Comparative Radiographic Analysis of Trochleoplasties for Patellar Luxation Correction: Inter-Observer Agreement of a Modified Osteoarthritis Scoring System
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Surgery
2.3. Radiographic Examination and Scoring
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Use of AI in Manuscript Preparation
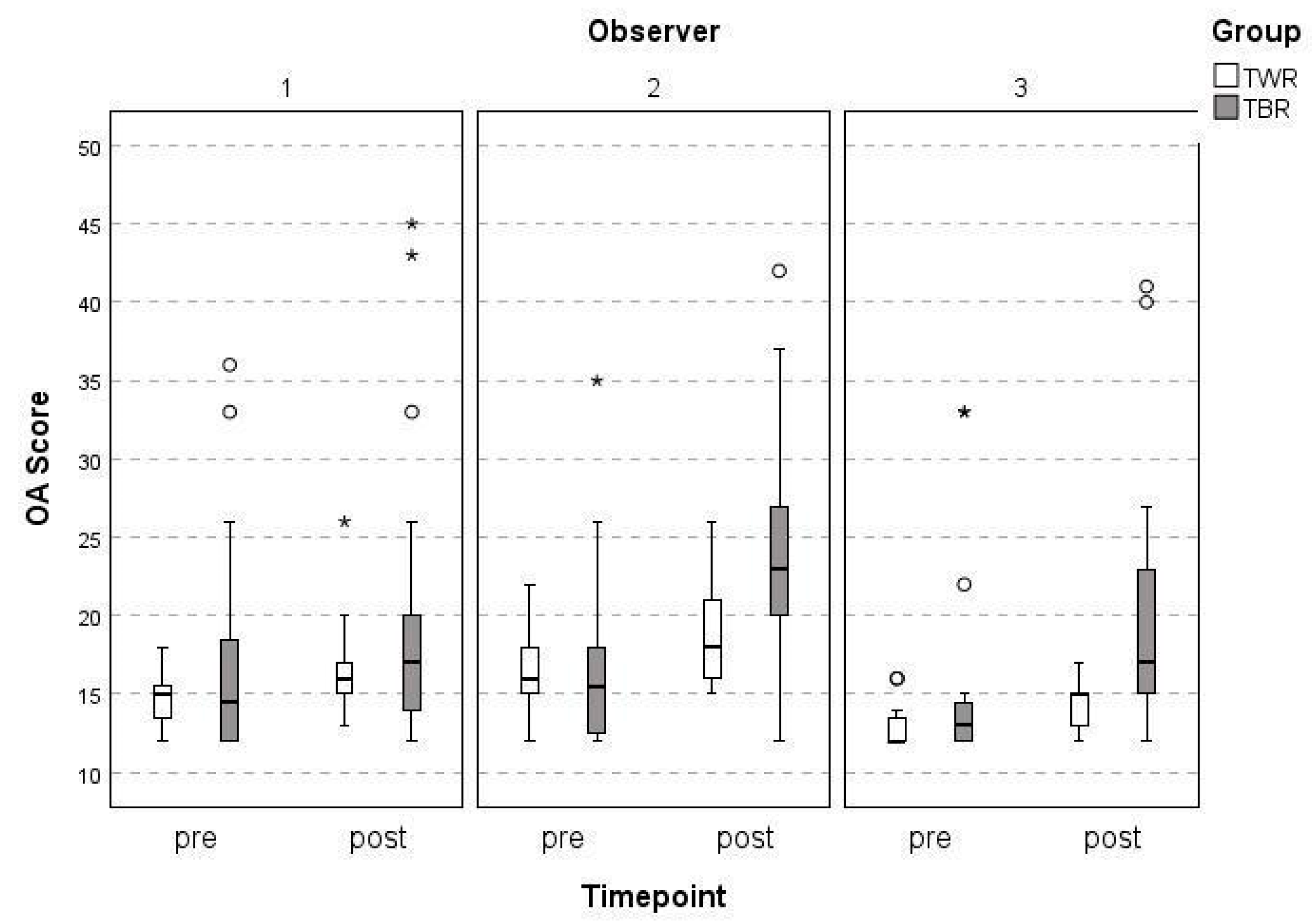
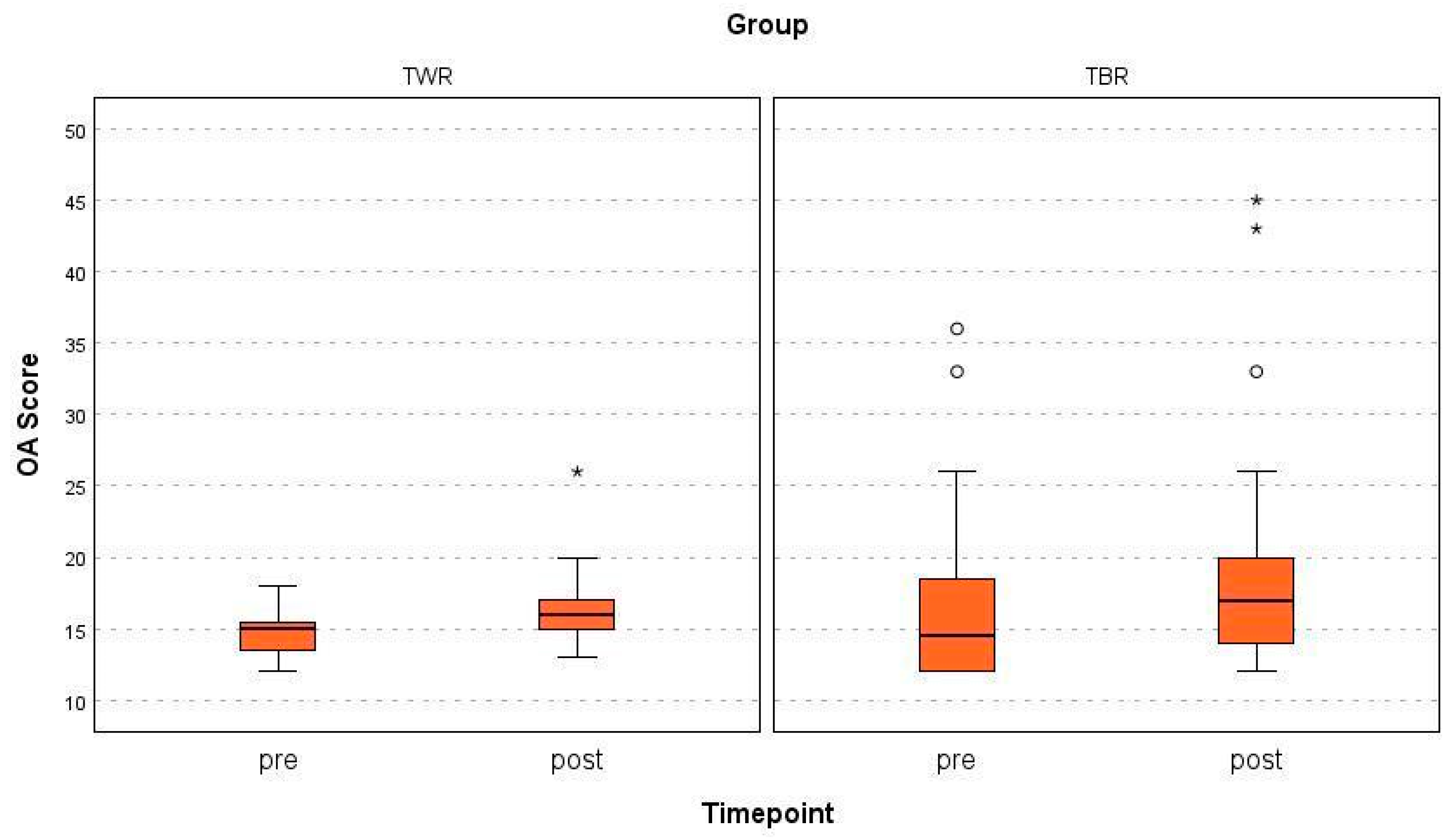
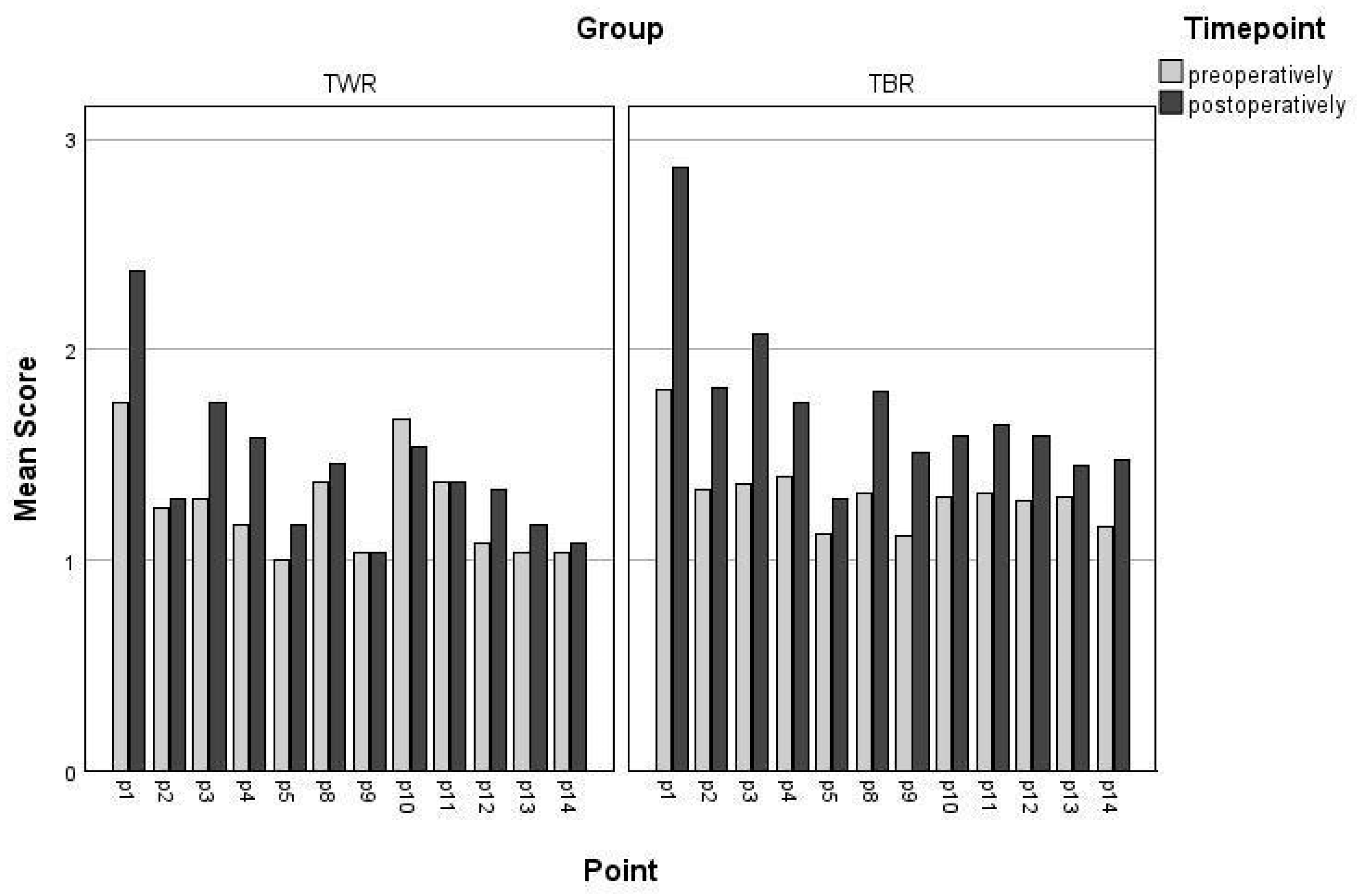
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPL | medial patellar luxation |
| TWR | trochlear wedge recession |
| TBR | trochlear block recession |
| DFO | distal femoral osteotomy |
| SCRT | semi-cylindrical recession trochleoplasty |
| OA | osteoarthritis |
References
- Perry, K.L.; Adams, R.J.; Andrews, S.J.; Tewson, C.; Bruce, M. Impact of femoral varus on complications and outcome associated with corrective surgery for medial patellar luxation. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2017, 30, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.R.; Lee, J.I.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, I.S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, K.C.; Kim, N.S. Frequency and distribution of patellar luxation in dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2007, 20, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bound, N.; Zakai, D.; Butterworth, S.J.; Pead, M. The prevalence of canine patellar luxation in three centres Clinical features and radiographic evidence of limb deviation. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2009, 22, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, K.L.; Déjardin, L.M. Canine medial patellar luxation. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdahl, K.; Bergström, A.; Höglund, O.; Hanson, J. The epidemiology of patellar luxation in an insured Swedish dog population. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 220, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermattei, C.E.; Flo, D.L.; DeCamp, G.L. The stifle joint. In Handbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics and Fracture Repair, 5th ed.; Dejardin, L.M., Schaefer, S., DeCamp, C.E., Johnston, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 597–669. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, H.E. The Muscular System. In Miller’s Anatomy of the Dog, 4th ed.; Evans, H.E., De Lahunta, A., Eds.; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013; pp. 185–280. [Google Scholar]
- LaFond, E.; Breur, G.J.; Austin, C.C. Breed susceptibility for developmental orthopedic diseases in dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2002, 38, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Eplattenier, H.; Montavon, P. Patellar luxation in dogs and cats: Management and prevention. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. N. Am. Ed. 2002, 24, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Willauer, C.C.; Vasseur, P.B. Clinical results of surgical correction of medial luxation of the patella in dogs. Vet. Surg. 1987, 16, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digiovanni, L.C.; Roush, J.K.; Berke, K. Preoperative and postop- erative stance analysis in dogs with patellar luxation confirms lameness improvement after surgery. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 84, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangdee, C.; Theyse, L.F.H.; Techakumphu, M.; Soontornvipart, K.; Hazewinkel, H.A.W. Evaluation of surgical treatment of medial patellar luxation in Pomeranian dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2013, 26, 435–439. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, B.E.; Kowaleski, M.P.; Peruski, A.M.; Pozzi, A.; Dyce, J.; Johnson, K.A.; Boudrieau, R.J. Distal femoral lateral closing wedge osteotomy as a component of comprehensive treatment of medial patellar luxation and distal femoral varus in dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2017, 30, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roch, S.P.; Gemmill, T.J. Treatment of medial patellar luxation by femoral closing wedge ostectomy using a distal femoral plate in four dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2008, 49, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, A.L.C.; Minto, B.W.; Curuci, E.H.P.; Paula, C.G.; Jassniker, J.B.; Cunha, O. Early Surgical management of medial patellar luxation in juvenile dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2024, 37, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichi, E.; Cappellari, F.; Burkhan, E.; Principato, G.; Currenti, M.; Tabbì, M.; Macrì, F. Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Osteotomy Guides and Titanium Plates for Distal Femoral Deformities in Dogs with Lateral Patellar Luxation. Animals 2024, 14, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichi, E.; Cappellari, F.; Olimpo, M.; Piras, L.A.; Radasch, R.; Ferretti, A.; Peirone, B. Distal femoral osteotomy using a novel deformity reduction device. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2016, 29, 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, W.B. Surgical correction of stifle deformities in the dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1969, 10, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowaleski, M.P.; Boudrieau, R.J.; Pozzi, A. Stifle Joint. In Veterinary Surgery: Small Animal, 2nd ed.; Johnston, S.A., Tobias, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 1071–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Blackford-Winders, C.L.; Daubert, M.; Rendahl, A.K.; Conzemius, M.G. Comparison of semi-cylindrical Recession Trochleoplasty and Trochlear Block Recession for the treatment of canine medial patellar luxation: A pilot study. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2021, 34, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deom, K.; Conzemius, M.G.; Tarricone, J.; Nye, C.; Veytsman, S. Short-term outcomes for surgical correction of feline medial patellar luxations via semi-cylindrical recession trochleoplasty. J. Feline Med. Surg. Open Rep. 2023, 9, 20551169231179544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Kang, J.; Kim, N.; Heo, S. Comparison of patellofemoral contact pressure after semi-cylindrical recession trochleoplasty and trochlear block recession in feline cadavers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1237291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.L.; Probst, C.W.; Decamp, C.E.; Rosenstein, D.S.; Hauptman, J.G.; Weaver, B.T.; Kern, T.L. Comparison of trochlear block recession and trochlear wedge recession for canine patellar luxation using a cadaver model. Vet. Surg. 2001, 30, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodnarek, J.; Schneider, E.; Bockstahler, B.; Schnabl-Feichter, E. Outcome of surgical correction of medial patellar luxation in dogs weighing less than 10 kg. Vet. Rec. 2024, 194, e3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessely, M.; Brühschwein, A.; Schnabl-Feichter, E. Evaluation of intra—And inter-observer measurement variability of a radiographic stifle osteoarthritis scoring system in dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2017, 30, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerfond, P.; Huneault, L.; Dupuis, J.; Moreau, M.; Auger, J. Unilateral or single-session bilateral surgery for correction of medial patellar luxation in small dogs: Short and long-term outcomes. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 27, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossanese, M.; German, A.J.; Comerford, E.; Pettitt, R.; Tomlinson, A.; De Vicente, F. Complications following surgical correction of medial patellar luxation in small-to-medium-size dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2019, 32, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.G.; Wallace, L.J.; Johnston, G.R.; Wickstrom, S.L. Retrospective evaluation of stifle osteoarthritis in dogs with bilateral medial patellar luxation and unilateral surgical repair. Vet. Surg. 1992, 21, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.A.; Horstman, C.L.; Mason, D.R.; Evans, R.B. Severity of patellar luxation and frequency of concomitant cranial cruciate ligament rupture in dogs: 162 cases (2004–2007). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 236, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnoeva, R.S.; Paskalev, M.D. Post-operative radiographic measures of pelvic limb alignment in dogs with medial patellar luxation after trochlear wedge recession versus trochlear block recession surgery. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daems, R.; Janssens, L.A.; Béosier, Y.M. Grossly apparent cartilage erosion of the patellar articular surface in dogs with congenital medial patellar luxation. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2009, 22, 222–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, W.K.; Kang, K.-W.; Kang, B.-J. Medial patellar luxation induces cartilage erosion in dogs: A retrospective study of prevalence and risk factors. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Flores, G.I.; Del Angel-Caraza, J.; Quijano-Hernández, I.A.; Hulse, D.A.; Beale, B.S.; Victoria-Mora, J.M. Correlation between osteoarthritic changes in the stifle joint in dogs and the results of orthopedic, radiographic, ultrasonographic and arthroscopic examinations. Vet. Res. Commun. 2017, 41, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karande, S.P.; Kini, S. Osteoarthritis: Clinical and radiological correlation. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2018, 66, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
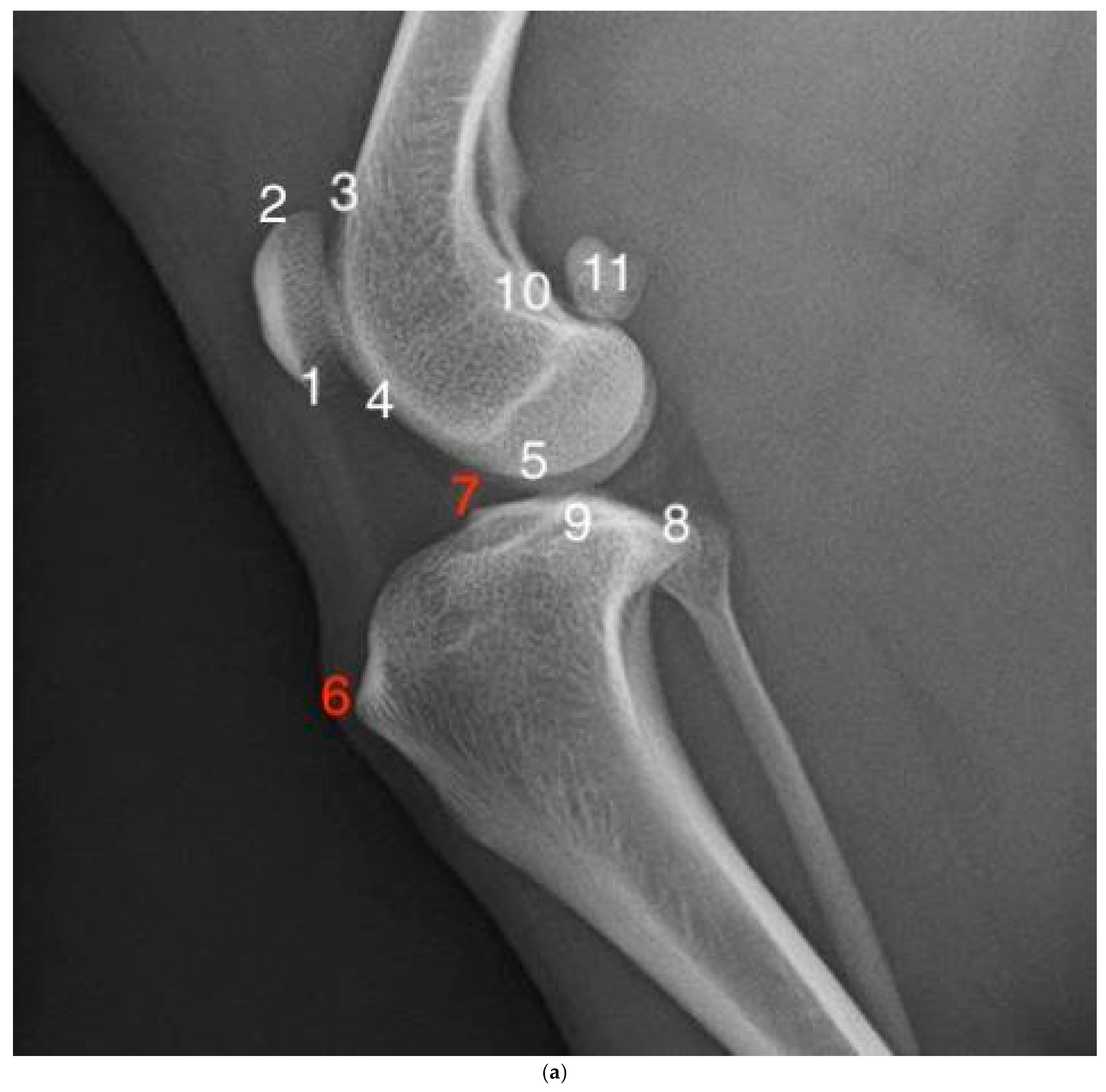
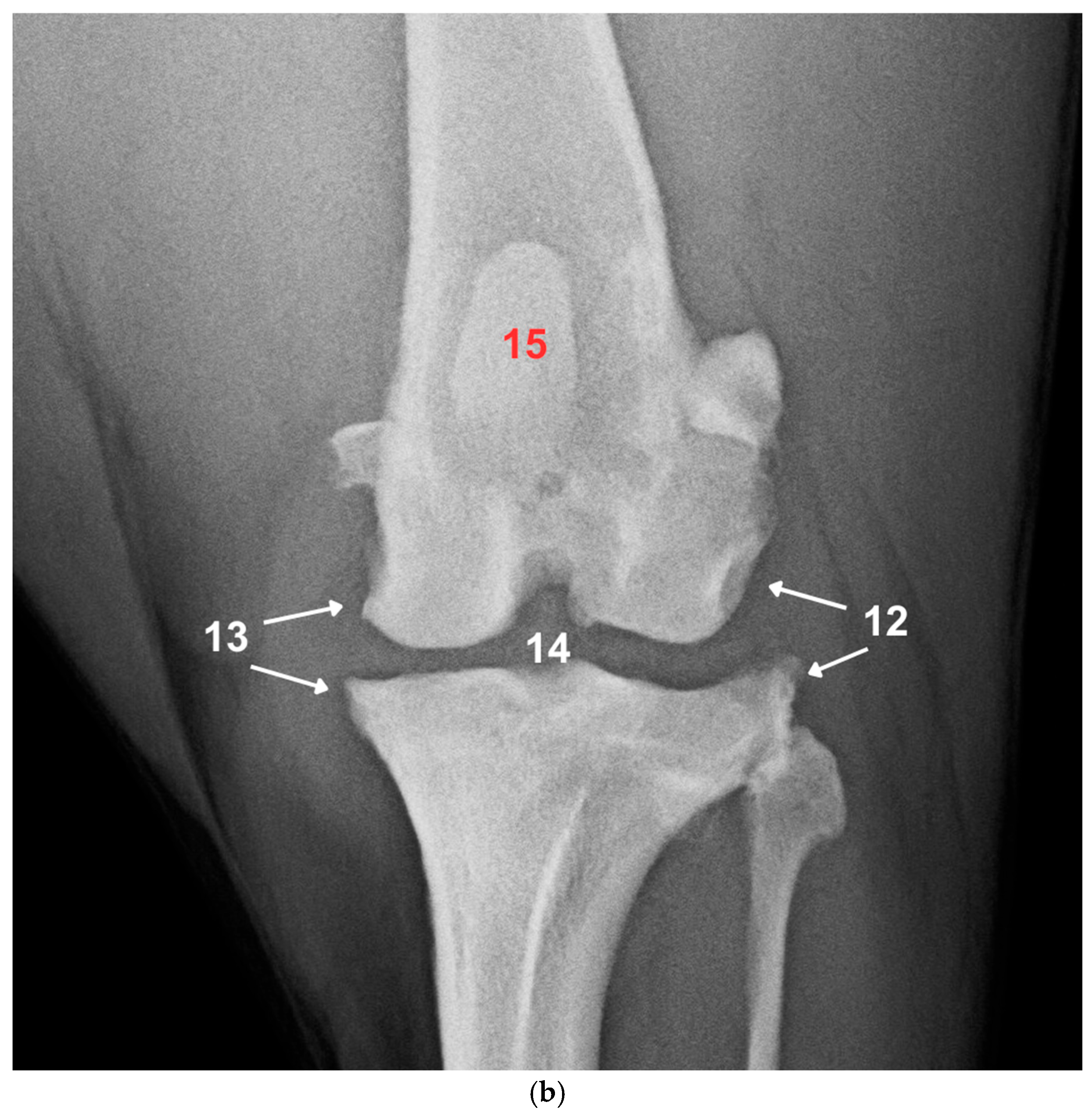
| Grade | Severity | Changes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No radiological signs of osteoarthritic changes | No osteophytes/enthesophytes detectable at bone points. The bone contour corresponds to normal anatomy. |
| 2 | Minor radiographic evidence of osteophytic changes | Osteophytes/enthesophytes are detectable but do not result in loss of distinctness of the bone contour. |
| 3 | Moderate radiographic evidence of osteoarthritic changes | Osteophytes/enthesophytes are clearly visible, and loss of bone contour may be present. |
| 4 | High-grade radiographic evidence of osteoarthritic changes | Osteophytes/enthesophytes extend well beyond the bone contour and may be associated with significant loss of distinctness of the bone contour. |
| Observer 1 | Observer 2 | Observer 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operative | Post-Operative | Pre-Operative | Post-Operative | Pre-Operative | Post-Operative | |||||||
| Mean + SD | Range | Mean + SD | Range | Mean + SD | Range | Mean + SD | Range | Mean + SD | Range | Mean + SD | Range | |
| TWR | 14.7 + 1.7 | 12–18 | 16.9 + 3.5 | 13–20 | 16.6 + 3.0 | 12–22 | 18.8 + 3.6 | 15–26 | 13.0 + 1.6 | 12–16 | 14.3 + 1.6 | 15–26 |
| TBR | 17.0 + 6.9 | 12–36 | 18.6 + 7.6 | 12–45 | 15.4 + 6.4 | 12–35 | 23.4 + 5.3 | 12–42 | 15.4 + 6.4 | 12–33 | 18.7 + 6.6 | 12–41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velich, N.; Vidoni, B.; Ludewig, E.; Tichy, A.; Schnabl-Feichter, E. Comparative Radiographic Analysis of Trochleoplasties for Patellar Luxation Correction: Inter-Observer Agreement of a Modified Osteoarthritis Scoring System. Animals 2025, 15, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111639
Velich N, Vidoni B, Ludewig E, Tichy A, Schnabl-Feichter E. Comparative Radiographic Analysis of Trochleoplasties for Patellar Luxation Correction: Inter-Observer Agreement of a Modified Osteoarthritis Scoring System. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111639
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelich, Nikolaus, Britta Vidoni, Eberhard Ludewig, Alexander Tichy, and Eva Schnabl-Feichter. 2025. "Comparative Radiographic Analysis of Trochleoplasties for Patellar Luxation Correction: Inter-Observer Agreement of a Modified Osteoarthritis Scoring System" Animals 15, no. 11: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111639
APA StyleVelich, N., Vidoni, B., Ludewig, E., Tichy, A., & Schnabl-Feichter, E. (2025). Comparative Radiographic Analysis of Trochleoplasties for Patellar Luxation Correction: Inter-Observer Agreement of a Modified Osteoarthritis Scoring System. Animals, 15(11), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111639





