Supplementary Feeding Regulates Muscle Development of Oula Sheep (Tibetan Sheep, Ovis aries) Through Glucose Metabolism Pathway
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Moral Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
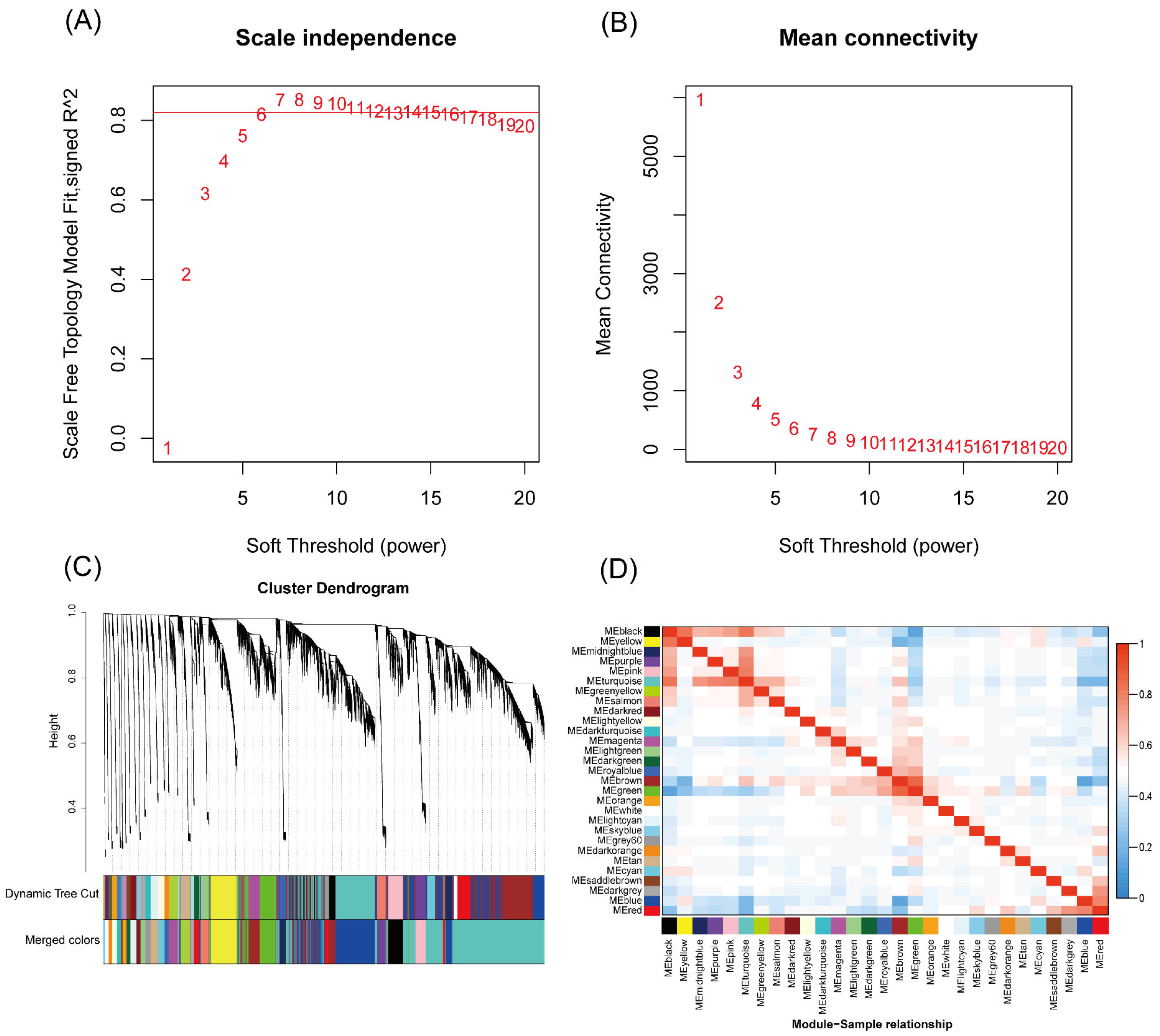
2.5. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
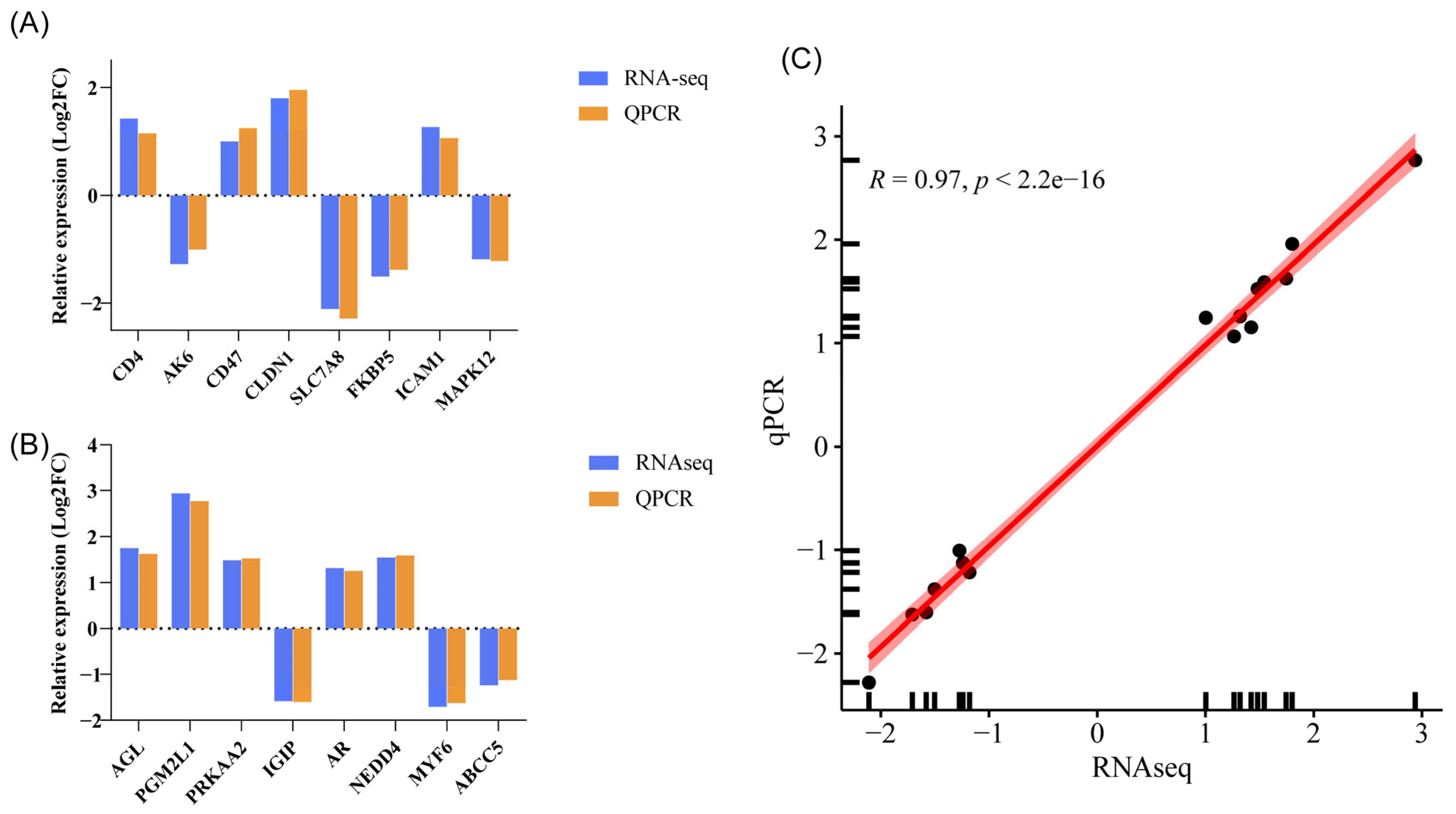
2.6. Validation by qPCR
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Differential Gene Expression Profiles
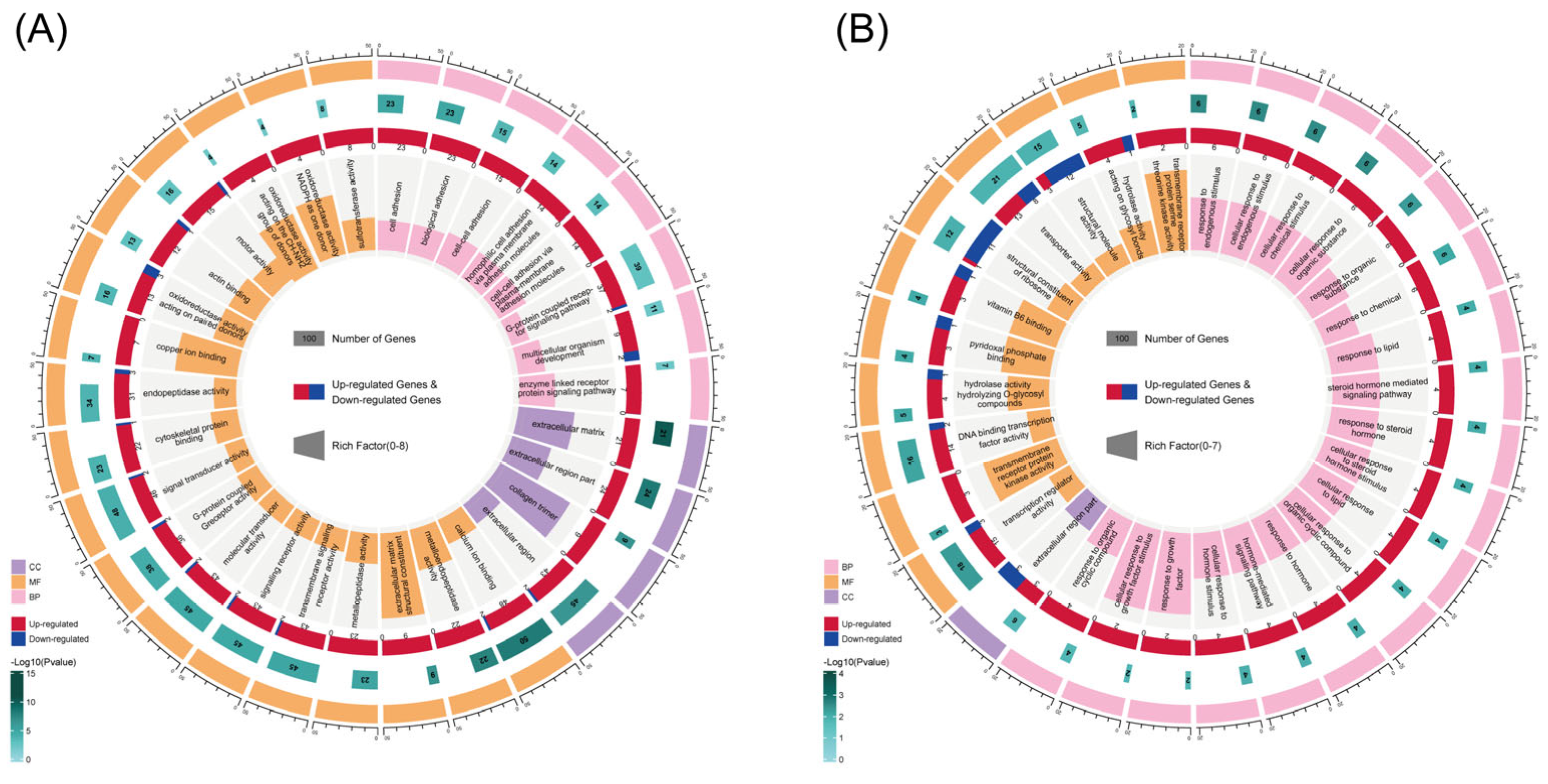
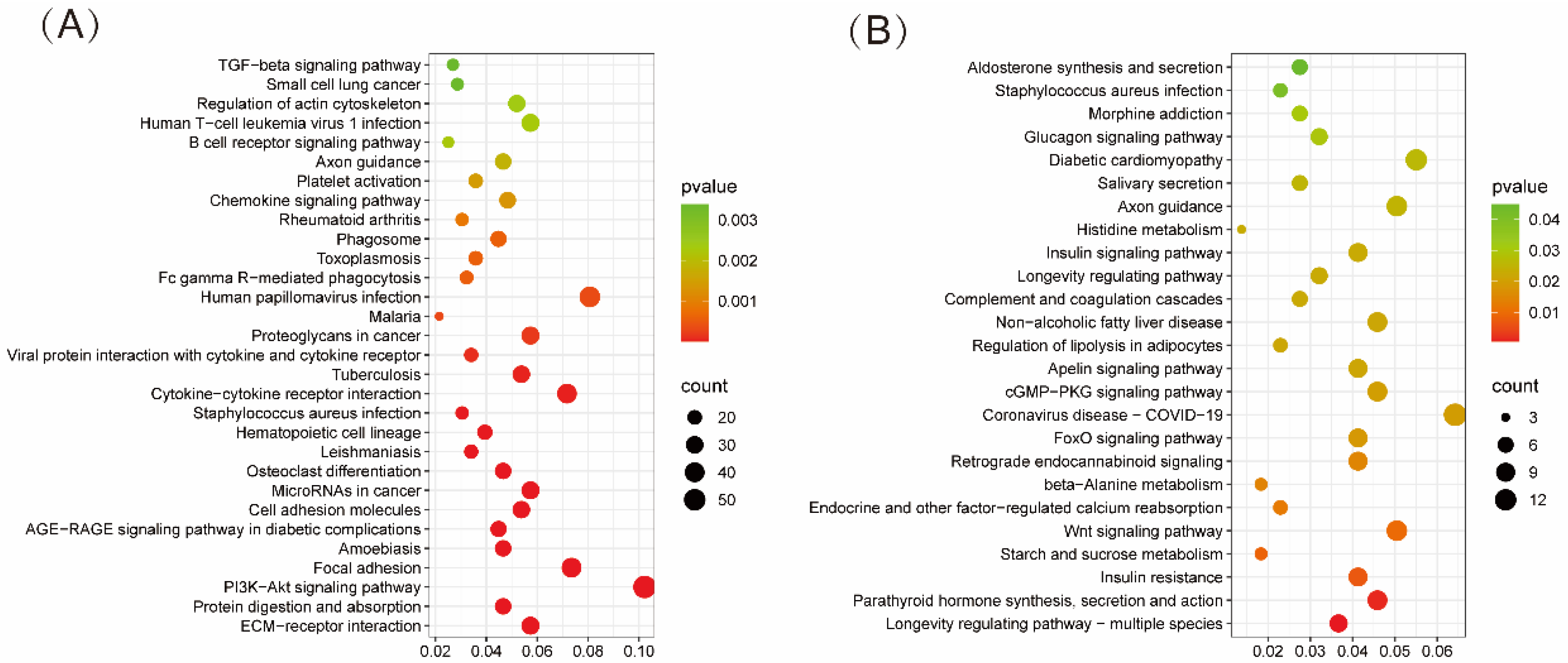
3.2. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
3.3. WGCNA Co-Expression Module
3.4. Construction of Gene Co-Expression Network and Screening of Hub Genes
3.5. qPCR Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, C.; Su, J. Single Base Editing System Mediates Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Genes GDF9 and FecB in Ouler Tibetan Sheep. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Tian, Z.; Chen, C.; Yu, Q. Concentrations of HSP27 and Aβ-crystallin in Oula Tibetan Sheep Meat and Their Relationship with Meat Quality during Postmortem Aging. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5253–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Wu, C.-C.; Li, N.; Weng, T.-H. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Myogenic Transcription Factors during Muscle Development and Pathogenesis. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2024, 45, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiargyrou, M. Mustn1: A Developmentally Regulated Pan-Musculoskeletal Cell Marker and Regulatory Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ye, J.; Lin, X.; Xue, H.; Zou, X.; Liu, G.; Deng, M.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Identification of Key Functional Genes and LncRNAs Influencing Muscle Growth and Development in Leizhou Black Goats. Genes 2023, 14, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, H.; Duan, M.; Shang, P.; Chamba, Y. The Role of the MYL4 Gene in Porcine Muscle Development and Its Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms. Animals 2024, 14, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, J.; Fu, L.; Cheng, S. Screening of Genes Related to Growth, Development and Meat Quality of Sahan Crossbred F1 Sheep Based on RNA-Seq Technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 831519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wei, Y.; Guo, D.; Liu, Z.; Niu, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; et al. Integration of ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq Analysis to Identify Key Genes in the Longissimus Dorsi Muscle Development of the Tianzhu White Yak. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Guo, D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Shi, B.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, J.; Han, X.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of mRNA and lncRNA Related to Muscle Growth and Development in Gannan Yak and Jeryak. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Liang, C.; Raza, S.H.A.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zan, L. Integration of RNA-Seq and ATAC-Seq Identifies Muscle-Regulated Hub Genes in Cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 925590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhao, X.; Xue, H.; Zou, X.; Liu, G.; Deng, M.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, Y. RNA-Seq Reveals miRNA and mRNA Co-Regulate Muscle Differentiation in Fetal Leizhou Goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 829769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Li, S.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Y. Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Role of lncRNA in Fatty Acid Metabolism in the Longissimus Thoracis Muscle of Tibetan Sheep at Different Ages. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 847077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, M.; Na, S.-Y.; Krishnamoorthy, G. A Novel CD4 Knockout Mouse Strain with a Spontaneous Frameshift Mutation in the CD4 Locus. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Willis-Owen, S.A.G.; Spiegel, S.; Lloyd, C.M.; Moffatt, M.F.; Cookson, W.O.C.M. The ORMDL3 Asthma Gene Regulates ICAM1 and Has Multiple Effects on Cellular Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Qiu, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Yu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Olanzapine Induces Adipogenesis and Glucose Uptake by Activating Glycolysis and Synergizing with the PI3K-AKT Pathway. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 23, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitaloka, D.M.I.; Ko, C.-H.; Lin, M.-T.; Yeh, S.-L.; Yeh, C.-L. Glutamine Administration Promotes Hepatic Glucose Homeostasis through Regulating the PI3K/Akt Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice with Limb Ischemia. Nutr. Res. 2019, 68, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Song, S.; Wang, G.; Su, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. AKT/mTOR-Mediated Autophagic Signaling Is Associated with TCDD-Induced Cleft Palate. Reprod. Toxicol. 2024, 130, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-T.; Leung, P.-C.; Wong, C.-K.; Wang, D.-J. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Vitamin D on COVID-19 Induced Glioblastoma Recurrence via the PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksbjerg, N.; Therkildsen, M. Chapter 3—Myogenesis and Muscle Growth and Meat Quality. In New Aspects of Meat Quality; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Purslow, P.P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 33–62. ISBN 978-0-08-100593-4. [Google Scholar]
- Herszberg, B.; Mata, X.; Giulotto, E.; Decaunes, P.; Piras, F.M.; Chowdhary, B.P.; Chaffaux, S.; Guérin, G. Characterization of the Equine Glycogen Debranching Enzyme Gene (AGL): Genomic and cDNA Structure, Localization, Polymorphism and Expression. Gene 2007, 404, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Rossmann, H.; Bucerzan, S.; Grigorescu-Sido, P. A Novel Nonsense Mutation of the AGL Gene in a Romanian Patient with Glycogen Storage Disease Type IIIa. Case Rep. Genet. 2016, 2016, 8154910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anushiravani, A.; Faghihi, M.A.; Dastsooz, H.; Lankarani, K.B. Glycogen Storage Disease IIIa: A Private Homozygous Splice Site Mutation in AGL Gene. Gene Rep. 2017, 9, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchiari, S.; Donati, M.a.; Melis, D.; Filocamo, M.; Parini, R.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.p. Mutational Analysis of the AGL Gene: Five Novel Mutations in GSD III Patients. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 22, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morava, E.; Schatz, U.A.; Torring, P.M.; Abbott, M.-A.; Baumann, M.; Brasch-Andersen, C.; Chevalier, N.; Dunkhase-Heinl, U.; Fleger, M.; Haack, T.B.; et al. Impaired Glucose-1,6-Biphosphate Production Due to Bi-Allelic PGM2L1 Mutations Is Associated with a Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliekal, P.; Sokolova, T.; Vertommen, D.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M.; Van Schaftingen, E. Molecular Identification of Mammalian Phosphopentomutase and Glucose-1,6-Bisphosphate Synthase, Two Members of the α-D-Phosphohexomutase Family*. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31844–31851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.S.; Woerl, P.; Garmsiri, C.; Weber, D.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Hotze, M.; Kuenkel, L.; Lang, L.; Erlacher, M.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Glucose-1,6-Bisphosphate: A New Gatekeeper of Cerebral Mitochondrial Pyruvate Uptake. Mol. Metab. 2024, 88, 102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Lu, H.; Cui, Y.; Yu, S.; Ma, R.; Yang, S.; He, J. PRKAA2-Mediated Mitophagy Regulates Oxygen Consumption in Yak Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells under Chronic Hypoxia. Cell. Signal. 2024, 124, 111450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Song, R. Study of the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Role in Energy Metabolism Changes during the Postmortem Aging of Yak Longissimus Dorsal. Animals 2020, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, D.; et al. Polymorphism of Sheep PRKAA2 Gene and Its Association with Growth Traits. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic, S.; Simeunovic, V.; Prvulovic, M.; Dakic, T.; Jevdjovic, T.; Sokanovic, S.; Kanazir, S.; Mladenovic, A. Dietary Restriction Alters Insulin Signaling Pathway in the Brain. BioFactors 2024, 50, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennicke, C.; Cochemé, H.M. Redox Regulation of the Insulin Signalling Pathway. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredients | Contents % | Nutrient Levels (2) | Contents % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 39.92 | CP | 15.09 |
| Soybean meal | 12.99 | ME (MJ/kg) | 2.62 |
| Wheat bran | 7.73 | Ca | 0.79 |
| Rapeseed cake | 6.93 | TP | 0.4 |
| Limestone | 1.42 | Lys | 0.67 |
| Premix (1) | 1.01 | Met | 0.26 |
| Dried corn stalk | 30.00 | NDF | 33.34 |
| Total | 100.00 | ADF | 19.79 |
| Gene | Accession No. | Forward (5′ → 3′) | Reverse (5′ → 3′) | Tm/°C | Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTB | XM_060405599.1 | GTCAGCCGGTCCCATGGTC | ACACGGAGTACTTGCGCTC | 61.4 | 102 |
| CD4 | NM_001129902.1 | AACACTGAACTGAGCCATCGAGT | ACAGGTATAAGTCCCCGAGTCA | 61.1 | 111 |
| ICAM1 | NM_001009731.1 | GCAGTATCTCCTGTGACCGA | AGTTTGAGTAGCACAACGGGT | 59.4 | 141 |
| CD47 | XM_060417299.1 | TGTCCAAGCCCAGCAGTAAC | TCCTACGACGGCATCACTCT | 60.3 | 104 |
| CLDN1 | NM_001185016.1 | AGTGACAACATCGTGACGGC | TCAGCAAGGAGTCGAAGACTTT | 60.3 | 106 |
| SLC7A8 | XM_004010333.6 | AAGGTGTGCTAGAGAATGCCG | GTGACCCCGAGCTCAGCATA | 61 | 109 |
| AK6 | NM_001285802.2 | GAATGGCCACTGCACAATCA | ATCCACCTCCTAGTCTAACAGC | 58.9 | 106 |
| FKBP5 | XM_042237057.2 | GAACGAGTTCGAGTCAGCCA | CTCGTTGTGCTCCTTAGCCT | 118 | 118 |
| AGL | XM_012176992.4 | AATTACCCACTTCCTGGAGAAGC | TGAAATGATCCAGCTTGTTGAAGAT | 59.8 | 131 |
| PGM2L1 | XM_042233221.2 | TTAGCCTTCGCCAGAACATCG | TGGCCAGATGACACACAGAGAG | 61.4 | 109 |
| PRKAA2 | NM_001112816.1 | AGCACGATGTCCACTGGATG | TCCAGCTGCTTCATAGCTCG | 60.0 | 144 |
| AR | NM_001308584.1 | CAGCTGCTCCACCGATCTTAAA | AGATGGTCGAACTGCCTCCTA | 60.5 | 179 |
| NEDD4 | XM_027971804.2 | CACTCAGGGTTTTGATGGCG | CTGAGAAGCATCAATGGCCAAG | 59.7 | 136 |
| MYF6 | XM_060411574.1 | GAACCGGGATGTGCCCTG | GTCCACGATGGAAGAGAGGC | 60.4 | 184 |
| IGIP | XM_060415335.1 | AAGAAGCGCAGTGTGTCGG | CAAGCCGGCTGATGCACAA | 61.3 | 118 |
| Sample | Raw Reads Number | Clean Reads Number | Clean Reads Rate (%) | Clean Q30 Bases Rate (%) | GC Content (%) | Mapping Ratio (%) | Unique Mapping Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUS1 | 46,648,844 | 42,782,078 | 91.71 | 93.42 | 48.45 | 93.81 | 80.77 |
| LUS2 | 42,687,700 | 39,800,028 | 93.24 | 92.08 | 50.71 | 94.30 | 83.45 |
| LUS3 | 48,102,646 | 47,210,960 | 98.15 | 93.07 | 52.03 | 95.93 | 84.65 |
| LUS4 | 49,855,830 | 48,932,740 | 98.15 | 93.05 | 52.03 | 95.93 | 84.65 |
| LUS5 | 49,225,048 | 47,874,618 | 97.26 | 93.50 | 52.05 | 95.87 | 84.82 |
| LS1 | 41,212,104 | 38,519,372 | 93.47 | 91.99 | 51.8 | 94.64 | 83.34 |
| LS2 | 46,013,906 | 43,545,542 | 94.64 | 92.17 | 49.36 | 95.43 | 81.43 |
| LS3 | 45,748,468 | 43,155,138 | 94.33 | 92.39 | 52.42 | 94.87 | 84.31 |
| LS4 | 45,241,120 | 41,792,798 | 92.38 | 92.5 | 49.01 | 94.89 | 80.92 |
| LS5 | 46,274,008 | 43,830,938 | 94.72 | 92.06 | 51.92 | 94.95 | 83.81 |
| GUS1 | 42,393,600 | 38,654,058 | 91.18 | 93.59 | 49.65 | 93.48 | 80.62 |
| GUS2 | 49,635,300 | 45,807,122 | 92.29 | 93.37 | 49.22 | 95.06 | 78.09 |
| GUS3 | 46,117,250 | 42,157,564 | 91.41 | 93.13 | 48.34 | 94.36 | 75.47 |
| GUS4 | 43,868,834 | 43,798,780 | 99.84 | 92.93 | 49.18 | 93.68 | 77.80 |
| GUS5 | 46,738,460 | 45,956,588 | 98.33 | 93.20 | 51.30 | 96.24 | 83.05 |
| GS1 | 43,475,578 | 39,881,436 | 91.73 | 93.4 | 51.23 | 95.01 | 82.66 |
| GS2 | 48,228,642 | 45,179,514 | 93.68 | 91.42 | 50.91 | 94.66 | 81.91 |
| GS3 | 47,582,042 | 45,289,166 | 95.18 | 92.23 | 51.92 | 95.32 | 84.98 |
| GS4 | 48,922,814 | 45,936,318 | 93.90 | 92.41 | 50.03 | 94.93 | 80.61 |
| GS5 | 50,433,518 | 49,632,898 | 98.41 | 93.39 | 52.25 | 96.45 | 85.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, M.; Raza, S.H.A. Supplementary Feeding Regulates Muscle Development of Oula Sheep (Tibetan Sheep, Ovis aries) Through Glucose Metabolism Pathway. Animals 2025, 15, 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172626
Li Y, Wang Y, Yan M, Wu S, Liu M, Raza SHA. Supplementary Feeding Regulates Muscle Development of Oula Sheep (Tibetan Sheep, Ovis aries) Through Glucose Metabolism Pathway. Animals. 2025; 15(17):2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172626
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yumeng, Yanhao Wang, Mingyi Yan, Sen Wu, Meng Liu, and Sayed Haidar Abbas Raza. 2025. "Supplementary Feeding Regulates Muscle Development of Oula Sheep (Tibetan Sheep, Ovis aries) Through Glucose Metabolism Pathway" Animals 15, no. 17: 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172626
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, Y., Yan, M., Wu, S., Liu, M., & Raza, S. H. A. (2025). Supplementary Feeding Regulates Muscle Development of Oula Sheep (Tibetan Sheep, Ovis aries) Through Glucose Metabolism Pathway. Animals, 15(17), 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172626






