Urinary NGAL as an Early Marker of Renal Dysfunction in Dogs with Heartworm Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
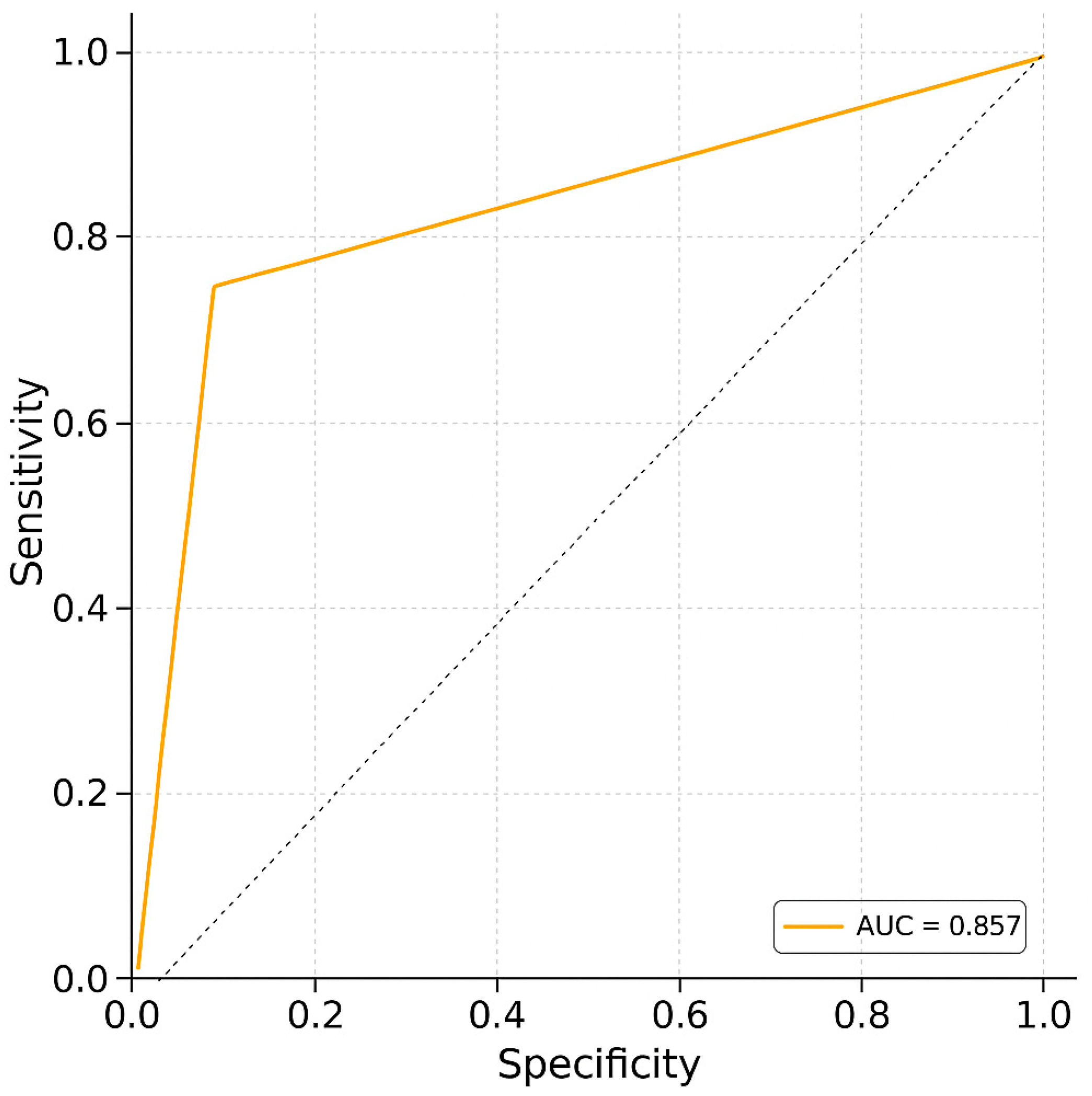
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simón, F.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Morchón, R.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado, I.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Human and animal dirofilariasis: The emergence of a zoonotic mosaic. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 507–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morchón, R.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Lambraño, R.E.H.; Agudo, J.Á.S.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Serafín-Pérez, I.; Fernández-Serafín, C.; Carretón, E. Assessment heartworm disease in the Canary Islands (Spain): Risk of transmission in a hyperendemic area by ecological niche modeling and its future projection. Animals 2023, 13, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.D.; Atkins, C.E. Heartworm biology, treatment, and control. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 1127–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerz, I. Clinical and diagnostic imaging findings in 37 rescued dogs with heartworm disease in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinero, C.; Visser, L.C.; Kellihan, H.B.; Masseau, I.; Rozanski, E.; Clercx, C.; Williams, K.; Abbott, J.; Borgarelli MScansen, B.A. ACVIM consensus statement guidelines for the diagnosis, classification, treatment, and monitoring of pulmonary hypertension in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 549–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuchi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Saito, T.; Yasumura, Y.; Teshima, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Koyama, H. Echocardiographic characteristics of dogs with pulmonary hypertension secondary to respiratory diseases. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; Grandi, G.; González-Miguel, J.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Simón, F.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. Anti-Wolbachia surface protein antibodies are present in the urine of dogs naturally infected with Dirofilaria immitis with circulating microfilariae but not in dogs with occult infections. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormaeche, M.; Carretón, E.; González-Miguel, J.; Gussoni, S.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Simón, F.; Morchón, R. Proteomic analysis of the urine of Dirofilaria immitis-infected dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.H.; Tamarozzi, F.; Morchón, R.; López-Belmonte, J.; Marcos-Atxutegi, C.; Martín-Pacho, R.; Simón, F. Immune response to and tissue localization of the Wolbachia surface protein (WSP) in dogs with natural heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 106, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes-de-Almeida, E.C.; Ferreira, A.M.; Labarthe, N.V.; Caldas, M.L.; McCall, J.W. Kidney ultrastructural lesions in dogs experimentally infected with Dirofilaria immitis (Leidy, 1856). Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 113, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretón, E.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Rodon, J.; Matos, J.I.; Morchón, R.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Evaluation of serum biomarkers and proteinuria for the early detection of renal damage in dogs with heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis). Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, C.A.M.; Meindl, A.G.; Lourenço, B.N.; Coyne, M.; Drake, C.; Murphy, R.; Roth, I.G.; Moorhead, A.R. Evaluation of Renal Values during Treatment for Heartworm Disease in 27 Client-Owned Dogs. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelander, L.; Häggström, J.; Larsson, A.; Syme, H.; Elliott, J.; Heiene, R. Association between Kidney Function and Long-Term Outcome in Dogs with Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Pelander, L.; Häggström, J.; Larsson, A.; Syme, H.; Elliott, J.; Heiene, R. Markers of Renal Tubular Injury in Dogs with Naturally Occurring Renal Disease and Their Association with Survival. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.S.; Moon, H.S.; Seo, S.H.; Hyun, C. Evaluation of serum cystatin-C and symmetric dimethylarginine concentrations in dogs with heart failure from chronic mitral valvular insufficiency. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouchelon, J.L.; Atkins, C.E.; Bussadori, C.; Oyama, M.A.; Vaden, S.L.; Bonagura, J.D.; Chetboul, V.; Cowgill, L.D.; Elliott, J.; Francey, T.; et al. Cardiovascular-Renal Axis Disorders in the Domestic Dog and Cat: A Veterinary Consensus Statement. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 56, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Yerramilli, M.; Obare, E.; Yerramilli, M.; Almes, K.; Jewell, D.E. Serum Concentrations of Symmetric Dimethylarginine and Creatinine in Dogs with Naturally Occurring Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvalho, J.S.; Cowgill, L.D. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Diagnosis and Management. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 47, 1083–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabity, M.B.; Lees, G.E.; Boggess, M.M.; Yerramilli, M.; Obare, E.; Yerramilli, M.; Rakitin, A.; Aguiar, J.; Relford, R. Symmetric Dimethylarginine Assay Validation, Stability, and Evaluation as a Marker for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monari, E.; Troìa, R.; Magna, L.; Gruarin, M.; Grisetti, C.; Fernandez, M.; Balboni, A.; Giunti, M.; Dondi, F. Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin to Diagnose and Characterize Acute Kidney Injury in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Borowski, A.G.; Troughton, R.W.; Thomas, J.D.; Klein, A.L.; Tang, W.H. Renal dysfunction is a stronger determinant of systemic neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels than myocardial dysfunction in systolic heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 17, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris, M.P.; Morales, M.; Ares-Gómez, S.; Esteban-Gil, A.; Gómez-Ochoa, P.; Gascón, M.; Moreno, B.; Castillo, J.A. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) Is Related with the Proteinuria Degree and the Microscopic Kidney Findings in Leishmania-Infected Dogs. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Polzin, D.J.; Rendahl, A.; Granick, J.L. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in dogs with stable or progressive kidney disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheemaeker, S.; Meyer, E.; Schoeman, J.P.; Defauw, P.; Duchateau, L.; Daminet, S. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an early biomarker for acute kidney injury in dogs. Vet. J. 2020, 255, 105423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, L.C.; Im, M.K.; Johnson, L.R.; Stern, J.A. Diagnostic Value of Right Pulmonary Artery Distensibility Index in Dogs with Pulmonary Hypertension: Comparison with Doppler Echocardiographic Estimates of Pulmonary Arterial Pressure. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Parreño, B.; Carretón, E.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Falcón-Cordón, S.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Evaluation of pulmonary hypertension and clinical status in dogs with heartworm by Right Pulmonary Artery Distensibility Index and other echocardiographic parameters. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Matos-Rivero, J.I.; Carretón, E. Persistence of pulmonary endarteritis in canine heartworm infection 10 months after the eradication of adult parasites of Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 273, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venco, L.; Genchi, C.; Vigevani Colson, P.; Kramer, L. Relative utility of echocardiography, radiography, serologic testing and microfilariae counts to predict adultworm burden in dogs naturally infected with heartworms. In Recent Advances in Heartworm Disease, Symposium’01; Seward, R.L., Knight, D.H., Eds.; American Heartworm Society: Batavia, IL, USA, 2003; pp. 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, J.W.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Guerrero, J.; Venco, L. Heartworm disease in animals and humans. Adv. Parasitol. 2008, 66, 193–285. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, R.; Yuchi, Y.; Kanno, H.; Saito, T.; Teshima, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Koyama, H. Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Estimated by Echocardiography in Dogs With Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension Probability. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 771726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.I.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; García-Rodríguez, S.N.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Carretón, E. Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension in Dogs with Heartworm Disease Using the Computed Tomographic Pulmonary Trunk to Aorta Diameter Ratio. Animals 2022, 12, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.I.; García-Rodríguez, S.N.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Right Ventricle Strain Assessed by 2-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography (2D-STE) to Evaluate Pulmonary Hypertension in Dogs with Dirofilaria immitis. Animals 2023, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, J.I.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; García-Rodríguez, S.N.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Echocardiographic Assessment of the Pulmonary Vein to Pulmonary Artery Ratio in Canine Heartworm Disease. Animals 2023, 13, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.; Seiler, S.; Held, M.; Bals, R.; Wilkens, H. Prognostic impact of renal function in precapillary pulmonary hypertension. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 275, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.A. Congestive renal failure: The pathophysiology and treatment of renal venous hypertension. J. Card. Fail. 2012, 18, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalenkova, M.A.; Mikhailova, Z.D.; Klimkin, P.F. NGAL as a marker for some extrarenal complications in acute coronary syndrome. Kardiologiia 2018, 17, 19–26. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, T.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, G.; Krittanawong, C.; El-Am, E.A.; Chaaya, R.G.B.; Xu, L.; Ye, Z.; et al. Lipocalin 2: Could it be a new biomarker in pediatric pulmonary hypertension associated with congenital heart disease? Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Meng, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Cui, C.; Meng, J.; Hu, S.; Wei, Y. Up-Regulated Lipocalin-2 in Pulmonary Hypertension Involving in Pulmonary Artery SMC Resistance to Apoptosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priebe, H.J.; Heimann, J.C.; Hedley-Whyte, J. Effects of renal and hepatic venous congestion on renal function in the presence of low and normal cardiac output in dogs. Circ. Res. 1980, 47, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretón, E.; Cerón, J.J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Acute phase proteins and markers of oxidative stress to assess the severity of the pulmonary hypertension in heartworm-infected dogs. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10 (Suppl. S2), 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Carretón, E. Evaluation of acute phase proteins, adiponectin and endothelin-1 to determine vascular damage in dogs with heartworm disease (Dirofilaria immitis), before and after adulticide treatment. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 309, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, H.W.; Splitter, G.A. Membranous glomerulonephritis in dogs infected with Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Pathol. 1975, 12, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirota, K.; Takahashi, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Hasegawa, A. Canine interstitial nephritis with special reference to glomerular lesions and filariasis. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi 1979, 41, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, C.F.; Gebhardt, B.M.; Bradley, R.E.; Jackson, R.F. Glomerulosclerosis in canine heartworm infection. Vet. Pathol. 1974, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.S.; Moon, H.; Suh, S.I.; Hyun, C. Evaluation of serum symmetric dimethylarginine in dogs with heartworm infection. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 81, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- El Karoui, K.; Viau, A.; Dellis, O.; Bagattin, A.; Nguyen, C.; Baron, W.; Burtin, M.; Broueilh, M.; Heidet, L.; Mollet, G.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress drives proteinuria-induced kidney lesions via Lipocalin 2. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, A.; Castellani, C.; Virzì, G.M.; Fedrigo, M.; Thiene, G.; Valente, M.; Ronco, C.; Vescovo, G. The Role of Congestion in Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 2: New Pathophysiological Insights into an Experimental Model of Heart Failure. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 6, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, T.; Brinkkoetter, P.; Rosenkranz, S. Right Heart Function in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2022, 19, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysz, J.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Jabłonowski, Z.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A. Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauta, F.L.; Boertien, W.E.; Bakker, S.J.; van Goor, H.; van Oeveren, W.; de Jong, P.E.; Bilo, H.; Gansevoort, R.T. Glomerular and Tubular Damage Markers Are Elevated in Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, L.; Langston, C. Proteinuria in dogs and cats. Can. Vet. J. 2012, 53, 631–638. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, F.J.; Feldman, J.D.; Vazquez, J.J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J. Exp. Med. 1961, 113, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagaki, K.; Hayasaki, M.; Ohishi, I. Histopathological and immunopathological evaluation of filarial glomerulonephritis in Dirofilaria immitis infected dogs. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 60, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakagaki, K.; Nogami, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Hammerberg, B.; Tanaka, H.; Ohishi, I. Dirofilaria immitis: Detection of parasite-specific antigen by monoclonal antibodies in glomerulonephritis in infected dogs. Parasitol. Res. 1993, 79, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, J.C.; Carretón, E.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Cerón, J.J.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Acute phase protein response in heartworm-infected dogs after adulticide treatment. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 209, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón-Cordón, S.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Matos, J.I.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Carretón, E. Assessment of Thoracic Radiographic Alterations in Dogs with Heartworm and Their Correlation with Pulmonary Hypertension, Pre- and Post-Adulticide Treatment. Animals 2024, 14, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dogs with Pulmonary Hypertension (n = 14) | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Values |
| FS (%) | 36.34 (29.31–42.94) |
| EF (%) | 65.27 (54.70–72.47) |
| LVIDd (cm) | 0.55 (0.52–0.60) |
| RVDd (cm) | 0.92 (0.77–1.17) |
| IVSd (cm) | 0.92 (0.80–1.12) |
| PA Vmax (m/s) | 0.80 (0.68–0.88) |
| PT:Ao | 1.04 (1.00–1.12) |
| TAPSE (cm) | 1.46 (1.05–1.54) |
| RAV (ml) | 4.93 (1.61–6.41) |
| RPAD index | 25.67 (7.93–33.01) |
| AT (ms) | 60.30 (60.30–80.40) |
| DT (ms) | 126.65 (118.65–144.05) |
| ET (ms) | 160.80 (32.62–185.93) |
| AT/ET | 0.16 (0.11–0.18) |
| TRV m/s | 3.33 (3.00–3.56) |
| Dogs Without Pulmonary Hypertension (n = 28) | |
| Parameter | Values |
| FS (%) | 37.70 (31.81–39.77) |
| EF (%) | 65.90 (58.80–72.09) |
| LVIDd (cm) | 0.57 (0.47–0.69) |
| RVDd (cm) | 0.96 (0.83–1.09) |
| IVSd (cm) | 1.05 (0.94–1.15) |
| PA Vmax (m/s) | 0.82 (0.73–0.92) |
| PT:Ao | 0.99 (0.96–1.05) |
| TAPSE (cm) | 1.35 (1.13–1.50) |
| RAV (ml) | 5.55 (3.44–10.37) |
| RPAD index | 30.27 (21.65–44.57) |
| AT (ms) | 64.00 (60.30–85.42) |
| DT (ms) | 117.25 (100.50–132.32) |
| ET (ms) | 33.95 (24.95–152.43) |
| AT/ET | 0.14 (0.12–0.18) |
| TRV m/s | 1.10 (0.97–1.24) |
| Concentrations of uNGAL | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Absent | ||
| PH | 66.49 ± 6.67 ng/mL (n = 14) | 49.01 ± 14.48 ng/mL (n = 28) | <0.0001 * |
| Microfilaremia | 51.41 ± 18.89 ng/mL (n = 28) | 46.66 ± 15.92 ng/mL (n = 14) | 0.588 |
| Symptoms | 62.09 ± 9.25 ng/mL (n = 19) | 43.70 ± 18.12 ng/mL (n = 23) | 0.427 |
| Proteinuria/Borderline Proteinuria | 62.09 ± 9.25 ng/mL (n = 14) | 43.70 ± 18.12 ng/mL (n = 28) | 0.076 |
| High | Low | ||
| Parasite Burden | 54.83 ± 16.41 ng/mL (n = 20) | 45.64 ± 19.97 ng/mL (n = 22) | 0.154 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Vera-Rodríguez, D.J.; Falcón-Cordón, S.; Morales, B.R.; Morchón, R.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Carretón, E. Urinary NGAL as an Early Marker of Renal Dysfunction in Dogs with Heartworm Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension. Animals 2025, 15, 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142003
Costa-Rodríguez N, Vera-Rodríguez DJ, Falcón-Cordón S, Morales BR, Morchón R, Montoya-Alonso JA, Carretón E. Urinary NGAL as an Early Marker of Renal Dysfunction in Dogs with Heartworm Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142003
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta-Rodríguez, Noelia, Daniel Julio Vera-Rodríguez, Soraya Falcón-Cordón, Beatriz Regina Morales, Rodrigo Morchón, José Alberto Montoya-Alonso, and Elena Carretón. 2025. "Urinary NGAL as an Early Marker of Renal Dysfunction in Dogs with Heartworm Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension" Animals 15, no. 14: 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142003
APA StyleCosta-Rodríguez, N., Vera-Rodríguez, D. J., Falcón-Cordón, S., Morales, B. R., Morchón, R., Montoya-Alonso, J. A., & Carretón, E. (2025). Urinary NGAL as an Early Marker of Renal Dysfunction in Dogs with Heartworm Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension. Animals, 15(14), 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142003










