Longitudinal Follow-Up of Clinical Superficial Ovine Caseous Lymphadenitis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Zone
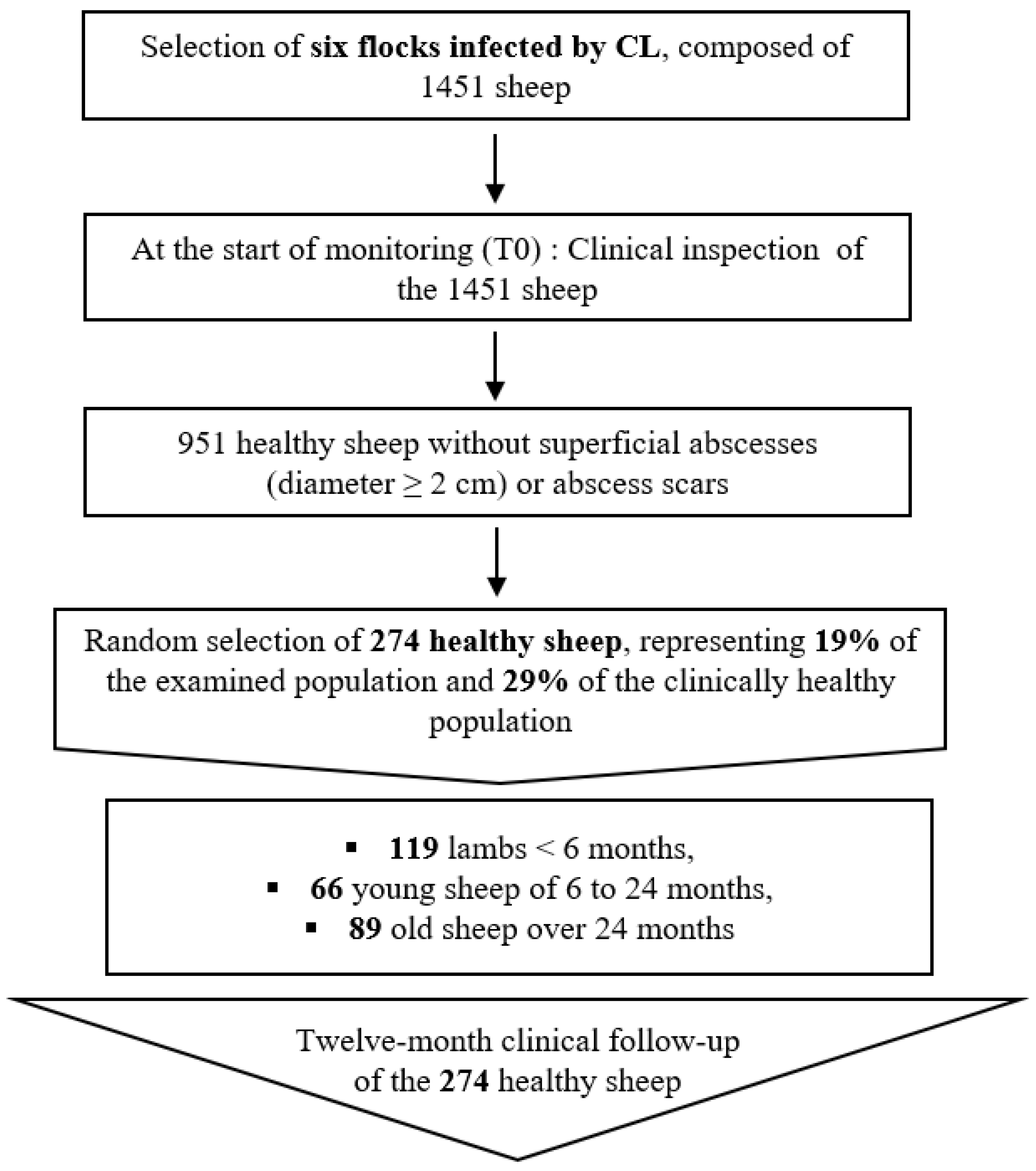
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Clinical Examination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
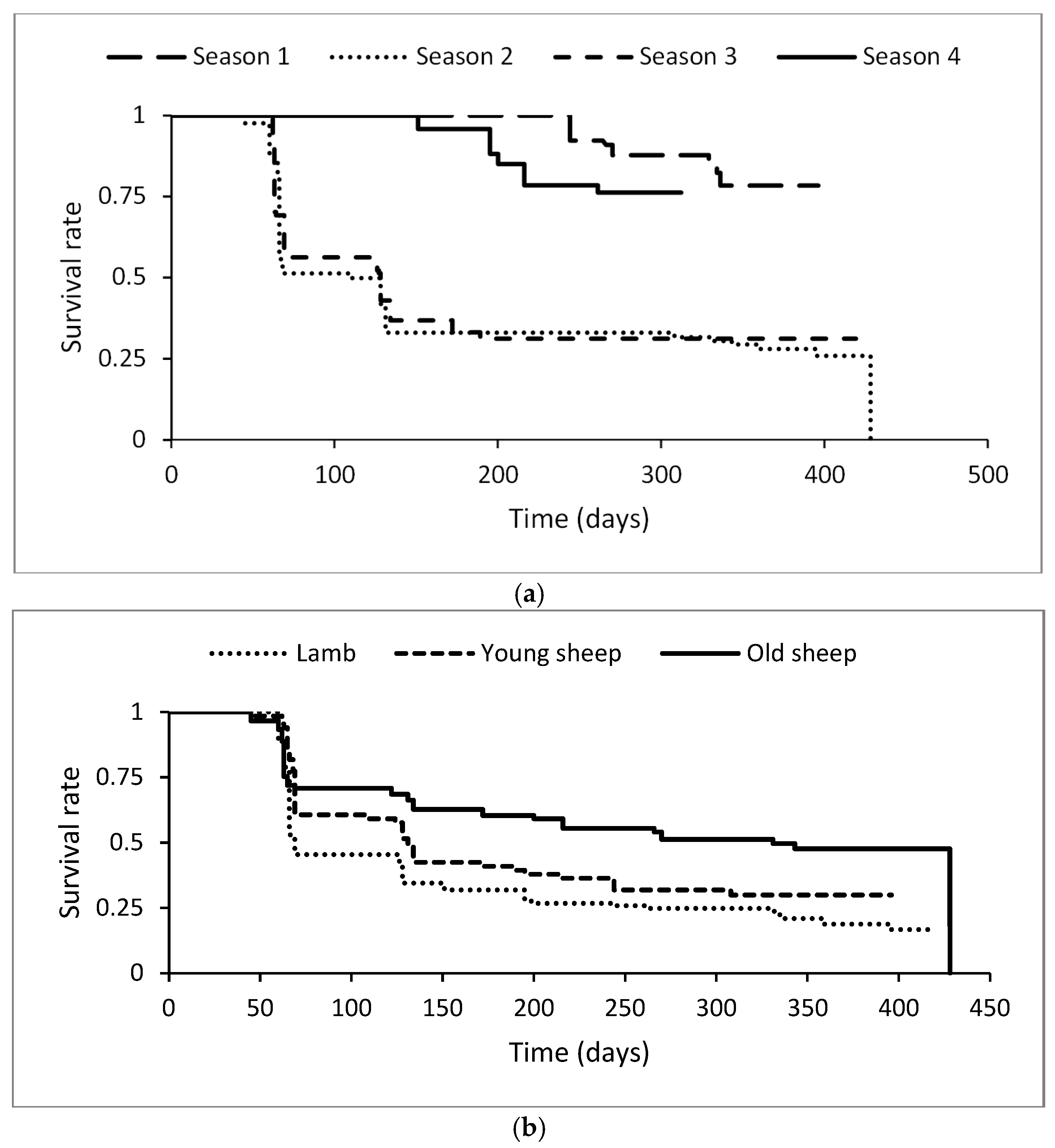
2.4.1. Survival Analysis of CL Incidence Risk
2.4.2. Age and Abscess Locations
2.4.3. Abscess Relapses
3. Results
3.1. Incidence of Superficial Caseous Lymphadenitis
3.2. Effect of Age on Abscess Locations
3.3. Abscess Relapse Considering Age and Sex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, P.R. Caseous Lymphadenitis (Chapter 11). In Sheep Medicine; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2015; pp. 291–292. ISBN 978-1-4987-0015-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ibtisam, B.; Azzam, M. Some Clinicopathological and Pathological Studies of C. Ovis Infection in Sheep. Egypt. J. Comp. Path. Clinic. Path. 2008, 21, 327–343. [Google Scholar]
- Odhah, M.N.; Abdullah Jesse, F.F.; Teik Chung, E.L.; Mahmood, Z.; Haron, A.W.; Mohd Lila, M.A.; Zamri-Saad, M. Clinico-Pathological Responses and PCR Detection of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and Its Immunogenic Mycolic Acid Extract in the Vital Organs of Goats. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, P.A. Managing Control Programs for Ovine Caseous Lymphadenitis and Paratuberculosis in Australia, and the Need for Persistent Vaccination. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2014, 5, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Williamson, L.H. Caseous Lymphadenitis in Small Ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2001, 17, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, P.A.; Bush, R.D. Caseous Lymphadenitis: Present and near Forgotten from Persistent Vaccination? Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 142, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichou, F.; Mechaal, A.; Bouslikhane, M.; Kadiri, A.; Zro, K.; Berrada, J. Facteurs de Risque et Caractéristiques Cliniques et Lésionnelles de La Lymphadénite Caséeuse Ou Maladie Des Abcès Chez Les Ovins Au Maroc. Rev. Elev. Med. Vet. Pays Trop. 2016, 69, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mills, A.E.; Mitchellt, R.D.; Limt, E.K. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Is a Cause of Human Necrotising Granulomatous Lymphadenitis. Pathology 1997, 29, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.M.; Palmer, G.G.; Stacpoole, A.M.; Kerr, T.G. Human Lymphadenitis Due to Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Report of Ten Cases from Australia and Review. CID 1997, 24, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, M.C.; Baird, G.J. Caseous Lymphadenitis. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 76, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgül, Ö.; Arslan, L.; Akgül, Y.; Ekici, T.P. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Infection in Holstein Dairy Cattle in Van Province. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2017, 9, 63267–63270. [Google Scholar]
- Zidan, K.H.; Mazloum, K.; Saran, M.A.; Hatem, M.E. Abscesses in Dromedary Camels, Sheep and Goats Etiology and Pathology. In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Conference of Pathology Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt, 25–27 April 2013; pp. 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, A.Y.; Nordin, M.L.; Kadir, A.A.; Saharee, A.A. The Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Caseous Lymphadenitis: A Review. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 1129. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Domínguez, M.C.; Montes de Oca Jiménez, R.; VarelaGuerreo, J.A.; Rodríguez Domínguez, M.C.; Montes de Oca Jiménez, R.; VarelaGuerreo, J.A. Caseous Lymphadenitis: Virulence Factors, Pathogenesis and Vaccines. Review. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2021, 12, 1221–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, M.; Paton, M.; Hodgson, A.L. Pathogenesis and Epidemiology of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Infection in Sheep. Curr. Top. Vet. Res. 1994, 1, 63–82. [Google Scholar]
- Windsor, P.A. Control of Caseous Lymphadenitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2011, 27, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oreiby, A.F. Diagnosis of Caseous Lymphadenitis in Sheep and Goat. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 123, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, B.L.; Portela, R.W.D.; Dorella, F.A.; Ribeiro, D.; Seyffert, N.; Castro, T.L.P.; Miyoshi, A.; Oliveira, S.C.; Meyer, R.; Azevedo, V. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Immunological Responses in Animal Models and Zoonotic Potential. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2012, S4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, T.D.; Mariutti, R.B.; Arni, R.K.; Santos, A.J.; Loureiro, D.; Sokolonski, A.R.; Azevedo, V.; Borsuk, S.; Meyer, R.; Portela, R.D. A Panel of Recombinant Proteins for the Serodiagnosis of Caseous Lymphadenitis in Goats and Sheep. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, A.S.; Seyffert, N.; Bastos, B.L.; Portela, R.W.D.; Meyer, R.; Carmo, F.B.; Cruz, J.C.M.; McCulloch, J.A.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B.; et al. Caseous Lymphadenitis in Sheep Flocks of the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil: Prevalence and Management Surveys. Small Rumin. Res. 2009, 87, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias, A.E.M.; Alves, J.R.A.; Alves, F.S.F.; Pinheiro, R.R.; Faccioli-Martins, P.Y.; Lima, A.M.C.; de Azevedo, S.S.; Alves, C.J. Seroepidemiological Characterization and Risk Factors Associated with Seroconversion to Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in Goats from Northeastern Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuria, J.K.N.; Mbuthia, P.G.; KanG’ethe, E.K.; Wahome, R.G. Caseous Lymphadenitis in Goats: The Pathogenesis, Incubation Period and Serological Response after Experimental Infection. Vet. Res. Commun. 2001, 25, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, K.E.; Bissett, W.T.; Fajt, V.R.; Libal, M.C.; Fosgate, G.T.; Miga, J.A.; Rockey, K.M. Comparison of Three Treatment Regimens for Sheep and Goats with Caseous Lymphadenitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 234, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftabuzzaman, M.D.; Cho, Y. Recent Perspectives on Caseous Lymphadenitis Caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in Goats-A Review. Korean J. Vet. Serv. 2021, 44, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoigne, E.; Ogden, N.; Lovatt, F.; Davies, P. Update on Caseous Lymphadenitis in Sheep. Practice 2020, 42, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawashdeh, O.F.; Al-Qudah, K.M. Effect of Shearing on the Incidence of Caseous Lymphadenitis in Awassi Sheep in Jordan. J. Vet. Med. B 2000, 47, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yitagesu, E.; Alemnew, E.; Olani, A.; Asfaw, T.; Demis, C. Survival Analysis of Clinical Cases of Caseous Lymphadenitis of Goats in North Shoa, Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Int. 2020, 8, 8822997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khalfaoui, N.; El Amiri, B.; Cabaraux, J.-F.; Chentouf, M.; Raes, M.; Marcotty, T.; Kirschvink, N. Rearing Management and Its Impact on Caseous Lymphadenitis in Sheep. Animals 2024, 14, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Carlos, D.; Abreu, V.; Sousa, C.; Alves, J.; Carneiro, A.; Bagano, P.; Spier, S.; Barh, D.; et al. Quadruplex PCR Assay for Identification of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Differentiating Biovar Ovis and Equi. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, L.G.C.; Pena, R.R.; Castro, T.L.P.; Dorella, F.A.; Bahia, R.C.; Carminati, R.; Frota, M.N.L.; Oliveira, S.C.; Meyer, R.; Alves, F.S.; et al. Multiplex PCR Assay for Identification of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis from Pure Cultures and for Rapid Detection of This Pathogen in Clinical Samples. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, A.d.S.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Andrade, G.I.; Lage, A.P.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.; Gouveia, A.M.G.; Heinemann, M.B. Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolates Using ERIC-PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneles, E.M.S.; Santana, J.A.; Ribeiro, D.; Dorella, F.A.; Guimarães, A.S. Evaluation of ERIC-PCR as Genotyping Method for Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 98758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office National du Conceil Agricole. Fiche Technique Détaillée Viande Rouge Ovine. Available online: https://admin.ardna.org/files/contenus_files/ticket_file62307ce628833-Guide-fran%C3%A7ais-ovin.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2020).
- EL Khalil, K.; Allai, L.; Fatet, A.; Benmoula, A.; Hamidallah, N.; Badi, A.; Moussafir, Z.; Ibnelbachyr, M.; El Amiri, B. Morphometry and Depth of Inseminating Catheter Penetration in Prolific and Non- Prolific Ewes at Different Ages: A Post Mortem Study. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 196, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gaabary, M.H.; Osman, S.A.; Oreiby, A.F. Caseous Lymphadenitis in Sheep and Goats: Clinical, Epidemiological and Preventive Studies. Small Rumin. Res. 2009, 87, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amiri, B.; Sibaoueih, M.; Harrak, H. Vers La Labellisation de La Race Ovine Sardi à Travers l’évaluation Du Savoir-Faire Local En Pratique d’élevage et La Caractérisation Des Carcasses et Des Viandes. FRIMED AJ–Al Awamia 2022, 134, 76–94. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, A.; Essamadi, A.; El Amiri, B. A Comprehensive Review on Endemic and Experimental Fluorosis in Sheep: Its Diverse Effects and Prevention. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saîd, M.S.B.; Maitigue, H.B.; Benzarti, M.; Messadi, L.; Amara, A.R. et A. Contribution a l’étude Épidemiologique et Clinique de La Lymphadenite Caseeuse Chez Les Ovins. Archs. Inst. Pasteur Tunis. 2002, 79, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Belchior, S.E. Effect of Quaternary Ammonium Compounds and Temperature on Shearing Utensils Contaminated by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Online J. Vet. Res. 2014, 18, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, M.C.A.; Oliveira, S.A.S.; Dantas Jr, E.M.; Gouveia, G.V.; Gouveia, J.J.S.; Veschi, J.L.A.; Costa, M.M.; Sá, M.C.A.; Oliveira, S.A.S.; Dantas Jr, E.M.; et al. Resistance of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in the Brazilian Semiarid Environment. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spier, S.J.; Toth, B.; Edman, J.; Quave, A.; Habasha, F.; Garrick, M.; Byrne, B.A. Survival of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Biovar Equi in Soil. Vet. Rec. 2012, 170, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, L.; William, A.; Castro, I.; Valenzuela, F.; Belchior, S.E. Survival Capacity of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Biovar Ovis in Different Soil Types from Chubut, Argentine Patagonia. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2017, 49, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.d.S.; Ribeiro, D.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B.; Miyoshi, A.; Gouveia, A.M.G. Caseous Lymphadenitis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Control. IIOAB J. 2011, 2, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, K.M.; Washburn, K.E. Caseous Lymphadenitis: Realities in Treatment and Prevention. Bov. Pract. 2012, 46, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Age Category | No Episode | 1 Episode | 2 Episodes | 3 Episodes | 4 Episodes or More | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lambs | 25 | 37 | 28 | 22 | 7 | 119 |
| Young sheep | 20 | 25 | 11 | 8 | 2 | 66 |
| Old sheep | 44 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 89 |
| Total | 89 | 94 | 47 | 34 | 10 | 274 |
| Explanatory Variables | Number of Clinical Observations (Total) | Number of New Clinical CL Cases | OR (95% IC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flock (Cox semi-parametric model) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Flock 1 | 317 | 55 | 1 |
| Flock 2 | 162 | 11 | 0.34 (0.2–0.6) |
| Flock 3 | 133 | 26 | 2.4 (1.5–3.97) |
| Flock 4 | 229 | 47 | 0.84 (0.6–1.2) |
| Flock 5 | 140 | 16 | 0.57 (0.3–1.6) |
| Flock 6 | 234 | 30 | 1.01 (0.6–1.6) |
| Seasons (frailty exponential model) | p < 0.001 | ||
| January–February–March (season 1) | 242 | 10 | 1 |
| April–May–June (season 2) | 329 | 81 | 4.0 (2.05–7.8) |
| July–August–September (season 3) | 295 | 78 | 4.8 (2.5–9.3) |
| October–November–December (season 4) | 349 | 16 | 1.3 (0.5–2.8) |
| Age categories (frailty exponential model) | p < 0.001 | ||
| Lambs (<6 month) | 524 | 94 | 1 |
| Young sheep (6–24 months) | 290 | 42 | 0.70 (0.5–1.03) |
| Old sheep (>24 months) | 401 | 49 | 0.50 (0.3–0.7) |
| Sex (frailty exponential model) | p = 0.52 | ||
| Male | 277 | 42 | 0.89 (0.6–1.3) |
| Female | 938 | 143 | 1 |
| Body score (min = 1, max= 5) (frailty exponential model) | p = 0.50 | ||
| Score 1 | 208 | 22 | 1 |
| Score 2 | 468 | 78 | 1.3 (0.8–2.1) |
| Score 3 | 463 | 71 | 1.4 (0.8–2.5) |
| Score 4 (3 observations of score 5 are included) | 76 | 14 | 1.7 (0.8–3.5) |
| Sheared since last examination (frailty exponential model) | p = 0.93 | ||
| No | 1069 | 166 | 1 |
| Yes | 146 | 19 | 0.97 (0.45–2.04) |
| Total of observations | 1215 | 185 | |
| Abscess Location | Total (n/%) | Lambs 1 (n/%) | Young Sheep 2 (n/%) | Old Sheep 3 (n/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parotid LN 4 | 170/50.2 | 110/57.0 | 31/38.3 | 29/44.6 |
| Submandibular LN | 22/6.5 | 12/6.2 | 7/8.6 | 3/4.6 |
| Retropharyngeal LN | 42/12.5 | 30/15.5 | 8/9.9 | 4/6.2 |
| Prescapular LN | 79/23.4 | 35/18.1 | 28/34.6 | 16/24.6 |
| Subtotal | 313/92.3 | 187/96.9 | 74/91.3 | 52/80.0 |
| Prefemoral LN | 21/6.2 | 4/2.1 | 5/6.2 | 12/18.5 |
| Popliteal LN | 2/0.6 | 0 | 2/2.4 | 0 |
| Testicular gland | 2/0.6 | 2/1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Mammary gland | 1/0.3 | 0 | 0 | 1/1.5 |
| Subtotal | 26/7.7 | 6/3.1 | 7/8.6 | 13/20.0 |
| Total | 339/100 | 193/100 | 81/100 | 65/100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Khalfaoui, N.; El Amiri, B.; Rahim, A.; Chentouf, M.; Raes, M.; Marcotty, T.; Kirschvink, N. Longitudinal Follow-Up of Clinical Superficial Ovine Caseous Lymphadenitis. Animals 2024, 14, 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243641
El Khalfaoui N, El Amiri B, Rahim A, Chentouf M, Raes M, Marcotty T, Kirschvink N. Longitudinal Follow-Up of Clinical Superficial Ovine Caseous Lymphadenitis. Animals. 2024; 14(24):3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243641
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Khalfaoui, Nora, Bouchra El Amiri, Abdellatif Rahim, Mouad Chentouf, Marianne Raes, Tanguy Marcotty, and Nathalie Kirschvink. 2024. "Longitudinal Follow-Up of Clinical Superficial Ovine Caseous Lymphadenitis" Animals 14, no. 24: 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243641
APA StyleEl Khalfaoui, N., El Amiri, B., Rahim, A., Chentouf, M., Raes, M., Marcotty, T., & Kirschvink, N. (2024). Longitudinal Follow-Up of Clinical Superficial Ovine Caseous Lymphadenitis. Animals, 14(24), 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243641





