Microsporidia in Rodents—Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, and Rattus rattus—A Public Health Concern in the Canary Islands, Spain
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Agreement
2.2. Experimental Design
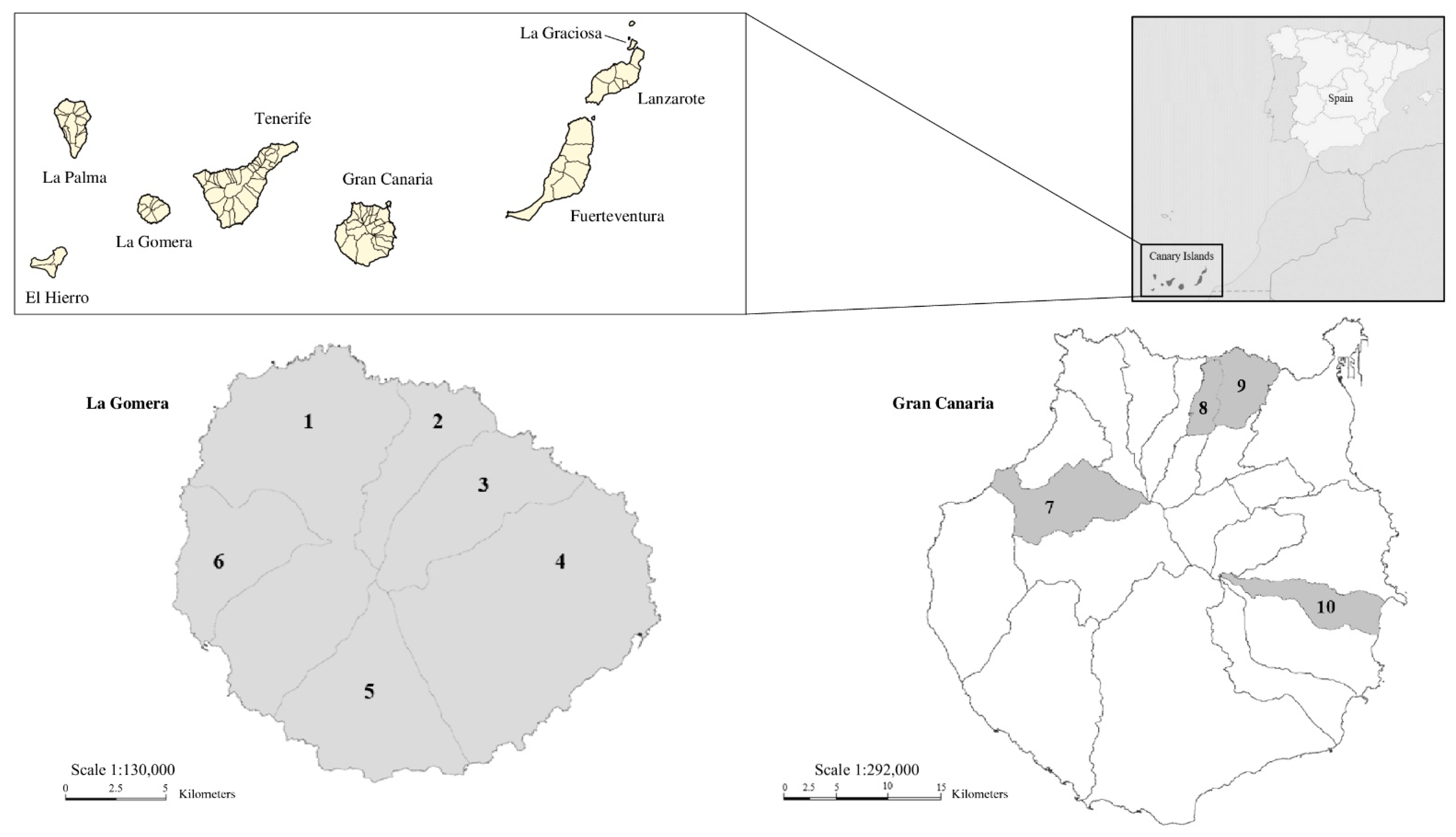
2.3. Study Area, Samples Collection, and Preparation
2.4. Microsporidian Spores
2.5. Microscopic Methods
2.5.1. Light Microscopy: Modified Trichrome Stain
2.5.2. Immunofluorescence Antibody Test
2.6. DNA Isolation
2.7. Nested PCR Amplification
2.8. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
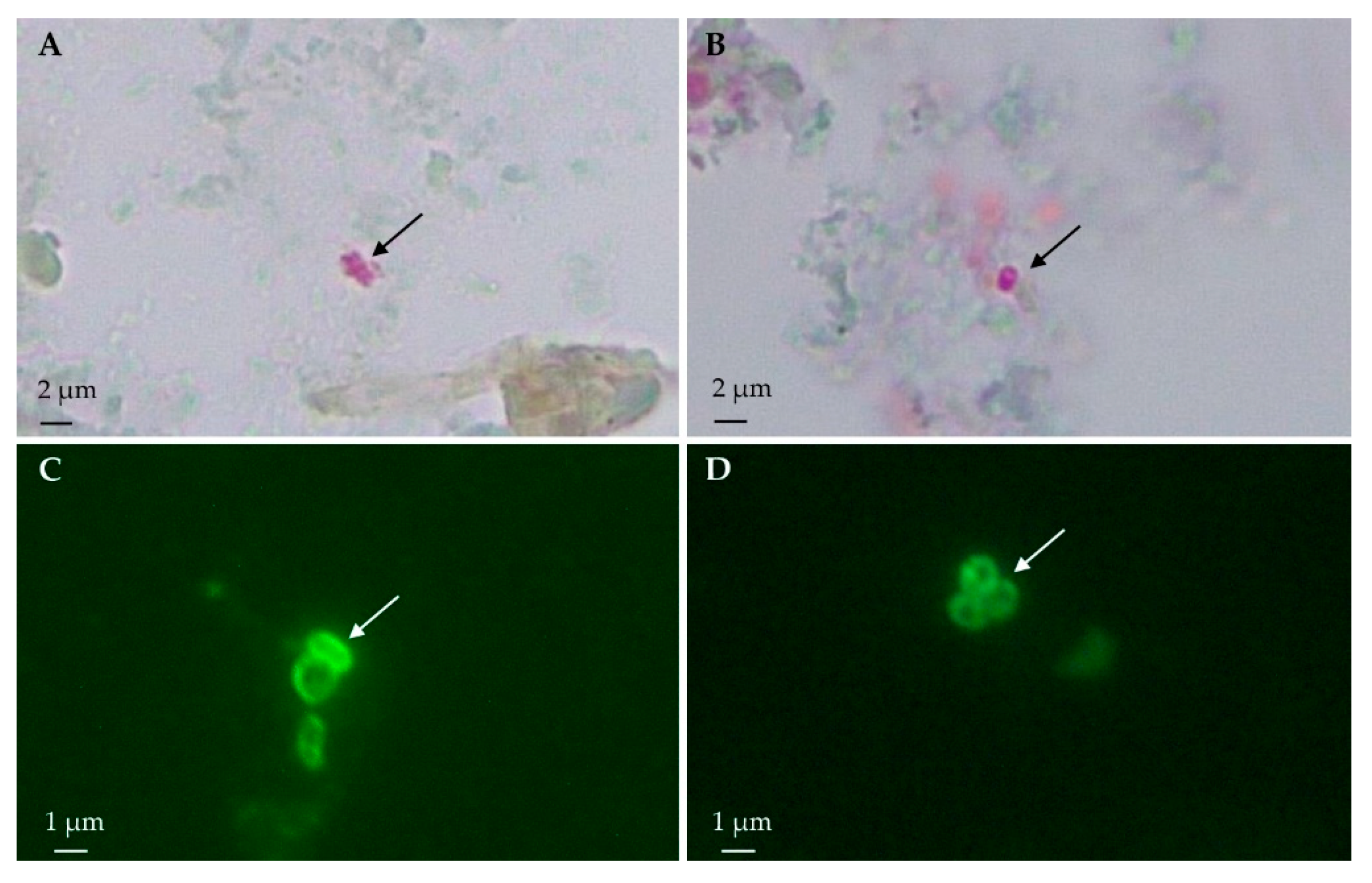
3.1. Light Microscopy: Modified Trichrome Stain
3.2. Immunofluorescence Antibody Test
3.3. Molecular Studies
3.4. Genotyping of Enterocytozoon bieneusi
3.5. Geographical Distribution
3.6. Statistical Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keeling, P.J.; Luker, M.A.; Palmer, J.D. Evidence from Beta-Tubulin Phylogeny That Microsporidia Evolved from Within the Fungi. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, E.S.; Didier, P.J.; Snowden, K.F.; Shadduck, J.A. Microsporidiosis in Mammals. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adl, S.M.; Bass, D.; Lane, C.E.; Lukeš, J.; Schoch, C.L.; Smirnov, A.; Agatha, S.; Berney, C.; Brown, M.W.; Burki, F.; et al. Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2019, 66, 4–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, E.S.; Stovall, M.E.; Green, L.C.; Brindley, P.J.; Sestak, K.; Didier, P.J. Epidemiology of Microsporidiosis: Sources and Modes of Transmission. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Díaz, A.L.; Magnet, A.; Fenoy, S.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Haro, M.; Gordo, F.P.; Miró, G.; Del Águila, C.; Izquierdo, F. Microsporidia Detection and Genotyping Study of Human Pathogenic E. bieneusi in Animals from Spain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, S.E.; Gerba, C.P.; Pepper, I.L. Confirmation of the Human-Pathogenic Microsporidia Enterocytozoon bieneusi, Encephalitozoon intestinalis, and Vittaforma corneae in Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3332–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Becnel, J.J.; Weiss, L.M.; Keeling, P.J.; Didier, E.S.; Williams, B.A.P.; Bjornson, S.; Kent, M.L.; Freeman, M.A.; Brown, M.J.F.; et al. Microsporidia–Emergent Pathogens in the Global Food Chain. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Pan, G.; Weiss, L.M. Microsporidiosis in Humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0001020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.M.; Becnel, J.J. Microsporidia: Pathogens of Opportunity; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, B.; Brady, D.; Pelikánová, M.; Květoňová, D.; Rost, M.; Kostka, M.; Tolarová, V.; Hůzová, Z.; Kváč, M. Unapparent Microsporidial Infection among Immunocompetent Humans in the Czech Republic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, E.S.; Weiss, L.M. Microsporidiosis: Not Just in AIDS Patients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichro, E.; Hoelzl, D.; Krause, R.; Bertha, G.; Reinthaler, F.; Wenisch, C. Microsporidiosis in Travel-Associated Chronic Diarrhea in Immune-Competent Patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu-Acosta, N.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Leal-Guio, Y.; Coronado-Álvarez, N.; Foronda, P.; Alcoba-Florez, J.; Izquierdo, F.; Batista-Díaz, N.; Del Águila, C.; Valladares, B. Enterocytozoon bieneusi (Microsporidia) in Clinical Samples from Immunocompetent Individuals in Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourrisson, C.; Lavergne, R.A.; Moniot, M.; Morio, F.; Poirier, P. Enterocytozoon bieneusi, a Human Pathogen. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2406276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.S. Laboratory Identification of the Microsporidia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Yu, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Santin, M.; Xiao, L.; Li, W. Widespread Distribution of Human-Infective Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes in Small Rodents in Northeast China and Phylogeny and Zoonotic Implications Revisited. Acta Trop. 2024, 253, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinney, B.; Sak, B.; Joachim, A.; Kváč, M. More than a Rabbit’s Tale—Encephalitozoon spp. in Wild Mammals and Birds. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2016, 5, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, M.; Fayer, R. Microsporidiosis: Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Domesticated and Wild Animals. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, A.; Weber, R.; Deplazes, P. Zoonotic Potential of the Microsporidia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.A.; Schmidt, J.P.; Bowden, S.E.; Drake, J.M. Rodent Reservoirs of Future Zoonotic Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7039–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, F.; Blumstein, D.T.; Morand, S. Rodent Sociality and Parasite Diversity. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.G.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Schlegel, M.; Jacob, J.; Pelz, H.J.; Mertens, M.; Wenk, M.; Büchner, T.; Masur, D.; Sevke, K.; et al. Network “Rodent-Borne Pathogens” in Germany: Longitudinal Studies on the Geographical Distribution and Prevalence of Hantavirus Infections. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traveset, A.; Nogales, M.; Alcover, J.A.; Delgado, J.D.; López-Darias, M.; Godoy, D.; Igual, J.M.; Bover, P. A Review on the Effects of Alien Rodents in the Balearic (Western Mediterranean Sea) and Canary Islands (Eastern Atlantic Ocean). Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 1653–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobierno de Canarias. Biota: Banco de Datos de Biodiversidad de Canarias. Available online: https://www.biodiversidadcanarias.es/biota/ (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Galván, A.L.; Sánchez, A.M.M.; Valentín, M.A.P.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Izquierdo, F.; Fenoy, S.; Del Águila, C. First Cases of Microsporidiosis in Transplant Recipients in Spain and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Carrillo, N.; Baz-González, E.; García-Livia, K.; Amaro-Ramos, V.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; Miquel, J.; Abreu-Yanes, E.; Pino-Vera, R.; Feliu, C.; Foronda, P. Data on New Intermediate and Accidental Hosts Naturally Infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis in La Gomera and Gran Canaria (Canary Islands, Spain). Animals 2023, 13, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Águila, C.; Moura, H.; Fenoy, S.; Navajas, R.; Lopez-Velez, R.; Li, L.; Xiao, L.; Leitch, G.J.; Da Silva, A.; Pieniazek, N.J.; et al. In Vitro Culture, Ultrastructure, Antigenic, and Molecular Characterization of Encephalitozoon cuniculi Isolated from Urine and Sputum Samples from a Spanish Patient with AIDS. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvesvara, G.S.; Leitch, G.J.; Da Silva, A.J.; Croppo, G.P.; Moura, H.; Wallace, S.; Slemenda, S.B.; Schwartz, D.A.; Moss, D.; Bryan, R.T.; et al. Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibody and PCR-Amplified Small-Subunit RRNA Identification of a Microsporidian, Encephalitozoon hellem, Isolated from an AIDS Patient with Disseminated Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Bryan, R.T.; Owen, R.L.; Wilcox, C.M.; Gorelkin, L.; Visvesvara, G.S. Improved Light-Microscopical Detection of Microsporidia Spores in Stool and Duodenal Aspirates. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, F.; Moura, H.; Bornay-Llinares, F.J.; Sriram, R.; Hurtado, C.; Magnet, Á.; Fenoy, S.; Visvesvara, G.; Del Águila, C. Production and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies against Encephalitozoon intestinalis and Encephalitozoon sp. Spores and Their Developmental Stages. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, F.; Hurtado-Marcos, C.; Izquierdo, F.; Cuéllar, C.; Fenoy, S.; Sáez, Y.; Magnet, Á.; Galindo-Regal, L.; Uribe, N.; López-Bañeres, M.; et al. Latent Microsporidia Infection Prevalence as a Risk Factor in Colon Cancer Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accoceberry, I.; Thellier, M.; Desportes-Livage, I.; Achbarou, A.; Biligui, S.; Danis, M.; Datry, A. Production of Monoclonal Antibodies Directed against the Microsporidium Enterocytozoon bieneusi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzwinkel-Wladarsch, S.; Lieb, M.; Heise, W.; Löscher, T.; Rinder, H. Direct Amplification and Species Determination of Microsporidian DNA from Stool Specimens. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1996, 1, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckholt, M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Tzipori, S. Prevalence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Swine: An 18-Month Survey at a Slaughterhouse in Massachusetts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2595–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz-González, E.; Martin-Carrillo, N.; García-Livia, K.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; Foronda, P. Molecular Detection of Microsporidia in Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain. Biology 2022, 11, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, M.; Trout, J.M.; Vecino, J.A.C.; Dubey, J.P.; Fayer, R. Cryptosporidium, Giardia and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Cats from Bogota (Colombia) and Genotyping of Isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 141, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz-González, E.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; Foronda, P. High Prevalence of Microsporidia in the North African Hedgehog (Atelerix algirus) in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals 2023, 13, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A Simple Method for Estimating Evolutionary Rates of Base Substitutions through Comparative Studies of Nucleotide Sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Obara, A.; Harada, N.; Sokai, K.; Hirosh, I. Cryptococcus neoformans Can Be Misidentified as a Microsporidian: Studies of Lung Lesions in Leprosy Patients. J. Protozool. 1991, 38, 95S–96S. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, N.J.; Sutherland, G.; Coughlan, K.; Globan, M.; Doultree, J.; Marshall, J.; Baird, R.W.; Pedersen, J.; Dwyer, B. A New Trichrome-Blue Stain for Detection of Microsporidial Species in Urine, Stool, and Nasopharyngeal Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro, M.; Izquierdo, F.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Andrés, I.; Alonso, F.; Fenoy, S.; Del Águila, C. First Detection and Genotyping of Human-Associated Microsporidia in Pigeons from Urban Parks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3153–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, F.; Ollero, D.; Magnet, A.; Galván-Díaz, A.L.; Llorens, S.; Vaccaro, L.; Hurtado-Marcos, C.; Valdivieso, E.; Miró, G.; Hernández, L.; et al. Microsporidia as a Potential Threat to the Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus). Animals 2022, 12, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, C.; Schielke, A.; Ellerbroek, L.; Johne, R. PCR Inhibitors—Occurrence, Properties and Removal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornay-Llinares, F.J.; Da Silva, A.J.; Moura, H.; Schwartz, D.A.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Pieniazek, N.J.; Cruz-López, A.; Hernández-Jaúregui, P.; Guerrero, J.; Javier Enriquez, F. Immunologic, Microscopic, and Molecular Evidence of Encephalitozoon intestinalis (Septata intestinalis) Infection in Mammals Other than Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Fayer, R.; Lal, A.A.; Trout, J.M.; Schaefer, F.W.; Xiao, L. Molecular Characterization of Microsporidia Indicates That Wild Mammals Harbor Host-Adapted Enterocytozoon spp. as Well as Human-Pathogenic Enterocytozoon bieneusi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4495–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Wang, H.T.; Hou, Q.Y.; Qin, Y.; Qin, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, H. Wild Rodents in Three Provinces of China Exhibit a Wide Range of Enterocytozoon bieneusi Diversity. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1427690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec-Matysiak, A.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Kváč, M.; Sak, B.; Hildebrand, J.; Leśniańska, K. Diversity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes among Small Rodents in Southwestern Poland. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danišová, O.; Valenčáková, A.; Stanko, M.; Luptáková, L.; Hasajová, A. First Report of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon intestinalis Infection of Wild Mice in Slovakia. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vioque, F.; Dashti, A.; Santín, M.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Köster, P.C.; Hernández-Castro, C.; García, J.T.; Bailo, B.; Ortega, S.; Olea, P.P.; et al. Wild Micromammal Host Spectrum of Zoonotic Eukaryotic Parasites in Spain. Occurrence and Genetic Characterisation. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2926–e2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Gosálvez, C.; Trelis, M.; Gómez-Samblás, M.; Solano-Parada, J.; Osuna, A.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Fuentes, M.V. Parasite Fauna and Coinfections in Urban Rats Naturally Infected by the Zoonotic Parasite Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Pathogens 2023, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Muadica, A.S.; Maloney, J.G.; Santín, M.; Chicharro, C.; Migueláñez, S.; Nieto, F.J.; Cano-Terriza, D.; et al. Occurrence and Genetic Diversity of Protist Parasites in Captive Non-Human Primates, Zookeepers, and Free-Living Sympatric Rats in the Córdoba Zoo Conservation Centre, Southern Spain. Animals 2021, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Águila, C.; Izquierdo, F.; Navajas, R.; Pieniazek, N.J.; Miró, G.; Alonso, A.I.; Da Silva, A.J.; Fenoy, S. Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Animals: Rabbits and Dogs as New Hosts. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol 1999, 46, 8S–9S. [Google Scholar]
- Santín, M.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Carmena, D.; Mateo, M.; Balseiro, A.; Barral, M.; Lima Barbero, J.F. Habela MÁ Molecular Characterization of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Wild Carnivores in Spain. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2018, 65, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, A.; Santín, M.; Köster, P.C.; Bailo, B.; Ortega, S.; Imaña, E.; Habela, M.Á.; Rivero-Juarez, A.; Vicente, J.; Conejero, C.; et al. Zoonotic Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes in Free-Ranging and Farmed Wild Ungulates in Spain. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, myac070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávalos, G.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Matas-Méndez, P.; Castro-Scholten, S.; Jiménez-Martín, D.; Köster, P.C.; Santín, M.; Bailo, B.; Cano-Terriza, D.; González-Barrio, D.; et al. Detection and Genotyping of Zoonotic Microsporidia in the Endangered Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus). Med. Mycol. 2024, 62, myae027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, S.; Figueiredo, A.M.; Moroni, B.; Abarca, N.; Dashti, A.; Köster, P.C.; Bailo, B.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Gonzálvez, M.; Fayos, M.; et al. Free-Ranging Wolves (Canis lupus) Are Natural Reservoirs of Intestinal Microeukaryotes of Public Health Significance in Southwestern Europe. Zoonoses Public Health 2024, 72, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, A.; Rivero-Juarez, A.; Santín, M.; López-López, P.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Frías-Casas, M.; Köster, P.C.; Bailo, B.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Briz, V.; et al. Enterocytozoon bieneusi (Microsporidia): Identification of Novel Genotypes and Evidence of Transmission between Sympatric Wild Boars (Sus scrofa ferus) and Iberian Pigs (Sus scrofa domesticus) in Southern Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, L.; Castro-Scholten, S.; Cano, C.; Jiménez-Martín, D.; Köster, P.C.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Bailo, B.; Dashti, A.; Hernández-Castro, C.; Cano-Terriza, D.; et al. Iberian Wild Leporidae as Hosts of Zoonotic Enteroparasites in Mediterranean Ecosystems of Southern Spain. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Padilla, A.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Magnet, Á.; Gómez-Guillamón, F.; Izquierdo, F.; Camacho-Sillero, L.; Jiménez-Ruiz, S.; Del Águila, C.; García-Bocanegra, I. Zoonotic Microsporidia in Wild Lagomorphs in Southern Spain. Animals 2020, 10, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, A.; Bahadory, S.; Abdoli, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Global Prevalence of Cattle Microsporidiosis with Focus on Enterocytozoon bieneusi: An Emerging Zoonotic Pathogen. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 200, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, T.; Ren, G.; Li, J.; Tan, F.; Li, W.; Zhu, C.; Lu, G.; Huang, H. Molecular Detection of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Farmed Asiatic Brush-Tailed Porcupines (Atherurus macrourus) and Bamboo Rats (Rhizomys pruinosus) from Hainan Province, China: Common Occurrence, Wide Genetic Variation and High Zoonotic Potential. Acta Trop. 2023, 242, 106915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Feng, Y.; Santin, M. Host Specificity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Public Health Implications. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, A.; Santín, M.; Cano, L.; de Lucio, A.; Bailo, B.; de Mingo, M.H.; Köster, P.C.; Fernández-Basterra, J.A.; Aramburu-Aguirre, J.; López-Molina, N.; et al. Occurrence and Genetic Diversity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi (Microsporidia) in Owned and Sheltered Dogs and Cats in Northern Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2979–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalali, H.; Mirhendi, H.; Meamar, A.R.; Mohebali, M.; Askari, Z.; Mirsamadi, E.S.; Rezaeian, M. Genotyping and Molecular Analysis of Enterocytozoon bieneusi Isolated from Immunocompromised Patients in Iran. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 36, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santín, M.; Fayer, R. Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotype Nomenclature Based on the Internal Transcribed Spacer Sequence: A Consensus. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, E.; Mirjalali, H.; Niyyati, M.; Jalilzadeh, E.; Seyed Tabaei, S.J.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, E.; Zali, M.R. Molecular and Phylogenetic Evidences of Dispersion of Human-Infecting Microsporidia to Vegetable Farms via Irrigation with Treated Wastewater: One-Year Follow Up. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojko, J.; Reinke, A.W.; Stentiford, G.D.; Williams, B.; Rogers, M.S.J.; Bass, D. Microsporidia: A New Taxonomic, Evolutionary, and Ecological Synthesis. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 642–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, B.; Kváč, M.; Květoňová, D.; Albrecht, T.; Piálek, J. The First Report on Natural Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon spp. Infections in Wild East-European House Mice (Mus musculus musculus) and West-European House Mice (M. m. domesticus) in a Hybrid Zone across the Czech Republic–Germany Border. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, C.; Nassonova, E.S.; Schölmerich, J.; Issi, I.V. Transfer of the Members of the Genus Brachiola (Microsporidia) to the Genus Anncaliia Based on Ultrastructural and Molecular Data. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarev, Y.S.; Sokolova, Y.Y.; Vasilieva, A.A.; Issi, I.V. Molecular and Morphological Characterization of Anncaliia azovica sp. n. (Microsporidia) Infecting Niphargogammarus intermedius (Crustacea, Amphipoda) from the Azov Sea. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2018, 65, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plischuk, S.; Sanscrainte, N.D.; Becnel, J.J.; Estep, A.S.; Lange, C.E. Tubulinosema pampeana sp. n. (Microsporidia, Tubulinosematidae), a Pathogen of the South American Bumble Bee Bombus atratus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 126, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, A.L.; Magnet, A.; Izquierdo, F.; Fenoy, S.; Rueda, C.; Vadillo, C.F.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Del Águila, C. Molecular Characterization of Human-Pathogenic Microsporidia and Cyclospora cayetanensis Isolated from Various Water Sources in Spain: A Year-Long Longitudinal Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Public Health and Ecological Significance of Rodents in Cryptosporidium Infections. One Health 2022, 14, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.R.; Dong, H.; Yu, F.; Jian, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Rume, F.I.; Ning, C.; Xiao, L. Genetic Diversity in Enterocytozoon bieneusi Isolates from Dogs and Cats in China: Host Specificity and Public Health Implications. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cama, V.A.; Pearson, J.; Cabrera, L.; Pacheco, L.; Gilman, R.; Meyer, S.; Ortega, Y.; Xiao, L. Transmission of Enterocytozoon bieneusi between a Child and Guinea Pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2708–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Jiang, A.; Xiao, Q.; Tan, F. Host Specificity and Zoonotic Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes in Wild Rodents from the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region and Liaoning Province of China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1409685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzwinkel-Wladarsch, S.; Deplazes, P.; Weber, R.; Löscher, T.; Rinder, H. Comparison of Polymerase Chain Reaction with Light Microscopy for Detection of Microsporidia in Clinical Specimens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1997, 16, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuehrer, H.P.; Blöschl, I.; Siehs, C.; Hassl, A. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, and Encephalitozoon cuniculi in the Brains of Common Voles (Microtus arvalis) and Water Voles (Arvicola terrestris) by Gene Amplification Techniques in Western Austria (Vorarlberg). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Host Species | Island | Sample Size (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Mus musculus | La Gomera | 33 |
| Gran Canaria | 21 | |
| Subtotal | 54 | |
| Rattus rattus | La Gomera | 29 |
| Gran Canaria | 6 | |
| Subtotal | 35 | |
| Rattus norvegicus | La Gomera | 4 |
| Subtotal | 4 | |
| Total | 93 |
| Host Species | Modified Trichrome Stain (%) (+/n) [95% CI] | IFAT Enceph. (%) (+/n) [95% CI] | IFAT Ent. bieneusi (%) (+/n) [95% CI] | Generic Nested PCR (%) (+/n) [95% CI] | Ent. bieneusi Nested PCR (%) (+/n) [95% CI] | Microsporidia Species (n) | Occurrence (%) (+/n) [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mus musculus | 35.2% (19/54) [22.7–49.4] | 1.9% (1/54) [0.05–9.9] | 9.3% (5/54) [3.1–20.3] | 24.1% (13/54) [13.5–37.6] | 5.6% (3/54) [1.2–15.4] | Ent. bieneusi (5) Undetermined (6) | 9.3% (5/54) [3.1–20.3] 11.1% (6/54) [4.2–22.6] |
| Rattus rattus | 37.1% (13/35) [21.5–55.1] | 5.7% (2/35) [0.70–19.2] | 2.9% (1/35) [0.07–14.9] | 28.6% (10/35) [14.6–46.3] | 2.9% (1/35) [0.07–14.9] | Ent. bieneusi (2) Undetermined (8) | 5.7% (2/35) [0.70–19.2] 22.9% (8/35) [10.4–40.1] |
| Rattus norvegicus | 100% (4/4) [39.8–100] | 0.0% (0/4) [0.0–60.2] | 0.0% (0/4) [0.0–60.2] | 100% (4/4) [39.8–100] | 50.0% (2/4) [6.8–93.2] | Ent. bieneusi (2) Undetermined (2) | 50.0% (2/4) [6.8–93.2] 50.0% (2/4) [6.8–93.2] |
| Total | 38.7% (36/93) [28.8–49.4] | 3.2% (3/93) [0.67–9.1] | 6.5% (6/93) [2.4–13.5] | 29.0% (27/93) [20.1–39.4] | 6.5% (6/93) [2.4–13.5] | Ent. bieneusi (9) Undetermined (16) | 9.7% (9/93) [4.5–17.6] 17.2% (16/93) [10.2–26.4] |
| Host Species | Genotype | Frequency (%) (+/n) | GenBank Reference Sequence (Accession nº) | Sequence Obtained in This Study (Accession nº) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRE1 | 20% (1/5) | - | PP873354 | |
| Mus musculus | GRE2 | 20% (1/5) | - | PP873356 |
| LGE1 | 40% (2/5) | - | PP873351 and PP873352 | |
| D | 20% (1/5) | MN747468 | PP873349 | |
| Rattus rattus | AAE1 | 50% (1/2) | OQ646734 | PP873355 |
| SBM1 | 50% (1/2) | MG491317 | PP873351 | |
| Rattus norvegicus | LGE1 LGE2 | 50% (1/2) | - | PP873353 |
| 50% (1/2) | - | PP873357 |
| Island | Host Species | Municipality | Sample Size (n) | Modified Trichrome Stain (+) | IFAT Enceph. (+) | IFAT Ent. bieneusi (+) | Generic Nested PCR (+) | Ent. bieneusi Nested PCR (+) | Ent. bieneusi Genotype(s) (n) | Undetermined Microsporidia Species (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La Gomera | Mus musculus | Agulo | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | 2 |
| Alajeró | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | ||
| Hermigua 1 | 14 | 7 | 1 2 | 4 2 | 6 | 2 | LGE1 (2) | 2 | ||
| San Sebastián de La Gomera | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | ||
| Vallehermoso | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | D (1) | 1 | ||
| Rattus rattus | Agulo | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | |
| Alajeró | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | ||
| Hermigua | 12 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | SBM1 (1) | 4 | ||
| San Sebastián de La Gomera | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | AAE1 (1) | - | ||
| Vallehermoso | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | ||
| Valle Gran Rey | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | ||
| Rattus norvegicus | Hermigua | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | LGE1 (1) LGE2 (1) | 1 | |
| Vallehermoso | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | ||
| Gran Canaria | Mus musculus | Artenara | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Arucas | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | ||
| Firgas | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | ||
| Ingenio 1 | 17 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | GRE1 (1) GRE2 (1) | - | ||
| Rattus rattus | Ingenio | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | - | 3 | |
| Total | 93 | 36 | 3 | 6 | 27 | 6 | 9 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Llorens-Berzosa, S.; Baz-González, E.; Martin-Carrillo, N.; García-Livia, K.; Amaro-Ramos, V.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; del Aguila, C.; Miquel, J.; Pino-Vera, R.; Abreu-Yanes, E.; et al. Microsporidia in Rodents—Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, and Rattus rattus—A Public Health Concern in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals 2025, 15, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121695
Llorens-Berzosa S, Baz-González E, Martin-Carrillo N, García-Livia K, Amaro-Ramos V, Abreu-Acosta N, del Aguila C, Miquel J, Pino-Vera R, Abreu-Yanes E, et al. Microsporidia in Rodents—Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, and Rattus rattus—A Public Health Concern in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals. 2025; 15(12):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121695
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlorens-Berzosa, Sergio, Edgar Baz-González, Natalia Martin-Carrillo, Katherine García-Livia, Virginia Amaro-Ramos, Néstor Abreu-Acosta, Carmen del Aguila, Jordi Miquel, Román Pino-Vera, Estefanía Abreu-Yanes, and et al. 2025. "Microsporidia in Rodents—Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, and Rattus rattus—A Public Health Concern in the Canary Islands, Spain" Animals 15, no. 12: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121695
APA StyleLlorens-Berzosa, S., Baz-González, E., Martin-Carrillo, N., García-Livia, K., Amaro-Ramos, V., Abreu-Acosta, N., del Aguila, C., Miquel, J., Pino-Vera, R., Abreu-Yanes, E., Feliu, C., Izquierdo, F., & Foronda, P. (2025). Microsporidia in Rodents—Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, and Rattus rattus—A Public Health Concern in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals, 15(12), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121695







