Significant Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Communities of Sympatric Bean Goose, Hooded Crane, and Domestic Goose
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Bird Species Determination
2.4. PCR and Amplicon Library Preparation
2.5. Bioinformatics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
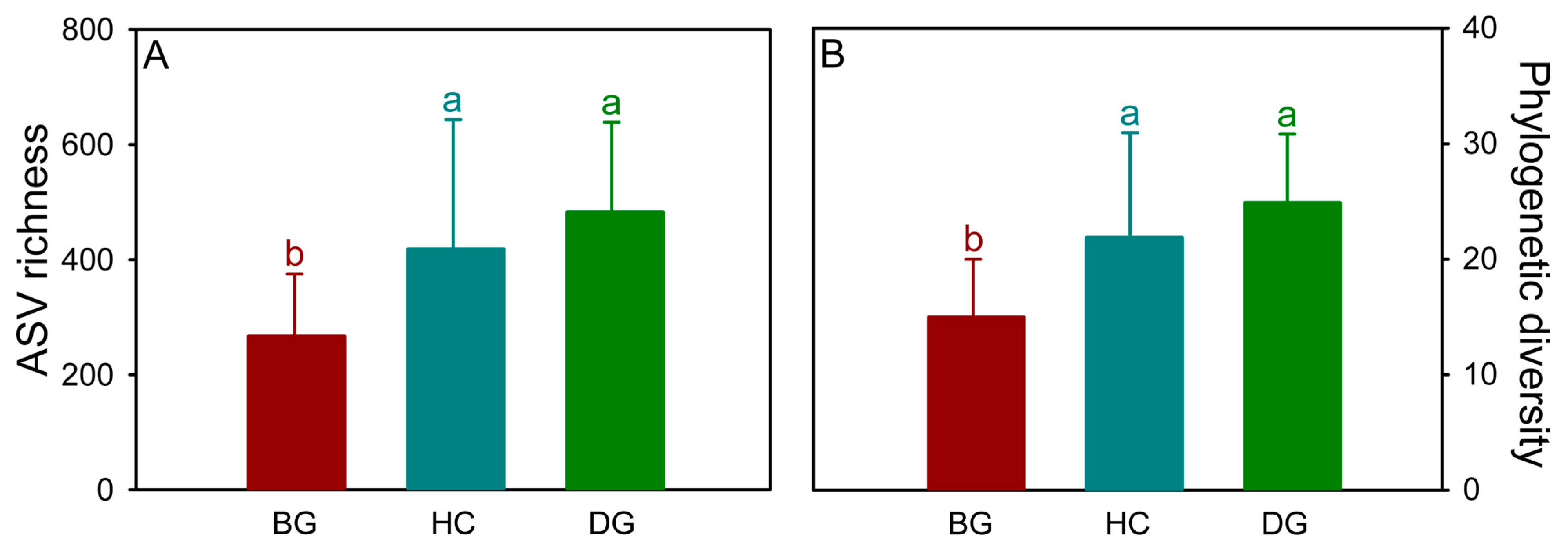
3.1. Bacterial Diversity
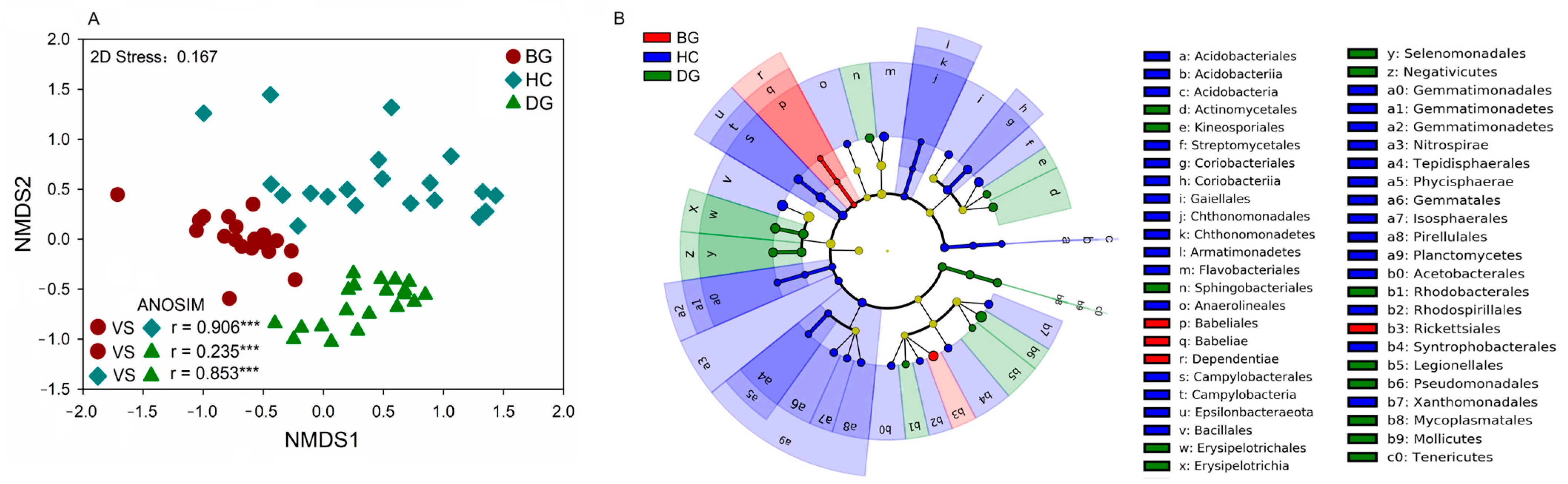
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition
3.3. Gut Bacterial PICRUSt Analysis
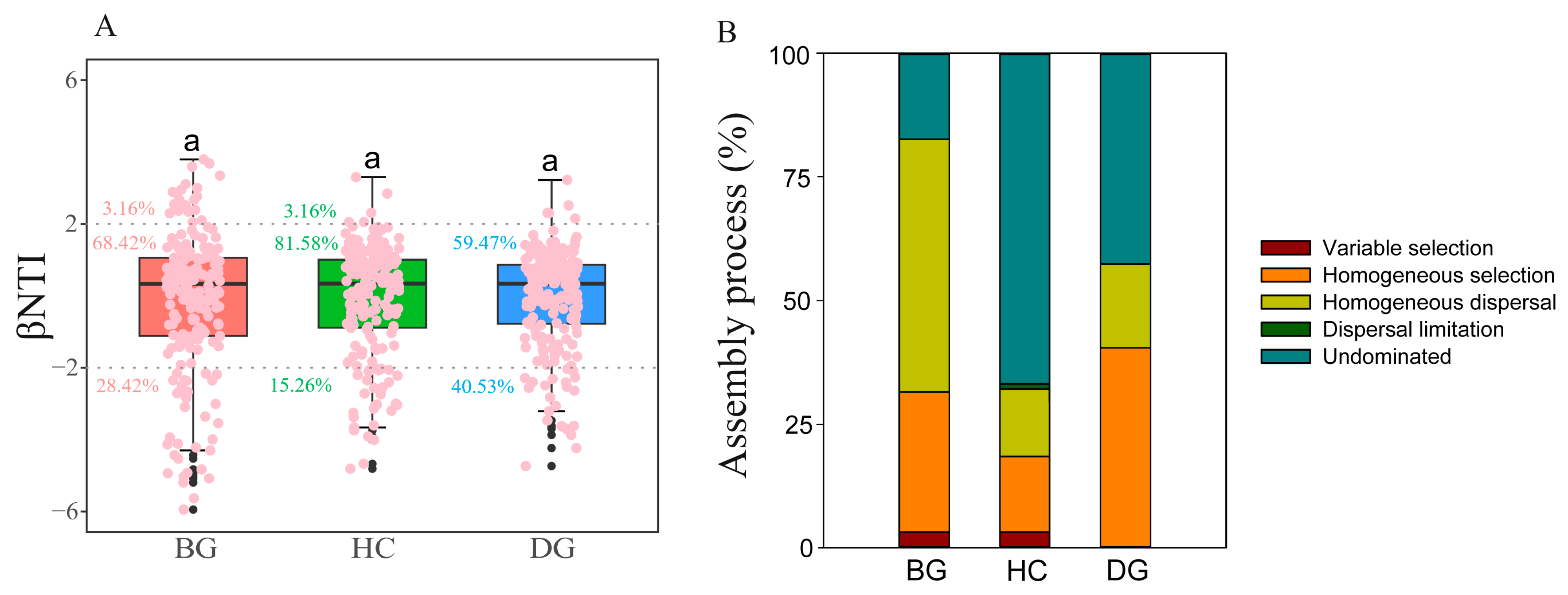
3.4. Gut Bacterial Community Assembly
3.5. Gut Bacterial Network Analysis
3.6. Gut Potential Pathogens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, P.; Liu, Y.; Le, B.; Qin, B.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, Z. A comparison of dynamic distributions of intestinal microbiota between Large White and Chinese Shanxi Black pigs. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Rao, M.C.; Chang, E.B. Gut microbiota as a transducer of dietary cues to regulate host circadian rhythms and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, S.L.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota-mediated protection against diarrheal infections. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24, S39–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, W.B.; Moore, F.R.; Wang, S. Characterization of the gut microbiota of migratory passerines during stopover along the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico. J. Avian Biol. 2016, 47, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cao, L.; Klaassen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fox, A.D. Avoiding competition? Site use, diet and foraging behaviours in two similarly sized geese wintering in China. Ardea 2015, 103, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Huang, B.H.; Lin, S.M.; Huang, C.L.; Liao, P.C. Changes of diet and dominant intestinal microbes in farmland frogs. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.; Kim, N. Roles of sex hormones and gender in the gut microbiota. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil 2021, 27, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Xiang, X.; Dong, Y.; Yan, S.; Song, Y.; Zhou, L. Significant differences in the gut bacterial communities of Hooded Crane (Grus monacha) in different seasons at a stopover site on the flyway. Animals 2020, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Ley, R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Sanders, J.G.; Delsuc, F.; Metcalf, J.; Amato, K.; Taylor, M.W.; Knight, R. Comparative analyses of vertebrate gut microbiomes reveal convergence between birds and bats. MBio 2020, 11, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Oakley, B.; Kim, W.K. Chicken gut microbiota: Importance and detection technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Carrasco, J.M.; Casanova, N.A.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Microbiota, gut health and chicken productivity: What is the connection? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, N.; Hughes, R.J.; Bajagai, Y.S.; Aspden, W.J.; Van, T.T.H.; Moore, R.J.; Stanley, D. Reduced environmental bacterial load during early development and gut colonisation has detrimental health consequences in Japanese quail. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grond, K.; Sandercock, B.K.; Jumpponen, A.; Zeglin, L.H. The avian gut microbiota: Community, physiology and function in wild birds. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, e01788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, F.; Guo, Y. Host-genotype-dependent cecal microbes are linked to breast muscle metabolites in Chinese chickens. Iscience 2022, 25, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benskin, C.M.H.; Wilson, K.; Jones, K.; Hartley, I.R. Bacterial pathogens in wild birds: A review of the frequency and effects of infection. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahtab, N.; Wu, Y.; Yin, J.; Lu, J.; Zhou, L.; Xiang, X. Comparison of the gut fungal communities among Hooded crane (Grus monacha), Greater white-fronted goose (Anser albifrons), and Bean goose (Anser fabalis) at Shengjin Lake, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 49, e02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, T.; Cui, R.; Xiang, X. Characteristics of cross transmission of gut fungal pathogens between wintering hooded cranes and sympatric domestic geese. Avian Res. 2023, 14, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, N.; Gao, Y. Cross-species infection potential of avian influenza H13 viruses isolated from wild aquatic birds to poultry and mammals. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, e2184177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, N.; Xu, W. Effects of variation in food resources on foraging habitat use by wintering Hooded Cranes (Grus monacha). Avian Res. 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Xue, B.; Yao, S.; Liu, J. Response of Cladocera fauna to environmental change based on sediments from Shengjin Lake, a Yangtze River-connected lake in China. Quat. Int. 2020, 536, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Gu, J. Effects of food changes on intestinal bacterial diversity of wintering Hooded Cranes (Grus monacha). Animals 2021, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, L. Is intestinal bacterial diversity enhanced by trans-species spread in the mixed-species flock of hooded crane (Grus monacha) and bean goose (Anser fabalis) wintering in the lower and middle Yangtze River floodplain? Animals 2021, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, C.; Møller, A.P.; Guo, Y. Annual spatio-temporal migration patterns of Hooded Cranes wintering in Izumi based on satellite tracking and their implications for conservation. Avian Res. 2018, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Xiang, X.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, L. Comparing the intestinal bacterial communies of sympatric wintering Hooded Crane (Grus monacha) and Domestic Goose (Anser anser domesticus). Avian Res. 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhou, D.; Ge, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Han, Y.; Shi, S. Intestinal Microbiota of Anser fabalis Wintering in Two Lakes in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Floodplain. Animals 2023, 13, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Cao, L.; Fox, A.D. Distribution and diet of wintering Tundra Bean Geese Anser fabalis serrirostris at Shengjin Lake. Yangtze River floodplain, China. Wildfowl 2010, 60, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Barter, M.; Zhao, M.; Meng, H.; Zhang, Y. A systematic scheme for monitoring waterbird populations at Shengjin Lake, China: Methodology and preliminary results. Avian Res. 2011, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F. Hydrology-driven responses of herbivorous geese in relation to changes in food quantity and quality. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, W.; Feng, X.; Ma, Q.; Ma, Z. Changes in wintering Hooded Cranes and their habitats at Chongming Dongtan over the past 20 years. Avian Res. 2023, 14, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Jin, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, F. Dramatic shifts in intestinal fungal community between wintering Hooded Crane and Domestic Goose. Avian Res. 2021, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Zhang, F.; Fu, R.; Yan, S.; Zhou, L. Significant differences in bacterial and potentially pathogenic communities between sympatric hooded crane and greater white-fronted goose. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, J.F.; Fitz-Gibbon, S.; Schuster, S.C.; Brenchley, J.E.; House, C.H. Metagenomic signatures of the Peru Margin subseafloor biosphere show a genetically distinct environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10583–10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, S.J.; Cox, M.J.; Turek, E.M.; Calus, S.T.; Cookson, W.O.; Moffatt, M.F.; Walker, A.W. Reagent and laboratory contamination can critically impact sequence-based microbiome analyses. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, A.; McDonald, D.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Kopylova, E.; Morton, J.T.; Zech Xu, Z.; Knight, R. Deblur rapidly resolves single-nucleotide community sequence patterns. MSystems 2017, 2, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, C.O. Exploring the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities: An example for rain forest trees. Am. Nat. 2000, 156, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. Data, information, knowledge and principle: Back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D199–D205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Yang, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, S.; Ravindran, B. Bacterial community dynamics and co-occurrence network patterns during different stages of biochar-driven composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Deng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W. Functional distribution of bacterial community under different land use patterns based on FaProTax function prediction. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boamah, H.; Puranam, P.; Sandre, R.M. Disseminated Nocardia farcinica in an immunocompetent patient. IDCases 2016, 6, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, R.J.; Tsukamura, M.; Brown, B.A.; Brown, J.; Steingrube, V.A.; Zhang, Y.S.; Nash, D.R. Cefotaxime-resistant Nocardia asteroides strains are isolates of the controversial species Nocardia farcinica. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2726–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Shu, Z.; Song, H. A rare case of a hard-to-heal ulcer caused by pulmonary Nocardia infection. J. Wound Care 2024, 33, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccin, M.; Wiener, D.J.; Rech, R.R.; Santoro, D.; Rodrigues Hoffmann, A. Common superficial and deep cutaneous bacterial infections in domestic animals: A review. Vet. Pathol. 2023, 60, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.M.; Wilson, M.E.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Nghia, H.D.T.; Taylor, W.; Schultsz, C. Streptococcus suis: An emerging human pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lu, S.; Jin, D.; Yang, J.; Pu, J.; Lai, X.H.; Xu, J. Roseomonas wenyumeiae sp. nov., isolated from faeces of Tibetan antelopes (Pantholops hodgsonii) on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano-Bertrand, S.; Bourdier, A.; Aujoulat, F.; Michon, A.L.; Masnou, A.; Parer, S.; Jumas-Bilak, E. Skin microbiota is the main reservoir of Roseomonas mucosa, an emerging opportunistic pathogen so far assumed to be environmental. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 737.e1–737.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinella, M.A. Cellulitis and sepsis due to Sphingobacterium. JAMA 2002, 288, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldenström, J.; On, S.L.; Ottvall, R.; Hasselquist, D.; Harrington, C.S.; Olsen, B. Avian reservoirs and zoonotic potential of the emerging human pathogen Helicobacter canadensis. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 7523–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robino, P.; Tomassone, L.; Tramuta, C.; Rodo, M.; Giammarino, M.; Vaschetti, G.; Nebbia, P. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli and enteric Helicobacter in domestic and free living birds in North-Western Italy. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2010, 152, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acheson, D.; Allos, B.M. Campylobacter jejuni infections: Update on emerging issues and trends. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiPuma, J.J. Update on the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2005, 11, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.W. Nocardiosis: Updates and clinical overview. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barash, J.R.; Arnon, S.S. A novel strain of Clostridium botulinum that produces type B and type H botulinum toxins. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, M.; Shehata, A.A.; Grosse-Herrenthey, A. Relationship between gastrointestinal dysbiosis and Clostridium botulinum in dairy cows. Anaerobe 2014, 27, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshy, J.; Aronson, J.F.; Vishwanath, B.; Williams-Bouyer, N. Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens sepsis in an autopsy patient: A troublesome diagnostic workup. IDCases 2014, 1, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, G.V.; Kar, P.; Mitra, S. Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens prosthetic joint infection. Anaerobe 2022, 79, 102689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaumburg, F.; Dieckmann, R.; Schmidt-Bräkling, T.; Becker, K.; Idelevich, E.A. First description of an Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens prosthetic joint infection. New Microbes New Infect. 2017, 18, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rood, J.I. Virulence genes of Clostridium perfringens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1998, 52, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immerseel, F.V.; Buck, J.D.; Pasmans, F.; Huyghebaert, G.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R. Clostridium perfringens in poultry: An emerging threat for animal and public health. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, B.; Ndayisenga, F. Gut region induces gastrointestinal microbiota community shift in Ujimqin sheep (Ovis aries): From a multi-domain perspective. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 7603–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, X. Significant differences in intestinal fungal community of hooded cranes along the wintering periods. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 991998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravigné, V.; Becker, N.; Massol, F.; Guichoux, E.; Boury, C.; Mahé, F.; Facon, B. Fruit fly phylogeny imprints bacterial gut microbiota. Evol. Appl. 2022, 15, 1621–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Mykytczuk, N.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I. Effects of the captive and wild environment on diversity of the gut microbiome of deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). ISME J. 2019, 13, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Shin, N.R.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Hyun, D.W.; Bae, J.W. Host habitat is the major determinant of the gut microbiome of fish. Microbiome 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honka, J.; Baini, S.; Searle, J.B.; Kvist, L.; Aspi, J. Genetic assessment reveals inbreeding, possible hybridization, and low levels of genetic structure in a declining goose population. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblut, N.D.; Reischer, G.H.; Walters, W.; Schuster, N.; Walzer, C.; Stalder, G.; Farnleitner, A.H. Host diet and evolutionary history explain different aspects of gut microbiome diversity among vertebrate clades. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münger, E.; Montiel-Castro, A.J.; Langhans, W.; Pacheco-López, G. Reciprocal interactions between gut microbiota and host social behavior. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y. Effect of sex on the gut microbiota characteristics of passerine migratory birds. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 917373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Huo, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, H.; Feng, J. Comparative analysis of the gut microbial communities of the Eurasian kestrel (Falco tinnunculus) at different developmental stages. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 592539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Du, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L. Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Microbiota of Relict Gull (Larus relictus) in Mu Us Desert (Hao Tongcha Nur) and Bojiang Haizi in Inner Mongolia, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 860540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Gong, M.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Liu, G. Diet-induced microbiome shifts of sympatric overwintering birds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5993–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Cao, Y. Potential effects of rapeseed peptide Maillard reaction products on aging-related disorder attenuation and gut microbiota modulation in d-galactose induced aging mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MahmoudAl-Atiyat, R. Dynamic of Bacterial Diversity in Ileum Digesta Under Water Supplements of Antibiotics and Probiotics. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 20, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Hong, Y.; Jiang, K.; Yu, L.; Xie, X.; Li, J. Transplantion of predominant Lactobacilli from native hens to commercial hens could indirectly regulate their ISC activity by improving intestinal microbiota. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 1235–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baráti-Deák, B.; Belák, Á.; Mohácsi-Farkas, C. Characterisation of Pseudomonas lundensis CP-P-5 as a potential antagonist of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Acta Aliment. 2021, 50, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Tu, Q.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, J. Network succession reveals the importance of competition in response to emulsified vegetable oil amendment for uranium bioremediation. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Kuang, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, R.; Hui, C. Evidence for cross transmission of pathogens between wild hooded cranes and domestic geese. J. Avian Biol. 2023, 2023, e03083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Indicator Value | p | Taxonomy | Relative Abundance (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 0.386 | 0.022 | s_Streptococcus suis | 0.260 |
| 0.469 | 0.001 | s_Kaistia geumhonensis | 0.112 | |
| 0.549 | 0.001 | s_Agaricicola taiwanensis | 0.068 | |
| 0.599 | 0.001 | s_Methylobacterium hispanicum | 0.058 | |
| 0.250 | 0.008 | s_Clostridium colinum | 0.010 | |
| HC | 0.905 | 0.001 | s_Paenibacillus xylanilyticus | 1.806 |
| 0.608 | 0.001 | s_Campylobacter canadensis | 0.896 | |
| 0.638 | 0.001 | s_Allorhizobium vitis | 0.231 | |
| 0.483 | 0.007 | s_Novosphingobium barchaimii | 0.086 | |
| 0.404 | 0.024 | s_Xanthomonas sacchari | 0.082 | |
| 0.426 | 0.031 | s_Clostridium gasigenes | 0.061 | |
| 0.317 | 0.005 | s_Stenotrophomonas rhizophila | 0.044 | |
| 0.300 | 0.005 | s_Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens | 0.038 | |
| 0.401 | 0.001 | s_Mesorhizobium ciceri | 0.031 | |
| 0.300 | 0.003 | s_Campylobacter jejuni | 0.012 | |
| DG | 0.539 | 0.003 | s_Lactobacillus aviarius | 78.87 |
| 0.732 | 0.001 | s_Pseudomonas lundensis | 11.46 | |
| 0.597 | 0.001 | s_Clostridium akagii | 0.923 | |
| 0.919 | 0.001 | s_Clostridium vincentii | 0.561 | |
| 0.832 | 0.001 | s_Sanguibacter inulinus | 0.523 | |
| 0.282 | 0.044 | s_Sphingobacterium faecium | 0.315 | |
| 0.299 | 0.006 | s_Chryseobacterium balustinum | 0.312 | |
| 0.365 | 0.004 | s_Pseudomonas graminis | 0.161 | |
| 0.250 | 0.007 | s_Lactobacillus siliginis | 0.092 | |
| 0.200 | 0.030 | s_Clostridium acidisoli | 0.056 | |
| 0.230 | 0.025 | s_Sphingomonas faeni | 0.043 | |
| 0.423 | 0.008 | s_Rhodococcus hoagii | 0.038 | |
| 0.400 | 0.002 | s_Weissella soli | 0.030 | |
| 0.237 | 0.047 | s_Pseudokineococcus lusitanus | 0.015 | |
| 0.299 | 0.004 | s_Clostridium bovipellis | 0.011 | |
| 0.350 | 0.001 | s_Massiliomicrobiota timonensis | 0.011 | |
| 0.225 | 0.030 | s_Paenibacillus turicensis | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Yuan, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, X. Significant Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Communities of Sympatric Bean Goose, Hooded Crane, and Domestic Goose. Animals 2024, 14, 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111688
Yin J, Yuan D, Xu Z, Wu Y, Chen Z, Xiang X. Significant Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Communities of Sympatric Bean Goose, Hooded Crane, and Domestic Goose. Animals. 2024; 14(11):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111688
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jing, Dandan Yuan, Ziqiu Xu, Yuannuo Wu, Zhong Chen, and Xingjia Xiang. 2024. "Significant Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Communities of Sympatric Bean Goose, Hooded Crane, and Domestic Goose" Animals 14, no. 11: 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111688
APA StyleYin, J., Yuan, D., Xu, Z., Wu, Y., Chen, Z., & Xiang, X. (2024). Significant Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Communities of Sympatric Bean Goose, Hooded Crane, and Domestic Goose. Animals, 14(11), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111688






