The Impact of MSTN Gene Editing on Meat Quality and Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Among Three Breeds of MSTN-Edited and Non-Edited Cattle
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Meat Traits Measurement
2.3.2. Metabolite Extraction
2.3.3. LC-MS Analysis
2.3.4. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR
2.3.5. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Meat Quality Traits
3.2. Metabolomics
3.2.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
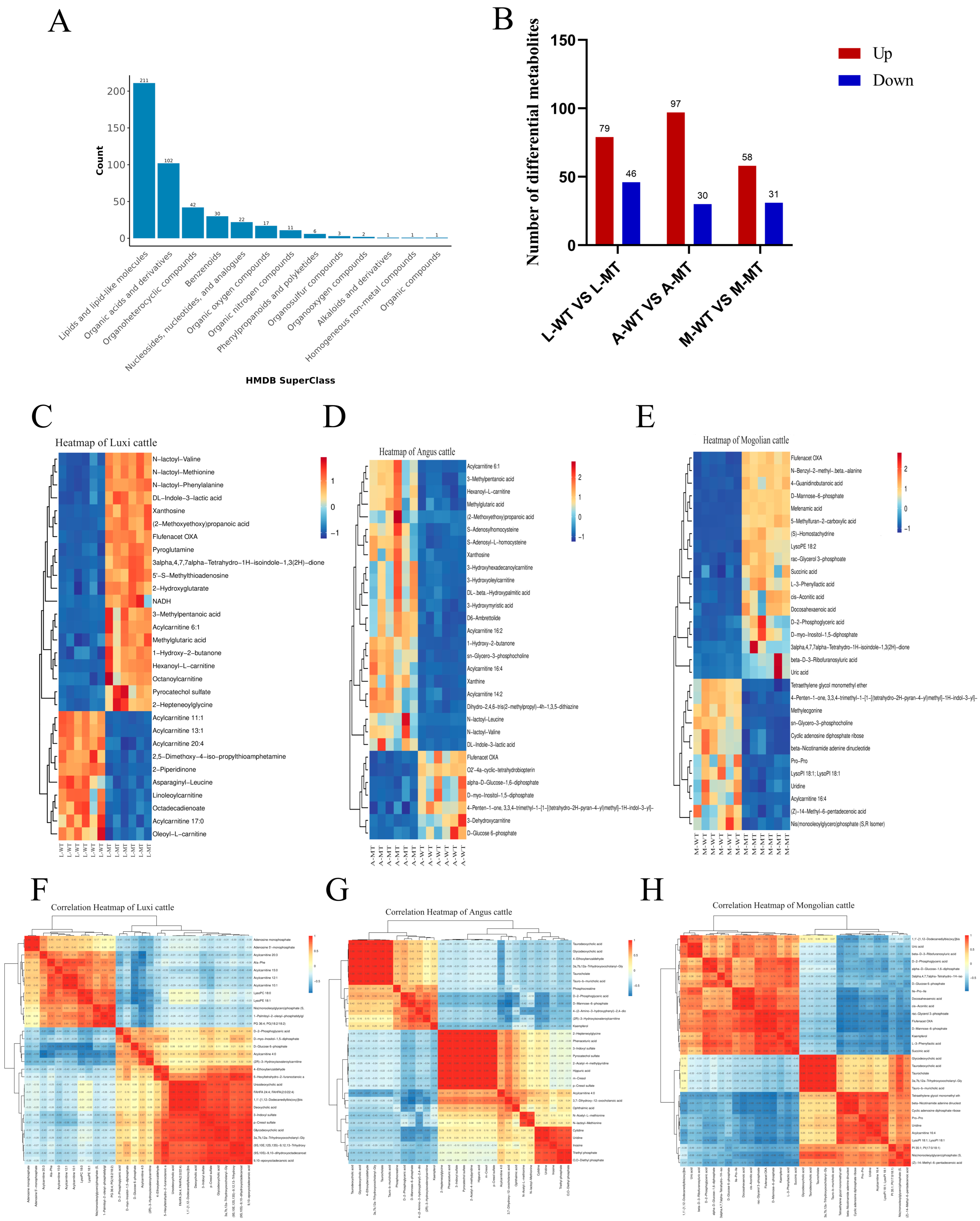
3.2.2. Identification of Differential Metabolites
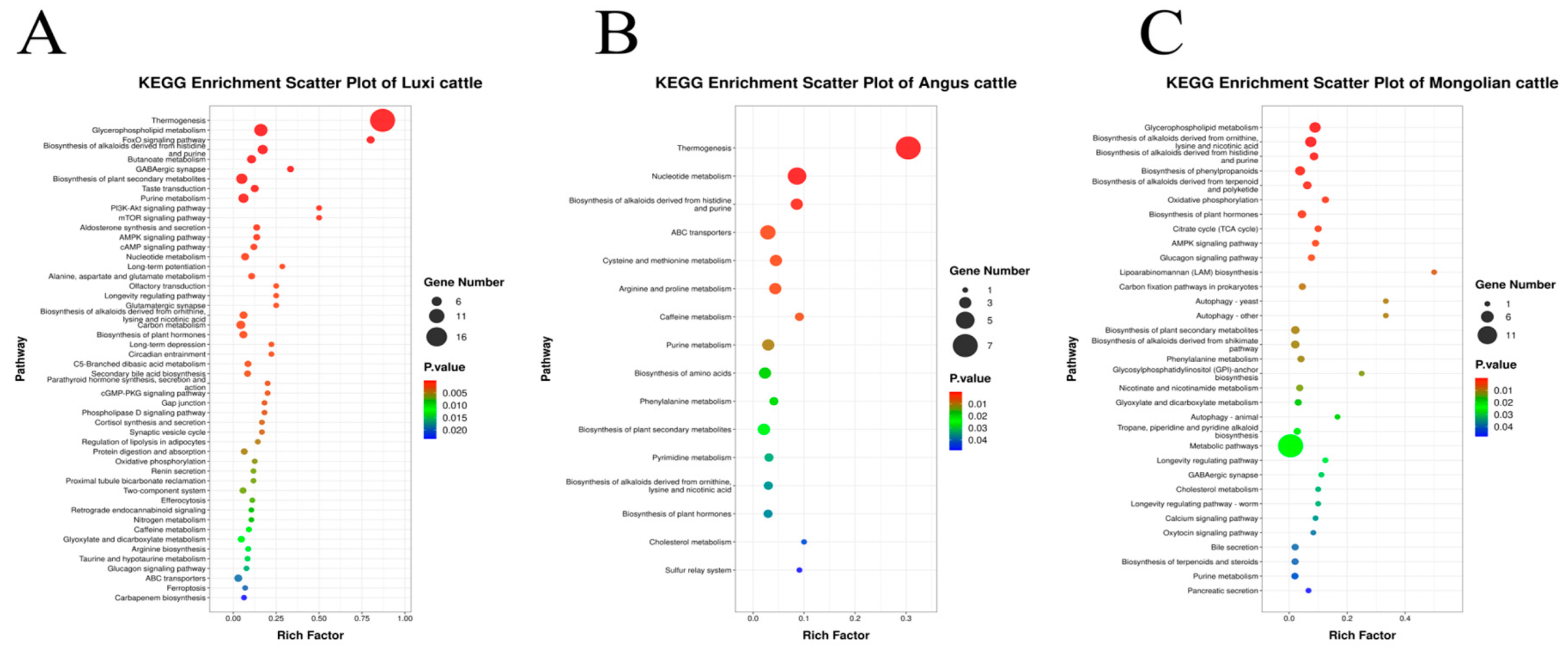
3.2.3. Screening Results and Analysis of Significantly Differential Metabolites
4. Discussion
4.1. Meat Quality Traits of MSTN Gene-Edited Cattle
4.2. Metabolomics Analysis of MSTN Gene-Edited Cattle
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, X. Economic Benefit Analysis of Luxi Cattle, Chinese Simenthal Cattle and Holstein Cattle. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2012. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&filename=1012318277.nh (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Tian, Q. Comparison of fattening performance between Luxi cattle and their hybrid cattle. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci. 2010, 31, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, H.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Feng, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, T.; Gu, Y. Transcriptome-based screening of key regulatory genes for meat quality traits in Black Angus cattle. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2021, 40, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Cha, G.B. A study on the carcass traits of Mongolian cattle in Xilin Gol League under natural grazing conditions. Contemp. Anim. Husb. Poult. Farming 2019, 11, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Preliminary observation on the effect of crossbreeding between Limousin and Luxi. Chin. Yellow Cattle 1986, 3, 19–22. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD8589&filename=BULL198603004 (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Huang, C.; Xiao, L.; Huugjilt; Wu, R.; Han, S.; Hou, R.; Hasi, S. Study on the effect of cross-breeding of Wagyu and Angus cattle to improve Mongolian cattle. Heilongjiang Anim. Husb. Vet. 2017, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Li, R.; Zeng, W.; Wang, M.; Shi, X.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; He, Z. Editing the cystine knot motif of MSTN enhances muscle development of Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs. Heredity 2021, 43, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobet, L.; Martin, L.J.; Poncelet, D.; Pirottin, D.; Brouwers, B.; Riquet, J.; Schoeberlein, A.; Dunner, S.; Ménissier, F.; Massabanda, J.; et al. A Deletion in the Bovine Myostatin Gene Causes the Double-Muscled Phenotype in Cattle. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Bai, C.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, G. Analysis of slaughter traits and meat quality of Luxi cattle edited by MSTN gene. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 31, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zan, L.; Wang, H. Genome array on differentially expressed genes of muscle tissue in intact male and castrated Qinchuan cattle. Hereditas 2010, 32, 11. Available online: https://lib.imu.edu.cn/articlesearch/web_searchingDetail?id=203141884891 (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Diesbourg, L.; Swatland, H.J.; Millman, B.M. X-Ray Diffraction Measurements of Postmortem Changes in the Myofilament Lattice of Pork. J. Anim. Sci. 1988, 66, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.J.; Warner, R.D. Ion distribution and protein proteolysis affect water holding capacity of Longissimus thoracis et lumborum in meat of lamb subjected to antemortem exercise. Meat Sci. 2007, 75, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moeseke, W.; De Smet, S. Effect of time of deboning and sample size on drip loss of pork. Meat Sci. 1999, 52, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, R.; Wu, Q.; Yong, J.; Dong, J.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals cell lineage specification in temporal-spatial patterns in human cortical development. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matteis, S.; Bonafè, M.; Giudetti, A.M. Urinary Metabolic Biomarkers in Cancer Patients: An Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2292, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanesi, L. Metabolomics and livestock genomics: Insights into a phenotyping frontier and its applications in animal breeding. Anim. Front. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldansaz, S.A.; Guo, A.C.; Sajed, T.; Steele, M.A.; Plastow, G.S.; Wishart, D.S. Livestock metabolomics and the livestock metabolome: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleníková, J.; Pipek, P.; Staruch, L. The influence of ante-mortem treatment on relationship between pH and tenderness of beef. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.C.; Hedrick, H.B. Chemical, Physical and Sensory Characteristics of Bovine Muscle from Four Quality Groups. J. Food Sci. 1977, 42, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Luo, Z.; Han, S.; Li, Z.; Choe, H.M.; Paek, H.J.; Quan, B.; Kang, J.; Yin, X. Analysis of meat color, meat tenderness and fatty acid composition of meat in second filial hybrid offspring of MSTN mutant pigs. Meat Sci. 2022, 193, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchenje, V.; Dzama, K.; Chimonyo, M.; Strydom, P.E.; Hugo, A.; Raats, J.G. Some biochemical aspects pertaining to beef eating quality and consumer health: A review. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hai, C.; Liu, C.; Bai, C.; Wei, Z.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y. Meat quality-related proteomics in cattle edited with myostatin gene (MSTN). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gu, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Lei, J.; Wei, Z.; Bai, C.; Yang, L. Histological Structure and Transcriptome Analysis of Skeletal Muscle in Myostatin Gene Editing Cattle (Bos taurus). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 30, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, K.; Weng, Q.; Li, P.; Wei, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. RNA-seq analysis reveals new candidate genes for drip loss in a Pietrain × Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire population. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A. Study on the Combined Bacteriostatic Effect and Mechanism of Phenyllactic Acid with Commonly Used Food Preservatives and Organic Acids; Hebei University of Science and Technology: Shijiazhuang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Chang, J.Y. Metabolites of Kimchi Lactic Acid Bacteria, Indole-3-Lactic Acid, Phenyllactic Acid, and Leucic Acid, Inhibit Obesity-Related Inflammation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforza, S.; Cavatorta, V.; Galaverna, G.; Dossena, A.; Marchelli, R. Accumulation of non-proteolytic aminoacyl derivatives in Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, S.; Prandi, B.; Falavigna, C.; Buhler, S.; Dossena, A.; Sforza, S.; Galaverna, G. Occurrence of non-proteolytic amino acyl derivatives in dry-cured ham. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christa, P.; Dunkel, A.; Krauss, A.; Stark, T.D.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T. Discovery and Identification of Tastants and Taste-Modulating N-Acyl Amino Acid Derivatives in Traditional Korean Fermented Dish Kimchi Using a Sensomics Approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7500–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Lin, J.; Cui, C.; Li, L.; He, S.; Brennan, C. Preparation and Taste Characteristics of Kokumi N-Lactoyl Phenylalanine in the Presence of Phenylalanine and Lactate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 5396–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, C.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Feng, Y. Discovery of N-l-Lactoyl-l-Trp as a Bitterness Masker via Structure-Based Virtual Screening and a Sensory Approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, L.; Huang, Z.; Xie, J. Recent advances in polysaccharide biomodification by microbial fermentation: Production, properties, bioactivities, and mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 12999–13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Product Lengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDHA | GCTGGATGGCACTTACCTTGT | TGGACTAGGCACCTTGGCTAA | 168 |
| CNDP2 | AGGTGGTCGGCAAGTTCTC | CAGGTAGTGAGGGTGGTTGAA | 182 |
| GAPDH | CAAGTTCAACGGCACAGTCAAG | CACATACTCAGCACCAGCATCA | 124 |
| Items | Muscle | L-WT | L-MT | A-WT | A-MT | M-WT | M-MT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | upper brain | 5.72 ± 0.14 a | 5.44 ± 0.04 b | 5.69 ± 0.05 a | 5.47 ± 0.12 b | 5.73 ± 0.05 a | 5.47 ± 0.08 b |
| eye meat | 5.74 ± 0.07 a | 5.44 ± 0.04 c | 5.68 ± 0.07 ab | 5.41 ± 0.04 c | 5.62 ± 0.10 b | 5.44 ± 0.03 c | |
| external spine | 5.64 ± 0.06 a | 5.43 ± 0.05 c | 5.57 ± 0.11 ab | 5.45 ± 0.03 bc | 5.68 ± 0.11 a | 5.46 ± 0.04 bc | |
| internal spine | 5.70 ± 0.05 a | 5.49 ± 0.03 b | 5.81 ± 0.17 a | 5.50 ± 0.01 b | 5.76 ± 0.12 a | 5.49 ± 0.03 b | |
| anterior tendon | 5.81 ± 0.04 a | 5.67 ± 0.15 abc | 5.72 ± 0.05 ab | 5.52 ± 0.07 bc | 5.76 ± 0.12 ab | 5.56 ± 0.07 bc | |
| posterior tendon | 5.76 ± 0.12 a | 5.56 ± 0.08 b | 5.69 ± 0.12 ab | 5.54 ± 0.08 b | 5.71 ± 0.03 ab | 5.56 ± 0.10 ab | |
| semitendinosus | 5.68 ± 0.14 ab | 5.50 ± 0.05 b | 5.57 ± 0.07 b | 5.50 ± 0.08 b | 5.79 ± 0.15 a | 5.52 ± 0.03 b | |
| Shear force (N) | upper brain | 10.64 ± 0.16 ab | 8.98 ± 0.68 d | 10.02 ± 0.48 bcd | 9.31 ± 0.65 cd | 11.56 ± 0.97 a | 10.26 ± 0.42 bc |
| eye meat | 11.83 ± 0.50 b | 10.45 ± 0.41 cd | 11.61 ± 0.76 bc | 10.06 ± 0.76 d | 13.17 ± 1.24 a | 10.68 ± 0.20 bcd | |
| external spine | 10.56 ± 0.84 ab | 9.55 ± 0.27 c | 9.30 ± 0.67 c | 8.31 ± 0.50 d | 10.74 ± 0.40 a | 9.81 ± 0.10 bc | |
| internal spine | 10.13 ± 0.72 bc | 8.51 ± 0.35 d | 10.44 ± 0.71 bc | 9.50 ± 0.15 cd | 12.82 ± 1.32 a | 10.92 ± 0.46 b | |
| anterior tendon | 22.16 ± 2.22 ab | 18.24 ± 0.98 b | 22.14 ± 2.21 ab | 19.68 ± 0.96 ab | 22.96 ± 2.75 a | 20.45 ± 2.49 ab | |
| posterior tendon | 22.05 ± 1.43 a | 19.71 ± 1.07 c | 24.97 ± 0.64 a | 23.39 ± 1.23 ab | 25.28 ± 0.23 a | 23.24 ± 2.06 ab | |
| semitendinosus | 17.56 ± 0.92 ab | 15.68 ± 1.50 bc | 16.86 ± 0.71 abc | 14.74 ± 0.59 d | 18.33 ± 0.15 a | 16.67 ± 0.62 bc | |
| Extrusion loss rate (%) | upper brain | 4.30 ± 0.16 c | 4.76 ± 0.20 c | 4.42 ± 0.24 b | 4.56 ± 0.01 ab | 4.91 ± 0.23 a | 4.65 ± 0.12 ab |
| eye meat | 5.47 ± 0.31 a | 5.63 ± 0.17 a | 5.77 ± 0.35 a | 5.83 ± 0.72 a | 5.33 ± 0.19 a | 5.55 ± 0.39 a | |
| external spine | 5.15 ± 0.09 a | 5.28 ± 0.08 a | 5.25 ± 0.42 a | 4.82 ± 0.68 a | 5.05 ± 0.58 a | 5.64 ± 0.25 a | |
| internal spine | 5.19 ± 1.01 a | 5.30 ± 0.83 a | 4.43 ± 0.47 a | 5.36 ± 0.73 a | 4.66 ± 0.97 a | 4.82 ± 0.40 a | |
| anterior tendon | 1.96 ± 0.05 bc | 1.72 ± 0.16 c | 3.25 ± 0.71 a | 3.24 ± 0.73 a | 2.77 ± 0.30 ab | 3.24 ± 0.36 a | |
| posterior tendon | 2.08 ± 0.33 b | 2.59 ± 0.12 b | 3.48 ± 0.31 a | 3.57 ± 0.40 a | 2.27 ± 0.41 b | 2.62 ± 0.33 b | |
| semitendinosus | 5.23 ± 1.19 bc | 4.24 ± 1.15 c | 4.78 ± 0.30 bc | 4.58 ± 0.36 c | 6.14 ± 0.35 ab | 6.93 ± 0.50 a | |
| Cooking loss rate (%) | upper brain | 31.42 ± 2.19 ab | 29.43 ± 1.40 b | 33.16 ± 0.76 a | 32.70 ± 2.03 a | 32.53 ± 1.25 a | 33.56 ± 0.90 a |
| eye meat | 23.06 ± 0.32 c | 24.47 ± 1.15 c | 32.27 ± 1.56 b | 31.83 ± 1.46 b | 34.40 ± 1.08 a | 34.56 ± 0.91 a | |
| external spine | 30.57 ± 2.00 abc | 29.70 ± 0.67 bc | 31.76 ± 2.94 abc | 28.40 ± 1.20 c | 33.73 ± 1.16 a | 32.00 ± 1.85 ab | |
| internal spine | 32.82 ± 2.55 ab | 33.85 ± 1.02 ab | 30.77 ± 1.46 ab | 32.19 ± 2.02 b | 34.00 ± 1.73 ab | 35.63 ± 1.03 a | |
| anterior tendon | 33.99 ± 2.66 a | 34.00 ± 0.61 a | 29.40 ± 3.40 b | 31.27 ± 1.61 ab | 29.27 ± 0.71 b | 29.26 ± 0.68 b | |
| posterior tendon | 31.03 ± 1.56 a | 30.43 ± 2.50 a | 31.20 ± 0.61 a | 31.50 ± 1.93 a | 32.53 ± 0.85 a | 32.56 ± 1.16 a | |
| semitendinosus | 31.17 ± 2.92 ab | 31.67 ± 1.05 a | 28.40 ± 0.92 b | 28.44 ± 0.75 b | 31.67 ± 1.07 a | 31.43 ± 1.22 a | |
| Moisture (%) | upper brain | 69.90 ± 0.17 a | 69.83 ± 0.64 a | 69.90 ± 0.10 a | 69.73 ± 0.21 a | 69.60 ± 0.20 a | 69.30 ± 0.20 a |
| eye meat | 70.07 ± 0.06 ab | 70.37 ± 0.23 a | 70.03 ± 0.15 b | 70.00 ± 0.10 b | 70.00 ± 0.10 b | 70.30 ± 0.20 ab | |
| external spine | 69.86 ± 0.12 b | 70.10 ± 0.17 ab | 70.30 ± 0.20 a | 70.03 ± 0.06 ab | 70.23 ± 0.25 a | 70.13 ± 0.06 ab | |
| internal spine | 70.20 ± 0.46 a | 70.43 ± 0.29 a | 69.90 ± 0.30 a | 70.10 ± 0.20 a | 69.90 ± 0.10 a | 70.13 ± 0.06 a | |
| anterior tendon | 70.37 ± 0.06 a | 70.43 ± 0.12 a | 70.23 ± 0.06 ab | 70.13 ± 0.15 b | 70.43 ± 0.15 a | 70.23 ± 0.06 ab | |
| posterior tendon | 70.33 ± 0.47 a | 70.46 ± 0.58 a | 70.00 ± 0.10 a | 70.00 ± 0.10 a | 69.93 ± 0.25 a | 70.20 ± 0.10 a | |
| semitendinosus | 70.16 ± 0.29 a | 70.17 ± 0.12 a | 70.30 ± 0.20 a | 70.10 ± 0.00 a | 70.50 ± 0.10 a | 70.30 ± 0.20 a | |
| Protein (%) | upper brain | 20.30 ± 0.00 a | 20.30 ± 0.17 a | 20.07 ± 0.06 a | 20.13 ± 0.15 a | 20.13 ± 0.05 a | 20.30 ± 0.20 a |
| eye meat | 20.30 ± 0.00 a | 20.47 ± 0.06 a | 20.10 ± 0.10 a | 20.10 ± 0.06 a | 20.03 ± 0.06 a | 20.13 ± 0.06 a | |
| external spine | 20.36 ± 0.06 ab | 20.30 ± 0.00 bc | 19.97 ± 0.15 abc | 20.00 ± 0.00 c | 20.13 ± 0.06 abc | 20.20 ± 0.10 a | |
| internal spine | 20.26 ± 0.12 ab | 20.47 ± 0.15 a | 20.13 ± 0.15 bc | 20.03 ± 0.06 c | 20.20 ± 0.00 bc | 20.20 ± 0.10 bc | |
| anterior tendon | 20.23 ± 0.12 a | 20.30 ± 0.20 a | 20.07 ± 0.15 a | 20.06 ± 0.06 a | 20.13 ± 0.06 a | 20.20 ± 0.10 a | |
| posterior tendon | 20.23 ± 0.12 ab | 20.33 ± 0.06 a | 20.10 ± 0.10 ab | 20.10 ± 0.17 b | 20.13 ± 0.06 ab | 20.03 ± 0.06 b | |
| semitendinosus | 20.43 ± 0.12 a | 20.30 ± 0.00 ab | 20.20 ± 0.10 bc | 20.10 ± 0.00 c | 20.23 ± 0.06 bc | 20.13 ± 0.15 bc | |
| Intramuscular Fat (%) | upper brain | 12.46 ± 0.40 a | 10.30 ± 0.17 c | 10.26 ± 0.06 c | 9.66 ± 0.11 d | 11.40 ± 0.10 b | 10.23 ± 0.15 c |
| eye meat | 11.43 ± 0.40 a | 10.00 ± 0.35 bc | 10.47 ± 0.40 b | 9.17 ± 0.12 d | 11.23 ± 0.66 a | 9.70 ± 0.10 cd | |
| external spine | 12.73 ± 0.81 a | 11.36 ± 0.75 b | 11.37 ± 0.32 c | 10.33 ± 0.72 c | 10.13 ± 0.06 c | 10.50 ± 0.00 bc | |
| internal spine | 11.27 ± 0.06 a | 8.83 ± 0.06 c | 10.90 ± 0.61 ab | 8.90 ± 0.80 c | 10.23 ± 0.06 b | 8.50 ± 0.40 c | |
| anterior tendon | 9.87 ± 0.28 abc | 9.23 ± 0.11 c | 10.07 ± 0.75 ab | 9.20 ± 0.10 c | 10.33 ± 0.46 a | 9.55 ± 0.05 bc | |
| posterior tendon | 10.07 ± 0.12 cd | 9.57 ± 0.12 d | 10.13 ± 0.12 bc | 9.73 ± 0.25 c | 10.83 ± 0.65 a | 10.63 ± 0.15 ab | |
| semitendinosus | 11.03 ± 0.40 ab | 10.13 ± 0.58 c | 9.50 ± 0.87 cd | 9.13 ± 0.15 d | 11.43 ± 0.06 a | 10.30 ± 0.20 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Bu, L.; Wang, D.; Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, G.; Yang, L. The Impact of MSTN Gene Editing on Meat Quality and Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Among Three Breeds of MSTN-Edited and Non-Edited Cattle. Animals 2025, 15, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010047
Luo S, Liu Y, Bu L, Wang D, Wen Z, Yang Y, Xu Y, Wu D, Li G, Yang L. The Impact of MSTN Gene Editing on Meat Quality and Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Among Three Breeds of MSTN-Edited and Non-Edited Cattle. Animals. 2025; 15(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Shan, Yuanqing Liu, Lige Bu, Dezheng Wang, Zhaoyu Wen, Yuqing Yang, Yanan Xu, Di Wu, Guangpeng Li, and Lei Yang. 2025. "The Impact of MSTN Gene Editing on Meat Quality and Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Among Three Breeds of MSTN-Edited and Non-Edited Cattle" Animals 15, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010047
APA StyleLuo, S., Liu, Y., Bu, L., Wang, D., Wen, Z., Yang, Y., Xu, Y., Wu, D., Li, G., & Yang, L. (2025). The Impact of MSTN Gene Editing on Meat Quality and Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Among Three Breeds of MSTN-Edited and Non-Edited Cattle. Animals, 15(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15010047






