A Deep Learning Framework for Multi-Object Tracking in Space Animal Behavior Studies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A multi-modal feature fusion framework: A deep learning architecture is proposed that separates and integrates appearance and motion features of space animals via a heterogeneous graph network, enhancing MOT performance in extreme space environments.
- A motion decoupling method: A local polynomial approximation method is introduced to decompose motion components, enabling accurate estimation of speed and acceleration and improving tracking robustness for space animals under microgravity.
- A cross-modal re-detection module: A cross-modal re-detection method is designed to align appearance and motion features for identity maintenance, facilitating recovery of lost tracks during occlusions or rapid movements of space animals.
2. Related Work
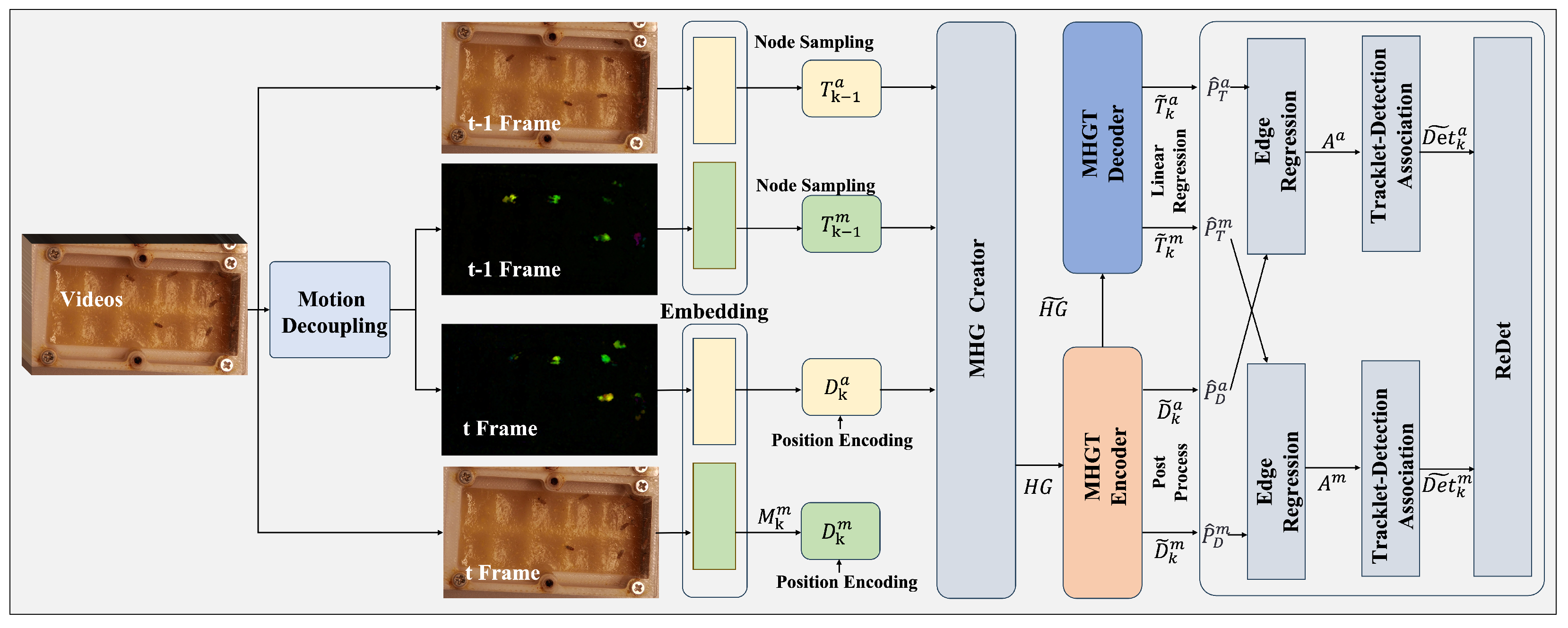
3. Method
3.1. Motion Decoupling
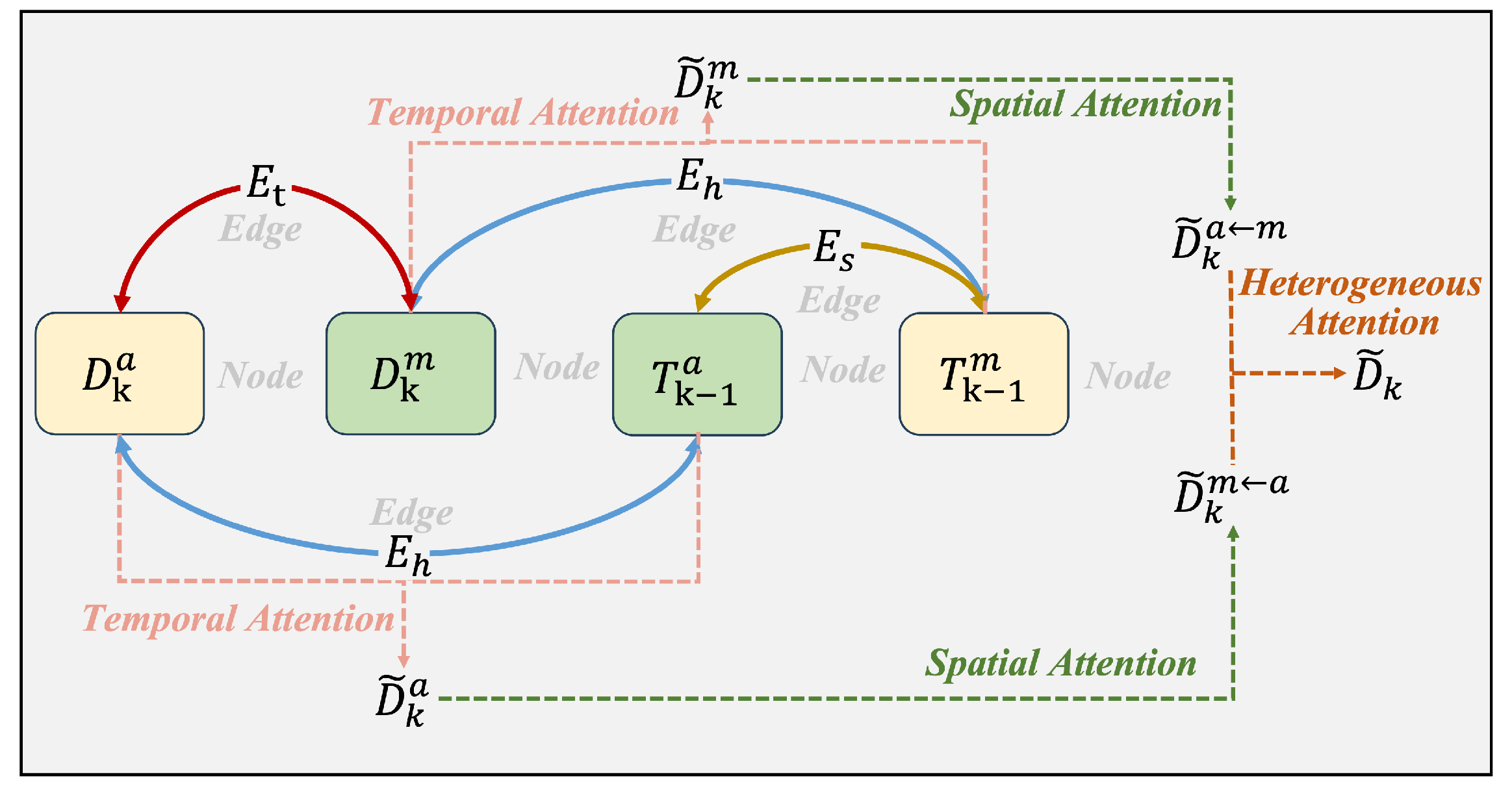
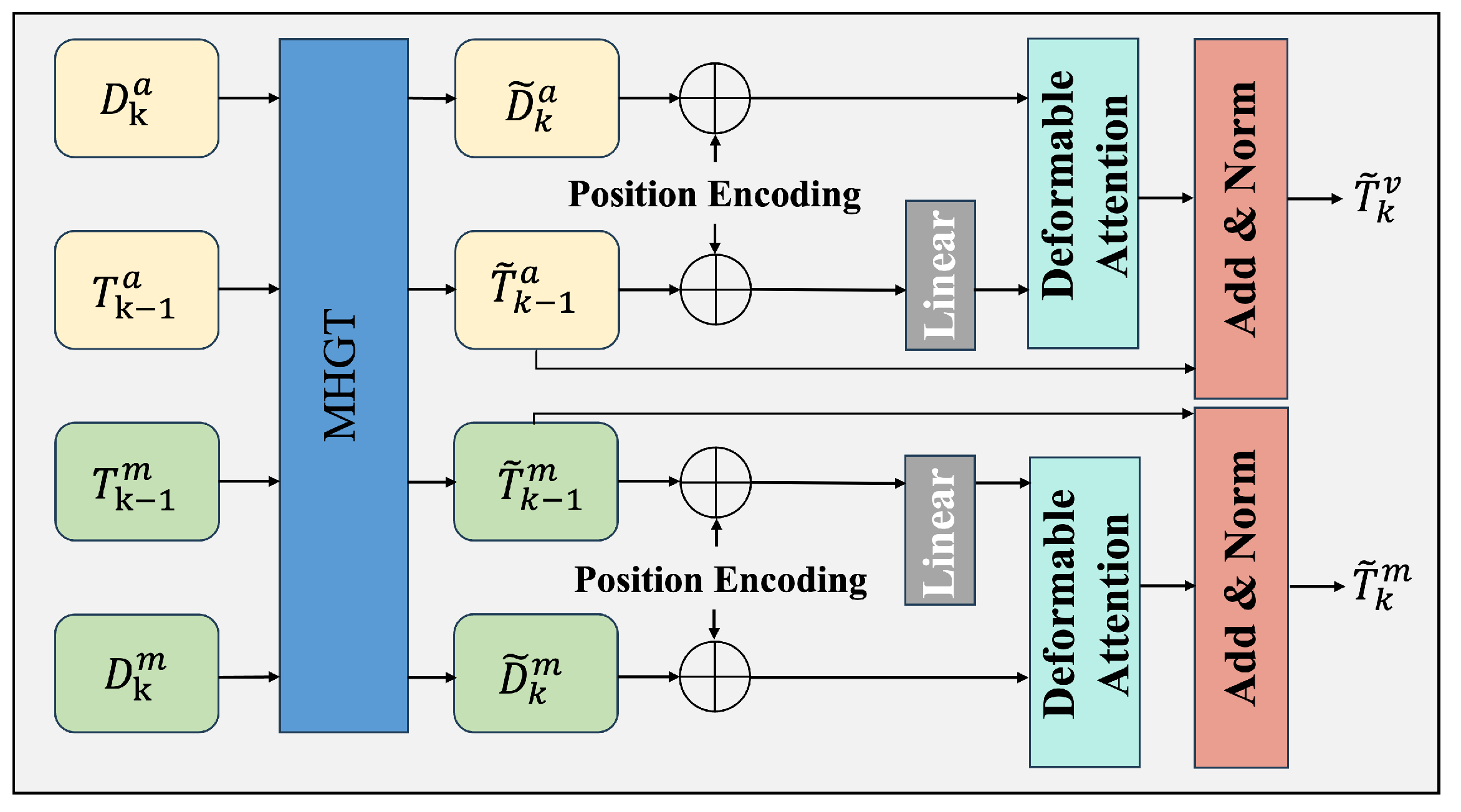
3.2. Cross-Modal Feature Fusion
| Algorithm 1 Cross-modal feature fusion |
 |
3.3. Unified Detection–Tracking Framework
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Data
4.2. Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
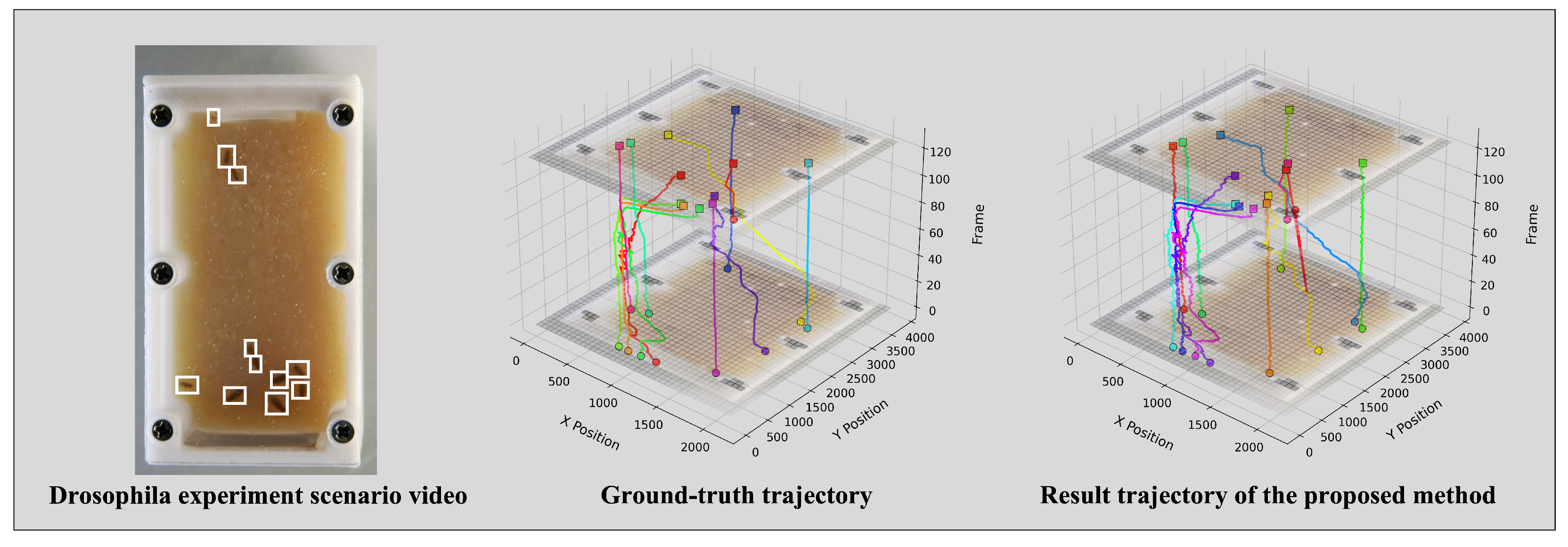
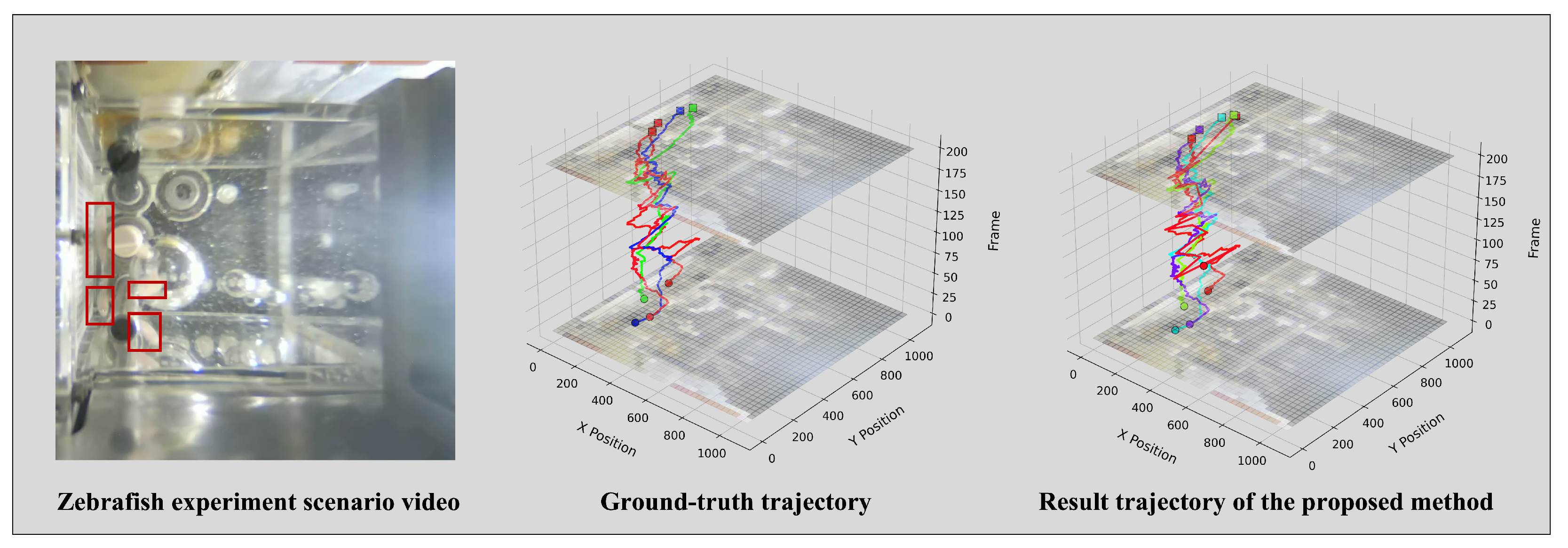
5. Results
5.1. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
5.2. Ablation Study
6. Discussion
6.1. Key Findings
6.2. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rutter, L.; Barker, R.; Bezdan, D.; Cope, H.; Costes, S.V.; Degoricija, L.; Fisch, K.M.; Gabitto, M.I.; Gebre, S.; Giacomello, S.; et al. A New Era for Space Life Science: International Standards for Space Omics Processing. Patterns 2020, 1, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, G. Introduction to Space Life Sciences. In Fundamentals of Space Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshti, A.; Shirazi-Fard, Y.; Choi, S.; Berrios, D.; Gebre, S.G.; Galazka, J.M.; Costes, S.V. Exploring the Effects of Spaceflight on Mouse Physiology Using the Open Access NASA GeneLab Platform. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 143, 58447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Masukawa, M.; Kamigaichi, S. NASDA Aquatic Animal Experiment Facilities for Space Shuttle and ISS. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 30, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y. The China Space Station: A New Opportunity for Space Science. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhao, G.; Gu, Y. Recent Progress in Space Science and Applications of China’s Space Station in 2020–2022. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2022, 42, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, K.; Zhao, M.; Li, S. Video Process Detection for Space Electrostatic Suspension Material Experiment in China’s Space Station. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 131, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y. China’s National Space Station: Opportunities, Challenges, and Solutions for International Cooperation. Space Policy 2021, 57, 101439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Gu, P.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, W.; Zheng, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G. Zebrafish Selection Strategy for the First Zebrafish Cultivation Experiment on the Chinese Space Station. Life Sci. Space Res. 2025, 46, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, O.; Plà-Aragonés, L.M.; Mac Cawley, A.; Albornoz, V.M. AI and Data Analytics in the Dairy Farms: A Scoping Review. Animals 2025, 15, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.; Cusimano, M.; Baglione, V.; Canestrari, D.; Chevallier, D.; DeSantis, D.L.; Jeantet, L.; Ladds, M.A.; Maekawa, T.; Mata-Silva, V.; et al. A Benchmark for Computational Analysis of Animal Behavior, Using Animal-Borne Tags. Mov. Ecol. 2024, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, J.V.; Hosseini, M.; Gading, E.F.; Masousi, M.; Franke, M.; MacDonald, S.E. The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Monitoring Animal Identification, Health, and Behaviour. Animals 2022, 12, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, T. Life Science Experiments Performed in Space in the ISS/Kibo Facility and Future Research Plans. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57 (Suppl. S1), i41–i46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bailey, J.; Hoehn, R.; Stodieck, L.; Globus, R.K. Effects of Spaceflight Aboard the International Space Station on Mouse Estrous Cycle and Ovarian Gene Expression. NPJ Microgravity 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amosa, T.I.; Sebastian, P.; Izhar, L.I.; Ibrahim, O.; Ayinla, L.S.; Bahashwan, A.A.; Bala, A.; Samaila, Y. Multi-Camera Multi-Object Tracking: A Review of Current Trends and Future Advances. Neurocomputing 2023, 552, 126558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; You, B.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, X. YOLO-SDD: An Effective Single-Class Detection Method for Dense Livestock Production. Animals 2025, 15, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Towards Real-Time Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, C.; Danelljan, M.; Paudel, D.P.; Van Gool, L. Learning Target Candidate Association to Keep Track of What Not to Track. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13444–13454. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xie, E.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, P. Transtrack: Multiple Object Tracking with Transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, W. Fairmot: On the Fairness of Detection and Re-Identification in Multiple Object Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3069–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhuo, J.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as Points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
- Fazzari, E.; Romano, D.; Falchi, F.; Stefanini, C. Animal Behavior Analysis Methods Using Deep Learning: A Survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 289, 128330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattal, K.A.; Fernandez, E.J. Grounding Applied Animal Behavior Practices in the Experimental Analysis of Behavior. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2022, 118, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, J.; Mathis, A.; Bethge, V.; Lopes, M.; Ullrich, B.; Spether, C.; Mamidanna, P.; Yartsev, M.; Mathis, M.W. Multi-Animal Pose Estimation, Identification and Tracking with DeepLabCut. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, T.; Couzin, I.D. TRex, a Fast Multi-Animal Tracking System with Markerless Identification, and 2D Estimation of Posture and Visual Fields. eLife 2021, 10, 64000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, A.I.; Bender, J.A.; Branson, K.; Couzin, I.D.; de Polavieja, G.G.; Noldus, L.P.J.J.; Pérez-Escudero, A.; Perona, P.; Straw, A.D.; Wikelski, M. Automated Image-Based Tracking and Its Application in Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, R.; Biyani, A.; Dalton, J.E.; Saltz, J.B.; Arbeitman, M.N.; Tower, J.; Nuzhdin, S.; Tavaré, S. Three-Dimensional Tracking and Behaviour Monitoring of Multiple Fruit Flies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoukis, N.C.; Butail, S.; Diallo, M.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Paley, D.A. Stereoscopic Video Analysis of Anopheles gambiae Behavior in the Field: Challenges and Opportunities. Acta Trop. 2014, 132, S80–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angarita-Jaimes, N.C.; Parker, J.E.A.; Abe, M.; Mashauri, F.; Martine, J.; Towers, C.E.; McCall, P.J.; Towers, D.P. A Novel Video-Tracking System to Quantify the Behaviour of Nocturnal Mosquitoes Attacking Human Hosts in the Field. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20150974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.S.; Zhao, Q.; Zou, D.; Chen, Y.Q. Automated 3D Trajectory Measuring of Large Numbers of Moving Particles. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 7646–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Su, H.F.; Cheng, X.E.; Liu, Y.; Quo, A.; Chen, Y.Q. Tracking the 3D Position and Orientation of Flying Swarms with Learned Kinematic Pattern Using LSTM Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1225–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Su, H. Long 3D-POT: A Long-Term 3D Drosophila-Tracking Method for Position and Orientation with Self-Attention Weighted Particle Filters. Applied Sci. 2024, 14, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, D.N.; Richardson, T.S.; Watson, M.; Meier, K.; Kline, J.M.; Reid, S.; Maalouf, G.; Hine, D.; Mirmehdi, M.; Burghardt, T. WildLive: Near Real-time Visual Wildlife Tracking onboard UAVs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops: Computer Vision for Animal Behavior Tracking and Modeling (CV4Animals), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Han, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, R.; Han, M.H.; Liu, Q.; Wei, P. Anti-Drift Pose Tracker (ADPT), a Transformer-Based Network for Robust Animal Pose Estimation Cross-Species. eLife 2025, 13, RP95709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y. Heterogeneous Graph Transformer. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2020, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 April 2020; pp. 2704–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.-P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid Vision Transformer: A Versatile Backbone for Dense Prediction without Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, R.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Pose Estimation and Tracking Dataset for Multi-Animal Behavior Analysis on the China Space Station. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardin, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Evaluating Multiple Object Tracking Performance: The CLEAR MOT Metrics. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2008, 2008, 246309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance Measures and a Data Set for Multi-Target, Multi-Camera Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Koltun, V.; Krähenbühl, P. Tracking Objects as Points. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 474–490. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Delorme, G.; Gan, C.; Rus, D.; Alameda-Pineda, X. TransCenter: Transformers with Dense Representations for Multiple-Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 7820–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinhardt, T.; Kirillov, A.; Leal-Taixe, L.; Feichtenhofer, C. Trackformer: Multi-Object Tracking with Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8844–8854. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Bytetrack: Multi-Object Tracking by Associating Every Detection Box. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. Motrv2: Bootstrapping End-to-End Multi-Object Tracking by Pretrained Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22056–22065. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Han, G.; Yan, B.; Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, D. Hybrid-SORT: Weak Cues Matter for Online Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, No. 7. pp. 6504–6512. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Initial Learning Rate | 2 × |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Training Epochs | 300 |
| Learning Rate Schedule | Cosine Annealing |
| Warmup Steps | 1000 |
| Weight Decay | 0.05 |
| Input Resolution | 512 × 512 |
| Augmentation | Random Flip, Rotation (±) |
| Method | Drosophila | Zebrafish | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | Frag ↓ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | Frag ↓ | |
| CenterTrack [42] | 74.41% | 79.59% | 98 | 74.12% | 60.14% | 85 |
| TransCenter [43] | 72.58% | 74.12% | 113 | 60.20% | 63.13% | 102 |
| TrackFormer [44] | 67.48% | 66.25% | 96 | 58.26% | 59.13% | 115 |
| ByteTrack [45] | 75.21% | 76.50% | 91 | 75.90% | 62.95% | 82 |
| MOTRv2 [46] | 61.93% | 75.35% | 125 | 78.14% | 64.24% | 78 |
| Hybrid-SORT [47] | 70.62% | 66.23% | 98 | 72.34% | 61.25% | 91 |
| Ours | 88.21% | 85.06% | 42 | 82.21% | 74.26% | 36 |
| Configuration | Drosophila | Zebrafish | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | MT ↑/ML ↓ | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | MT ↑/ML ↓ | |
| Baseline | 74.41% | 79.59% | 61/12 | 74.12% | 60.14% | 58/15 |
| + Motion | 81.63% | 82.45% | 73/8 | 79.09% | 67.79% | 65/11 |
| ++ MHGN | 86.45% | 84.36% | 82/5 | 80.74% | 71.22% | 72/8 |
| +++ ReDet | 88.21% | 85.06% | 86/4 | 82.21% | 74.26% | 78/6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Lv, Y.; Liu, K.; Cao, Y.; Guo, S. A Deep Learning Framework for Multi-Object Tracking in Space Animal Behavior Studies. Animals 2025, 15, 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162448
Zhou Z, Li S, Lv Y, Liu K, Cao Y, Guo S. A Deep Learning Framework for Multi-Object Tracking in Space Animal Behavior Studies. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162448
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhuang, Shengyang Li, Yixuan Lv, Kang Liu, Yuxuan Cao, and Shicheng Guo. 2025. "A Deep Learning Framework for Multi-Object Tracking in Space Animal Behavior Studies" Animals 15, no. 16: 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162448
APA StyleZhou, Z., Li, S., Lv, Y., Liu, K., Cao, Y., & Guo, S. (2025). A Deep Learning Framework for Multi-Object Tracking in Space Animal Behavior Studies. Animals, 15(16), 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162448






