GRA86 Is a Novel Dense Granule Protein Important for Virulence and Bradyzoite Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. T. gondii Strains and Cell Culture
2.3. Construction of Transgenic Parasite Strains
2.4. Bradyzoite Conversion
2.5. Indirect Immunofluorescence Analysis (IFA)
2.6. Subcellular Localization of Novel GRAs
2.7. Plaque Assays
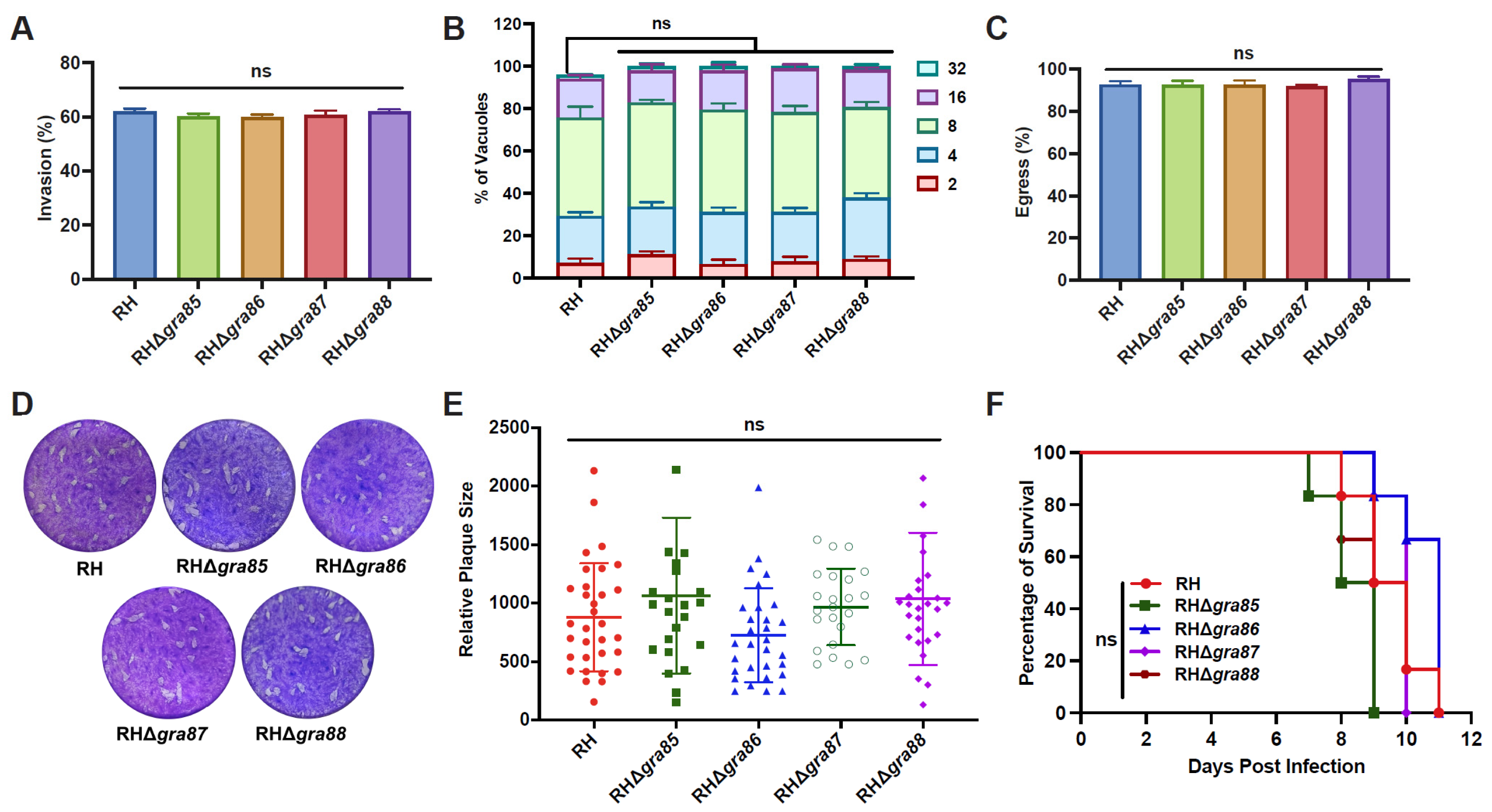
2.8. Invasion Assays
2.9. Intracellular Replication and Egress Assays
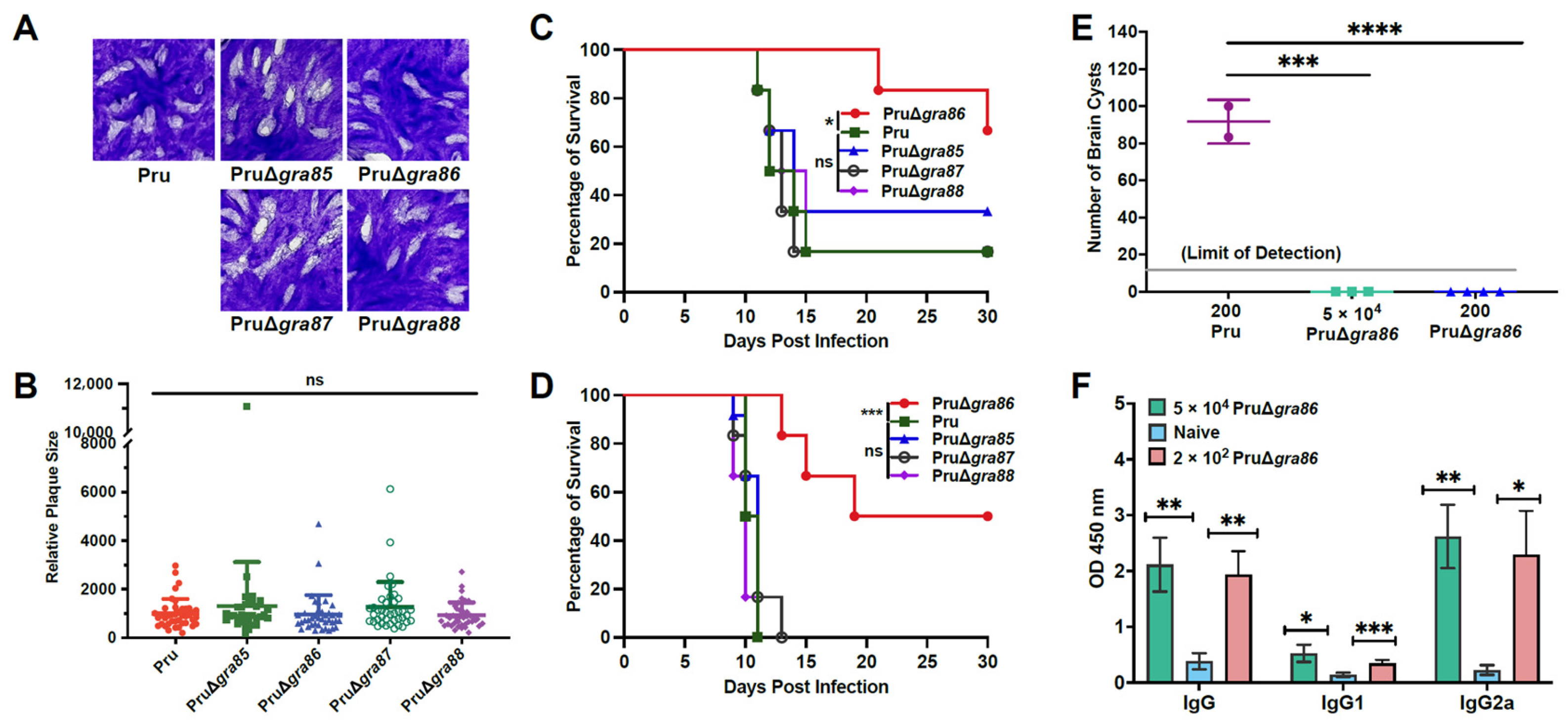
2.10. Virulence Assessment
2.11. RNA Sequencing and Real-Time Quantitative qPCR (RT-qPCR)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression of Four Newly Identified Toxoplasma Dense Granule Proteins in Both Tachyzoite and Bradyzoite Stages
3.2. Successful Construction of Four Novel GRA Gene Knockout Strains
3.3. Four Novel GRAs Are Dispensable for In Vitro and In Vivo Fitness of the RH Strain
3.4. Knockout of the GRA86 Gene Reduces Pru Strain Virulence and Brain Cyst Burden In Vivo
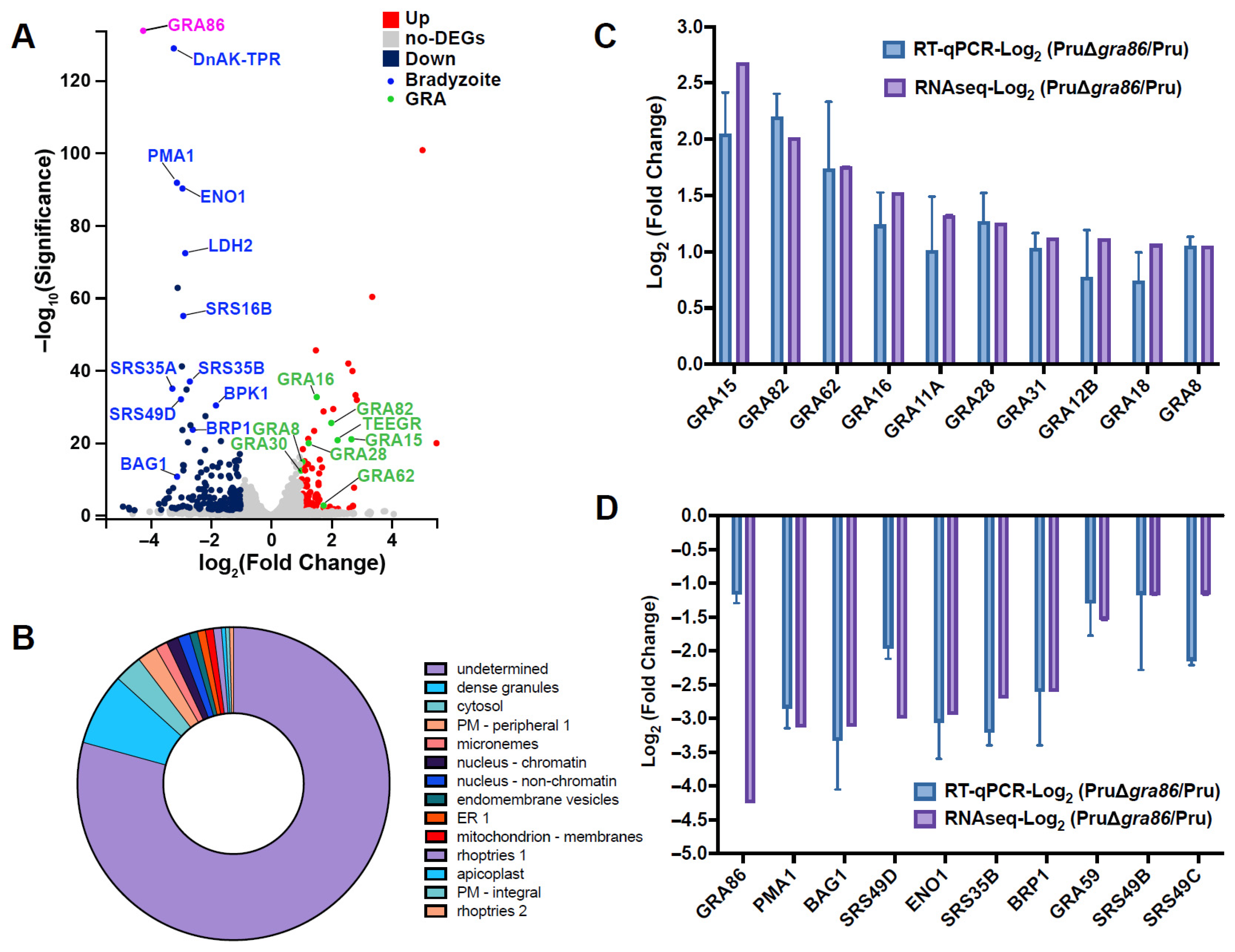
3.5. Deletion of gra86 Upregulates Host-Interaction Associated GRAs
3.6. Deletion of gra86 Downregulates Bradyzoite-Associated Genes
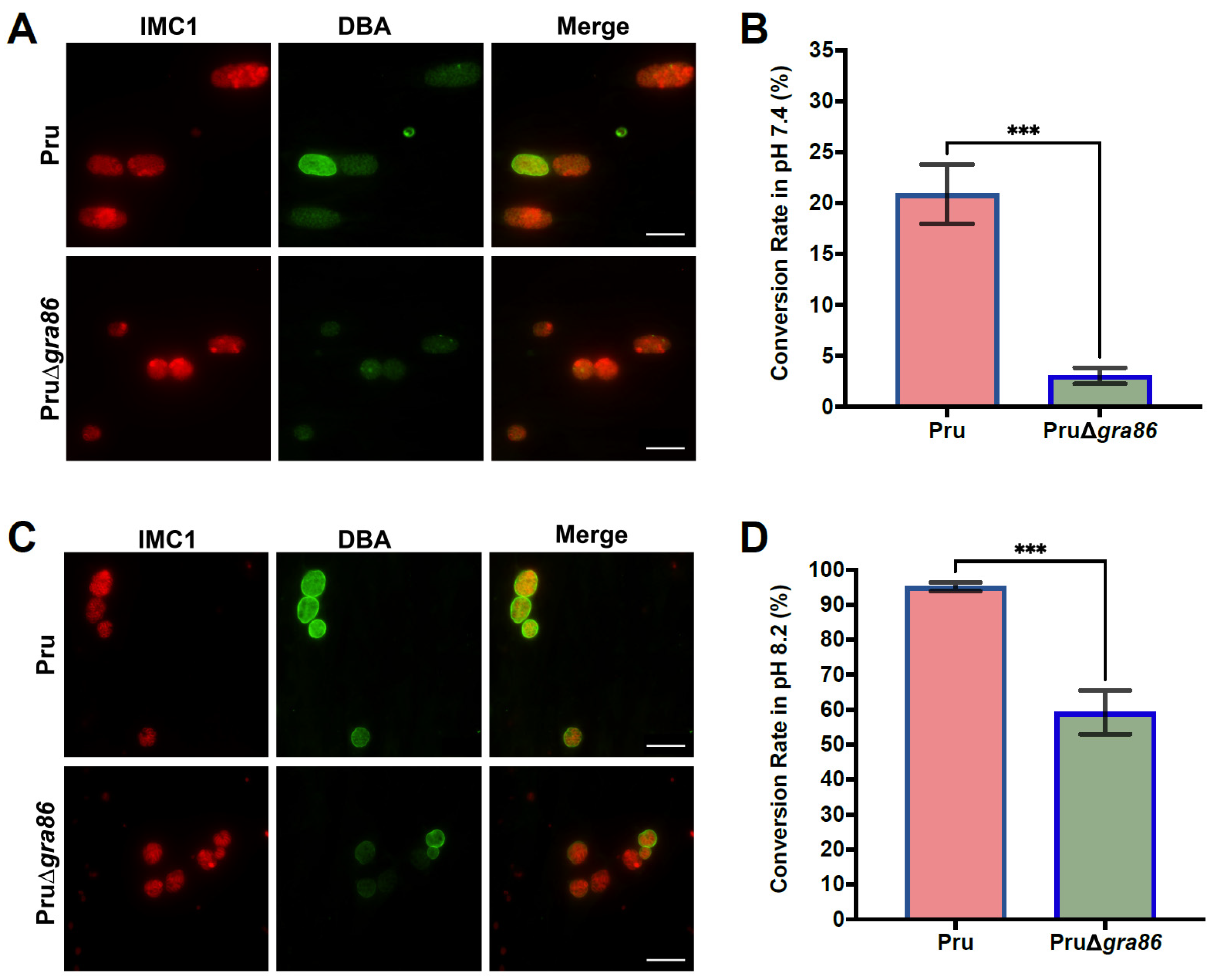
3.7. Loss of gra86 Impairs Bradyzoite Differentiation In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Milne, G.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Toxoplasma gondii: An underestimated threat? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Rinkenberger, N.; Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii infection and its implications within the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of cerebral toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, F.; Mc Leod, R.; Ajzenberg, D.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.; Kieffer, F.; Mandelbrot, L.; Sibley, L.D.; Pelloux, H.; Villena, I.; Wallon, M.; et al. Congenital toxoplasmosis in France and the United States: One parasite, two diverging approaches. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G.; Gamble, H.R.; Fakhri, Y.; Shiadeh, M.N.; Foroutan, M.; Behniafar, H.; Taghipour, A.; Maldonado, Y.A.; et al. Acute Toxoplasma infection in pregnant women worldwide: Asystematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Darde, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blader, I.; Coleman, B.; Chen, C.; Gubbels, M. Lytic cycle of Toxoplasma gondii: 15 years later. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, R.E.; McLeod, R.; Roberts, C.W. Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite interconversion. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, V.; Tampaki, Z.; Kim, K.; Sullivan, W.J., Jr. A latent ability to persist: Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, B.; Frickel, E.M. The Toxoplasma parasitophorous vacuole: An evolving host-parasite frontier. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sangare, L.O.; Paredes-Santos, T.C.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma mechanisms for delivery of proteins and uptake of nutrients across the host-pathogen interface. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.B.; Pearce, C.S.; Heaslip, A.T. Dense granule biogenesis, secretion, and function in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2022, 69, e12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.A.; Olias, P.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma effectors targeting host signaling and transcription. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 615–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, M.L.; Shah, N.; Boothroyd, J.C. The Toxoplasma pseudokinase ROP5 is an allosteric inhibitor of the immunity-related GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27849–27858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheridge, R.D.; Alaganan, A.; Tang, K.; Lou, H.J.; Turk, B.E.; Sibley, L.D. The Toxoplasma pseudokinase ROP5 forms complexes with ROP18 and ROP17 kinases that synergize to control acute virulence in mice. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanns, T.; Muller, U.B.; Konen-Waisman, S.; Howard, J.C.; Steinfeldt, T. The Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein ROP18 is an Irga6-specific kinase and regulated by the dense granule protein GRA7. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.; Yogavel, M.; Curt-Varesano, A.; Curt-Bertini, R.; Hussain, T.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; Coute, Y.; Pelloux, H.; Tardieux, I.; et al. A Toxoplasma dense granule protein, GRA24, modulates the early immune response to infection by promoting a direct and sustained host p38 MAPK activation. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2071–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Olias, P.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Park, E.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii effector TgIST blocks type I interferon signaling to promote infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17480–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, G.; Braun, L.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.; Vollaire, J.; Josserand, V.; Bertini, R.; Varesano, A.; Touquet, B.; De Bock, P.; Coute, Y.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii TgIST co-opts host chromatin repressors dampening STAT1-dependent gene regulation and IFN-γ-mediated host defenses. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyonda, M.; Hammoudi, P.; Ye, S.; Maire, J.; Marq, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Soldati-Favre, D. Toxoplasma gondii GRA60 is an effector protein that modulates host cell autonomous immunity and contributes to virulence. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, W.J.; Holmes, M.J.; Arrizabalaga, G. The secreted acid phosphatase domain-containing GRA44 from Toxoplasma gondii is required for c-Myc induction in infected cells. Msphere 2020, 5, e00877-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, A.M.; Theisen, T.C.; Mendoza, A.G.; Marino, N.D.; Panas, M.W.; Boothroyd, J.C. Coimmunoprecipitation with MYR1 identifies three additional proteins within the Toxoplasma gondii parasitophorous vacuole required for translocation of dense granule effectors into host cells. Msphere 2020, 5, e00858-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sangare, L.; Paredes-Santos, T.; Hassan, M.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Furuta, A.; Markus, B.; Lourido, S.; Saeij, J. Genome-wide screens identify Toxoplasma gondii determinants of parasite fitness in IFNγ-activated murine macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Panas, M.W.; Marino, N.D.; Lee, M.C.; Buchholz, K.R.; Kelly, F.D.; Bednarski, J.J.; Sleckman, B.P.; Pourmand, N.; Boothroyd, J.C. A novel secreted protein, MYR1, is central to Toxoplasma’s manipulation of host cells. mBio 2016, 7, e02231-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panas, M.; Naor, A.; Cygan, A.; Boothroyd, J. Toxoplasma controls host cyclin E expression through the use of a novel MYR1-dependent effector protein, HCE1. mBio 2019, 10, e00674-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougdour, A.; Durandau, E.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.; Ortet, P.; Barakat, M.; Kieffer, S.; Curt-Varesano, A.; Curt-Bertini, R.; Bastien, O.; Coute, Y.; et al. Host cell subversion by Toxoplasma GRA16, an exported dense granule protein that targets the host cell nucleus and alters gene expression. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, L.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.; Hammoudi, P.; Cannella, D.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; Vollaire, J.; Josserand, V.; Touquet, B.; Coute, Y.; Tardieux, I.; et al. The Toxoplasma effector TEEGR promotes parasite persistence by modulating NF-κB signalling via EZH2. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosowski, E.E.; Lu, D.; Julien, L.; Rodda, L.; Gaiser, R.A.; Jensen, K.D.; Saeij, J.P. Strain-specific activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by GRA15, a novel Toxoplasma gondii dense granule protein. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, V.; Tomita, T.; Sugi, T.; Mayoral, J.; Han, B.; Yakubu, R.R.; Williams, T.; Horta, A.; Ma, Y.; Weiss, L.M. The Toxoplasma gondii cyst wall interactome. mBio 2020, 11, e02699-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, R.; Fox, B.; Falla, A.; Bzik, D. Toxoplasma gondii intravacuolar-network-associated dense granule proteins regulate maturation of the cyst matrix and cyst wall. Msphere 2019, 4, e00487-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, R.; Fox, B.; Bzik, D. Toxoplasma gondii parasitophorous vacuole membrane-associated dense granule proteins regulate maturation of the cyst wall. Msphere 2020, 5, e00851-19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tu, V.; Mayoral, J.; Sugi, T.; Tomita, T.; Han, B.; Ma, Y.F.; Weiss, L.M. Enrichment and proteomic characterization of the cyst wall from in vitro Toxoplasma gondii cysts. mBio 2019, 10, e00469-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadipuram, S.M.; Thind, A.C.; Rayatpisheh, S.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Bradley, P.J. Proximity biotinylation reveals novel secreted dense granule proteins of Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoites. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232552. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.N.; Sun, L.X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Li, T.T.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Fu, B.Q.; Zhu, X.Q.; et al. A newly characterized dense granule protein (GRA76) is important for the growth and virulence of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.N.; Li, T.T.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.X.; Wu, X.J.; Fu, B.Q.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, J.L. GRA47 is important for the morphology and permeability of the parasitophorous vacuole in Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kang, Y.; Wu, Z.X.; Yang, S.F.; Tian, Y.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zheng, X.N. Live-attenuated PruΔgra72 strain of Toxoplasma gondii induces strong protective immunity against acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. Parasit. Vectors 2024, 17, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Bai, M.J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liang, Q.L.; Li, T.T.; Cao, X.Z.; Zhu, X.Q. Novel roles of dense granule protein 12 (GRA12) in Toxoplasma gondii infection. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 3165–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Sibley, L.D. Modulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii virulence effectors. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L.D.; Ajioka, J.W. Population structure of Toxoplasma gondii: Clonal expansion driven by infrequent recombination and selective sweeps. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L.D.; Boothroyd, J.C. Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 1992, 359, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Liang, Q.L.; Li, T.T.; He, J.J.; Bai, M.J.; Cao, X.Z.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Toxoplasma gondii tkl1 deletion mutant is a promising vaccine against acute, chronic, and congenital toxoplasmosis in mice. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Brown, K.M.; Lee, T.D.; Sibley, L.D. Efficient gene disruption in diverse strains of Toxoplasma gondii using CRISPR/CAS9. mBio 2014, 5, e01114-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, N.Z.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.X.; Zhang, Z.W.; Fu, B.Q.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. The transcription factor AP2XI-2 is a key negative regulator of Toxoplasma gondii merogony. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Lei, C.L.; Wang, J.L.; Fu, B.Q.; Luo, J.X.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, T.T. Trx4, a novel thioredoxin protein, is important for Toxoplasma gondii fitness. Parasit. Vectors 2024, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liang, Q.L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Sibley, L.D.; Zhu, X.Q. The protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme is a key regulator of starch metabolism and bradyzoite differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.J.; Gao, J.; Li, R.; Ma, Z.Y.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Wu, X.J.; Zheng, X.N.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.Q. Functional characterization of six eukaryotic translation initiation factors of Toxoplasma gondii using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.N.; Wang, J.L.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Sun, L.X.; Wang, X.C.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, T.T. Functional characterization of 15 novel dense granule proteins in Toxoplasma gondii using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0307822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.L.; Nie, L.B.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Li, T.T.; Sun, L.X.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Fu, B.Q.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, J.L. The Toxoplasma protein phosphatase 6 catalytic subunit (TgPP6C) is essential for cell cycle progression and virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.L.; Sun, L.X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Cao, X.Z.; Nie, L.B.; Li, T.T.; Li, T.S.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, J.L. RHΔgra17Δnpt1 strain of Toxoplasma gondii elicits protective immunity against acute, chronic and congenital Toxoplasmosis in mice. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.B.; Zou, Y.; He, J.J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liu, G.H.; Hu, M.H.; Wang, S.L.; Zhu, X.Q. Global profiling of lncRNAs-miRNAs-mRNAs reveals differential expression of coding genes and non-coding RNAs in the lung of beagle dogs at different stages of Toxocara canis infection. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barylyuk, K.; Koreny, L.; Ke, H.; Butterworth, S.; Crook, O.M.; Lassadi, I.; Gupta, V.; Tromer, E.; Mourier, T.; Stevens, T.J.; et al. A comprehensive subcellular atlas of the Toxoplasma proteome via hyperLOPIT provides spatial context for protein functions. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 752–766.E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, D.; Kaplan, A.; Lis, A.; Bett, G.; Rosowski, E.; Cirelli, K.; Bougdour, A.; Sidik, S.; Beck, J.; Lourido, S.; et al. The Toxoplasma dense granule proteins GRA17 and GRA23 mediate the movement of small molecules between the host and the parasitophorous vacuole. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme-Walker, V.; Abrivard, M.; Lagal, V.; Anderson, K.; Perazzi, A.; Gonzalez, V.; Page, C.; Chauvet, J.; Ochoa, W.; Volkmann, N.; et al. Toxofilin upregulates the host cortical actin cytoskeleton dynamics, facilitating Toxoplasma invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4333–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Feng, J.X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, X.H.; Tardieux, I.; Liu, L.X. Protein phosphatase 2C of Toxoplasma gondii interacts with human SSRP1 and negatively regulates cell apoptosis. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 883–893. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, J.D.; Nolan, S.J.; Porter, C.; Ehrenman, K.; Hartman, E.J.; Hsia, R.C.; Coppens, I. The parasite Toxoplasma sequesters diverse Rab host vesicles within an intravacuolar network. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 4235–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.A.; Gaete, P.S.; Swale, C.; Maru, P.; Contreras, J.E.; Saeij, J.P.J. Two Toxoplasma gondii putative pore-forming proteins, GRA47 and GRA72, influence small molecule permeability of the parasitophorous vacuole. mBio 2024, 15, e0308123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougdour, A.; Tardieux, I.; Hakimi, M.A. Toxoplasma exports dense granule proteins beyond the vacuole to the host cell nucleus and rewires the host genome expression. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.D.; Ravindran, S.; Kim, S.K.; Boothroyd, J.C. The Toxoplasma gondii dense granule protein GRA7 is phosphorylated upon invasion and forms an unexpected association with the rhoptry proteins ROP2 and ROP4. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5853–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangare, L.O.; Yang, N.; Konstantinou, E.K.; Lu, D.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Young, L.H.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma GRA15 Activates the NF-κB Pathway through Interactions with TNF Receptor-Associated Factors. mBio 2019, 10, e00808-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olias, P.; Etheridge, R.D.; Zhang, Y.; Holtzman, M.J.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma effector recruits the Mi-2/NuRD complex to repress STAT1 transcription and block IFN-γ-dependent gene expression. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Bzik, D.J.; Ma, Y.F.; Fox, B.A.; Markillie, L.M.; Taylor, R.C.; Kim, K.; Weiss, L.M. The Toxoplasma gondii cyst wall protein CST1 is critical for cyst wall integrity and promotes bradyzoite persistence. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.S.; Sasai, M.; Ohshima, J.; Lee, Y.; Bando, H.; Takeda, K.; Yamamoto, M. Selective and strain-specific NFAT4 activation by the Toxoplasma gondii polymorphic dense granule protein GRA6. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2013–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Braun, L.; Kraut, A.; Touquet, B.; Coute, Y.; Tardieux, I.; Hakimi, M.A.; Bougdour, A. Characterization of a Toxoplasma effector uncovers an alternative GSK3/beta-catenin-regulatory pathway of inflammation. eLife 2018, 7, e39887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hoeve, A.L.; Braun, L.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Olivera, G.C.; Bougdour, A.; Belmudes, L.; Coute, Y.; Saeij, J.P.J.; Hakimi, M.A.; Barragan, A. The Toxoplasma effector GRA28 promotes parasite dissemination by inducing dendritic cell-like migratory properties in infected macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1570–1588.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panas, M.W.; Ferrel, A.; Naor, A.; Tenborg, E.; Lorenzi, H.A.; Boothroyd, J.C. Translocation of dense granule effectors across the parasitophorous vacuole membrane in Toxoplasma-infected cells requires the activity of ROP17, a rhoptry protein kinase. Msphere 2019, 4, e00276-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cirelli, K.; Barros, P.; Sangare, L.; Butty, V.; Hassan, M.; Pesavento, P.; Mete, A.; Saeij, J. Three Toxoplasma gondii dense granule proteins are required for induction of lewis rat macrophage pyroptosis. mBio 2019, 10, e02388-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, Y.; Hashizaki, E.; Sasai, M.; Yamamoto, M. Host genetics highlights IFN-γ-dependent Toxoplasma genes encoding secreted and non-secreted virulence factors in in vivo CRISPR screens. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
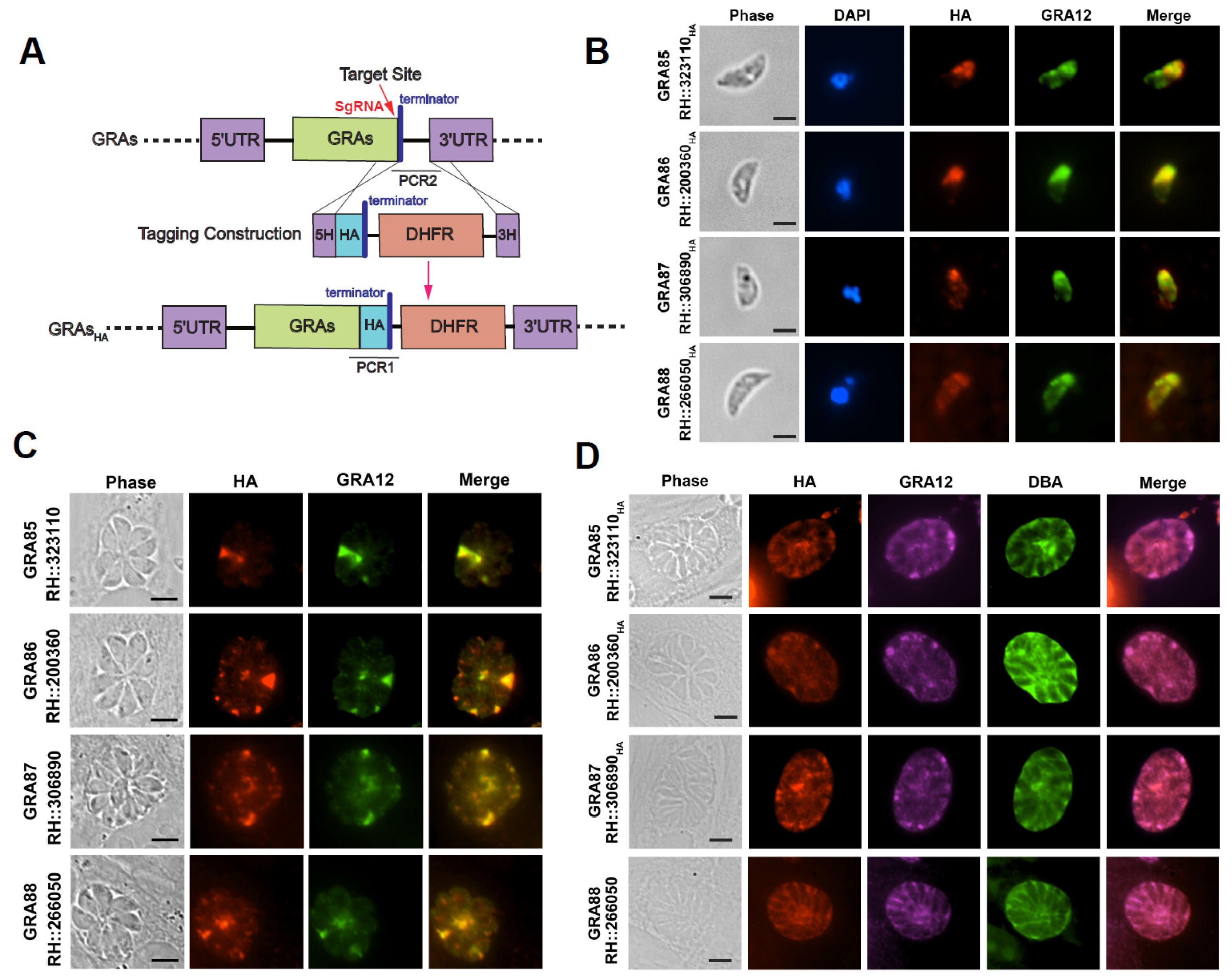

| GRAs | Gene ID | Product Description | Predicted Location | Exons | Phenotype Value | Mol Wt (kDa) | Predicted Signal Peptide | TMHMM * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRA85 | TGME49_323110 | Hypothetical protein | Dense granules | 1 | NA | 36.315 | no | yes |
| GRA86 | TGME49_200360 | Hypothetical protein | Dense granules | 1 | 2.63 | 20.299 | yes | no |
| GRA87 | TGME49_306890 | Hypothetical protein | Dense granules | 1 | 1.78 | 147.459 | no | no |
| GRA88 | TGME49_266050 | Hypothetical protein | Dense granules | 1 | 2.1 | 27.276 | no | no |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.-N.; Li, J.; Lu, X.-S.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.-Q. GRA86 Is a Novel Dense Granule Protein Important for Virulence and Bradyzoite Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Animals 2025, 15, 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172591
Zheng X-N, Li J, Lu X-S, Elsheikha HM, Zhu X-Q. GRA86 Is a Novel Dense Granule Protein Important for Virulence and Bradyzoite Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Animals. 2025; 15(17):2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172591
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xiao-Nan, Jing Li, Xin-Sheng Lu, Hany M. Elsheikha, and Xing-Quan Zhu. 2025. "GRA86 Is a Novel Dense Granule Protein Important for Virulence and Bradyzoite Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii" Animals 15, no. 17: 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172591
APA StyleZheng, X.-N., Li, J., Lu, X.-S., Elsheikha, H. M., & Zhu, X.-Q. (2025). GRA86 Is a Novel Dense Granule Protein Important for Virulence and Bradyzoite Differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Animals, 15(17), 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172591






