Disparities in Body Color Adaptability and Ambient Light Color Preference between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Holding Conditions
2.2. Experimental Protocol
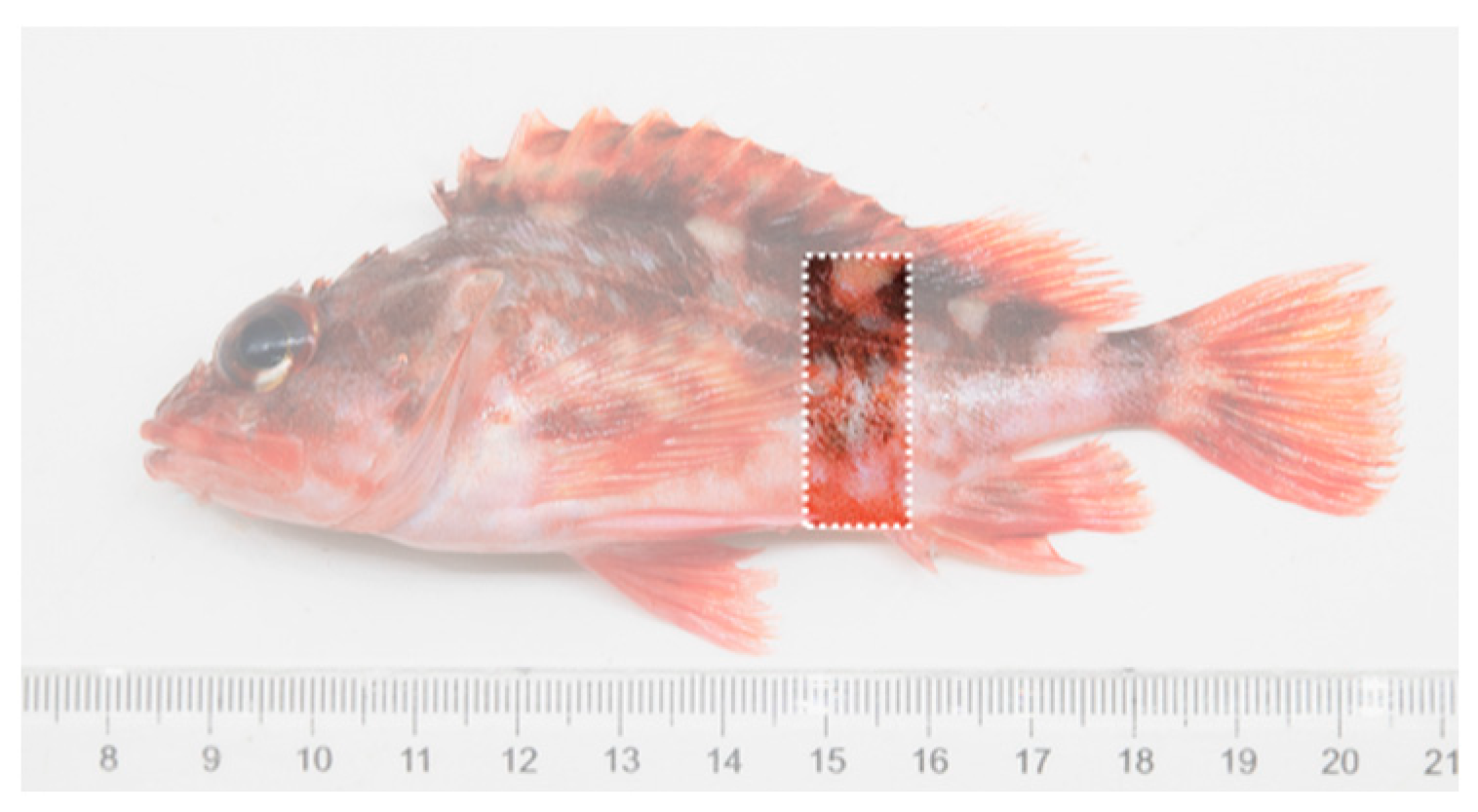
2.2.1. Disparities in External Body Color between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish
2.2.2. Differences in Morphological Color-Changing Ability between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish
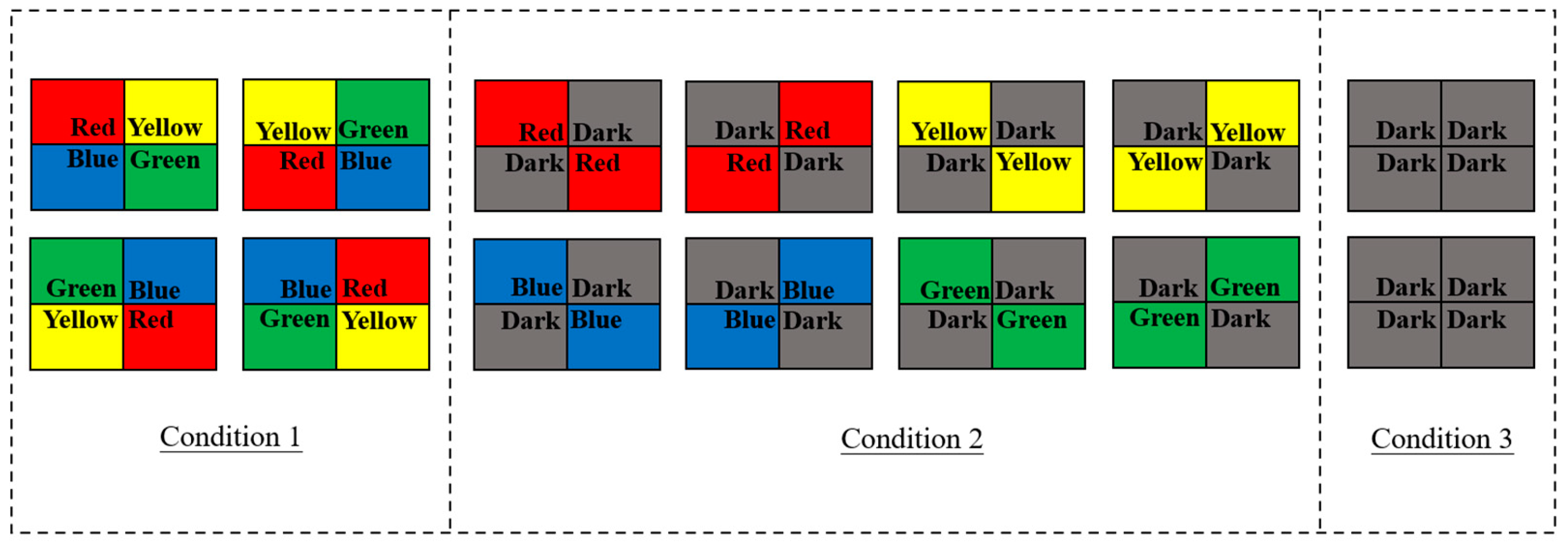
2.2.3. Variation in Light Color Preferences between Wild and Hatchery-Marbled Rockfish
2.2.4. Body Color Analyses
2.2.5. Calculations
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Body Color
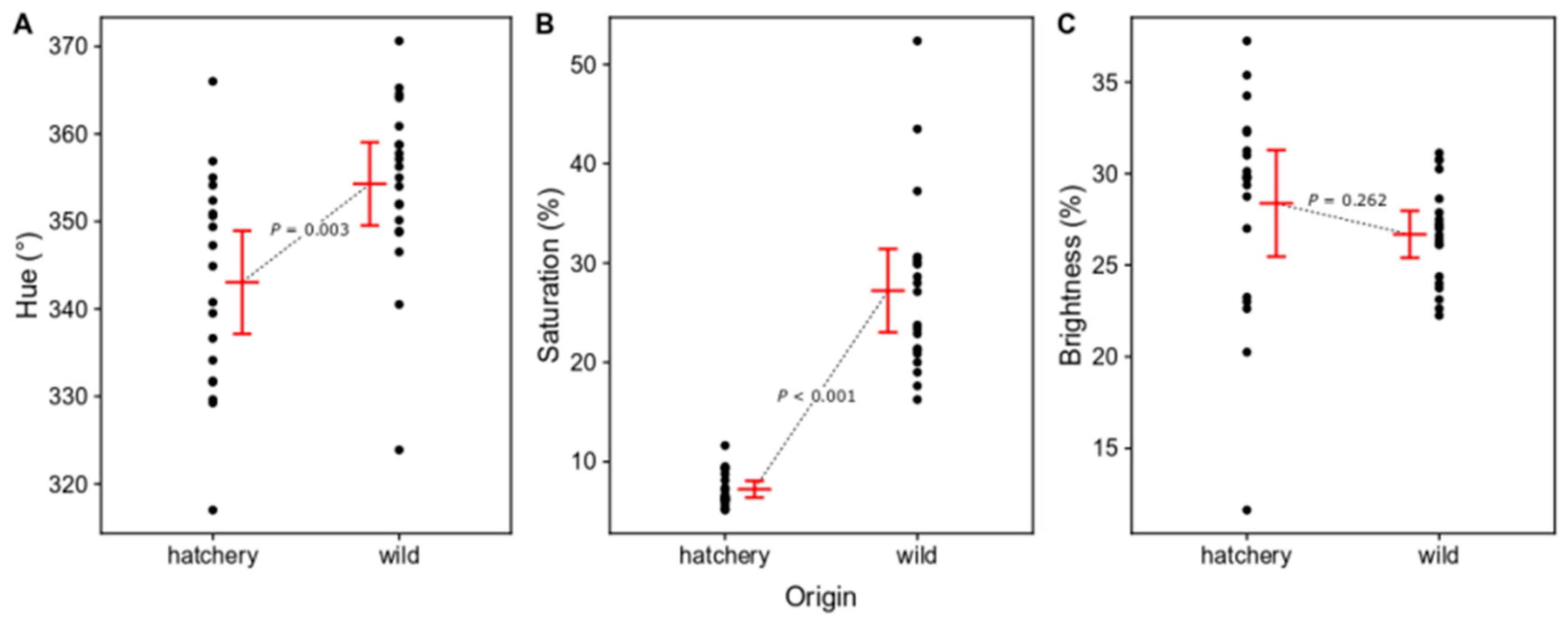
3.1.1. Differences in Body Color between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish
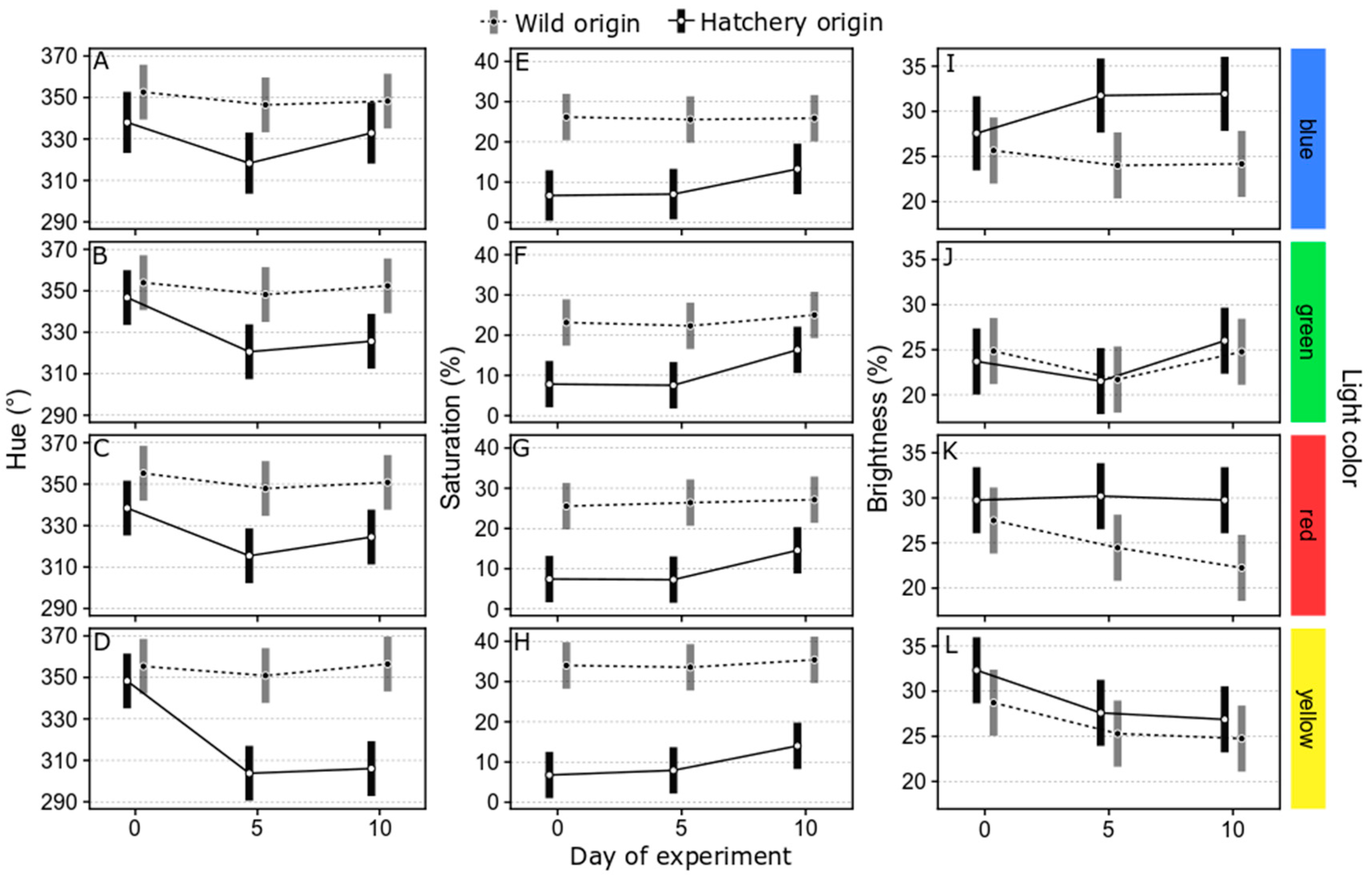
3.1.2. Changes in Body Color of Marbled Rockfish under Varied Ambient Light Colors
3.2. Light Color Preference
3.2.1. Light Color Preferences
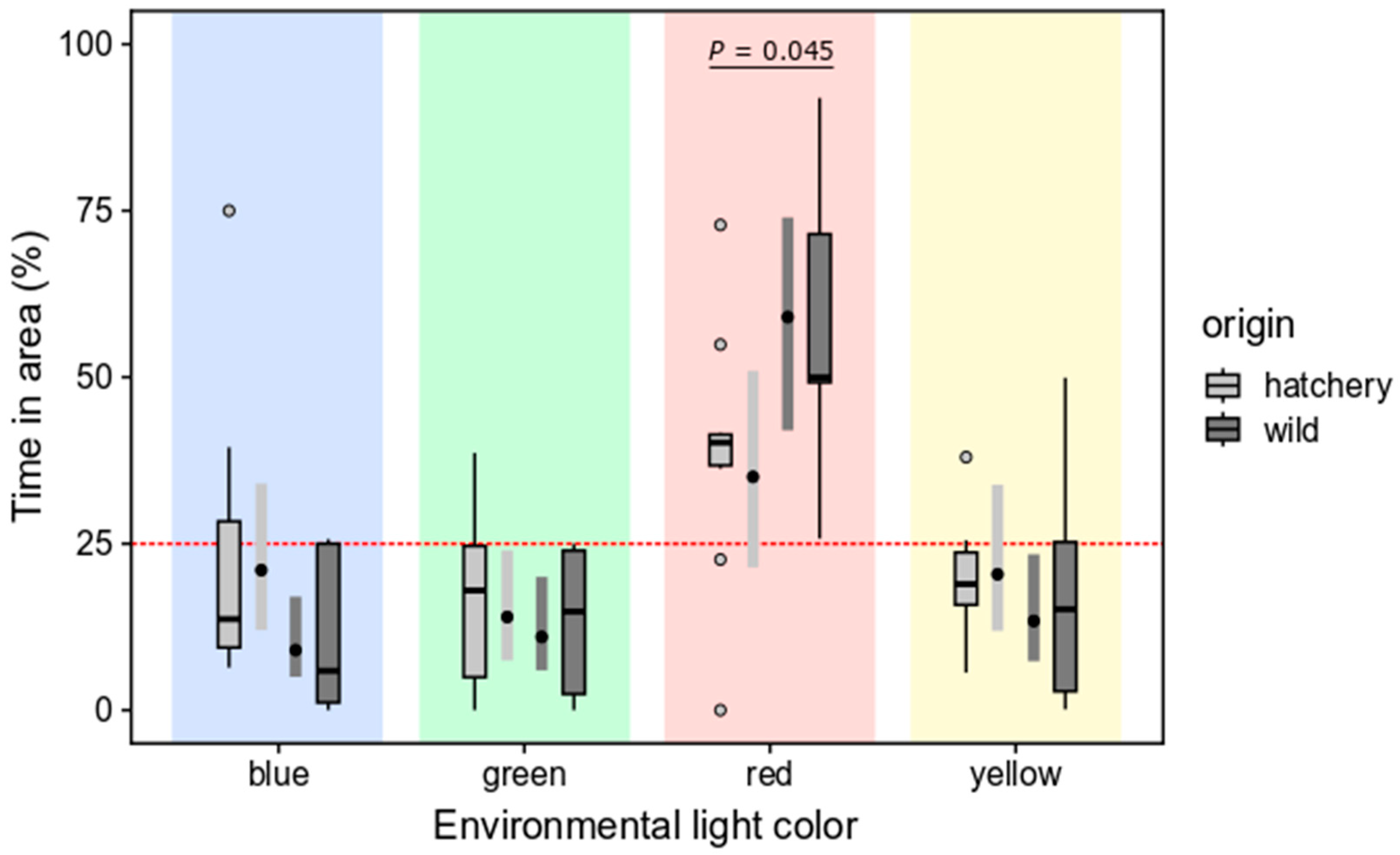
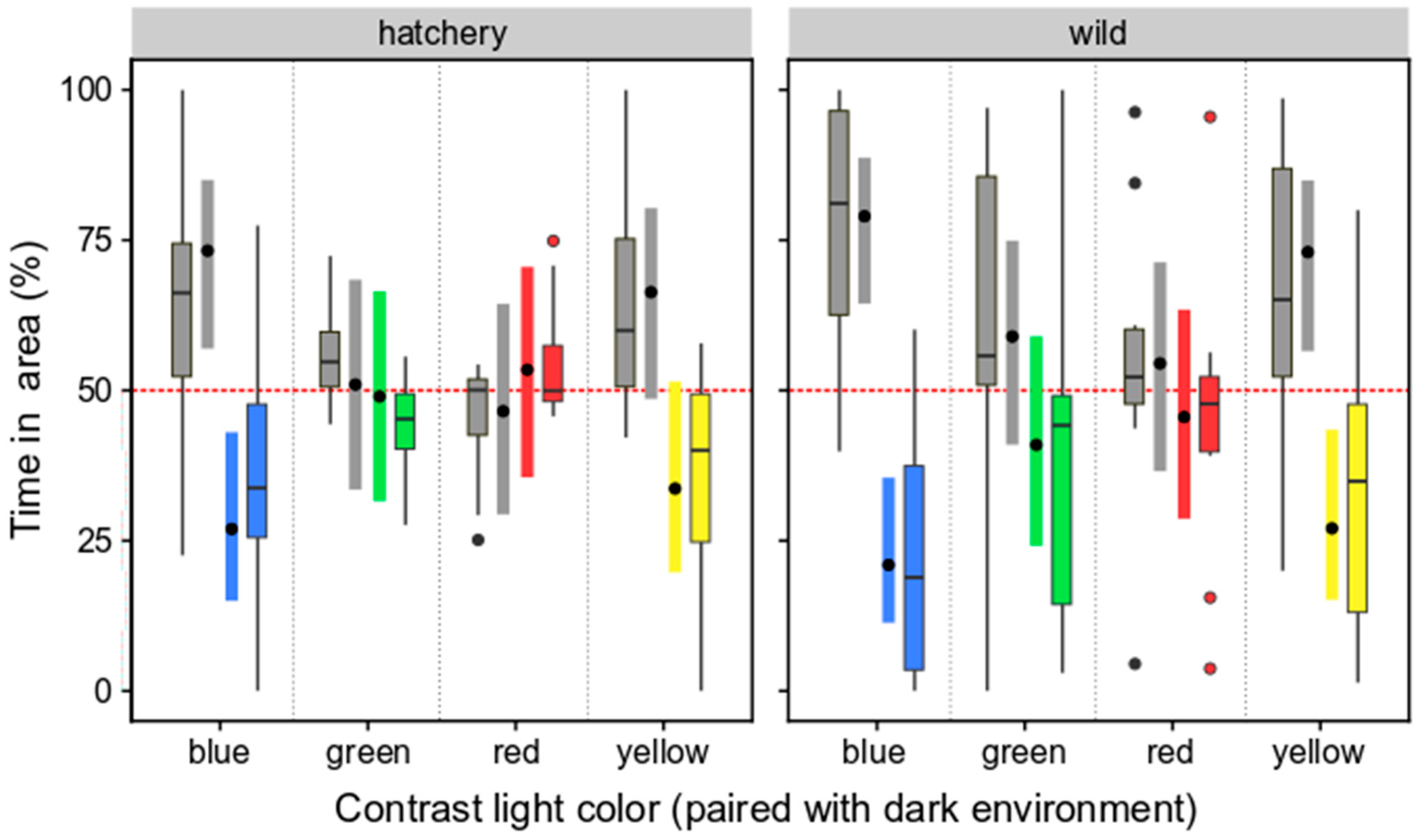
3.2.2. Selection Preferences of Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish under Varied Ambient Light Colors and Darkness
4. Discussions
4.1. Body Color Differences
4.2. Effects of Environmental Ambient Light Color on Body Color
4.3. Selection Preferences for Ambient Light
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnsson, J.I.; Brockmark, S.; Näslund, J. Environmental effects on behavioural development consequences for fitness of captive-reared fishes in the wild. J. Fish. Biol. 2014, 85, 1946–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näslund, J. Reared to become wild-like: Addressing behavioral and cognitive deficits in cultured aquatic animals destined for stocking into natural environments-a critical review. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2021, 97, 489–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Day, R.L. The future of stock enhancements: Lessons for hatchery practice from conservation biology. Fish Fish. 2002, 3, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagg, T.A.; Berejikian, B.A.; Colt, J.; Dickhoff, W.W.; Harrell, L.W.; Maynard, D.J.; Nash, C.E.; Strom, M.S.; Iwamoto, R.N.; Mahnken, C.V. Ecological and behavioral impacts of artificial production strategies on the abundance of wild salmon populations: A review of practices in the Pacific Northwest. In NOAA Technical Memorandum; National Marine Fisheries Service, Northwest Fisheries Science Center: Seattle, WA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, H.; Masuda, R.; Tanaka, M. Environmental stimuli improve learning capability in striped knifejaw juveniles: The stage-specific effect of environmental enrichment and the comparison between wild and hatchery-reared fish. Fish. Sci. 2015, 81, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson Sköld, H.; Aspengren, S.; Wallin, M. Rapid color change in fish and amphibians–function, regulation, and emerging applications. Pigm. Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawkey, M.D.; D’Alba, L. Interactions between colour-producing mechanisms and their effects on the integumentary colour palette. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2017, 372, 20160536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, R. The regulation of motile activity in fish chromatophores. Pigm. Cell Melanoma Res. 2000, 13, 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parichy, D.M. Pigment patterns: Fish in stripes and spots. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, R947–R950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B.; Cech, J.J. Fishes: An Introduction to Ichthyology, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figon, F.; Casas, J. Morphological and physiological colour changes in the animal kingdom. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M. Morphological color changes in fish: Regulation of pigment cell density and morphology. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 58, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerq, E.; Taylor, J.F.; Migaud, H. Morphological skin colour changes in teleosts. Fish Fish. 2010, 11, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.M.; Schluter, D. Colour plasticity and background matching in a threespine stickleback species pair. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 102, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.L.; Phillips, B.; Cummins, G.H.; Shand, J. Changes in the visual environment affect colour signal brightness and shoaling behaviour in a freshwater fish. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrongiello, J.R.; Bond, N.R.; Crook, D.A.; Wong, B.B.M. Nuptial coloration varies with ambient light environment in a freshwater fish. J. Evol. Biol. 2010, 23, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughman, J.W. Divergent sexual selection enhances reproductive isolation in sticklebacks. Nature 2001, 411, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sang, W.; Dai, H.; Lin, C.; Ke, S.; Mao, J.; Shi, X. A detailed analysis of the effect of different environmental factors on fish phototactic behavior: Directional fish guiding and expelling technique. Animals 2022, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, M.M.; Cameron, D.A. Photoreceptor differentiation during retinal development, growth, and regeneration in a metamorphic vertebrate. J. Nanoneurosci. 2004, 24, 11463–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, M.A.; Warner-Smith, R.J.; Allan, G.L.; Glencross, B.D. Effects of dietary astaxanthin source and light manipulation on the skin colour of Australian snapper Pagrus auratus (Bloch & Schneider, 1801). Aquacult. Res. 2004, 35, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Salm, A.L.; Martinez, M.; Flik, G.; Bonga, S.W. Effects of husbandry conditions on the skin colour and stress response of red porgy, Pagrus pagrus. Aquaculture 2004, 241, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotllant, J.; Tort, L.; Monteroc, D.; Pavlidisd, M.; Martinezb, M.; Wendelaar Bongae, S.E.; Balme, P.H.M. Background colour influence on the stress response in cultured red porgy Pagrus pagrus. Aquaculture 2003, 223, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.L.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.J.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, H.J.; Ji, Q.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yuan, X.Y. Comparative study on body parameters, colour and meat quality characteristics of crucian carp (Carasslius auratus) cultured under two modes. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2023, 39, 148–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, R.Q.; Xiong, D.M.; Li, Z.G.; Jiang, H.B.; An, M.; Shao, J. Retinal structure and opsin expression characteristics of the second filial generation and wild population of Brachymystax tsinlingensis Li, 1966. J. Fish. Sci. Chin. 2023, 30, 1445–1456. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yearsley, G.K.; Last, P.R.; Ward, R.D.; Daley, R.K. Australian Seafood Handbook: An Identification Guide to Imported Species; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, VIC, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazoe, J. Effects of supplemental carotenoid pigments on the carotenoid accumulation in young sea bream, Chrysophrys major. Bull. Tokai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1984, 113, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Xie, S.; Lei, W.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y. Effect of light intensity on growth, survival and skin color of juvenile Chinese longsnout catfish (Leiocassis longirostris Günther). Aquaculture 2005, 248, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeuf, G.; Le Bail, P.Y. Does light have an influence on fish growth? Aquaculture 1999, 177, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shand, J.; Lythgoe, J.N. Light-induced changes in corneal iridescence in fish. Vision Res. 1987, 27, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.J.; Caballero, C. Effect of the light intensity upon the agonistic behaviour of juvenile of white-seabream (Diplodus sargus cadenati de la Paz, Bauchot and Daget, 1974). Aggress. Behav. 2004, 30, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, M.; Spoto, M.; Verginella, L.; Ferrero, E.A. Behavioural effects of artificial light on fish species of commercial interest. Fish. Res. 2005, 73, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginés, R.; Afonso, J.M.; Argüello, A.; Zamorano, M.J.; López, J.L. The effects of long-day photoperiod on growth, body composition and skin colour in immature gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Aquacult. Res. 2004, 35, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.C.; Sadovy, Y.; Leung, F.C. Mating system of the rockfish, Sebastiscus marmoratus as revealed by DNA fingerprinting. Ichthyol. Res. 2003, 50, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Kohda, M. Timing and sites of parturition of the viviparous scorpionfish, Sebastiscus marmoratus. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1998, 52, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W. Biological studies on Sebastiscus marmomtus off Zhoushan. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. 1999, 18, 185–190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Näslund, J.; Peng, L.; Liu, C.; Tian, M.; Chai, X.; Zhan, D.; Zhang, X. Differences in external morphology, body composition and swimming performance between hatchery-and wild-origin marbled rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 912129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhong, J.M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, H. Habitat use of juvenile rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus) in mussel farming waters: A preliminary study. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1900–1913. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Song, J. Sound production in marbled rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus) and implications for fisheries. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xian, W. Stock assessment using LBB method for eight fish species from the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. Study on the suitability of important links of reef fish breeding and release. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heydarnejad, M.S.; Parto, M.; Pilevarian, A.A. Influence of light colours on growth and stress response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under laboratory conditions. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 97, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhao, S. Ecological capacity assessment of Sepiella maindroni in the sea area of Zhongjieshan archipelago based on Ecopath model. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 43, 51–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.X.; Cui, D.L.; Wang, J.; Qin, J. The distribution and resources of benthic algae in the protected Zhongjieshan Islands Area. Fish. Sci. 2011, 30, 269–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.X.; Fang, T.K. Nutrients and eutrophication evaluation of waters mariculture zone in Zhongjieshan archipelago. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2014, 14, 164–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, M.; Lin, J. Dietary composition and food competition of six main fish species in rocky reef habitat off Gouqi Island. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 536–544. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Shi, Y.H.; Xie, Y.D.; Deng, P.P.; Yuan, X.C. Study on indoor artificial breeding technology of Sebastiscus marmoratus. Fish. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2018, 45, 322–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, L.; Dimitrova, T.; Angelov, N. RGB and HSV colour models in colour identification of digital traumas images. Int. Conf. Comput. Syst. Technol. CompSysTech 2005, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yasir, I.; Qin, J.G. Embryonic development and early ontogeny of false clownfish Amphiprion ocellaris Cuvier. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S.; Christensen, R.H.B. lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using ‘Eigen’ and S4. R Package. CRAN. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Lenth, R.V. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R Package. CRAN. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S.; Price, B. car: Companion to Applied Regression. R Package. CRAN. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=car (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D.; van den Brand, T. ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. R Package. CRAN. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggplot2 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Wilke, C.O. cowplot: Streamlined Plot Theme and Plot Annotations for ‘ggplot2’. R Package. CRAN. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cowplot (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Tanaka, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Kamata, T.; Simpson, K.L. Biochemical study on the carotenoids in the anemonefish, Amphiprion spp. Mem. Fac. Fish. Kagoshima Univ. 1992, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Iraklio, C. Culture of the red porgy, Pagrus pagrus, in Crete. Present knowledge, problems and perspectives. Cah. Options Méditerranéennes 1995, 16, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsh, R.N. Genetics and evolution of pigment patterns in fish. Pigm. Cell Res. 2004, 17, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.T.; Beleza, S.; Pollen, A.A.; Schluter, D.; Kittles, R.A.; Shriver, M.D.; Kingsley, D.M. Cis-Regulatory changes in Kit ligand expression and parallel evolution of pigmentation in sticklebacks and humans. Cell 2007, 131, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, A.K.; Jones, F.C.; Chan, Y.F.; Brady, S.D.; Absher, D.M.; Grimwood, J.; Schmutz, J.; Myers, R.M.; Kingsley, D.M.; Peichel, C.L. The genetic basis of divergent pigment patterns in juvenile threespine sticklebacks. Heredity 2011, 107, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsushima, M.; Nemoto, H.; Matsuno, T. The accumulation of pigments from paprika in the integument of goldfish Carassius auratus. Fish. Sci. 1998, 64, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttle, L.G.; Crampton, V.O.; Williams, P.D. The effect of feed pigment type on flesh pigment deposition and colour in farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Aquacult. Res. 2001, 32, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, M.; Erçen, Z.; Hunt, A.Ö.; Büyükçapar, H.M. The use of alfalfa, Medicago sativa as a natural carotenoid source in diets of goldfish, Carassius auratus. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cal, L.; Suarez-Bregua, P.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Braasch, I.; Rotllant, J. Fish pigmentation and the melanocortin system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 211, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Mizusawa, K.; Amano, M. Multifunctional roles of melanocyte-stimulating hormone and melanin-concentrating hormone in fish: Evolution from classical body color change. Aqua-Bio Sci. Monogr. 2014, 7, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, M.; Karkana, M.; Fanouraki, E.; Papandroulakis, N. Environmental control of skin color in the red porgy, Pagrus pagrus. Aquacult. Res. 2008, 39, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, L.; Rema, P. Effect of microalgal biomass concentration and temperature on ornamental goldfish (Carassius auratus) skin pigmentation. Aquacult. Nutr. 2005, 11, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Salm, A.L.; Spanings, F.A.T.; Gresnigt, R.; Bonga, S.W.; Flik, G. Background adaptation and water acidification affect pigmentation and stress physiology of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 144, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Yuki, M.; Miyakoshi, T.; Maruko, K. The influence of long-term chromatic adaptation on pigment cells and striped pigment patterns in the skin of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2005, 303, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Salm, A.L.; Metz, J.R.; Bonga, S.W.; Flik, G. Alpha-MSH, the melanocortin-1 receptor and background adaptation in the Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 144, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Hong, W.S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Chen, S.X. The regulation of melanocyte-stimulating hormone on the pigment granule dispersion in the xanthophores and melanophores of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2019, 507, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masazumi, S. Morphological color changes in the medaka, Oryzias latipes, after prolonged background adaptation-I. Changes in the population and morphology of melanophores. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1993, 104, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.I.; Ball, J.N. Evidence for a dual pituitary control of teleost melanophores. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1975, 25, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchiari, A.C.; do Amaral Duarte, C.R.; de Morais Freire, F.A.; Nissinen, K. Hierarchical status and colour preference in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Ethol. 2007, 25, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lin, C.; Dai, H.; Mao, J.; Ke, S.; Yin, R.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Influence of low-intensity light on phototactic behaviour of Schizothorax oconnori Lloyd. River Res. Appl. 2020, 36, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, J.A.; Bowmaker, J.K. Visual pigments in the four-eyed fish, Anableps anableps. Nature 1982, 298, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novales Flamarique, I.; Hiebert, S.; Sechrist, J. Visual performance and ocular system structure of kokanee and sockeye salmon following strobe light exposure. N. Am. J. Fish. Managem. 2006, 26, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, G.L.; Barreto, R.E. Environmental blue light prevents stress in the fish Nile tilapia. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2001, 34, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.Y.; Li, L.P. Studies on the receptor system of retinal of Sebastiscus marmoratus and their adaptive properties. J. Xiamen Univ. 1988, 27, 86–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| Area 1 (F1) | Area 2 (F2) | Area 3 (F3) | Area 4 (F4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average time (%) | 17.4 (8.1–26.7) | 34.9 (18.7–51.1) | 22.2 (11.6–32.7) | 25.6 (17.2–34.0) |
| p (H0: μ = 25%) | 0.102 | 0.215 | 0.579 | 0.884 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Liu, C.; Yuan, G.; Guo, H.; Näslund, J.; Wang, Y.; Ru, J.; Ou, Y.; Chai, X.; Zhang, X. Disparities in Body Color Adaptability and Ambient Light Color Preference between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus). Animals 2024, 14, 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111701
Qi Y, Liu C, Yuan G, Guo H, Näslund J, Wang Y, Ru J, Ou Y, Chai X, Zhang X. Disparities in Body Color Adaptability and Ambient Light Color Preference between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus). Animals. 2024; 14(11):1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111701
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yulu, Chenhui Liu, Guozi Yuan, Haoyu Guo, Joacim Näslund, Yucheng Wang, Jiangfeng Ru, Yingying Ou, Xuejun Chai, and Xiumei Zhang. 2024. "Disparities in Body Color Adaptability and Ambient Light Color Preference between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus)" Animals 14, no. 11: 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111701
APA StyleQi, Y., Liu, C., Yuan, G., Guo, H., Näslund, J., Wang, Y., Ru, J., Ou, Y., Chai, X., & Zhang, X. (2024). Disparities in Body Color Adaptability and Ambient Light Color Preference between Wild and Hatchery-Reared Marbled Rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus). Animals, 14(11), 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111701






