Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Diet Supplementation Affects Nutrient Digestibility and Milk and Mozzarella Cheese Yield in Dairy Buffalo Cows During the Transition
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
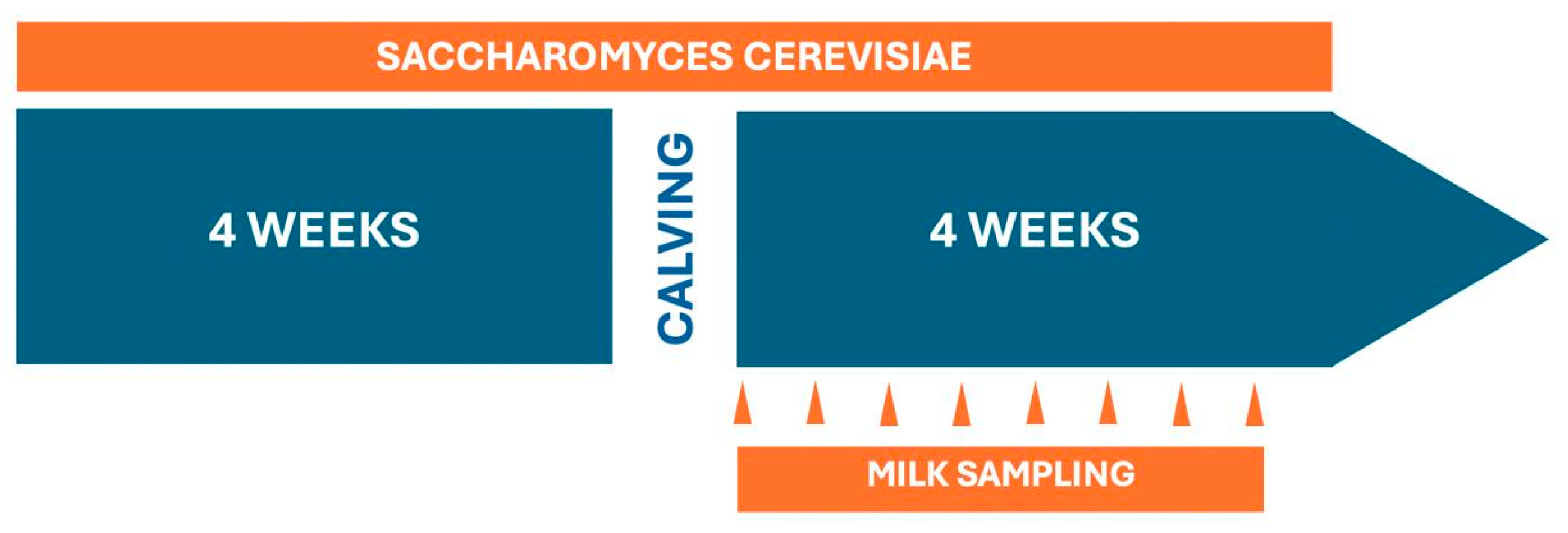
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Diet Analysis and Digestibility
2.3. Milk
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lotito, D.; Pacifico, E.; Matuozzo, S.; Musco, N.; Iommelli, P.; Zicarelli, F.; Tudisco, R.; Infascelli, F.P. Lombardi. Colostrum Composition, Characteristics and Management for Buffalo Calves: A Review. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghese, A.; Chiarotti, A.; Barile, V.L. Buffalo in the world: Situation and perspectives. In Biotechnological Applications in Buffalo Research; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zicarelli, F.; Iommelli, P.; Musco, N.; Wanapat, M.; Lotito, D.; Lombardi, P.; Infascelli, F.; Tudisco, R. Growth Performance of Buffalo Calves in Response to Different Diets with and without Saccharomyces cerevisiae Supplementation. Animals 2024, 14, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-González, D.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Orihuela, A.; Bertoni, A.; Morales-Canela, D.A.; Álvarez-Macías, A.; José-Pérez, N.; Domínguez-Oliva, A.; Mota-Rojas, D. Handling and Physiological Aspects of the Dual-Purpose Water Buffalo Production System in the Mexican Humid Tropics. Animals 2022, 28, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanapat, M.; Pilajun, R.; Kongmun, P. Ruminal ecology of swamp buffalo as influenced by dietary sources. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2009, 151, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.N.; Bannink, A.; Crompton, L.A.; Huhtanen, P.; Kreuzer, M.; McGee, M.; Nozière, P.; Reynolds, C.K.; Bayat, A.R.; Yáñez-Ruiz, D.R.; et al. Invited review: Nitrogen in ruminant nutrition: A review of measurement techniques. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5811–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingvartsen, K.L.; Andersen, J.B. Integration of metabolism and intake regulation: A review focusing on periparturient animals. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1573–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Wanapat, M.; Shah, A.M.; Luo, X.; Peng, Q.; Kang, K.; Hu, R.; Guan, J.; Wang, Z. Ruminal pH pattern, fermentation characteristics and related bacteria in response to dietary live yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) supplementation in beef cattle. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaucheras-Durand, F.; Ameilbonne, A.; Auffret, P.; Bernard, M.; Mialon, M.M.; Duniere, L.; Forano, E. Supplementation of live yeast based feed additive in early life promotes rumen microbial colonization and fibrolytic potential in lambs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phesatcha, K.; Phesatcha, B.; Wanapat, M.; Cherdthong, A. Roughage to Concentrate Ratio and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Inclusion Could Modulate Feed Digestion and In Vitro Ruminal Fermentation. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, C.; Crispie, F.; Lewis, E.; Reid, M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. The rumen microbiome: A crucial consideration when optimising milk and meat production and nitrogen utilisation efficiency. Gut Microbes 2010, 10, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaworski, E.M.; Shriver-Munsch, C.M.; Fadden, N.A.; Sanchez, W.K.; Yoon, I.; Bobe, G. Effects of feeding various dosages of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product in transition dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 3081–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, B.X.; Yao, K.Y.; Yoon, I.; Chung, Y.H.; Wang, J.K.; Liu, J.X. Effects of supplemental levels of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product on lactation performance in dairy cows under heat stress. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 29, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doreau, M.; Jouany, J.P. Effect of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture on nutrient digestion in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 3214–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.H.; Erasmus, L.J. Effects of analyzable diet components on responses of lactating dairy cows to Saccharomyces cerevisiae based yeast products: A systematic review of the literature. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2009, 149, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccioli-Cappelli, F.; Seal, C.J.; Parker, D.S.; Loor, J.J.; Minuti, A.; Lopreiato, V.; Trevisi, E. Effect of stage of lactation and dietary starch content on endocrine-metabolic status, blood amino acid concentrations, milk yield, and composition in Holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, H.A.; Hassan, M.S.; Giadinis, N.D.; Panousis, N.; Ostojic, D.; Abd El-Tawab, M.M.; Bojkovski, J. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae supplementation on health and performance of dairy cows during transition and early lactation period. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2015, 31, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infascelli, F.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Calabrò, S.; Bovera, F.; Tudisco, R.; Zicarelli, F.; Piccolo, G. Effects of inclusion of yeast culture (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) in the diet of dairy buffaloes on milk yield in the first 120 days of lactation. In Proceedings of the 7th World Buffalo Congress, Manila, Philippines, 20–23 October 2004; Volume 2, pp. 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Campanile, G.; Di Palo, R.; De Filippo, C.; Zicarelli, L. Tempi di ingestione e di ruminazione nella bufala in funzione della distanza dal parto. In Proceedings of the Atti 12th National Congress ASPA, Pisa, Italy, 28 March–1 April 1997; pp. 211–212. [Google Scholar]
- Masucci, F.; Uzun, P.; Grasso, F.; De Rosa, G.; Di Francia, A. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Live Cells on In Vivo Digestibility and Nitrogen Excretion in Lactating Buffaloes. J. Buffalo Sci. 2014, 3, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmencioglu, T.; Ozcan, T.; Ozbilgin, S.; Senlurklu, L. Effects of yeast culture addition (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) to Anatolian water buffalo diets on milk composition and somatic cell count. Scienza Tecnica Lattiero Casearia 2013, 40, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.H.; El-Bordeny, N.E.; Ebeid, H.M. Response of primiparous and multiparous buffaloes to yeast culture supplementation during early and mid-lactation. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francia, A.; Masucci, F.; De Rosa, G.; Varricchio, M.L.; Proto, V. Effects of Aspergillus oryzae extract and a Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product on intake, body weight gain and digestibility in buffalo calves. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 140, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Rao, K.S.; Suresh, J.; Moorthy, P.S.; Reddy, Y.K. A body condition score (BCS) system in Murrah buffaloes. Buffalo Bull. 2011, 30, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists). Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INRA Feeding System for Ruminants; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; Available online: https://www.wageningenacademic.com/doi/book/10.3920/978-90-8686-292-4 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Heinrichs, J.; Kononoff, P. The Penn State Particle Separator; Penn State Extension, Department of Animal Science, DSE: University Park, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 13, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Van Keulen, J.; Young, B.A. Evaluation of acid-insoluble ash as a natural marker in ruminant digestibility studies. J. Anim. Sci. 1977, 44, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Palo, R. Produzione Lattea Nella Bufala con Diete Tradizionali e con L’impiego di Acidi Grassi. Ph.D Thesis, University of Naples, Naples, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Altiero, V.; Moio, L.; Addeo, F. Previsione della resa in mozzarella sulla base del contenuto in grasso e proteine del latte di bufala. Sci. E Tec. Latt. Casearia 1989, 40, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Infascelli, F.; Tudisco, R.; Pacelli, C.; Borghese, A. Nutrition and Feeding. In Buffalo Livestock and Product; Borghese, A., Ed.; CRA: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 175–212. [Google Scholar]
- Abeni, F. Effects of extrinsic factors on some rumination patterns: A review. Front. Anim. Sci. 2022, 3, 1047829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocchi Jasinski, F.; Evangelista, C.; Basiricò, L.; Bernabucci, U. Responses of Dairy Buffalo to Heat Stress Conditions and Mitigation Strategies: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Pradhan, K.; Sangwan, D.C.; Singh, S.; Sagar, V. Effect of fibrous diets on feeding pattern, digestibility and physiological reactions in cattle and buffalo. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 64, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, P.M. Intake and digestion swamp buffaloes and cattle. 4. Particle size and buoyancy in relation to volontary intake. J. Agric. Sci. 1995, 124, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartocci, S.; Amici, A.; Verna, M.; Terramoccia, S.; Martillotti, F. Solid and fluid passage rate in buffalo, cattle and sheep fed diets with different forage to concentrate ratios. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1997, 52, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, S.; Infascelli, F.; Bovera, F.; Moniello, G.; Piccolo, V. In vitro degradability of three forages: Fermentation kinetics and gas production of NDF and neutral detergent-soluble fraction of forages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, S.; Williams, B.A.; Piccolo, V.; Infascelli, F.; Tamminga, S. A comparison between buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) and cow (Bos taurus) rumen fluids in terms of the invitro fermentation characteristics of three fibrous feedstuffs. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, S.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Bovera, F.; Piccolo, G.; Infascelli, F. In vitro fermentation kinetics of carbohydrate fractions of fresh forage, silage and hay of Avena sativa. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, S.; Tudisco, R.; Balestrieri, A.; Piccolo, G.; Infascelli, F.; Cutrignelli, M.I. Fermentation characteristics of different grain legumes cultivars with the in vitro gas production technique. Italian J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iommelli, P.; Zicarelli, F.; Musco, N.; Sarubbi, F.; Grossi, M.; Lotito, D.; Lombardi, P.; Infascelli, F.; Tudisco, R. Effect of Cereals and Legumes Processing on In Situ Rumen Protein Degradability: A Review. Fermentation 2022, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, L.A.; Ranson, K.A.; Ames, S.J.; Wilde, D. The effect of including a yeast culture on the intake and performance of high yielding dairy cows fed a diet high in starch. Proc. Br. Soc. Anim. Sci. 2006, 2006, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Campanile, G.; Zicarelli, F.; Vecchio, D.; Pacelli, C.; Neglia, G.; Balestrieri, A.; Di Palo, R.; Infascelli, F. Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on in vivo organic matter digestibility and milk yield in buffalo cows. Livestock Sci. 2008, 114, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, S.; Khalid, N.; Ahmed, I.; Imran, M. Probiotic Yeast: Mode of Action and Its Effects on Ruminant Nutrition. In Yeast-Industrial Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 179–202. [Google Scholar]
- Dann, H.M.; Drackley, J.K.; McCoy, G.C.; Hutjens, M.F.; Garrett, J.E. Effects of yeast culture (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) on prepartum intake and postpartum intake and milk production of Jersey cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, M.; Ahmad, N.; Tariq, M.N.; Usman, M.; Sardar, A.A. Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae live cells and culture on growth and productive performance in lactating Nili-Ravi buffaloes. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlt, J.E.; Corcione, T.T.; Zajac, P.K. Effect of yeast on feed intake and performance of cows fed diets based on corn silage during early lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, E.S.; Martin, S.A. Effects of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture on ruminal bacteria that utilize lactate and digest cellulose. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs, J.P.; Suli, A.; Halasz, T.; Arany, A.; Bodor, Z. Effect of live yeast culture Saccharomyces cerevisiae on milk production and some blood parameters. Anim. Sci. Biotech. 2013, 46, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zicarelli, F.; Addi, L.; Tudisco, R.; Calabrò, S.; Lombardi, P.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Moniello, G.; Grossi, M.; Tozzi, B.; Musco, N.; et al. The influence of diet supplementation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Saccharomyces cerevisiae plus Aspergillus oryzae on milk yield of Cilentana grazing dairy goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 135, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.L.A.; Mendoza, M.G.D.; Bárcena-Gama, J.R.; González, M.S.S.; Ferrara, R.; Ortega, C.M.E.; Cobos, P.M.A. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Aspergillus oryzae cultures and NDF level on parameters of ruminal fermentation. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 1996, 63, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Liang, T.; Muckey, M.B.; Mendonça, L.G.D.; Hulbert, L.E.; Elrod, C.C.; Bradford, B.J. Yeast product supplementation modulated feeding behavior and metabolism in transition dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.G.; Rutigliano, H.M.; Cerri, R.L.; Robinson, P.H.; Santos, J.E. Effect of feeding Saccharomyces cerevisiae on performance of dairy cows during summer heat stress. Animal Feed Sci. Tech. 2009, 150, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutrignelli, M.I.; Piccolo, G.; D’urso, S.; Calabrò, S.; Bovera, F.; Tudisco, R.; Infascelli, F. Urinary excretion of purine derivatives in dry buffalo and Fresian cows. Ita. J. An. Sci. 2007, 6, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Corn silage | 3.8 |
| Alfalfa haylage (1st cut) | 3.0 |
| Corn mash | 2.7 |
| Polyphite hay * | 1.9 |
| Concentrate ** | 4.1 |
| Hydrogenated fats plus vitamins | 0.2 |
| Salts | 0.06 |
| (g/kg DM) | Diet |
|---|---|
| Crude protein | 154.2 ± 15.3 |
| Ether extract | 44.0 ± 10.4 |
| NDF | 383.6 ± 24.3 |
| ADF | 209.2 ± 16.2 |
| ADL | 57.2 ± 9.1 |
| PeNDF | 276.1 ± 16.2 |
| Starch | 223.2 ± 14.1 |
| Ash | 72.4 ± 11.2 |
| UFL (kg DM) | 0.9 |
| Item | Control | Treated | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCS | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.2 | NS |
| DMI (kg/day) | 14.5 ± 1.5 | 14.5 ± 1.8 | NS |
| Digestibility (%) | |||
| Organic matter | 58.2 ± 3.1 | 68.1 ± 2.2 | <0.01 |
| Crude protein | 55.3 ± 1.8 | 63.9 ± 1.7 | <0.01 |
| Ether extract | 88.2 ± 1.1 | 88.8 ± 1.6 | NS |
| NDF | 37.9 ± 2.7 | 49.6 ± 2.1 | <0.01 |
| ADF | 34.3 ± 3.1 | 42.3 ± 2.9 | <0.01 |
| Starch | 89.3 ± 1.2 | 96.8 ± 1.1 | <0.01 |
| Item | Control | Treated | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
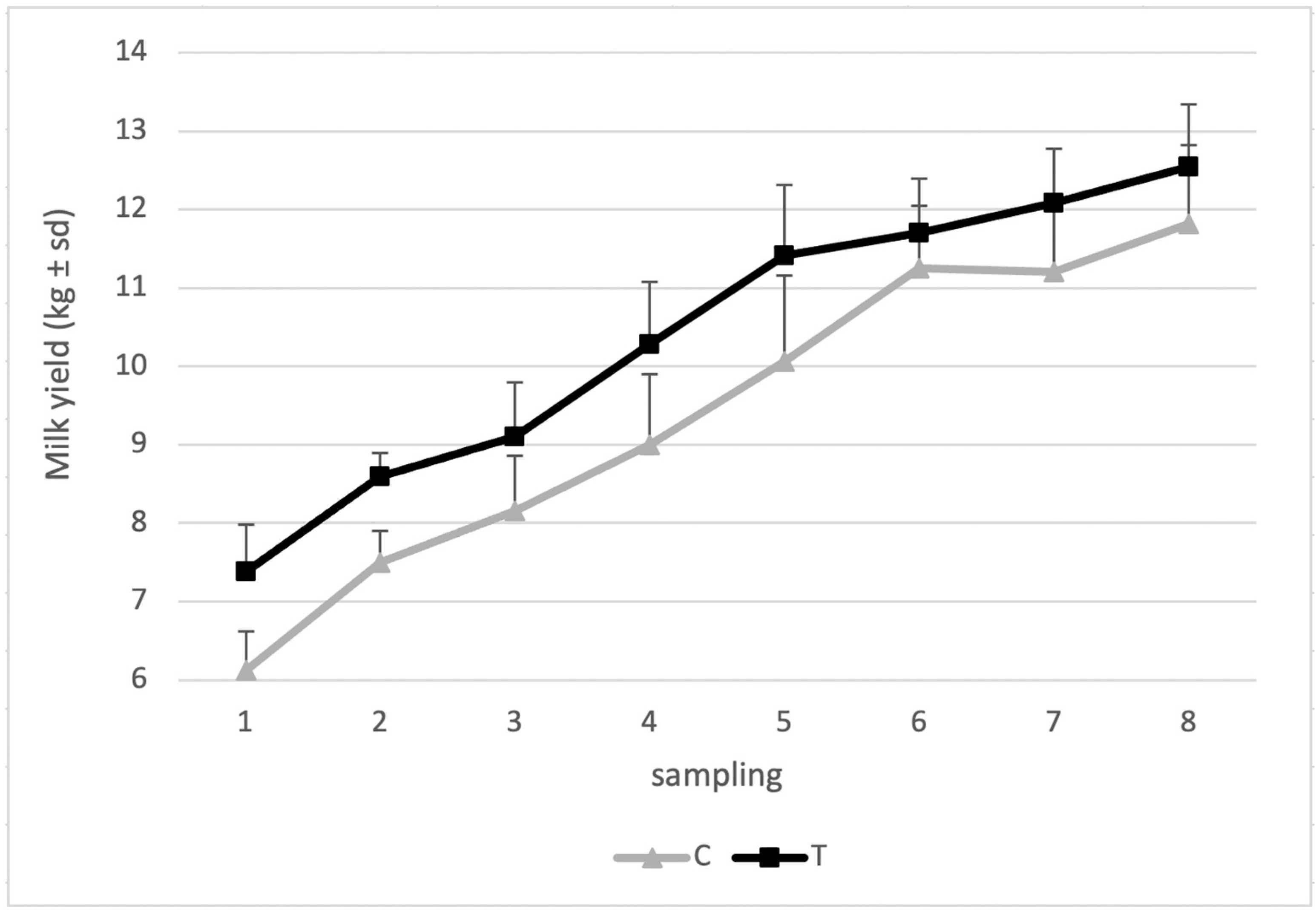
| MY | 9.2 ± 2.8 | 10.5 ± 1.9 | <0.05 |
| Fat | 80.1 ± 1.3 | 76.0 ± 1.0 | <0.05 |
| Protein | 46.1 ± 0.3 | 47.1 ± 1.5 | NS |
| Lactose | 45.0 ± 0.2 | 44.8 ± 1.4 | NS |
| FPCM | 15.0 ± 3.1 | 16.8 ± 3.6 | <0.05 |
| MUN | 42.2 ± 0.9 | 40.5 ± 0.7 | NS |
| Caseins | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 4.1 ± 1.3 | NS |
| MCY | 25.2 ± 2.6 | 24.8 ± 7.6 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zicarelli, F.; Vianello, R.C.; Masiello, I.; Musco, N.; Iommelli, P.; Wanapat, M.; Lotito, D.; Lombardi, P.; Grossi, M.; Infascelli, F.; et al. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Diet Supplementation Affects Nutrient Digestibility and Milk and Mozzarella Cheese Yield in Dairy Buffalo Cows During the Transition. Animals 2024, 14, 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243689
Zicarelli F, Vianello RC, Masiello I, Musco N, Iommelli P, Wanapat M, Lotito D, Lombardi P, Grossi M, Infascelli F, et al. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Diet Supplementation Affects Nutrient Digestibility and Milk and Mozzarella Cheese Yield in Dairy Buffalo Cows During the Transition. Animals. 2024; 14(24):3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243689
Chicago/Turabian StyleZicarelli, Fabio, Remus Costantin Vianello, Isabella Masiello, Nadia Musco, Piera Iommelli, Metha Wanapat, Daria Lotito, Pietro Lombardi, Micaela Grossi, Federico Infascelli, and et al. 2024. "Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Diet Supplementation Affects Nutrient Digestibility and Milk and Mozzarella Cheese Yield in Dairy Buffalo Cows During the Transition" Animals 14, no. 24: 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243689
APA StyleZicarelli, F., Vianello, R. C., Masiello, I., Musco, N., Iommelli, P., Wanapat, M., Lotito, D., Lombardi, P., Grossi, M., Infascelli, F., & Tudisco, R. (2024). Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Diet Supplementation Affects Nutrient Digestibility and Milk and Mozzarella Cheese Yield in Dairy Buffalo Cows During the Transition. Animals, 14(24), 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243689










