Investigating the IgM and IgG B Cell Receptor Repertoires and Expression of Ultralong Complementarity Determining Region 3 in Colostrum and Blood from Holstein-Friesian Cows at Calving
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sampling
2.2. Isolation of Blood Mononuclear Cells (BMCs) and Colostral Cells
2.3. Magnetic-Activated Positive B Cell Sorting (MACS)
2.4. cDNA and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.5. MinION Sequencing
2.6. Cleaning
2.7. Filtering
2.7.1. IgM Filtering Process
2.7.2. IgG Filtering Process
2.8. Sequence Analysis
3. Results
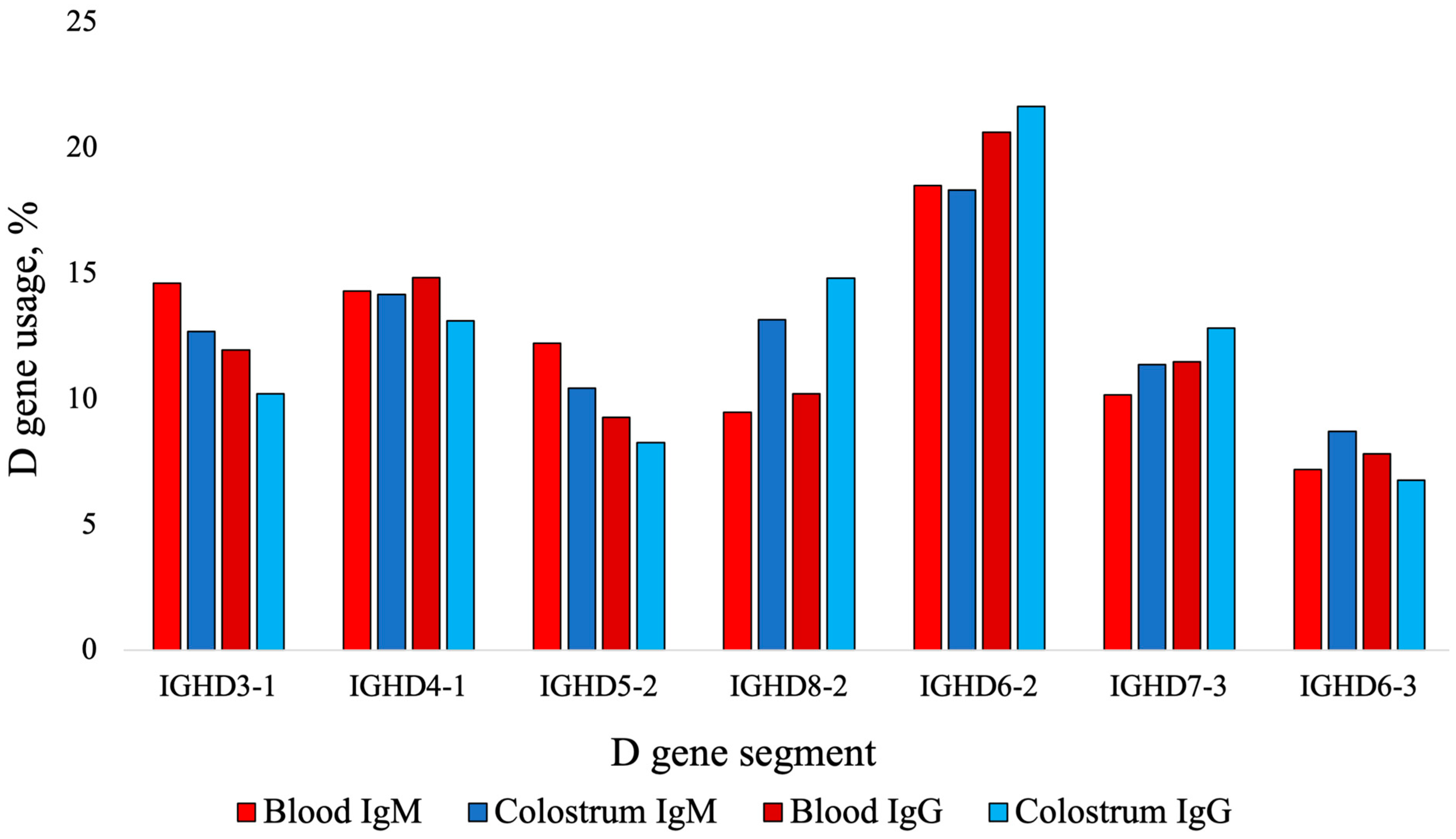
3.1. Blood-Derived IgM Sequences with Ultralong CDR3s and VDJ Gene Usage
3.2. Blood-Derived IgG Sequences with Ultralong CDR3s and VDJ Gene Usage
3.3. Colostrum-Derived IgM Sequences with Ultralong CDR3s and VDJ Gene Usage
3.4. Colostrum-Derived IgG Sequences with Ultralong CDR3s and VDJ Gene Usage
3.5. Blood- and Colostrum-Derived IgM and IgG Sequences with Short CDR3s
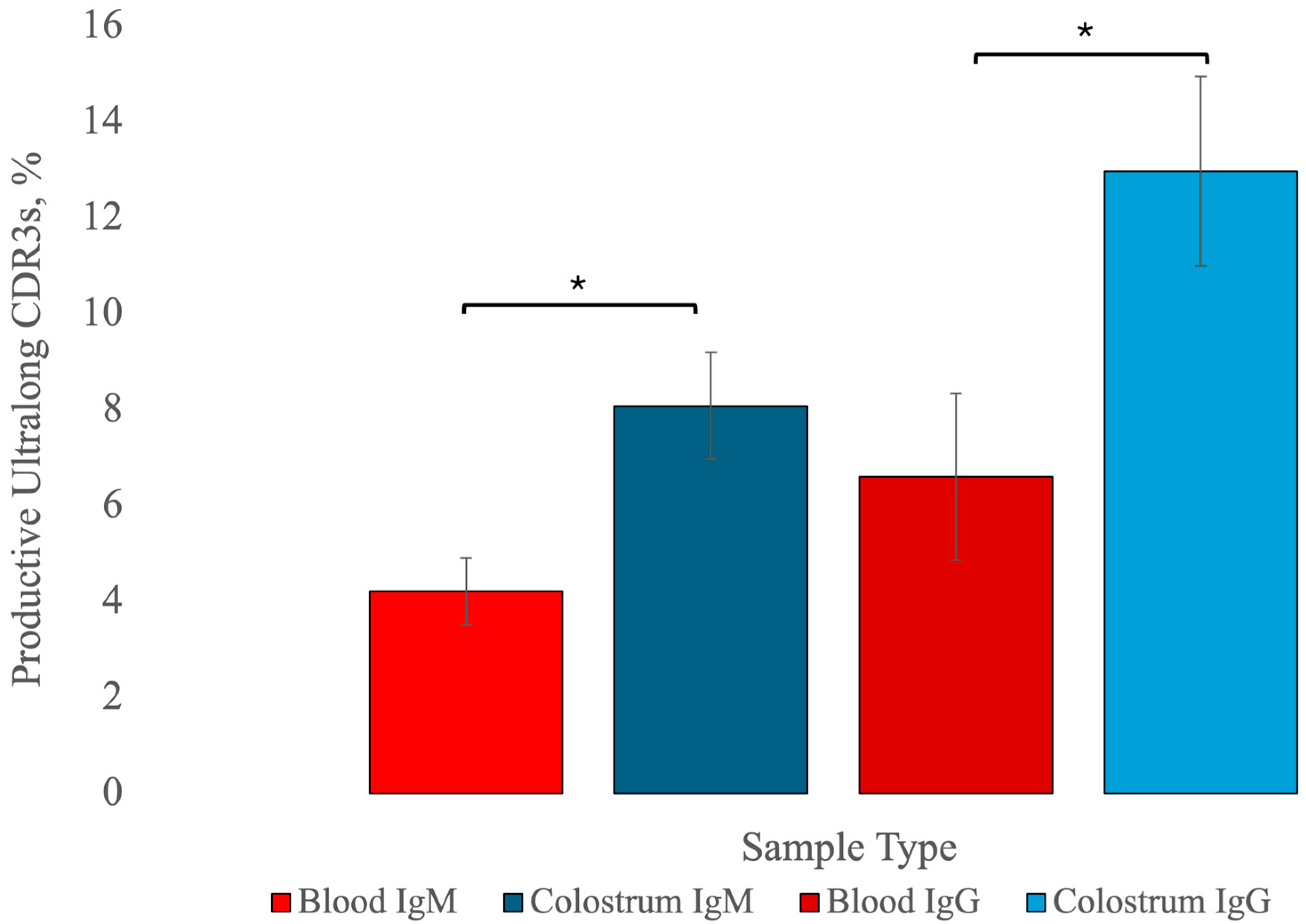
3.6. Summary of Statistical Findings
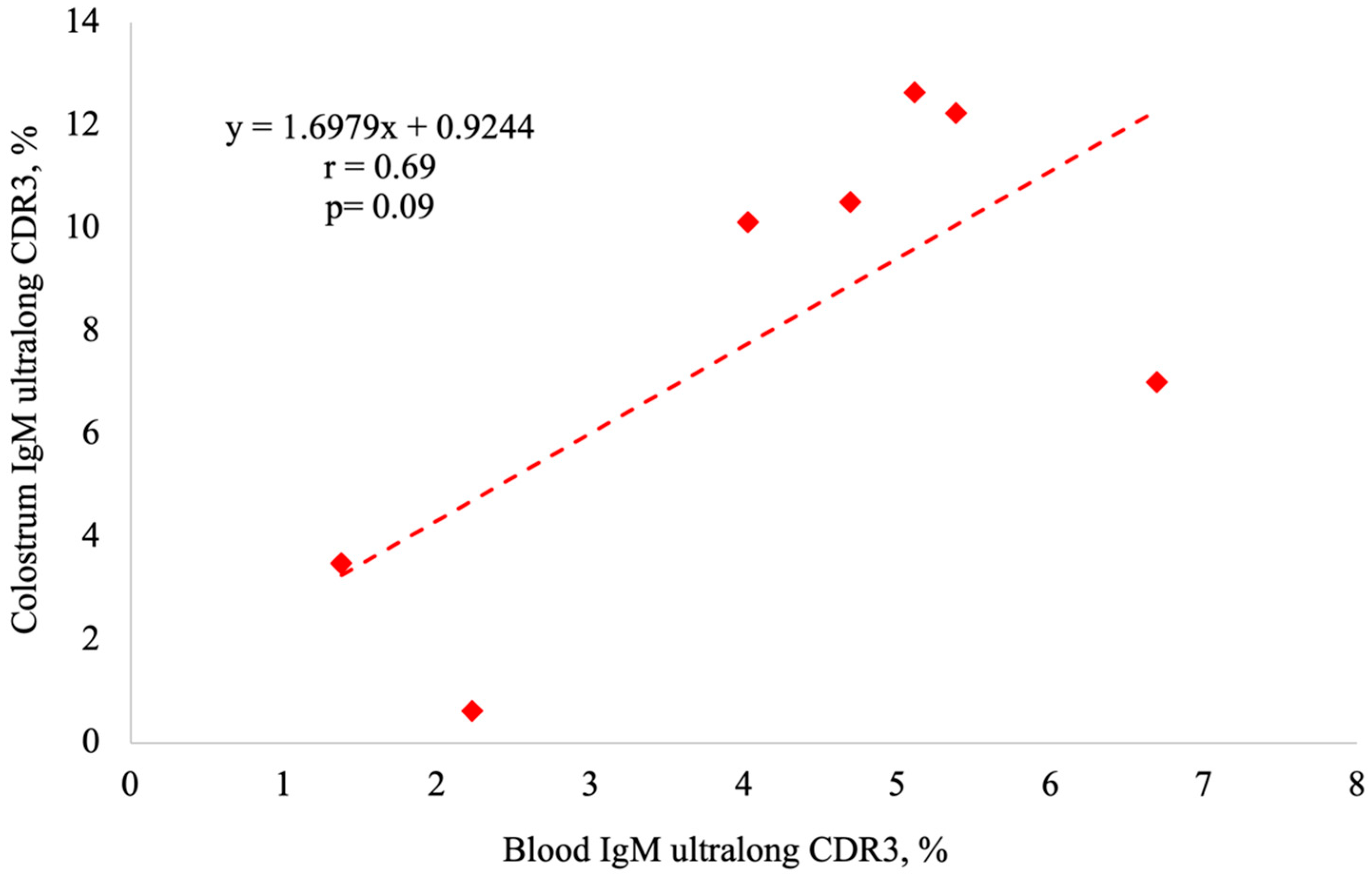
3.7. Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godden, S.M.; Lombard, J.E.; Woolums, A.R. Colostrum Management for Dairy Calves. Veter. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langel, S.N.; Wark, W.A.; Garst, S.N.; James, R.E.; McGilliard, M.L.; Petersson-Wolfe, C.S.; Kanevsky-Mullarky, I. Effect of feeding whole compared with cell-free colostrum on calf immune status: The neonatal period. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, M.R.; Watson, D.L.; Lascelles, A.K. The mechanism of transfer of immunoglobulin into mammary secretion of cows. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1971, 49, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Davis, C.; Larson, B. Production and Turnover of IgG1 and IgG2 Immunoglobulins in the Bovine around Parturition. J. Dairy Sci. 1976, 59, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, M.A.; McFadden, T.B.; Cockrell, D.C.; Besser, T.E. Regulation of Colostrum Formation in Beef and Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 3002–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Nickerson, S.C.; Akers, R.M.; Oliver, S.P. Secretion composition during bovine mammary involution and the relationship with mastitis. Int. J. Biochem. 1987, 19, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrucker, C.R.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Colostrogenesis: IgG 1 transcytosis mechanisms. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2014, 19, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E.; Rainard, P.; Lippolis, J.; Salmon, H.; Kacskovics, I. The mammary gland in mucosal and regional immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 2, 2269–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaro, S.; Marrero, M.G.; Madrid DM, C.; Prim, J.G.; Nelson, C.D.; Galvão, K.N.; Laporta, J.; Driver, J.P. Flow cytometry panels for immunophenotyping dairy cattle peripheral blood leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2022, 248, 110417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, A.J.; Hippen, A.R.; Hurley, D.J. Effects of the ingestion of whole colostrum or cell-free colostrum on the capacity of leukocytes in newborn calves to stimulate or respond in one-way mixed leukocyte cultures. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langel, S.N.; Wark, W.A.; Garst, S.N.; James, R.E.; McGilliard, M.L.; Petersson-Wolfe, C.S.; Kanevsky-Mullarky, I. Effect of feeding whole compared with cell-free colostrum on calf immune status: Vaccination response. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3979–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reber, A.J.; Donovan, D.C.; Gabbard, J.; Galland, K.; Aceves-Avila, M.; Holbert, K.A.; Marshall, L.; Hurley, D.J. Transfer of maternal colostral leukocytes promotes development of the neonatal immune system: I. Effects on monocyte lineage cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reber, A.J.; Donovan, D.C.; Gabbard, J.; Galland, K.; Aceves-Avila, M.; Holbert, K.A.; Marshall, L.; Hurley, D.J. Transfer of maternal colostral leukocytes promotes development of the neonatal immune system: Part II. Effects on neonatal lymphocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel-Caspari, G. The influence of colostral leukocytes on the course of an experimental Escherichia coli infection and serum antibodies in neonatal calves. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1993, 35, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collis, A.V.; Brouwer, A.P.; Martin, A.C. Analysis of the antigen combining site: Correlations between length and sequence composition of the hypervariable loops and the nature of the antigen. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.S.; Allore, B.; Jacobs, R.M.; Kaushik, A. Exceptionally long CDR3H region with multiple cysteine residues in functional bovine IgM antibodies. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyola, S.O.; Henson, S.P.; Nzau, B.; Kibwana, E.; Nene, V. Access to ultra-long IgG CDRH3 bovine antibody sequences using short read sequencing technology. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 139, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, J.A.; Mitchell, C.; Sheppard, M.; Deiss, T.C.; Horton, J.C.; Haakenson, J.K.; Huang, R.; Kelley, A.R.; Davis, B.W.; Derr, J.N.; et al. Evolution of immunogenetic components encoding ultralong CDR H3. Immunogenetics. 2023, 75, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; de Villavicencio Diaz, T.N.; Lange, V.; Wu, L.; Le Bihan, T.; Ma, B. Exploring the sheep (Ovis aries) immunoglobulin repertoire by next generation sequencing. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 156, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, T.C.; Groenner-Penna, M.; Minozzo, J.C.; Antunes, B.C.; Ippolito, G.C.; Molina, F.; Felicori, L.F. Next-generation sequencing reveals new insights about gene usage and CDR-H3 composition in the horse antibody repertoire. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.M.; Yang, X.F.; Qin, P.; Wang, B.; Huang, Y.W. High-throughput sequencing of the porcine antibody repertoire with or without PEDV infection: A proof-of-concept study. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 292, 114125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Finn, J.A.; Larsen, P.A.; Smith, T.P.; Crowe, J.E., Jr. Structural diversity of ultralong CDRH3s in seven bovine antibody heavy chains. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ekiert, D.C.; Ahmad, I.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bazirgan, O.; Torkamani, A.; Raudsepp, T.; Mwangi, W.; Criscitiello, M.F.; et al. Reshaping antibody diversity. Cell 2013, 153, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haakenson, J.K.; Deiss, T.C.; Warner, G.F.; Mwangi, W.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Smider, V.V. A broad role for cysteines in bovine antibody diversity. Immunohorizons 2019, 3, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.D.; Douangamath, A.; Mikolajek, H.; Placido, B.D.; Ren, J.; Fry, E.E.; Stuart, D.I.; Hammond, J.A.; Owens, R.J. The impact of exchanging the light and heavy chains on the structures of bovine ultralong antibodies. Acta. Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2024, 80, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanfield, R.L.; Wilson, I.A.; Smider, V.V. Conservation and diversity in the ultralong third heavy-chain complementarity-determining region of bovine antibodies. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, aaf7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.S.; Hein, W.R.; Kaushik, A. A single predominantly expressed polymorphic immunoglobulin VH gene family, related to mammalian group, I, clan, II, is identified in cattle. Mol. Immunol. 1997, 34, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanfield, R.L.; Haakenson, J.; Deiss, T.C.; Criscitiello, M.F.; Wilson, I.A.; Smider, V.V. The unusual genetics and biochemistry of bovine immunoglobulins. Adv. Immunol. 2018, 137, 135–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, D.; Le, K.M.; Vadnais, M.; Saye-Francisco, K.L.; Jardine, J.G.; Torres, J.L.; Berndsen, Z.T.; Kong, K.; Stanfield, R.; Ruiz, J.; et al. Rapid elicitation of broadly neutralizing antibodies to HIV by immunization in cows. Nature 2017, 548, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passon, M.; De Smedt, S.; Svilenov, H.L. Principles of antibodies with ultralong complementarity-determining regions and picobodies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 64, 108120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Qin, T.; Chu, D.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Han, H.; Ren, L.; Aitken, R.; et al. Internal duplications of DH, JH, and C region genes create an unusual IgH gene locus in cattle. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4358–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, S.; Tietze, M.; Czerny, C.P.; König, S.; Diesterbeck, U.S. Development of a bioinformatics framework for the detection of gene conversion and the analysis of combinatorial diversity in immunoglobulin heavy chains in four cattle breeds. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altvater-Hughes, T.; Hodgins, H.; Hodgins, D.; Gallo, N.; Chalmers, G.; Ricker, N.; Mallard, B. Estimates of Sequences with Ultralong and Short-CDR3s in the Bovine IgM B-Cell Receptor Repertoire Using the Long-Read Oxford Nanopore MinION Platform. ImmunoHorizons 2024, 8, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.P. Unique database numbering system for immunogenetic analysis. Immunol. Today 1997, 18, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Giudicelli, V.; Duroux, P.; Jabado-Michaloud, J.; Folch, G.; Aouinti, S.; Carillon, E.; Duvergey, H.; Houles, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; et al. IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system® 25 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D413–D422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, F.; Saini, S.S.; Kaushik, A.K. Unusually long germline DH genes contribute to large sized CDR3H in bovine antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 40, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.A.; Smith, T.P. Application of circular consensus sequencing and network analysis to characterize the bovine IgG repertoire. BMC. Immunol. 2012, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koti, M.; Kataeva, G.; Kaushik, A.K. Novel atypical nucleotide insertions specifically at VH–DH junction generate exceptionally long CDR3H in cattle antibodies. Mol Immunol. 2010, 47, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, Y.; Shin, S.B.; Kramer, L.; Reecy, J.; Watson, C.T.; Smith, T.P.; Pevzner, P.A. Variations in antibody repertoires correlate with vaccine responses. Genome. Res. 2022, 32, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Sarkar, A.; Kulp, D.W.; Toy, L.; Hu, X.; Deresa, I.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Kaushik, K.; Upadhyay, A.A.; Menis, S.; et al. The human naive B cell repertoire contains distinct subclasses for a germline-targeting HIV-1 vaccine immunogen. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat0381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, K.; Winter, D.B.; Tarone, R.E.; Skovgaard, G.L.; Bohr, V.A.; Gearhart, P.J. Third complementarity-determining region of mutated VH immunoglobulin genes contains shorter V, D, J, P, and N components than non-mutated genes. Immunology 2001, 103, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laouar, A. Maternal leukocytes and infant immune programming during breastfeeding. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbers, L.; van de Mheen, R.; Benedictus, L.; Jorritsma, R.; Nielen, M.; Bijkerk, H.J.; van der Grein, S.G.; Ravesloot, L.; Koets, A.P. Evidence for transfer of maternal antigen specific cellular immunity against Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis via colostrum in a goat twin model. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2022, 246, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, A.J.; Lockwood, A.; Hippen, A.R.; Hurley, D.J. Colostrum induced phenotypic and trafficking changes in maternal mononuclear cells in a peripheral blood leukocyte model for study of leukocyte transfer to the neonatal calf. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 109, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinder, J.M.; Stelzer, I.A.; Arck, P.C.; Way, S.S. Immunological implications of pregnancy-induced microchimerism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.; Atalla, H.; Karrow, N.; Mallard, B.A. The bioactivity of colostrum and milk exosomes of high, average, and low immune responder cows on human intestinal epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hese, I.; Goossens, K.; Vandaele, L.; Opsomer, G. Invited review: MicroRNAs in bovine colostrum—Focus on their origin and potential health benefits for the calf. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, C.A. Mechanisms by which maternal antibodies influence infant vaccine responses: Review of hypotheses and definition of main determinants. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavinder, J.J.; Horton, A.P.; Georgiou, G.; Ippolito, G.C. Next-generation sequencing and protein mass spectrometry for the comprehensive analysis of human cellular and serum antibody repertoires. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 24, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H.S.M.; Steele, M.A.; Costa, J.H.C.; Renaud, D.L. Evaluating the effectiveness of colostrum as a therapy for diarrhea in preweaned calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 9982–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, K.T.; Tennant, S.M.; Reymann, M.K.; Simon, R.; Konstantopoulos, N.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Barry, E.M.; Pasetti, M.F. Bioactive immune components of anti-diarrheagenic enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli hyperimmune bovine colostrum products. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00186-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Warner Jenkins, G.; Kim, Y.; Stanfield, R.L.; Singh, A.; Martinez-Yamout, M.; Kroon, G.J.; Torres, J.L.; Jackson, A.M.; Kelley, A.; et al. The smallest functional antibody fragment: Ultralong CDR H3 antibody knob regions potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2023, 120, e2303455120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| # of Raw Reads | DNA RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Total Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Clonotype Ultralong CDR3, % | Productive Protein RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | Parity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow 1 | 3.56 1 | 2.70 | 2.83 | 2.23 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 497,638 | 215,330 2 | 100,082 | 130,754 | 173,940 | |
| Cow 2 | 5.86 | 4.46 | 4.69 | 4.03 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 157,862 | 71,509 | 46,142 | 43,584 | 57,774 | |
| Cow 3 | 8.20 | 5.99 | 6.17 | 5.39 | 2 | |
| # of sequences | 436,718 | 185,161 | 118,255 | 114,368 | 145,390 | |
| Cow 4 | 10.84 | 8.18 | 8.58 | 6.70 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 255,239 | 101,786 | 57,033 | 54,193 | 75,862 | |
| Cow 5 | 7.69 | 5.44 | 5.95 | 5.12 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 317,908 | 139,049 | 91,368 | 80,896 | 110,377 | |
| Cow 6 | 6.96 | 5.16 | 5.61 | 4.70 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 331,635 | 157,811 | 105,500 | 96,091 | 128,226 | |
| Cow 7 | 2.14 | 1.59 | 1.70 | 1.38 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 696,430 | 341,700 | 219,045 | 204,463 | 277,010 | |
| Mean | 384,776 | 6.46 | 4.79 | 5.08 | 4.22 | |
| SEM | 1.11 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.70 |
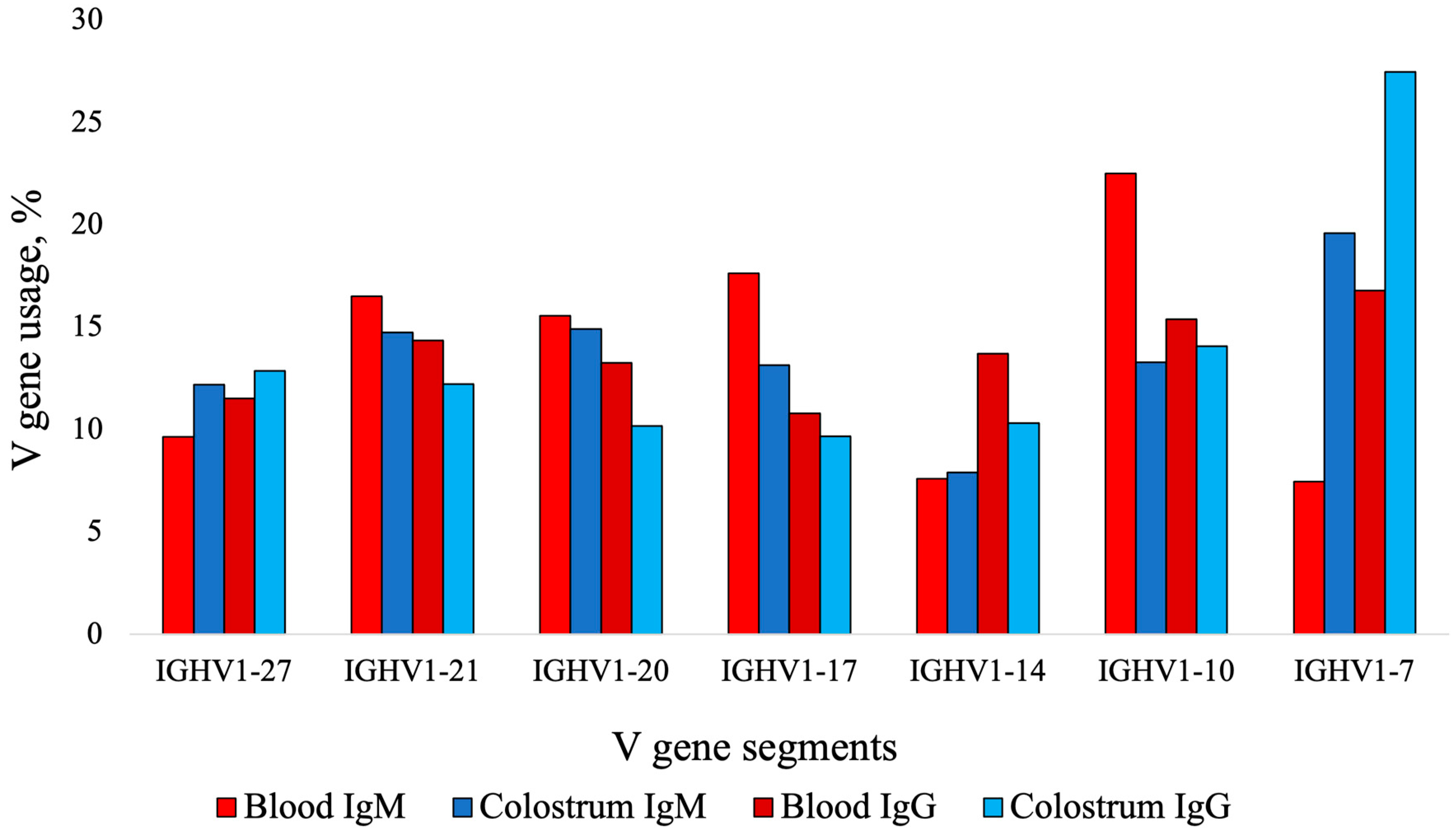
| V Genes 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | IGHV1-27 | IGHV1-21 | IGHV1-20 | IGHV1-17 | IGHV1-14 | IGHV1-10 | IGHV1-7 |
| Blood IgM | 9.65 1 | 16.50 | 15.56 | 17.63 | 7.60 | 22.50 | 7.46 |
| Blood IgG | 11.53 | 14.35 | 13.27 | 10.80 | 13.69 | 15.38 | 16.78 |
| Colostrum IgM | 12.21 | 14.75 | 14.92 | 13.16 | 7.91 | 13.28 | 19.61 |
| Colostrum IgG | 12.86 | 12.22 | 10.18 | 9.67 | 10.32 | 14.08 | 27.46 |
| # of Raw Reads | DNA RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Total Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Clonotype Ultralong CDR3, % | Productive Protein RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | Parity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow 1 | 5.85 1 | 4.57 | 8.09 | 3.88 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 775,589 | 309,822 2 | 221,948 | 100,082 | 251,431 | |
| Cow 2 | 14.97 | 10.41 | 13.38 | 10.86 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 149,760 | 35,295 | 41,924 | 29,308 | 27,604 | |
| Cow 3 | 4.75 | 3.56 | 8.01 | 3.04 | 2 | |
| # of sequences | 930,963 | 399,527 | 282,485 | 94,177 | 320,304 | |
| Cow 4 | 7.58 | 5.80 | 9.17 | 4.66 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 1,209,166 | 504,873 | 306,619 | 181,970 | 385,161 | |
| Cow 5 | 11.28 | 8.61 | 12.85 | 7.49 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 704,778 | 274,667 | 201,418 | 122,482 | 215,610 | |
| Cow 6 | 9.88 | 7.34 | 12.20 | 6.75 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 844,737 | 360,397 | 260,017 | 137,433 | 288,277 | |
| Cow 7 | 13.76 | 10.28 | 12.81 | 9.59 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 185,961 | 56,664 | 53,575 | 38,914 | 44,510 | |
| Mean | 685,851 | 9.72 | 7.22 | 10.93 | 6.61 | |
| SEM | 1.47 | 1.02 | 0.91 | 1.11 |
| # of Raw Reads | DNA RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Total Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Clonotype Ultralong CDR3, % | Productive Protein RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | Parity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow 1 | 1.23 1 | 1.14 | 4.38 | 0.62 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 365,677 | 165,151 2 | 127,307 | 22,600 | 137,907 | |
| Cow 2 | 14.36 | 10.10 | 19.57 | 10.11 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 179,539 | 87,438 | 64,482 | 17,423 | 70,251 | |
| Cow 3 | 17.54 | 12.73 | 22.49 | 12.24 | 2 | |
| # of sequences | 132,933 | 61,647 | 41,372 | 17,307 | 48,237 | |
| Cow 4 | 10.87 | 8.16 | 15.18 | 7.01 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 234,861 | 92,554 | 56,091 | 27,109 | 69,879 | |
| Cow 5 | 17.38 | 13.02 | 24.23 | 12.64 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 257,848 | 115,503 | 81,483 | 30,824 | 91,572 | |
| Cow 6 | 17.51 | 11.21 | 20.09 | 10.51 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 300,714 | 142,558 | 97,306 | 35,194 | 113,210 | |
| Cow 7 | 5.10 | 3.92 | 10.15 | 3.48 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 205,788 | 109,198 | 79,278 | 19,393 | 92,796 | |
| Mean | 239,623 | 12.00 | 8.61 | 16.58 | 8.09 | - |
| SEM | 2.49 | 1.71 | 2.70 | 1.73 |
| # of Raw Reads | DNA RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Total Ultralong CDR3, % | IMGT Clonotype Ultralong CDR3, % | Productive Protein RSLB Ultralong CDR3, % | Parity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow 1 | 19.85 1 | 18.24 | 21.15 | 18.03 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 511,813 | 169,945 2 | 132,546 | 40,611 | 134,194 | |
| Cow 2 | 9.44 | 7.15 | 13.80 | 6.67 | 3 | |
| # of sequences | 244,094 | 94,780 | 74,925 | 27,425 | 73,284 | |
| Cow 3 | 16.79 | 13.62 | 19.84 | 10.96 | 2 | |
| # of sequences | 261,534 | 76,998 | 72,384 | 44,238 | 57,739 | |
| Cow 4 | 11.03 | 8.64 | 16.47 | 6.96 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 962,730 | 370,121 | 252,572 | 113,456 | 278,054 | |
| Cow 5 | 17.25 | 13.17 | 24.74 | 11.89 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 625,793 | 254,916 | 224,483 | 87,308 | 201,066 | |
| Cow 6 | 26.17 | 20.47 | 32.41 | 19.54 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 841,032 | 371,226 | 274,073 | 91,643 | 282,998 | |
| Cow 7 | 27.26 | 19.77 | 32.71 | 16.79 | 1 | |
| # of sequences | 171,832 | 61,504 | 55,111 | 21,776 | 45,795 | |
| Mean | 516,975 | 18.26 | 14.44 | 23.02 | 12.98 | |
| SEM | 2.58 | 2.00 | 2.79 | 1.98 |
| Blood IgM Short CDR3s, % 1 | Colostral IgM Short CDR3s, % 2 | Blood IgG Short CDR3s, % 1 | Colostrum IgG Short CDR3s, % 2 | Parity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow 1 | 2.98 | 1.75 | 7.13 | 1.80 | 3 |
| Cow 2 | 2.48 | 2.54 | 4.46 | 5.01 | 3 |
| Cow 3 | 2.16 | 8.31 | 2.22 | 11.47 | 2 |
| Cow 4 | 3.44 | 3.69 | 9.48 | 8.74 | 1 |
| Cow 5 | 5.67 | 8.47 | 11.25 | 13.36 | 1 |
| Cow 6 | 4.13 | 6.00 | 6.22 | 9.11 | 1 |
| Cow 7 | 3.47 | 13.77 | 6.16 | 1.88 | 1 |
| Mean | 3.48 | 6.36 | 6.70 | 7.34 | |
| SEM | 0.44 | 1.59 | 1.14 | 1.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altvater-Hughes, T.E.; Hodgins, H.P.; Hodgins, D.C.; Bauman, C.A.; Paibomesai, M.A.; Mallard, B.A. Investigating the IgM and IgG B Cell Receptor Repertoires and Expression of Ultralong Complementarity Determining Region 3 in Colostrum and Blood from Holstein-Friesian Cows at Calving. Animals 2024, 14, 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192841
Altvater-Hughes TE, Hodgins HP, Hodgins DC, Bauman CA, Paibomesai MA, Mallard BA. Investigating the IgM and IgG B Cell Receptor Repertoires and Expression of Ultralong Complementarity Determining Region 3 in Colostrum and Blood from Holstein-Friesian Cows at Calving. Animals. 2024; 14(19):2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192841
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltvater-Hughes, Tess E., Harold P. Hodgins, Douglas C. Hodgins, Cathy A. Bauman, Marlene A. Paibomesai, and Bonnie A. Mallard. 2024. "Investigating the IgM and IgG B Cell Receptor Repertoires and Expression of Ultralong Complementarity Determining Region 3 in Colostrum and Blood from Holstein-Friesian Cows at Calving" Animals 14, no. 19: 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192841
APA StyleAltvater-Hughes, T. E., Hodgins, H. P., Hodgins, D. C., Bauman, C. A., Paibomesai, M. A., & Mallard, B. A. (2024). Investigating the IgM and IgG B Cell Receptor Repertoires and Expression of Ultralong Complementarity Determining Region 3 in Colostrum and Blood from Holstein-Friesian Cows at Calving. Animals, 14(19), 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192841





