New Insights into the Phylogeographic History of Dirofilaria immitis in the Canary Islands, Spain
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gran Canaria
2.2. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic, Genetic Diversity, Differentiation and Statistical Analyses
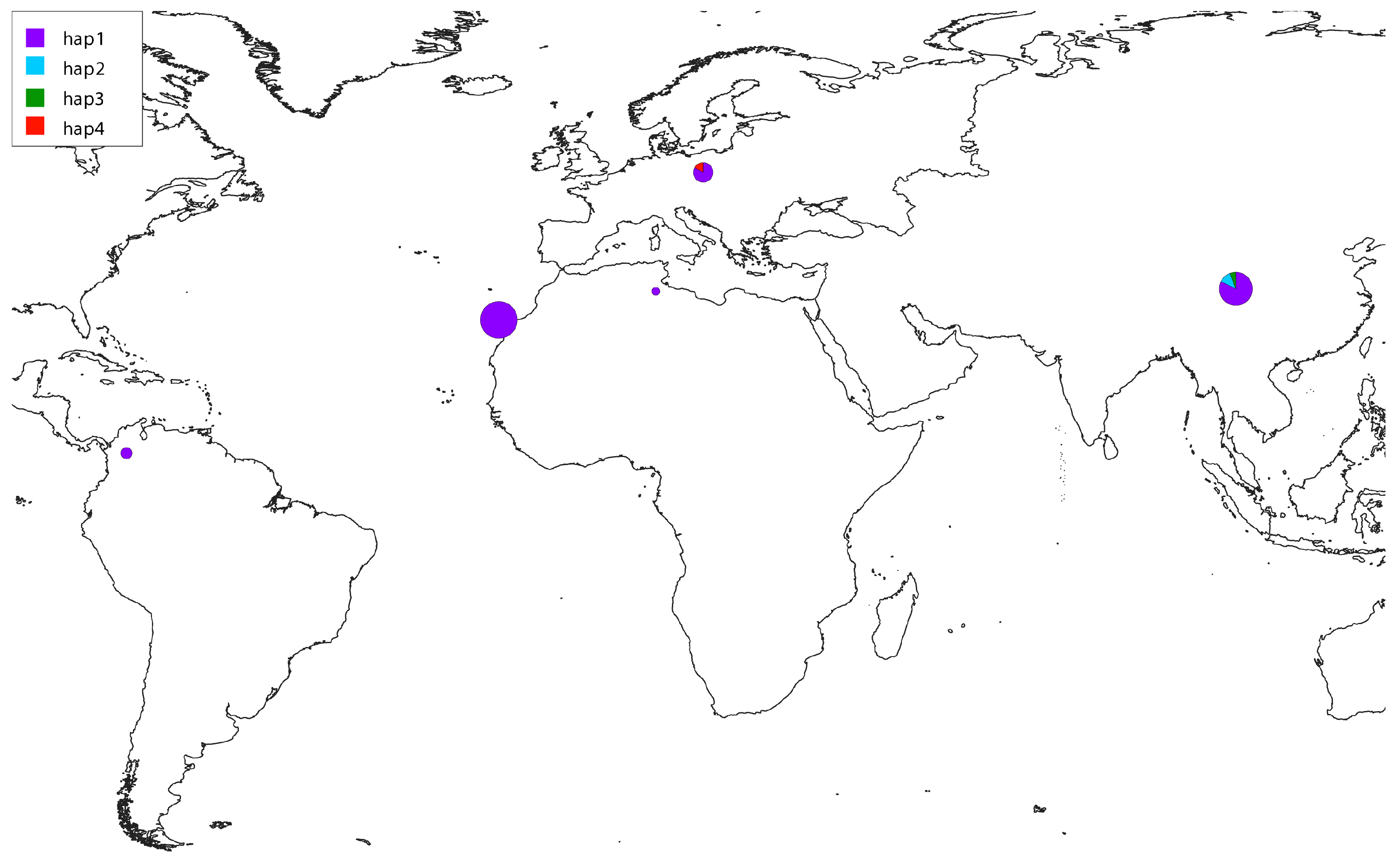
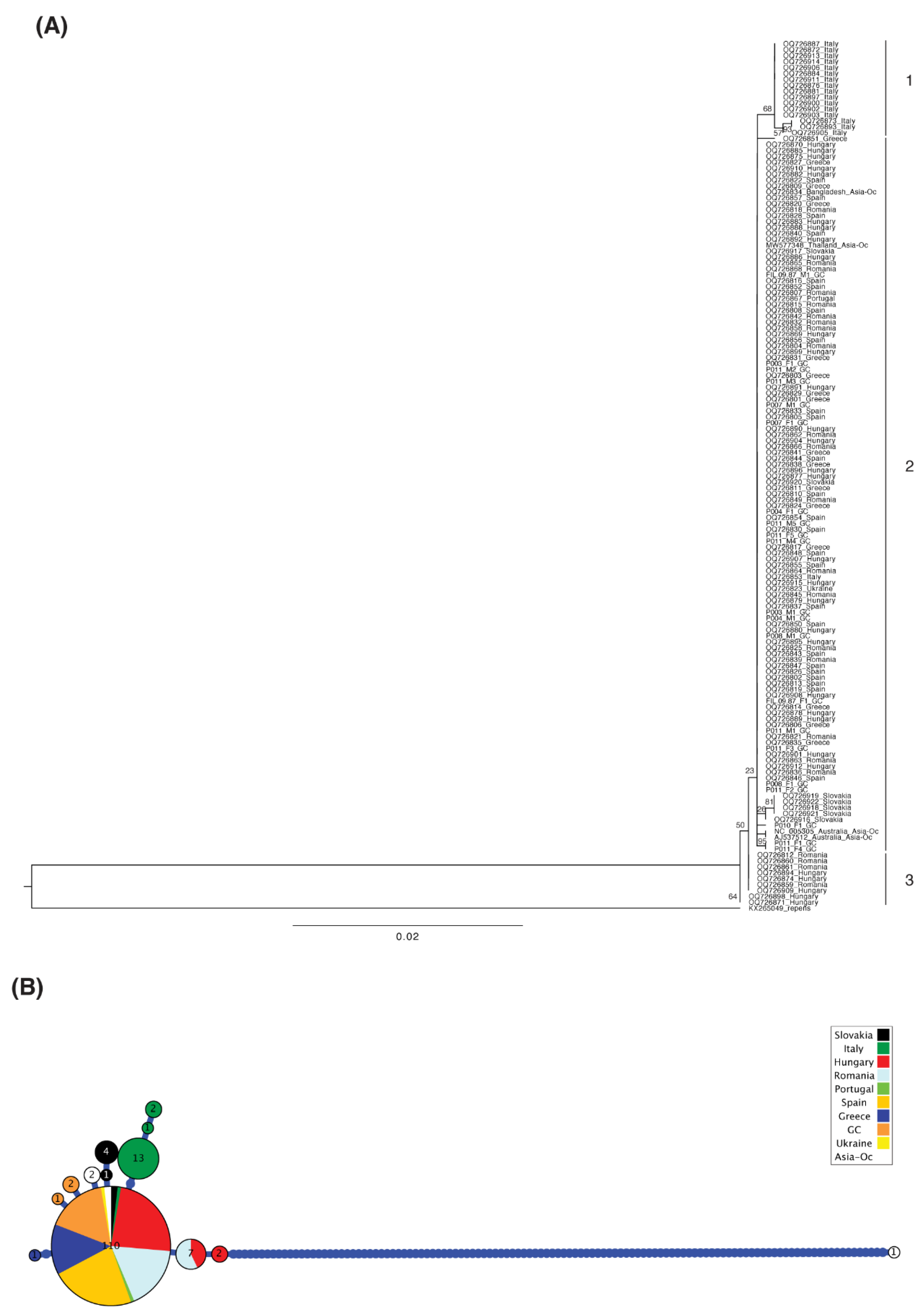
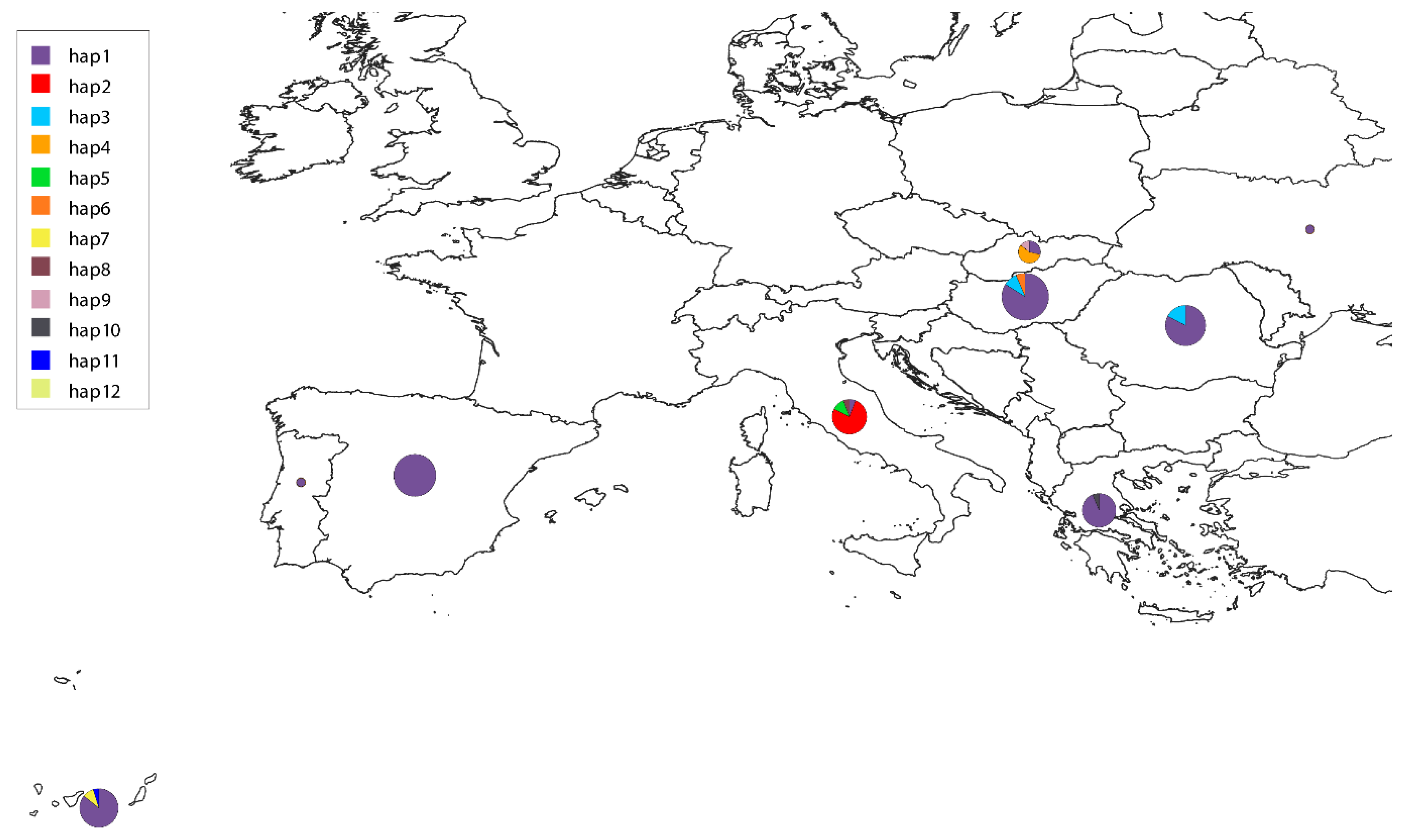
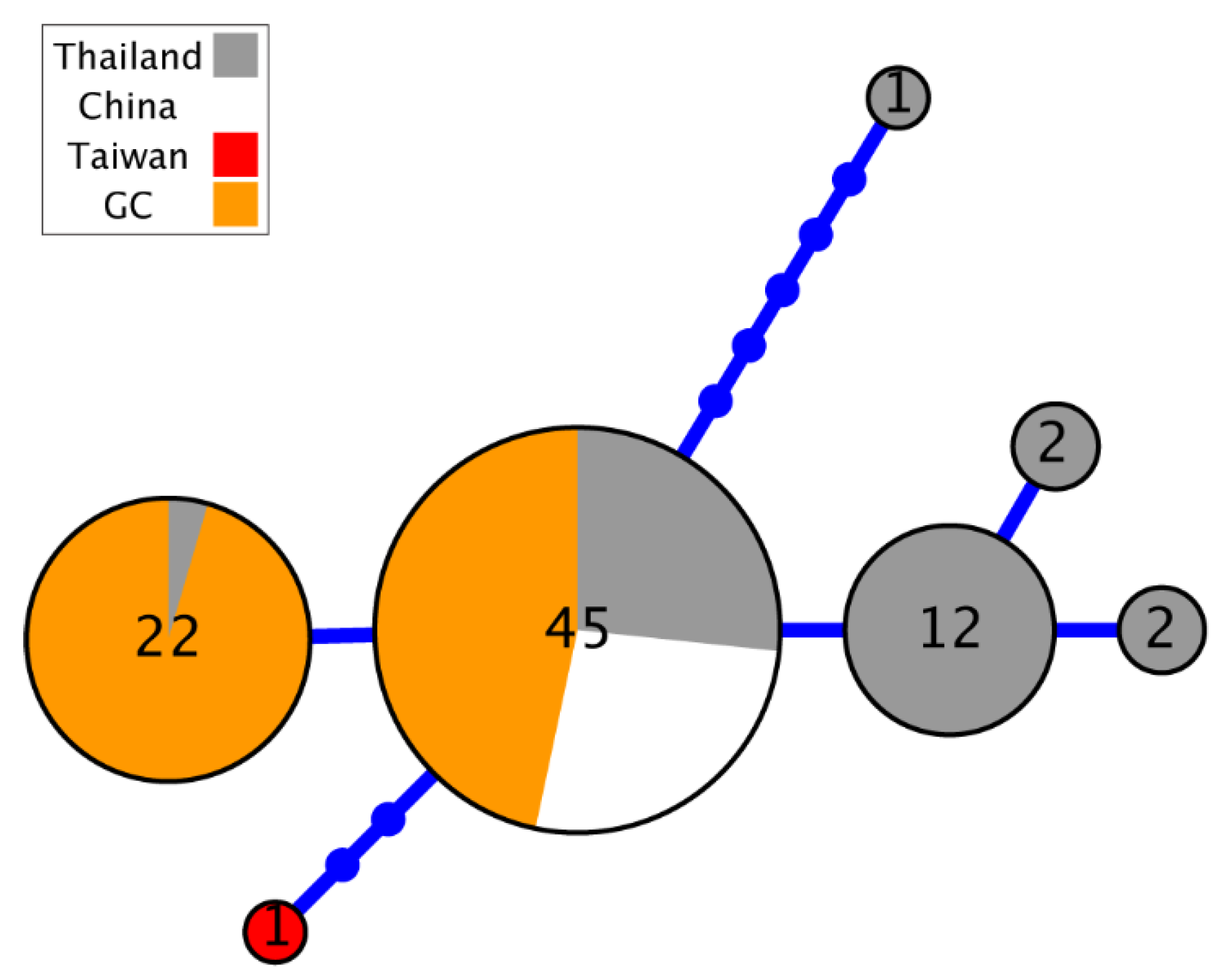
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCall, J.W.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Guerrero, J.; Venco, L. Heartworm disease in animals and humans. Adv. Parasitol. 2008, 66, 193–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noack, S.; Harrington, J.; Carithers, D.S.; Kaminsky, R.; Selzer, P.M. Heartworm disease—Overview, intervention, and industry perspective. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2021, 16, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, F.; Diosdado, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Kartashev, V.; González-Miguel, J. Human dirofilariosis in the 21st century: A scoping review of clinical cases reported in the literature. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2424–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampiglione, S.; Rivasi, F.; Angeli, G.; Boldorini, R.; Incensati, R.M.; Pastormerlo, M.; Pavesi, M.; Ramponi, A. Dirofilariasis due to Dirofilaria repens in Italy, an emergent zoonosis: Report of 60 new cases. Histopathology 2001, 38, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perles, L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Krücken, J.; Morchón, R.; Walochnik, J.; Otranto, D. Zoonotic dirofilariases: One, no one, or more than one parasite. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corimanya, J.; Chávez, A.; Casas, E.; Díaz, D. Frecuencia de Dirofilaria immitis en caninos del distrito de San Juan de Lurigancho. Rev. Inv. Vet. Perú 2004, 15, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Mendoza, M.V.; Arcila-Quiceno, V.; Albarracín-Navas, J.; Hernández, I.; Flechas-Alarcón, M.C.; Morchón, R. Current situation of the presence of Dirofilaria immitis in dogs and humans in Bucaramanga, Colombia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.K.; Bonnier, A.; Chong, W.H.; Chieng, H.; Austin, A.; Hu, K.; Shkolnik, B. Human Pulmonary Dirofilariasis: A Review for the Clinicians. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 363, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Carretón, E. What Has Happened to Heartworm Disease in Europe in the Last 10 Years? Pathogens 2022, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.J.; O’Handley, R.; Nielsen, T.; Caraguel, C.G.B. Heterogeneous distribution of the reported prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis infections in Australian canids—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 237, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izenour, K.; Salib, F.; Eckert, J.; Jesudoss Chelladurai, J.R.J.; Starkey, L.; Blagburn, B.; Sundermann, C.; Willoughby, J.; Zohdy, S. A meta-analysis on Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in countries of North Africa and the Middle East. Parasitology 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves-Guimarães, J.; Matos, J.I.; Leal-Sousa, B.; Oliveira, P.; Lobo, L.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C.; Soares, C.S.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Carretón, E.; Morchón, R.; et al. Current State of Canine Heartworm in Portugal. Animals 2024, 14, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Morchón, R.; García-Rodríguez, S.N.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Matos, J.I.; Rodríguez Escolar, I.; Carretón, E. Expansion of Canine Heartworm in Spain. Animals 2022, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; Ferreira, A.C.; Martín-Pacho, J.R.; Montoya, A.; Mortarino, M.; Genchi, C.; Simón, F. Specific IgG antibody response against antigens of Dirofilaria immitis and its Wolbachia endosymbiont bacterium in cats with natural and experimental infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 125, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; García-Rodríguez, S.N.; Matos, J.I.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Carretón, E.; Morchón, R. Change in the Distribution Pattern of Dirofilaria immitis in Gran Canaria (Hyperendemic Island) between 1994 and 2020. Animals 2024, 14, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Afonso, A.; Calado, M.; Maurício, I.; Alho, A.M.; Meireles, J.; Madeira de Carvalho, L.; Belo, S. Molecular characterization of Dirofilaria spp. circulating in Portugal. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar, P.H.; Yang, I.C.; Chang, G.N.; Fei, A.C.Y. Specific polymerase chain reaction for differential diagnosis of Dirofilaria immitis and Dipetalonema reconditum using primers derived from internal transcribed spacer region 2 (ITS2). Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, G.; Lecová, L.; Genchi, M.; Ferri, E.; Genchi, C.; Mortarino, M. Highly sensitive multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection and discrimination of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in canine peripheral blood. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 172, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanchomnang, T.; Intapan, P.M.; Lulitanond, V.; Sangmaneedet, S.; Chungpivat, S.; Taweethavonsawat, P.; Choochote, W.; Maleewong, W. Rapid detection of Dirofilaria immitis in mosquito vectors and dogs using a real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer PCR and melting curve analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadeh, F.; Khaghaninia, S.; Maleki-Ravasan, N.; Koosha, M.; Oshaghi, M.A. Molecular detection of Dirofilaria spp. and host blood-meal identification in the Simulium turgaicum complex (Diptera: Simuliidae) in the Aras River Basin, northwestern Iran. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Valiente-Echeverría, F.; Carrasco, M.; Mercado, R.; Abarca, K. Identificación morfológica y molecular de filarias caninas en una comuna semi-rural de la Región Metropolitana, Chile. Rev. Chil. De infectología 2012, 29, 248–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandasegui, J.; Power, R.I.; Curry, E.; Lau, D.C.W.; O’Neill, C.M.; Wolstenholme, A.; Prichard, R.; Šlapeta, J.; Doyle, S.R. Genome structure and population genomics of the canine heartworm Dirofilaria immitis. Intern. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Viloria, M.A.; García-Bocanegra, I.; de Lavalle-Galvis, R.J.; Martínez, R.; de la Rosa-Jaramillo, S.; Castillo-Castañeda, A.; Ramírez, J.D.; Cano-Terriza, D. Dirofilaria immitis in pet dogs from the metropolitan area of the Colombian Caribbean. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 102, 102064. [Google Scholar]
- Alsarraf, M.; Carretón, E.; Ciuca, L.; Diakou, A.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Genchi, M.; Ionica, A.M.; Kloch, A.; Kramer, L.H.; et al. Diversity and geographic distribution of haplotypes of Dirofilaria immitis across European endemic countries. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, M.; Baneth, G.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Ciuca, L.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Kloch, A.; Kołodziej, P.; Levytska, V.; Mierzejewska, E.; et al. Haplotypes of Dirofilaria repens from Poland and selected countries of Central, North-Eastern Europe and the Middle East: An evaluation on the relation between the genetic diversity and the geographic distribution of the fast-spreading parasite. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 315, 109882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZOOCAN. Animal Canary Identification Register. 2024. Available online: https://zoocan.net (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Morchón, M.; Bargues, M.D.; Latorre-Estivalis, J.M.; Pou-Barreto, C.; Melero-Alcibar, R.; Moreno, M.; Valladares, B.; Molina, R.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Mas-Coma, S.; et al. Molecular characterization of Culex theileri from Canary Islands, Spain, a potential vector of Dirofilaria immitis. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, S3, 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Gasser, R.B.; El-Osta, Y.A.; Chilton, N.B. Structure and organization of the mitochondrial genome of the canine heartworm, Dirofilaria immitis. Parasitology 2003, 127, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, M.; Bain, O.; Guerrero, R.; Martin, C.; Pocacqua, V.; Gardner, S.L.; Franceschi, A.; Bandi, C. Mapping the presence of Wolbachia pipientis on the phylogeny of filarial nematodes: Evidence for symbiont loss during evolution. Intern. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanchomnang, T.; Intapan, P.M.; Chungpivat, S.; Lulitanond, V.; Maleewong, W. Differential detection of Brugia malayi and Brugia pahangi by real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer PCR and its evaluation for diagnosis of B. pahangi-infected dogs. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Okata, U.; Matsuzaki, H.; Mori, M.; Chen, K.R.; Iwata, S. Molecular analysis of Dirofilaria repens removed from a subcutaneous nodule in a Japanese woman after a tour to Europe. Parasite 2015, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, M.; Levytska, V.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Poliukhovych, V.; Rodo, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Kavalevich, D.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Emerging risk of Dirofilaria spp. infection in Northeastern Europe: High prevalence of Dirofilaria repens in sled dog kennels from the Baltic countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneious Prime 2023.2.1. Available online: https://www.geneious.com (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; Smith, N.J.; Donnelly, P. A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS 2020. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open-Source Geospatial Foundation Project. Available online: http://qgis.org (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Paradis, E. Pegas: An R package for population genetics with an integrated–modular approach. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. Ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. HIERFSTAT, a package for R to compute and test hierarchical F-statistics. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junsiri, W.; Kamkong, P.; Chinkangsadarn, T.; Ouisuwan, S.; Taweethavonsawat, P. Molecular identification and genetic diversity of equine ocular setariasis in Thailand based on the COI, 12S rDNA, and ITS1 regions. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 110, 105425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satjawongvanit, H.; Phumee, A.; Tiawsirisup, S.; Sungpradit, S.; Brownell, N.; Siriyasatien, P.; Preativatanyou, K. Molecular Analysis of Canine Filaria and Its Wolbachia Endosymbionts in Domestic Dogs Collected from Two Animal University Hospitals in Bangkok Metropolitan Region, Thailand. Pathogens 2019, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aher, A.M.; Caudill, D.; Caudill, G.; Butryn, R.S.; Wolf, D.; Fox, M.; Blake, D.P.; Cunningham, M.W. Prevalence, genetic analyses, and risk factors associated with heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) in wild coyotes (Canis latrans) from Florida, USA. J. Wildl Dis. 2016, 52, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yssouf, A.; Lagadec, E.; Bakari, A.; Foray, C.; Stachurski, F.; Cardinale, E.; Plantard, O.; Tortosa, P. Colonization of Grande Comore Island by a lineage of Rhipicephalus appendiculatus ticks. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitsitt, J.; Karimkhani, C.; Boyers, L.N.; Lott, J.P.; Dellavalle, R.P. Comparing burden of dermatologic disease to search interest on google trends. Dermatol. Online J. 2015, 21, 13030/qt5xg811qp. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, E.; Tan, D.; Daffalla, O.; Almutairi, H.; Ghzwani, J.; Torno, M.; Mashi, O.; Hobani, Y.; Ding, H.; Alamri, A.; et al. DNA Barcoding of Potential Mosquito Disease Vectors (Diptera, Culicidae) in Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia. Pathogens 2022, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.; Subhani, M.I.; H Wakid, M.; A M Alkhaldi, A.; Hussain, S.; Malik, M.A.; Saqib, M.; Qamar, W.; Alvi, M.A. Genetic diversity and population structure of Echinococcus multilocularis: An in-silico global analysis. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2024, 11, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishniw, M.; Barr, S.C.; Simpson, K.W.; Frongillo, M.F.; Franz, M.; Dominguez Alpizar, J.L. Discrimination between six species of canine microfilariae by a single polymerase chain reaction. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 135, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, M.; Bazzocchi, C.; Mortarino, M.; Ottina, E.; Genchi, C. A simple molecular method for discriminating common filarial nematodes of dogs (Canis familiaris). Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 141, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequence 5′ to 3′ | Fragment | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| COI_I_F * | GGTTTATTTTTGTTATTTAGTATGAA | Mitochondrial (COX1_I) | 797 |
| COI_I_R * | TATCAGTCAAAAATAAAACACATT | Mitochondrial (COX1_I) | |
| COI_II_F * | GTGAATGTGTTTTATTTTTGAC | Mitochondrial (COX1_II) | 755 |
| COI_II_R * | CCCTTCTAATAACCTTCCAATGAA | Mitochondrial (COX1_II) | |
| 12SF | GTTCCAGAATAATCGGCTA | Mitochondrial (12S) | 475 |
| 12SdegR | ATTGACGGATG(AG)TTTGTACC | Mitochondrial (12S) | |
| ITS_F * | ACATACA(CT)ACATACAATAATA | Nuclear (ITS) | 180 |
| DI-R | GATAATCTGATCGATATTGACCCT | Nuclear (ITS) |
| Population | Length | N | H | S | Hd | π × 103 | Tajima’s D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. immitis (excluding GC) | 1322 | 125 | 10 | 8 | 0.446 | 0.671 | −0.94 (n.s.) |
| D. immiitis (GC) | 1322 | 21 | 3 | 2 | 0.267 | 0.209 | −1.16 (n.s.) |
| D. immitis (whole) | 1322 | 146 | 12 | 10 | 0.423 | 0.614 | −1.33 (n.s.) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morchón, R.; Balmori-de la Puente, A.; Collado-Cuadrado, M.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Costa-Rodríguez, N.; Infante González-Mohino, E.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. New Insights into the Phylogeographic History of Dirofilaria immitis in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals 2025, 15, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121694
Morchón R, Balmori-de la Puente A, Collado-Cuadrado M, Rodríguez-Escolar I, Costa-Rodríguez N, Infante González-Mohino E, Carretón E, Montoya-Alonso JA. New Insights into the Phylogeographic History of Dirofilaria immitis in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals. 2025; 15(12):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121694
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorchón, Rodrigo, Alfonso Balmori-de la Puente, Manuel Collado-Cuadrado, Iván Rodríguez-Escolar, Noelia Costa-Rodríguez, Elena Infante González-Mohino, Elena Carretón, and José Alberto Montoya-Alonso. 2025. "New Insights into the Phylogeographic History of Dirofilaria immitis in the Canary Islands, Spain" Animals 15, no. 12: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121694
APA StyleMorchón, R., Balmori-de la Puente, A., Collado-Cuadrado, M., Rodríguez-Escolar, I., Costa-Rodríguez, N., Infante González-Mohino, E., Carretón, E., & Montoya-Alonso, J. A. (2025). New Insights into the Phylogeographic History of Dirofilaria immitis in the Canary Islands, Spain. Animals, 15(12), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121694










