Pharmacokinetics of Tolfenamic Acid Administered Orally and Intravenously at Different Doses in Pekin Ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. HPLC Conditions
2.4. Validation of the Analytical Method
2.5. Sample Extraction
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.7. Plasma Protein Binding
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animals
3.2. Intravenous Administration
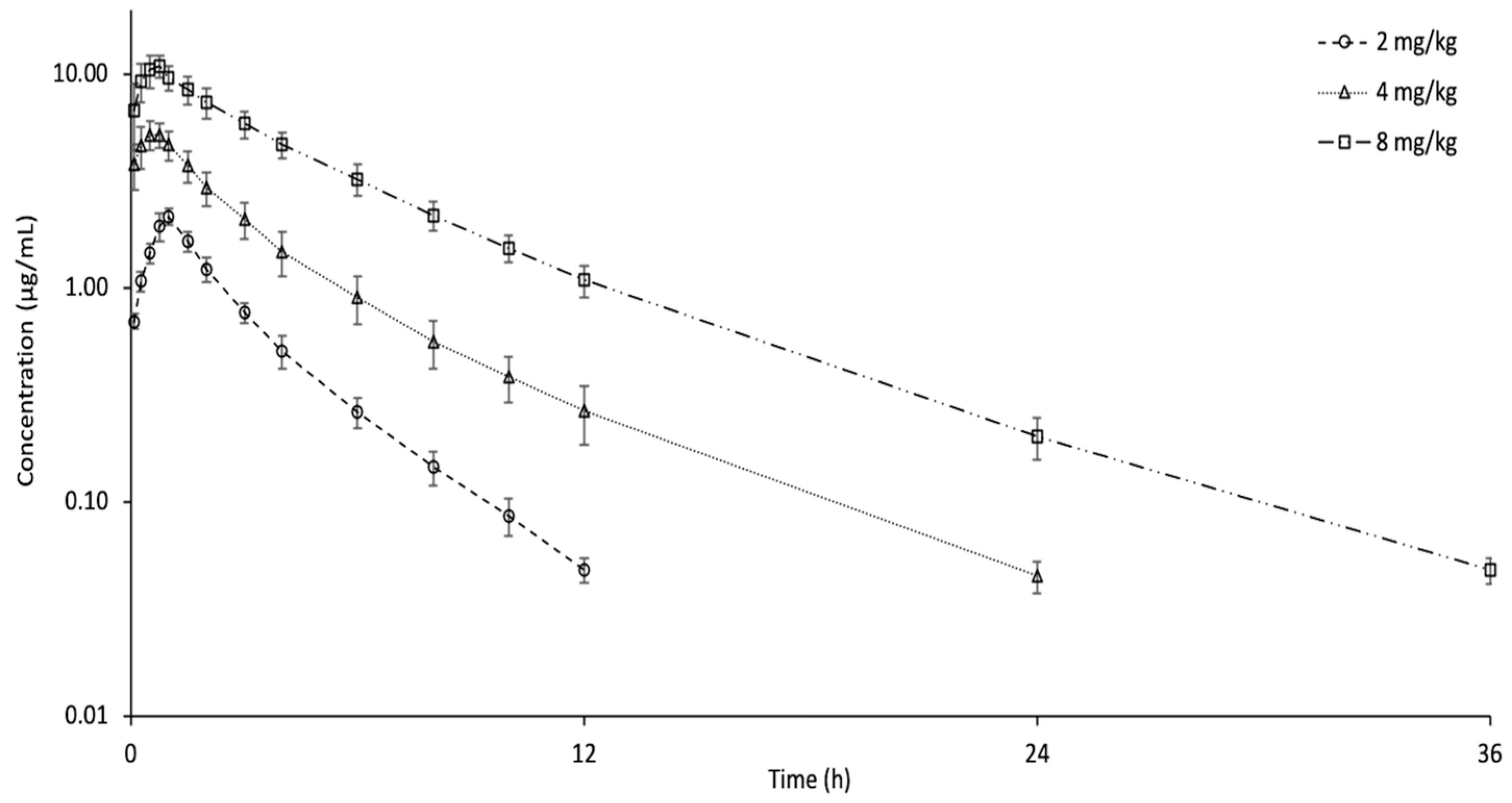
3.3. Oral Administration
3.4. Plasma Protein Binding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corum, O.; Uney, K.; Coskun, D.; Durna Corum, D.; Cetin, G.; Elmas, M. Plasma and milk pharmacokinetics and estimated milk withdrawal time of tolfenamic acid in lactating sheep. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e70047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CVMP. Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products: Tolfenamic Acid Summary Report; EMEA/MRL/183/97-FINAL. European Medicinces Agency (EMEA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/mrl-report/tolfenamic-acid-summary-report-committee-veterinary-medicinal-products_en.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Ahmed, S.; Sheraz, M.A.; Ahmad, I. Tolfenamic acid. Profiles Drug Subst. Excip. Relat. Methodol. 2018, 43, 255–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lees, P.; McKellar, Q.A.; Foot, R.; Gettinby, G. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid in ruminating calves: Evaluation in models of acute inflammation. Vet. J. 1998, 155, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landoni, M.F.; Cunningham, F.M.; Lees, P. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tolfenamic acid in calves. Res. Vet. Sci. 1996, 61, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, P.K.; Landoni, M.F.; Lees, P. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions of tolfenamic acid and marbofloxacin in goats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 80, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machin, K. Controlling avian pain. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. N. Am. Ed. 2005, 27, 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Durna Corum, D.; Corum, O.; Uney, K.; Turk, E.; Sakin, F.; Giorgi, M. Pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid in ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica) after different administration routes. Br. Poult. Sci. 2025, 66, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, J.M.; Kreyenbuhl, K.; Kummrow, M. Methods of analgesia and euthanasia in backyard poultry. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2023, 165, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, K. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Birds. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, A.; Valentine, A. Pain in birds: A review for veterinary nurses. Vet. Nurs. J. 2018, 33, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.H. Bacterial and parasitic diseases of anseriformes. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2009, 12, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Available online: https://www.fao.org/poultry-production-products/production/poultry-species/en/ (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Corum, O.; Coskun, D.; Karahan, M.; Durna Corum, D. Effect of different doses of tolfenamic acid administration to ducks on biochemical parameters. Harran Univ. J. Vet. Med. 2024, 13, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, J.Z.; Zhu, M.Y.; Yang, F.X.; Hao, J.P.; He, Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Hou, Z.C.; Zhu, F. Optimizing breeding strategies for pekin ducks using genomic selection: Genetic parameter evaluation and selection progress analysis in reproductive traits. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKellar, Q.A.; Lees, P.; Gettinby, G. Pharmacodynamics of tolfenamic acid in dogs. Evaluation of dose response relationships. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 253, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, O.; Corum, D.D.; Er, A.; Yildiz, R.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of tolfenamic acid in sheep. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekeli, I.O.; Turk, E.; Durna Corum, D.; Corum, O.; Kirgiz, F.C.; Uney, K. Effect of dose on the intravenous pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid in goats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 43, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/other/overview-comments-received-guideline-validation-bioanalytical-methods-emeachmpewp1922172009_en.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Cetin, G.; Corum, O.; Durna Corum, D.; Atik, O.; Altan, F.; Turk, E.; Tekeli, I.O.; Eser Faki, H.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous meloxicam, ketoprofen and tolfenamic acid in chukar partridge (Alectoris chukar). Br. Poult. Sci. 2022, 63, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corum, O.; Durna Corum, D.; Marin, P.; Acar, O.F.; Aksoy, M.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and plasma protein binding of tolfenamic acid in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, E.; Tekeli, I.O.; Durna Corum, D.; Corum, O.; Sakin, F.; Uney, K. Pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid after different administration routes in geese (Anser cygnoides). J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 44, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakaran, V.; Dumka, V.K. Pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid following two oral dose levels in buffalo calves. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 36, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, H.P.; Laroute, V.; Alvinerie, M.; Schneider, M.; Vinclair, P.; Braun, J.P.; Toutain, P.L. The effect of experimental renal failure on tolfenamic acid disposition in the dog. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1997, 18, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laut, S.; Poapolathep, S.; Khidkhan, K.; Klangkaew, N.; Phaochoosak, N.; Wongwaipairoj, T.; Giorgi, M.; Escudero, E.; Marin, P.; Poapolathep, A. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of tolfenamic acid in freshwater crocodiles (Crocodylus siamensis). Animals 2025, 15, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raweewan, N.; Chomcheun, T.; Laovechprasit, W.; Jongkolpath, W.; Klangkaew, N.; Phaochoosak, N.; Poapolathep, S. Pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid in green sea turtles (Chelonia mydas) after intravenous and intramuscular administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 43, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raweewan, N.; Laovechprasit, W.; Giorgi, M.; Chomcheun, T.; Klangkaew, N.; Imsilp, K.; Poapolathep, S. Pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid in Hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) after single intravenous and intramuscular administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 43, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, P.L.; Bousquetmélou, A. Plasma clearance. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuninaka, T.; Sugai, K.; Saito, T.; Mori, N.; Kimura, R.; Murata, T. Studies on the metabolism of N-(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl) anthranilic acid (GEA 6414), a new anti-inflammatory agent. I. Urinary metabolites of GEA 6414 in human, dogs, rabbits and rats (author’s transl). Yakugaku Zasshi 1981, 101, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.M.; Henrich, W.L.; Stoff, J.S. The renal effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Summary and recommendations. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1996, 28, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrestein, G.M. The pharmacokinetics of avian therapeutics. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1991, 21, 1241–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasfi, I.A.; ElGhazali, M.; Hadi, A.A.; Zorob, O.; Boni, N.S.; Alkatheeri, N.A.; Barezaiq, I.M. Pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid and its detection time in urine after intravenous administration of the drug in camels (Camelus dromedarius). Am. J. Vet. Res. 1998, 59, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, J.A.; Remsberg, C.M.; Sayre, C.L.; Forrest, M.L.; Davies, N.M. Flip-flop pharmacokinetics--delivering a reversal of disposition: Challenges and opportunities during drug development. Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 643–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratiwi, R.; Ramadhanti, S.P.; Amatulloh, A.; Megantara, S.; Subra, L. Recent advances in the determination of veterinary drug residues in food. Food 2023, 12, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A. Pharmacokinetics: Disposition and fate of drugs in the body. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 8th ed.; Adams, H.R., Ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 15–56. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | 2 mg/kg | 4 mg/kg | 8 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous | ||||
| t1/2ʎz | h | 1.72 (1.62–1.84) c | 2.98 (2.78–3.15) b | 4.16 (3.97–4.34) a |
| AUC0-last | h *µg/mL | 12.90 (10.67–17.02) c | 38.23 (30.52–50.17) b | 128.44 (100.72–155.83) a |
| AUC0-∞ | h *µg/mL | 13.03 (10.85–17.19) b | 38.45 (30.69–50.51) b | 128.76 (100.96–156.29) a |
| AUCextrap | % | 1.02 (0.76–1.63) | 0.57 (0.48–0.70) | 0.25 (0.18–0.32) |
| MRT0-∞ | h | 1.94 (1.68–2.11) c | 2.94 (2.74–3.45) b | 3.87 (3.63–4.36) a |
| ClT | L/h/kg | 0.15 (0.12–0.18) c | 0.10 (0.80–0.13) b | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) a |
| Vdss | L/kg | 0.30 (0.24–0.39) | 0.31 (0.27–0.36) | 0.24 (0.21–0.29) |
| Ebody | 0.011 (0.009–0.013) c | 0.008 (0.006–0.010) b | 0.005 (0.004–0.006) a | |
| Oral | ||||
| t1/2ʎz | h | 2.13 (1.90–2.37) c# | 3.62 (3.34–3.98) b* | 4.62 (4.48–4.81) a† |
| AUC0-last | h *µg/mL | 6.18 (5.71–6.53) c# | 19.28 (16.24–24.30) b* | 56.34 (44.34–62.41) a† |
| AUC0-∞ | h *µg/mL | 6.32 (5.89–6.70) c# | 19.52 (16.46–24.58) b* | 56.66 (44.60–62.80) a† |
| AUCextrap | % | 2.32 (1.79–2.96) | 1.19 (0.92–1.56) | 0.56 (0.48–0.62) |
| MRT0-∞ | h | 3.14 (2.79–3.41) c | 4.44 (4.06–5.08) b | 5.99 (5.59–6.53) a |
| MAT | h | 1.17 (0.81–1.45) | 1.49 (1.19–1.81) | 2.11 (1.89–2.39) |
| Tmax (median) | h | 1.00 (0.75–1.00) b | 0.63 (0.25–1.00) a | 0.63 (0.25–0.75) a |
| Cmax | µg/mL | 2.25 (2.02–2.48) b | 5.94 (5.56–6.20) a | 11.40 (10.46–13.60) a |
| F | % | 48.52 (39.00–56.18) | 50.77 (48.66–53.93) | 44.00 (40.18–51.77) |
| Tolfenamic Acid Concentration (μg/mL) | Binding Ratio (%) |
|---|---|
| 0.4 | 99.56 ± 0.08 |
| 2 | 99.83 ± 0.01 |
| 10 | 99.85 ± 0.02 |
| 40 | 99.73 ± 0.35 |
| Mean ± SD | 99.74 ± 0.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corum, O.; Uney, K.; Marin, P.; Corum, D.D.; Coskun, D.; Badillo, E.; Elmas, M. Pharmacokinetics of Tolfenamic Acid Administered Orally and Intravenously at Different Doses in Pekin Ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica). Animals 2025, 15, 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162326
Corum O, Uney K, Marin P, Corum DD, Coskun D, Badillo E, Elmas M. Pharmacokinetics of Tolfenamic Acid Administered Orally and Intravenously at Different Doses in Pekin Ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica). Animals. 2025; 15(16):2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162326
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorum, Orhan, Kamil Uney, Pedro Marin, Duygu Durna Corum, Devran Coskun, Elena Badillo, and Muammer Elmas. 2025. "Pharmacokinetics of Tolfenamic Acid Administered Orally and Intravenously at Different Doses in Pekin Ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica)" Animals 15, no. 16: 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162326
APA StyleCorum, O., Uney, K., Marin, P., Corum, D. D., Coskun, D., Badillo, E., & Elmas, M. (2025). Pharmacokinetics of Tolfenamic Acid Administered Orally and Intravenously at Different Doses in Pekin Ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica). Animals, 15(16), 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162326






