Effect of Benzoic Acid on Nutrient Digestibility and Rectal Microbiota of Weaned Holstein Dairy Calves
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Diets, and Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Feed and Feces Sampling and Analysis
2.2.2. Blood Sampling and Determination
2.2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nutrient Digestibility
3.2. Blood Biochemistry
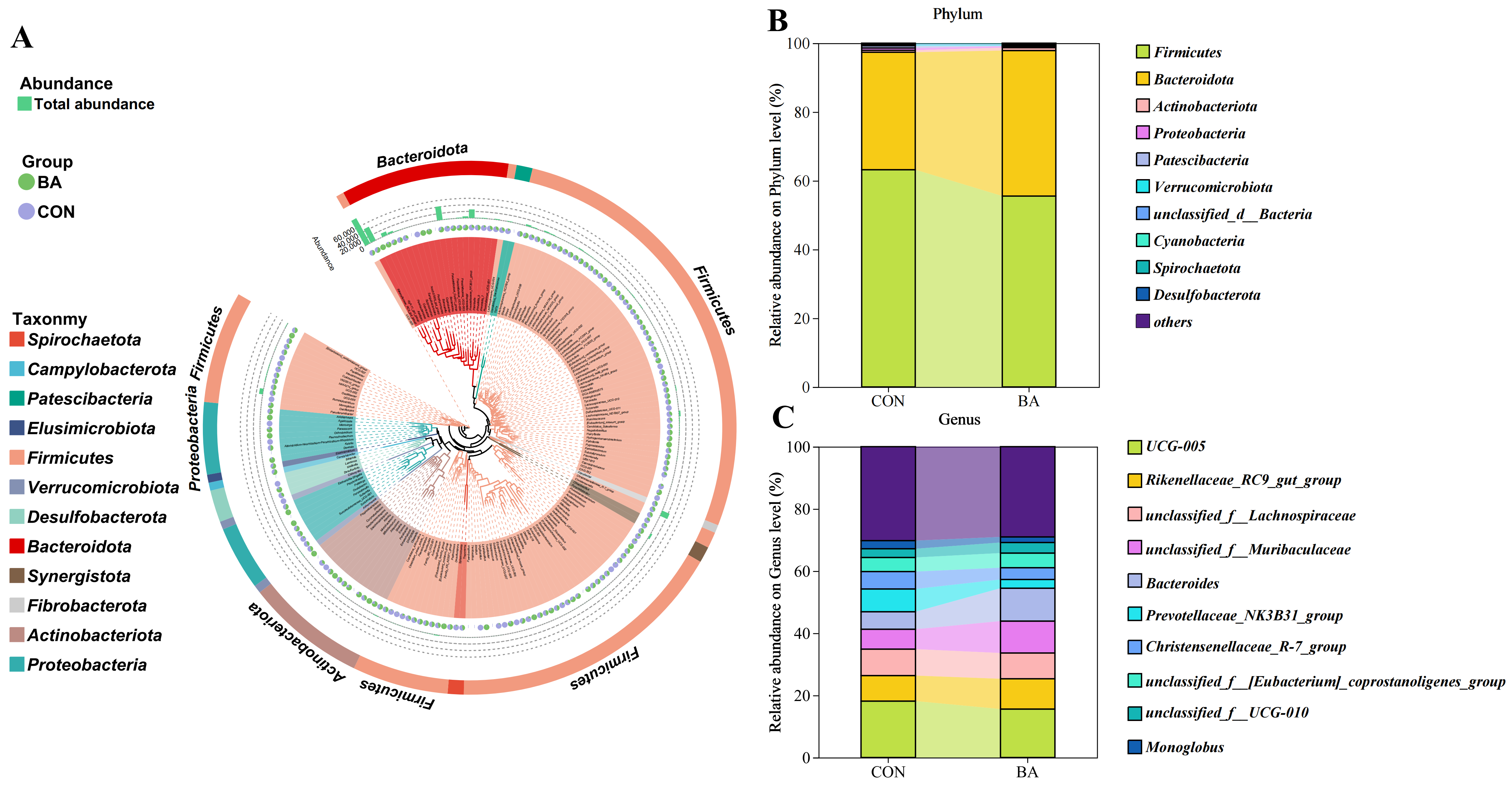
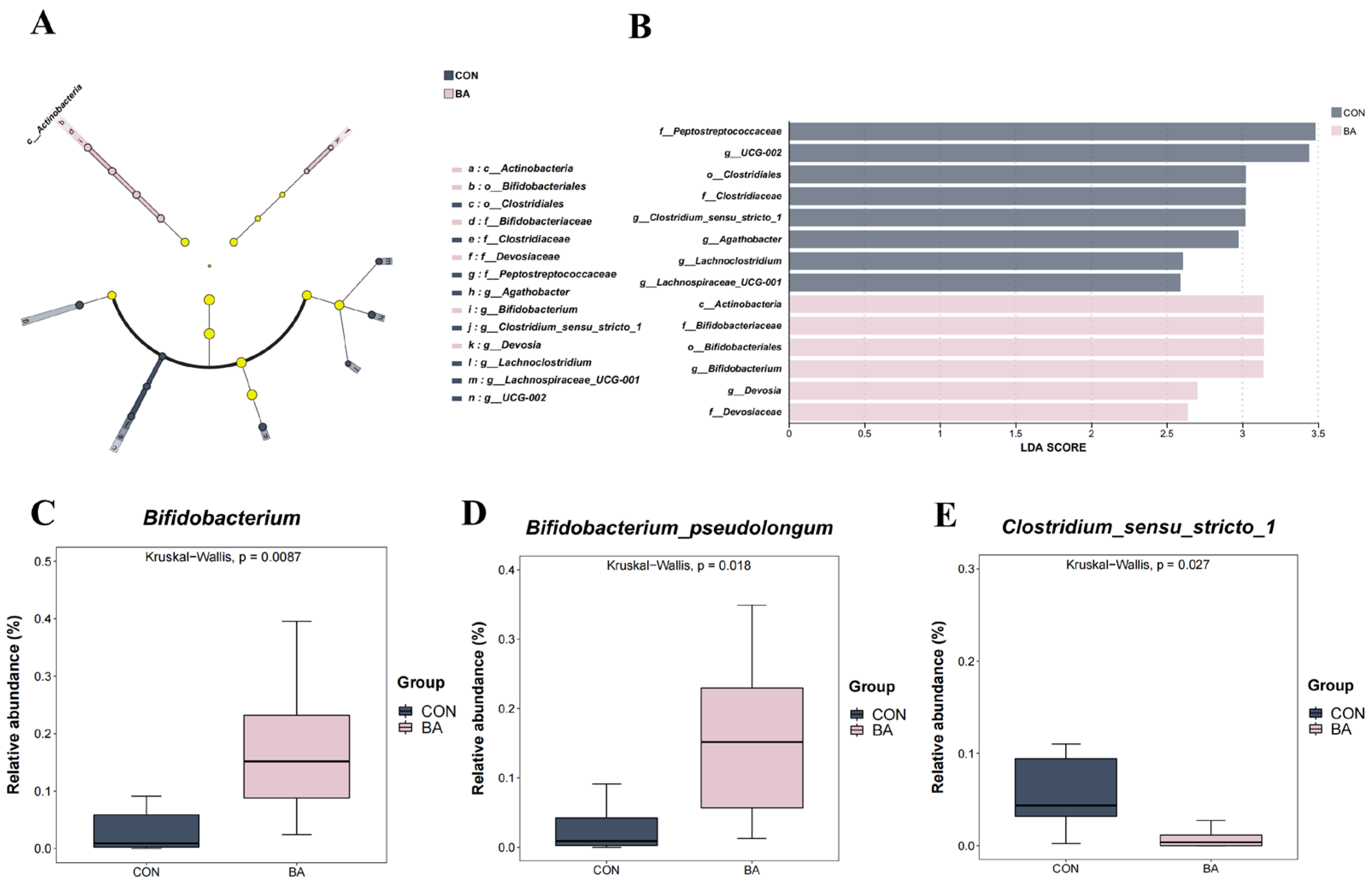
3.3. Rectal Microbial Compositions
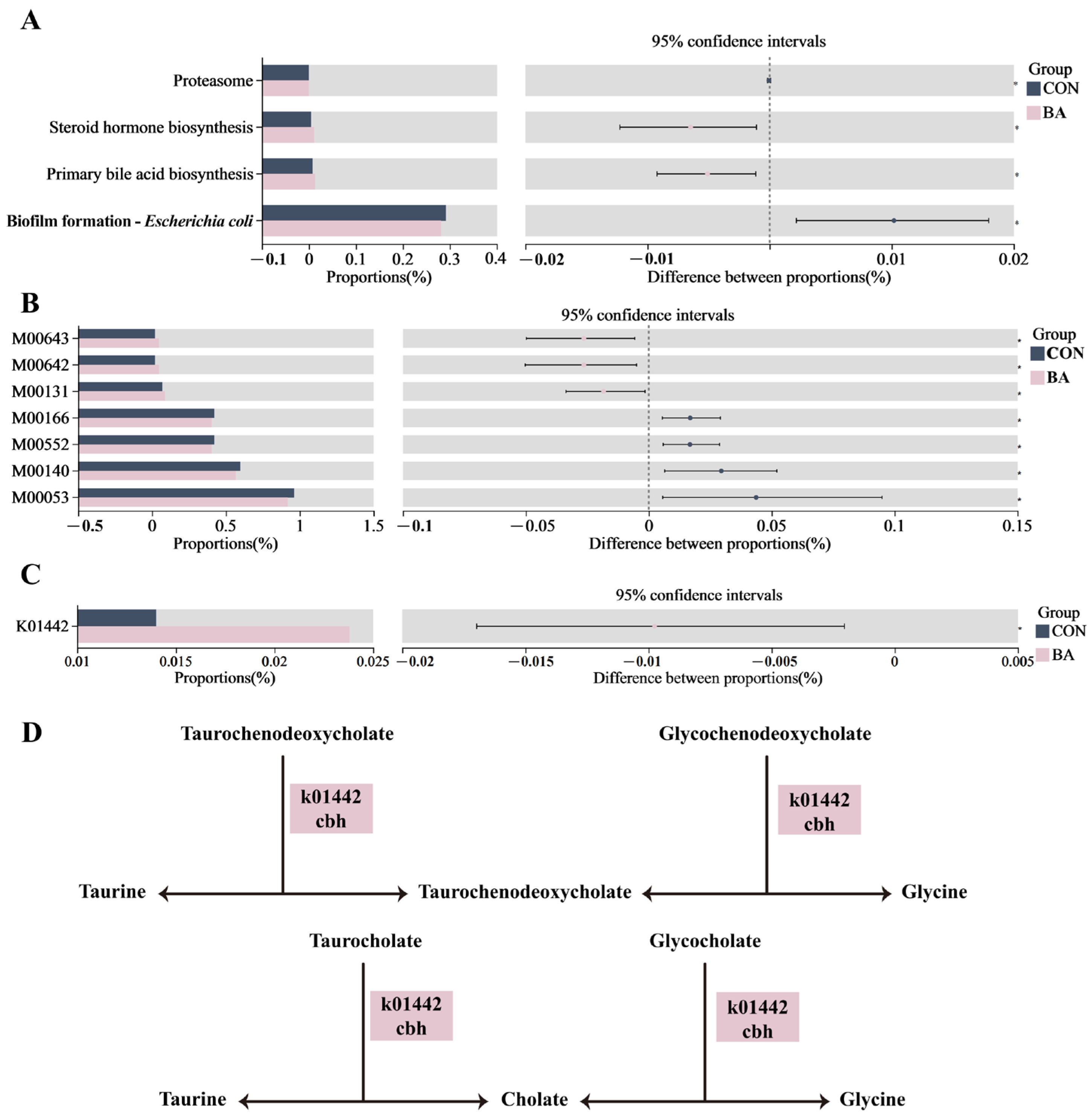
3.4. Functional Prediction in Rectal Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Kong, F.; Cao, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Li, S. Effect of supplementing different levels of l-glutamine on holstein calves during weaning. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, J.; Kaya, C.A.; Beitz, D.; Appuhamy, R. Early stepdown weaning of dairy calves with glutamine and branched-chain amino acid supplementations. Animals 2022, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Gilliam, J.N.; Mourer, G.; Stansberry, C. Comparison of effects of four weaning methods on health and performance of beef calves. Animal 2020, 14, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulbert, L.E.; Moisa, S.J. Stress, immunity, and the management of calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3199–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shah, A.M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zou, H.; Kang, K. Dietary supplementation of yeast cell wall improves the gastrointestinal development of weaned calves. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z. Effect of dietary lactoferrin on the immune functions and serum iron level of weanling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasper, J.; Budzynska, M.; Weary, D.M. Weaning distress in dairy calves: Acute behavioural responses by limit-fed calves. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 110, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yin, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Yao, K.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y. 4-phenylbutyric acid accelerates rehabilitation of barrier function in ipec-j2 cell monolayer model. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, H.K.J.P.; Kaya, C.A.; Baumgard, L.H.; Appuhamy, J.A.D.R. Early step-down weaning of dairy calves from a high milk volume with glutamine supplementation. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Qi, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, K.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S. Dietary organic acids ameliorate high stocking density stress-induced intestinal inflammation through the restoration of intestinal microbiota in broilers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, E.N.; Ragaa, N.M. Eubiotic effect of a dietary acidifier (potassium diformate) on the health status of cultured oreochromis niloticus. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 621–629. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, H.; Ren, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Guggenbuhl, P.; Kluenter, A.M. Growth performance of nursery and grower-finisher pigs fed diets supplemented with benzoic acid. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Yang, Z.; Celi, P.; Yan, L.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, S.; Su, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; et al. Effect of benzoic acid on production performance, egg quality, intestinal morphology, and cecal microbial community of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.M.; Huang, S.; Chalupa-Krebzdak, S.; Vasquez, M.S.; Mandell, I.B.; Bohrer, B.M. Effects of essential oils and (or) benzoic acid in beef finishing cattle diets on the fatty acid profile and shelf life stability of ribeye steaks and ground beef. Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychen, G.; Aquilina, G.; Azimonti, G.; Bampidis, V.; Bastos, M.L.; Bories, G.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Flachowsky, G.; Gropp, J.; et al. Assessment of the application for renewal of authorisation of vevovitall® (benzoic acid) as feed additive for weaned piglets and pigs for fattening. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e5093. [Google Scholar]
- Obeidat, B.S.; Ata, M.; Subih, H.S. Impacts of substituting soybean meal with cold extraction sesame meal on growth accomplishment and health in growing awassi lambs. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Du, D.; Yu, W.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Ma, F.; Sun, P. Effect of dietary benzoic acid supplementation on growth performance, rumen fermentation, and rumen microbiota in weaned holstein dairy calves. Animals 2024, 14, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Effects of biochanin a on lactational performance, nitrogen metabolism, and blood metabolites in dairy cows. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 18, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official’s Analytical Chemists, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Arlington, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; AOAC International: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Z.; Li, J.G.; Gao, Y.X.; Tan, Z.L.; Ren, G.P. Effects of substitution of different levels of steam-flaked corn for finely ground corn on lactation and digestion in early lactation dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 3931–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every base matters: Assessing small subunit rrna primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Hua, D.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.; et al. Dietary supplementation with inulin improves lactation performance and serum lipids by regulating the rumen microbiome and metabolome in dairy cows. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Zhou, M. The impact of diet on the composition and relative abundance of rumen microbes in goat. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsattar, M.M.; Vargas-Bello-Perez, E.; Zhuang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. Impact of dietary supplementation of beta-hydroxybutyric acid on performance, nutrient digestibility, organ development and serum stress indicators in early-weaned goat kids. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Diao, Q.; Wang, H.; Tu, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, N. Effects of weaning age on growth, nutrient digestibility and metabolism, and serum parameters in hu lambs. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 1, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K. Benzoic acid supplementation improves the growth performance, nutrient digestibility and nitrogen metabolism of weaned lambs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1351394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, H.; Gao, Z.; Yu, B.; Zheng, P.; He, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Mao, X. Effects of benzoic acid (vevovitall®) on the performance and jejunal digestive physiology in young pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, D.C.; Bergstrom, J.R.; Calvo, E.P.; Trabue, S.L.; Scoggin, K.D.; Greiner, L.L. The effect of benzoic acid with or without a direct-fed microbial on the nutrient metabolism and gas emissions of growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, H.; Broz, J.; Eder, K. Effect of benzoic acid on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, nitrogen balance, gastrointestinal microflora and parameters of microbial metabolism in piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 90, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, T.; Kluge, H.; Hirche, F.; Broz, J.; Stangl, G.I. Effects of dietary benzoic acid and sodium-benzoate on performance, nitrogen and mineral balance and hippuric acid excretion of piglets. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 66, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Abe, S.; Tada, N.; Sako, A. Effects of dietary fat intake on hdl metabolism. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015, 7, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F. Cholesterol: Another salty pathway to cardiovascular disease? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, D.D.; Li, H.; Li, Z.J.; Han, R.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, X.J.; Kang, X.T.; et al. Effects of different starch sources on glucose and fat metabolism in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2019, 60, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khukhodziinai, J.S.; Das, P.K.; Mukherjee, J.; Banerjee, D.; Ghosh, P.R.; Das, A.K.; Samanta, I.; Jas, R.; Mondal, S.; Patra, A.K. Effect of dietary benzoic acid and oregano essential oil as a substitute for an anti-coccidial agent on growth performance and physiological and immunological responses in broiler chickens challenged with eimeria species. Animals 2024, 14, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, Z.H.; Zhai, C.P.; Li, J.; Ji, C.F.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.M.; Chan, R.; et al. Associations of decreased serum total protein, albumin, and globulin with depressive severity of schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 957671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmat, M.; Cheng, J.; Abbas, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Fan, Z.; Ahmad, B.; Hou, M.; Osman, G.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Effects of bacillus amyloliquefaciens lfb112 on growth performance, carcass traits, immune, and serum biochemical response in broiler chickens. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Kong, R.; Han, X. Association between globulin and diabetic nephropathy in type2 diabetes mellitus patients: A cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 890273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viennois, E.; Merlin, D.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Dietary emulsifier-induced low-grade inflammation promotes colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J. Benzoic acid used as food and feed additives can regulate gut functions. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5721585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; You, J.; Zou, T. A blend of formic acid, benzoic acid, and tributyrin alleviates etec k88-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction by regulating intestinal inflammation and gut microbiota in a murine model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, K.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.; Zeng, Q.; Chu, L.; Hou, D.; Xuan, Y.; Yin, H.; et al. Effect of benzoic acid, enterococcus faecium, and essential oil complex on intestinal microbiota of laying hens under coccidia and clostridium perfringens challenge. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Shen, Z. Mechanisms of gastrointestinal microflora on drug metabolism in clinical practice. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Gao, D.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Hou, G.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Core microbe bifidobacterium in the hindgut of calves improves the growth phenotype of young hosts by regulating microbial functions and host metabolism. Microbiome 2025, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Wan, P.; Cheng, L.; Yan, X. Integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis reveals altered gut microbial communities and metabolite profiles in dairy cows with subclinical mastitis. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J. Arecoline alleviates depression via gut-brain axis modulation, neurotransmitter balance, neuroplasticity enhancement, and inflammation reduction in cums mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 10201–10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, L.F.; Burkhard, R.; Pett, N.; Cooke, N.C.A.; Brown, K.; Ramay, H.; Paik, S.; Stagg, J.; Groves, R.A.; Gallo, M.; et al. Microbiome-derived inosine modulates response to checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Science 2020, 369, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Tan, B.; Chen, J. Supplementation with lycium barbarum polysaccharides reduce obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice by modulation of gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 719967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Johnston, L.; Wang, F. Dietary supplementation with fine-grinding wheat bran improves lipid metabolism and inflammatory response via modulating the gut microbiota structure in pregnant sow. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 835950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzior, D.V.; Quinn, R.A. Review: Microbial transformations of human bile acids. Microbiome 2021, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Gaskins, H.R. Another renaissance for bile acid gastrointestinal microbiology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Yi, S.; Lee, B.H. Purification and characterization of three different types of bile salt hydrolases from bifidobacterium strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lei, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Bifidobacterium pseudolongum-derived bile acid from dietary carvacrol and thymol supplementation attenuates colitis via cgmp-pkg-mtorc1 pathway. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2406917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Items | Proportion (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 2 Starter | 3 Growth Feed | |
| Diet composition (as-fed basis) | ||
| Corn | 32.00 | 39.73 |
| Soybean Meal | 17.00 | 9.73 |
| Cottonseed Meal | 2.73 | 3.27 |
| DDGS | 13.18 | 13.63 |
| Bran | 10.55 | 16.09 |
| Puffed Soybean Flour | 2.73 | |
| Wheat Flour | 4.54 | |
| NaHCO3 | 0.45 | 0.73 |
| 1 Premix | 7.73 | 7.73 |
| Oat Grass | 9.09 | 9.09 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Nutrient Levels (as dry matter basis) | ||
| Dry Matter | 89.03 | 88.64 |
| Crude Protein | 19.13 | 17.63 |
| Ether Extract | 2.88 | 2.48 |
| Ash | 9.47 | 6.40 |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber | 27.92 | 34.57 |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 13.36 | 13.27 |
| Ca | 1.10 | 0.97 |
| P | 0.73 | 0.71 |
| Items (%) | Groups | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | BA | ||
| DM | 70.89 ± 4.14 | 72.74 ± 3.44 | 0.736 |
| CP | 81.11 ± 3.56 | 81.18 ± 1.64 | 0.988 |
| EE | 80.04 ± 3.48 | 80.09 ± 3.18 | 0.993 |
| NDF | 61.22 ± 2.58 | 62.51 ± 2.08 | 0.704 |
| ADF | 57.11 ± 2.84 | 57.75 ± 2.16 | 0.859 |
| Ca | 63.50 ± 3.54 | 64.43 ± 2.19 | 0.827 |
| P | 85.98 ± 2.27 | 86.69 ± 1.28 | 0.788 |
| Items | Groups | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | BA | ||
| TC (mmol/L) | 2.39 ± 0.16 | 2.03 ± 0.10 | 0.067 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.923 |
| AST (U/L) | 82.03 ± 5.0 | 82.88 ± 4.9 | 0.906 |
| ALT (U/L) | 26.12 ± 2.71 | 30.36 ± 4.93 | 0.463 |
| ALP (U/L) | 273.76 ± 31.95 | 263.01 ± 24.39 | 0.793 |
| TP (g/L) | 68.15 ± 1.22 | 67.40 ± 1.13 | 0.662 |
| ALB (g/L) | 34.07 ± 0.84 | 35.00 ± 0.62 | 0.390 |
| GLB (g/L) | 34.08 ± 1.86 | 32.40 ± 0.98 | 0.441 |
| GLU (mmol/L) | 6.38 ± 0.10 | 6.36 ± 0.13 | 0.920 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 12.39 ± 1.36 | 14.06 ± 0.79 | 0.307 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, H.; Du, D.; Huang, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, P. Effect of Benzoic Acid on Nutrient Digestibility and Rectal Microbiota of Weaned Holstein Dairy Calves. Animals 2025, 15, 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142080
Dai H, Du D, Huang Q, Guo J, Li S, Yu W, Zhao Z, Sun P. Effect of Benzoic Acid on Nutrient Digestibility and Rectal Microbiota of Weaned Holstein Dairy Calves. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142080
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Haonan, Dewei Du, Qi Huang, Jia Guo, Shujing Li, Wenli Yu, Zengyuan Zhao, and Peng Sun. 2025. "Effect of Benzoic Acid on Nutrient Digestibility and Rectal Microbiota of Weaned Holstein Dairy Calves" Animals 15, no. 14: 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142080
APA StyleDai, H., Du, D., Huang, Q., Guo, J., Li, S., Yu, W., Zhao, Z., & Sun, P. (2025). Effect of Benzoic Acid on Nutrient Digestibility and Rectal Microbiota of Weaned Holstein Dairy Calves. Animals, 15(14), 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142080





