Detection of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Wild Boars from Romania
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Molecular Analysis for Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp.
2.4. Conventional PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sampling and Detection of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Wild Boars via Real-Time PCR
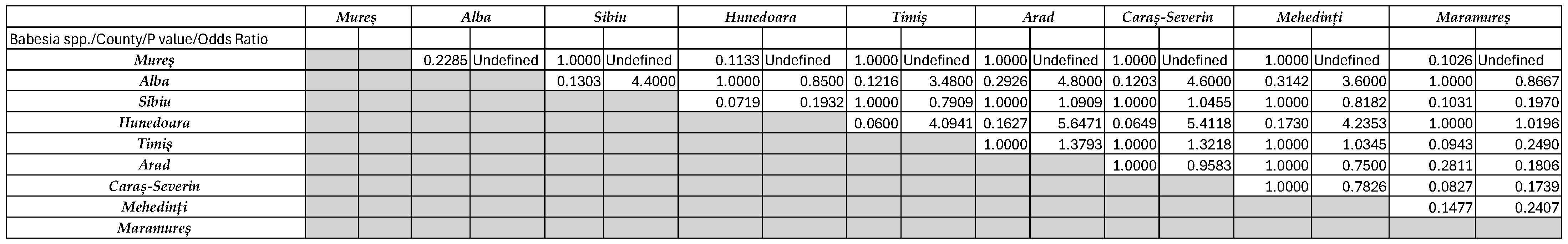
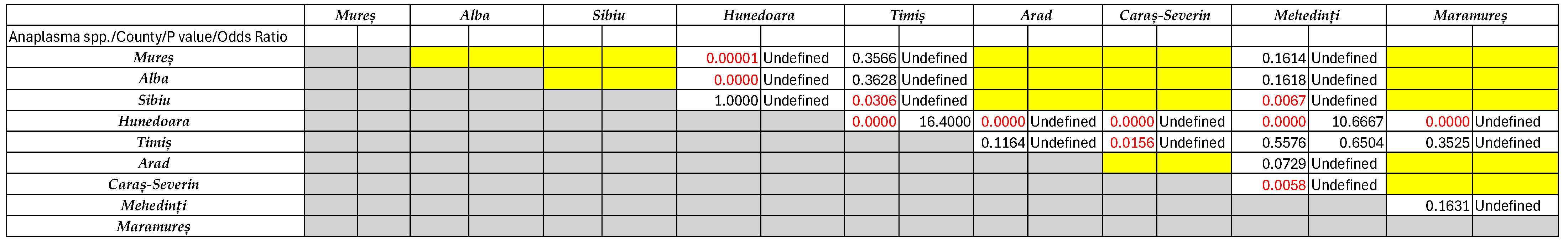
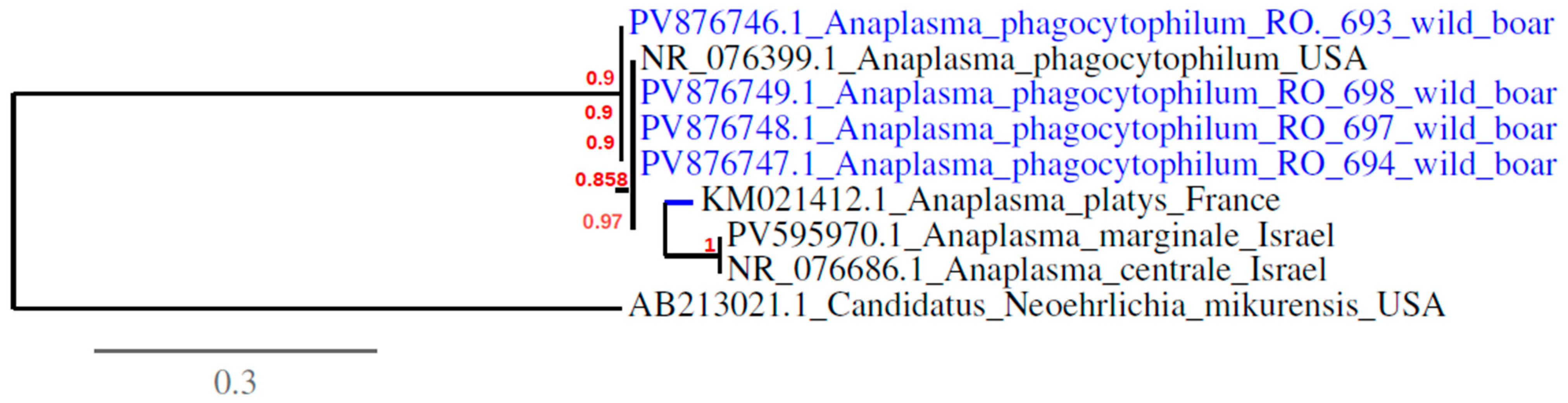
3.2. Detection and Sequencing of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. Via Conventional PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz-Fons, F. A Review of the Current Status of Relevant Zoonotic Pathogens in Wild Swine (Sus scrofa) Populations: Changes Modulating the Risk of Transmission to Humans. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licoppe, A.; Prevot, C.; Heymans, M.; Bovy, C.; Casaer, J.; Cahill, S. Wild Boar/Feral Pig in (Peri-)Urban Areas. In Managing Wild Boar in Human-Dominated Landscapes, Proceedings of the International Union of Game Biologists—Congress IUGB; Brussels, Belgium, 28 August 2013, IUGB: Cernier, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Maillard, D.; Gaillard, J.M.; Hewison, M.; Ballon, P.; Duncan, P.; Loison, A.; Toïgo, C.E.B.; Bonenfant, C.; Garel, M. Ungulates and Their Management in France. In European Ungulates and Their Management in the 21st Century; Apollonio, M., Andersen, R., Putman, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 441–474. [Google Scholar]
- Morelle, K.; Fattebert, J.; Mengal, C.; Lejeune, P. Invading or Recolonizing? Patterns and Drivers of Wild Boar Population Expansion into Belgian Agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 222, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, N.; Pankova, N.; Morelle, K. Where Winter Rules: Modeling Wild Boar Distribution in Its North-Eastern Range. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, C.; Ruf, T. Population Dynamics in Wild Boar Sus scrofa: Ecology, Elasticity of Growth Rate and Implications for the Management of Pulsed Resource Consumers. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.P.; Burrow, J.F.; Dytham, C.; Aegerter, J.N. Modelling with Uncertainty: Introducing a Probabilistic Framework to Predict Animal Population Dynamics. Ecol. Modell. 2009, 220, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejewski, W.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Okarma, H.; Ruprecht, A.L. Wolf Predation and Snow Cover as Mortality Factors in the Ungulate Community of the Białowieża National Park, Poland. Oecologia 1992, 90, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, G.; Kindberg, J.; Licoppe, A.; Gačić, D.; Šprem, N.; Kamler, J.; Baubet, E.; Hohmann, U.; Monaco, A.; Ozoliņš, J.; et al. Wild Boar Populations Up, Numbers of Hunters Down? A Review of Trends and Implications for Europe. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nores, C.; Llaneza, L.; Álvarez, A. Wild Boar Sus scrofa Mortality by Hunting and Wolf Canis lupus Predation: An Example in Northern Spain. Wildl. Biol. 2008, 14, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okarma, H.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Jędrzejewski, W.; Krasiński, Z.A.; Miłkowski, L. The Roles of Predation, Snow Cover, Acorn Crop, and Man-Related Factors on Ungulate Mortality in Białowieża Primeval Forest, Poland. Acta Theriol. 1995, 40, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, M.; Meriggi, A.; Fozzi, A. Factors Influencing Wild Boar Damage to Agricultural Crops in Sardinia (Italy). Curr. Zool. 2017, 63, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oja, R.; Soe, E.; Valdmann, H.; Saarma, U. Non-Invasive Genetics Outperforms Morphological Methods in Faecal Dietary Analysis, Revealing Wild Boar as a Considerable Conservation Concern for Ground-Nesting Birds. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavier-Widén, D.; Ståhl, K.; Neimanis, A.S.; Hård Av Segerstad, C.; Gortázar, C.; Rossi, S.; Kuiken, T. African Swine Fever in Wild Boar in Europe: A Notable Challenge. Vet. Rec. 2015, 176, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gortázar, C.; Ferroglio, E.; Höfle, U.; Frölich, K.; Vicente, J. Diseases Shared between Wildlife and Livestock: A European Perspective. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2007, 53, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, N.; Boyer, P.; Talagrand-Reboul, E.; Hansmann, Y. Ticks and Tickborne Diseases. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, F.S.; Khoo, J.J.; Tan, K.K.; Zainal, N.; Loong, S.K.; Khor, C.S.; AbuBakar, S. Bacterial Communities in Haemaphysalis, Dermacentor and Amblyomma Ticks Collected from Wild Boar of an Orang Asli Community in Malaysia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masatani, T.; Hayashi, K.; Andoh, M.; Tateno, M.; Endo, Y.; Asada, M.; Kusakisako, K.; Tanaka, T.; Gokuden, M.; Hozumi, N.; et al. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Babesia, Theileria, and Hepatozoon Species in Hard Ticks Collected from Kagoshima, the Southern Region in Japan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, M.M.; Boughton, R.K.; Lord, C.C.; Sayler, K.A.; Wight, B.; Anderson, W.M.; Wisely, S.M. Wild Pigs as Sentinels for Hard Ticks: A Case Study from Southcentral Florida. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2018, 7, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, V.; Carolan, H.E.; Vavruskova, Z.; Massire, C.; Mosel, M.R.; Crowder, C.D.; Rounds, M.A.; Ecker, D.J.; Ruzek, D.; Grubhoffer, L.; et al. Broad-Range Survey of Vector-Borne Pathogens and Tick Host Identification of Ixodes ricinus from Southern Czech Republic. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, C.; Pfister, K.; Overzier, E. Molecular Investigation for Bacterial and Protozoan Tick-Borne Pathogens in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Southern Germany. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotarczak, B.; Adamska, M.; Sawczuk, M.; Maciejewska, A.; Wodecka, B.; Rymaszewska, A. Coexistence of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Game Animals and Ticks in Western Poland. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimírová, M.; Hamsíková, Z.; Špitalská, E.; Minichová, Ľ.; Mahríková, L.; Caban, R.; Sprong, H.; Fonville, M.; Schnittger, L.; Kocianová, E. Diverse Tick-Borne Microorganisms Identified in Free-Living Ungulates in Slovakia. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maioli, G.; Pistone, D.; Bonilauri, P.; Pajoro, M.; Barbieri, I.; Patrizia, M.; Vicari, N.; Dottori, M. Ethiological Agents of Rickettsiosis and Anaplasmosis in Ticks Collected in Emilia-Romagna Region (Italy) during 2008 and 2009. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 57, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, A.; Quesada, M.; López, S.; Miret, J.; Cardeñosa, N.; Castella, J.; Antón, E.; Segura, F. Prevalence of Rickettsia slovaca in Dermacentor marginatus Ticks Removed from Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Northeastern Spain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1078, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Naranjo, V.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Höfle, U.; Fernández de Mera, I.G.; Villanúa, D.; Almazán, C.; Torina, A.; Caracappa, S.; Kocan, K.M.; et al. Potential Vertebrate Reservoir Hosts and Invertebrate Vectors of Anaplasma marginale and A. phagocytophilum in Central Spain. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005, 5, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, A.; Pérez-Martínez, L.; Santibáñez, S.; Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Anaplasma spp. in Wild Mammals and Ixodes ricinus from the North of Spain. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torina, A.; Alongi, A.; Naranjo, V.; Scimeca, S.; Nicosia, S.; Di Marco, V.; Caracappa, S.; Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J. Characterization of Anaplasma Infections in Sicily, Italy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1149, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabri, N.D.; Sprong, H.; Hofmeester, T.R.; Heesterbeek, H.; Donnars, B.F.; Widemo, F.; Ecke, F.; Cromsigt, J.P.G.M. Wild Ungulate Species Differ in Their Contribution to the Transmission of Ixodes ricinus-Borne Pathogens. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahayo, A.; Bardiau, M.; Volpe, R.; Pirson, J.; Paternostre, J.; Fett, T.; Linden, A. Molecular Evidence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Belgium. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Parreira, R.; Nunes, M.; Casadinho, A.; Vieira, M.L.; Campino, L.; Maia, C. Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Bacteria and Protozoa in Cervids and Wild Boars from Portugal. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrdel, K.S.; Bidovec, A.; Malovrh, T.; Petrovec, M.; Duh, D.; Zupanc, T.A. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Wild Boar in Slovenia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Cadar, D.; Krupaci, F.A.; Bordeanu, A.D.; Spînu, M. Prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum Infection in European Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Populations from Transylvania, Romania. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, J.; Stańczak, J.; Cieniuch, S.; Racewicz, M.; Sikora, B.; Dabert, M. Wild Boars as Hosts of Human-Pathogenic Anaplasma phagocytophilum Variants. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2094–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, C.; Winter, C.; Wolfsperger, T.; Wüppenhorst, N.; Strašek Smrdel, K.; Skuballa, J.; Pfäffle, M.; Petney, T.; Silaghi, C.; Dyachenko, V.; et al. Analysis of the Population Structure of Anaplasma phagocytophilum Using Multilocus Sequence Typing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, W.; Schauer, S.; Freyburger, F.; Petrovec, M.; Schaarschmidt-Kiener, D.; Liebisch, G.; Runge, M.; Ganter, M.; Kehl, A.; Dumler, J.S.; et al. Distinct Host Species Correlate with Anaplasma phagocytophilum ankA Gene Clusters. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smrdel, K.S.; Petrovec, M.; Furlan, S.L.; Županc, T.A. The Sequences of groESL Operon of Anaplasma phagocytophilum among Human Patients in Slovenia. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrdel, K.S.; von Loewenich, F.D.; Petrovec, M.; Županc, T.A. Diversity of ankA and msp4 Genes of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Slovenia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, I.A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Cutler, S.J.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Varela-Castro, L.; Potkonjak, A.; Zeller, H.; Mihalca, A.D. A Review on the Eco-Epidemiology and Clinical Management of Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis and Its Agent in Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrazdilová, K.; Rybarová, M.; Siroký, P.; Votýpka, J.; Zintl, A.; Burgess, H.; Steinbauer, V.; Zakovčík, V.; Modrý, D. Diversity of Babesia spp. in Cervid Ungulates Based on the 18S rDNA and Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I Phylogenies. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; Sugár, L.; Fernández de Mera, I.G.; de la Fuente, J.; Horváth, G.; Kovács, T.; Micsutka, A.; Gönczi, E.; Flaisz, B.; Takács, N.; et al. Tick- and Fly-Borne Bacteria in Ungulates: The Prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Haemoplasmas and Rickettsiae in Water Buffalo and Deer Species in Central Europe, Hungary. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampieri, M.P.; Galuppi, R.; Bonoli, C.; Cancrini, G.; Moretti, A.; Pietrobelli, M. Wild Ungulates as Babesia Hosts in Northern and Central Italy. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanet, S.; Trisciuoglio, A.; Bottero, E.; De Mera, I.G.F.; Gortázar, C.; Carpignano, M.G.; Ferroglio, E. Piroplasmosis in Wildlife: Babesia and Theileria Affecting Free-Ranging Ungulates and Carnivores in the Italian Alps. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobba, R.; Parpaglia, M.L.P.; Spezzigu, A.; Pittau, M.; Alberti, A. First Molecular Identification and Phylogeny of a Babesia sp. from a Symptomatic Sow (Sus scrofa Linnaeus 1758). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2321–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobba, R.; Nuvoli, A.M.; Sotgiu, F.; Lecis, R.; Spezzigu, A.; Dore, G.M.; Masia, M.A.; Cacciotto, C.; Parpaglia, M.L.P.; Dessì, D.; et al. Molecular Epizootiology and Diagnosis of Porcine Babesiosis in Sardinia, Italy. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racewicz, M. Detection and quantification of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Babesia spp. in Ixodes ricinus ticks from urban and rural environment, northern Poland, by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 66, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boularias, G.; Azzag, N.; Galon, C.; Šimo, L.; Boulouis, H.-J.; Moutailler, S. High-Throughput Microfluidic Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Multiple Microorganisms in Ixodid Cattle Ticks in Northeast Algeria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, M.; Marié, J.L.; Mediannikov, O.; Raoult, D.; Davoust, B. First Identification of Anaplasma platys in the Blood of Dogs from French Guiana. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempereur, L.; Beck, R.; Fonseca, I.; Marques, C.; Duarte, A.; Santos, M.; Zúquete, S.; Gomes, J.; Walder, G.; Domingos, A.; et al. Guidelines for the Detection of Babesia and Theileria Parasites. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust Phylogenetic Analysis for the Non-Specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MapChart. Available online: https://www.mapchart.net/romania.html (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Dreghiciu, I.C.; Imre, M.; Oprescu, I.; Florea, T.; Ghilean, B.M.; Sîrbu, B.A.M.; Iorgoni, V.; Badea, C.; Giubega, S.; Mederle, N.; et al. Molecular Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) from Hunedoara and Timiș Counties—Preliminary Study. Rev. Rom. Med. Vet. 2023, 33, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Defaye, B.; Moutailler, S.; Pietri, C.; Galon, C.; Grech-Angelini, S.; Pasqualini, V.; Quilichini, Y. Molecular Detection of Zoonotic and Non-Zoonotic Pathogens from Wild Boars and Their Ticks in the Corsican Wetlands. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Auriemma, C.; Salant, H.; Gallo, A.; Riccardi, M.G.; Alfano, F.; Rea, S.; Scarcelli, S.; Ottaviano, M.; et al. First Molecular Detection of Babesia vulpes and Babesia capreoli in Wild Boars from Southern Italy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1201476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebani, V.V.; Bertelloni, F.; Cecconi, G.; Sgorbini, M.; Cerri, D. Zoonotic Tick-Borne Bacteria among Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) in Central Italy. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 7, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Cao, J.M.; Adaszek, Ł.; Dzięgiel, B.; Paniagua, J.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Winiarczyk, S.; Winiarczyk, D.; Cano-Terriza, D.; García-Bocanegra, I. Prevalence of Selected Tick-Borne Pathogens in Wild Ungulates and Ticks in Southern Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myczka, A.W.; Steiner-Bogdaszewska, Ż.; Filip-Hutsch, K.; Oloś, G.; Czopowicz, M.; Laskowski, Z. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Wild and Farmed Cervids in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polin, H.; Hufnagl, P.; Hauschmid, R.; Gruber, F.; Guther, L. Molecular Evidence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Ixodes ricinus Ticks and Wild Animals in Austria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2285–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
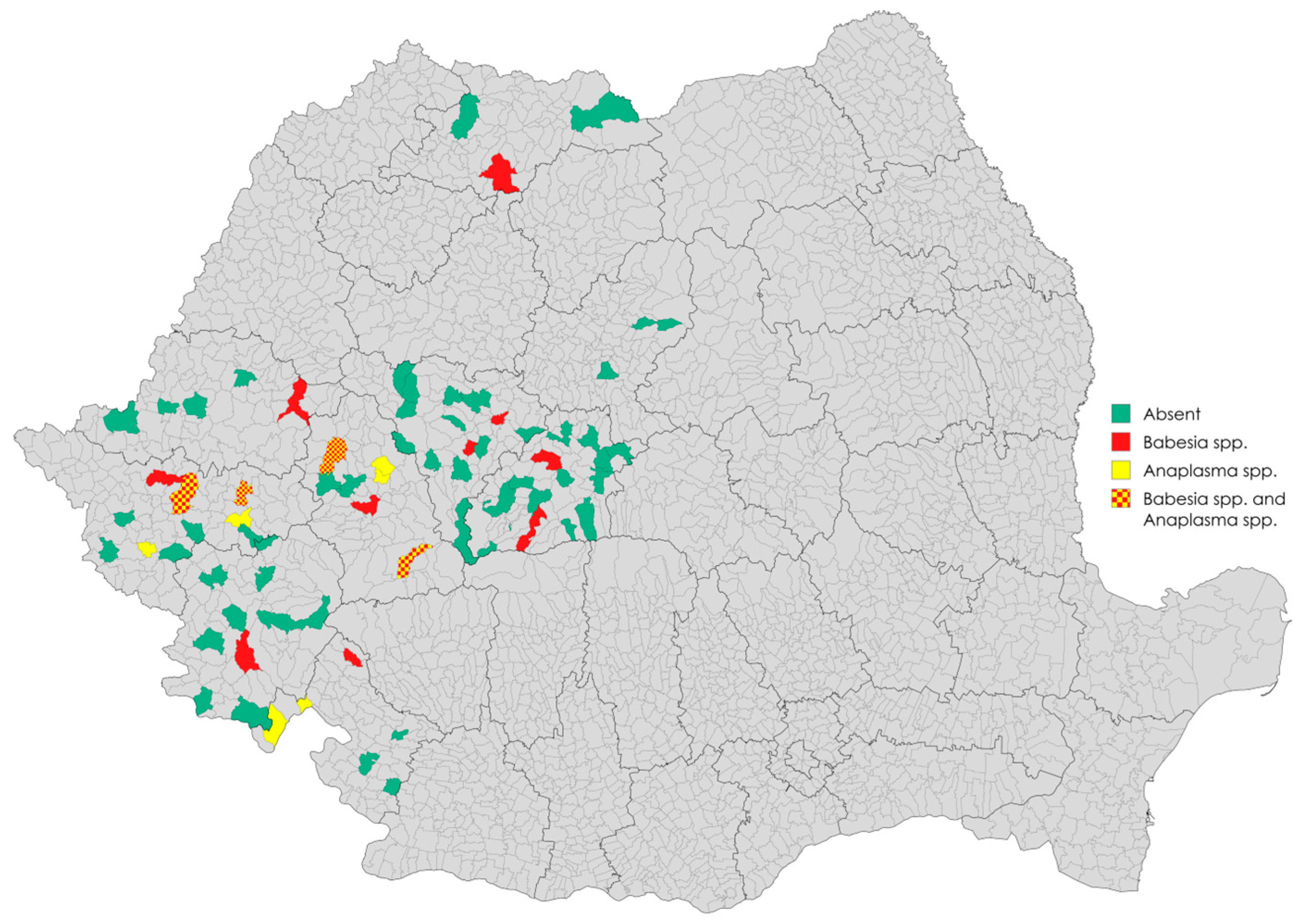
| County | Hunting Grounds | Nr. of Samples | Positivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Babesia spp. | Anaplasma spp. | |||
| Mureș | 2 | 17 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Alba | 14 | 18 | 3 (16.6%) | 0 (0%) |
| Sibiu | 14 | 46 | 2 (4.3%) | 0 (0%) |
| Hunedoara | 7 | 21 | 4 (19%) | 14 (66.7%) |
| Timiș | 10 | 92 | 5 (5.4%) | 10 (10.9%) |
| Arad | 5 | 25 | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) |
| Caraș-Severin | 9 | 48 | 2 (4.2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Mehedinți | 6 | 38 | 2 (5.3%) | 6 (15.8%) |
| Maramureș | 3 | 16 | 3 (18.8%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total | 70 | 321 | 22 (6.9%) | 30 (9.3%) |
| Sample Number | Date | Ct | County | Hunting Ground | Age | Positivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | 12 January 2022 | 27.650 | Timiș | 42 Buziaș | 12 | A. phagocytophilum |
| 127 | 17 February 2022 | 33.154 | Hunedoara | 20 Bobâlna | 30 | A. phagocytophilum |
| 08 | 17 February 2022 | 38.350 | Hunedoara | 16 Băița | 16 | A. phagocytophilum |
| 258 | 15 December 2023 | 33.847 | Mehedinți | 02 Dubova | 16 | A. phagocytophilum |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dreghiciu, I.C.; Hoffman, D.; Dumitru, S.; Florea, T.; Imre, M.; Rugea, T.; Iorgoni, V.; Plesko, A.; Morariu, S.; Oprescu, I.; et al. Detection of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Wild Boars from Romania. Animals 2025, 15, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172542
Dreghiciu IC, Hoffman D, Dumitru S, Florea T, Imre M, Rugea T, Iorgoni V, Plesko A, Morariu S, Oprescu I, et al. Detection of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Wild Boars from Romania. Animals. 2025; 15(17):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172542
Chicago/Turabian StyleDreghiciu, Ioan Cristian, Diana Hoffman, Simona Dumitru, Tiana Florea, Mirela Imre, Tatiana Rugea, Vlad Iorgoni, Anamaria Plesko, Sorin Morariu, Ion Oprescu, and et al. 2025. "Detection of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Wild Boars from Romania" Animals 15, no. 17: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172542
APA StyleDreghiciu, I. C., Hoffman, D., Dumitru, S., Florea, T., Imre, M., Rugea, T., Iorgoni, V., Plesko, A., Morariu, S., Oprescu, I., & Ilie, M. S. (2025). Detection of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in Wild Boars from Romania. Animals, 15(17), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172542









