Synovial Fluid Biomarker Profile After Intra-Articular Administration of Neosaxitoxin in Horses: A Feasibility Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
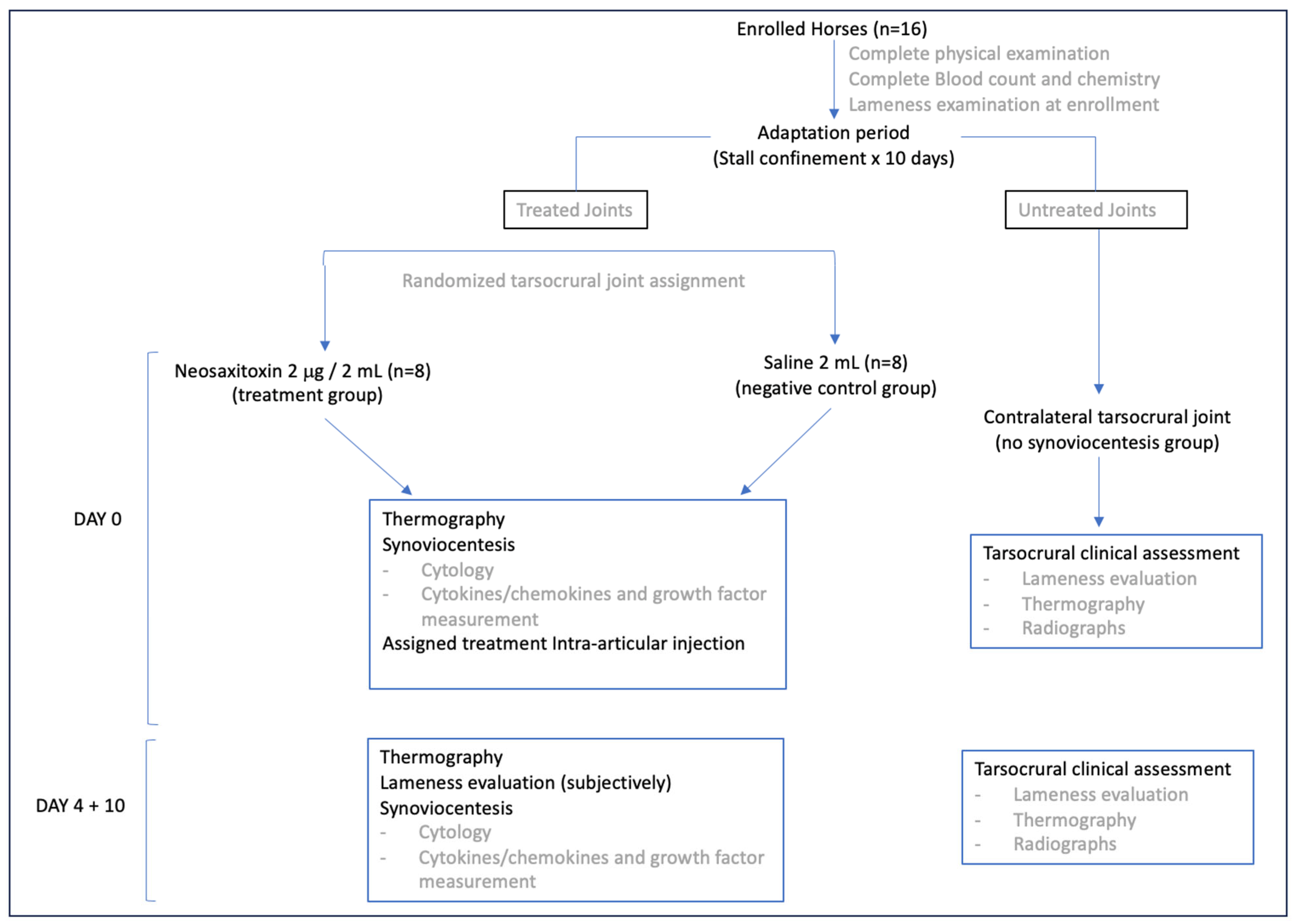
2.1. Experimental Design and Animal Selection
2.2. Animal Maintenance
2.3. Neosaxitoxin Purification Procedure
2.4. Synovial Fluid (SF) Sampling and Assessment
2.5. Cytokine Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Demographics
3.2. NeoSTX Did Not Induce Clinical Adverse Effects
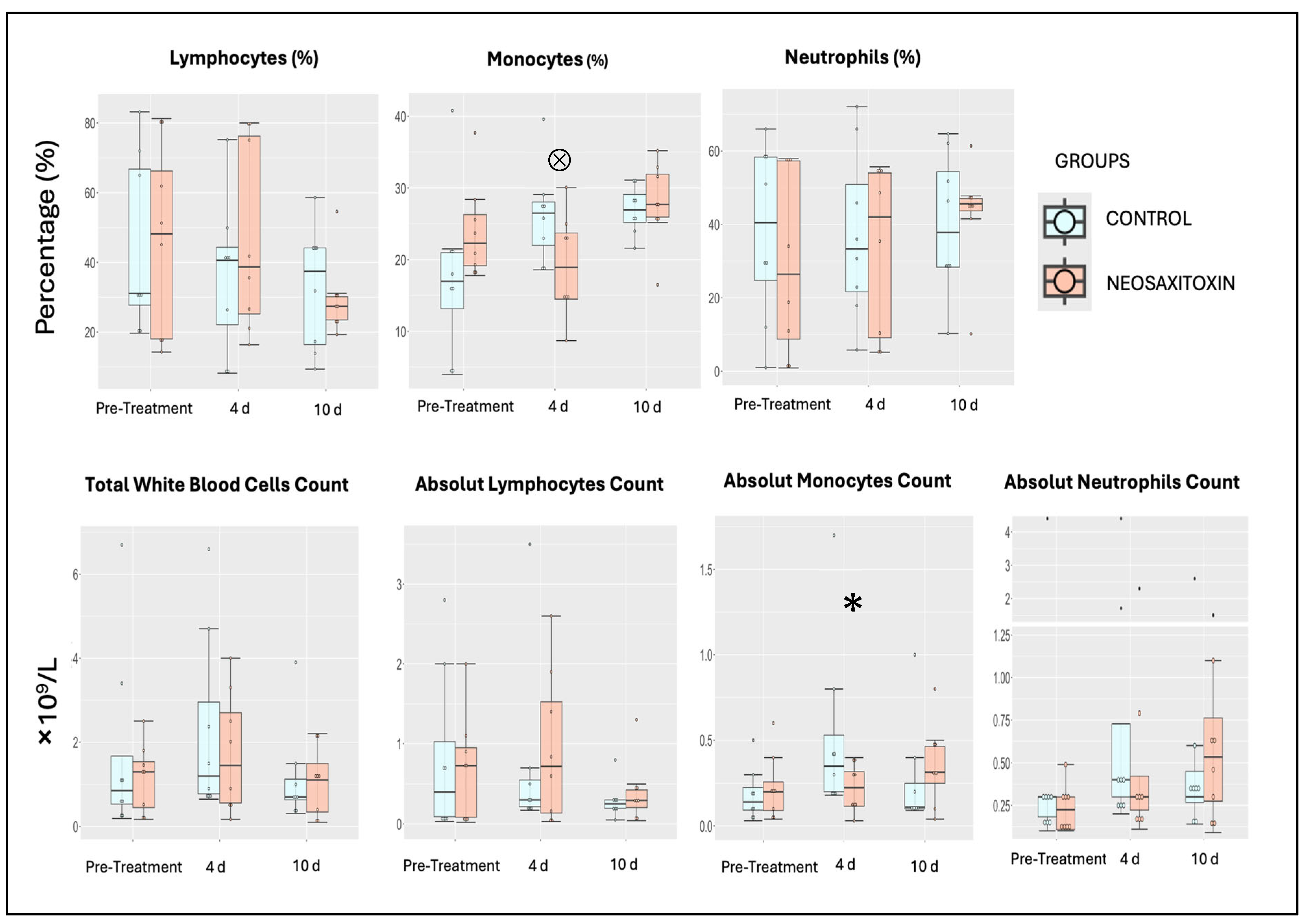
3.3. NeoSTX Did Not Alter the Cellular Profile of Synovial Fluid
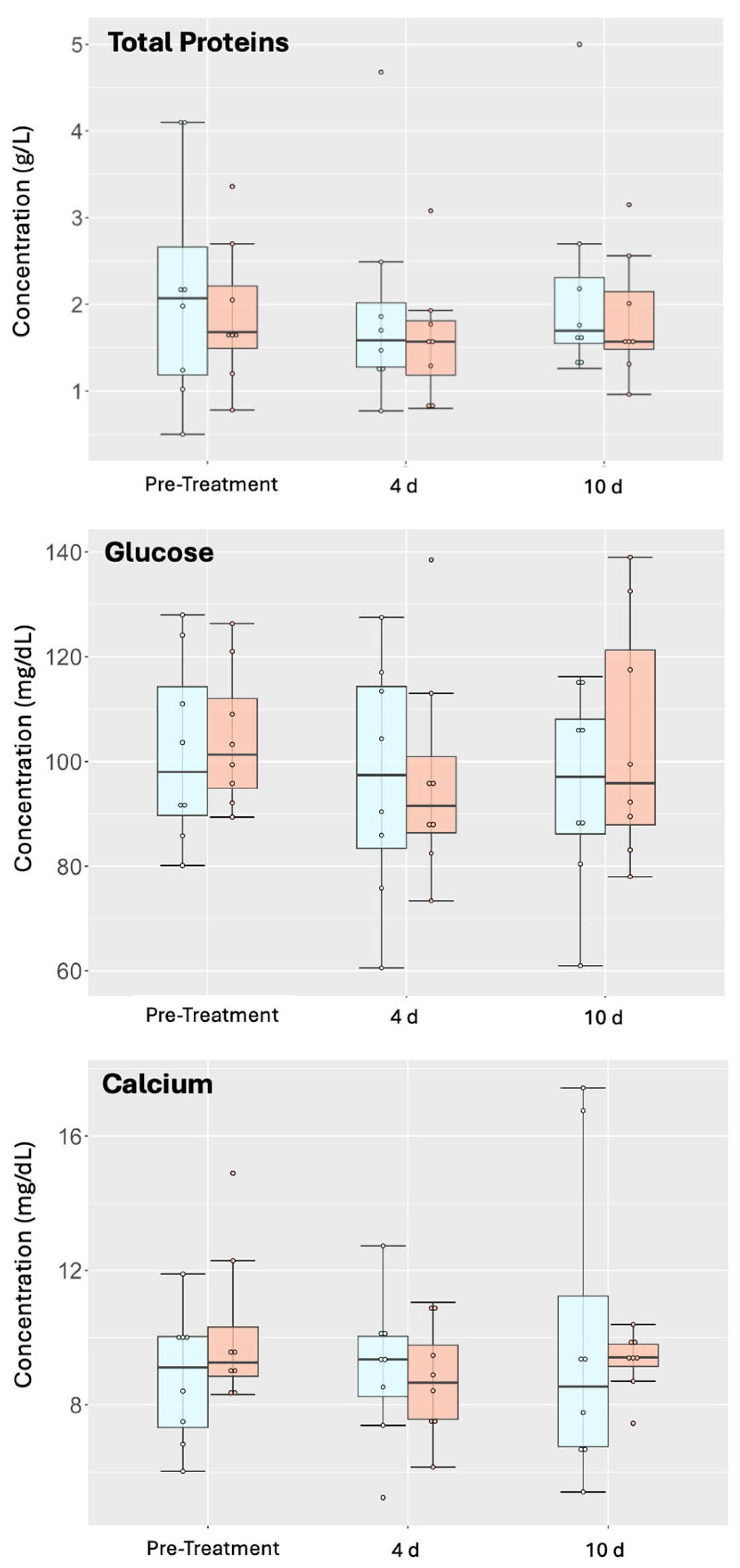
3.4. Intra-Articular Administration of NeoSTX Did Not Alter the Profile of Synovial Fluid Biomolecules
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cisternas, M.G.; Murphy, L.; Sacks, J.J.; Solomon, D.; Pasta, D.J.; Helmick, C.G. Alternative methods for defining osteoarthritis and the impact on estimating prevalence in a US population-based survey. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torio, C.M.; Moore, B.J. National inpatient hospital costs: The most expensive conditions by payer, 2013. In Statistical Brief. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, M.V. Osteoarthritis in horses—Part 2: A review of the intra-articular use of corticosteroids as a method of treatment. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016, 59, e16150025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydd, A.S.; Reno, C.R.; Tsao, H.W.; Hart, D.A. Early inflammatory arthritis in the rabbit: The influence of intraarticular and systemic corticosteroids on mRNA levels in connective tissues of the knee. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 34, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lent, P.L.; Van den Hoek, A.E.; Van den Bersselaar, L.A.; Spanjaards, M.F.; Van Rooijen, N.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Van de Putte, L.B.; Van den Berg, W.B. In vivo role of phagocytic synovial lining cells in onset of experimental arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Bondeson, J.; Wainwright, S.D.; Lauder, S.; Amos, N.; Hughes, C.E. The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage-produced cytokines in driving aggrecanases, matrix metalloproteinases, and other destructive and inflammatory responses in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.; Fearon, U.; Veale, D.J.; Godson, C. Macrophages in synovial inflammation. Front. Inmunol. 2011, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichadiya, A.; Bertram, K.L.; Ren, G.; Yates, R.M.; Krawetz, R.J. Characterizing heterogeneity in the response of synovial mesenchymal progenitor cells to synovial macrophages in normal individuals and patients with osteoarthritis. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D. Anatomy of a discovery: M1 and M2 macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olingy, C.E.; San Emeterio, C.L.; Ogle, M.E.; Krieger, J.C.; Bruce, A.C.; Pfau, D.D.; Jordan, B.T.; Peirce, S.M.; Botchwey, E.A. Non-classical monocytes are biased progenitors of wound healing macrophages during soft tissue injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Liu, A.M.; Huang, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.Q.; Hu, X.Y. Macrophages-derived small extracellular vesicles regulate chondrocyte proliferation and affect osteoarthritis progression via upregulating Osteopontin expression. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2025, 19, e70008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W. From ionic currents to molecular mechanism: The structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron 2000, 26, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos, N.; Andrinolo, D. Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP): Toxicology and kinetics. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxin: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lagos, N. Clinical applications of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins. In Toxins and Biologically Active Compound from Microalgae; Rossini, G.P., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 309–329. [Google Scholar]
- Roselli, F.; Livrea, P.; Jirillo, E. Voltage-gated sodium channel blockers as immunomodulators. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2006, 1, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, L.; MacKenzie, A.B.; Sluyter, R. Roles of ion channels in immune cells. Front. Inmunol. 2016, 7, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Feske, S.; Wulff, H.; Skolnik, E.Y. Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 291–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, M.C.; Del Campo, M.; Bono, M.; Simon, M.V.; Guerrero, J.; Lagos, N. Neosaxitoxin inhibits the expression of inflammation markers of the M1 phenotype in macrophages. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrithers, M.D.; Dib-Hajj, S.; Carrithers, L.M.; Tokmoulina, G.; Pypaert, M.; Jonas, E.A.; Waxman, S.G. Expression of the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.5 in the macrophage late endosome regulates endosomal acidification. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7822–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, O.; Bolshakov, V.N.; Raines, S.; Newham, P.; Perkins, N.D. Transcriptional profiling of the LPS induced NF-κB response in macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2007, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrington, M.G.; Fraser, I.D.C. NF-κB signaling in macrophages: Dynamics, crosstalk, and signal integration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.; Tsai, P.S.; Huang, Y.H.; Huang, C.J. Inhibition of toll-like receptor-4, nuclear factor-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase by lignocaine may involve voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinzpeter, J.; Barrientos, C.; Zamorano, Á.; Martinez, Á.; Palet, M.; Wulf, R.; Barahona, M.; Sepúlveda, J.M.; Guerra, M.; Bustamante, T.; et al. Gonyautoxins: First evidence in pain management in total knee arthroplasty. Toxicon 2016, 119, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinzpeter, J.; Zamorano, A.; Barahona, M.; Möller, G.; Espinoza, J.; Del Campo, M.; Piron, R.; Sepúlveda, J.M.; Bustamante, T.; Lagos, N. Management of Aarthrofibrosis of the knee after an arthroscopic meniscectomy with paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin. Case Report. Intern. Physiol. J. 2018, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörner, C.D.; Del Campo, M.; Lagos, N. Neosaxitoxin, a long-lasting local anesthetic and its potential clinical applications in horses. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 55, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaneder, L.M.; Lagos, N.; Dörner, C.D. Systemic, hemodynamic and neurological effects of caudal epidural administration of neosaxitoxin in horses. Toxicon 2025, 257, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, N.; Onodera, H.; Zagatto, P.; Andrinolo, D.; Azevedo, S.M.; Oshima, Y. The first evidence of paralytic shellfish toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, isolated from brazil. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.E.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Martin, G.S. Effect of intra-articular injection of orgotein and saline solution on equine synovia. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1982, 43, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawcak, C.; McIlwraith, W. Comparison of synovial fluid in middle carpal joints undergoing needle aspiration, infusion with saline, and Infusion with a combination of N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine, hyaluronic acid, and sodium chondroitin sulfate. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2011, 31, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R.; Phelan, M.M.; Clegg, P.D.; Peffers, M.; Rubio-Martinez, L.M. Synovial fluid metabolites differentiate between septic and nonseptic joint pathologies. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2735–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorskyy, A.; Hernández-Santana, A.; Short, B.; McCarthy, G.; McMahon, G. Determination of calcium in synovial fluid samples as an aid to diagnosing osteoarthritis. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, E.; Jefferson, T.E.; Amirtham, S.M.; Prince, N.; Geevar, T.; Rebekah, G.; Ramasamy, B.; Kachroo, U. Correlation between synovial fluid calcium containing crystal estimation and varying grades of osteoarthritis created using a rabbit model: Potential diagnostic tool. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, S506–S511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, K.G.; Dent, E.V.; Wilson, D.A.; Janicek, J.; Kramer, J.; Lacarrubba, A.; Walsh, D.M.; Cassells, M.W.; Esther, T.M.; Schiltz, P.; et al. Repeatability of subjective evaluation of lameness in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2010, 42, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, S. Can lameness be graded reliably? Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D.; Serteyn, D.; Franck, T.; Jorgensen, E.; Christophersen, M.; Denwood, M.; Verwilghen, D. Effects of intra-articular administration of lidocaine, mepivacaine, and the preservative methyl parahydroxybenzoate on synovial fluid biomarkers of horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 81, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Kim, K.-I.; Park, K.-B.; Park, Y.-G.; Bae, J.H.; Seo, Y.-J.; Seon, J.-K.; Shon, O.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of intra-articular injection of a highly cross-linked hyaluronic acid, LBSA0103 (Synovian): Results from a post-marketing surveillance study in South Korea. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, C.; Schramme, M.; Febre, M.; Cauvin, E.; Labadie, F.; Saulnier, N.; François, I.; Lechartier, A.; Aebischer, D.; Moncelet, A.-S.; et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of single versus repeated intra-articular injection of allogeneic neonatal mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of osteoarthritis of the metacarpophalangeal/metatarsophalangeal joint in horses: A clinical pilot study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischer, C.; Warner, K. Complications after intra-articular application of ACS (IRAP®) in horses—Retrospective study. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2017, 33, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Soroko, M. Analyses of superficial temperature distribution of lower part of the limbs in young racing horses. Meas. Autom. Monit. 2011, 57, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Soroko, M.; Henklewski, R.; Filipowski, H.; Jodkowska, E. The effectiveness of thermographic analysis in equine orthopedics. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 760–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T. Diagnostic thermography. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2001, 17, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.N.; Kisiday, J.D.; Hess, T.; McIlwraith, C.W. Evaluation of the inflammatory response in experimentally induced synovitis in the horse: A comparison of recombinant equine interleukin 1 beta and lipopolysaccharide. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menarim, B.C.; Gillis, K.H.; Oliver, A.; Mason, C.; Ngo, Y.; Werre, S.R.; Barrett, S.H.; Luo, X.; Byron, C.R.; Dahlgren, L.A. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells modulate joint homeostasis in an equine in vivo model of synovitis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 14337–14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.L.; MacKay, R.J.; Gum, G.G.; Colahan, P.T.; Meyer, J.C. Effects of intra-articularly administered endotoxin on clinical signs of disease and synovial fluid tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 6, and prostaglandin E2 values in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1993, 54, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenek, N.; Andrews, F.; Maddux, J.; Sander, W.; Faulk, D. Determination of total protein concentration and viscosity of synovial fluid from the tibiotarsal joints of horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 53, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.A.; Carbajal, B. Sistemática para el estudio del líquido sinovial (LS). Rev. Asoc. Bioquímica Argent. 1977, 231, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Perman, V. Synovial fluid. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals; Kaneko, J., Ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1980; pp. 749–783. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Russo, M.J.; Desroches, P.E.; Silva, S.M.; Quigley, A.F.; Kapsa, R.M.; Moulton, S.E.; Green, G.W. Calcium ions have a detrimental impact on the boundary lubrication property of hyaluronic acid and lubricin (PRG-4) both alone and in combination. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 234, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Anshita, D.; Ravichandiran, V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, A. The role of G-CSF in adaptive inmunty. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, C.H.; Roberts, A.I.; Das, J.; Xu, G.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.R.; Tan, H.S.; et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and T-cell responses: What we do and don’t know. Cell Res. 2006, 1, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Size Effect (η2) | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 0.016 | [−1.38, 1.57] |
| Glucose | 0.029 | [−7.40, 15.03] |
| Total Protein | 0.039 | [−0.91, 0.27] |
| Red Blood Cells | 0.046 | [−0.026, 0.087] |
| WBC (×109/L) | 0.076 | [−1.30, 0.48] |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 0.078 | [−0.39, 0.53] |
| Monocytes (×109/L) | 0.066 | [−0.23, 0.11] |
| Neutrophils (×109/L) | 0.045 | [−0.88, 0.24] |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 0.077 | [−9.89, 15.87] |
| Monocytes (%) | 0.12 | [1.11, 11.96] |
| Neutrophils (%) | 0.029 | [−15.44, 9.44] |
| IL-1a | 0.066 | [−0.64, 2.36] |
| IL-1b | 0.045 | [−0.37, 1.21] |
| IL-2 | 0.052 | [−0.47, 0.55] |
| IL-4 | 0.125 | [0.03 to 1.80] |
| IL-5 | 0.004 | [−0.21, 0.19] |
| IL-6 | 0.053 | [−0.37, 0.29] |
| IL-8 | 0.051 | [−1.16, 2.76] |
| IL-10 | 0.109 | [−11.06, 28.93] |
| IL-12p70 | 0.012 | [−0.09, 0.05] |
| IL-13 | 0.013 | [−0.015, 0.009] |
| IL-17A | 0.23 | [−0.73, −0.21] |
| IL-18 | 0.03 | [−0.49, 0.29] |
| TNF-a | 0.052 | [−0.39, 0.96] |
| FGF-2 | 0.079 | [−1.49, 2.84] |
| GRO/KC | 0.069 | [−0.007, 0.027] |
| IFN-g | 0.055 | [−3.39, 1.71] |
| IP10 | 0.052 | [−0.08, 0.05] |
| MCP-1 | 0.020 | [−2.31, 4.49] |
| Eotaxin | 0.067 | [−0.07, 0.04] |
| Fractalkine | 0.063 | [−0.33, 2.24] |
| G-CSF | 0.134 | [−0.67, 0.35] |
| GM-CSF | 0.019 | [−0.007, 0.015] |
| RANTES | 0.031 | [−0.002, 0.002] |
| Parameter | Group | Pre-Treatment (Mean ± sd) | 4 d. (Mean ± sd) | 10 d. (Mean ± sd) | Reference Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Protein (mg/dL) | NeoSTX | 1.88 ± 0.82 | 1.61 ± 0.72 | 1.83 ± 0.71 | <2.5 g/dL [45] |
| Control | 2.16 ± 1.33 | 1.94 ± 1.22 | 2.19 ± 1.22 | ||
| Ca2+ (mg/dL) | NeoSTX | 10.1 ± 2.29 | 8.71 ± 1.67 | 9.30 ± 0.9 | 8.3–10.7 [46] |
| Control | 8.83 ± 1.98 | 9.10 ± 2.19 | 9.93 ± 4.63 | ||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | NeoSTX | 104.16 ± 13.4 | 96.9 ± 20.4 | 104.28 ± 23.0 | 33–105 mg/dL [47] |
| Control | 102.55 ± 17.7 | 96.9 ± 22.7 | 95.26 ± 18.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dörner, C.; Lagos, N.; Oyaneder, L.; Menarim, B.C.; Ramírez-Toloza, G. Synovial Fluid Biomarker Profile After Intra-Articular Administration of Neosaxitoxin in Horses: A Feasibility Study. Animals 2025, 15, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162453
Dörner C, Lagos N, Oyaneder L, Menarim BC, Ramírez-Toloza G. Synovial Fluid Biomarker Profile After Intra-Articular Administration of Neosaxitoxin in Horses: A Feasibility Study. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162453
Chicago/Turabian StyleDörner, Cristóbal, Néstor Lagos, Lissette Oyaneder, Bruno C. Menarim, and Galia Ramírez-Toloza. 2025. "Synovial Fluid Biomarker Profile After Intra-Articular Administration of Neosaxitoxin in Horses: A Feasibility Study" Animals 15, no. 16: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162453
APA StyleDörner, C., Lagos, N., Oyaneder, L., Menarim, B. C., & Ramírez-Toloza, G. (2025). Synovial Fluid Biomarker Profile After Intra-Articular Administration of Neosaxitoxin in Horses: A Feasibility Study. Animals, 15(16), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162453







