A Novel Weizmannia coagulans Strain WC412 with Superior Environmental Resilience Improves Growth Performance of Mice by Regulating the Intestinal Microbiota
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Isolation and Identification of W. coagulans from Pickle Water
2.3.1. Isolation of Strains
2.3.2. Morphological Identification
2.3.3. Strain Identification
2.4. Evaluation of Bacterial Tolerance
2.4.1. High Temperature Tolerance
2.4.2. Acid Tolerance Measurement
2.4.3. Bile Salt Tolerance Assay
2.5. Mouse Feeding Model of W. coagulans
2.5.1. Experimental Animals and Group Design
2.5.2. Serum Biochemical Assessment
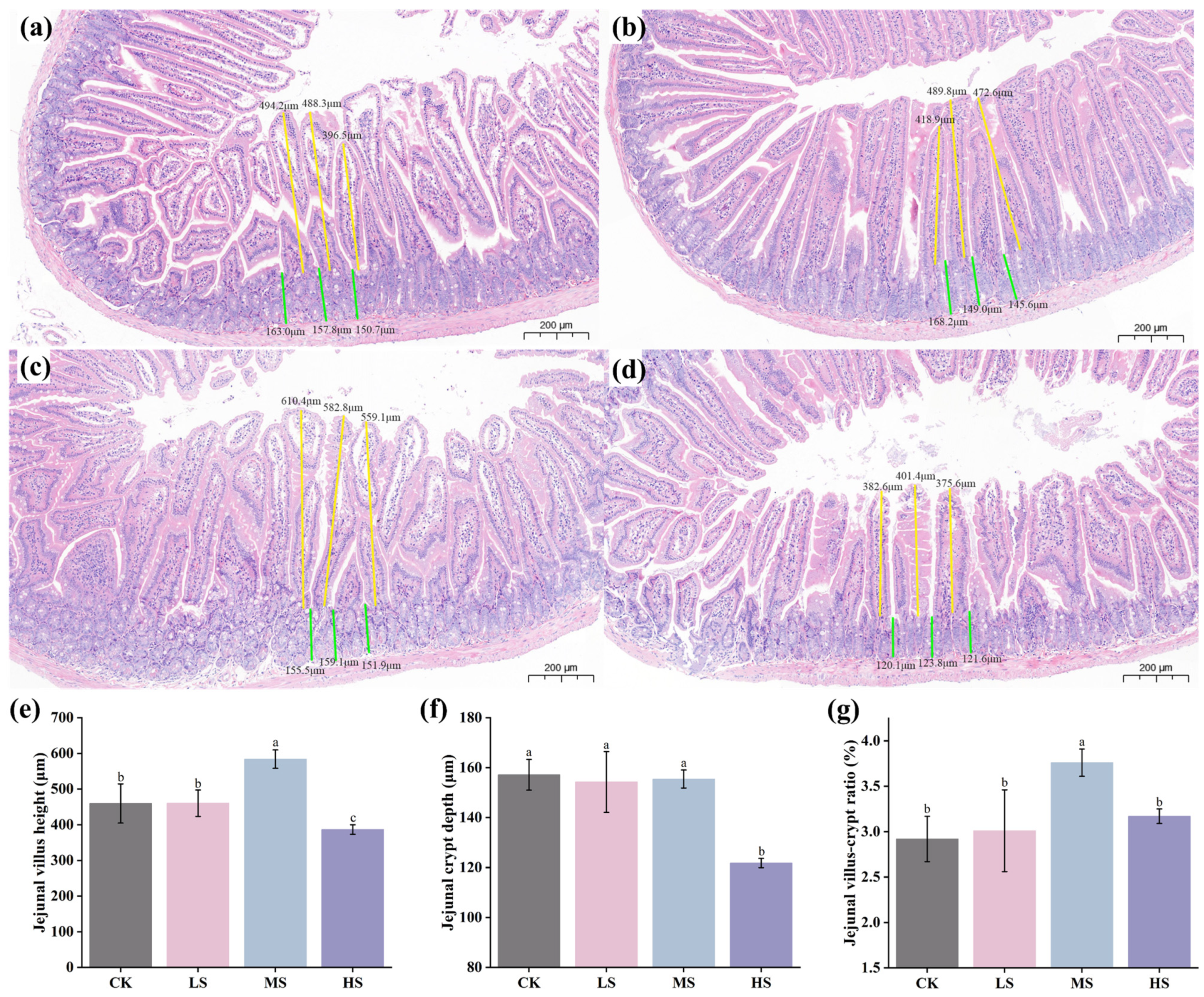
2.5.3. Histopathological Evaluation
2.5.4. 16S rDNA Sequencing and Analysis of Intestinal Flora
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of W. coagulans in Pickle Water
3.2. Evaluation of Tolerance of W. coagulans
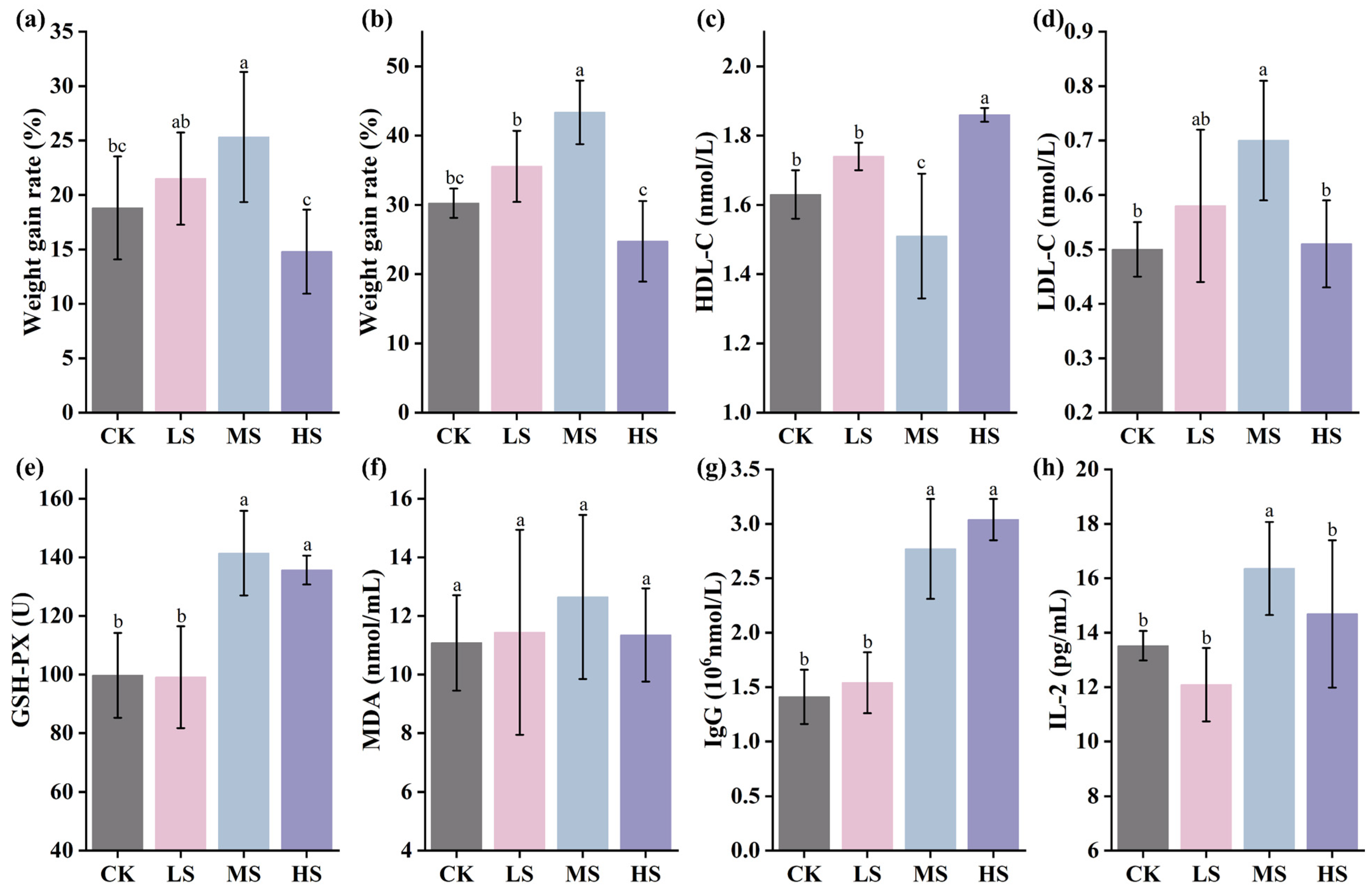
3.3. Effect of Supplementation with W. coagulans WC412 on Physiological Metabolism in Mice
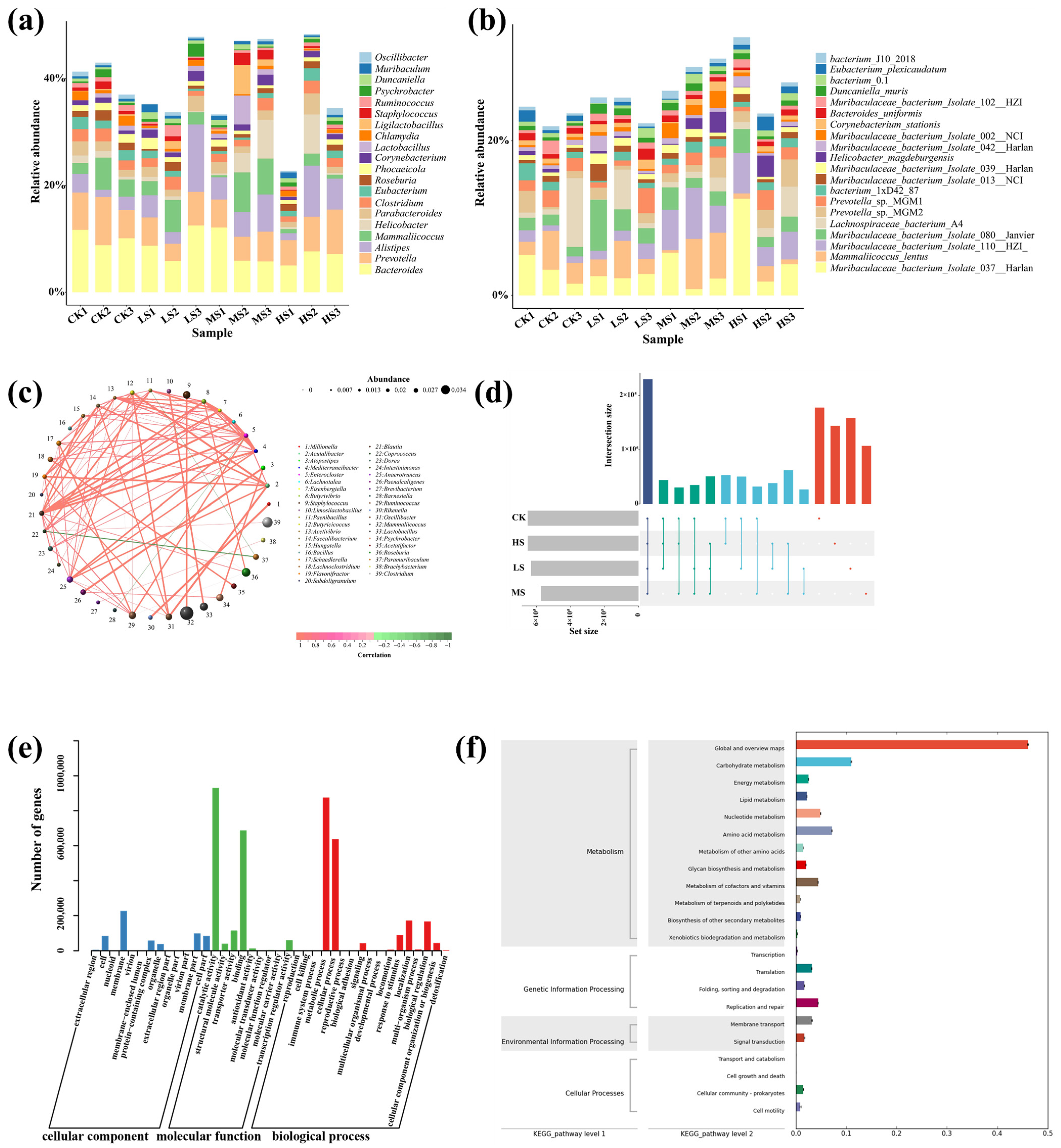
3.4. Supplementation of WC412 Regulates the Intestinal Flora of Mice
3.5. Effects of WC412 on the Gut Microbiota of Mice
3.5.1. Community Diversity Assessment
3.5.2. Community Metabolism Pathway Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barreto-Cruz, O.T.; Henao Zambrano, J.C.; Ospina Barrero, M.A.; Castañeda-Serrano, R.D. Effects of Tithonia diversifolia extract as a feed additive on digestibility and performance of hair lambs. Animals 2024, 14, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Faheem, M.; Liaqat, I.; Van Doan, H.; Ghosh, K.; Ringø, E. Promising probiotic candidates for sustainable aquaculture: An updated review. Animals 2024, 14, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamojska, D.; Nowak, A.; Nowak, I.; Macierzyńska-Piotrowska, E. Probiotics and postbiotics as substitutes of antibiotics in farm animals: A Review. Animals 2021, 11, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ying, J.; Wang, B.; Majeed, M.; Majeed, S.; Pande, A.; Li, W. Application of Bacillus coagulans in animal husbandry and its underlying mechanisms. Animals 2020, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Z.; Anjum, M.Z.; Akhter, S.; Irfan, M.; Amin, S.; Jamal, Y.; Khalid, S.; Ghazanfar, S. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus pentosaceus on the growth performance and morphometry of the genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Pak. J. Zool. 2024, 56, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slizewska, K.; Markowiak-Kopec, P.; Zbikowski, A.; Szeleszczuk, P. The effect of synbiotic preparations on the intestinal microbiota and her metabolism in broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, A.K.M.H.; Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Mehwish, H.M.; Villena, J.; Kitazawa, H. Immunomodulation potential of probiotics: A novel strategy for improving livestock health, immunity, and productivity. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingmongkolchai, S.; Panbangred, W. Bacillus probiotics: An alternative to antibiotics for livestock production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Lian, L.; Lu, L.; Gu, T.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Li, G.; Wu, H.; Tian, Y. Effects of dietary Bacillus coagulans and Tributyrin on growth performance, serum antioxidants, intestinal morphology, and cecal microbiota of growing yellow-feathered broilers. Animals 2023, 13, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J. Amelioration of Cd-induced bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and immune damage by probiotic Bacillus coagulans in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, A.; Yang, W.; Lv, F.; Liu, F.; Liu, B.; Sun, C. Effects of various feeding patterns of Bacillus coagulans on growth performance, antioxidant response and Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in juvenile gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Qi, T.; Hong, Y.; Deng, L.; Zeng, K. Screening of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria in Chinese homemade pickle and dry-cured meat, and bacteriocin identification by genome sequencing. LWT 2020, 125, 109177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madushanka, D.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Kodithuwakku, S.; Nayanajith, G.R.A.; Jayatilake, S.; Priyashantha, H. Isolation and characterization of probiotic lactic acid bacteria from fermented traditional rice for potential applications in food and livestock production. Appl. Food Res. 2025, 5, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiong, T.; Zhang, L.; Du, T.; Madjirebaye, P.; Zhao, M.; Kang, X. Novel lactic acid bacteria with anti-hyperglycaemic properties: In vitro screening and probiotic assessment. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, A.; Anjum, H.; Habib, H.; Abony, M.; Begum, A.; Ahmed, Z. Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from street pickles of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Panahi, B.; Mazlumi, A.; Hejazi, M.A.; Komi, D.E.A.; Nami, Y. Screening of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria with antimicrobial properties and selection of superior bacteria for application as biocontrol using machine learning models. LWT 2022, 162, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ren, R.; Lang, X.; Li, X.; Qin, L.; Zeng, H. Effect of whole-grain Tartary buckwheat fermentation with Monascus purpureus on the metabolic syndrome and intestinal flora in mice. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzer, A.; Fauteux-Daniel, S.; Verhoeven, P.; Cantais, A.; Novoa, M.Y.; Jospin, F.; Chanut, B.; Rochereau, N.; Bourlet, T.; Roblin, X.; et al. Impact of dextran-sodium-sulfate-induced enteritis on murine cytomegalovirus reactivation. Viruses 2022, 14, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertsriwong, S.; Glinwong, C. Newly-isolated hydrogen-producing bacteria and biohydrogen production by Bacillus coagulans MO11 and Clostridium beijerinckii CN on molasses and agricultural wastewater. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 26812–26821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.; Huang, F.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; And Zeng, X. Weizmannia coagulans: Screening, functional properties, and current applications in the food industry. Food Rev. Int. 2025, 2184–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, T.; Lee, S.; Lim, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, P. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of efficacy and safety of Weizmannia coagulans HOM5301 for boosting immunity. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 107, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Vignolles, M.L.; Chen, X.D.; Le Loir, Y.; Jan, G.; Schuck, P.; Jeantet, R. Spray drying of probiotics and other food-grade bacteria: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuray Altun, G.; Erginkaya, Z. Identification and characterization of Bacillus coagulans strains for probiotic activity and safety. LWT 2021, 151, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenadh, M.; Kumar, K.R.; Nath, S. In vitro evaluation of Weizmannia coagulans strain LMG S-31876 isolated from fermented rice for potential probiotic properties, safety assessment and technological properties. Life 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.L.; Shi, Y.Q.; Li, P.L.; Pan, K.H.; Li, G.Q.; Li, X.G.; Yao, S.; Zhang, D.H. Application of principal component analysis (PCA) to the evaluation and screening of multiactivity fungi. J. Ocean Univ. 2022, 21, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Chen, D.; Tian, G.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; He, J.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yu, B. Effect of dietary supplementation of Bacillus coagulans or yeast hydrolysates on growth performance, antioxidant activity, cytokines and intestinal microflora of growing-finishing pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 5, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Du, L.; Fang, X.; Liao, Z. Application of Weizmannia coagulans in the medical and livestock industry. Ann. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Guo, Z.T.; Liu, L.B.; Ren, D.X.; Zu, H.; Li, B.L.; Liu, F. Potential probiotic Weizmannia coagulans WC10 improved antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by regulating the gut microbiota and metabolic homeostasis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Li, W.; Lin, Q.; Lin, X.; Lin, J.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, H.; Huang, Z. Dietary administration of laminarin improves the growth performance and immune responses in Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, M.; Kale-Pradhan, P.; Coyle, M.; Giuliano, C.; Johnson, L.B. Clinical and drug resistance characteristics of providencia infections. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Relaño, A.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Barrero-Domínguez, B.; Luque, I.; Jurado-Martos, F.; Vela, A.I.; Sanz-Tejero, C.; Tarradas, C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Trueperella pyogenes isolated from food-producing ruminants. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 242, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faden, H. The role of Faecalibacterium, Roseburia, and Butyrate in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. 2022, 40, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.X.; Ye, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.L.; Qiu, X.M. Analysis of intestinal flora and environmental microbial diversity of Takifugu rubripes. Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2022, 74, 1817737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcelin, R.; Luche, E.; Serino, M.; Chabo, C. The intestinal flora: New concepts for the regulation of energetic metabolism. Sang Thrombose Vaisseaux 2009, 21, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Cui, L.R.; Li, Y.; Ling, H.; Tan, X.; Xu, H.Y. Integrative analysis revealed the role of glucagon-like peptide-2 in improving experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory pathways, regulating glucose metabolism, and modulating gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1174308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, J.C.; Chen, G.N.; Guo, Y.L. The role of G protein-coupled receptors in the regulation of orthopaedic diseases by gut microbiota. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Hou, R.; Wang, Y.C.; Huang, Q.Y.; Lin, L.; Li, H.X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Z.J.; Huang, X.P.; Xu, X.R. Xenobiotic metabolism activity of gut microbiota from six marine species: Combined taxonomic, metagenomic, and in vitro transformation analysis. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 480, 136152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.X.; Li, J.N.; Wu, D. The role of short-chain fatty acids in acute pancreatitis. Molecules 2023, 28, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Lee, S.; Wang, Y.; Tan, C.; Shang, N. Weizmannia coagulans: An ideal probiotic for gut health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtasun, R.; Díaz-Gómez, J.; Araña, M.; Pajares, M.J.; Oneca, M.; Torre, P.; Jiménez, M.; Munilla, G.; Barajas, M.; Encío, I. A combination of apple vinegar drink with Bacillus coagulans ameliorates high fat diet-induced body weight gain, insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Sun, M.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Chu, T.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.H.; Jin, S.Z.; Yuan, X.C. Gut microbiota adaptation to low and high carbohydrate-to-protein ratio diets in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 32, 101742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Zhang, R.X.; Li, X.; Li, J.H.; Ji, W.B.; Zeng, X.Y.; Bao, J. Exposure to the environmental pollutant ammonia causes changes in gut microbiota and inflammatory markers in fattening pigs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xu, G.W.; Guo, Z.T.; Lu, X.R.; Liang, C.H.; Gu, X.Y.; Huang, L.P.; Liu, S.Q.; et al. Cordyceps militaris solid medium extract alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulating gut microbiota and metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2025, 15, 1528222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Coercive Conditions | Survival Rate (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S8 | S15 | S17 | WC412 | WC413 | |||
| Tolerance to high temperatures | 80 °C | 10 min | 82.51 ± 3.42 Aa | 69.95 ± 0.86 Ab | 55.89 ± 0.39 Ac | 71.22 ± 2.58 Ab | 55.30 ± 1.52 Ac |
| 20 min | 53.60 ± 1.91 Bab | 56.68 ± 0.87 Bb | 51.07 ± 0.87 Bc | 73.31 ± 0.67 Aa | 57.06 ± 1.51 Ab | ||
| 90 °C | 10 min | 22.71 ± 1.32 Cc | 19.83 ± 1.76 Cc | 37.95 ± 0.56 Cb | 59.65 ± 1.99 Ba | 43.11 ± 1.31 Bb | |
| 20 min | 17.73 ± 1.16 Cd | 9.49 ± 0.61 De | 24.82 ± 1.15 Dc | 51.35 ± 0.70 Ca | 44.86 ± 2.96 Bb | ||
| 100 °C | 10 min | 16.06 ± 0.11 Cd | 3.03 ± 0.35 Ee | 21.28 ± 1.17 Ec | 34.92 ± 1.51 Da | 28.71 ± 0.47 Cb | |
| 20 min | 19.61 ± 0.87 Ca | 1.36 ± 0.06 Ec | 7.62 ± 0.50 Fb | 1.24 ± 0.03 Ec | 2.91 ± 0.07 Dc | ||
| Tolerance to acids | pH 2 | 15.17 ± 0.61 Ca | 9.04 Cb | 4.36 ± 0.62 Cc | 3.17 ± 0.11 Cc | 3.90 ± 0.34 Cc | |
| pH 2.5 | 55.05 ± 0.31 Ba | 12.06 ± 0.14 Bd | 31.20 ± 2.04 Bc | 40.06 ± 1.82 Bb | 50.22 ± 2.20 Ba | ||
| pH 3 | 96.05 ± 1.23 Aa | 90.12 ± 4.11 Aa | 69.50 ± 1.89 Ab | 95.07 ± 0.03 Aa | 97.35 ± 1.07 Aa | ||
| Tolerance to bile salts | 0.10% | 48.07 ± 0.48 Ad | 85.67 ± 1.09 Ac | 93.28 ± 2.24 Ab | 92.21 ± 0.96 Ab | 98.70 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| 0.30% | 45.34 ± 1.19 Bc | 82.07 ± 1.54 Ab | 90.30 ± 5.22 Aa | 81.55 ± 1.86 Bb | 90.93 ± 0.37 Ba | ||
| 0.50% | 41.19 ± 0.45 Cd | 73.29 ± 3.40 Bc | 85.82 ± 0.75 Aab | 78.44 ± 0.92 Bbc | 88.56 ± 0.57 Ca | ||
| Ingredient | Initial Eigenvalue | Rotational Load Sum of Squares | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Percentage of Variance (%) | Cumulative (%) | Total | Percentage of Variance (%) | Cumulative (%) | |
| 1 | 6.733 | 56.108 | 56.108 | 6.102 | 50.85 | 50.85 |
| 2 | 3.25 | 27.086 | 83.195 | 3.331 | 27.759 | 78.609 |
| 3 | 1.399 | 11.66 | 94.854 | 1.949 | 16.246 | 94.854 |
| Serial No. | Strain | Y1 Score | Y2 Score | Y3 Score | Combined Score | Ranking |
| 1 | WC412 | 1.97 | 1.96 | 0.95 | 1.75 | 1 |
| 2 | WC413 | 1.95 | 0.63 | −0.64 | 1.19 | 2 |
| 3 | S17 | 1.05 | −1.69 | −1.34 | −0.02 | 3 |
| 4 | S15 | −0.8 | −2.11 | 1.5 | −0.85 | 4 |
| 5 | S8 | −4.18 | 1.2 | −0.47 | −2.07 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, X.; Huang, H.; Yu, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X. A Novel Weizmannia coagulans Strain WC412 with Superior Environmental Resilience Improves Growth Performance of Mice by Regulating the Intestinal Microbiota. Animals 2025, 15, 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162446
Xiao X, Huang H, Yu W, Liu J, Hu Y, Yu X, Zhang X. A Novel Weizmannia coagulans Strain WC412 with Superior Environmental Resilience Improves Growth Performance of Mice by Regulating the Intestinal Microbiota. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162446
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Xue, Hao Huang, Wendi Yu, Jun Liu, Yuanliang Hu, Xiang Yu, and Xicai Zhang. 2025. "A Novel Weizmannia coagulans Strain WC412 with Superior Environmental Resilience Improves Growth Performance of Mice by Regulating the Intestinal Microbiota" Animals 15, no. 16: 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162446
APA StyleXiao, X., Huang, H., Yu, W., Liu, J., Hu, Y., Yu, X., & Zhang, X. (2025). A Novel Weizmannia coagulans Strain WC412 with Superior Environmental Resilience Improves Growth Performance of Mice by Regulating the Intestinal Microbiota. Animals, 15(16), 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162446





