Tea Catechins: Potential Plant-Derived Feed Additives for Improving Chicken Intestinal Health and Productivity
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Chemical Structural Properties of Catechins
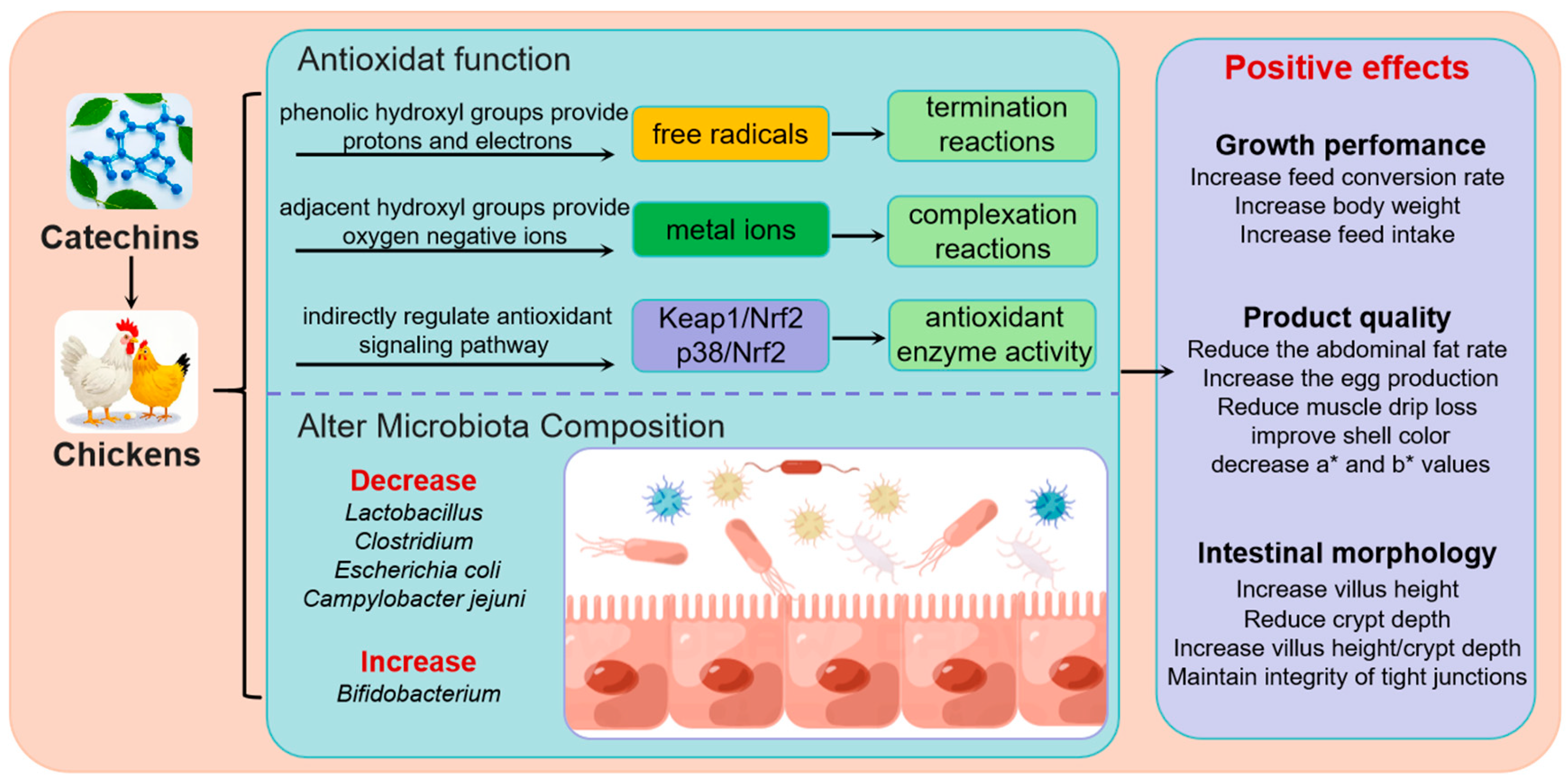
3. Catechins Promote Growth Performance and Product Quality
4. The Antioxidant Property of Catechins
5. Catechins Improve Intestinal Morphology and Alter Microbiota Composition
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gadde, U.; Kim, W.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lillehoj, H.S. Alternatives to antibiotics for maximizing growth performance and feed efficiency in poultry: A review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huemer, M.; Mairpady Shambat, S.; Brugger, S.D.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Antibiotic resistance and persistence-Implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e51034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obianwuna, U.E.; Chang, X.; Oleforuh-Okoleh, V.U.; Onu, P.N.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, K.; Wu, S. Phytobiotics in poultry: Revolutionizing broiler chicken nutrition with plant-derived gut health enhancers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Li, T.; Dai, M.; Tan, C.; Xu, Z.; Wu, B.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance and population genomics of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in pig farms in mainland China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, M.S.; Malouin, F. Antibiotics in Canadian poultry productions and anticipated alternatives. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. Molecular and virulence characteristics of multi-drug resistant Salmonella Enteritidis strains isolated from poultry. Vet. J. 2011, 189, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsene, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Andreevna, S.L.; Sarra, S.; Khelifi, I.; Sergueievna, D.M. The public health issue of antibiotic residues in food and feed: Causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Vet. World 2022, 15, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamojska, D.; Nowak, A.; Nowak, I.; Macierzynska-Piotrowska, E. Probiotics and Postbiotics as Substitutes of Antibiotics in Farm Animals: A Review. Animals 2021, 11, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, N.; Khan, W.; Md, S.; Ali, A.; Saluja, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Al-Allaf, F.A.; Abduljaleel, Z.; Ibrahim, I.A.A.; Abdel-Wahab, A.F.; et al. Phytosterols as a natural anticancer agent: Current status and future perspective. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latek, U.; Chlopecka, M.; Karlik, W.; Mendel, M. Phytogenic Compounds for Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function in Poultry-A Review. Planta Med. 2022, 88, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciaro, B.; Mangiardi, L.; Cappiello, F.; Romeo, I.; Loffredo, M.R.; Iazzetti, A.; Calcaterra, A.; Goggiamani, A.; Ghirga, F.; Mangoni, M.L.; et al. Naturally-Occurring Alkaloids of Plant Origin as Potential Antimicrobials against Antibiotic-Resistant Infections. Molecules 2020, 25, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwinski, H.; Wodz, K.; Chodkowska, K.; Nowak, T.; Rozanski, H. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Effect of Phytobiotics Mixture on Salmonella spp. Isolated from Chicken Broiler. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolba, N.; Zarei, A.; Cheng, J.; Agarwal, N.; Dadmohammadi, Y.; Khazdooz, L.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Tako, E. Alterations in Intestinal Brush Border Membrane Functionality and Bacterial Populations Following Intra-Amniotic Administration (Gallus gallus) of Catechin and Its Derivatives. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, D.Y. Docking Characterization and in vitro Inhibitory Activity of Flavan-3-ols and Dimeric Proanthocyanidins Against the Main Protease Activity of SARS-Cov-2. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 601316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Naparlo, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Antioxidant properties of catechins: Comparison with other antioxidants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Saito, S.; Endo, K.; Kono, M.; Kakei, T.; Taketa, H.; Kato, M.; Hamamoto, S.; Grenzi, M.; Costa, A.; et al. Green Tea Catechins, (-)-Catechin Gallate, and (-)-Gallocatechin Gallate are Potent Inhibitors of ABA-Induced Stomatal Closure. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2201403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Lee, W.D.; Kim, H.; Hong, E.C.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, Y.S.; Kang, H.K. A comparative study on feeding timing and additive types of broilers in a high-temperature environment. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101, skad290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Pandey, R.; Schmitt, V. Part 1. Evaluation of Epigallocatechin Gallate or Tannic Acid Formulations of Hydrophobic Drugs for Enhanced Dermal and Bladder Uptake or for Local Anesthesia Effects. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, I.; Wilairatana, P.; Saqib, F.; Nasir, B.; Wahid, M.; Latif, M.F.; Iqbal, A.; Naz, R.; Mubarak, M.S. Plant Polyphenols and Their Potential Benefits on Cardiovascular Health: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Tabata, M.; Suzuki, M.; Degawa, M.; Miyase, T.; Maeda-Yamamoto, M. Simultaneous determination of twelve tea catechins by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Analyst 2001, 126, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.M.; Rabalski, I.; Mats, L.; Rai, I. Identification and Quantification of Anthocyanin and Catechin Compounds in Purple Tea Leaves and Flakes. Molecules 2022, 27, 6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, A.; Dodd, G.F.; Spencer, J.P.E. The Effects of Flavonoids on Cardiovascular Health: A Review of Human Intervention Trials and Implications for Cerebrovascular Function. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.W.; Chuang, W.Y.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Lin, H.H.; Lin, W.C.; Lin, L.J.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Effects of dietary supplementation with Taiwanese tea byproducts and probiotics on growth performance, lipid metabolism, and the immune response in red feather native chickens. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.B.; Wan, X.C.; Zhang, J.S. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on lipid metabolism and its underlying molecular mechanism in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, S.; Fukagawa, S.; Nakamura, K.; Ohtsuka, A.; Ijiri, D. Effect of a Mixed Fermented Loquat Leaf Tea By-Product on the Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Tsushima-Jidori Crossbred Chicken. J. Poult. Sci. 2024, 61, 2024024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, S.G.; Qi, G.H. Dietary tea polyphenol supplementation improved egg production performance, albumen quality, and magnum morphology of Hy-Line Brown hens during the late laying period. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambula, M.K.; Oduho, G.W.; Tuitoek, J.K. Effects of high-tannin sorghum and bentonite on the performance of laying hens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2003, 35, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Song, J.; Liu, L.; Xue, B.; Tian, G.; Yang, Y. Effect of epigallocatechin gallate on growth performance and serum biochemical metabolites in heat-stressed broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Song, J.; Liu, L.; Luo, J.; Tian, G.; Yang, Y. Effect of epigallocatechin gallate on growth performance and antioxidant capacity in heat-stressed broilers. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 71, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, H.; Celi, P. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protected vanadium-induced eggshell depigmentation via P38MAPK-Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumoto, M.; O’Grady, M.N.; Kerry, J.P.; Joe Buckley, D. Addition of tea catechins and vitamin C on sensory evaluation, colour and lipid stability during chilled storage in cooked or raw beef and chicken patties. Meat Sci. 2005, 69, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.S.; Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Von Laer, A.E.; Lovato, L.T.; Sarturi, J.A.; Herrmann, G.P.; de Moura, A.B.; Favaretto, J.A.; Frias-De-Diego, A.; et al. Relation of reproductive disturbance in sheep and Leptospira interrogans serovar Icterohaemorrhagiae infection: Impacts on cellular oxidation status. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, K.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. An update on immunotoxicity and mechanisms of action of six environmental mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 163, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Different oxidative status and expression of calcium channel components in stress-induced dysfunctional chicken muscle. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, O.; Virolainen, E.; Fagerstedt, K.V. Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: A review. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirgozliev, V.; Mansbridge, S.C.; Whiting, I.M.; Arthur, C.; Rose, S.P.; Atanasov, A.G. Antioxidant status and growth performance of broiler chickens fed diets containing graded levels of supplementary dihydroquercetin. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 141, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.G.; Huang, Z.H.; Chen, W.; Fouad, A.M.; Abouelezz, K.F.M.; Li, K.C.; Huang, X.B.; Wang, S.; Ruan, D.; Zhang, Y.N.; et al. Effects of maternal and progeny dietary selenium supplementation on growth performance and antioxidant capacity in ducklings. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Z.; Kerry, J.P.; Sheehan, D.; Buckley, D.J.; Morrissey, P.A. Dietary tea catechins and iron-induced lipid oxidation in chicken meat, liver and heart. Meat Sci. 2000, 56, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.Y.; Sang, L.X.; Jiang, M. Catechins and Their Therapeutic Benefits to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Galleano, M.; Verstraeten, S.V.; Oteiza, P.I. Basic biochemical mechanisms behind the health benefits of polyphenols. Mol. Aspects Med. 2010, 31, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Sofic, E.; Prior, R.L. Antioxidant and prooxidant behavior of flavonoids: Structure-activity relationships. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intra, J.; Kuo, S.M. Physiological levels of tea catechins increase cellular lipid antioxidant activity of vitamin C and vitamin E in human intestinal caco-2 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 169, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaveri, N.T. Green tea and its polyphenolic catechins: Medicinal uses in cancer and noncancer applications. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pi, J.; Zhang, Q. Signal amplification in the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE antioxidant response pathway. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wu, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, S. Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Damage in Chicken Lymphocytes. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 7386239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Q.; Ma, W. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Alleviates Vanadium-Induced Reduction of Antioxidant Capacity via Keap1-Nrf2-sMaf Pathway in the Liver, Kidney, and Ovary of Laying Hens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2707–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jia, R.; Celi, P.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.; Zeng, Q.; Mao, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, K. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves the antioxidant capacity of eggs. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, M.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, C.; Khalique, A.; Ni, X.; Zeng, D.; et al. Effects of Bacillus methylotrophicus SY200 Supplementation on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Status, Intestinal Morphology, and Immune Function in Broiler Chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.N.; Zhang, H.H.; Wang, F.; Yin, Y.X.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, J.S. Research Note: Effects of polysaccharide-enriched Acanthopanax senticosus extract on growth performance, immune function, antioxidation, and ileal microbial populations in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguelli, T.S.; Kolba, N.; Misra, A.; Dionisio, A.P.; Pelissari Kravchychyn, A.C.; Da Silva, B.P.; Stampini Duarte Martino, H.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Tako, E. Intra-Amniotic Administration of Cashew Nut (Anacardium occidentale L.) Soluble Extract Improved Gut Functionality and Morphology In Vivo (Gallus gallus). Nutrients 2023, 15, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Bibi, S.; Du, M.; Suzuki, T.; Zhu, M.J. Regulation of the intestinal tight junction by natural polyphenols: A mechanistic perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3830–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, U.; Aich, P. Postnatal intestinal mucosa and gut microbial composition develop hand in hand: A mouse study. Biomed. J. 2023, 46, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Earle-Payne, K. Antioxidant Defences and Redox Homeostasis in Animals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, S.; Viveros, A.; Rebole, A.; Arija, I.; Romero, C.; Alvarez, I.; Rey, A.; Brenes, A. Addition of exogenous enzymes to diets containing grape pomace: Effects on intestinal utilization of catechins and antioxidant status of chickens. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lei, X.; Luo, J.; Everaert, N.; Zhao, G.; Wen, J.; Yang, Y. The effect of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on small intestinal morphology, antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory effect in heat-stressed broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, U.; Rubab, M.; Daliri, E.B.; Chelliah, R.; Javed, A.; Oh, D.H. Curcumin, Quercetin, Catechins and Metabolic Diseases: The Role of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Alarcon, M.F.; Trottier, N.; Steibel, J.P.; Lunedo, R.; Campos, D.M.B.; Santana, A.M.; Pizauro, J.M., Jr.; Furlan, R.L.; Furlan, L.R. Interference of age and supplementation of direct-fed microbial and essential oil in the activity of digestive enzymes and expression of genes related to transport and digestion of carbohydrates and proteins in the small intestine of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2920–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Tako, E. The In Ovo Feeding Administration (Gallus Gallus)—An Emerging In Vivo Approach to Assess Bioactive Compounds with Potential Nutritional Benefits. Nutrients 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ding, S.J.; Fei, Y.Q.; Liu, G.; Jang, H.M.; Fang, J. Antimicrobial activity of anthocyanins and catechins against foodborne pathogens Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Food Control 2019, 106, 106712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, S.; Hakeem, W.G.A.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. Necrotic Enteritis in Broiler Chickens: A Review on the Pathogen, Pathogenesis, and Prevention. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, D.; Martel, A.; van Deun, K.; van Immerseel, F.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. The cinnamon-oil ingredient trans-cinnamaldehyde fails to target Campylobacter jejuni strain KC 40 in the broiler chicken cecum despite marked in vitro activity. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, S.; Romero, C.; Brenes, A.; Sanchez-Patan, F.; Bartolome, B.; Viveros, A.; Arija, I. Impact of a sustained consumption of grape extract on digestion, gut microbial metabolism and intestinal barrier in broiler chickens. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, B.; Zhuang, W.; Fan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, S. Tea Catechins: Potential Plant-Derived Feed Additives for Improving Chicken Intestinal Health and Productivity. Animals 2025, 15, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111553
Tian B, Zhuang W, Fan Y, Hu Y, Cui X, Li T, Zhang L, Luo X, Wang S. Tea Catechins: Potential Plant-Derived Feed Additives for Improving Chicken Intestinal Health and Productivity. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111553
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Bing, Wenjing Zhuang, Yanle Fan, Yun Hu, Xiaoyan Cui, Tingting Li, Liyang Zhang, Xugang Luo, and Shengchen Wang. 2025. "Tea Catechins: Potential Plant-Derived Feed Additives for Improving Chicken Intestinal Health and Productivity" Animals 15, no. 11: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111553
APA StyleTian, B., Zhuang, W., Fan, Y., Hu, Y., Cui, X., Li, T., Zhang, L., Luo, X., & Wang, S. (2025). Tea Catechins: Potential Plant-Derived Feed Additives for Improving Chicken Intestinal Health and Productivity. Animals, 15(11), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111553






