Functional Characterization of 11 Tentative Microneme Proteins in Type I RH Strain of Toxoplasma gondii Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis of 11 Tentative MICs
2.2. Mice
2.3. Parasite Strains
2.4. Construction of Epitope Tagging Strains
2.5. Construction of Gene Knockout Strains
2.6. Immunofluorescence Assay and Western Blotting Analysis
2.7. Parasite Plaque Assay
2.8. Invasion Assay
2.9. Intracellular Replication and Egress Assay
2.10. Virulence Assessment in Mice
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatic Characteristics of 11 Tentative mic Genes in T. gondii
3.2. Subcellular Localization of 11 Tentative MICs
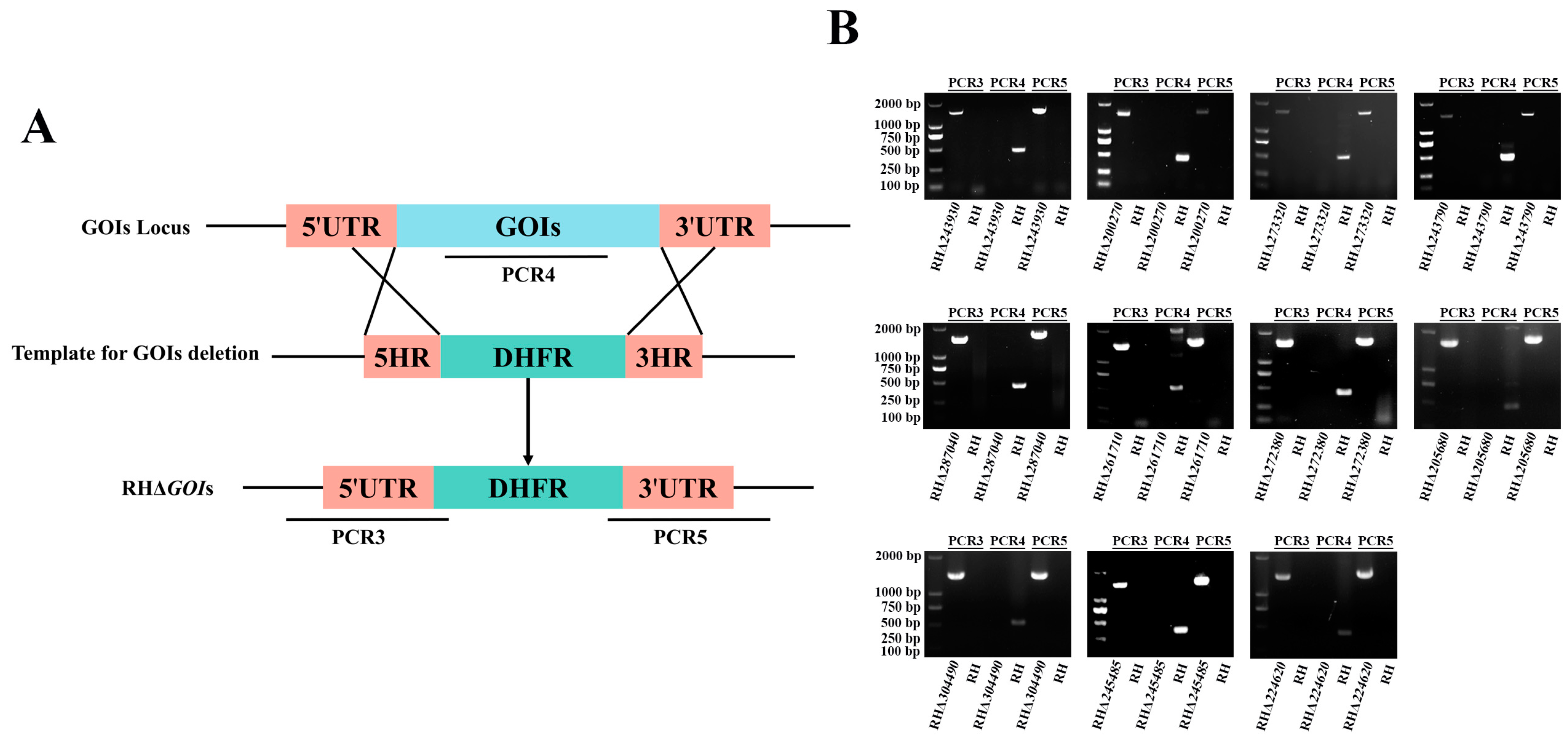
3.3. Successful Construction of 11 GOIs Knockout Strains
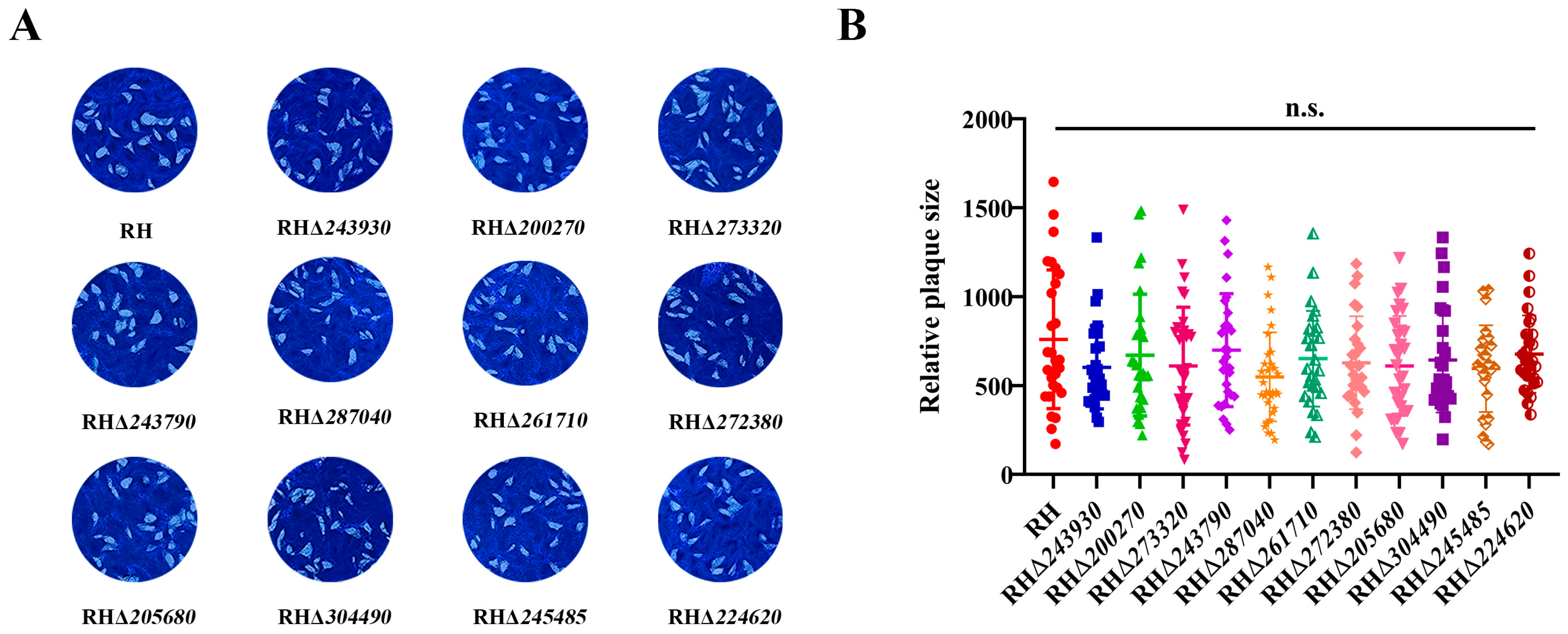
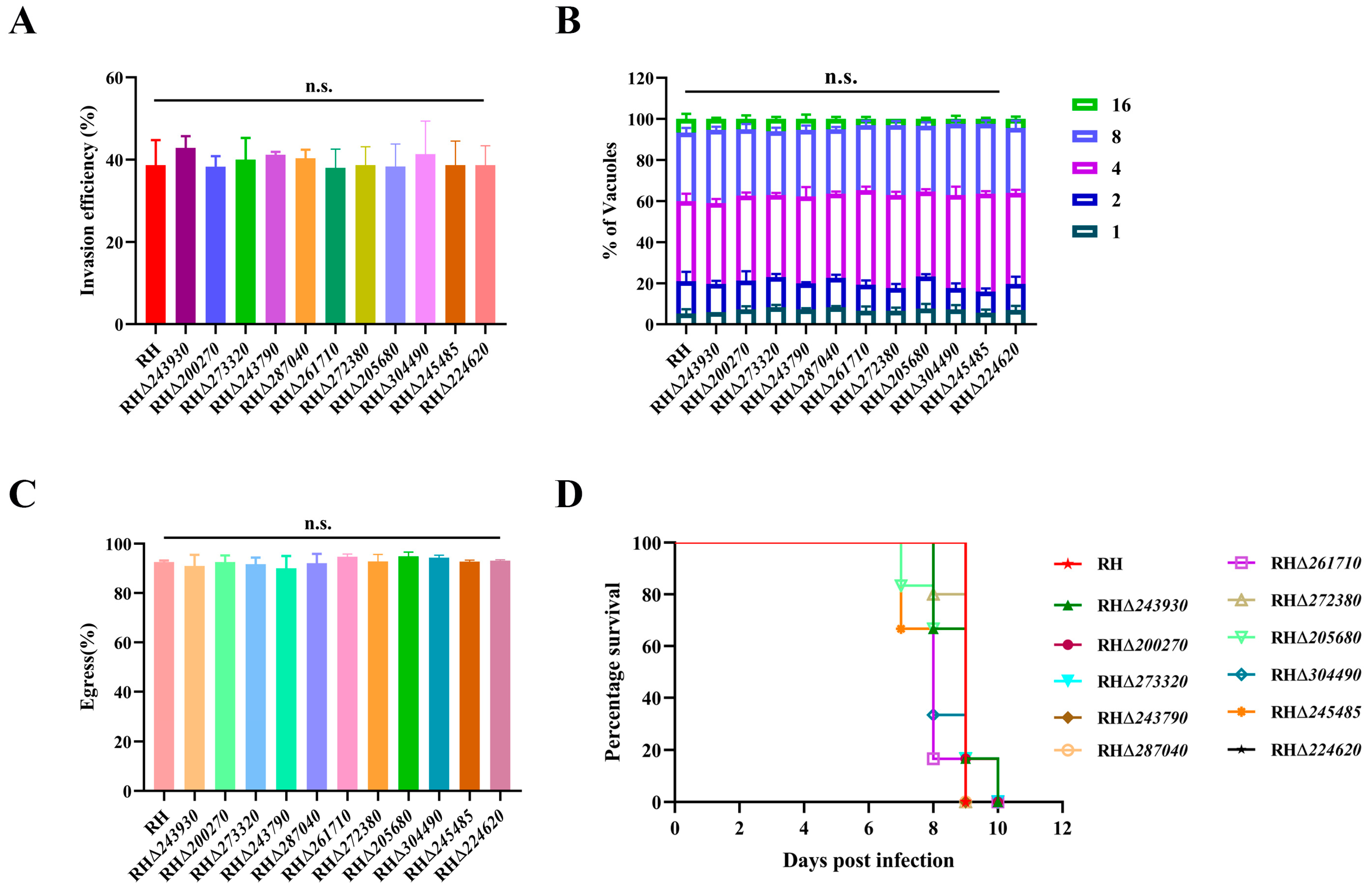
3.4. Deletion of 11 GOIs Does Not Affect T. gondii Growth
3.5. Deletion of 11 GOIs Does Not Affect the Virulence of T. gondii
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–542. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, S.G.; Besteiro, S. The pathogenicity and virulence of Toxoplasma gondii. Virulence 2021, 12, 3095–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of cerebral toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Toxoplasma gondii: An underestimated threat? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alday, P.H.; Doggett, J.S. Drugs in development for toxoplasmosis: Advances, challenges, and current status. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valleau, D.; Sidik, S.M.; Godoy, L.C.; Acevedo-Sánchez, Y.; Pasaje, C.F.A.; Huynh, M.H.; Carruthers, V.B.; Niles, J.C.; Lourido, S. A conserved complex of microneme proteins mediates rhoptry discharge in Toxoplasma. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e113155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, B.S.; Juhas, M.; Zhang, Y. Toxoplasma gondii secretory proteins and their role in invasion and pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 227, 126293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomley, F.M.; Soldati, D.S. Mix and match modules: Structure and function of microneme proteins in apicomplexan parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2001, 17, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, V.B.; Sibley, L.D. Mobilization of intracellular calcium stimulates microneme discharge in Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.C.; Zhou, C.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Research advances in interactions related to Toxoplasma gondii microneme proteins. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 176, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, S.; Carruthers, V.B.; Ferguson, D.J.; Giddings, O.K.; Wang, G.; Jakle, U.; Harper, J.M.; Sibley, L.D.; Soldati, D. The Toxoplasma micronemal protein MIC4 is an adhesin composed of six conserved apple domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4119–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Shen, J.; Yu, L. Diverse roles of TgMIC1/4/6 in the Toxoplasma infection. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 666506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, M.; Viebig, N.; Brecht, S.; Fourmaux, M.N.; Soete, M.; Di Cristina, M.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Soldati, D. Identification and characterization of an escorter for two secretory adhesins in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cérède, O.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Soête, M.; Deslée, D.; Vial, H.; Bout, D.; Lebrun, M. Synergistic role of micronemal proteins in Toxoplasma gondii virulence. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.M.; Huynh, M.H.; Coppens, I.; Parussini, F.; Moreno, S.; Carruthers, V.B. A cleavable propeptide influences Toxoplasma infection by facilitating the trafficking and secretion of the TgMIC2-M2AP invasion complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 4551–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.H.; Rabenau, K.E.; Harper, J.M.; Beatty, W.L.; Sibley, L.D.; Carruthers, V.B. Rapid invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma requires secretion of the MIC2-M2AP adhesive protein complex. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, M.; Reiss, M.; Viebig, N.; Carruthers, V.B.; Toursel, C.; Tomavo, S.; Ajioka, J.W.; Soldati, D. A family of transmembrane microneme proteins of Toxoplasma gondii contain EGF-like domains and function as escorters. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, H.; Herm-Götz, A.; Hegge, S.; Rauch, M.; Soldati-Favre, D.; Frischknecht, F.; Meissner, M. Microneme protein 8--a new essential invasion factor in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barylyuk, K.; Koreny, L.; Ke, H.; Butterworth, S.; Crook, O.M.; Lassadi, I.; Gupta, V.; Tromer, E.; Mourier, T.; Stevens, T.J.; et al. A comprehensive subcellular atlas of the Toxoplasma proteome via hyperLOPIT provides spatial context for protein functions. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 752–766.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Bai, M.J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liang, Q.L.; Li, T.T.; Cao, X.Z.; Zhu, X.Q. Novel roles of dense granule protein 12 (GRA12) in Toxoplasma gondii infection. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 3165–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.L.; Nie, L.B.; Li, T.T.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Sun, L.X.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhao, D.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, J.L. Functional characterization of 17 protein serine/threonine phosphatases in Toxoplasma gondii using CRISPR-Cas9 system. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 738794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.N.; Wang, J.L.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Sun, L.X.; Wang, X.C.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, T.T. Functional characterization of 15 novel dense granule proteins in Toxoplasma gondii using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0307822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Li, T.T.; Wang, J.L.; Liang, Q.L.; Zhang, H.S.; Sun, L.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Functional characterization of two thioredoxin proteins of Toxoplasma gondii using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 614759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.N.; Sun, L.X.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Li, T.T.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Fu, B.Q.; Zhu, X.Q.; et al. A newly characterized dense granule protein (GRA76) is important for the growth and virulence of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.J.; Gao, J.; Zheng, X.N.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Li, T.T.; Kou, Y.J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.Q. The splicing factor SR2 is an important virulence factor of Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1302512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, X.J.; Zheng, X.N.; Li, T.T.; Kou, Y.J.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.Q. Functional characterization of eight zinc finger motif-containing proteins in Toxoplasma gondii Type I RH strain using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, D.R.; Hogh, B.; Andersen, O.; Hansen, S.H.; Dalhoff, K.; Petersen, E. Treatment of infants with congenital toxoplasmosis: Tolerability and plasma concentrations of sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2006, 165, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, M.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Mehrzadi, S.; Ahmadpour, E.; Daryani, A. A systematic review of in vitro and in vivo activities of anti-Toxoplasma drugs and compounds (2006–2016). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodangeh, S.; Daryani, A.; Sharif, M.; Aghayan, S.A.; Pagheh, A.S.; Sarvi, S.; Rezaei, F. A systematic review on efficiency of microneme proteins to induce protective immunity against Toxoplasma gondii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serranti, D.; Buonsenso, D.; Valentini, P. Congenital toxoplasmosis treatment. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffari, A.D.; Dalimi, A.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Pirestani, M. Protective immunity induced with a DNA vaccine encoding B- and T-cells multi-epitope SAG1, ROP16, MIC4, GRA12, M2AP, and multi-epitope ROP8 against acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in BALB/c mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 242, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezz Eldin, H.M.; Kamel, H.H.; Badawy, A.F.; Shash, L.S. A comparative study between excretory/secretory and autoclaved vaccines against RH strain of Toxoplasma gondii in murine models. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.J.; Soldati-Favre, D. Biogenesis and secretion of micronemes in Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K. How does Toxoplasma gondii invade host cells? J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, M.; Besteiro, S.; Papoin, J.; Roques, M.; Vulliez-Le Normand, B.; Morlon-Guyot, J.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Fauquenoy, S.; Tomavo, S.; Faber, B.W.; et al. The RON2-AMA1 interaction is a critical step in moving junction-dependent invasion by apicomplexan parasites. PloS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cova, M.M.; Lamarque, M.H.; Lebrun, M. How apicomplexa parasites secrete and build their invasion machinery. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 76, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidik, S.M.; Huet, D.; Ganesan, S.M.; Huynh, M.H.; Wang, T.; Nasamu, A.S.; Thiru, P.; Saeij, J.P.J.; Carruthers, V.B.; Niles, J.C.; et al. A genome-wide CRISPR screen in Toxoplasma identifies essential apicomplexan genes. Cell 2016, 166, 1423–1435.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shwab, E.K.; Saraf, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhou, D.H.; McFerrin, B.M.; Ajzenberg, D.; Schares, G.; Hammond-Aryee, K.; van Helden, P.; Higgins, S.A.; et al. Human impact on the diversity and virulence of the ubiquitous zoonotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6956–E6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Rinkenberger, N.; Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii infection and its implications within the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosowski, E.E.; Lu, D.; Julien, L.; Rodda, L.; Gaiser, R.A.; Jensen, K.D.; Saeij, J.P. Strain-specific activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by GRA15, a novel Toxoplasma gondii dense granule protein. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene ID | Product Description | Exons | Phenotype Value | Mol wt (kDa) | TMHMM * | Predicted Signal Peptide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGME49_243930 | hypothetical protein | 6 | 0.25 | 101.348 | no | yes |
| TGME49_200270 | PAN/Apple domain-containing protein | 1 | 0.93 | 39.104 | no | yes |
| TGME49_273320 | hypothetical protein | 6 | 0.27 | 25.589 | yes | yes |
| TGME49_243790 | SAG-related sequence SRS33 | 1 | −0.5 | 31.839 | yes | no |
| TGME49_287040 | hypothetical protein | 3 | −1.1 | 36.230 | no | yes |
| TGME49_261710 | ankyrin repeat-containing protein | 8 | 1.7 | 23.448 | no | no |
| TGME49_272380 | hypothetical protein | 3 | 1.71 | 61.026 | yes | no |
| TGME49_205680 | hypothetical protein | 5 | 1.77 | 79.066 | yes | yes |
| TGME49_304490 | hypothetical protein | 5 | 1.49 | 31.978 | yes | no |
| TGME49_245485 | microneme protein MIC9 | 1 | 1.59 | 31.558 | yes | yes |
| TGME49_224620 | hypothetical protein | 8 | 1.02 | 32.578 | yes | no |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.-Y.; Wu, X.-J.; Li, C.; Gao, J.; Kou, Y.-J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Zheng, X.-N. Functional Characterization of 11 Tentative Microneme Proteins in Type I RH Strain of Toxoplasma gondii Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Animals 2024, 14, 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172543
Ma Z-Y, Wu X-J, Li C, Gao J, Kou Y-J, Wang M, Zhu X-Q, Zheng X-N. Functional Characterization of 11 Tentative Microneme Proteins in Type I RH Strain of Toxoplasma gondii Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Animals. 2024; 14(17):2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172543
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhi-Ya, Xiao-Jing Wu, Chuan Li, Jin Gao, Yong-Jie Kou, Meng Wang, Xing-Quan Zhu, and Xiao-Nan Zheng. 2024. "Functional Characterization of 11 Tentative Microneme Proteins in Type I RH Strain of Toxoplasma gondii Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System" Animals 14, no. 17: 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172543
APA StyleMa, Z.-Y., Wu, X.-J., Li, C., Gao, J., Kou, Y.-J., Wang, M., Zhu, X.-Q., & Zheng, X.-N. (2024). Functional Characterization of 11 Tentative Microneme Proteins in Type I RH Strain of Toxoplasma gondii Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Animals, 14(17), 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172543






