The Effects of Vessel Traffic on the Behavior Patterns of Common Dolphins in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
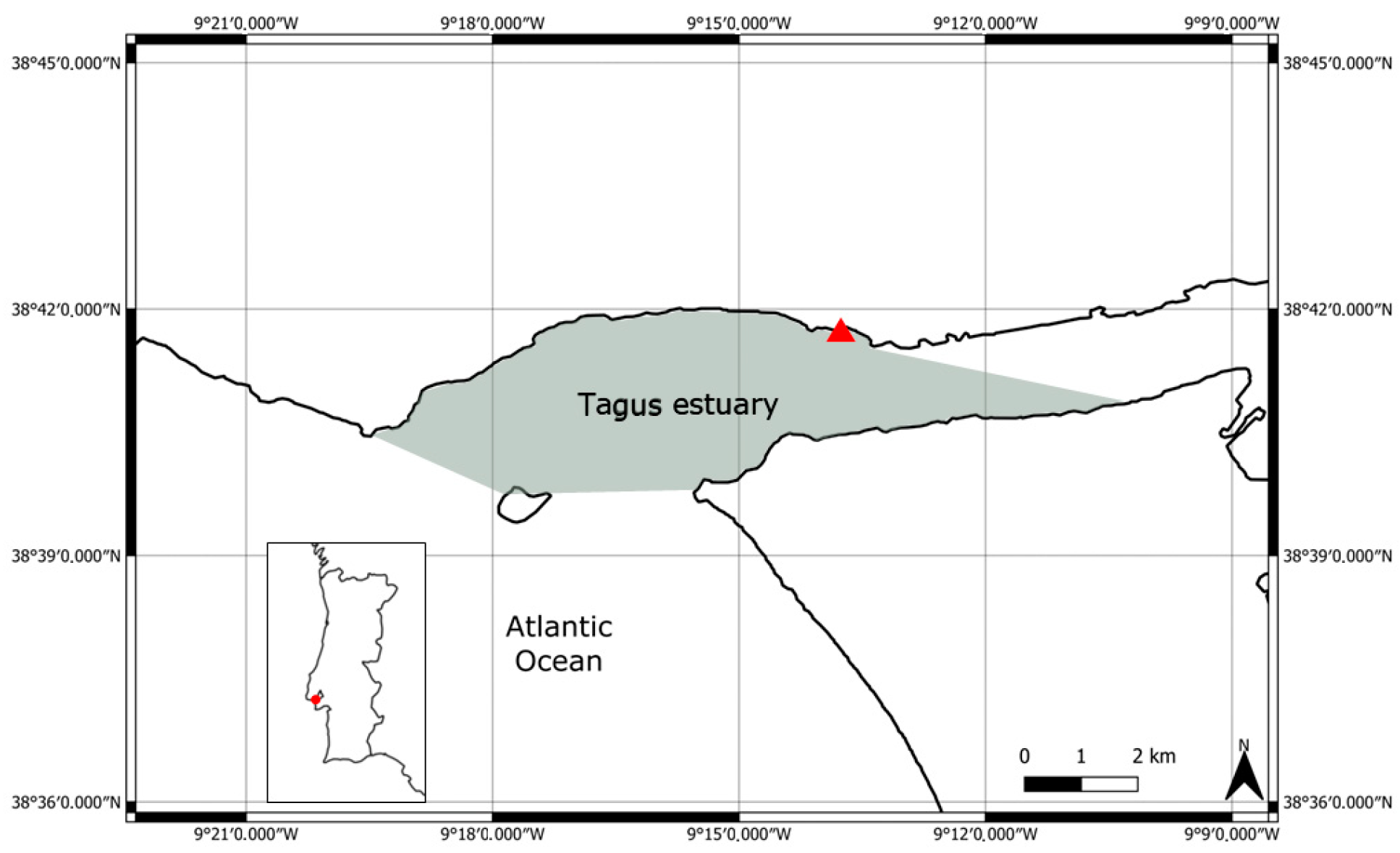
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Video and Audio Recording Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Absence of vessels;
- Presence of vessels.
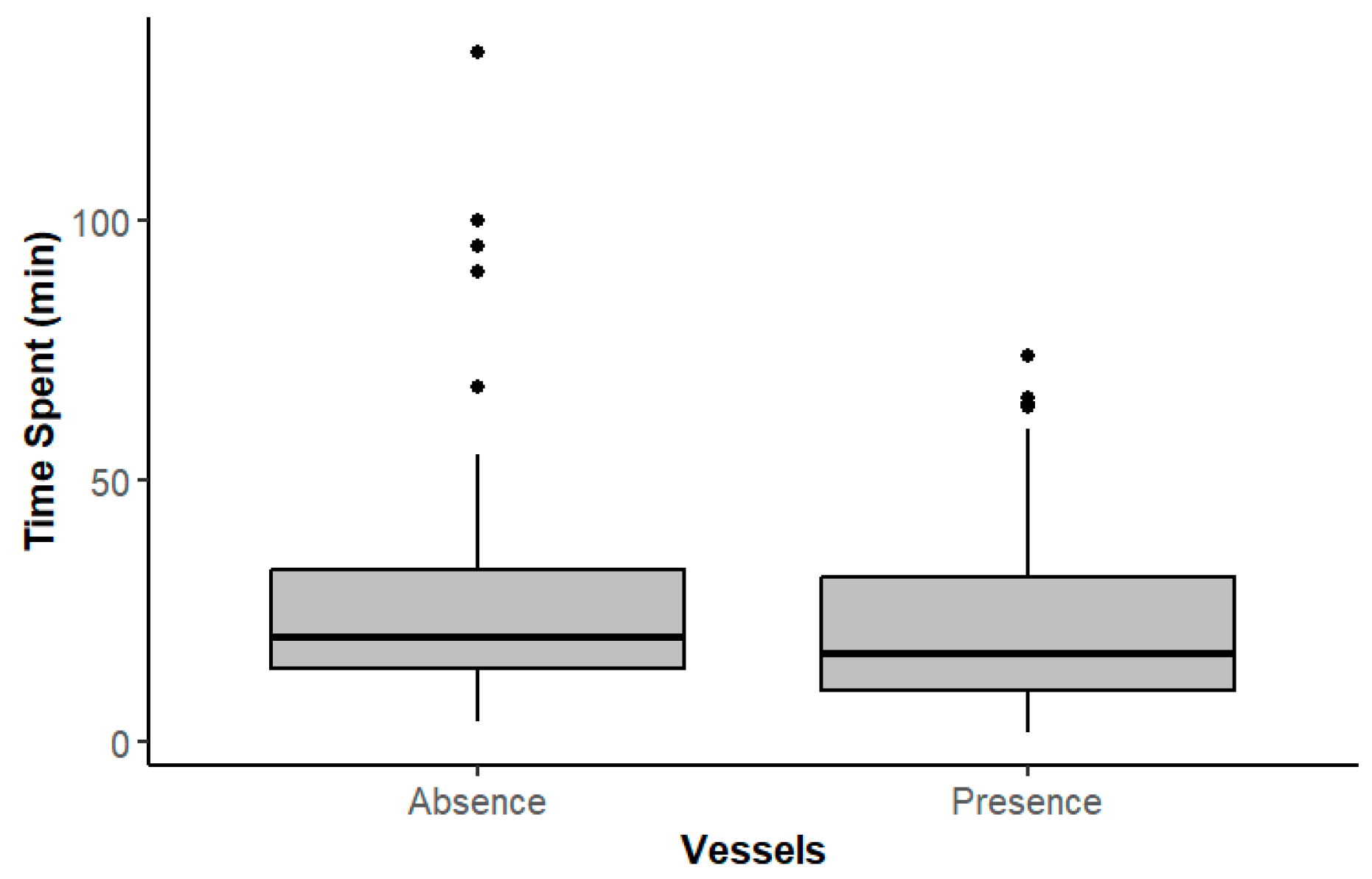
3. Results
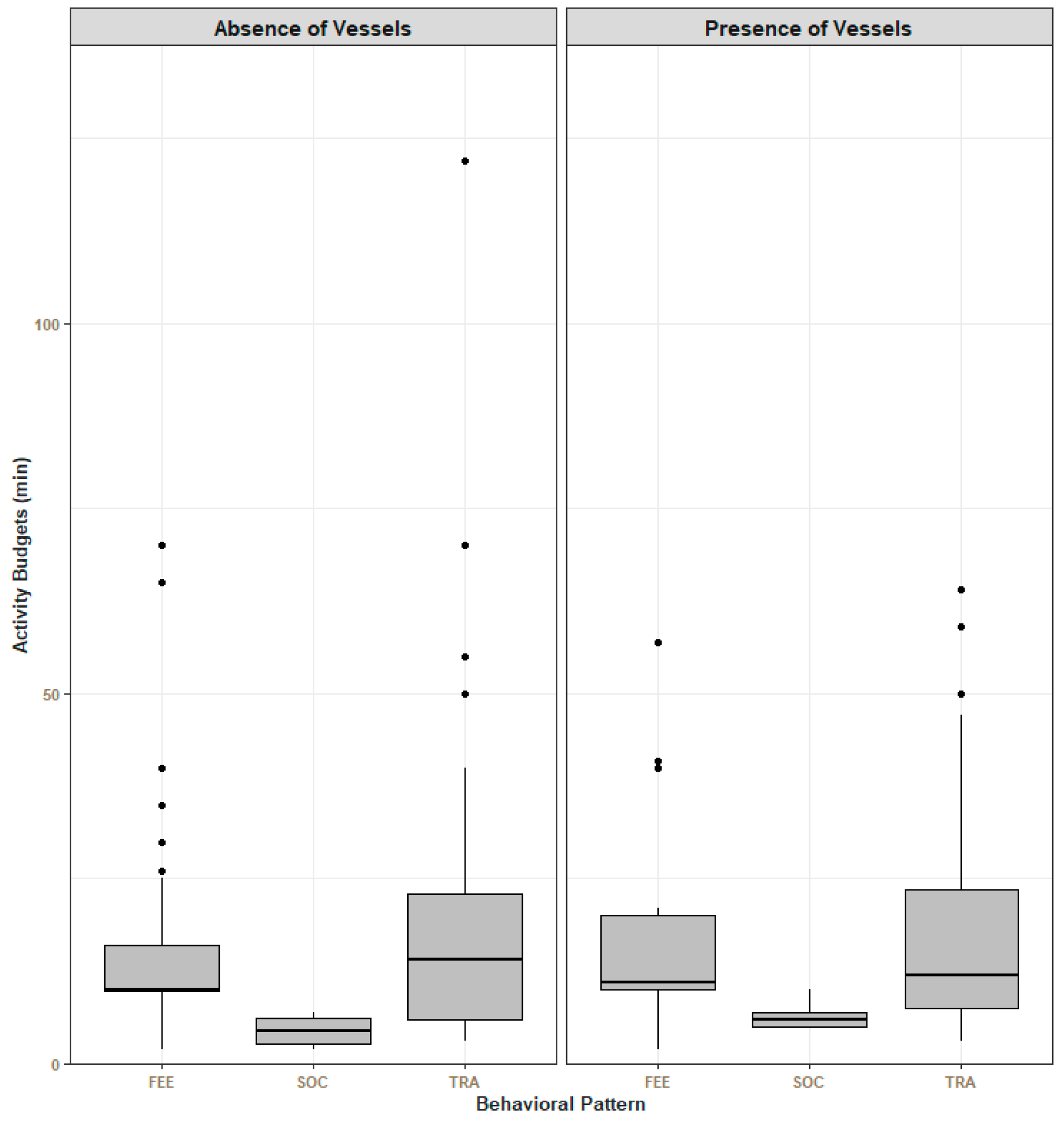
3.1. Activity Behavioral Budgets
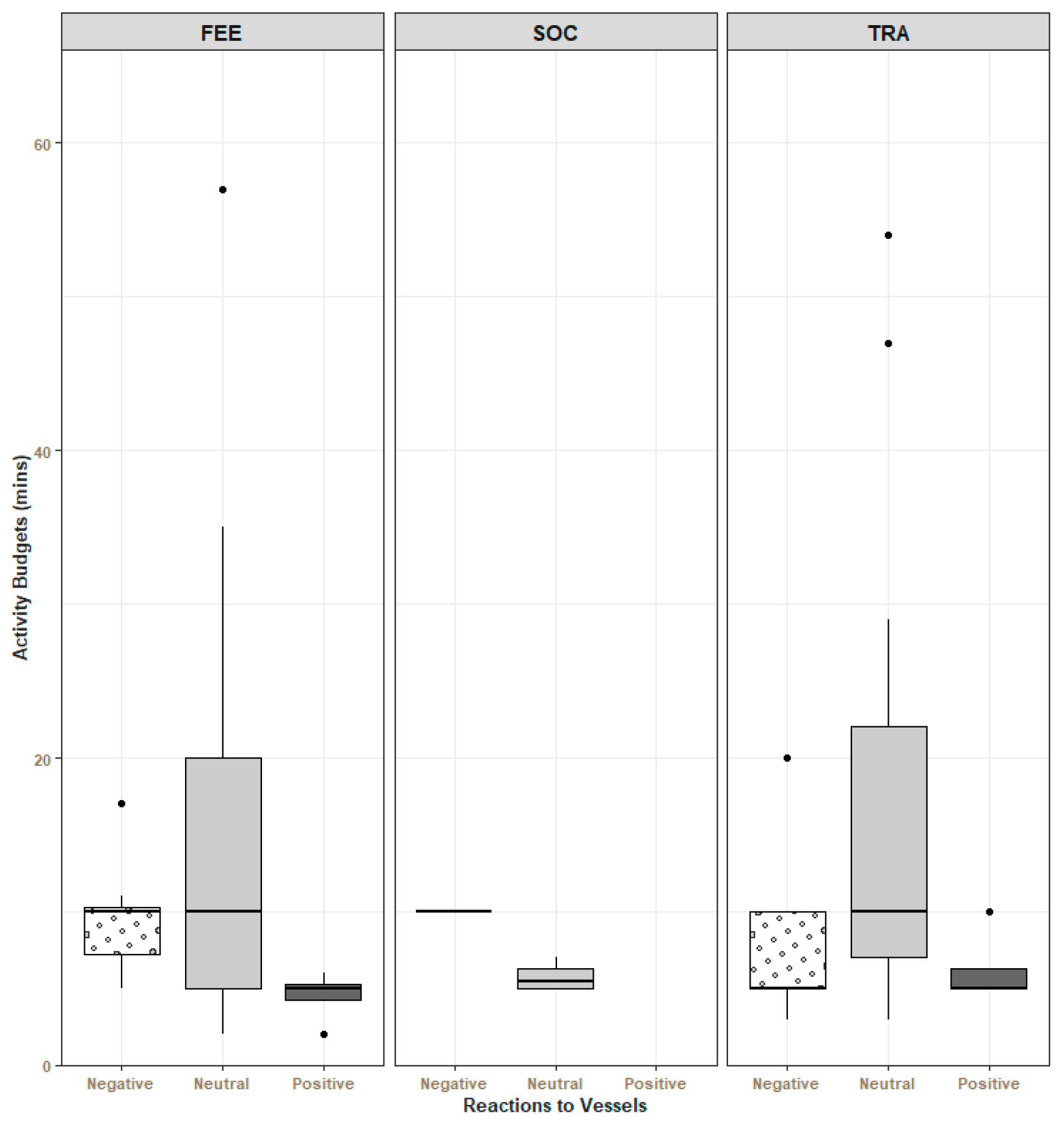
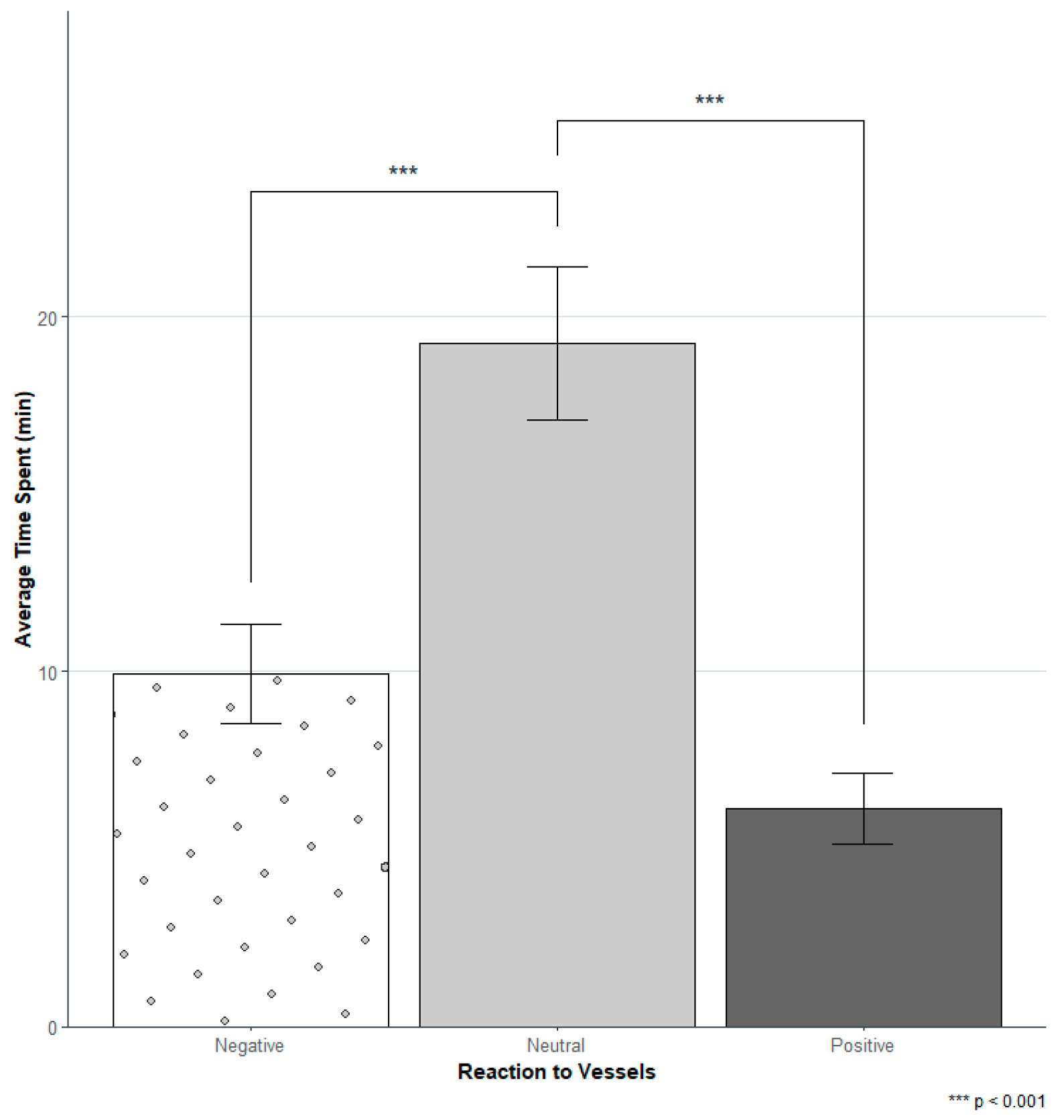
3.2. Reaction to Vessels
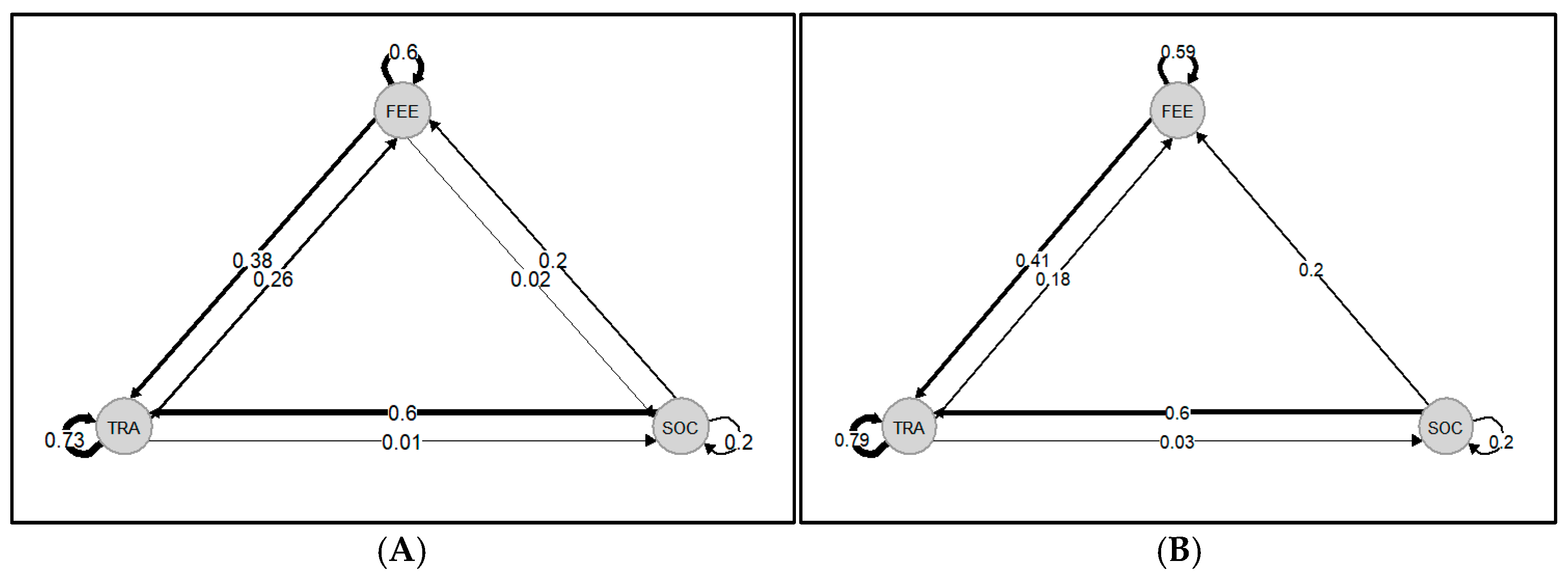
3.3. Behavioral Transitions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNCTAD: Review of Maritime Transport 2022. 2022. Available online: https://unctad.org/rmt2022 (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Cecchetti, A.; Stockin, K.A.; Gordon, J.; Azevedo, J.M.N. Short-term effects of tourism on the behaviour of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in the Azores. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2018, 98, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMaster, D.P.; Fowler, C.W.; Perry, S.L.; Richlen, M.F. Predation and competition: The impact of fisheries on marine-mammal populations over the next one hundred years. J. Mammal. 2001, 82, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, M.; Lynch, T.P.; Cato, D.H.; Harcourt, R.G. Response of travelling bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) to experimental approaches by a powerboat in Jervis Bay, New South Wales, Australia. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 127, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussean, D. The hidden cost of tourism: Detecting long-term effects of tourism using behavioral information. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, A.M.; Christiansen, F.; Martinez, E.; Pawley, M.D.M.; Orams, M.B.; Stockin, K.A. Behavioural effects of tourism on oceanic common dolphins, Delphinus sp., in New Zealand: The effects of markov analysis variations and current tour operator compliance with regulations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacek, S.; Wells, R.; Solow, A. Short-term effects of boat traffic on bottlenose dolphis, Tursiops truncatus, in Sarasota Bay, Florida. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 2001, 17, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockin, K.; Lusseau, D.; Binedell, V.; Wiseman, N.; Orams, M. Tourism affects the behavioural budget of the common dolphin Delphinus sp. in the Hauraki Gulf, New Zealand. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 355, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, I.; Crosti, R.; Angeletti, D.; Carosso, L.; David, L.; Di-Méglio, N.; Moulins, A.; Rosso, M.; Tepsich, P.; Arcangeli, A. Cetacean response to summer maritime traffic in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 109, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, C.O.; Akkaya, A.; Affinito, F.; Öztürk, B.; Öztürk, A.A. Behavioural changes and potential consequences of cetacean exposure to purse seine vessels in the Istanbul Strait, Turkey. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2020, 100, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, A.A.; Christiansen, F.; Öztürk, B.; Öztürk, A.A.; Erdoğan, M.A.; Watson, L.J. Marine vessels alter the behaviour of bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus in the Istanbul Strait, Turkey. Endanger. Species Res. 2017, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, F.; Rasmussen, M.; Lusseau, D. Whale watching disrupts feeding activities of minke whales on a feeding ground. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 478, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmuth, C.L.; Barrett-Lennard, L.G.; Steyn, D.Q.; Milsom, W.K. Estimation of southern resident killer whale exposure to exhaust emissions from whale-watching vessels and potential adverse health effects and toxicity thresholds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejder, L.; Samuels, A.; Whitehead, H.; Gales, N. Interpreting short-term behavioural responses to disturbance within a longitudinal perspective. Anim. Behav. 2006, 72, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassamali-Fox, A.; Christiansen, F.; May-Collado, L.J.; Ramos, E.A.; Kaplin, B.A. Tour boats affect the activity patterns of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Bocas del Toro, Panama. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, I.; Freitas, L.; Alves, F.; Ribeira, C.; Nicolau, C.; Ferreira, R.; Gonçalves, J.; Formingo, N. Marine traffic and potential impacts towards cetaceans within the Madeira EZZ. J. Cetacean Reasearch Manag. 2017, 16, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D. Male and female bottlenose dolphins Tursiops spp. have different strategies to avoid interactions with tour boats in Doubtful Sound, New Zealand. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 257, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Bain, D.; Smith, J.; Lusseau, D. Effects of vessels on behaviour patterns of individual southern resident killer whales Orcinus orca. Endanger. Species Res. 2009, 6, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, A.; Dill, L.M. Human-caused Disturbance Stimuli as a Form of Predation Risk. Conserv. Ecol. 2002, 6, art11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Green, M. Acoustic interaction of humpback whales and whale-watching boats. Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 49, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, D.; Gemmell, N.J.; Würsig, B. Behavioural Responses of Dusky Dolphin Groups (Lagenorhynchus obscurus) to Tour Vessels off Kaikoura, New Zealand. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamation, K.A.; Croft, D.B.; Shaughnessy, P.D.; Waples, K.A.; Briggs, S.V. Behavioral responses of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) to whale-watching vessels on the southeastern coast of Australia. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2009, 26, 98–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmel, G.; Courbis, S.; Sargeant-Green, H.; Markowitz, H. Effects of Human Traffic on the Movement Patterns of Hawaiian Spinner Dolphins (Stenella longirostris) in Kealakekua Bay, Hawaii. Aquat. Mamm. 2008, 34, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, S.A.; Salgado Kent, C.P.; Erbe, C.; Parnum, I.M. Effects of vessel traffic and underwater noise on the movement, behaviour and vocalisations of bottlenose dolphins in an urbanised estuary. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C. Underwater noise of whale-watching boats and the potential effects on killer whales (Orcinus orca), based on an acoustic impact model. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2002, 18, 394–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.R.; Couchinho, M.N.; dos Santos, M.E. Changes in the acoustic behavior of resident bottlenose dolphins near operating vessels. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2014, 30, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirotta, E.; Milor, R.; Quick, N.; Moretti, D.; Di Marzio, N.; Tyack, P.; Boyd, I.; Hastie, G. Vessel Noise Affects Beaked Whale Behavior: Results of a Dedicated Acoustic Response Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, W.D.; Scharffenberg, K.; MacPhee, S.; Hilliard, R.C.; Mouy, X.; Whalen, D.; Loseto, L.L.; Insley, S.J. Beluga Vocalizations Decrease in Response to Vessel Traffic in the Mackenzie River Estuary. Arctic 2019, 72, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwetz, S. Short Note: Influence of Vessel Traffic on Movements of Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins (Sousa chinensis) Off Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Aquat. Mamm. 2012, 38, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, D.; He, T.; Liang, B.; Zhang, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. A framework for the assessment of the spatial and temporal patterns of threatened coastal delphinids. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D. Effects of Tour Boats on the Behavior of Bottlenose Dolphins: Using Markov Chains to Model Anthropogenic Impacts. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakes, P.; Dall, S.R.X. Marine Mammal Behavior: A Review of Conservation Implications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.; França, S.; Luís, A.R.; Henriques, A.; Sá, R.; Grilo, C. Golfinhos no Tejo: Por um Estuário Mais Saudável. 2022. Available online: https://wwfeu.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/relatorio_golfinhos_no_tejo___por_um_estuario_mais_saudavel_2022.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Bearzi, G.; Reeves, R.R.; Notarbartolo-di-sciara, G.; Politi, E.; Cañadas, A.; Frantzis, A.; Mussi, B. Ecology, status and conservation of short-beaked common dolphins Delphinus delphis in the Mediterranean Sea. Mamm. Rev. 2003, 33, 224–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; Faustino, C.; Cid, A.; Quirin, A.; Matos, F.L.; Rosa, R.; Pearson, H.C. Common dolphin (Delphinus delphis) fission-fusion dynamics in the south coast of Portugal. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2022, 76, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.R.; Orams, M.B. Impacts of Ecotourism on Short-Beaked Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in Mercury Bay, New Zealand. Aquat. Mamm. 2006, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, R.; Brunton, D.H.; Dennis, T. Dolphin-watching tour boats change bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) behaviour. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 117, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, N.; Mateus, M.; Pinto, L.; Neves, R.; Dias, J.M. The Tagus Estuary as a Numerical Modeling Test Bed: A Review. Geosciences 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, M.; Fortunato, A.B.; Freire, P.; Rilo, A.; Taborda, R.; Freitas, M.C.; Andrade, C.; Silva, T.; Rodrigues, M.; Bertin, X.; et al. Evolution of the hydrodynamics of the Tagus estuary (Portugal) in the 21st century. Rev. Gestão Costeira Integr.-J. Integr. Coast. Zone Manag. 2015, 15, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto de Lisboa: Acessibilidades. Available online: https://www.portodelisboa.pt/acessibilidades (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Neumann, D. The Activity budget of free-ranging common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in the northwestern Bay of Plenty, New Zealand. Aquat. Mamm. 2001, 27, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Halekoh, U.; Højsgaard, S.; Yan, J. The R Package geepack for Generalized Estimating Equations. J. Stat. Softw. 2006, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, C.; Thomas, L. An Expert Elicitation of the Effects of Low Salinity Water Exposure on Bottlenose Dolphins. Oceans 2021, 2, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintzer, V.J.; Fazioli, K.L. Salinity and Water Temperature as Predictors of Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Encounter Rates in Upper Galveston Bay, Texas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 754686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.K.; Fandel, A.D.; Colbert, B.R.; Testa, J.C.; Bailey, H. Spatial and temporal variation in the occurrence of bottlenose dolphins in the Chesapeake Bay, USA, using citizen science sighting data. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, F.; Fernández, J.E.; Paladines, A.; Centeno, R.; Romero, J.; Burneo, S.F. Habitat use of the common bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) in the Gulf of Guayaquil, Ecuador: Management needs for a threatened population. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 223, 106174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fury, C.A.; Harrison, P.L. Seasonal variation and tidal influences on estuarine use by bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, S.A.; Salgado Kent, C.P.; Erbe, C. Occupancy of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus) in relation to vessel traffic, dredging, and environmental variables within a highly urbanised estuary. Hydrobiologia 2016, 792, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.; Mathews, M. Identifying Foraging Hotspots of Bottlenose Dolphins in a Highly Dynamic System: A Method to Enhance Conservation in Estuaries. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, P.H.; Dalla Rosa, L.; Fruet, P.F. Activity budgets and distribution of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Patos Lagoon estuary, southern Brazil. Latin Am. J. Aquat. Mamm. 2007, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cremer, M.J.; Simões-Lopes, P.C. The occurrence of Pontoporia blainvillei (Gervais & d’Orbigny) (Cetacea, Pontoporiidae) in an estuarine area in southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2005, 22, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, F.; Lusseau, D.; Stensland, E.; Berggren, P. Effects of tourist boats on the behaviour of Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins off the south coast of Zanzibar. Endanger. Species Res. 2010, 11, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.L.; Leung, S. Behavioral response of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis) to vessel traffic. Mar. Environ. Res. 2003, 56, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, E.; Azzolin, M.; Giacoma, C. Vessel traffic affects bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) behaviour in waters surrounding Lampedusa Island, south Italy. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2012, 92, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Marley, S.A.; Schoeman, R.P.; Smith, J.N.; Trigg, L.E.; Embling, C.B. The Effects of Ship Noise on Marine Mammals—A Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana Martín-Montalvo, B.; Hoarau, L.; Deffes, O.; Delaspre, S.; Delfour, F.; Landes, A.-E. Dolphin Watching and Compliance to Guidelines Affect Spinner Dolphins’ (Stenella longirostris) Behaviour in Reunion Island. Animals 2021, 11, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D.; Bejder, L. The Long-term Consequences of Short-term Responses to Disturbance Experiences from Whalewatching Impact Assessment. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.D.; Cockcroft, V.G. Diet of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) off the south-east coast of southern Africa: Opportunism or specialization? J. Zool. 1994, 234, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynier, L.; Pusineri, C.; Spitz, J.; Santos, M.B.; Pierce, G.J.; Ridoux, V. Intraspecific dietary variation in the short-beaked common dolphin Delphinus delphis in the Bay of Biscay: Importance of fat fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 354, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Behavioral Pattern (Abbreviation) | Definition |
|---|---|
| Feeding activities (FEE) | Individuals change direction frequently with variable diving periods (medium submersions (±1 min) to longer submersions (>1 min)). |
| Traveling (TRA) | Individuals move in a consistent direction with variable diving periods. |
| Socializing (SOC) | Individuals move in different directions with short submersions. It is frequent to find dolphins in physical contact with one another and having synchronized movements. |
| Resting (RES) | Individuals clustered at the surface in a constant direction. |
| Candidate Models | ||
|---|---|---|
| M1: Time~reaction to vessels M2: Time~reaction to vessels + activity patterns M3: Time~reaction to vessels + activity patterns + reaction to vessels * activity patterns | ||
| Model comparison | DF | p-Value |
| M1 vs. M2 | 1 | 0.75 |
| M1 vs. M3 | 3 | 0.27 |
| M3 vs. M3 | 2 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, I.M.; Jesus, N.; Castro, J.; Luís, A.R. The Effects of Vessel Traffic on the Behavior Patterns of Common Dolphins in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Animals 2024, 14, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202998
Silva IM, Jesus N, Castro J, Luís AR. The Effects of Vessel Traffic on the Behavior Patterns of Common Dolphins in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Animals. 2024; 14(20):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202998
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Iolanda M., Nádia Jesus, Joana Castro, and Ana Rita Luís. 2024. "The Effects of Vessel Traffic on the Behavior Patterns of Common Dolphins in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal)" Animals 14, no. 20: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202998
APA StyleSilva, I. M., Jesus, N., Castro, J., & Luís, A. R. (2024). The Effects of Vessel Traffic on the Behavior Patterns of Common Dolphins in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Animals, 14(20), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202998





