Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Effects of α-Mangostin Against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus: In Vitro Assay
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Compound Preparation
2.2. Cell Culture and Virus Preparation
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Antiviral Activity Assays
2.5. Immunoperoxidase Monolayer Assay (IPMA)
2.6. Viral Load Quantification and Cytokine mRNA Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR
| Genes | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size | Accession Numbers and References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viral load quantification | |||
| FCoV 3′UTR-F | GGCAACCCGATGTTTAAAACTGG | 210 | DQ010921.1 [28] |
| FCoV 3′UTR-R | CACTAGATCCAG ACGTTAGCTC | ||
| mRNA cytokines | |||
| fe-TNF-α-F | TGGCCTGCAACTAATCAACC | 251 | NM_001009835.1 [29] |
| fe-TNF-α-R | GTGTGGAAGGACATCCTTGG | ||
| fe-IFN-β-F | GAAGGAGGAAGCCATATTGGT | 172 | NM_001009297.1 [30] |
| fe-IFN-β-R | CTCCATGATTTCCTCCAGGAT | ||
| fe-IL-6-F | CCCTGCAGACAAAATGGAAGA | 110 | L16914.1 [31] |
| fe-IL-6-R | GTGCCTCCTTGCTGTCCTCA | ||
| fe-GAPDH-F | CATCAATGGAAAGCCCATCAC | 97 | NM 001009307.1 [32] |
| fe-GAPDH-R | CCCAGTAGACTCCACAACATAC | ||
2.7. Drug Combination Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxicity of α-MG and α-Mangostin-Rich Extracts (AMEs)
3.2. Antiviral Activity of α-MG and Its Enriched Extracts (AMEs)
3.3. α-MG and Its Enriched Extracts (AMEs) Potently Inhibit FIPV Infection in Infected Cells
3.4. Virucidal Effect of α-MG and α-Mangostin-rich Extracts (AMEs)
3.5. α-MG and α-Mangostin-Rich Extracts (AMEs) Reduced FIPV Replication and Modulated Cytokine Expression in a Dose-Dependent Manner
3.6. Drug Combination Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| α-MG | α-mangostin |
| β-MG | β-mangostin |
| γ-MG | γ-mangostin |
| AMEs | α-mangostin-rich extracts |
| CRFK cell | Crandell Rees feline kidney cell |
| FCoV | Feline coronavirus |
| FECV | Feline enteric coronavirus |
| FIP | Feline infectious peritonitis |
| IPMA | Immunoperoxidase monolayer assay |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| TCID50 | Tissue culture infectious dose |
| ZIP | Zero interaction potency |
References
- Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, D.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.B.; Wang, K.; Hu, G.X.; Gao, F.S. An updated review of feline coronavirus: Mind the two biotypes. Virus Res. 2023, 326, 199059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasker, S.; Addie, D.D.; Egberink, H.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hosie, M.J.; Truyen, U.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Frymus, T.; Lloret, A.; et al. Feline infectious peritonitis: European advisory board on cat diseases guidelines. Viruses 2023, 15, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L. Feline infectious peritonitis: Still an enigma? Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C. An update on feline infectious peritonitis: Virology and immunopathogenesis. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbon, A.J.; Meli, M.L.; Barker, E.N.; Davidson, A.D.; Tasker, S.; Kipar, A. Inflammatory mediators in the mesenteric lymph nodes, site of a possible intermediate phase in the immune response to feline coronavirus and the pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis? J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 166, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.E.; Vogel, H.; Castillo, D.; Olsen, M.; Pedersen, N.; Murphy, B.G. Investigation of monotherapy and combined anticoronaviral therapies against feline coronavirus serotype II In Vitro. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, P.J.; Bannasch, M.; Thomasy, S.M.; Murthy, V.D.; Vernau, K.M.; Liepnieks, M.; Montgomery, E.; Knickelbein, K.E.; Murphy, B.; Pedersen, N.C. Antiviral treatment using the adenosine nucleoside analogue GS-441524 in cats with clinically diagnosed neurological feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Perron, M.; Bannasch, M.; Montgomery, E.; Murakami, E.; Liepnieks, M.; Liu, H. Efficacy and safety of the nucleoside analog GS-441524 for treatment of cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triratapiban, C.; Lueangaramkul, V.; Phecharat, N.; Pantanam, A.; Lekcharoensuk, P.; Theerawatanasirikul, S. First study on in vitro antiviral and virucidal effects of flavonoids against feline infectious peritonitis virus at the early stage of infection. Vet. World 2023, 16, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundeesomchok, K.; Filly, A.; Rakotomanomana, N.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Chemat, F. Extraction of α-mangostin from Garcinia mangostana L. using alternative solvents: Computational predictive and experimental studies. LWT 2016, 65, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathy, S.U.P.; Lalitha, L.C.P.; Rahim, S.; Gopinath, C.; Haleema, S.; SarojiniAmma, S.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. A review on synthetic and pharmacological potential of compounds isolated from Garcinia mangostana Linn. Phytomed. Plus 2022, 2, 100253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.Y.; Hashim, N.M.; Mariod, A.A.; Mohan, S.; Abdulla, M.A.; Abdelwahab, S.I.; Arbab, I.A. α-Mangostin from Garcinia mangostana Linn: An updated review of its pharmacological properties. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meah, M.S.; Lertcanawanichakul, M.; Pedpradab, P.; Lin, W.; Zhu, K.; Li, G.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Synergistic effect on anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among combinations of α-mangostin-rich extract, lawsone methyl ether and ampicillin. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Wan, M.; Loh, B.N. Active constituents against HIV-1 protease from Garcinia mangostana. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaneyfelt, M.E.; Burke, A.D.; Graff, J.W.; Jutila, M.A.; Hardy, M.E. Natural products that reduce rotavirus infectivity identified by a cell-based moderate-throughput screening assay. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, S.; Chin, Y.W.; Lee, C. Mangosteen xanthones suppress hepatitis C virus genome replication. Virus Genes 2014, 49, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasuk, M.; Songprakhon, P.; Chimma, P.; Sratongno, P.; Na-Bangchang, K.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T. Alpha-mangostin inhibits both dengue virus production and cytokine/chemokine expression. Virus Res. 2017, 240, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Agrawal, M.; Almelkar, S.; Jeengar, M.K.; More, A.; Alagarasu, K.; Kumar, N.V.; Mainkar, P.S.; Parashar, D.; Cherian, S. In Vitro and in vivo studies reveal α-Mangostin, a xanthonoid from Garcinia mangostana, as a promising natural antiviral compound against chikungunya virus. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suroengrit, A.; Cao, V.; Wilasluck, P.; Deetanya, P.; Wangkanont, K.; Hengphasatporn, K.; Harada, R.; Chamni, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Shigeta, Y.; et al. Alpha and gamma mangostins inhibit wild-type B SARS-CoV-2 more effectively than the SARS-CoV-2 variants and the major target is unlikely the 3C-like protease. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasuk, M.; Songprakhon, P.; Chieochansin, T.; Choomee, K.; Na-Bangchang, K.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T. Alpha-mangostin inhibits viral replication and suppresses nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-mediated inflammation in dengue virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Keach, J.E.; Behl, T.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Synergistic effect of α-mangostin on antibacterial activity of tetracycline, erythromycin, and clindamycin against acne involved bacteria. Chin. Herb. Med. 2019, 11, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meah, M.S.; Panichayupakaranant, P. α-Mangostin-rich extract: A potential oral antibacterial agent prepared by green extraction. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Chin. Med. 2020, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Kuo, C.J.; Phecharat, N.; Chootip, J.; Lekcharoensuk, C.; Lekcharoensuk, P. Structural-based virtual screening and in vitro assays for small molecules inhibiting the feline coronavirus 3CL protease as a surrogate platform for coronaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekcharoensuk, P.; Nanakorn, J.; Wajjwalku, W.; Webby, R.; Chumsing, W. First whole genome characterization of swine influenza virus subtype H3N2 in Thailand. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New mathematical model for relative quantification in Real-Time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; de Groot, R.J.; Cepica, A.; Egberink, H.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J. Detection of feline coronavirus RNA in feces, tissues, and body fluids of naturally infected cats by reverse transcriptase PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Hohdatsu, T.; Toda, A.; Tanabe, M.; Koyama, H. TNF-alpha, produced by feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV)-infected macrophages, upregulates expression of type II FIPV receptor feline aminopeptidase N in feline macrophages. Virology 2007, 364, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, J.; Li, Z.; Kang, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Yin, H.; Hu, X.; Qu, L. Feline infectious peritonitis virus Nsp5 inhibits type I interferon production by cleaving NEMO at multiple sites. Viruses 2020, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hetzel, U.; Akens, M.K.; Mislin, C.N.; Reinacher, M.; Lutz, H. Cytokine mRNA levels in isolated feline monocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 78, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, M.S.R.; Kuan, C.O.; Selvarajah, G.T.; Wei, T.S.; Arshad, S.S.; Bejo, M.H.; Omar, A.R. Transcriptional profiling of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection in CRFK cells and in PBMCs from FIP diagnosed cats. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 3.0: An interactive analysis and consensus interpretation of multi-drug synergies across multiple samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W739–W743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, K.; Alagarasu, K.; Patil, P.; Agrawal, M.; More, A.; Kumar, N.V.; Mainkar, P.S.; Parashar, D.; Cherian, S. In Vitro antiviral activity of α-mangostin against dengue virus serotype-2 (DENV-2). Molecules 2021, 26, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saputro, A.H.; Amelia, T.; Mahardhika, A.B.; Widyawaruyanti, A.; Wahyuni, T.S.; Permanasari, A.A.; Artarini, A.A.; Tjahjono, D.H.; Damayanti, S. Alpha-mangostin, piperine and beta-sitosterol as hepatitis C antivirus (HCV): In Silico and In Vitro studies. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megat Mazhar Khair, M.H.; Selvarajah, G.T.; Omar, A.R.; Mustaffa-Kamal, F. Expression of Toll-like receptors 3, 7, 9 and cytokines in feline infectious peritonitis virus-infected CRFK cells and feline peripheral monocytes. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, Y.; Ritz, S.; Weber, K.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Randomized, placebo controlled study of the effect of propentofylline on survival time and quality of life of cats with feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doki, T.; Takano, T.; Kawagoe, K.; Kito, A.; Hohdatsu, T. Therapeutic effect of anti-feline TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody for feline infectious peritonitis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 104, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagade, S.B.; Patil, M. Recent Advances in Microwave Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Complex Herbal Samples: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 51, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvanatemiya, V.; Srean, P.; Klangbud, W.K.; Venkatachalam, K.; Wongsa, J.; Parametthanuwat, T.; Charoenphun, N. A review of the influence of various extraction techniques and the biological effects of the xanthones from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) Pericarps. Molecules 2022, 27, 8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannavacciuolo, C.; Pagliari, S.; Celano, R.; Campone, L.; Rastrelli, L. Critical analysis of green extraction techniques used for botanicals: Trends, priorities, and optimization strategies—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, D.; Zenger, K.; Alberer, M.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Dorsch, R.; Matiasek, K.; Kolberg, L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Meli, M.L.; et al. Curing cats with feline Iinfectious peritonitis with an oral multi-component drug containing GS-441524. Viruses 2021, 13, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wen, G. Strategies for combating FIPV infection: Antiviral agents and vaccines. Res. Vet. Sci. 2025, 192, 105709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
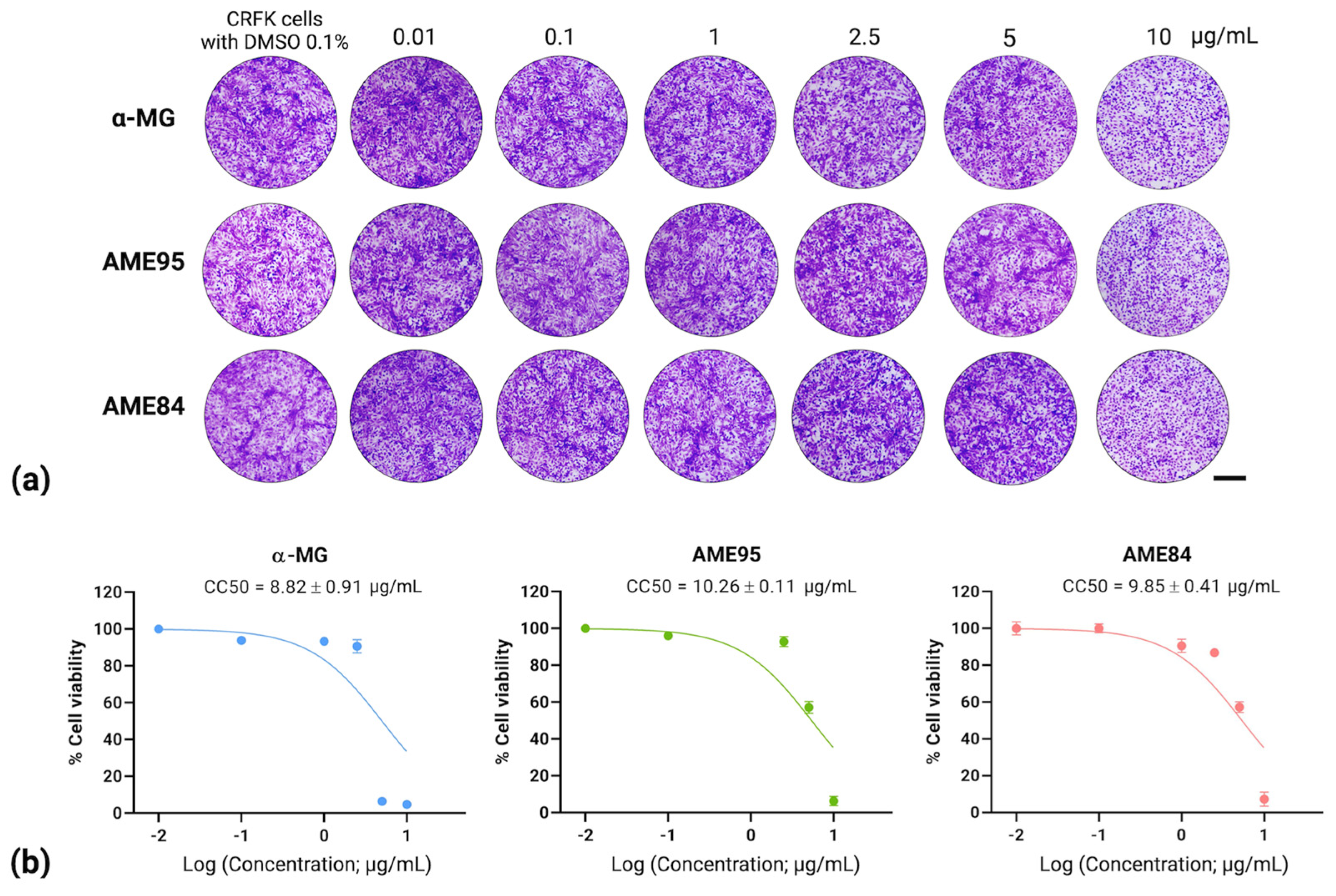
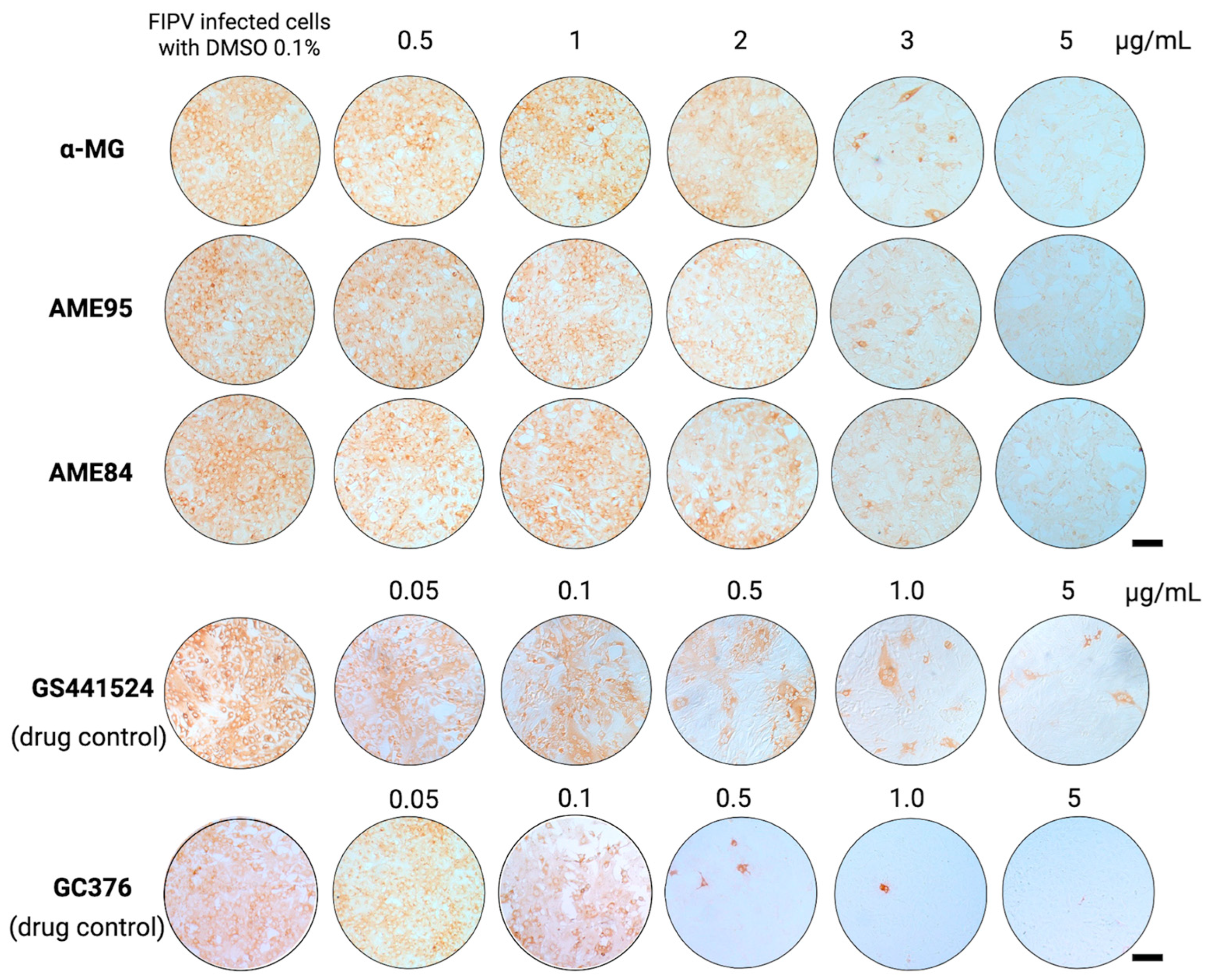

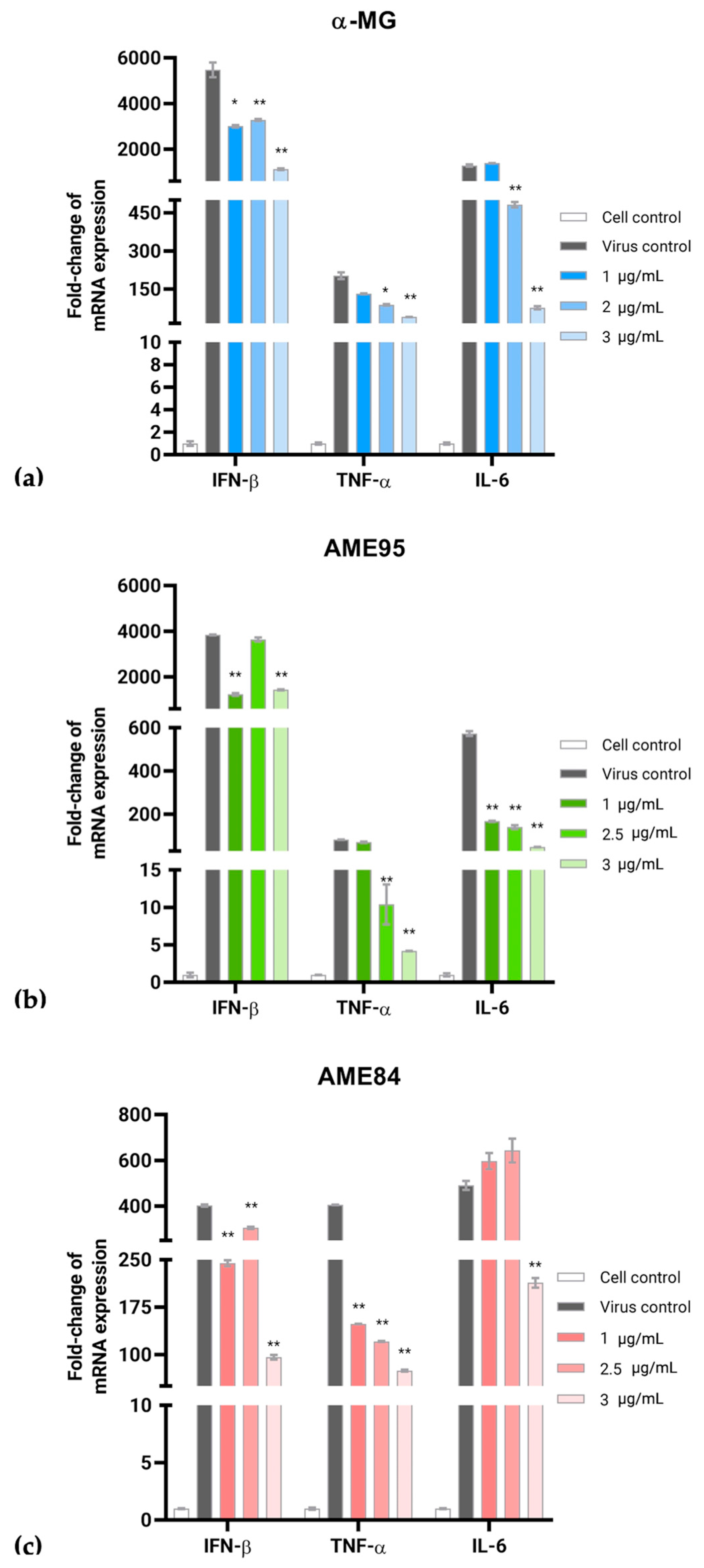

| Compounds | Cytotoxicity (CC50; µg/mL) 1 | Antiviral Activity Assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-infection Assay (EC50; µg/mL) 2 | Selective Index (CC50/EC50) | Virucidal Effect (log TCID50/mL) 3 | ||
| α-MG | 8.82 ± 0.91 | 2.71 ± 0.42 | 3.25 | 0.17 |
| AME95 | 10.26 ± 0.11 | 2.80 ± 0.45 | 3.66 | 1.17 |
| AME84 | 9.85 ± 0.41 | 2.88 ± 0.46 | 3.42 | 1.17 |
| GS-441524 (Drug control) | 58.06 ± 0.67 | 0.62 ± 0.09 | 93.65 | ND |
| GC-376 (Drug control) | 44.47 ± 0.92 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 404.27 | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lueangaramkul, V.; Termthongthot, P.; Mana, N.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Semkum, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P.; Theerawatanasirikul, S. Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Effects of α-Mangostin Against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus: In Vitro Assay. Animals 2025, 15, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162417
Lueangaramkul V, Termthongthot P, Mana N, Panichayupakaranant P, Semkum P, Lekcharoensuk P, Theerawatanasirikul S. Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Effects of α-Mangostin Against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus: In Vitro Assay. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162417
Chicago/Turabian StyleLueangaramkul, Varanya, Pratipa Termthongthot, Natjira Mana, Pharkphoom Panichayupakaranant, Ploypailin Semkum, Porntippa Lekcharoensuk, and Sirin Theerawatanasirikul. 2025. "Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Effects of α-Mangostin Against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus: In Vitro Assay" Animals 15, no. 16: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162417
APA StyleLueangaramkul, V., Termthongthot, P., Mana, N., Panichayupakaranant, P., Semkum, P., Lekcharoensuk, P., & Theerawatanasirikul, S. (2025). Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Effects of α-Mangostin Against Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus: In Vitro Assay. Animals, 15(16), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162417









