J.; Biggs, D. Sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) habitat in the Gulf of Mexico: Satellite observed ocean color and altimetry applied to small-scale variability in distribution. Aquat. Mamm. 2009, 35, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fléchet, A.; Pillet, M.; Bordes, R.; Morissette, L.; Scanga, V.; De Montgolfier, B. Characterization of short-finned pilot whales (Globicephala macrorhynchus) population along the Caribbean coast of Martinique. Adv. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2009, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smultea, M.A. Segregation by humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) cows with a calf in coastal habitat near the island of Hawaii. Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víkingsson, G.A.; Pike, D.G.; Schleimer, A.; Øien, N.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Desportes, G.; Bloch, D. Distribution, abundance, and feeding ecology of baleen whales in Icelandic and adjacent waters during summer. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 542–559. [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun, A.; Safi, M.; de Montgolfier, B. État des connaissances sur la fréquentation des cétacés en baie de Fort de France et les risques de perturbations liés au trafic maritime. Rapp. Pour Le Grand Port Marit. Martinique. 2019, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.; O’Hara, P.D. Modelling ship strike risk to fin, humpback and killer whales in British Columbia, Canada. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2010, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, G.K.; Slutsky, J.; Bettridge, S. Hydrodynamics of a ship/whale collision. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 391, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arregui, M.; Bernaldo de Quirós, Y.; Saavedra-Santana, P.; Sierra, E.; Suárez-Santana, C.M.; Arbelo, M.; Díaz-Delgado, J.; Puig-Lozano, R.; Andrada, M.; Fernández, A. Fat embolism and sperm whale ship strikes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borobia, M.; Vail, C.S.; Pusineri, C.; Conruyt, G. Review of threats and implementation of the Regional Action Plan for the Conservation of Marine Mammals in the Wider Caribbean Region. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Mamm. 2023, 18, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilgart, L.S. The impacts of anthropogenic ocean noise on cetaceans and implications for management. Can. J. Zool. 2007, 85, 1091–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatcher, H.; Mayette, A.; Rasmussen, M. Impacts of whale watching vessels on humpback whales and compliance with voluntary guidelines in Skjálfandi Bay, Iceland. IWC J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2025, 26, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza Rodríguez, I.J.; Chávez Dagostino, R.M.; Heckel, G. Resilience components in Mexican whale-watching regulation. Tour. Hosp. 2024, 5, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, A.R.; Piwetz, S.; Di Clemente, J.; Steckler, D.; Mueter, F.; Pearson, H.C. Humpback whale movements and behavior in response to whale-watching vessels in Juneau, AK. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Behavioral Examples | Observation Criteria | Behaviors |
|---|---|---|
| Long and repeated dives, temporary group dispersion followed by regrouping, active surfacing, seabirds diving nearby. | Erratic or circular movements, prolonged dives, coordination among individuals, presence of seabirds or visible prey. | Foraging |
| Parallel alignment of individuals, prolonged floating, slow or stationary movement. | Compact formation, low speed, steady direction, regular and spaced breathing, limited social interaction. | Resting |
| Synchronized swimming, leaping, tail slapping, playing at the boat’s bow, rolling | Frequent physical contact (rubbing, overlapping), vocalizations, playful behaviors (e.g., leaps, rolls, bow-riding) | Socialization |
| Straight-line movement, steady group travel without clear signs of other activities. | Linear or slightly dispersed formation, constant speed, steady direction, limited interaction among individuals. | Traveling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Violo, C.; Gros-Martial, A.; Ortolé, C.; Poupard, M.; Safi, M.; de Montgolfier, B. Cetacean Habitat Use and Occurrence in Fort-de-France Bay (Martinique). Animals 2025, 15, 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182640
Violo C, Gros-Martial A, Ortolé C, Poupard M, Safi M, de Montgolfier B. Cetacean Habitat Use and Occurrence in Fort-de-France Bay (Martinique). Animals. 2025; 15(18):2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182640
Chicago/Turabian StyleViolo, Coline, Anatole Gros-Martial, Célia Ortolé, Marion Poupard, Morjane Safi, and Benjamin de Montgolfier. 2025. "Cetacean Habitat Use and Occurrence in Fort-de-France Bay (Martinique)" Animals 15, no. 18: 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182640
APA StyleViolo, C., Gros-Martial, A., Ortolé, C., Poupard, M., Safi, M., & de Montgolfier, B. (2025). Cetacean Habitat Use and Occurrence in Fort-de-France Bay (Martinique). Animals, 15(18), 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182640






